5f241a6c224e7cf0ee148717cae0cd51.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 3 GPP System Architecture Evolution ATIS LTE Conference January 26, 2009 3 GPP TSG SA Chairman Stephen Hayes 1
3 GPP System Architecture Evolution ATIS LTE Conference January 26, 2009 3 GPP TSG SA Chairman Stephen Hayes 1
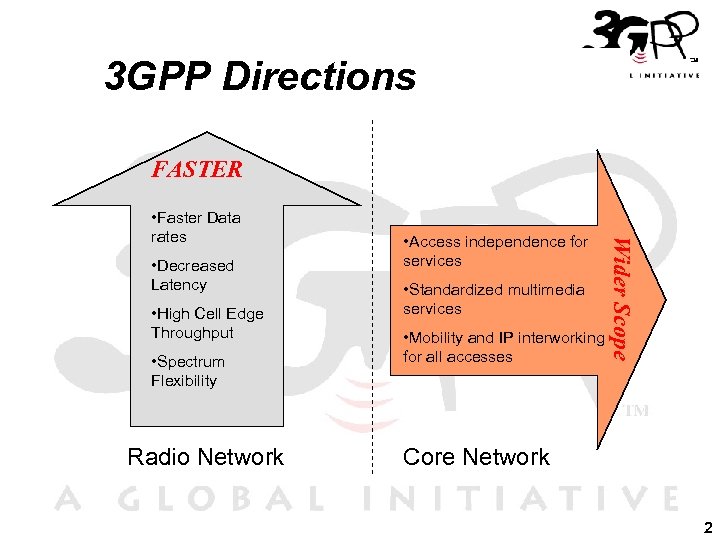 3 GPP Directions FASTER • Decreased Latency • High Cell Edge Throughput • Spectrum Flexibility Radio Network • Access independence for services • Standardized multimedia services • Mobility and IP interworking for all accesses Wider Scope • Faster Data rates Core Network 2
3 GPP Directions FASTER • Decreased Latency • High Cell Edge Throughput • Spectrum Flexibility Radio Network • Access independence for services • Standardized multimedia services • Mobility and IP interworking for all accesses Wider Scope • Faster Data rates Core Network 2
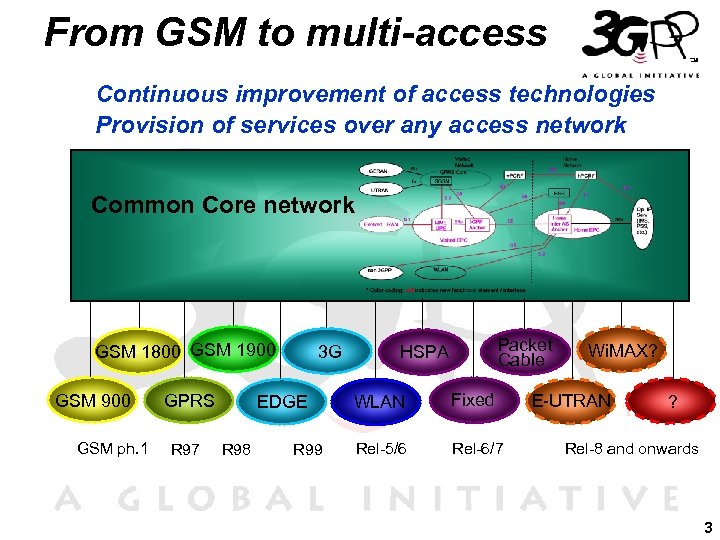 From GSM to multi-access Continuous improvement of access technologies Provision of services over any access network Common Core network GSM 1800 GSM 1900 GSM ph. 1 GPRS R 97 3 G EDGE R 98 R 99 Packet Cable HSPA WLAN Fixed Rel-5/6 Rel-6/7 Wi. MAX? E-UTRAN ? Rel-8 and onwards 3
From GSM to multi-access Continuous improvement of access technologies Provision of services over any access network Common Core network GSM 1800 GSM 1900 GSM ph. 1 GPRS R 97 3 G EDGE R 98 R 99 Packet Cable HSPA WLAN Fixed Rel-5/6 Rel-6/7 Wi. MAX? E-UTRAN ? Rel-8 and onwards 3
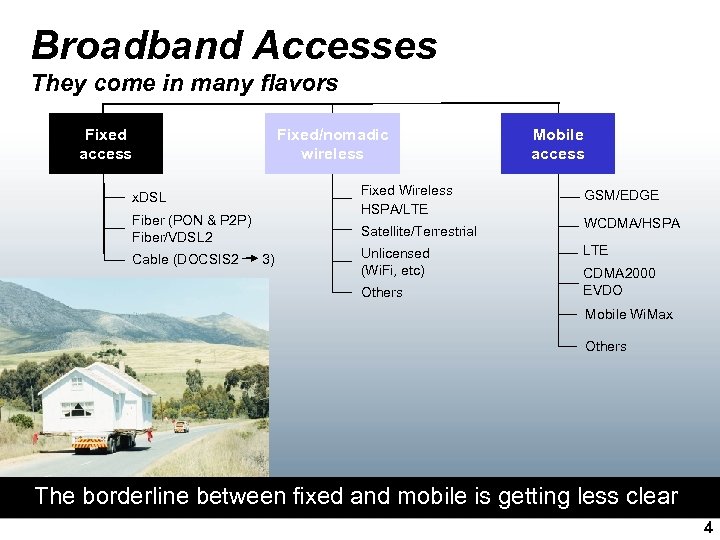 Broadband Accesses They come in many flavors Fixed access Fixed/nomadic wireless Fixed Wireless HSPA/LTE x. DSL Fiber (PON & P 2 P) Fiber/VDSL 2 Cable (DOCSIS 2 Satellite/Terrestrial 3) Unlicensed (Wi. Fi, etc) Others Mobile access GSM/EDGE WCDMA/HSPA LTE CDMA 2000 EVDO Mobile Wi. Max Others The borderline between fixed and mobile is getting less clear 4
Broadband Accesses They come in many flavors Fixed access Fixed/nomadic wireless Fixed Wireless HSPA/LTE x. DSL Fiber (PON & P 2 P) Fiber/VDSL 2 Cable (DOCSIS 2 Satellite/Terrestrial 3) Unlicensed (Wi. Fi, etc) Others Mobile access GSM/EDGE WCDMA/HSPA LTE CDMA 2000 EVDO Mobile Wi. Max Others The borderline between fixed and mobile is getting less clear 4
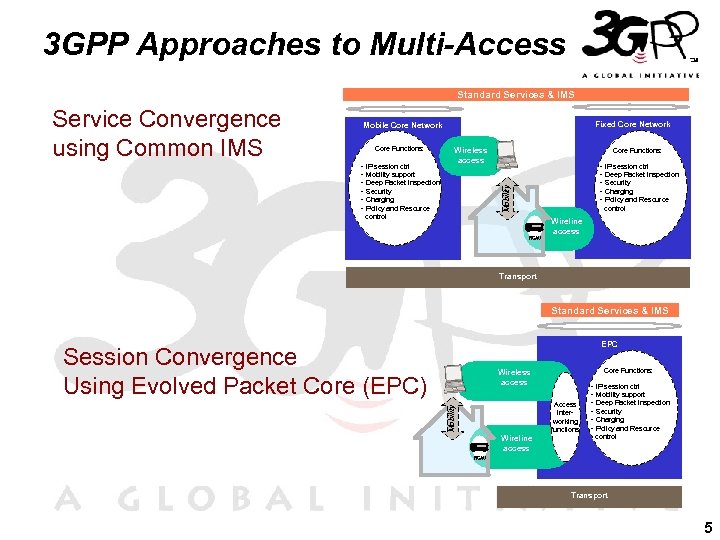 3 GPP Approaches to Multi-Access Standard Services & IMS Fixed Core Network Mobile Core Network Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Mobility Service Convergence using Common IMS control Wireline access RGW Transport Standard Services & IMS EPC Session Convergence Using Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Core Functions: Wireless access Mobility Access interworking functions Wireline access - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource control RGW Transport 5
3 GPP Approaches to Multi-Access Standard Services & IMS Fixed Core Network Mobile Core Network Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Mobility Service Convergence using Common IMS control Wireline access RGW Transport Standard Services & IMS EPC Session Convergence Using Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Core Functions: Wireless access Mobility Access interworking functions Wireline access - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource control RGW Transport 5
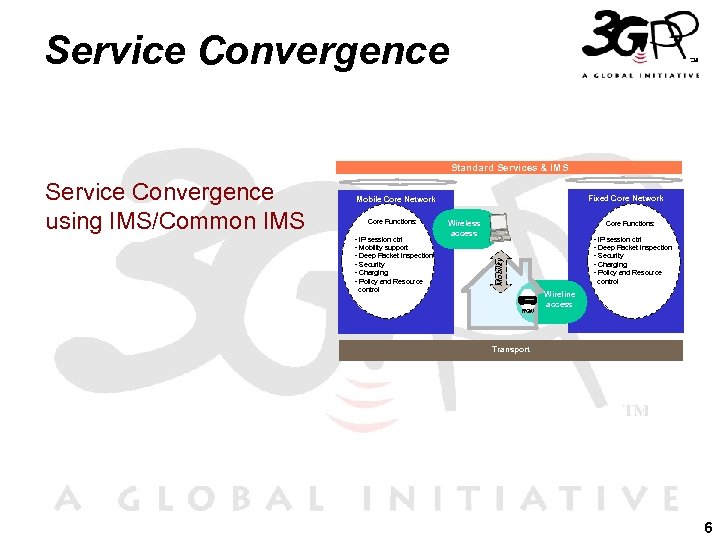 Service Convergence Standard Services & IMS Fixed Core Network Mobile Core Network Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Mobility Service Convergence using IMS/Common IMS control Wireline access RGW Transport 6
Service Convergence Standard Services & IMS Fixed Core Network Mobile Core Network Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Wireless access Core Functions: - IP session ctrl - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource Mobility Service Convergence using IMS/Common IMS control Wireline access RGW Transport 6
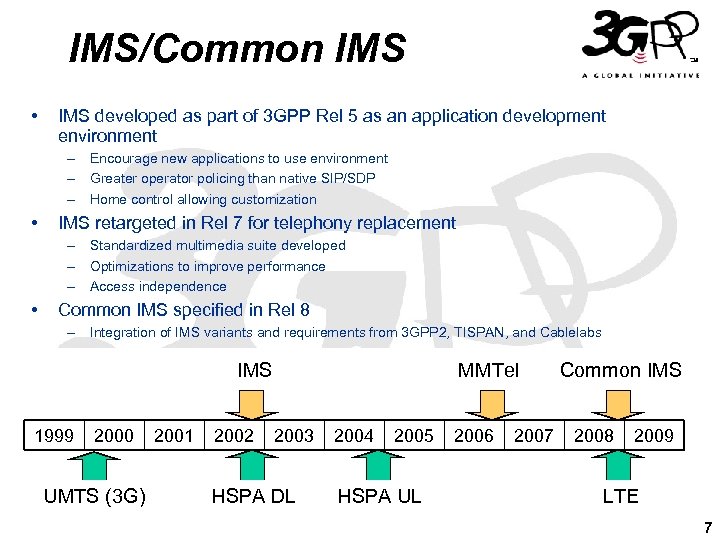 IMS/Common IMS • IMS developed as part of 3 GPP Rel 5 as an application development environment – Encourage new applications to use environment – Greater operator policing than native SIP/SDP – Home control allowing customization • IMS retargeted in Rel 7 for telephony replacement – Standardized multimedia suite developed – Optimizations to improve performance – Access independence • Common IMS specified in Rel 8 – Integration of IMS variants and requirements from 3 GPP 2, TISPAN, and Cablelabs IMS 1999 2000 UMTS (3 G) 2001 2002 MMTel 2003 HSPA DL 2004 2005 HSPA UL 2006 2007 Common IMS 2008 2009 LTE 7
IMS/Common IMS • IMS developed as part of 3 GPP Rel 5 as an application development environment – Encourage new applications to use environment – Greater operator policing than native SIP/SDP – Home control allowing customization • IMS retargeted in Rel 7 for telephony replacement – Standardized multimedia suite developed – Optimizations to improve performance – Access independence • Common IMS specified in Rel 8 – Integration of IMS variants and requirements from 3 GPP 2, TISPAN, and Cablelabs IMS 1999 2000 UMTS (3 G) 2001 2002 MMTel 2003 HSPA DL 2004 2005 HSPA UL 2006 2007 Common IMS 2008 2009 LTE 7
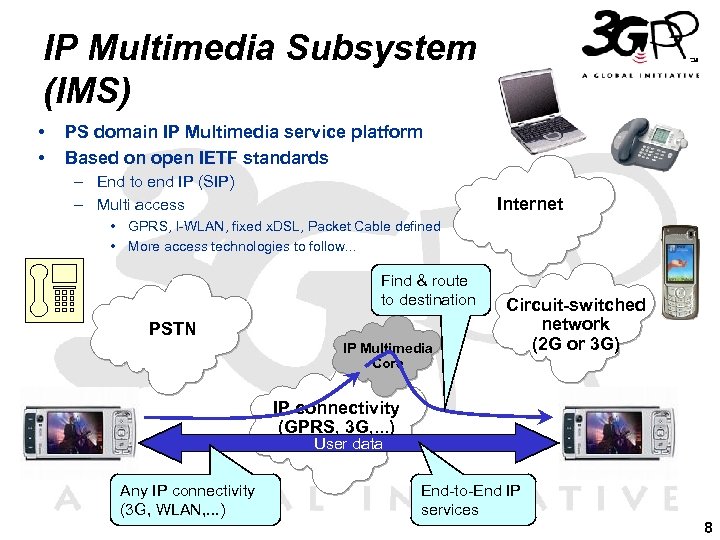 IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) • • PS domain IP Multimedia service platform Based on open IETF standards – End to end IP (SIP) – Multi access Internet • GPRS, I-WLAN, fixed x. DSL, Packet Cable defined • More access technologies to follow. . . Find & route to destination PSTN IP Multimedia Core Circuit-switched network (2 G or 3 G) IP connectivity (GPRS, 3 G, . . . ) User data Any IP connectivity (3 G, WLAN, . . . ) End-to-End IP services 8
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) • • PS domain IP Multimedia service platform Based on open IETF standards – End to end IP (SIP) – Multi access Internet • GPRS, I-WLAN, fixed x. DSL, Packet Cable defined • More access technologies to follow. . . Find & route to destination PSTN IP Multimedia Core Circuit-switched network (2 G or 3 G) IP connectivity (GPRS, 3 G, . . . ) User data Any IP connectivity (3 G, WLAN, . . . ) End-to-End IP services 8
 Common IMS • 3 GPP members, 3 GPP 2, Wi. MAX forum, ETSI TISPAN and Cable. Labs contribute to 3 GPP common IMS specifications – Different requirements are supported in common implementation • All IMS specifications are harmonized to 3 GPP specifications – Common parts are defined in 3 GPP specifications only • Core IMS entities (CSCFs, AS, UE IMS client, . . . ) + agreed common functions – Other organisations either reference or re-use 3 GPP specification as it stands – Any changes or additions in the Common IMS area are made in 3 GPP • All 3 GPP members can contribute on their favourite work items • Ongoing work initiated by 3 GPP members, Cable. Labs, 3 GPP 2 and ETSI TISPAN – The scope and coverage of Common IMS have been agreed by the SDOs • Common version of IMS specifications in Rel-8 – Business or architecture specific additions to 3 GPP Common IMS are possible outside the agreed Common IMS area 9
Common IMS • 3 GPP members, 3 GPP 2, Wi. MAX forum, ETSI TISPAN and Cable. Labs contribute to 3 GPP common IMS specifications – Different requirements are supported in common implementation • All IMS specifications are harmonized to 3 GPP specifications – Common parts are defined in 3 GPP specifications only • Core IMS entities (CSCFs, AS, UE IMS client, . . . ) + agreed common functions – Other organisations either reference or re-use 3 GPP specification as it stands – Any changes or additions in the Common IMS area are made in 3 GPP • All 3 GPP members can contribute on their favourite work items • Ongoing work initiated by 3 GPP members, Cable. Labs, 3 GPP 2 and ETSI TISPAN – The scope and coverage of Common IMS have been agreed by the SDOs • Common version of IMS specifications in Rel-8 – Business or architecture specific additions to 3 GPP Common IMS are possible outside the agreed Common IMS area 9
 Multimedia Telephony Service • Multiple Simultaneous Media Streams – – – • Voice Text Video File Transfer Video/Photo/Audio Sharing Multimedia analogs of traditional PSTN supplementary services – – – – – Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) Malicious Communication IDentification (MCID) Anonymous Communication Rejection (ACR) Communication Diversion (CDIV) Communication Waiting (CW) Communication Hold (HOLD) Communication Barring (CB) Completion of Communications to Busy Subscriber (CCBS) Message Waiting Indication (MWI) Conference (CONF) Advice Of Charge (AOC) Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) Reverse charging Closed User Group (CUG) Three-Party (3 PTY) 10
Multimedia Telephony Service • Multiple Simultaneous Media Streams – – – • Voice Text Video File Transfer Video/Photo/Audio Sharing Multimedia analogs of traditional PSTN supplementary services – – – – – Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) Malicious Communication IDentification (MCID) Anonymous Communication Rejection (ACR) Communication Diversion (CDIV) Communication Waiting (CW) Communication Hold (HOLD) Communication Barring (CB) Completion of Communications to Busy Subscriber (CCBS) Message Waiting Indication (MWI) Conference (CONF) Advice Of Charge (AOC) Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) Reverse charging Closed User Group (CUG) Three-Party (3 PTY) 10
 But what if you need? • Session Continuity • Mobility for non IMS applications • Common IP level services – Filtering – Deep Packet Inspection – Firewall • Common Management 11
But what if you need? • Session Continuity • Mobility for non IMS applications • Common IP level services – Filtering – Deep Packet Inspection – Firewall • Common Management 11
 Session Convergence Standard Services & IMS EPC Session Convergence Using Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Core Functions: Wireless access Mobility Access interworking functions Wireline access - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource control RGW Transport 12
Session Convergence Standard Services & IMS EPC Session Convergence Using Evolved Packet Core (EPC) Core Functions: Wireless access Mobility Access interworking functions Wireline access - IP session ctrl - Mobility support - Deep Packet Inspection - Security - Charging - Policy and Resource control RGW Transport 12
 Examples of non-IMS apps • Multimedia Broadcast Messaging Service (MBMS) • High Quality Audio • Packet Streaming 13
Examples of non-IMS apps • Multimedia Broadcast Messaging Service (MBMS) • High Quality Audio • Packet Streaming 13
 System Architecture Evolution (SAE) • LTE = E-UTRAN = evolved radio network – Megabit class data rates – Short delays – Short transition from idle to active • SAE = System Architecture evolution – SAE is the project name, the evolved network is called EPC – Evolved IP oriented multi access architecture • • • E-UTRAN integrates only to SAE, A/Gb or Iu not possible Strongly IP based PS only network EPC covers both 3 GPP and non-3 GPP access technologies Seamless roaming between E-UTRAN, 2 G and 3 G (tight interworking) Loose interworking with non-3 GPP accesses GTP solution for intra-3 GPP mobility and IETF based solution for non 3 GPP mobility – The main Architecture specifications 23. 401 and 23. 402 frozen in June 2008 – Protocol work is ongoing and frozen with exceptions in December 2008 14
System Architecture Evolution (SAE) • LTE = E-UTRAN = evolved radio network – Megabit class data rates – Short delays – Short transition from idle to active • SAE = System Architecture evolution – SAE is the project name, the evolved network is called EPC – Evolved IP oriented multi access architecture • • • E-UTRAN integrates only to SAE, A/Gb or Iu not possible Strongly IP based PS only network EPC covers both 3 GPP and non-3 GPP access technologies Seamless roaming between E-UTRAN, 2 G and 3 G (tight interworking) Loose interworking with non-3 GPP accesses GTP solution for intra-3 GPP mobility and IETF based solution for non 3 GPP mobility – The main Architecture specifications 23. 401 and 23. 402 frozen in June 2008 – Protocol work is ongoing and frozen with exceptions in December 2008 14
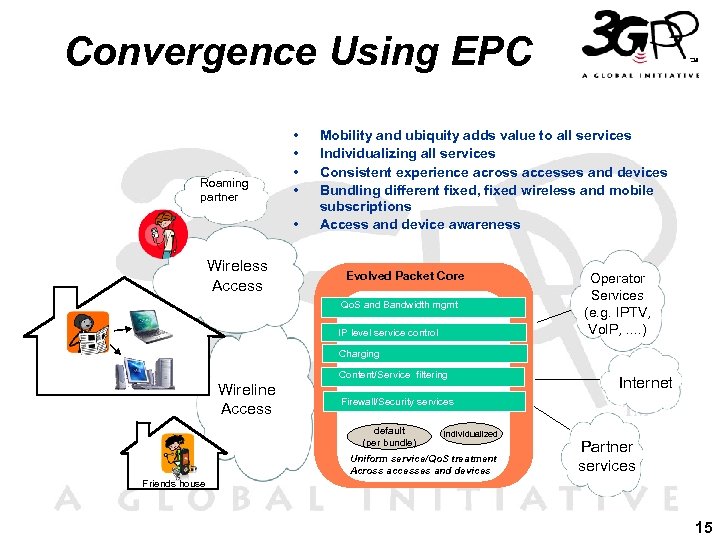 Convergence Using EPC Roaming partner • • • Wireless Access Mobility and ubiquity adds value to all services Individualizing all services Consistent experience across accesses and devices Bundling different fixed, fixed wireless and mobile subscriptions Access and device awareness Evolved Packet Core Qo. S and Bandwidth mgmt IP level service control Operator Services (e. g. IPTV, Vo. IP, . . ) Charging Content/Service filtering Wireline Access Internet Firewall/Security services default (per bundle) individualized Uniform service/Qo. S treatment Across accesses and devices Partner services Friends house 15
Convergence Using EPC Roaming partner • • • Wireless Access Mobility and ubiquity adds value to all services Individualizing all services Consistent experience across accesses and devices Bundling different fixed, fixed wireless and mobile subscriptions Access and device awareness Evolved Packet Core Qo. S and Bandwidth mgmt IP level service control Operator Services (e. g. IPTV, Vo. IP, . . ) Charging Content/Service filtering Wireline Access Internet Firewall/Security services default (per bundle) individualized Uniform service/Qo. S treatment Across accesses and devices Partner services Friends house 15
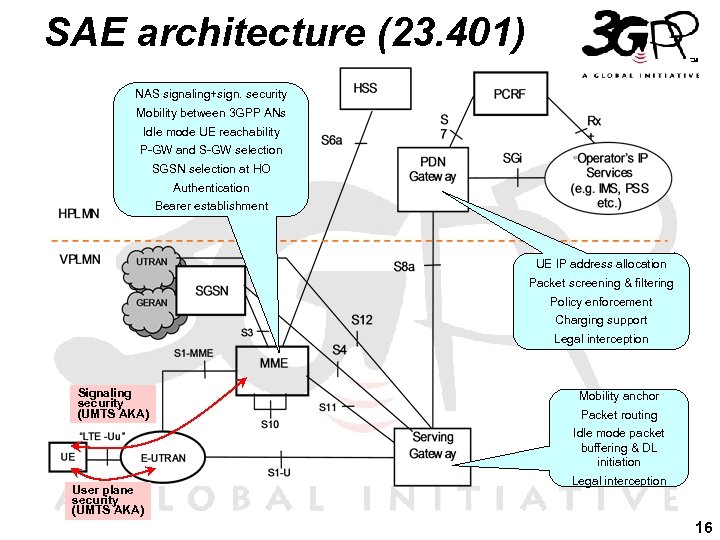 SAE architecture (23. 401) NAS signaling+sign. security Mobility between 3 GPP ANs Idle mode UE reachability P-GW and S-GW selection SGSN selection at HO Authentication Bearer establishment UE IP address allocation Packet screening & filtering Policy enforcement Charging support Legal interception Signaling security (UMTS AKA) Mobility anchor Packet routing Idle mode packet buffering & DL initiation User plane security (UMTS AKA) Legal interception 16
SAE architecture (23. 401) NAS signaling+sign. security Mobility between 3 GPP ANs Idle mode UE reachability P-GW and S-GW selection SGSN selection at HO Authentication Bearer establishment UE IP address allocation Packet screening & filtering Policy enforcement Charging support Legal interception Signaling security (UMTS AKA) Mobility anchor Packet routing Idle mode packet buffering & DL initiation User plane security (UMTS AKA) Legal interception 16
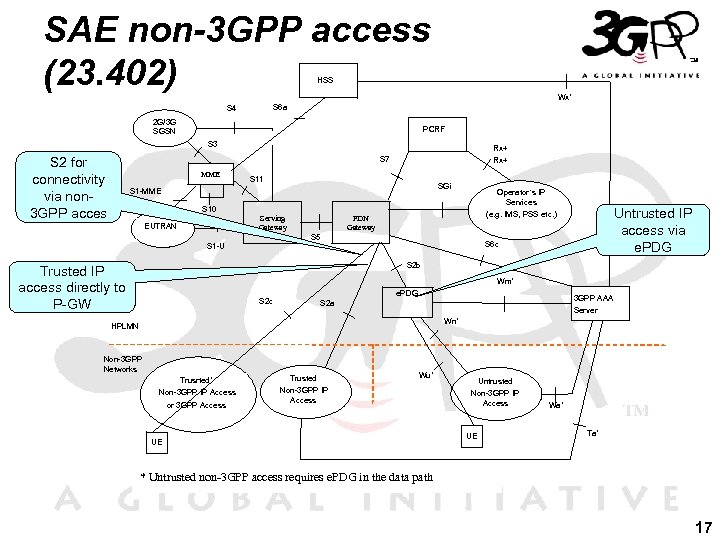 SAE non-3 GPP access (23. 402) HSS Wx* S 6 a S 4 2 G/3 G SGSN PCRF S 3 S 2 for connectivity via non 3 GPP acces Rx+ S 7 MME Rx+ S 11 SGi S 1 -MME Operator’s IP Services S 10 Serving Gateway EUTRAN Untrusted IP access via e. PDG (e. g. IMS, PSS etc. ) PDN Gateway S 5 S 6 c S 1 -U S 2 b Trusted IP access directly to P-GW Wm* e. PDG S 2 c 3 GPP AAA S 2 a Server Wn* HPLMN Non-3 GPP Networks Trusrted* Trusted Non-3 GPP IP Access Wu* Non-3 GPP IP Access or 3 GPP Access UE Untrusted Non-3 GPP IP Access UE Wa* Ta* * Untrusted non-3 GPP access requires e. PDG in the data path 17
SAE non-3 GPP access (23. 402) HSS Wx* S 6 a S 4 2 G/3 G SGSN PCRF S 3 S 2 for connectivity via non 3 GPP acces Rx+ S 7 MME Rx+ S 11 SGi S 1 -MME Operator’s IP Services S 10 Serving Gateway EUTRAN Untrusted IP access via e. PDG (e. g. IMS, PSS etc. ) PDN Gateway S 5 S 6 c S 1 -U S 2 b Trusted IP access directly to P-GW Wm* e. PDG S 2 c 3 GPP AAA S 2 a Server Wn* HPLMN Non-3 GPP Networks Trusrted* Trusted Non-3 GPP IP Access Wu* Non-3 GPP IP Access or 3 GPP Access UE Untrusted Non-3 GPP IP Access UE Wa* Ta* * Untrusted non-3 GPP access requires e. PDG in the data path 17
 SAE/LTE Deployment • Deployments are expected to start with overlapping cellular coverage – E-UTRAN overlapping with legacy 3 GPP GERAN / UTRAN coverage – E-UTRAN overlapping with legacy 3 GPP 2 coverage – Multi-mode networks and terminals • E-UTRAN is a packet-only radio with no CS capacity • Initially E-UTRAN is foreseen as “islands” in the sea of legacy cellular access – – Mobility between E-UTRAN and legacy access is required Mobility between PS and CS domains is required Multi-mode terminals expect to use PS coverage where available Desire to keep the connectivity and services 18
SAE/LTE Deployment • Deployments are expected to start with overlapping cellular coverage – E-UTRAN overlapping with legacy 3 GPP GERAN / UTRAN coverage – E-UTRAN overlapping with legacy 3 GPP 2 coverage – Multi-mode networks and terminals • E-UTRAN is a packet-only radio with no CS capacity • Initially E-UTRAN is foreseen as “islands” in the sea of legacy cellular access – – Mobility between E-UTRAN and legacy access is required Mobility between PS and CS domains is required Multi-mode terminals expect to use PS coverage where available Desire to keep the connectivity and services 18
 Other Improvements • Continuously Improving Security – EPC requires USIM (or non-3 GPP equivalent) • Multi-mode terminals and networks – – – Service continuity Multiple registration Voice Call Continuity CS Fallback Network selection • Rel 9 will focus on – Regulatory enhancements to LTE/EPC – Home(e) Node. B enhancements to EPC 19
Other Improvements • Continuously Improving Security – EPC requires USIM (or non-3 GPP equivalent) • Multi-mode terminals and networks – – – Service continuity Multiple registration Voice Call Continuity CS Fallback Network selection • Rel 9 will focus on – Regulatory enhancements to LTE/EPC – Home(e) Node. B enhancements to EPC 19
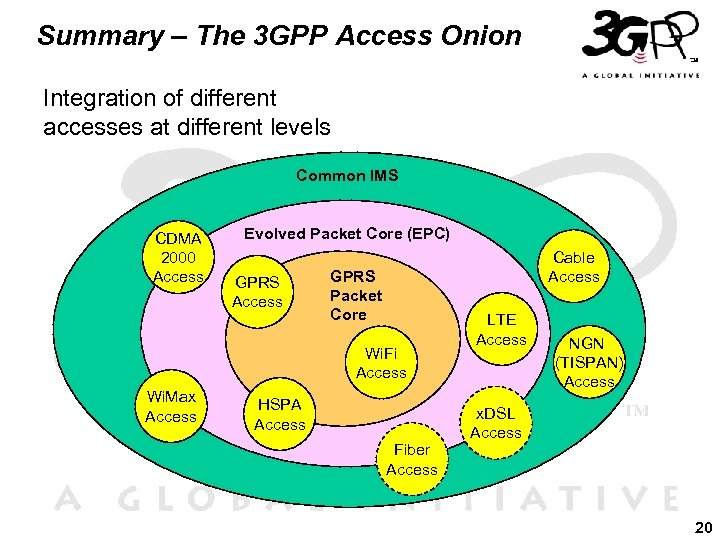 Summary – The 3 GPP Access Onion Integration of different accesses at different levels Common IMS CDMA 2000 Access Evolved Packet Core (EPC) GPRS Access Cable Access GPRS Packet Core Wi. Fi Access Wi. Max Access HSPA Access Fiber Access LTE Access NGN (TISPAN) Access x. DSL Access 20
Summary – The 3 GPP Access Onion Integration of different accesses at different levels Common IMS CDMA 2000 Access Evolved Packet Core (EPC) GPRS Access Cable Access GPRS Packet Core Wi. Fi Access Wi. Max Access HSPA Access Fiber Access LTE Access NGN (TISPAN) Access x. DSL Access 20
 Summary • LTE is only part of what 3 GPP works on • EPC (SAE) is the core network for LTE …but • IMS and EPC (SAE) can be used to provide service and session convergence across a variety of accesses For further information: www. 3 gpp. org 21
Summary • LTE is only part of what 3 GPP works on • EPC (SAE) is the core network for LTE …but • IMS and EPC (SAE) can be used to provide service and session convergence across a variety of accesses For further information: www. 3 gpp. org 21


