lecture 3.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 29
3 – Lecture Chemical bonding and Molecular Structure Azamat Amzebek

Topics Covered Ionic Bonds and Compounds Covalent Bonds Lewis Structures Types of Covalent Bonding Geometry and Polarity of Covalent Molecules Orbital Hybridization Sigma and Pi Bonds

Chemical bond The atoms in molecules held together by strong attractive forces called chemical bonds Formed by interaction of valence electrons of the combining atoms In the formation chemical bonds atoms bond according to the octet rule

Ionic bond Two atoms with large difference in electronegativity reactivity, there is complete electron transfer High electronegativity == anion Low electronegativity == cation

Ionic bond These two ions are held together by electrostatic forces This force of attraction between the charged ions is called an ionic bond
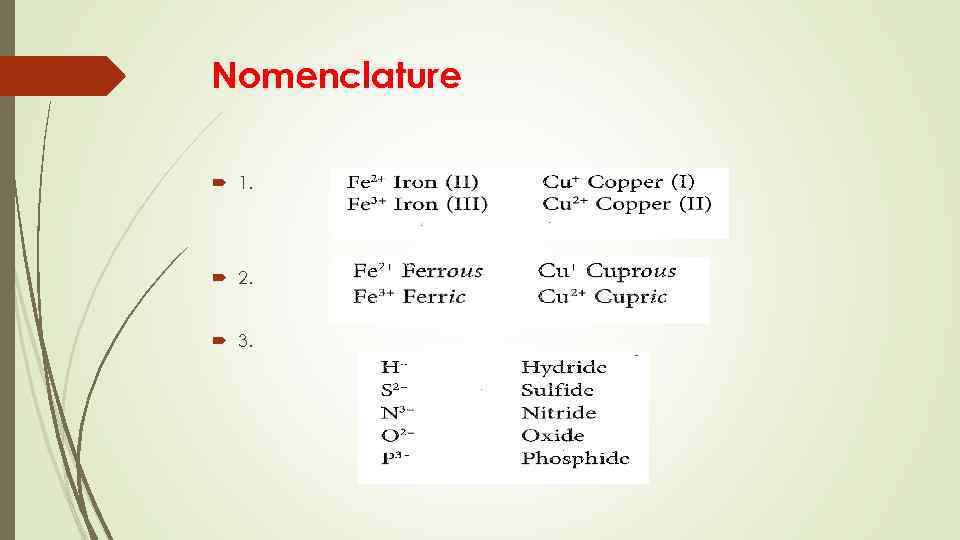
Nomenclature 1. 2. 3.

Nomenclature 4. 5.

Nomenclature 6.

Ionic bond High melting and boiling point – strong electrostatic force Conduct electricity in liquid and aqueous states

Covalent Bonds Forms when two elements have similar electronegativities They achieve a noble gas electron configuration by sharing electrons in what is known as a covalent bond Sometimes need more than one electron to form octet

Covalent bond Bonds length is the average distance between the two nuclei of the atoms involved Bond energy is the energy required to separate two bonded atoms

Bonds Primary bonding – covalent and ionic Secondary – hydrogen and Van der Vaals

Lewis Structures Valence electrons of a covalent bond – bonding electrons Valence electrons not involved in the covalent bond – lone electron pairs(nonbonding) Lewis structure – convenient representation of bonding and nonbonding electrons in a molecule
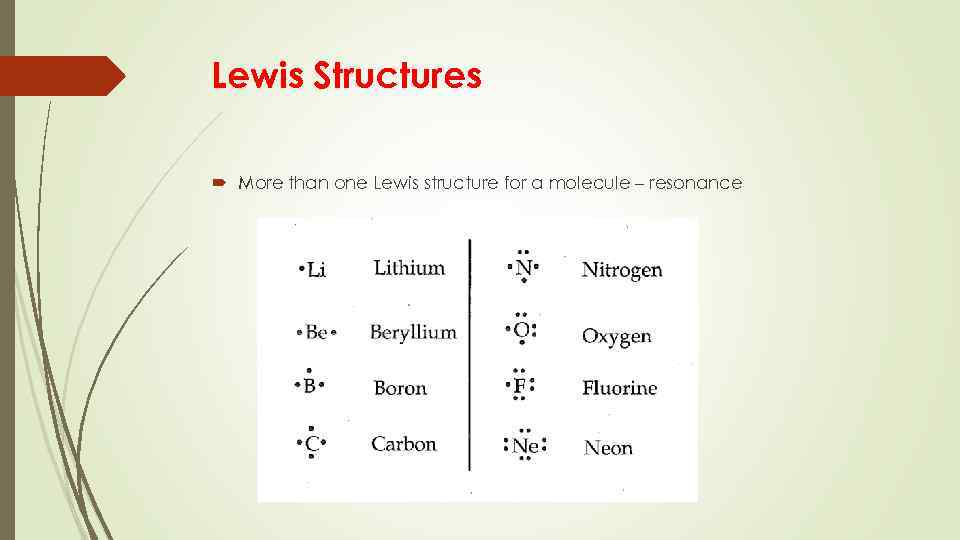
Lewis Structures More than one Lewis structure for a molecule – resonance

Formal Charge
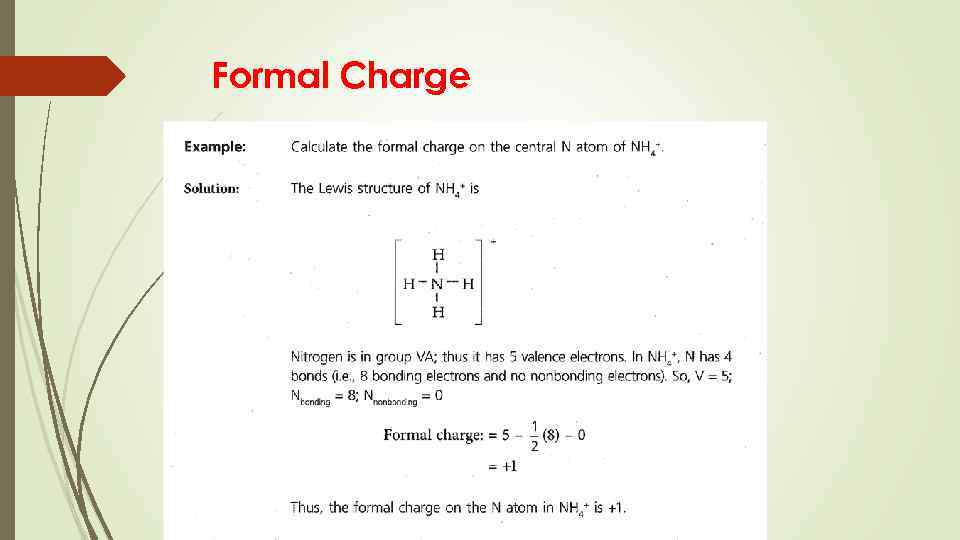
Formal Charge
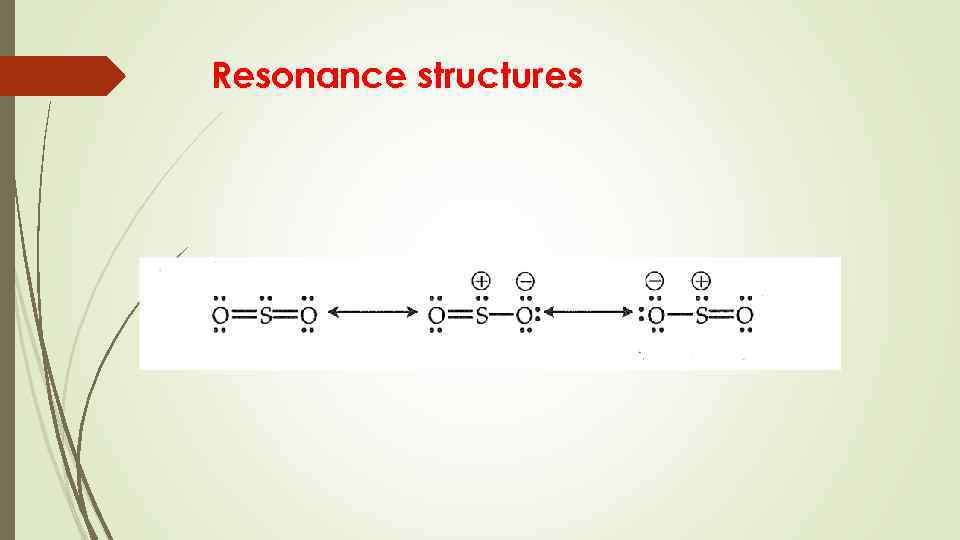
Resonance structures

Types of covalent bonds Polar covalent bonds – occurs between atoms with small difference in electronegativity Nonpolar covalent bond occurs between atoms that have the same electronegativites Coordinate Covalent Bond – the shared electron pair comes from the lone pair of one of the atoms in the molecules
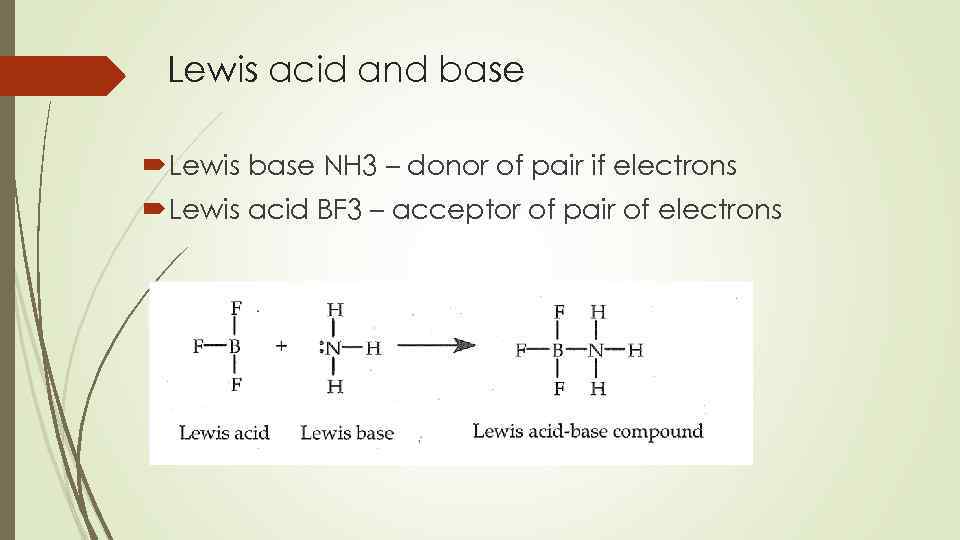
Lewis acid and base Lewis base NH 3 – donor of pair if electrons Lewis acid BF 3 – acceptor of pair of electrons
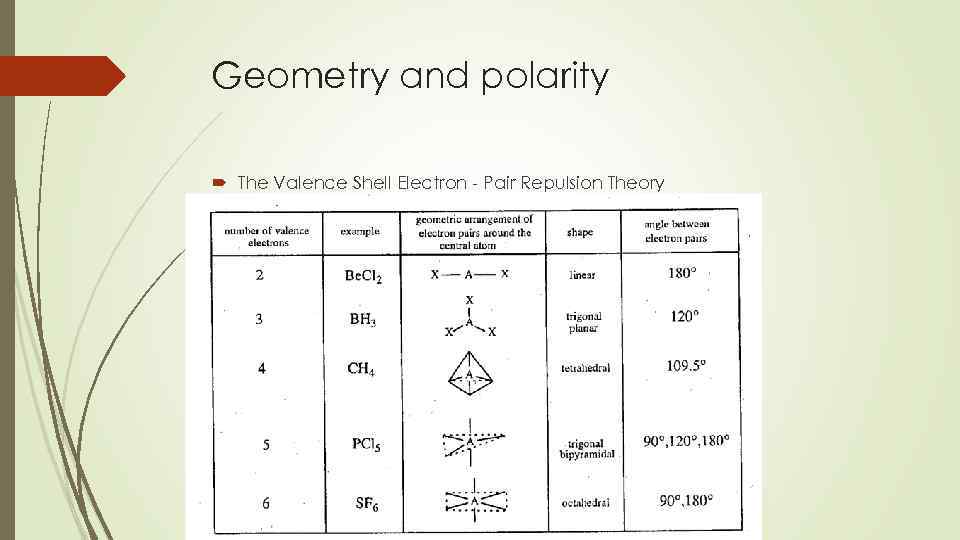
Geometry and polarity The Valence Shell Electron - Pair Repulsion Theory
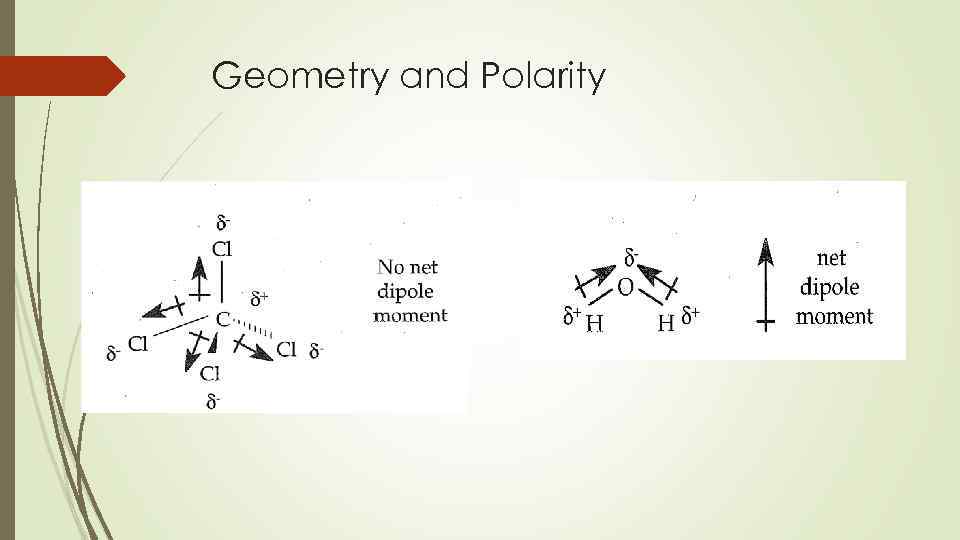
Geometry and Polarity
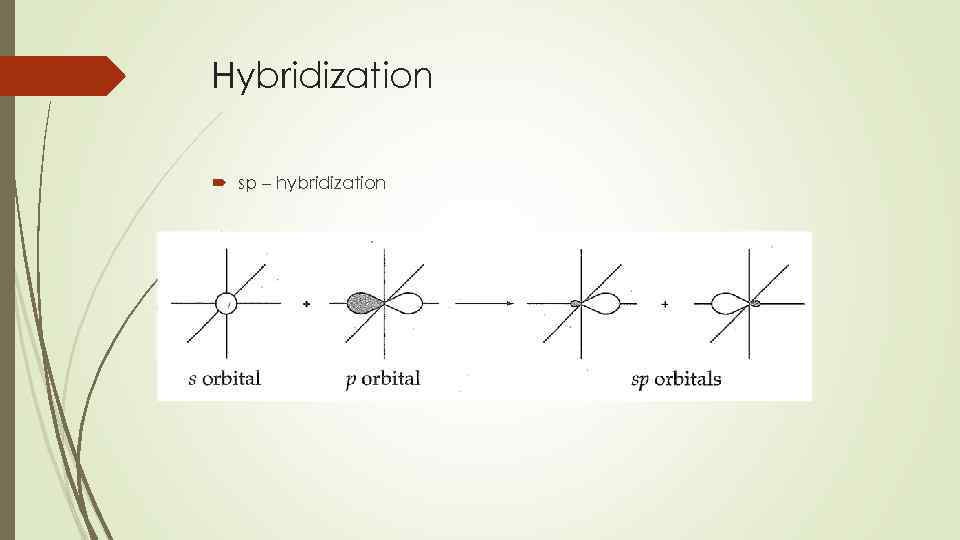
Hybridization sp – hybridization
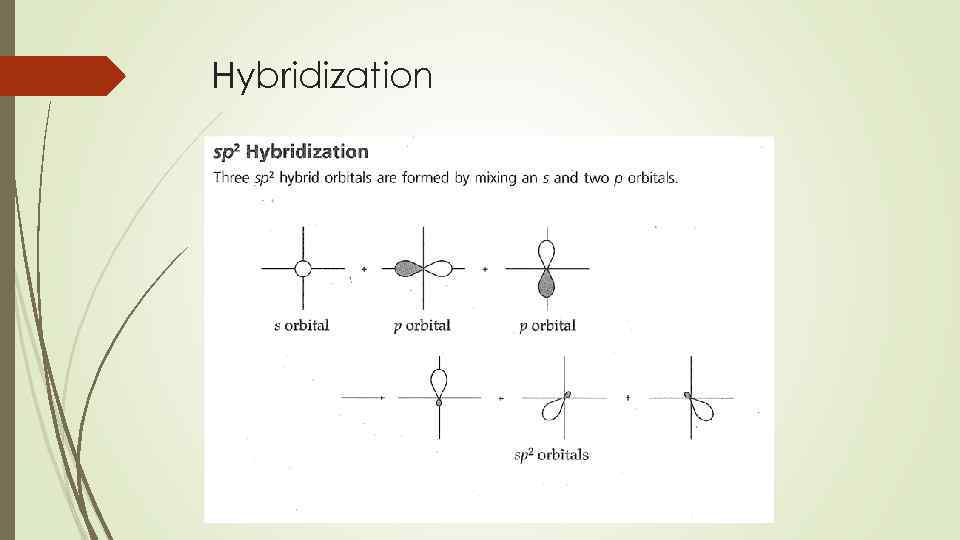
Hybridization
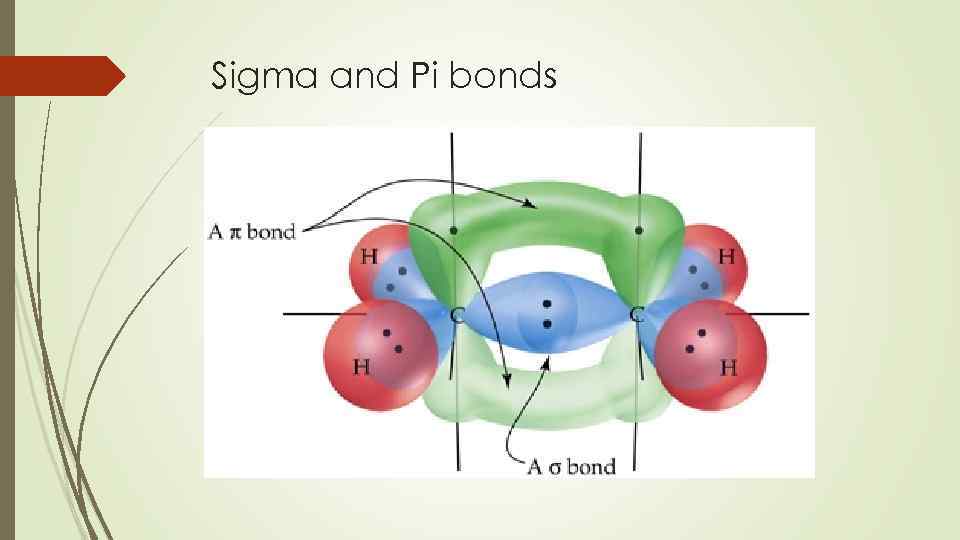
Sigma and Pi bonds
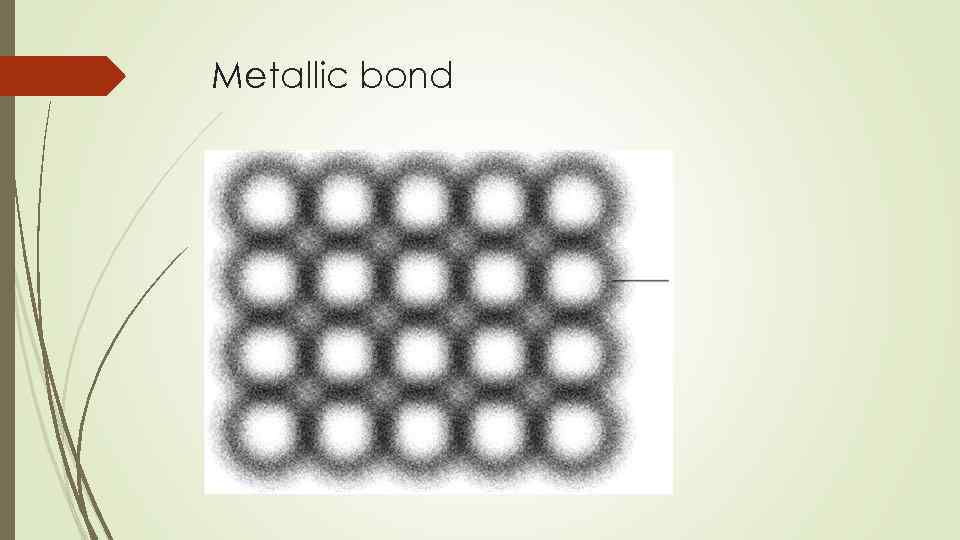
Metallic bond
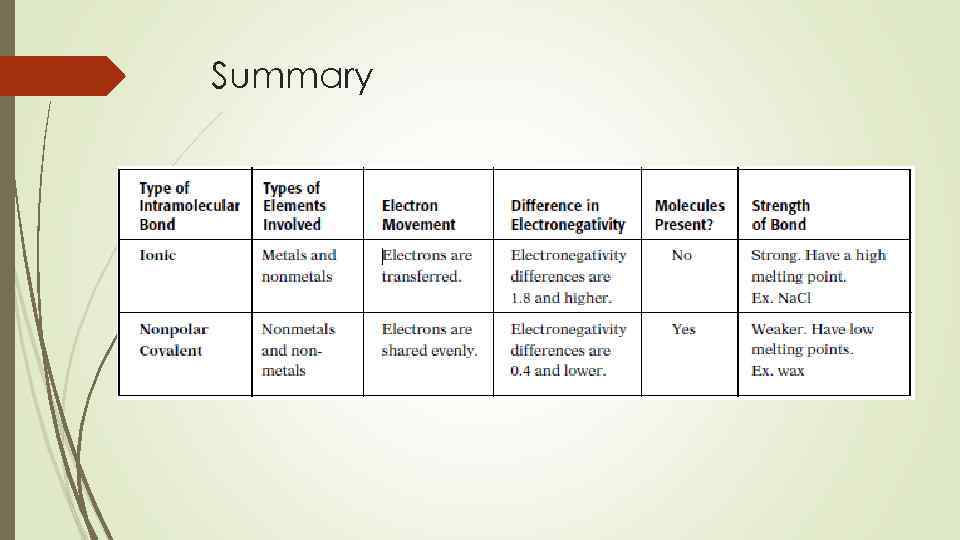
Summary
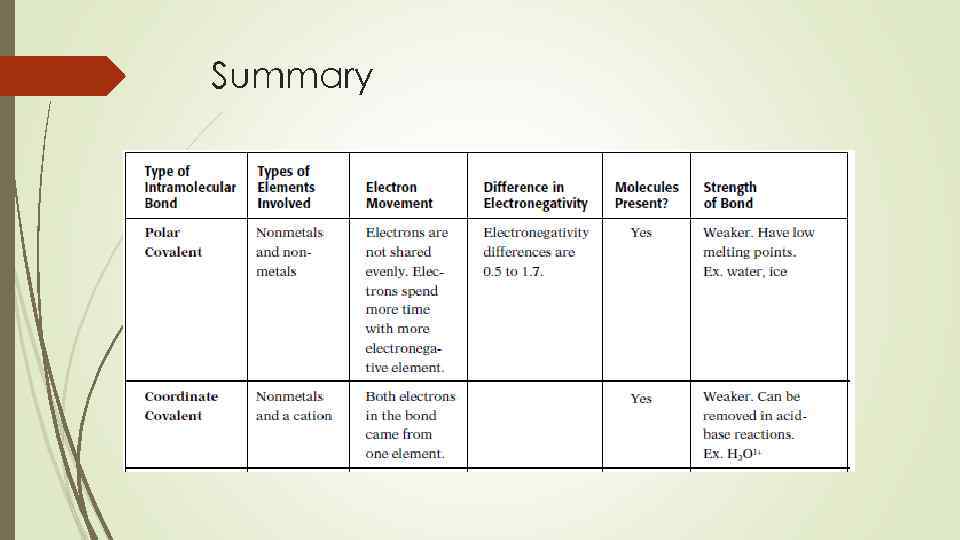
Summary
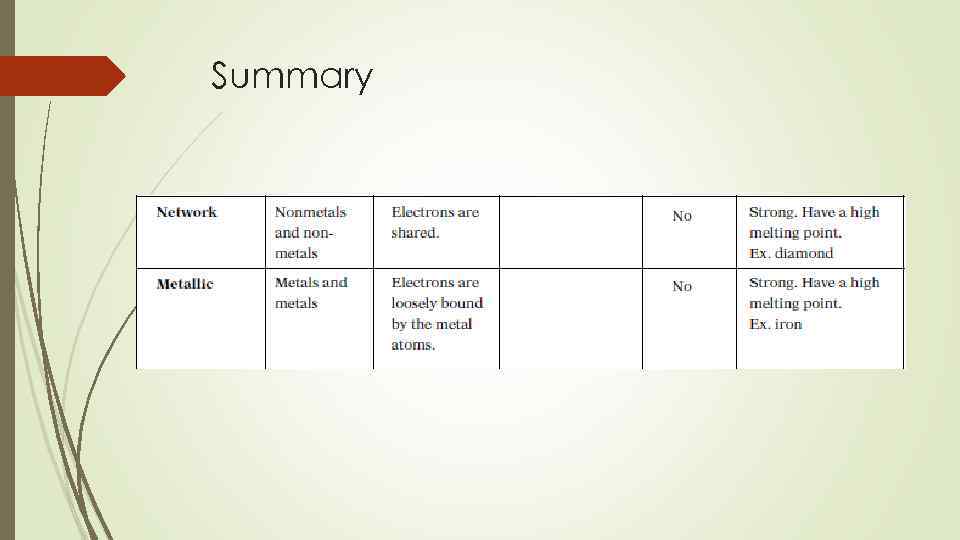
Summary

Summary
lecture 3.pptx