ceed6901d3d1b39c2017586360a601e2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 3. Higher-Level Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 1
3. Higher-Level Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 1
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 2
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 2
 Motivation Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 3
Motivation Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 3
 Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 4
Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 4
 Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 5
Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 5
 Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 6
Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 6
 Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 7
Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 7
 Hoare Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 8
Hoare Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 8
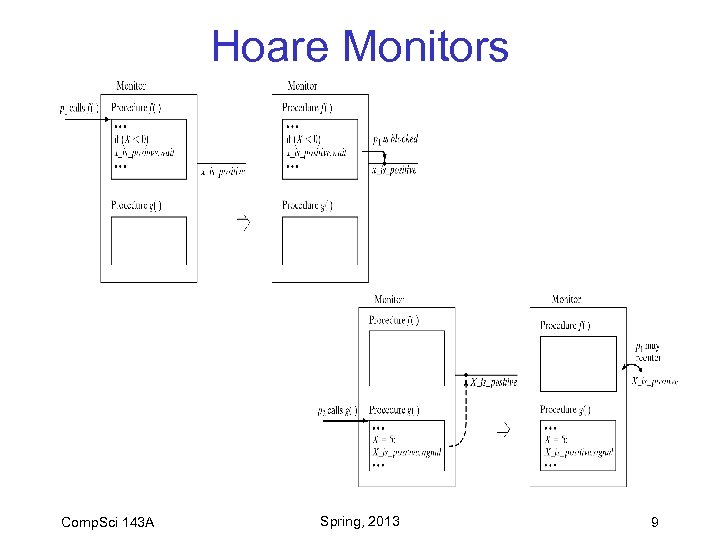 Hoare Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 9
Hoare Monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 9
 Bounded buffer problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 10
Bounded buffer problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 10
![deposit(char data) { if (full. Count==n) notfull. wait; buffer[nextin] = data; nextin = (nextin+1) deposit(char data) { if (full. Count==n) notfull. wait; buffer[nextin] = data; nextin = (nextin+1)](https://present5.com/presentation/ceed6901d3d1b39c2017586360a601e2/image-11.jpg) deposit(char data) { if (full. Count==n) notfull. wait; buffer[nextin] = data; nextin = (nextin+1) % n; full. Count = full. Count+1; notempty. signal; } remove(char data) { if (full. Count==0) notempty. wait; data = buffer[nextout]; nextout = (nextout+1) % n; full. Count = full. Count - 1; notfull. signal; } Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 11
deposit(char data) { if (full. Count==n) notfull. wait; buffer[nextin] = data; nextin = (nextin+1) % n; full. Count = full. Count+1; notempty. signal; } remove(char data) { if (full. Count==0) notempty. wait; data = buffer[nextout]; nextout = (nextout+1) % n; full. Count = full. Count - 1; notfull. signal; } Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 11
 Priority waits Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 12
Priority waits Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 12
 Example: alarm clock Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 13
Example: alarm clock Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 13
 Example: alarm clock monitor Alarm. Clock { int now=0; condition wakeup; } wake. Me(int n) { int alarm; alarm = now + n; while (now
Example: alarm clock monitor Alarm. Clock { int now=0; condition wakeup; } wake. Me(int n) { int alarm; alarm = now + n; while (now
 Example: alarm clock Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 15
Example: alarm clock Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 15
 Mesa-style monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 16
Mesa-style monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 16
 Mesa monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 17
Mesa monitors Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 17
 Monitors in Java Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 18
Monitors in Java Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 18
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 19
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 19
 Protected types (Ada 95) Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 20
Protected types (Ada 95) Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 20
![Example entry deposit(char c) when (full. Count < n) { buffer[nextin] = c; nextin Example entry deposit(char c) when (full. Count < n) { buffer[nextin] = c; nextin](https://present5.com/presentation/ceed6901d3d1b39c2017586360a601e2/image-21.jpg) Example entry deposit(char c) when (full. Count < n) { buffer[nextin] = c; nextin = (nextin + 1) % n; full. Count = full. Count + 1; } entry remove(char c) when (full. Count > 0) { c = buffer[nextout]; nextout = (nextout + 1) % n; full. Count = full. Count - 1; } Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 21
Example entry deposit(char c) when (full. Count < n) { buffer[nextin] = c; nextin = (nextin + 1) % n; full. Count = full. Count + 1; } entry remove(char c) when (full. Count > 0) { c = buffer[nextout]; nextout = (nextout + 1) % n; full. Count = full. Count - 1; } Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 21
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 22
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 22
 Distributed Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 23
Distributed Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 23
 Distributed Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 24
Distributed Synchronization Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 24
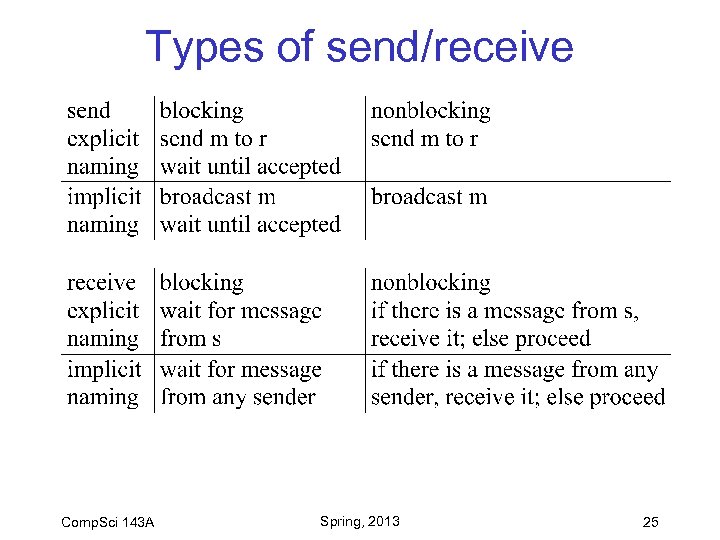 Types of send/receive Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 25
Types of send/receive Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 25
 Channels, Ports, and Mailboxes Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 26
Channels, Ports, and Mailboxes Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 26
 Named Message Channels Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 27
Named Message Channels Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 27
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 28
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 28
 Example: Bounded buffer with CSP Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 29
Example: Bounded buffer with CSP Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 29
 Bounded Buffer with CSP Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 30
Bounded Buffer with CSP Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 30
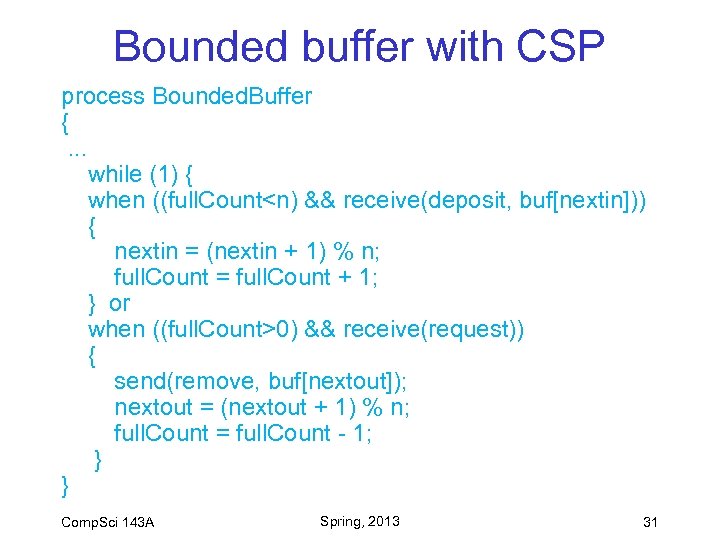 Bounded buffer with CSP process Bounded. Buffer {. . . while (1) { when ((full. Count
Bounded buffer with CSP process Bounded. Buffer {. . . while (1) { when ((full. Count
 Ports and Mailboxes Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 32
Ports and Mailboxes Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 32
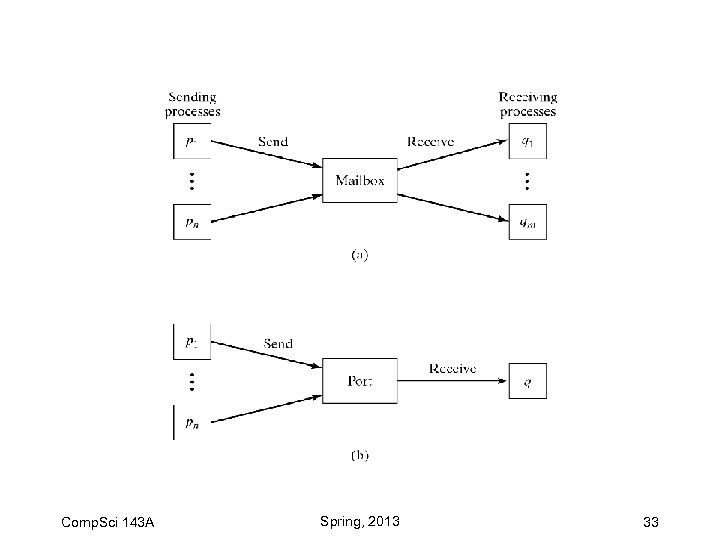 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 33
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 33
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 34
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 34
 Procedure-Based Communication Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 35
Procedure-Based Communication Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 35
 RPC Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 36
RPC Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 36
 Rendezvous Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 37
Rendezvous Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 37
 Rendezvous (Ada 95) Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 38
Rendezvous (Ada 95) Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 38
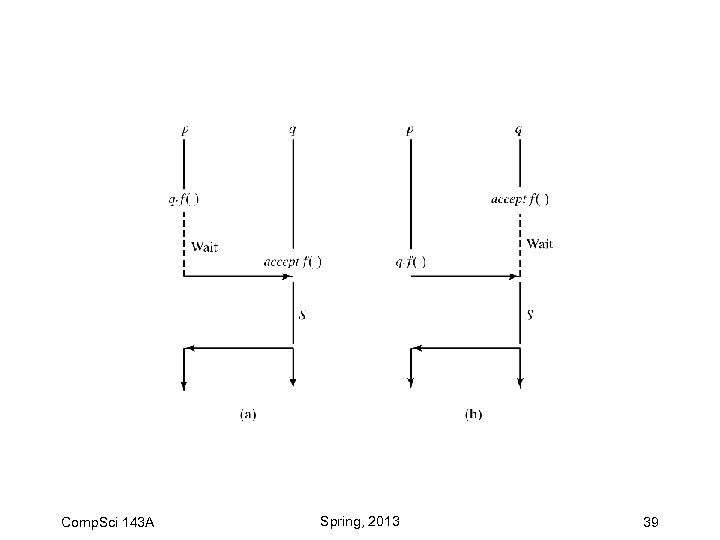 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 39
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 39
 Rendezvous Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 40
Rendezvous Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 40
 Example: Bounded Buffer Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 41
Example: Bounded Buffer Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 41
 Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 42
Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 42
 Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 43
Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 43
 Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 44
Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 44
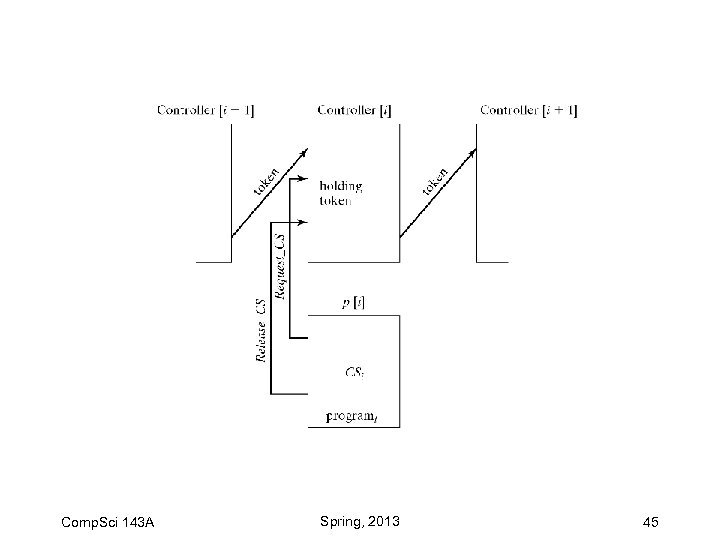 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 45
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 45
 Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 46
Distributed Mutual Exclusion Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 46
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 47
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 47
 Readers/Writers Problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 48
Readers/Writers Problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 48
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 49
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 49
 Readers/Writers Problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 50
Readers/Writers Problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 50
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 51
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 51
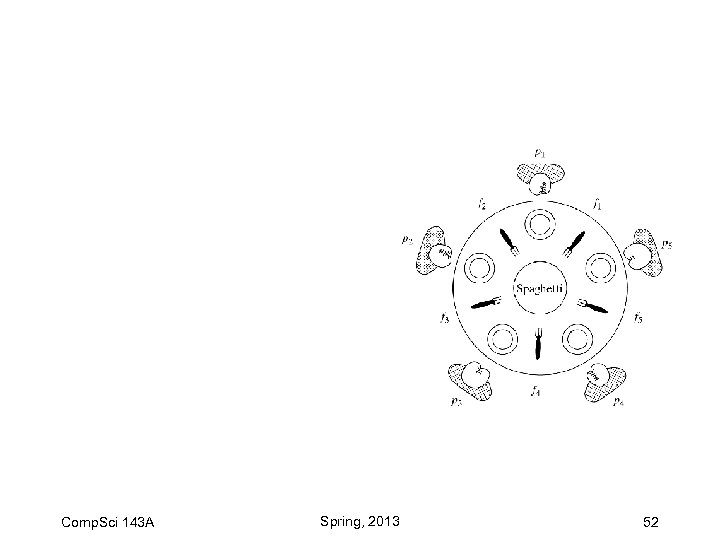 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 52
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 52
 Dining philosophers problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 53
Dining philosophers problem Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 53
 Dining Philosophers Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 54
Dining Philosophers Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 54
 Dining Philosophers Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 55
Dining Philosophers Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 55
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 56
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 56
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 57
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 57
 Elevator algorithm Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 58
Elevator algorithm Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 58
 Elevator algorithm Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 59
Elevator algorithm Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 59
 Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 60
Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 60
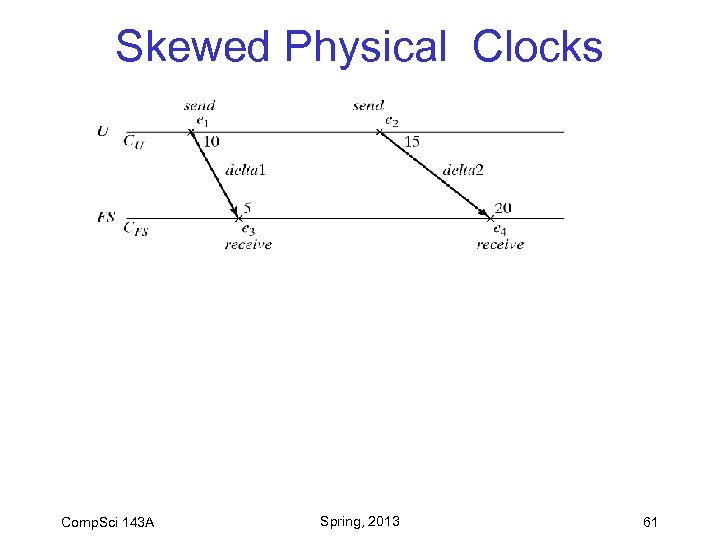 Skewed Physical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 61
Skewed Physical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 61
 Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 62
Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 62
 Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 63
Logical Clocks Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 63
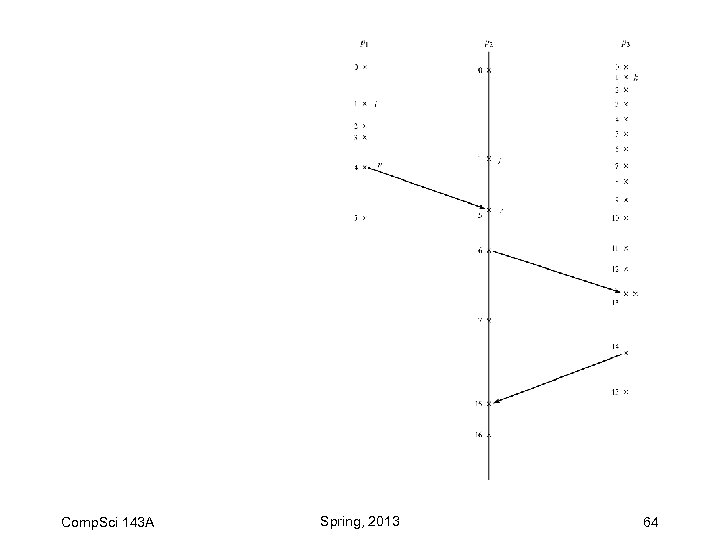 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 64
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 64
 Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 65
Comp. Sci 143 A Spring, 2013 65


