 3 Practice Free Response Questions Have Fun!
3 Practice Free Response Questions Have Fun!
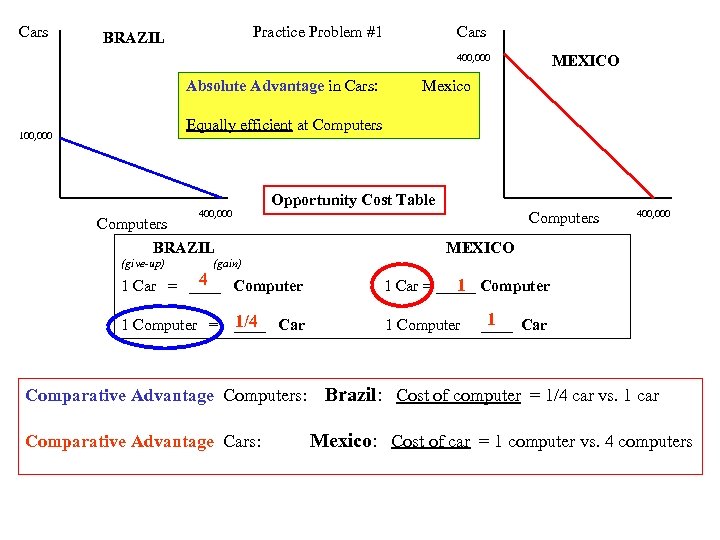 Cars Practice Problem #1 BRAZIL Cars MEXICO 400, 000 Absolute Advantage in Cars: Mexico Equally efficient at Computers 100, 000 Opportunity Cost Table 400, 000 Computers BRAZIL (give-up) (gain) 4 1 Car = ____ Computer 1 Computer = 1/4 ____ Car Comparative Advantage Computers: Comparative Advantage Cars: 400, 000 MEXICO 1 1 Car = _____ Computer 1 ____ Car Brazil: Cost of computer = 1/4 car vs. 1 car Mexico: Cost of car = 1 computer vs. 4 computers
Cars Practice Problem #1 BRAZIL Cars MEXICO 400, 000 Absolute Advantage in Cars: Mexico Equally efficient at Computers 100, 000 Opportunity Cost Table 400, 000 Computers BRAZIL (give-up) (gain) 4 1 Car = ____ Computer 1 Computer = 1/4 ____ Car Comparative Advantage Computers: Comparative Advantage Cars: 400, 000 MEXICO 1 1 Car = _____ Computer 1 ____ Car Brazil: Cost of computer = 1/4 car vs. 1 car Mexico: Cost of car = 1 computer vs. 4 computers
 Ranges for Efficient Trade (Terms of Trade) Brazil must buy cars at a ratio above 1/4 car per computer Mexico must sell cars at a ratio below 1 computer per car ¼ & less than 1 car per computer or > 1 & less than 4 computers per car Terms of Trade: >
Ranges for Efficient Trade (Terms of Trade) Brazil must buy cars at a ratio above 1/4 car per computer Mexico must sell cars at a ratio below 1 computer per car ¼ & less than 1 car per computer or > 1 & less than 4 computers per car Terms of Trade: >
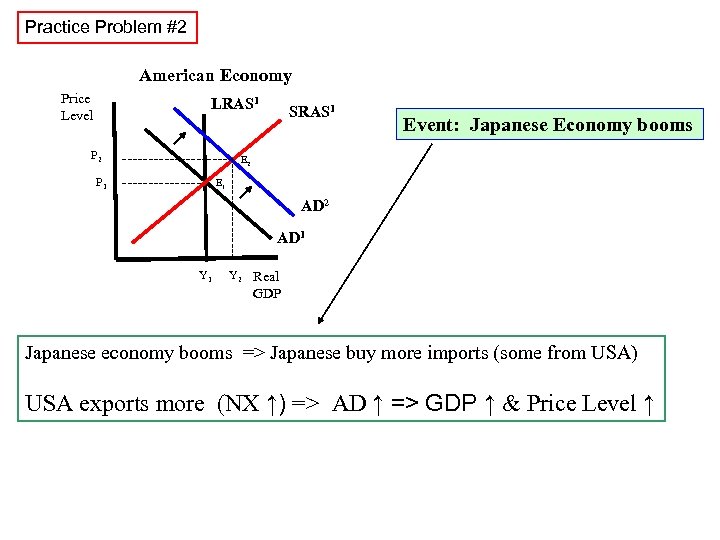 Practice Problem #2 American Economy Price Level LRAS 1 P 1 ------------------ E 1 Y 1 Event: Japanese Economy booms E 2 ---------- P 2 SRAS 1 AD 2 AD 1 Y 2 Real GDP Japanese economy booms => Japanese buy more imports (some from USA) USA exports more (NX ↑) => AD ↑ => GDP ↑ & Price Level ↑
Practice Problem #2 American Economy Price Level LRAS 1 P 1 ------------------ E 1 Y 1 Event: Japanese Economy booms E 2 ---------- P 2 SRAS 1 AD 2 AD 1 Y 2 Real GDP Japanese economy booms => Japanese buy more imports (some from USA) USA exports more (NX ↑) => AD ↑ => GDP ↑ & Price Level ↑
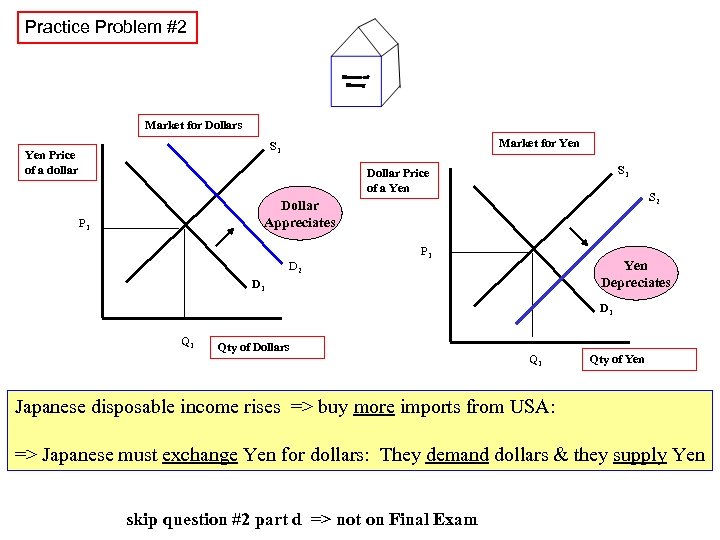 Practice Problem #2 Market for Dollars Market for Yen S 1 Yen Price of a dollar S 1 Dollar Price of a Yen ---------- Q 1 D 2 P 1 ---------- D 1 Qty of Dollars ---------------------- P 1 S 2 Dollar Appreciates Q 1 Yen Depreciates D 1 Qty of Yen Japanese disposable income rises => buy more imports from USA: => Japanese must exchange Yen for dollars: They demand dollars & they supply Yen skip question #2 part d => not on Final Exam
Practice Problem #2 Market for Dollars Market for Yen S 1 Yen Price of a dollar S 1 Dollar Price of a Yen ---------- Q 1 D 2 P 1 ---------- D 1 Qty of Dollars ---------------------- P 1 S 2 Dollar Appreciates Q 1 Yen Depreciates D 1 Qty of Yen Japanese disposable income rises => buy more imports from USA: => Japanese must exchange Yen for dollars: They demand dollars & they supply Yen skip question #2 part d => not on Final Exam
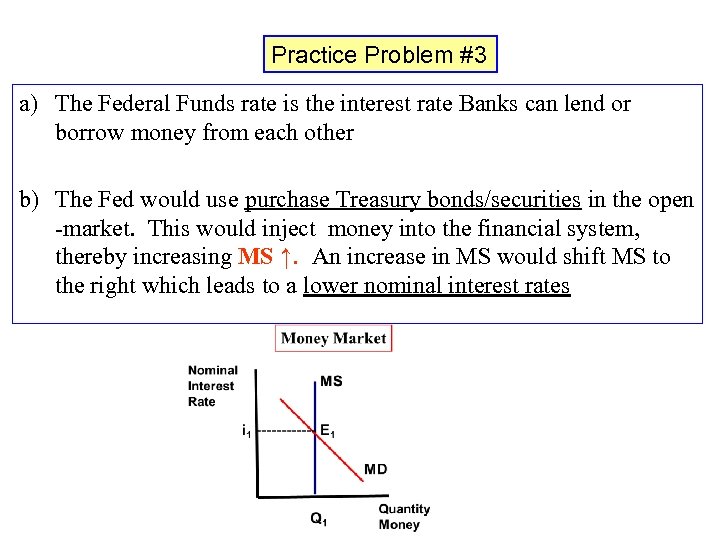 Practice Problem #3 a) The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate Banks can lend or borrow money from each other b) The Fed would use purchase Treasury bonds/securities in the open -market. This would inject money into the financial system, thereby increasing MS ↑. An increase in MS would shift MS to the right which leads to a lower nominal interest rates
Practice Problem #3 a) The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate Banks can lend or borrow money from each other b) The Fed would use purchase Treasury bonds/securities in the open -market. This would inject money into the financial system, thereby increasing MS ↑. An increase in MS would shift MS to the right which leads to a lower nominal interest rates
 Practice Problem #3 continued c) The multiplier is 1/r. r. so 1/. 20 = 5 multiplier. -Therefore, a 10 million purchase of bonds would lead to a 50 million ↑ MS. -However, only 8 million could be loaned out…. Therefore, Loans could increase by $40 million d) Nominal Interest rates = Real Interest Rates + Expected Inflation If inflation rises and is expected to be permanent then inflation expectations nominal interest rates ( think long term) would rise. Real interest rates would remain unchanged based on rising inflation expectations and the equation above
Practice Problem #3 continued c) The multiplier is 1/r. r. so 1/. 20 = 5 multiplier. -Therefore, a 10 million purchase of bonds would lead to a 50 million ↑ MS. -However, only 8 million could be loaned out…. Therefore, Loans could increase by $40 million d) Nominal Interest rates = Real Interest Rates + Expected Inflation If inflation rises and is expected to be permanent then inflation expectations nominal interest rates ( think long term) would rise. Real interest rates would remain unchanged based on rising inflation expectations and the equation above