03_Intercultural Communicative Competence.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 33
 3. INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE
3. INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE
 DEFINITION • Competence • Communicative Competence • Cross-cultural communicative competence
DEFINITION • Competence • Communicative Competence • Cross-cultural communicative competence
 THE FOUR STAGES OF COMPETENCE • UNCONSCIOUS INCOMPETENCE The individual neither understands nor knows how to do something, nor recognizes the deficit, nor has a desire to address it. • CONSCIOUS INCOMPETENCE Though the individual does not understand or know how to do something, he or she does recognize the deficit, without yet addressing it. • CONSCIOUS COMPETENCE The individual understands or knows how to do something. However, demonstrating the skill or knowledge requires a great deal of consciousness or concentration. • UNCONSCIOUS COMPETENCE The individual has had so much practice with a skill that it becomes "second nature" and can be performed easily (often without concentrating too deeply). He or she may or may not be able to teach it to others, depending upon how and when it was learned.
THE FOUR STAGES OF COMPETENCE • UNCONSCIOUS INCOMPETENCE The individual neither understands nor knows how to do something, nor recognizes the deficit, nor has a desire to address it. • CONSCIOUS INCOMPETENCE Though the individual does not understand or know how to do something, he or she does recognize the deficit, without yet addressing it. • CONSCIOUS COMPETENCE The individual understands or knows how to do something. However, demonstrating the skill or knowledge requires a great deal of consciousness or concentration. • UNCONSCIOUS COMPETENCE The individual has had so much practice with a skill that it becomes "second nature" and can be performed easily (often without concentrating too deeply). He or she may or may not be able to teach it to others, depending upon how and when it was learned.
 OVERALL COMMUNICATION PROCESS COMMUNICATION: The process of transferring meanings from sender to receiver. On surface appears straightforward However, a great many problems can result in failure to transfer meanings correctly!
OVERALL COMMUNICATION PROCESS COMMUNICATION: The process of transferring meanings from sender to receiver. On surface appears straightforward However, a great many problems can result in failure to transfer meanings correctly!
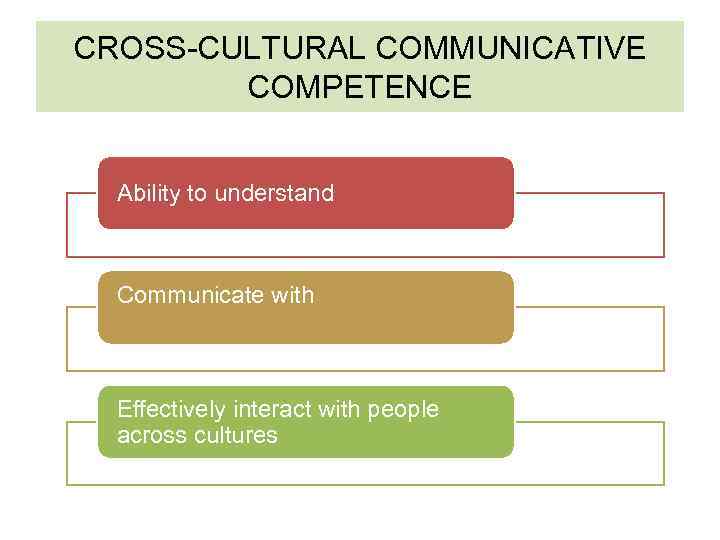 CROSS-CULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE Ability to understand Communicate with Effectively interact with people across cultures
CROSS-CULTURAL COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE Ability to understand Communicate with Effectively interact with people across cultures
 ADOPTATION • Cross-cultural shock • Xenophobia • Senior brother
ADOPTATION • Cross-cultural shock • Xenophobia • Senior brother
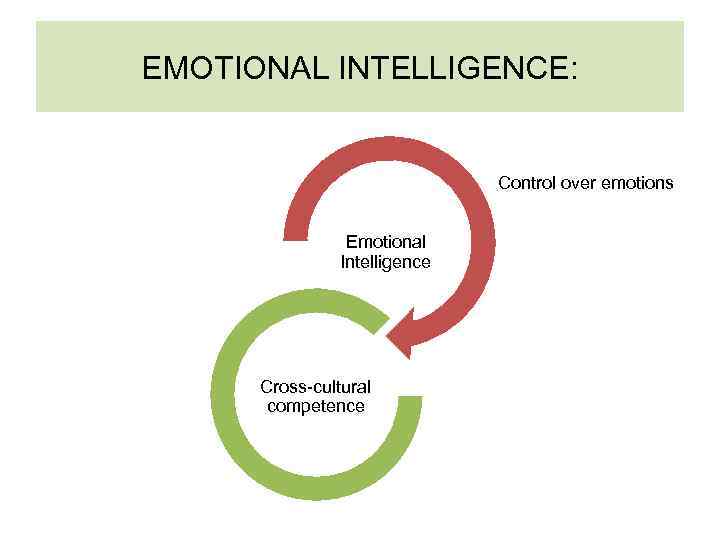 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE: Control over emotions Emotional Intelligence Cross-cultural competence
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE: Control over emotions Emotional Intelligence Cross-cultural competence
 MANAGEMENT STYLE ANALYSING BACKGROUND • • Values Stereotype and “Double Stereotype” Dimensions Corporate culture
MANAGEMENT STYLE ANALYSING BACKGROUND • • Values Stereotype and “Double Stereotype” Dimensions Corporate culture
 VALUES • • Peace Family Respect for nature and the environment Social equality and solidarity Freedom of opinion Tolerance and openness to others Cultural diversity Entrepreneurship
VALUES • • Peace Family Respect for nature and the environment Social equality and solidarity Freedom of opinion Tolerance and openness to others Cultural diversity Entrepreneurship
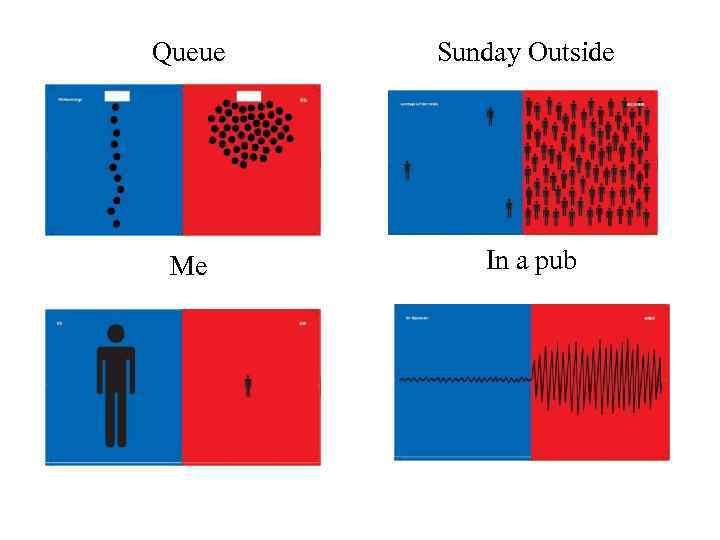 Queue Sunday Outside Me In a pub
Queue Sunday Outside Me In a pub
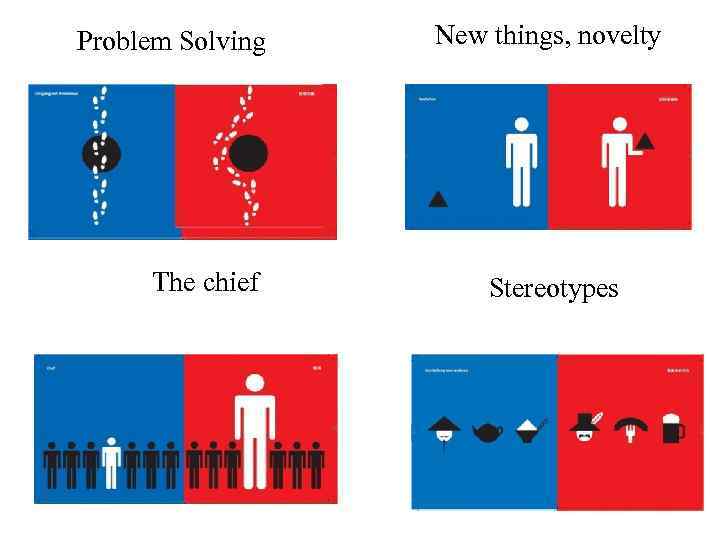 Problem Solving The chief New things, novelty Stereotypes
Problem Solving The chief New things, novelty Stereotypes
 TASK: RUSSIAN-&&& COMPARISON • Business Letter • Opinion • Punctuality • Networking • Me • Problem solving • Attitude to novelty • The chief • Stereotypes
TASK: RUSSIAN-&&& COMPARISON • Business Letter • Opinion • Punctuality • Networking • Me • Problem solving • Attitude to novelty • The chief • Stereotypes
 CASE GLOBAL FARMATIC Develop the criteria and questions for interviewing the candidates.
CASE GLOBAL FARMATIC Develop the criteria and questions for interviewing the candidates.
 VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Greeting • Small talk (political affairs) • Name/Patronymic/Surname
VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Greeting • Small talk (political affairs) • Name/Patronymic/Surname
 NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Shaking hands • Personal space • Smiling • Gestures
NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Shaking hands • Personal space • Smiling • Gestures
 BUSINESS TRADITIONS • Personal Relationships (Networking) • Bureaucracy • Gift giving
BUSINESS TRADITIONS • Personal Relationships (Networking) • Bureaucracy • Gift giving
 COMMUNICATION EFFECIENCY • Improve feedback systems • Language training • Cultural training • Flexibility and cooperation
COMMUNICATION EFFECIENCY • Improve feedback systems • Language training • Cultural training • Flexibility and cooperation
 PERCEPTUAL BARRIERS • PERCEPTION: a person’s view of reality • ADVERTISING MESSAGES: countless advertising blunders when words are misinterpreted by others • HOW OTHERS SEE US: May be different than we think
PERCEPTUAL BARRIERS • PERCEPTION: a person’s view of reality • ADVERTISING MESSAGES: countless advertising blunders when words are misinterpreted by others • HOW OTHERS SEE US: May be different than we think
 Symbols • • Attitude to flag Attitude to hymn Attitude to national emblem Attitude to national symbols
Symbols • • Attitude to flag Attitude to hymn Attitude to national emblem Attitude to national symbols
 Процесс мышления • Умножение по-китайски 1 • Умножение по-китайски 2
Процесс мышления • Умножение по-китайски 1 • Умножение по-китайски 2
 KINESICS Gestures: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Японские жесты с Хироко Американцы глазами китайцев Обмен визитными карточками BBC Поклоны в Японии BBC Обмен визитными карточками в Японии Сравнение жестов в Японии и Польше
KINESICS Gestures: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Японские жесты с Хироко Американцы глазами китайцев Обмен визитными карточками BBC Поклоны в Японии BBC Обмен визитными карточками в Японии Сравнение жестов в Японии и Польше
 NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION Transfer of meaning through means such as body language and use of physical space CHROMATICS Цветовой контекст KINESICS Язык тела и жестов PROXEMICS Пространство CHRONEMICS Время
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION Transfer of meaning through means such as body language and use of physical space CHROMATICS Цветовой контекст KINESICS Язык тела и жестов PROXEMICS Пространство CHRONEMICS Время
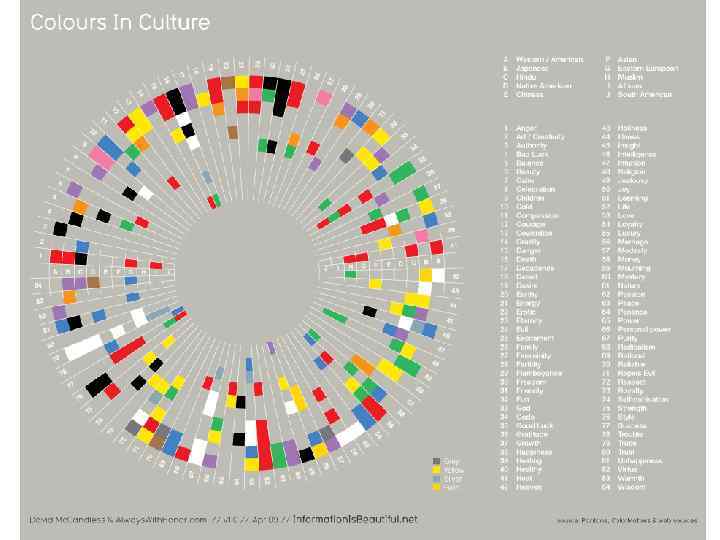
 NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 1. CHROMATICS Use of color to communicate messages
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 1. CHROMATICS Use of color to communicate messages
 NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 2. KINESICS Study of communication through body movement and facial expression – Eye contact – Posture – Gestures – Greeting – Touching – Silence
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 2. KINESICS Study of communication through body movement and facial expression – Eye contact – Posture – Gestures – Greeting – Touching – Silence
 NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 3. PROXEMICS Study of way people use physical space to convey messages • Intimate distance used for very confidential communications • Personal distance used for talking with family/close friends • Social distance used to handle most business transactions • Public distance used when calling across room or giving talk to group
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 3. PROXEMICS Study of way people use physical space to convey messages • Intimate distance used for very confidential communications • Personal distance used for talking with family/close friends • Social distance used to handle most business transactions • Public distance used when calling across room or giving talk to group
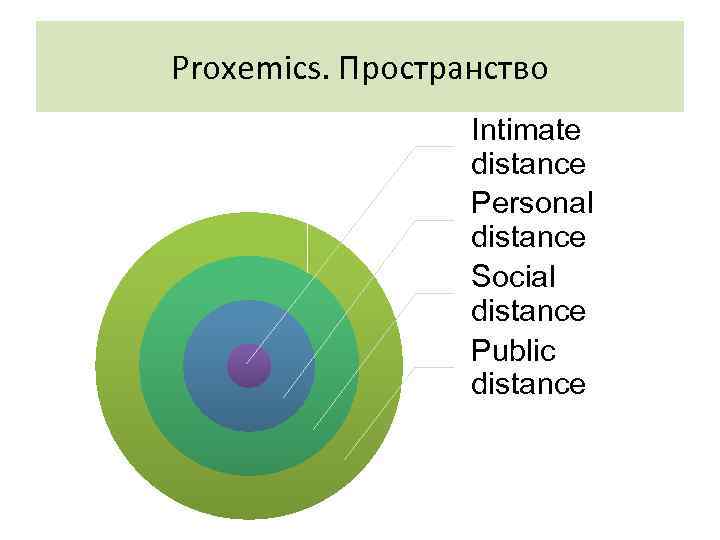 Proxemics. Пространство Intimate distance Personal distance Social distance Public distance
Proxemics. Пространство Intimate distance Personal distance Social distance Public distance
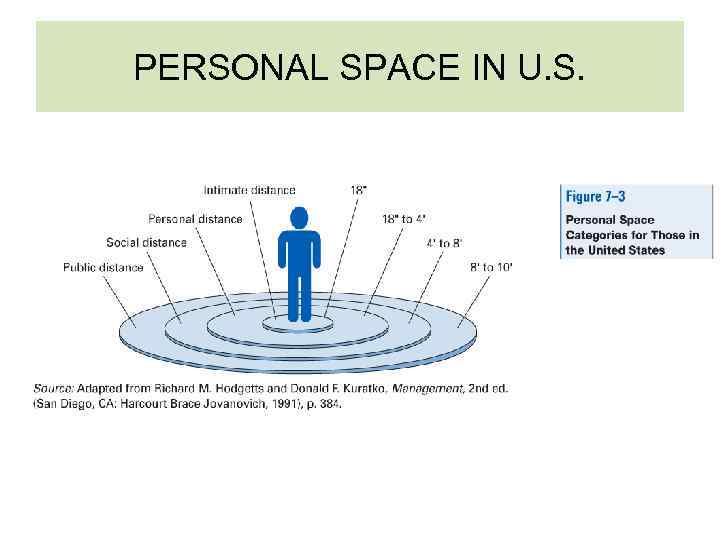 PERSONAL SPACE IN U. S.
PERSONAL SPACE IN U. S.
 NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 4. CHRONEMICS: the way time is used in a culture. Two Types: – MONOCHRONIC time schedule: things done in linear fashion – POLYCHRONIC time schedule: people do several things at same time and place higher value on personal involvement than on getting things done on time
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION 4. CHRONEMICS: the way time is used in a culture. Two Types: – MONOCHRONIC time schedule: things done in linear fashion – POLYCHRONIC time schedule: people do several things at same time and place higher value on personal involvement than on getting things done on time
 TASK 1. Please, define or show your personal space in your culture. • • Intimate distance Personal distance Social distance Public distance 2. Define your chronemics profile: monochronic or polychronic
TASK 1. Please, define or show your personal space in your culture. • • Intimate distance Personal distance Social distance Public distance 2. Define your chronemics profile: monochronic or polychronic
 VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Greeting • Small talk (political affairs)
VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Greeting • Small talk (political affairs)
 BUSINESS TRADITIONS • Personal Relationships (Networking) • Bureaucracy • Gift giving
BUSINESS TRADITIONS • Personal Relationships (Networking) • Bureaucracy • Gift giving
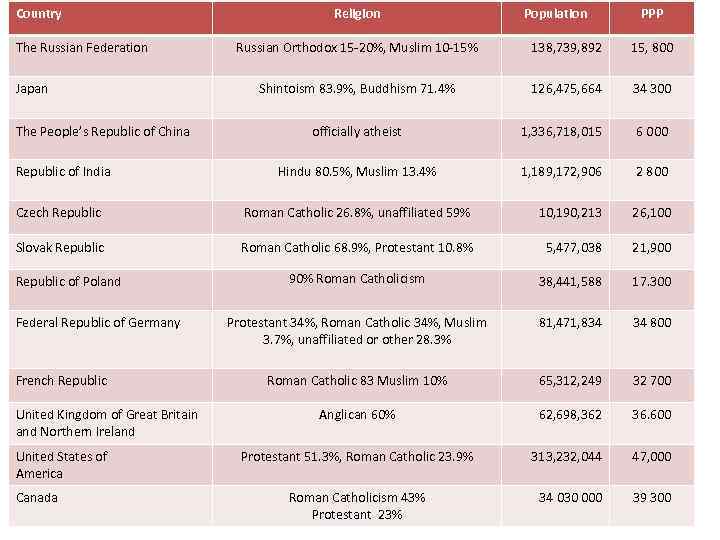 Country The Russian Federation Japan The People’s Republic of China Republic of India Religion Population PPP Russian Orthodox 15 -20%, Muslim 10 -15% 138, 739, 892 15, 800 Shintoism 83. 9%, Buddhism 71. 4% 126, 475, 664 34 300 officially atheist 1, 336, 718, 015 6 000 Hindu 80. 5%, Muslim 13. 4% 1, 189, 172, 906 2 800 Czech Republic Roman Catholic 26. 8%, unaffiliated 59% 10, 190, 213 26, 100 Slovak Republic Roman Catholic 68. 9%, Protestant 10. 8% 5, 477, 038 21, 900 90% Roman Catholicism 38, 441, 588 17. 300 Protestant 34%, Roman Catholic 34%, Muslim 3. 7%, unaffiliated or other 28. 3% 81, 471, 834 34 800 Roman Catholic 83 Muslim 10% 65, 312, 249 32 700 Anglican 60% 62, 698, 362 36. 600 Protestant 51. 3%, Roman Catholic 23. 9% 313, 232, 044 47, 000 Roman Catholicism 43% Protestant 23% 34 030 000 39 300 Republic of Poland Federal Republic of Germany French Republic United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland United States of America Canada
Country The Russian Federation Japan The People’s Republic of China Republic of India Religion Population PPP Russian Orthodox 15 -20%, Muslim 10 -15% 138, 739, 892 15, 800 Shintoism 83. 9%, Buddhism 71. 4% 126, 475, 664 34 300 officially atheist 1, 336, 718, 015 6 000 Hindu 80. 5%, Muslim 13. 4% 1, 189, 172, 906 2 800 Czech Republic Roman Catholic 26. 8%, unaffiliated 59% 10, 190, 213 26, 100 Slovak Republic Roman Catholic 68. 9%, Protestant 10. 8% 5, 477, 038 21, 900 90% Roman Catholicism 38, 441, 588 17. 300 Protestant 34%, Roman Catholic 34%, Muslim 3. 7%, unaffiliated or other 28. 3% 81, 471, 834 34 800 Roman Catholic 83 Muslim 10% 65, 312, 249 32 700 Anglican 60% 62, 698, 362 36. 600 Protestant 51. 3%, Roman Catholic 23. 9% 313, 232, 044 47, 000 Roman Catholicism 43% Protestant 23% 34 030 000 39 300 Republic of Poland Federal Republic of Germany French Republic United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland United States of America Canada


