83074a25ebc2f6b46604b9f52b376206.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 104
 3 rd International Conference on Second Language Pedagogies Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal 1
3 rd International Conference on Second Language Pedagogies Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal 1
 2
2
 Before we start ~ New on Lextutor ! • Vocabprofile scheme incorporate both British and North American frequency schemes • All schemes launch from a common interface • Free Text-to-Speech is – A. recovered, B. cross-browser, C. discourse not words • Word. Reference standardized as the dictionary 3 + All original research reported today performed on Lextutor
Before we start ~ New on Lextutor ! • Vocabprofile scheme incorporate both British and North American frequency schemes • All schemes launch from a common interface • Free Text-to-Speech is – A. recovered, B. cross-browser, C. discourse not words • Word. Reference standardized as the dictionary 3 + All original research reported today performed on Lextutor
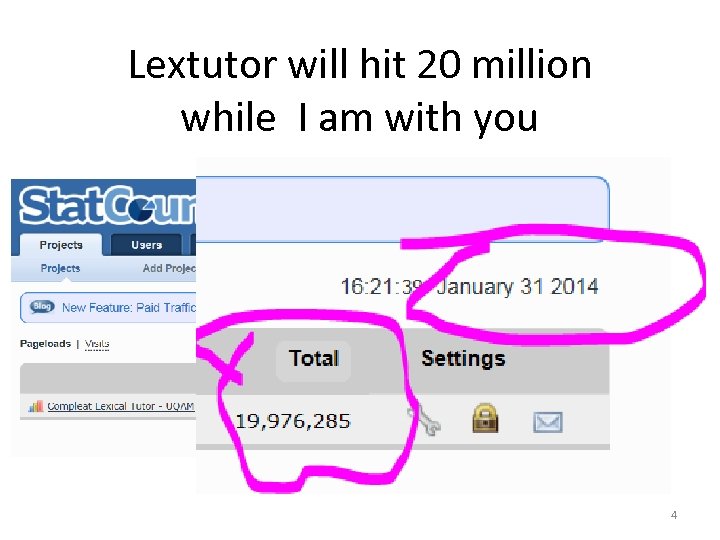 Lextutor will hit 20 million while I am with you 4
Lextutor will hit 20 million while I am with you 4
 Warning • When I give these talks. . . • I gather up my current concerns • And fashion them into the best narrative I can come up with • So this is not a tight little canned presentation Great to have a whole hour ! – For me, anyway 5
Warning • When I give these talks. . . • I gather up my current concerns • And fashion them into the best narrative I can come up with • So this is not a tight little canned presentation Great to have a whole hour ! – For me, anyway 5
 To improve learners’ Proficiency and Accuracy Can Research help? 6
To improve learners’ Proficiency and Accuracy Can Research help? 6
 Improving Learners’ Proficiency and Accuracy Can Applied Linguistics Research help? 7
Improving Learners’ Proficiency and Accuracy Can Applied Linguistics Research help? 7
 Abstract as of mid-Nov 2013 Few L 2 practitioners doubt the value of “evidence based” or “research based” language instruction, in principle. But few can cite the research behind the instructional decisions they make, and fewer keep up with the research literature – even when they have done a research degree. My presentation will look at why research is not taken seriously in frontline ESL or FSL. It will argue that an “applied linguistics” is yet to emerge, and will describe what this would look like. 8
Abstract as of mid-Nov 2013 Few L 2 practitioners doubt the value of “evidence based” or “research based” language instruction, in principle. But few can cite the research behind the instructional decisions they make, and fewer keep up with the research literature – even when they have done a research degree. My presentation will look at why research is not taken seriously in frontline ESL or FSL. It will argue that an “applied linguistics” is yet to emerge, and will describe what this would look like. 8
 So, a doom & gloom talk • … which is not to say that applied linguistics has not had some huge successes recently! 9
So, a doom & gloom talk • … which is not to say that applied linguistics has not had some huge successes recently! 9
 “Learning Strategies” no longer vague and unsubstantiated truisms ! E. g. , LVG’s work to ground listening strategy research in what learners actually do, and to what effect 10
“Learning Strategies” no longer vague and unsubstantiated truisms ! E. g. , LVG’s work to ground listening strategy research in what learners actually do, and to what effect 10
 Pronunciation instruction no longer idolizes the Native Speaker! Comprehensibility is the new focus in a largely Canadian picture - Derwing, Munro, Trofimovich 11
Pronunciation instruction no longer idolizes the Native Speaker! Comprehensibility is the new focus in a largely Canadian picture - Derwing, Munro, Trofimovich 11
 No student leaves an L 2 course without “communicating” at some point 20+ years of communicative research and proselytising have had some effect 12
No student leaves an L 2 course without “communicating” at some point 20+ years of communicative research and proselytising have had some effect 12
 Vocab is no longer a neglected area! About 20 -30% of AAAL presentations are on vocab, collocations, lexical profiles, etc 13
Vocab is no longer a neglected area! About 20 -30% of AAAL presentations are on vocab, collocations, lexical profiles, etc 13
 Vocab is no longer a neglected area! ~ Real corpus-based word frequencies ~ The number of hits to learn a word ~ The number of words to read a text ~ Collocation discovered lurking in corpora + Many others 14
Vocab is no longer a neglected area! ~ Real corpus-based word frequencies ~ The number of hits to learn a word ~ The number of words to read a text ~ Collocation discovered lurking in corpora + Many others 14
 English no longer the only research language ! Corpus based word lists and learner dictionaries in… 15
English no longer the only research language ! Corpus based word lists and learner dictionaries in… 15
 16
16
 17
17
 Corpus studies are booming Corpora of ~ Learner writing, Learner talk, Text books, Teacher talk 18
Corpus studies are booming Corpora of ~ Learner writing, Learner talk, Text books, Teacher talk 18
 And yet 19
And yet 19
 And yet… Anecdote • Portfolio Day at DDL/UQAM TESL Program • “What did I learn? ” • No research finding, principle, or inspiration is ever mentioned • After four years, 7 stages, and 100+ research papers… 20
And yet… Anecdote • Portfolio Day at DDL/UQAM TESL Program • “What did I learn? ” • No research finding, principle, or inspiration is ever mentioned • After four years, 7 stages, and 100+ research papers… 20
 Isn’t this research supposed to be for teachers ? Or is it really for other researchers ? 21
Isn’t this research supposed to be for teachers ? Or is it really for other researchers ? 21
 Teachers’ lukewarm response to research Why? This is itself an interesting question for a corpus study 22
Teachers’ lukewarm response to research Why? This is itself an interesting question for a corpus study 22
 4 -year study “Rank these 10 elements by importance in the decisions you will make as a teacher” Those who ranked research in the bottom two categories of 10 were asked to elaborate views on research Elaboration categorization factor analysis 23
4 -year study “Rank these 10 elements by importance in the decisions you will make as a teacher” Those who ranked research in the bottom two categories of 10 were asked to elaborate views on research Elaboration categorization factor analysis 23
 What were the top four factors ? 1. The materials we will use are not research based 2. Our own training program preaches but does not model research-based teaching 3. Much research deals with situations of theoretical but not practical interest 4. There are contradictory studies on every topic and we cannot get an overview – Are these legitimate concerns? 24
What were the top four factors ? 1. The materials we will use are not research based 2. Our own training program preaches but does not model research-based teaching 3. Much research deals with situations of theoretical but not practical interest 4. There are contradictory studies on every topic and we cannot get an overview – Are these legitimate concerns? 24
 Plus one “almost significant” • 5. Learning technologies studies tell us about software that we cannot access 25
Plus one “almost significant” • 5. Learning technologies studies tell us about software that we cannot access 25
 Let’s look at these in the context of vocab research It is more practice-oriented than some other kinds • No major legacy in either linguistics or literature • But much of it still fails to connect with the teacher’s world • Corpus studies can pin down some basis for the TESL students’ misgivings 26
Let’s look at these in the context of vocab research It is more practice-oriented than some other kinds • No major legacy in either linguistics or literature • But much of it still fails to connect with the teacher’s world • Corpus studies can pin down some basis for the TESL students’ misgivings 26
 Factor 1. “The materials we will use are not research based” 27
Factor 1. “The materials we will use are not research based” 27
 Ex 1. Research tells TESL students that learners need to work most on the most frequent words • Learning proceeds pretty much sequentially by frequency • The most frequent words are the most useful in terms of average coverage – 1000 word families claim c. 70% of the lexis in a printed text, c. 80% of the spoken words in a conversation, etc 28
Ex 1. Research tells TESL students that learners need to work most on the most frequent words • Learning proceeds pretty much sequentially by frequency • The most frequent words are the most useful in terms of average coverage – 1000 word families claim c. 70% of the lexis in a printed text, c. 80% of the spoken words in a conversation, etc 28
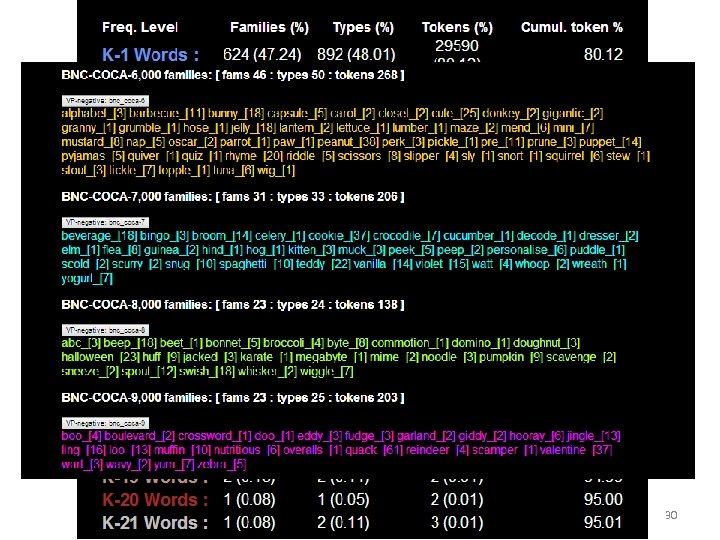
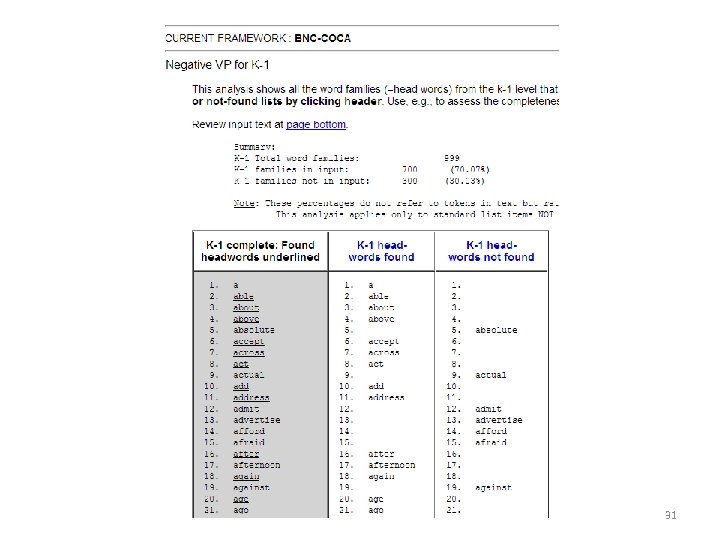
 So are primary ESL materials made to present mainly frequent words? • Jacinthe Corpus, – Three years, • Course + Activity Books – 36, 393 words / 1321 families • Vocabprofile BNC-Coca Scheme 29
So are primary ESL materials made to present mainly frequent words? • Jacinthe Corpus, – Three years, • Course + Activity Books – 36, 393 words / 1321 families • Vocabprofile BNC-Coca Scheme 29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 In other words… • 53% of the word families introduced in these three years do not match primary learners’ needs to get control of 1 k – Except the need for amusement (hippo, ‘gator, splat, etc) • While 30% of the families in the first 1000 will never be met at all – Against, afraid, afford, admit 33
In other words… • 53% of the word families introduced in these three years do not match primary learners’ needs to get control of 1 k – Except the need for amusement (hippo, ‘gator, splat, etc) • While 30% of the families in the first 1000 will never be met at all – Against, afraid, afford, admit 33
 Ex 2. Students read studies about how many encounters are needed to learn a word • Answers range from fast mapping (something is learned in just one encounter) • ~ to power law learning (still more is learned even in the 100 th encounter) • With “stable learning” variously located at 8, 10, 15, and 20 encounters 34
Ex 2. Students read studies about how many encounters are needed to learn a word • Answers range from fast mapping (something is learned in just one encounter) • ~ to power law learning (still more is learned even in the 100 th encounter) • With “stable learning” variously located at 8, 10, 15, and 20 encounters 34
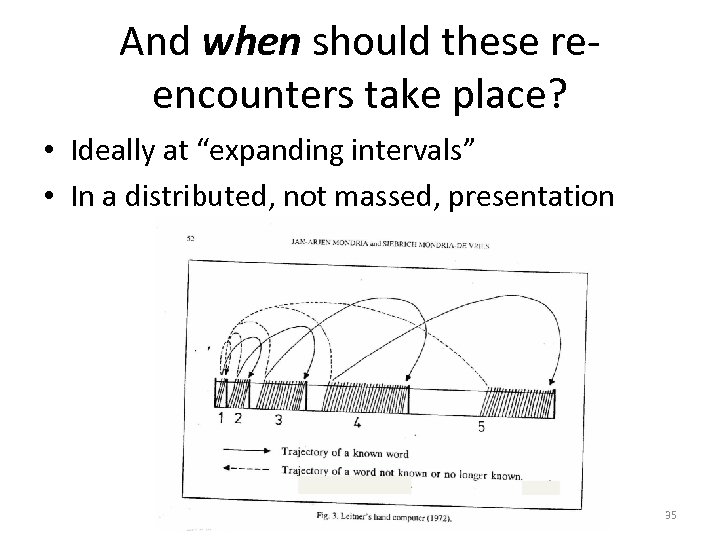 And when should these reencounters take place? • Ideally at “expanding intervals” • In a distributed, not massed, presentation 35
And when should these reencounters take place? • Ideally at “expanding intervals” • In a distributed, not massed, presentation 35
 In reality, however, Bean-counting (word-count) studies of ESL textbooks (25+) consistently show… • Most of the words presented to learners occur only once ! – Even if you count words as “families” • IE Cat and cats count as one word twice, not two words once each 36
In reality, however, Bean-counting (word-count) studies of ESL textbooks (25+) consistently show… • Most of the words presented to learners occur only once ! – Even if you count words as “families” • IE Cat and cats count as one word twice, not two words once each 36
 37
37
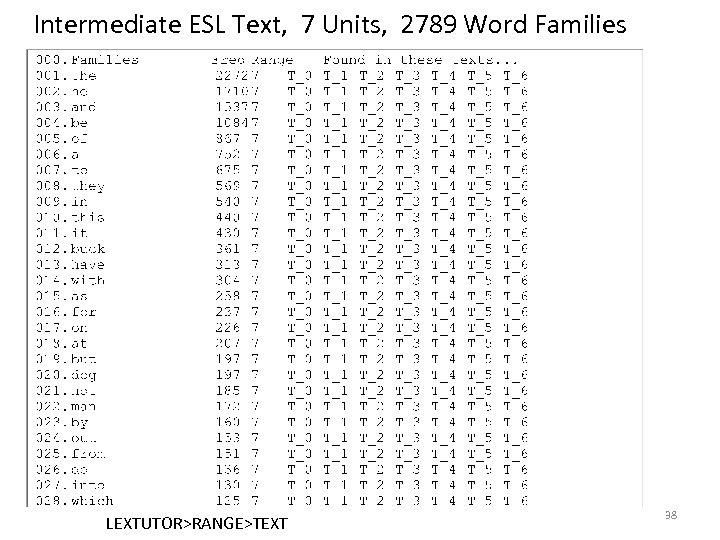 Intermediate ESL Text, 7 Units, 2789 Word Families LEXTUTOR>RANGE>TEXT 38
Intermediate ESL Text, 7 Units, 2789 Word Families LEXTUTOR>RANGE>TEXT 38
 So out of 2789 Word Families ~ • 1092 ( 39 % ) appeared once • 1557 ( 56 %) appeared once or twice • 1805 ( 65 %) appeared 1, 2, or 3 times • So about 980 words were candidates for acquisition – And since half of the words in texts are function words… 39
So out of 2789 Word Families ~ • 1092 ( 39 % ) appeared once • 1557 ( 56 %) appeared once or twice • 1805 ( 65 %) appeared 1, 2, or 3 times • So about 980 words were candidates for acquisition – And since half of the words in texts are function words… 39
 But maybe some of these words recur in the activity book? That usually accompanies the main book 40
But maybe some of these words recur in the activity book? That usually accompanies the main book 40
 Juliani corpus Three years of a well known Quebec secondary ESL course book – 3 Course Books + 3 accompanying Activity Books • 277, 130 individual words in Course Books • 83, 947 individual words in Activity Books • 15, 354 word types in all, 5027 word families • Plenty of learning opportunities, right? 41
Juliani corpus Three years of a well known Quebec secondary ESL course book – 3 Course Books + 3 accompanying Activity Books • 277, 130 individual words in Course Books • 83, 947 individual words in Activity Books • 15, 354 word types in all, 5027 word families • Plenty of learning opportunities, right? 41
 42
42
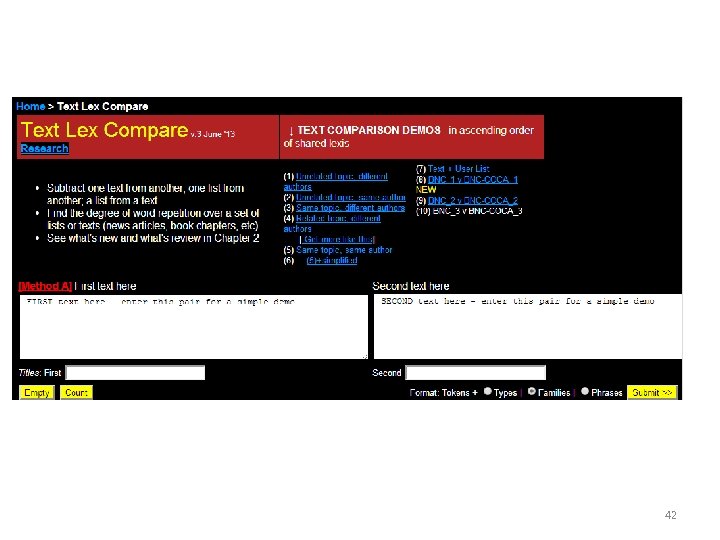
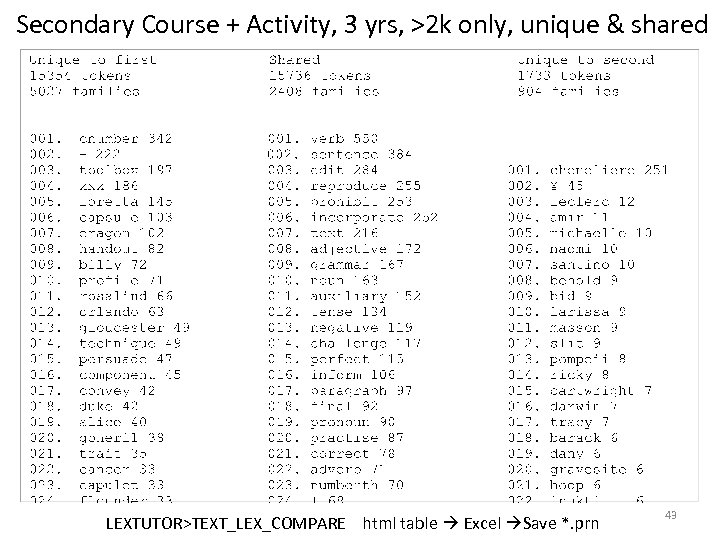 Secondary Course + Activity, 3 yrs, >2 k only, unique & shared LEXTUTOR>TEXT_LEX_COMPARE html table Excel Save *. prn 43
Secondary Course + Activity, 3 yrs, >2 k only, unique & shared LEXTUTOR>TEXT_LEX_COMPARE html table Excel Save *. prn 43
 So out of 5, 027 post-2 k word families (10% junk) • 3557 word families that appeared only once or twice in course books – Did not re-appear in the activity book • Scroll 1470 to bottom on left • And further, the activity books themselves introduced another 794 once/twice items • Scroll 110 to bottom on right 44
So out of 5, 027 post-2 k word families (10% junk) • 3557 word families that appeared only once or twice in course books – Did not re-appear in the activity book • Scroll 1470 to bottom on left • And further, the activity books themselves introduced another 794 once/twice items • Scroll 110 to bottom on right 44
 Factor 2. “Our own training program preaches but does not model research-based teaching” 45
Factor 2. “Our own training program preaches but does not model research-based teaching” 45
 Carrying on with the lack of recycling in course books… But maybe teacher trainers model the recycling of words in the classroom? As supplement to whatever text or other input 46
Carrying on with the lack of recycling in course books… But maybe teacher trainers model the recycling of words in the classroom? As supplement to whatever text or other input 46
 Kennsa corpus 18 hours of instruction modeled by a trainer, and recorded 2 hours/week, 9 weeks Academic learners Already admitted to Canadian University Vocab Tested – under 2000 word families known receptively big need for 2 k-5 k vocab Norbert’s famous “mid-frequency vocab” 47 Formerly known as AWL
Kennsa corpus 18 hours of instruction modeled by a trainer, and recorded 2 hours/week, 9 weeks Academic learners Already admitted to Canadian University Vocab Tested – under 2000 word families known receptively big need for 2 k-5 k vocab Norbert’s famous “mid-frequency vocab” 47 Formerly known as AWL
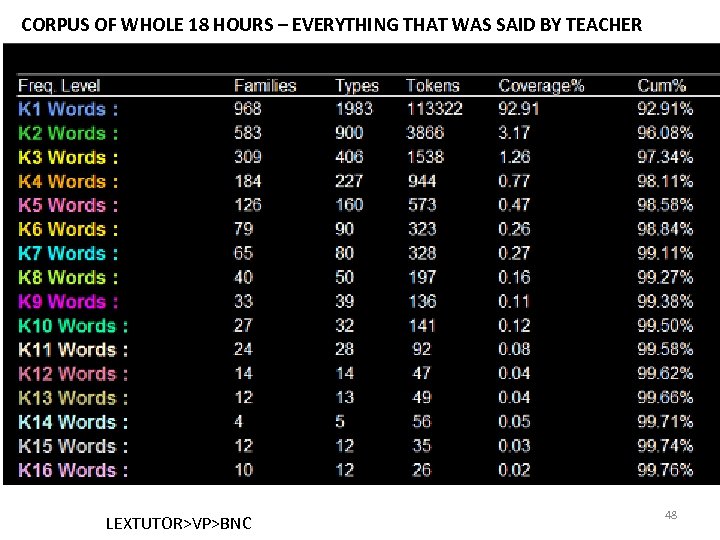 CORPUS OF WHOLE 18 HOURS – EVERYTHING THAT WAS SAID BY TEACHER LEXTUTOR>VP>BNC 48
CORPUS OF WHOLE 18 HOURS – EVERYTHING THAT WAS SAID BY TEACHER LEXTUTOR>VP>BNC 48
 Looks good at first sight 1202 mid-frequency k 2 -k 5 word families – In a good variety of types • And a decent number of tokens But when viewed hour by hour… 49
Looks good at first sight 1202 mid-frequency k 2 -k 5 word families – In a good variety of types • And a decent number of tokens But when viewed hour by hour… 49
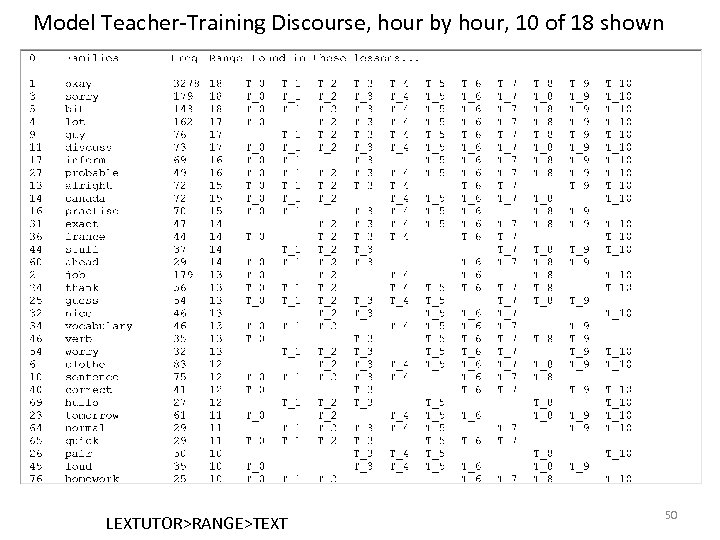 Model Teacher-Training Discourse, hour by hour, 10 of 18 shown LEXTUTOR>RANGE>TEXT 50
Model Teacher-Training Discourse, hour by hour, 10 of 18 shown LEXTUTOR>RANGE>TEXT 50
 Out of 1570 high value (k 2 -k 5) word families 400 appear once (37%) • And are dropped – Odds on basic retention? 10% 900 Appear several times (60%) • But in one class-hour only • And never again – Odds on basic retention? 20% Leaving just 270 that appear both >1 time and in >1 class-hour 51
Out of 1570 high value (k 2 -k 5) word families 400 appear once (37%) • And are dropped – Odds on basic retention? 10% 900 Appear several times (60%) • But in one class-hour only • And never again – Odds on basic retention? 20% Leaving just 270 that appear both >1 time and in >1 class-hour 51
 So while researchers… • Debate the fine points on 8, 10, and 15 encounters – And the ideal temporal spacing between encounters • 3, then 6, then 9, then 12 days apart • Teachers see that in the real world, three encounters with a word is a luxury – And three encounters on three different days ? • Extremely rare 52
So while researchers… • Debate the fine points on 8, 10, and 15 encounters – And the ideal temporal spacing between encounters • 3, then 6, then 9, then 12 days apart • Teachers see that in the real world, three encounters with a word is a luxury – And three encounters on three different days ? • Extremely rare 52
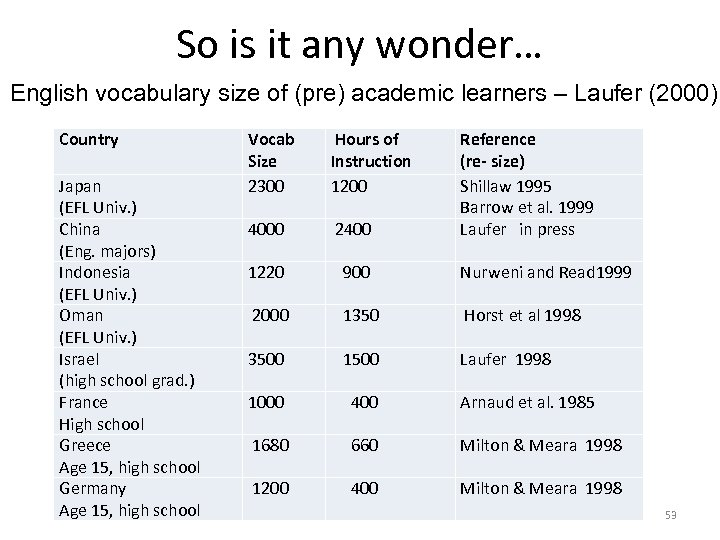 So is it any wonder… English vocabulary size of (pre) academic learners – Laufer (2000) Country Japan (EFL Univ. ) China (Eng. majors) Indonesia (EFL Univ. ) Oman (EFL Univ. ) Israel (high school grad. ) France High school Greece Age 15, high school Germany Age 15, high school Vocab Size 2300 Hours of Instruction 1200 Reference (re- size) Shillaw 1995 Barrow et al. 1999 Laufer in press 4000 1220 2400 900 2000 1350 Horst et al 1998 3500 1500 Laufer 1998 1000 400 Arnaud et al. 1985 1680 660 Milton & Meara 1998 1200 400 Milton & Meara 1998 Nurweni and Read 1999 53
So is it any wonder… English vocabulary size of (pre) academic learners – Laufer (2000) Country Japan (EFL Univ. ) China (Eng. majors) Indonesia (EFL Univ. ) Oman (EFL Univ. ) Israel (high school grad. ) France High school Greece Age 15, high school Germany Age 15, high school Vocab Size 2300 Hours of Instruction 1200 Reference (re- size) Shillaw 1995 Barrow et al. 1999 Laufer in press 4000 1220 2400 900 2000 1350 Horst et al 1998 3500 1500 Laufer 1998 1000 400 Arnaud et al. 1985 1680 660 Milton & Meara 1998 1200 400 Milton & Meara 1998 Nurweni and Read 1999 53
 Factor 3. “Much research deals with situations of theoretical but not practical interest” • I. e. , ignores what actually goes on in classrooms – Fixates instead on questions that while interesting do not correspond to any need or achievable goal 54
Factor 3. “Much research deals with situations of theoretical but not practical interest” • I. e. , ignores what actually goes on in classrooms – Fixates instead on questions that while interesting do not correspond to any need or achievable goal 54
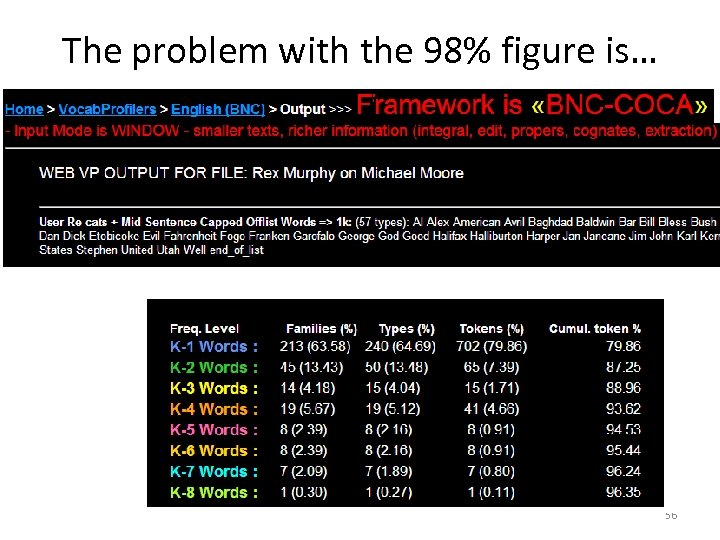
 Ex, What proportion of a text’s words must an L 2 academic reader know to comprehend the text ? • Is it 90%, 95%, or 98% of the words in a text that must be known • to assure comprehension of a general interest text ? (Unaided by dictionaries, Google, etc) 55
Ex, What proportion of a text’s words must an L 2 academic reader know to comprehend the text ? • Is it 90%, 95%, or 98% of the words in a text that must be known • to assure comprehension of a general interest text ? (Unaided by dictionaries, Google, etc) 55
 The problem with the 98% figure is… 56
The problem with the 98% figure is… 56
 The problem with the 98% figure (and the 95% for that matter) – 98% 8000 word families known – 95% 5000 word families known – 90% 3000 word families known 57
The problem with the 98% figure (and the 95% for that matter) – 98% 8000 word families known – 95% 5000 word families known – 90% 3000 word families known 57
 While, in fact, the actual vocabulary size of academic ESL learners… • In 10 countries, ESL learners were tackling MA and Ph. D reading knowing only – 1500 -2500 word families – Plus some specialist vocabulary – Adding up to well under 90% coverage by known items in any academic discipline 58
While, in fact, the actual vocabulary size of academic ESL learners… • In 10 countries, ESL learners were tackling MA and Ph. D reading knowing only – 1500 -2500 word families – Plus some specialist vocabulary – Adding up to well under 90% coverage by known items in any academic discipline 58
 So isn’t the real question of interest ~ • Given the words most academic learners typically know – 2000 to 3000, long road to 8, 000 • And given that these learners are not required to read without resources – How many words should they know to • Get their reading done? • Within the time available? • Making successful lookups? 59
So isn’t the real question of interest ~ • Given the words most academic learners typically know – 2000 to 3000, long road to 8, 000 • And given that these learners are not required to read without resources – How many words should they know to • Get their reading done? • Within the time available? • Making successful lookups? 59
 And isn’t it more interesting ~ • To find ways to crack domain-specific lexicons out of a corpus Medicine – Create real English for courses Physics • Architecture Nursing Rather than calculate and recalculate theoretical lexicon needed – for a task that does not exist • Resource-free independent reading of domain-general texts 60
And isn’t it more interesting ~ • To find ways to crack domain-specific lexicons out of a corpus Medicine – Create real English for courses Physics • Architecture Nursing Rather than calculate and recalculate theoretical lexicon needed – for a task that does not exist • Resource-free independent reading of domain-general texts 60
 Factor 4. “There are contradictory studies on every topic and we cannot get an overview” 61
Factor 4. “There are contradictory studies on every topic and we cannot get an overview” 61
 TESL students see that there are 1, 000+ studies on any topic Of which they will read one or two Showing about 50 -50 for each side of every question 62
TESL students see that there are 1, 000+ studies on any topic Of which they will read one or two Showing about 50 -50 for each side of every question 62
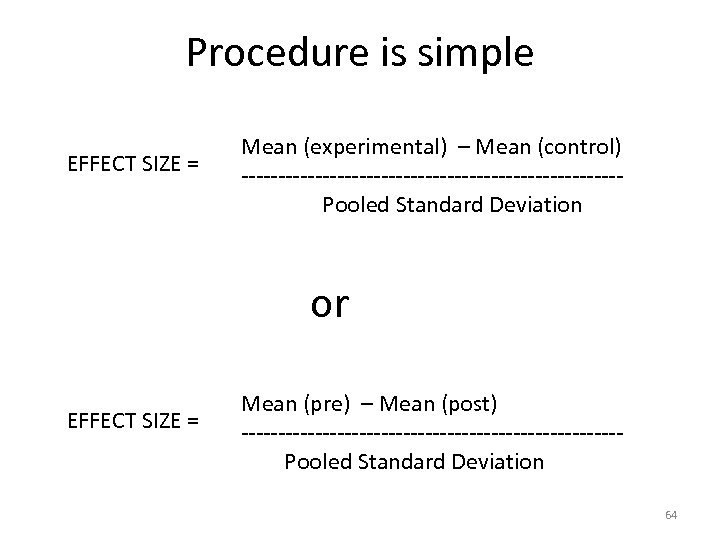
 In fact… • This is not strictly true • As can be shown by bringing together all studies for a topic in a Meta-Analysis – Strong , clear findings have emerged – Which provide practice-ready principles to build proficiency and accuracy • Ex, Norris & Ortega (2000): Explicit formfocused instruction is more effective than implicit and communicative only 63
In fact… • This is not strictly true • As can be shown by bringing together all studies for a topic in a Meta-Analysis – Strong , clear findings have emerged – Which provide practice-ready principles to build proficiency and accuracy • Ex, Norris & Ortega (2000): Explicit formfocused instruction is more effective than implicit and communicative only 63
 Procedure is simple EFFECT SIZE = Mean (experimental) – Mean (control) -------------------------- Pooled Standard Deviation or EFFECT SIZE = Mean (pre) – Mean (post) -------------------------- Pooled Standard Deviation 64
Procedure is simple EFFECT SIZE = Mean (experimental) – Mean (control) -------------------------- Pooled Standard Deviation or EFFECT SIZE = Mean (pre) – Mean (post) -------------------------- Pooled Standard Deviation 64
 Producing a comprehensible outcome Mean 1 65
Producing a comprehensible outcome Mean 1 65
 And has the added advantage… Of shifting the criterion of proficiency & accuracy of instruction • Away from “significance testing” – Which is hugely dependent on n-size Producing non-usable findings • To effect-size testing – Which is not n-size dependent – Incorporates non-significant findings Producing highly usable findings 66
And has the added advantage… Of shifting the criterion of proficiency & accuracy of instruction • Away from “significance testing” – Which is hugely dependent on n-size Producing non-usable findings • To effect-size testing – Which is not n-size dependent – Incorporates non-significant findings Producing highly usable findings 66
 Meta-Analysis • Common in medicine – The case against smoking could never have been made without it 67
Meta-Analysis • Common in medicine – The case against smoking could never have been made without it 67
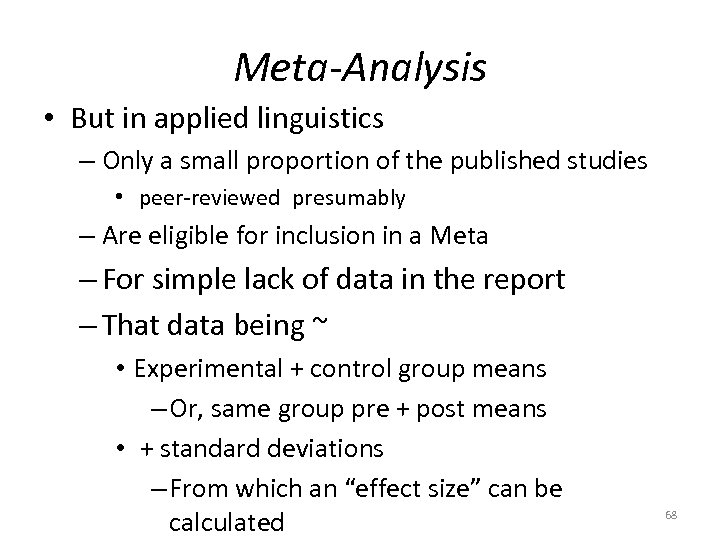 Meta-Analysis • But in applied linguistics – Only a small proportion of the published studies • peer-reviewed presumably – Are eligible for inclusion in a Meta – For simple lack of data in the report – That data being ~ • Experimental + control group means – Or, same group pre + post means • + standard deviations – From which an “effect size” can be calculated 68
Meta-Analysis • But in applied linguistics – Only a small proportion of the published studies • peer-reviewed presumably – Are eligible for inclusion in a Meta – For simple lack of data in the report – That data being ~ • Experimental + control group means – Or, same group pre + post means • + standard deviations – From which an “effect size” can be calculated 68
 Example, Cobb & Bolton (in press) • Attempts a meta-analysis on the overall effectiveness of “Data-Driven Learning” – DDL = learners use a corpus for some part of their second language learning – As compared to other type of information resource 69
Example, Cobb & Bolton (in press) • Attempts a meta-analysis on the overall effectiveness of “Data-Driven Learning” – DDL = learners use a corpus for some part of their second language learning – As compared to other type of information resource 69
 Why is this important? • Many instructors refuse to believe that their students can profit from high-level use of computer resources – Or even use them at all • Even as 80+% of them now use Google as a writing aid – And do most of their reading on mobile devices with click-on dictionaries 70
Why is this important? • Many instructors refuse to believe that their students can profit from high-level use of computer resources – Or even use them at all • Even as 80+% of them now use Google as a writing aid – And do most of their reading on mobile devices with click-on dictionaries 70
 Example, Lextutor’s many concordance based “games” That allow fairly deep processing of new words in an economical format 71
Example, Lextutor’s many concordance based “games” That allow fairly deep processing of new words in an economical format 71
 72
72
 As feedback to writing 73
As feedback to writing 73
 The support for DDL • Consists in a handful of little DDL studies by plucky practitioners – Mainly in odd corners of the world • The vast majority – Are the researcher’s MA study • Done up for publication 74
The support for DDL • Consists in a handful of little DDL studies by plucky practitioners – Mainly in odd corners of the world • The vast majority – Are the researcher’s MA study • Done up for publication 74
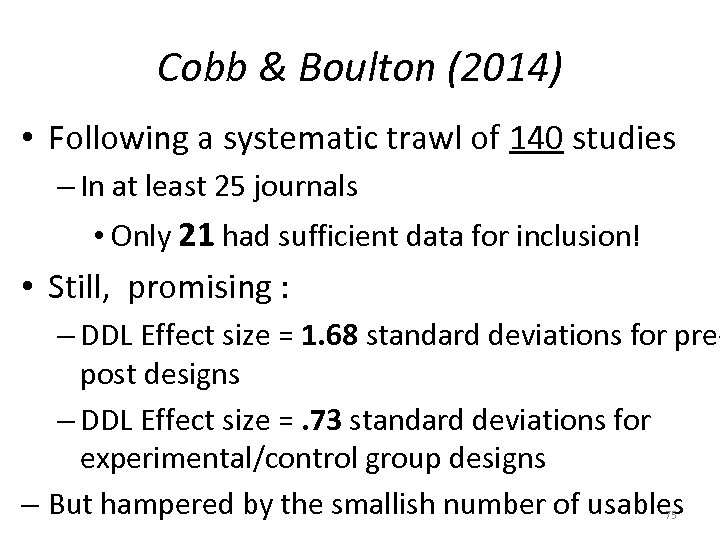 Cobb & Boulton (2014) • Following a systematic trawl of 140 studies – In at least 25 journals • Only 21 had sufficient data for inclusion! • Still, promising : – DDL Effect size = 1. 68 standard deviations for prepost designs – DDL Effect size =. 73 standard deviations for experimental/control group designs – But hampered by the smallish number of usables 75
Cobb & Boulton (2014) • Following a systematic trawl of 140 studies – In at least 25 journals • Only 21 had sufficient data for inclusion! • Still, promising : – DDL Effect size = 1. 68 standard deviations for prepost designs – DDL Effect size =. 73 standard deviations for experimental/control group designs – But hampered by the smallish number of usables 75
 So ~ Only a few topics in Applied Linguistics Of the many possible Have been brought together in a Meta-Analysis 76
So ~ Only a few topics in Applied Linguistics Of the many possible Have been brought together in a Meta-Analysis 76
 Factor 5. “Learning technologies studies tell us about software that we cannot access” Almost no technology research report offer a technology that is anywhere near “ready to go” 77
Factor 5. “Learning technologies studies tell us about software that we cannot access” Almost no technology research report offer a technology that is anywhere near “ready to go” 77
 • 1995 78
• 1995 78
 From these pieces, try to Google up something current on… – The Bridge Project – Project Athena – Ling. Worlds – Anderson’s Geometry Tutor – Etc • Few mentions since mid 1990 s • Even in projects that one assumes are “standing on the shoulders…” 79
From these pieces, try to Google up something current on… – The Bridge Project – Project Athena – Ling. Worlds – Anderson’s Geometry Tutor – Etc • Few mentions since mid 1990 s • Even in projects that one assumes are “standing on the shoulders…” 79
 Note that 1/2 of Lextutor is backengineered, un-available software from published studies 80
Note that 1/2 of Lextutor is backengineered, un-available software from published studies 80
 The reason for this problem is simple R>D • Researcher-developers are rewarded for results in principle from a computational learning tool – Publications – Tenure – Funding – Good Ph. D students • But not rewarded for broad implementation 81
The reason for this problem is simple R>D • Researcher-developers are rewarded for results in principle from a computational learning tool – Publications – Tenure – Funding – Good Ph. D students • But not rewarded for broad implementation 81
 Broad implementation… • Is often quite long after a case in principle • And without support would take years • So is more likely to get dropped I decided not to drop one of mine • Example, Cobb 1997 – My most cited paper by far • A toy frequency and corpus-based DDL vocabulary trainer 82
Broad implementation… • Is often quite long after a case in principle • And without support would take years • So is more likely to get dropped I decided not to drop one of mine • Example, Cobb 1997 – My most cited paper by far • A toy frequency and corpus-based DDL vocabulary trainer 82
 The 15 -year project • To produce a non-toy version of my best word -trainer – best result – most cited paper – best simulation of natural inductive vocabulary acquisition • GOAL: rapid list-based vocab learning without superficial learning – Breadth + depth 83
The 15 -year project • To produce a non-toy version of my best word -trainer – best result – most cited paper – best simulation of natural inductive vocabulary acquisition • GOAL: rapid list-based vocab learning without superficial learning – Breadth + depth 83
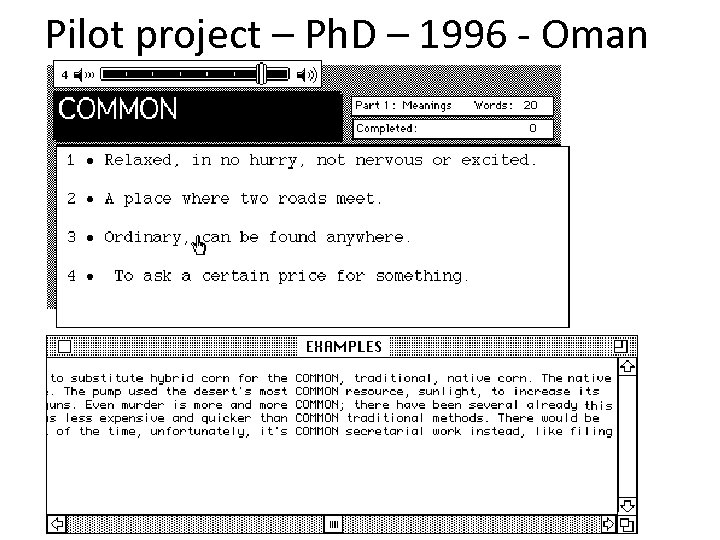 Pilot project – Ph. D – 1996 - Oman
Pilot project – Ph. D – 1996 - Oman
 85
85
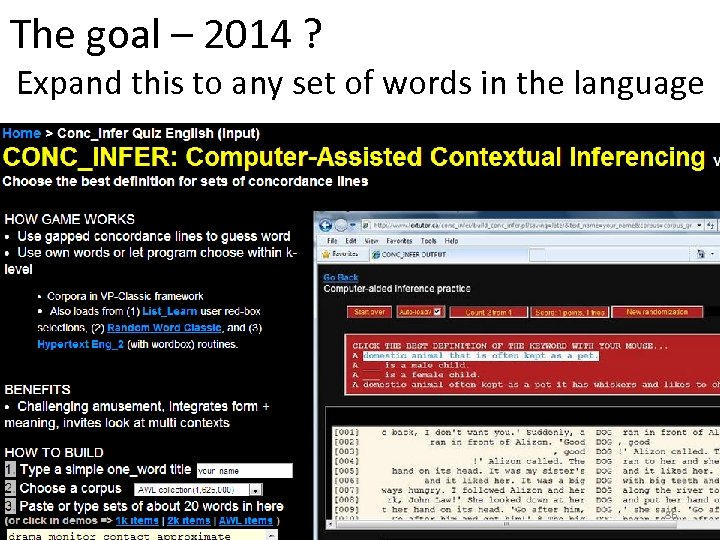 The goal – 2014 ? Expand this to any set of words in the language 86
The goal – 2014 ? Expand this to any set of words in the language 86
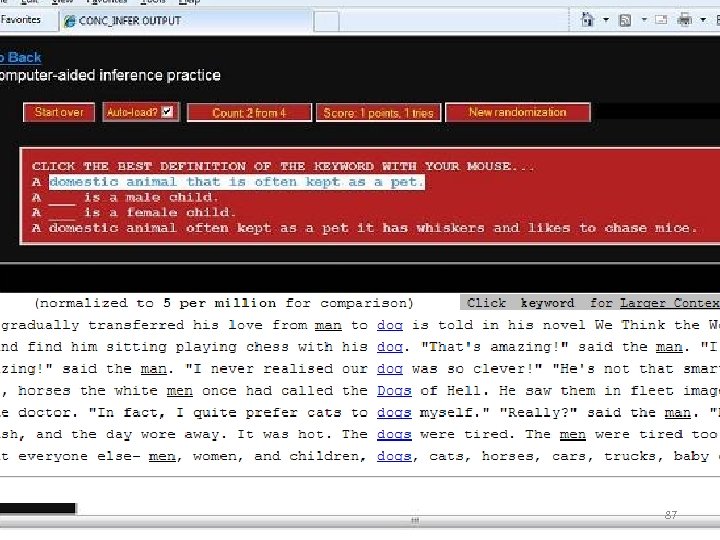 87
87
 Four missing pieces to scale this up 1. Frequency word lists up to 10 k, in US+UK versions 2. Short encompassing (monosemic) definitions for these 3. Several corpora at different k-levels to use as basis to select definitions 4. A means to generate concordances that do not mix homographs 88
Four missing pieces to scale this up 1. Frequency word lists up to 10 k, in US+UK versions 2. Short encompassing (monosemic) definitions for these 3. Several corpora at different k-levels to use as basis to select definitions 4. A means to generate concordances that do not mix homographs 88
 BIG-CORPUS, US+UK, FREQ LISTS √ 89
BIG-CORPUS, US+UK, FREQ LISTS √ 89
 SHORT, ENCOMPASSING DEFINITIONS √
SHORT, ENCOMPASSING DEFINITIONS √
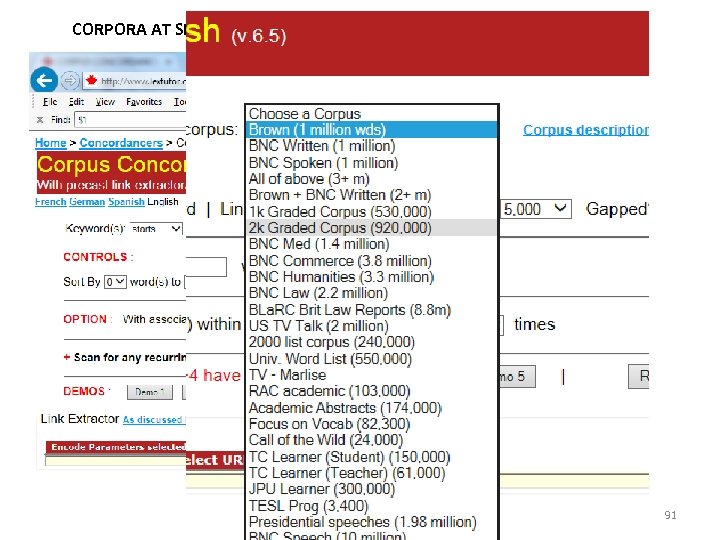 CORPORA AT SEVERAL LEVELS √ 91
CORPORA AT SEVERAL LEVELS √ 91
 A way to distinguish homoforms automatically √ Necessary if I am going to hook up unpredictable word forms to a corpus Cannot hook up bank to a concordance that mixes river banks and money banks! 92
A way to distinguish homoforms automatically √ Necessary if I am going to hook up unpredictable word forms to a corpus Cannot hook up bank to a concordance that mixes river banks and money banks! 92
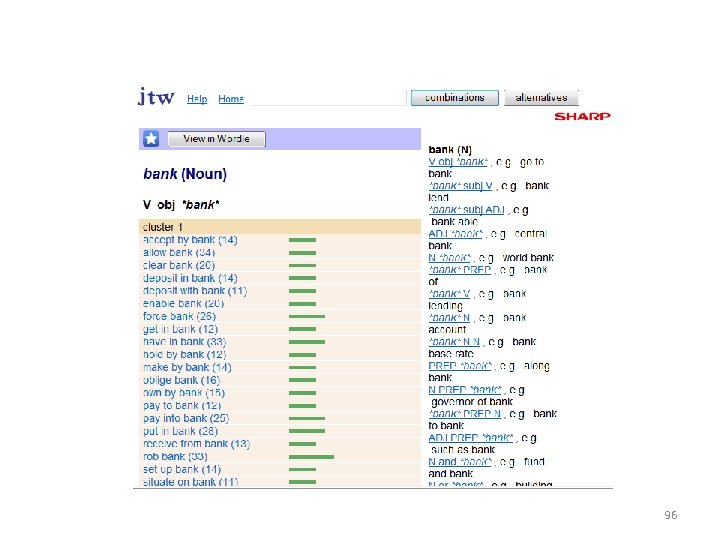
 A lot of banks! Can collocates tell them apart? Vocab@Vic 19 Dec 2013 Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal
A lot of banks! Can collocates tell them apart? Vocab@Vic 19 Dec 2013 Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal
 A lot of banks! Can collocates tell them apart? Vocab@Vic 19 Dec 2013 Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal
A lot of banks! Can collocates tell them apart? Vocab@Vic 19 Dec 2013 Tom Cobb Université du Québec à Montréal
 A way to distinguish homoforms √ Which homoforms to start with ? Kevin Parent`s work 95
A way to distinguish homoforms √ Which homoforms to start with ? Kevin Parent`s work 95
 96
96
 Broaden out, plenty of cases, all corpora, <1% errors IF TIME GO LIVE 97
Broaden out, plenty of cases, all corpora, <1% errors IF TIME GO LIVE 97
 … to form coherent inference tasks for ANY FREQUENCY LEVEL using ANY CORPUS circular shape, sometimes made of metal and worn around a finger 98
… to form coherent inference tasks for ANY FREQUENCY LEVEL using ANY CORPUS circular shape, sometimes made of metal and worn around a finger 98
 So, a long way ~ From in-principle finding with 200 words To a full-size learning tool for any part of the lexicon or in specialist domains Without support this journey will rarely be made 99
So, a long way ~ From in-principle finding with 200 words To a full-size learning tool for any part of the lexicon or in specialist domains Without support this journey will rarely be made 99
 Admittedly, this work awaited developments in Applied Corpus Linguistics generally 100
Admittedly, this work awaited developments in Applied Corpus Linguistics generally 100
 Pulling all this together… In a least one domain, the student-skeptics have a point about how much the research is going to help them or their students I believe that ~ 101
Pulling all this together… In a least one domain, the student-skeptics have a point about how much the research is going to help them or their students I believe that ~ 101
 Language teaching professionals would happily take research seriously As hugely affecting their learners’ proficiency and accuracy, if ~ 1+2. Materials producers and Teacher trainers believed more in research findings – The recycling issue 3. Researchers targeted consequential as well as merely « interesting » issues – The 90 -95 -98% reading issue 102
Language teaching professionals would happily take research seriously As hugely affecting their learners’ proficiency and accuracy, if ~ 1+2. Materials producers and Teacher trainers believed more in research findings – The recycling issue 3. Researchers targeted consequential as well as merely « interesting » issues – The 90 -95 -98% reading issue 102
 If… 4. Research journals and MA-TESOL Programs insisted on complete data reporting - In MA theses - In small journals – So that Meta-analysis could become commonplace and convincing 5. The D was rewarded as highly as the R in learning technology work (Implementation as highly as research) 103
If… 4. Research journals and MA-TESOL Programs insisted on complete data reporting - In MA theses - In small journals – So that Meta-analysis could become commonplace and convincing 5. The D was rewarded as highly as the R in learning technology work (Implementation as highly as research) 103
 cobb. tom@uqam. ca Write me for the link to this PPT 104
cobb. tom@uqam. ca Write me for the link to this PPT 104


