8c11e2db09c5414dfb71ff012b0668ce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 76
 3. PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
3. PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
 PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT: LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this module, you will q q q Have a good understanding of the main concepts addressed within the module Be able to apply these concepts in the hotel context Be aware of both the strengths and limitations of different approaches to product development in the hotel industry
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT: LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this module, you will q q q Have a good understanding of the main concepts addressed within the module Be able to apply these concepts in the hotel context Be aware of both the strengths and limitations of different approaches to product development in the hotel industry
 TODAY’S LEARNING USP’S & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES PRODUCT & BRAND DEVELOPMENT
TODAY’S LEARNING USP’S & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES PRODUCT & BRAND DEVELOPMENT
 USP’S & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
USP’S & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
 UNIQUE SELLING POINT q USPs are the characteristics of the product or service that differentiates it from similar products produced by other companies. q It’s is not about having a unique product or service; it's about making your product stand out - even in a market filled with similar items. q It also needs to do everything possible to make sure that its USPs are recognized and understood by its customers.
UNIQUE SELLING POINT q USPs are the characteristics of the product or service that differentiates it from similar products produced by other companies. q It’s is not about having a unique product or service; it's about making your product stand out - even in a market filled with similar items. q It also needs to do everything possible to make sure that its USPs are recognized and understood by its customers.
 EXAMPLES q “ We are Ladies and gentlemen serving ladies and gentlemen" (the very classy Ritz Carlton Hotel chain). q Head & Shoulders: "You get rid of dandruff" Oil of Olay: "You get younger-looking skin" M&M’s: "The milk chocolate melts in your mouth, not in your hand q q
EXAMPLES q “ We are Ladies and gentlemen serving ladies and gentlemen" (the very classy Ritz Carlton Hotel chain). q Head & Shoulders: "You get rid of dandruff" Oil of Olay: "You get younger-looking skin" M&M’s: "The milk chocolate melts in your mouth, not in your hand q q
 Domino's Pizza was a struggling business started by two university students. One of them decided to move on whilst the other went on to develop a multibillion dollar empire based on one unique promise "Piping hot pizza delivered to your door in 30 minutes or it's free" q Were Domino's the first company to deliver pizza? No! But they cleverly created a unique promise that has reshaped the pizza industry. q
Domino's Pizza was a struggling business started by two university students. One of them decided to move on whilst the other went on to develop a multibillion dollar empire based on one unique promise "Piping hot pizza delivered to your door in 30 minutes or it's free" q Were Domino's the first company to deliver pizza? No! But they cleverly created a unique promise that has reshaped the pizza industry. q
 EGYPT’S USP Nothing Compares to Egypt….
EGYPT’S USP Nothing Compares to Egypt….
 EXERCISE: USPS AND THE HOTEL INDUSTRY Brainstorming between us, how many real USPs can we think of in the international hotel industry? The Ice Hotel?
EXERCISE: USPS AND THE HOTEL INDUSTRY Brainstorming between us, how many real USPs can we think of in the international hotel industry? The Ice Hotel?
 WHAT IS A USP? Add valu s e! q Most hotel services and companies need to market themselves by pointing out a characteristic they have that their competitors lack. q A cafe may be the last one before the highway, a hotel may be the oldest in Luxor.
WHAT IS A USP? Add valu s e! q Most hotel services and companies need to market themselves by pointing out a characteristic they have that their competitors lack. q A cafe may be the last one before the highway, a hotel may be the oldest in Luxor.
 A ROOM WITH A VIEW….
A ROOM WITH A VIEW….
 EXAMPLE On UK TV is an ad for a national chain of 'overnight stop-overs'. Motels. They're modern, comfortable etc but they lack the 'extras' offered by conventional hotels. Here's how the TV Ad goes. . Open with picture of a guy blissfully sound asleep in bed. Superimposed dissolving text reads. . "No swimming pool" "No gymnasium" "No karaoke" "No discotheque". . . Female voice-over softly says. . . "Just everything you need for a good night's sleep. XYZ Travel Inns. " Now in the eyes of the 'targeted' audience, THAT'S a USP!
EXAMPLE On UK TV is an ad for a national chain of 'overnight stop-overs'. Motels. They're modern, comfortable etc but they lack the 'extras' offered by conventional hotels. Here's how the TV Ad goes. . Open with picture of a guy blissfully sound asleep in bed. Superimposed dissolving text reads. . "No swimming pool" "No gymnasium" "No karaoke" "No discotheque". . . Female voice-over softly says. . . "Just everything you need for a good night's sleep. XYZ Travel Inns. " Now in the eyes of the 'targeted' audience, THAT'S a USP!
 THE VALUE OF USP’S q q Dyson never tires of telling its potential customers that it builds the only vacuum cleaner that is free of the inconvenience and inefficiency of a dust bag. The makers of Polo mints always insist that theirs is the only 'mint with the hole'. In such cases, the USP has become the company's most successful advertising slogan. Dyson vacuum cleaners and Polo mints are sold on the basis that there is no other product quite like them.
THE VALUE OF USP’S q q Dyson never tires of telling its potential customers that it builds the only vacuum cleaner that is free of the inconvenience and inefficiency of a dust bag. The makers of Polo mints always insist that theirs is the only 'mint with the hole'. In such cases, the USP has become the company's most successful advertising slogan. Dyson vacuum cleaners and Polo mints are sold on the basis that there is no other product quite like them.
 USP & BRANDING q A USP can often enable a company to give its services a 'personality', thereby encouraging the customer to enter into a kind of relationship with a product – Breakfast with Mickey in Disney hotels q This is called 'branding'.
USP & BRANDING q A USP can often enable a company to give its services a 'personality', thereby encouraging the customer to enter into a kind of relationship with a product – Breakfast with Mickey in Disney hotels q This is called 'branding'.
 COCA COLA USP q q The famous Coco-Cola bottle, for example, with its strong 'Gotham City' styling looks distinctly American. As a result, using the bottle as a USP, Coco. Cola can associate itself with 'American values': freedom, equality, multi -culturalism. q The Coco-Cola USP gives the brand an emotional appeal, and consumers feel they are taking on these set of values.
COCA COLA USP q q The famous Coco-Cola bottle, for example, with its strong 'Gotham City' styling looks distinctly American. As a result, using the bottle as a USP, Coco. Cola can associate itself with 'American values': freedom, equality, multi -culturalism. q The Coco-Cola USP gives the brand an emotional appeal, and consumers feel they are taking on these set of values.
 SO WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF USP? q A USP, then, is much more than simply a peg on which to hang an advertising campaign. q It can give a business focus and direction, and its service irresistible appeal.
SO WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF USP? q A USP, then, is much more than simply a peg on which to hang an advertising campaign. q It can give a business focus and direction, and its service irresistible appeal.
 A CYNICS VIEW OF USP! q A USP describes a unique feature or benefit that a company will concentrate on to make their offering appear different from others available to the target market q Cynics could say that this allows a company to avoid price competition but if the unique feature or benefit is important to the consumer then it may be a deciding factor in making the sale q Companies protect their USPs by all means, including the law courts
A CYNICS VIEW OF USP! q A USP describes a unique feature or benefit that a company will concentrate on to make their offering appear different from others available to the target market q Cynics could say that this allows a company to avoid price competition but if the unique feature or benefit is important to the consumer then it may be a deciding factor in making the sale q Companies protect their USPs by all means, including the law courts
 EXERCISE: YOUR TURN… Which is the best hotel company for the business traveller? What are the reasons for your choices? White board What is the best hotel company for high quality service? Again, what are the reasons for your choices? Do any of the hotel companies mentioned have anything unique that makes them different from other hotels? Do they have a money back guarantee, the biggest beds etc?
EXERCISE: YOUR TURN… Which is the best hotel company for the business traveller? What are the reasons for your choices? White board What is the best hotel company for high quality service? Again, what are the reasons for your choices? Do any of the hotel companies mentioned have anything unique that makes them different from other hotels? Do they have a money back guarantee, the biggest beds etc?
 WHAT IMAGES DO YOU ASSOCIATE WITH THESE PRODUCTS AND SERVICES q KLM q Kentucky Fried Chicken q British Airways q Singapore Airlines q Mc. Donalds What does the USP tagline focus on?
WHAT IMAGES DO YOU ASSOCIATE WITH THESE PRODUCTS AND SERVICES q KLM q Kentucky Fried Chicken q British Airways q Singapore Airlines q Mc. Donalds What does the USP tagline focus on?
 HERE THEY ARE …. . q KLM – the reliable airline q Kentucky Fried Chicken – finger lickin’ good q British Airways – The World’s favourite airline q Singapore Airlines – Singapore Girl. A great way to fly q Mc. Donalds – billions and billions served
HERE THEY ARE …. . q KLM – the reliable airline q Kentucky Fried Chicken – finger lickin’ good q British Airways – The World’s favourite airline q Singapore Airlines – Singapore Girl. A great way to fly q Mc. Donalds – billions and billions served
 DON’T LIVE UP TO THE HYPE! q In America, Domino’s Pizza dominated the delivery market by offering, "Fresh, hot pizza delivered in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed. " Domino’s virtually took over the deliver pizza market with that USP. Notice Domino’s doesn’t even promise that the pizza tastes good. They were the only ones to offer a delivery guarantee, and this made them stand out from the rest. q Wash and Go is another huge success story. "Why take two bottles into the shower when you can take one? “ Other products on the market could also do the same thing, but none of them made use of this feature as a USP, so Wash and Go sales went ballistic. q Notice that often the USP does not actually have to be unique, but may market your company in a way that makes it look unique or different. As a customer, you should be aware that USPs don't always live up to the hype!
DON’T LIVE UP TO THE HYPE! q In America, Domino’s Pizza dominated the delivery market by offering, "Fresh, hot pizza delivered in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed. " Domino’s virtually took over the deliver pizza market with that USP. Notice Domino’s doesn’t even promise that the pizza tastes good. They were the only ones to offer a delivery guarantee, and this made them stand out from the rest. q Wash and Go is another huge success story. "Why take two bottles into the shower when you can take one? “ Other products on the market could also do the same thing, but none of them made use of this feature as a USP, so Wash and Go sales went ballistic. q Notice that often the USP does not actually have to be unique, but may market your company in a way that makes it look unique or different. As a customer, you should be aware that USPs don't always live up to the hype!
 A 7 -STEP GUIDE TO WRITING YOUR USP 1. Define your target customer 2. Think about your target customer’s problems 3. Think about how you resolve those problems 4. Look for uniqueness 5. What can you guarantee? 6. Crafting and refining your USP 7. Using your USP
A 7 -STEP GUIDE TO WRITING YOUR USP 1. Define your target customer 2. Think about your target customer’s problems 3. Think about how you resolve those problems 4. Look for uniqueness 5. What can you guarantee? 6. Crafting and refining your USP 7. Using your USP
 EXERCISE: WHAT OTHER USP’S CAN YOU THINK OF? Ryanair? Apple Ipod? Dell? Subway? Sodexo? Egyptair? Luxor Las Vegas? In what ways can a USP help a business?
EXERCISE: WHAT OTHER USP’S CAN YOU THINK OF? Ryanair? Apple Ipod? Dell? Subway? Sodexo? Egyptair? Luxor Las Vegas? In what ways can a USP help a business?
 EXERCISE: YOUR TASK IN GROUPS OF 4 … q Your team has to come up with a USP tagline for a ‘specific’ hotel businesses. q You should think about what makes each of the hotel and its services unique, and use this as a basis for the tagline. q The answers will be fed back to the group and the favourite for each business voted for. (Obviously you can’t vote for your own team!)
EXERCISE: YOUR TASK IN GROUPS OF 4 … q Your team has to come up with a USP tagline for a ‘specific’ hotel businesses. q You should think about what makes each of the hotel and its services unique, and use this as a basis for the tagline. q The answers will be fed back to the group and the favourite for each business voted for. (Obviously you can’t vote for your own team!)
 USP AND COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE By defining your USP you have arrived at the major competitive advantage you have – and that means you can use it in all your marketing communications.
USP AND COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE By defining your USP you have arrived at the major competitive advantage you have – and that means you can use it in all your marketing communications.
 WHAT IS COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE? A competitive advantage is the thing that differentiates a business from its competitors. q q q Distinctive competence What you can do that others cannot What you have that others don’t It answers the question "Why should I buy from you? " or "How are you better than my current supplier? "
WHAT IS COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE? A competitive advantage is the thing that differentiates a business from its competitors. q q q Distinctive competence What you can do that others cannot What you have that others don’t It answers the question "Why should I buy from you? " or "How are you better than my current supplier? "
 SUSTAINABLE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE A firm possesses a sustainable competitive advantage when it has value-creating products, processes and services for their customers that cannot be duplicated or imitated by its competitors.
SUSTAINABLE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE A firm possesses a sustainable competitive advantage when it has value-creating products, processes and services for their customers that cannot be duplicated or imitated by its competitors.
 HAS YOUR COMPANY A COMPETITIVE EDGE? Have I clearly defined my company and its target market? Who are my competitors? What is my company's clear-cut strategy and plan for success? Do I regularly track my competitors' moves? Do I take advantage of my competitors' weaknesses? What have I learned from my competitors' mistakes? What have I learned from my competitors' strengths? Do I take advantage of competitive opportunities? Does my company possess a uniqueness that easily separates it from my competitors?
HAS YOUR COMPANY A COMPETITIVE EDGE? Have I clearly defined my company and its target market? Who are my competitors? What is my company's clear-cut strategy and plan for success? Do I regularly track my competitors' moves? Do I take advantage of my competitors' weaknesses? What have I learned from my competitors' mistakes? What have I learned from my competitors' strengths? Do I take advantage of competitive opportunities? Does my company possess a uniqueness that easily separates it from my competitors?
 HAS YOUR COMPANY A COMPETITIVE EDGE? Would I pay money to use my own product or service? How do my prices compare with the rest of my industry? Who are my customers? Do I have a loyal customer base? Am I sensitive to my customers' needs and requests? Are my employees trained in customer service? What trends do I see for my industry in the future? Do I have the capabilities and resources to compete in the market five to 10 years from now? What is my vision for my company five to 10 years from now?
HAS YOUR COMPANY A COMPETITIVE EDGE? Would I pay money to use my own product or service? How do my prices compare with the rest of my industry? Who are my customers? Do I have a loyal customer base? Am I sensitive to my customers' needs and requests? Are my employees trained in customer service? What trends do I see for my industry in the future? Do I have the capabilities and resources to compete in the market five to 10 years from now? What is my vision for my company five to 10 years from now?
 STRATEGIES FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE The three methods for creating a competitive advantage are: Cost leadership Prices lower than the competition. Differentiation Products with some quality that makes them more attractive than the competition. Focus Concentration on a single aspect of the market (a niche). (Porter, 1980)
STRATEGIES FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE The three methods for creating a competitive advantage are: Cost leadership Prices lower than the competition. Differentiation Products with some quality that makes them more attractive than the competition. Focus Concentration on a single aspect of the market (a niche). (Porter, 1980)
 MAFIA OFFER 1) 2) Having a competitive advantage, even a sustainable one, does not necessarily mean that you or your customers are aware of it. There is a need to create an offer or positioning in the market that clearly states your competitive advantage. This is known as a unrefuseable market offer or a "Mafia Offer". A mafia offer is an offer so good that your customers can't refuse it, and that your competition can't or won't match
MAFIA OFFER 1) 2) Having a competitive advantage, even a sustainable one, does not necessarily mean that you or your customers are aware of it. There is a need to create an offer or positioning in the market that clearly states your competitive advantage. This is known as a unrefuseable market offer or a "Mafia Offer". A mafia offer is an offer so good that your customers can't refuse it, and that your competition can't or won't match

 EXERCISE: HOW DO YOU ESTABLISH COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE? q Think of three things that your hotel/ department that sets it out as different from local competitors? Do these give you competitive advantage (they could be disadvantages!!)? q Share these three things with your neighbour (unless he/she is from a near by hotel!!) and explain what sets them apart
EXERCISE: HOW DO YOU ESTABLISH COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE? q Think of three things that your hotel/ department that sets it out as different from local competitors? Do these give you competitive advantage (they could be disadvantages!!)? q Share these three things with your neighbour (unless he/she is from a near by hotel!!) and explain what sets them apart
 SAFETY AS A COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE q Taiwan recently announced in the trade media that it was a safe tourist destination. Their claim, based on the low level of crime in the country, was timely as it appeared soon after the terrorist attacks in Mumbai. Promoting itself as a safe destination was a bold move by Taiwan and signals an important change in tourism marketing. q Safety is increasingly seen as a competitive advantage for tourism destinations; well at least those destinations that can legitimately substantiate the claim.
SAFETY AS A COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE q Taiwan recently announced in the trade media that it was a safe tourist destination. Their claim, based on the low level of crime in the country, was timely as it appeared soon after the terrorist attacks in Mumbai. Promoting itself as a safe destination was a bold move by Taiwan and signals an important change in tourism marketing. q Safety is increasingly seen as a competitive advantage for tourism destinations; well at least those destinations that can legitimately substantiate the claim.

 PRODUCT (SERVICE) & BRAND DEVELOPMENT WORKSHOP
PRODUCT (SERVICE) & BRAND DEVELOPMENT WORKSHOP

 THINK OF A PRODUCT…. THAT APPEALS TO YOU ♦ Does it appeal because it looks good? ♦ Helps you do something not possible before? ♦ Is fantastic value for money? ♦ Improves your quality of life?
THINK OF A PRODUCT…. THAT APPEALS TO YOU ♦ Does it appeal because it looks good? ♦ Helps you do something not possible before? ♦ Is fantastic value for money? ♦ Improves your quality of life?
 w hoboken RESIDENTIAL DEVELOPMENT & OPERATIONS 39
w hoboken RESIDENTIAL DEVELOPMENT & OPERATIONS 39
 WHY IS PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IMPORTANT? ♦ To satisfy consumers ♦ To create new jobs ♦ To maintain margins ♦ To expand the business All organizations must do this or eventually die. . …use the firm’s resources to meet objectives in the changing environment.
WHY IS PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IMPORTANT? ♦ To satisfy consumers ♦ To create new jobs ♦ To maintain margins ♦ To expand the business All organizations must do this or eventually die. . …use the firm’s resources to meet objectives in the changing environment.
 PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE SERVICE SECTOR Many manufacturing people think they are the only ones who develop new products. Yet the service sector develop products all the time and are often very creative and successful at it. No matter who develops it, a new product is something that satisfies customer needs in a new way, be it manufactured or a service that is delivered. § § § Examples: new banking and credit card products new telephone services faster and more reliable package delivery
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE SERVICE SECTOR Many manufacturing people think they are the only ones who develop new products. Yet the service sector develop products all the time and are often very creative and successful at it. No matter who develops it, a new product is something that satisfies customer needs in a new way, be it manufactured or a service that is delivered. § § § Examples: new banking and credit card products new telephone services faster and more reliable package delivery
 PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE HOTEL SECTOR Courtyard by Marriott In 1983, Marriott opened up the Courtyard hotels, its version of a moderately priced hotel chain. When it went after this niche opportunity, Marriott did a good job of identifying customer needs and wants. It empowered a cross-functional team to develop the new product, which first appeared as a prototype hotel Maryland (USA). After a successful test marketing of the new hotels in Atlanta, Courtyard has become an important addition to the Marriott product line, with more than 800 hotels worldwide.
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT IN THE HOTEL SECTOR Courtyard by Marriott In 1983, Marriott opened up the Courtyard hotels, its version of a moderately priced hotel chain. When it went after this niche opportunity, Marriott did a good job of identifying customer needs and wants. It empowered a cross-functional team to develop the new product, which first appeared as a prototype hotel Maryland (USA). After a successful test marketing of the new hotels in Atlanta, Courtyard has become an important addition to the Marriott product line, with more than 800 hotels worldwide.
 NEW PRODUCT ADOPTION PROCESS The Adoption Process (also known as the Diffusion of Innovation) is more than forty years old and remains an important marketing tool. It describes the behaviour of consumers as they purchase new products and services. The individual categories of innovator, early adoptor, early majority, late majority and laggards.
NEW PRODUCT ADOPTION PROCESS The Adoption Process (also known as the Diffusion of Innovation) is more than forty years old and remains an important marketing tool. It describes the behaviour of consumers as they purchase new products and services. The individual categories of innovator, early adoptor, early majority, late majority and laggards.
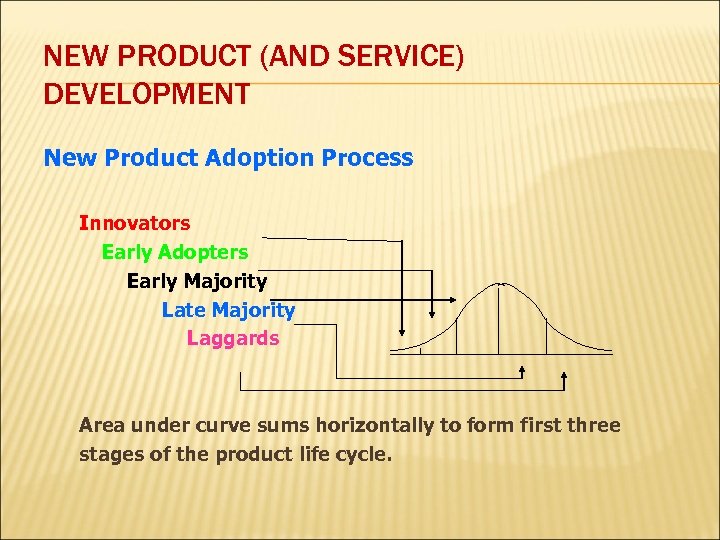 NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT New Product Adoption Process Innovators Early Adopters Early Majority Late Majority Laggards Area under curve sums horizontally to form first three stages of the product life cycle.
NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT New Product Adoption Process Innovators Early Adopters Early Majority Late Majority Laggards Area under curve sums horizontally to form first three stages of the product life cycle.
 EXAMPLES q q 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ipods DVD players (or even video players and digital watches) Initially only a small group of younger or informed, well off people bought into these products. Opinion leaders, or the early adoptors then buy the product and tend to be a target for marketing companies wishing to gain an early foot hold. The early majority are slightly ahead of the average, and follow. Then the late majority buy into the product, Followed by any laggards. New adoption process or curves begin all the time.
EXAMPLES q q 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ipods DVD players (or even video players and digital watches) Initially only a small group of younger or informed, well off people bought into these products. Opinion leaders, or the early adoptors then buy the product and tend to be a target for marketing companies wishing to gain an early foot hold. The early majority are slightly ahead of the average, and follow. Then the late majority buy into the product, Followed by any laggards. New adoption process or curves begin all the time.
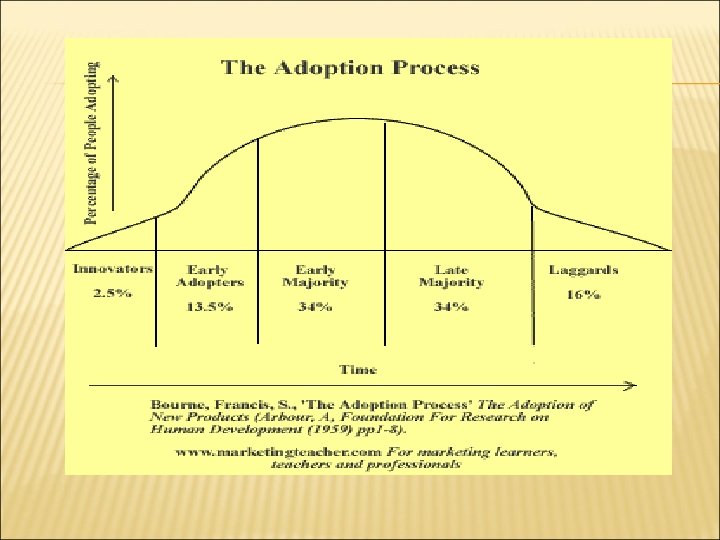
 NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT Each successive set of consumers behaves differently. Rate of Adoption is a function of: £ £ £ relative advantage compatibility complexity availability of trial observability
NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT Each successive set of consumers behaves differently. Rate of Adoption is a function of: £ £ £ relative advantage compatibility complexity availability of trial observability
 PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS q q q To convert ideas/ technology into profitable products or services A form of research But requires a high degree of co-operation with other functions
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS q q q To convert ideas/ technology into profitable products or services A form of research But requires a high degree of co-operation with other functions
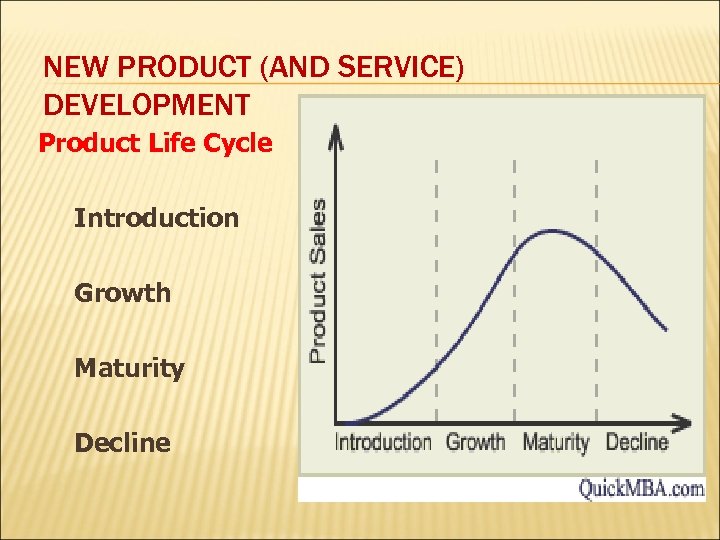 NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT Product Life Cycle Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
NEW PRODUCT (AND SERVICE) DEVELOPMENT Product Life Cycle Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
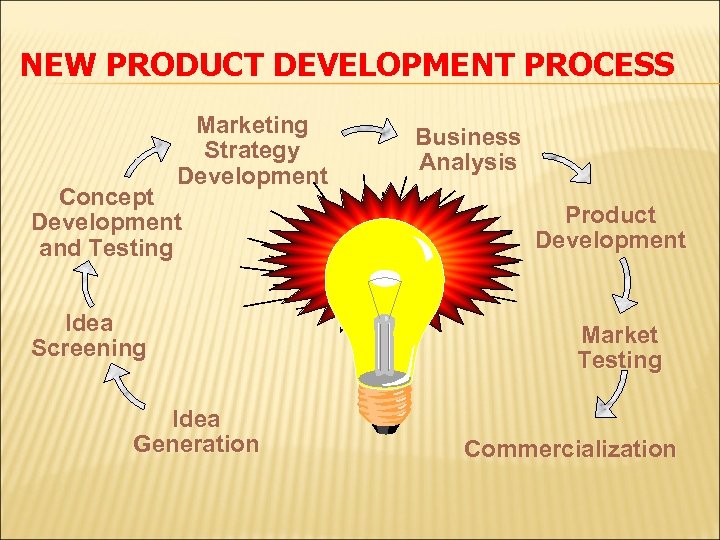 NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Marketing Strategy Development Concept Development and Testing Idea Screening Idea Generation Business Analysis Product Development Market Testing Commercialization
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Marketing Strategy Development Concept Development and Testing Idea Screening Idea Generation Business Analysis Product Development Market Testing Commercialization
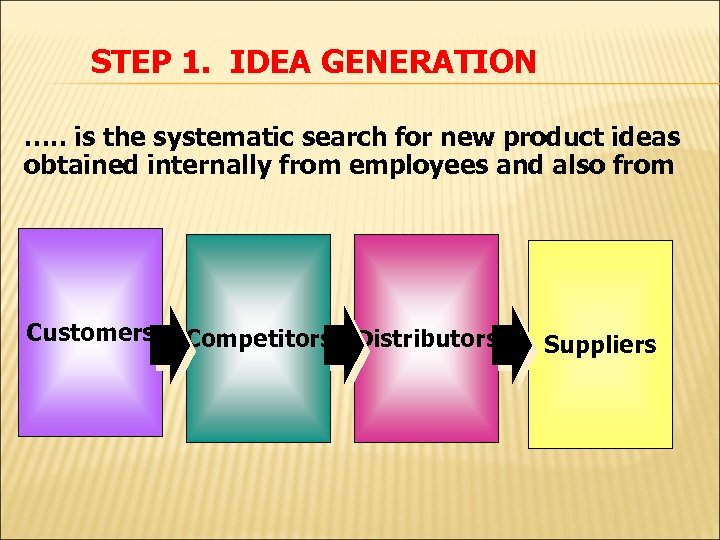 STEP 1. IDEA GENERATION …. . is the systematic search for new product ideas obtained internally from employees and also from Customers Competitors Distributors Suppliers
STEP 1. IDEA GENERATION …. . is the systematic search for new product ideas obtained internally from employees and also from Customers Competitors Distributors Suppliers
 STEP 2. IDEA SCREENING q Process to spot good ideas and drop poor ones as soon as possible q Many companies have systems for rating and screening ideas which estimate: q Market size q Product price q Development time and costs q Unit costs q Rate of return q Then, the idea is evaluated against a set of general company criteria
STEP 2. IDEA SCREENING q Process to spot good ideas and drop poor ones as soon as possible q Many companies have systems for rating and screening ideas which estimate: q Market size q Product price q Development time and costs q Unit costs q Rate of return q Then, the idea is evaluated against a set of general company criteria
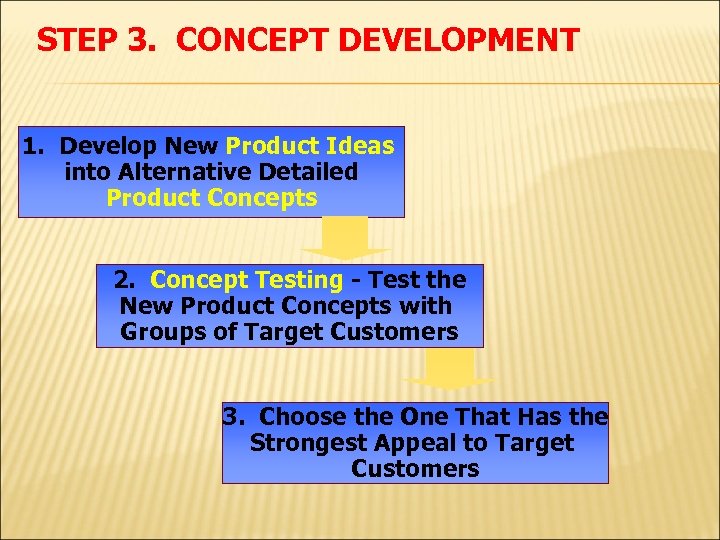 STEP 3. CONCEPT DEVELOPMENT 1. Develop New Product Ideas into Alternative Detailed Product Concepts 2. Concept Testing - Test the New Product Concepts with Groups of Target Customers 3. Choose the One That Has the Strongest Appeal to Target Customers
STEP 3. CONCEPT DEVELOPMENT 1. Develop New Product Ideas into Alternative Detailed Product Concepts 2. Concept Testing - Test the New Product Concepts with Groups of Target Customers 3. Choose the One That Has the Strongest Appeal to Target Customers
 STEP 4. MARKETING STRATEGY Part One Describes Overall: Target Market Planned Product Positioning Sales & Profit Goals Market Share Part Two Describes First-Year: Product’s Planned Price Distribution Marketing Budget Part Three Describes Long-Term: Sales & Profit Goals Marketing Mix Strategy
STEP 4. MARKETING STRATEGY Part One Describes Overall: Target Market Planned Product Positioning Sales & Profit Goals Market Share Part Two Describes First-Year: Product’s Planned Price Distribution Marketing Budget Part Three Describes Long-Term: Sales & Profit Goals Marketing Mix Strategy
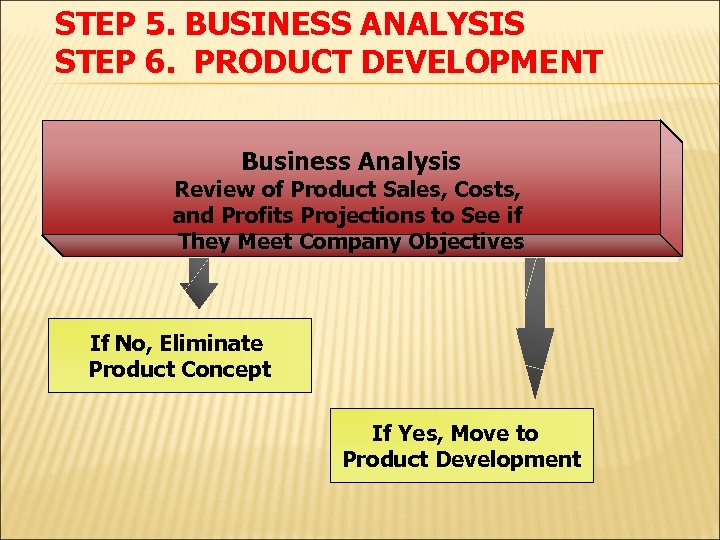 STEP 5. BUSINESS ANALYSIS STEP 6. PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Business Analysis Review of Product Sales, Costs, and Profits Projections to See if They Meet Company Objectives If No, Eliminate Product Concept If Yes, Move to Product Development
STEP 5. BUSINESS ANALYSIS STEP 6. PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Business Analysis Review of Product Sales, Costs, and Profits Projections to See if They Meet Company Objectives If No, Eliminate Product Concept If Yes, Move to Product Development
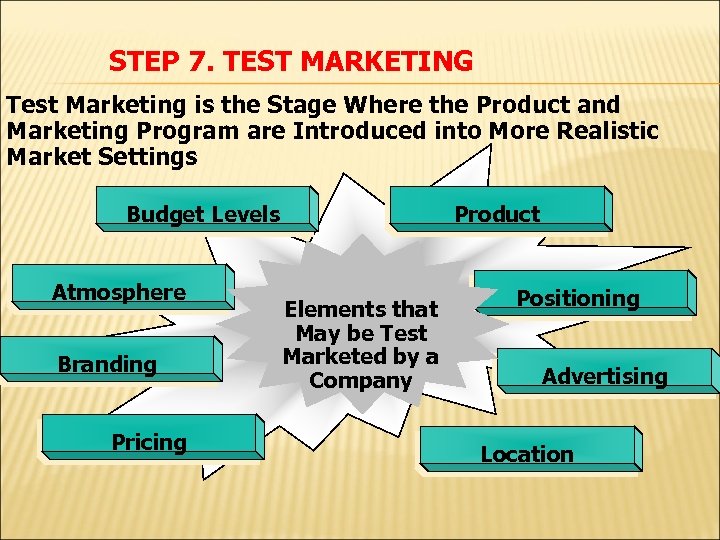 STEP 7. TEST MARKETING Test Marketing is the Stage Where the Product and Marketing Program are Introduced into More Realistic Market Settings Product Budget Levels Atmosphere Branding Pricing Elements that May be Test Marketed by a Company Positioning Advertising Location
STEP 7. TEST MARKETING Test Marketing is the Stage Where the Product and Marketing Program are Introduced into More Realistic Market Settings Product Budget Levels Atmosphere Branding Pricing Elements that May be Test Marketed by a Company Positioning Advertising Location
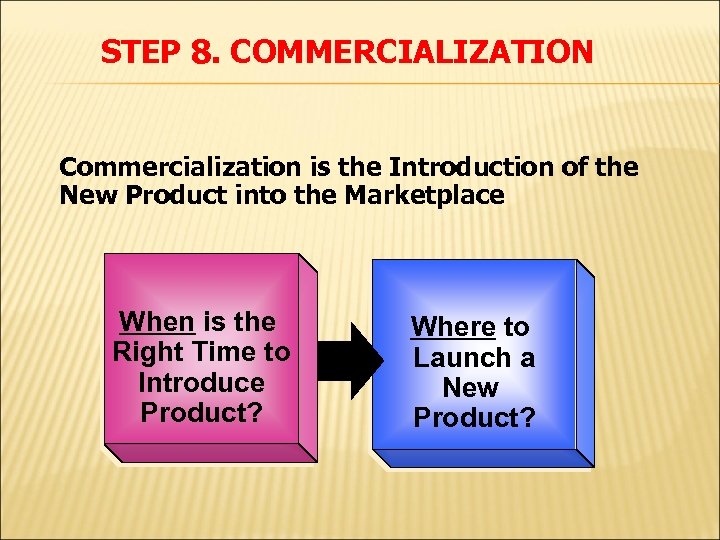 STEP 8. COMMERCIALIZATION Commercialization is the Introduction of the New Product into the Marketplace When is the Right Time to Introduce Product? Where to Launch a New Product?
STEP 8. COMMERCIALIZATION Commercialization is the Introduction of the New Product into the Marketplace When is the Right Time to Introduce Product? Where to Launch a New Product?
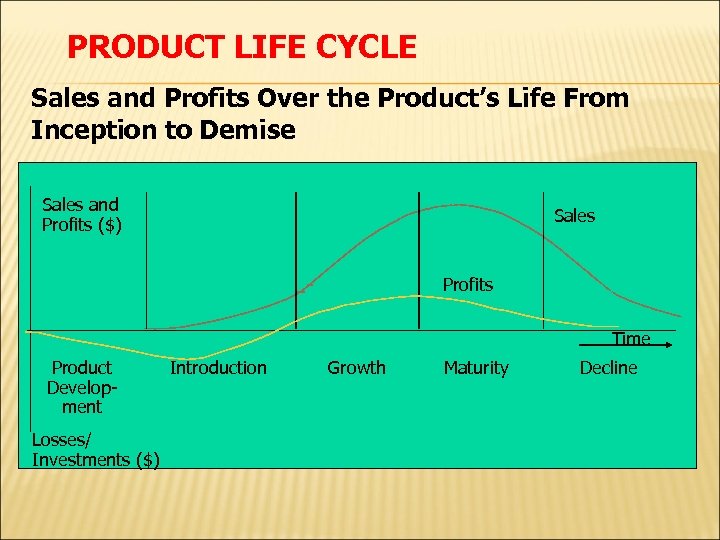 PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Losses/ Investments ($) Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Losses/ Investments ($) Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
 PRODUCTS/ SERVICES INTO BRANDS What is a brand ? A brand is more than a logo, tag line or product A brand is a perception or emotion, maintained by somebody other, that describes the total experience with the company, product, service or person
PRODUCTS/ SERVICES INTO BRANDS What is a brand ? A brand is more than a logo, tag line or product A brand is a perception or emotion, maintained by somebody other, that describes the total experience with the company, product, service or person
 q q Brands are among a company’s most valuable assets A Brand represents what the company is and what it stands for A Brand implies trust , consistency, and a defined set of expectations The strongest brands own a place in the customer’s mind
q q Brands are among a company’s most valuable assets A Brand represents what the company is and what it stands for A Brand implies trust , consistency, and a defined set of expectations The strongest brands own a place in the customer’s mind
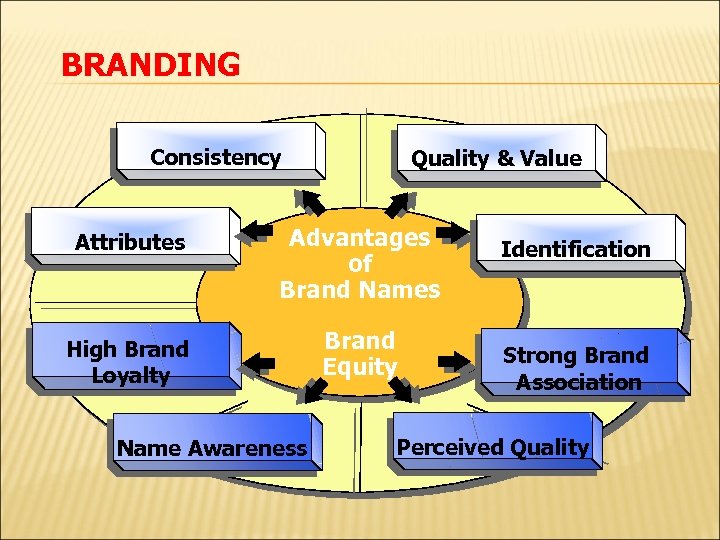 BRANDING Consistency Quality & Value Attributes Advantages of Brand Names High Brand Loyalty Brand Equity Name Awareness Identification Strong Brand Association Perceived Quality
BRANDING Consistency Quality & Value Attributes Advantages of Brand Names High Brand Loyalty Brand Equity Name Awareness Identification Strong Brand Association Perceived Quality
 CONDITIONS THAT SUPPORT BRANDING q q q Product is easy to identify Product is perceived to be the best value for the price Quality and standards are easy to maintain Demand is enough to support branding effort There are economies of scale
CONDITIONS THAT SUPPORT BRANDING q q q Product is easy to identify Product is perceived to be the best value for the price Quality and standards are easy to maintain Demand is enough to support branding effort There are economies of scale

 HOTEL BRANDS Ritz Carlton Marriott Hotels & Resorts JW Marriott Hotels & Resorts Renaissance Hotels Courtyard Residence Inn Fairfield Inn Conference Centers Towne. Place Suites Spring. Hill Suites Marriott Vacation Club Hilton® Conrad Hotels and Resorts® Doubletree by Hilton® Embassy Suites by Hilton® Hampton Inn by Hilton® Hilton Garden Inn® Hilton Grand Vacations® Homewood Suites by Hilton The Waldorf-Astoria Collection®
HOTEL BRANDS Ritz Carlton Marriott Hotels & Resorts JW Marriott Hotels & Resorts Renaissance Hotels Courtyard Residence Inn Fairfield Inn Conference Centers Towne. Place Suites Spring. Hill Suites Marriott Vacation Club Hilton® Conrad Hotels and Resorts® Doubletree by Hilton® Embassy Suites by Hilton® Hampton Inn by Hilton® Hilton Garden Inn® Hilton Grand Vacations® Homewood Suites by Hilton The Waldorf-Astoria Collection®
 “A brand is a distinguishing name or symbol intended to identify goods or services of a seller and to differentiate those goods or services from competitors. ” Clyde C. Tuggle Coca-Cola, Senior Vice President Worldwide Public Affairs & Communications
“A brand is a distinguishing name or symbol intended to identify goods or services of a seller and to differentiate those goods or services from competitors. ” Clyde C. Tuggle Coca-Cola, Senior Vice President Worldwide Public Affairs & Communications
 PURPOSE OF A BRAND q q q Inspire Inject your organization with heart and soul Motivate Spur action Connect Unify departments and divisions for “global” presence Link products and services to a “promise” Simplify Clarify and crystallize your mission Inform Convey values, attributes, and advantages
PURPOSE OF A BRAND q q q Inspire Inject your organization with heart and soul Motivate Spur action Connect Unify departments and divisions for “global” presence Link products and services to a “promise” Simplify Clarify and crystallize your mission Inform Convey values, attributes, and advantages
 LESSONS FROM HYATT: SIMPLE WAYS TO DAMAGE YOUR BRAND Hyatt is a hospitality company. Hospitality companies rely on the currency of brand maintained by superior customer service — to sustain and grow their businesses. Hyatt managers came to the conclusion that they could save money by firing the housekeeping staffs at three hotels and replacing them with vendormanaged contractors. More than 584 comments had been posted on the Boston Globe's website about Hyatt's actions. Most people don't like doing business with companies that do distasteful things; moreover, this issue raises questions about the Hyatt commitment to quality. Boston Hyatt September 2009
LESSONS FROM HYATT: SIMPLE WAYS TO DAMAGE YOUR BRAND Hyatt is a hospitality company. Hospitality companies rely on the currency of brand maintained by superior customer service — to sustain and grow their businesses. Hyatt managers came to the conclusion that they could save money by firing the housekeeping staffs at three hotels and replacing them with vendormanaged contractors. More than 584 comments had been posted on the Boston Globe's website about Hyatt's actions. Most people don't like doing business with companies that do distasteful things; moreover, this issue raises questions about the Hyatt commitment to quality. Boston Hyatt September 2009
 LESSONS LEARNED Imagine what this move — and the way it was carried out — says to remaining workers at the affected hotels (let alone the rest of Hyatt's employees). Is this the way you'd want your management treating your fellow workers? Would this inspire you to go "above and beyond" for your customers? To do your job at its highest level? There's at least a small lesson here: think about the way your actions will be perceived by all your stakeholders before you take them. Will these actions affect the way your customers feel about you? Might they impact worker morale?
LESSONS LEARNED Imagine what this move — and the way it was carried out — says to remaining workers at the affected hotels (let alone the rest of Hyatt's employees). Is this the way you'd want your management treating your fellow workers? Would this inspire you to go "above and beyond" for your customers? To do your job at its highest level? There's at least a small lesson here: think about the way your actions will be perceived by all your stakeholders before you take them. Will these actions affect the way your customers feel about you? Might they impact worker morale?
 IS THERE A DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE PRODUCT/SERVICE AND A BRAND? Which will be more successful? § § Great Product or Service / Good Brand? OR Good Product or Service / Great Brand?
IS THERE A DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE PRODUCT/SERVICE AND A BRAND? Which will be more successful? § § Great Product or Service / Good Brand? OR Good Product or Service / Great Brand?
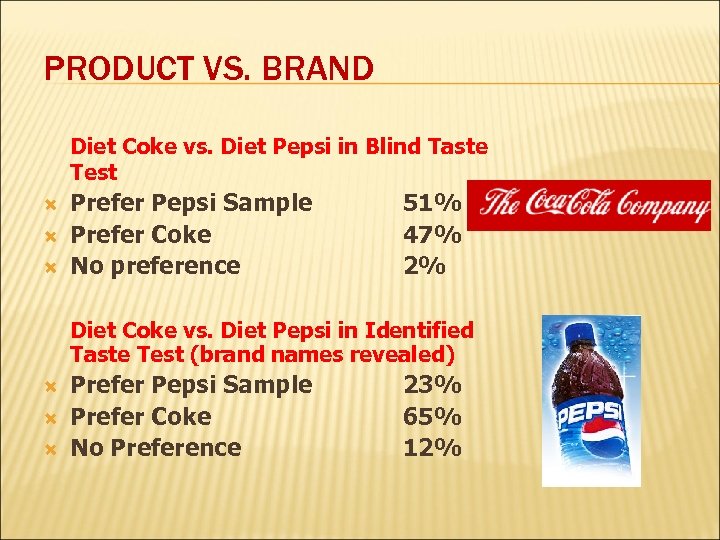 PRODUCT VS. BRAND Diet Coke vs. Diet Pepsi in Blind Taste Test Prefer Pepsi Sample Prefer Coke No preference 51% 47% 2% Diet Coke vs. Diet Pepsi in Identified Taste Test (brand names revealed) Prefer Pepsi Sample Prefer Coke No Preference 23% 65% 12%
PRODUCT VS. BRAND Diet Coke vs. Diet Pepsi in Blind Taste Test Prefer Pepsi Sample Prefer Coke No preference 51% 47% 2% Diet Coke vs. Diet Pepsi in Identified Taste Test (brand names revealed) Prefer Pepsi Sample Prefer Coke No Preference 23% 65% 12%
 POTENTIAL HOTEL BRANDING PROBLEMS § Multiple brands in the same company may cause consumer confusion § The company's image may become blurred § Cross-over competition within chain may dilute market share § Clear distinctions between brands hard to maintain § Consistent service standards hard to maintain
POTENTIAL HOTEL BRANDING PROBLEMS § Multiple brands in the same company may cause consumer confusion § The company's image may become blurred § Cross-over competition within chain may dilute market share § Clear distinctions between brands hard to maintain § Consistent service standards hard to maintain

 WORKSHOP ACTIVITY Beautiful Hotels is considering the development of a budget hotel brand to roll out in all its current operating countries, primarily in secondary cities and within the transport network.
WORKSHOP ACTIVITY Beautiful Hotels is considering the development of a budget hotel brand to roll out in all its current operating countries, primarily in secondary cities and within the transport network.
 WORKSHOP ACTIVITY Your task is to prepare the brand specifications for this new budget hotel chain in terms of its products and services, indicating price relative to local averages for 1*, 2*, 3*, 4* or 5*. You will share your conclusions with the whole group in a presentation of up to 15 minutes
WORKSHOP ACTIVITY Your task is to prepare the brand specifications for this new budget hotel chain in terms of its products and services, indicating price relative to local averages for 1*, 2*, 3*, 4* or 5*. You will share your conclusions with the whole group in a presentation of up to 15 minutes
 THE END
THE END


