6d3485c087a3e5a22c5fdb0a78bc5bc3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 3 G and 4 G Wireless – Advances and Challenges SRB 041406 ver 1 Suresh R. Borkar Adjunct Faculty, Dept of ECE, Ill Instt. of Tech. sureshbo@hotmail. com Apr 14, 2006 1
3 G and 4 G Wireless – Advances and Challenges SRB 041406 ver 1 Suresh R. Borkar Adjunct Faculty, Dept of ECE, Ill Instt. of Tech. sureshbo@hotmail. com Apr 14, 2006 1
 3 G and 4 G Wireless – Advances and Challenges § § § Where are we? 3 G Wireless Summary Where do we Want to go? Evolution to Seamless Networking 4 G Wireless Challenges The one who stays still is left behind SRB 041406 ver 1 2
3 G and 4 G Wireless – Advances and Challenges § § § Where are we? 3 G Wireless Summary Where do we Want to go? Evolution to Seamless Networking 4 G Wireless Challenges The one who stays still is left behind SRB 041406 ver 1 2
 Where are We? § Classic Wireline Ma. Bell Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) § § – US Universal coverage achieved early 1980’s “Wireless” First Generation Analog Systems – Speech – AMPS, TACS Second Generation Digital Systems – Enhanced Capacity – CDMA, D-AMPS, TDMA, GSM, DECT, PDC 2. 5 Generation Systems – Low Speed Data – GPRS, EDGE Third Generation Systems – “INTERNET” on Wireless – Wi. Fi/Hyper. LAN <-> Wi. MAX/Hyper. WAN <-> CDMA 2000/WCDMA – Evolution to All IP Network including Vo. IP SRB 041406 ver 1 3
Where are We? § Classic Wireline Ma. Bell Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) § § – US Universal coverage achieved early 1980’s “Wireless” First Generation Analog Systems – Speech – AMPS, TACS Second Generation Digital Systems – Enhanced Capacity – CDMA, D-AMPS, TDMA, GSM, DECT, PDC 2. 5 Generation Systems – Low Speed Data – GPRS, EDGE Third Generation Systems – “INTERNET” on Wireless – Wi. Fi/Hyper. LAN <-> Wi. MAX/Hyper. WAN <-> CDMA 2000/WCDMA – Evolution to All IP Network including Vo. IP SRB 041406 ver 1 3
 Representative Wireless Standards § GSM/TDMA – Time Division Multiplexing based access § CDMA – Code Division Multiplexing based access § OFDM – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Many toys to play with SRB 041406 ver 1 4
Representative Wireless Standards § GSM/TDMA – Time Division Multiplexing based access § CDMA – Code Division Multiplexing based access § OFDM – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Many toys to play with SRB 041406 ver 1 4
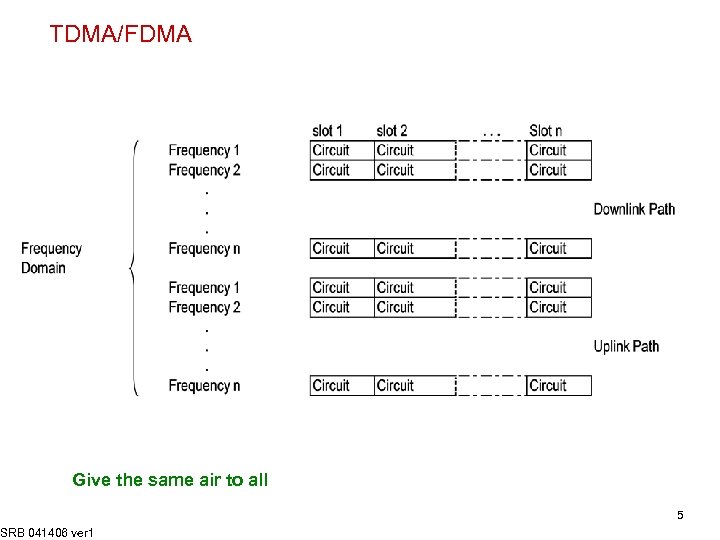 TDMA/FDMA Give the same air to all SRB 041406 ver 1 5
TDMA/FDMA Give the same air to all SRB 041406 ver 1 5
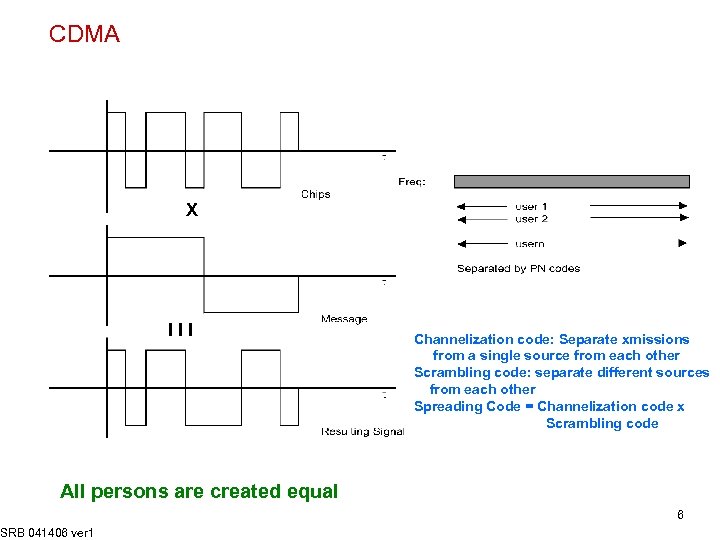 CDMA X III Channelization code: Separate xmissions from a single source from each other Scrambling code: separate different sources from each other Spreading Code = Channelization code x Scrambling code All persons are created equal SRB 041406 ver 1 6
CDMA X III Channelization code: Separate xmissions from a single source from each other Scrambling code: separate different sources from each other Spreading Code = Channelization code x Scrambling code All persons are created equal SRB 041406 ver 1 6
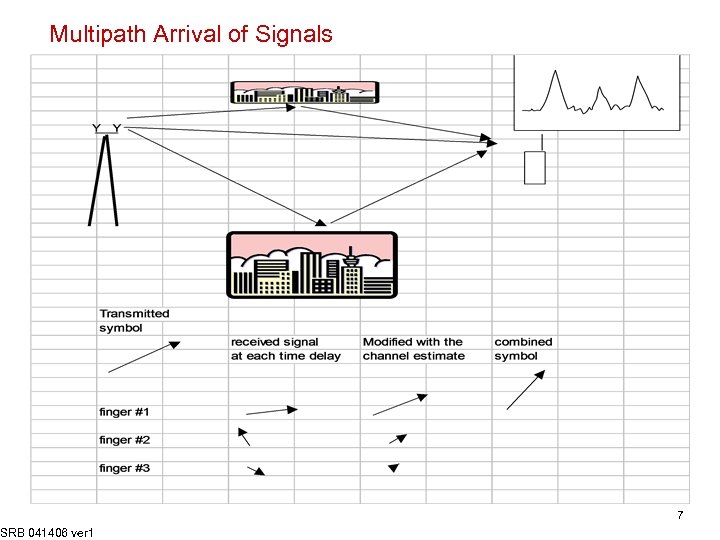 Multipath Arrival of Signals SRB 041406 ver 1 7
Multipath Arrival of Signals SRB 041406 ver 1 7
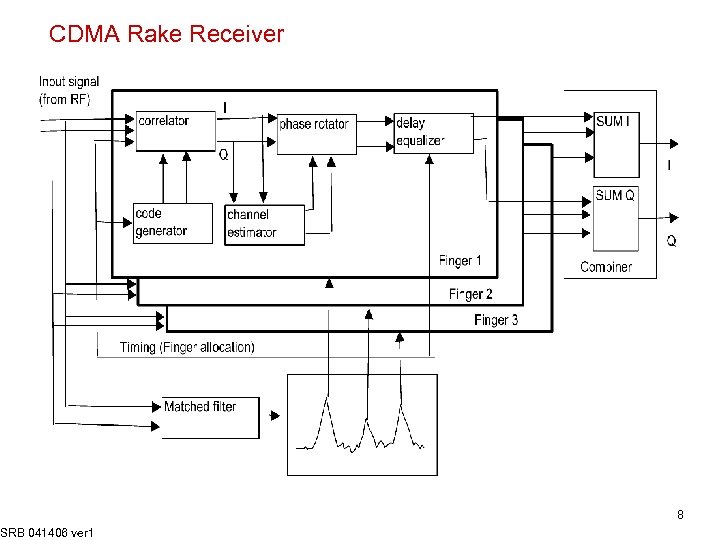 CDMA Rake Receiver SRB 041406 ver 1 8
CDMA Rake Receiver SRB 041406 ver 1 8
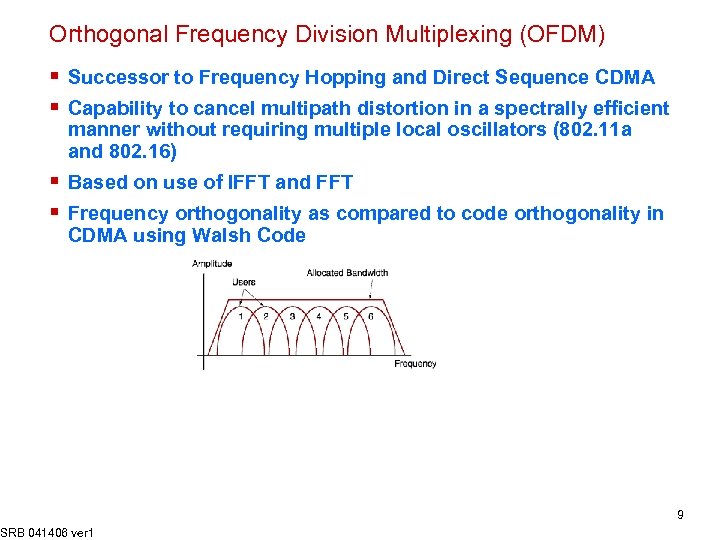 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) § Successor to Frequency Hopping and Direct Sequence CDMA § Capability to cancel multipath distortion in a spectrally efficient manner without requiring multiple local oscillators (802. 11 a and 802. 16) § Based on use of IFFT and FFT § Frequency orthogonality as compared to code orthogonality in CDMA using Walsh Code SRB 041406 ver 1 9
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) § Successor to Frequency Hopping and Direct Sequence CDMA § Capability to cancel multipath distortion in a spectrally efficient manner without requiring multiple local oscillators (802. 11 a and 802. 16) § Based on use of IFFT and FFT § Frequency orthogonality as compared to code orthogonality in CDMA using Walsh Code SRB 041406 ver 1 9
 3 G Services Who is first? – the customer; who is second? - No one SRB 041406 ver 1 10
3 G Services Who is first? – the customer; who is second? - No one SRB 041406 ver 1 10
 Key Mobility Services § Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS) – Text, sounds, images, and video – Transition from Short Message Service (SMS) – Open Internet standards for messaging § Web Applications – Information portals – Wireless Markup Language (WML) with signals using Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) § Location Communications Services – Location Awareness Based § Personalization of information presentation format – Service capability negotiations (MEx. E environment) SRB 041406 ver 1 11
Key Mobility Services § Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS) – Text, sounds, images, and video – Transition from Short Message Service (SMS) – Open Internet standards for messaging § Web Applications – Information portals – Wireless Markup Language (WML) with signals using Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) § Location Communications Services – Location Awareness Based § Personalization of information presentation format – Service capability negotiations (MEx. E environment) SRB 041406 ver 1 11
 Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) § CAMEL = IN + Service portability (incl mobility and roaming) § Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Mobile user <-> ISP <-> corporate server • Mobility, Security, Capacity and quality § Prepaid, Usage Limitations, Advanced Routing Services § Virtual Home Environment (VHE) • Subscriber profile, charging information, Service information, numbering information • Integration of array of services, content conversion to heterogeneous services, network user profile, location aware services Take the claims with a grain of salt SRB 041406 ver 1 12
Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) § CAMEL = IN + Service portability (incl mobility and roaming) § Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Mobile user <-> ISP <-> corporate server • Mobility, Security, Capacity and quality § Prepaid, Usage Limitations, Advanced Routing Services § Virtual Home Environment (VHE) • Subscriber profile, charging information, Service information, numbering information • Integration of array of services, content conversion to heterogeneous services, network user profile, location aware services Take the claims with a grain of salt SRB 041406 ver 1 12
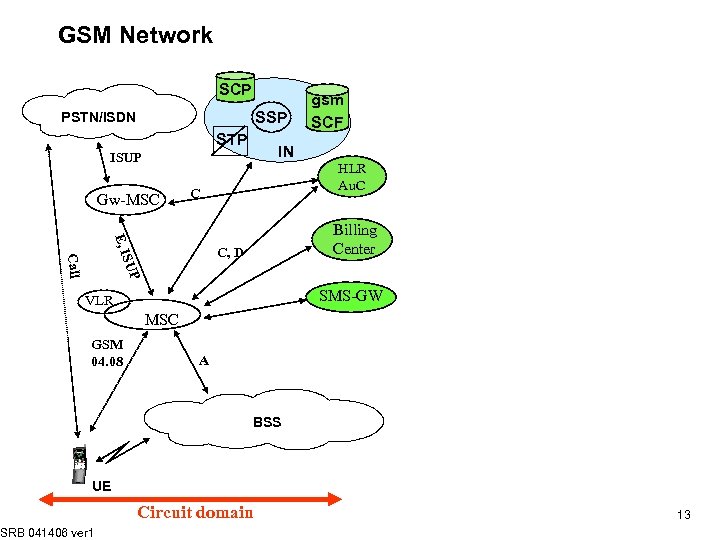 GSM Network SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP IN ISUP Gw-MSC gsm SCF HLR Au. C C E, I C, D SUP Call Billing Center SMS-GW VLR MSC GSM 04. 08 A BSS UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain 13
GSM Network SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP IN ISUP Gw-MSC gsm SCF HLR Au. C C E, I C, D SUP Call Billing Center SMS-GW VLR MSC GSM 04. 08 A BSS UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain 13
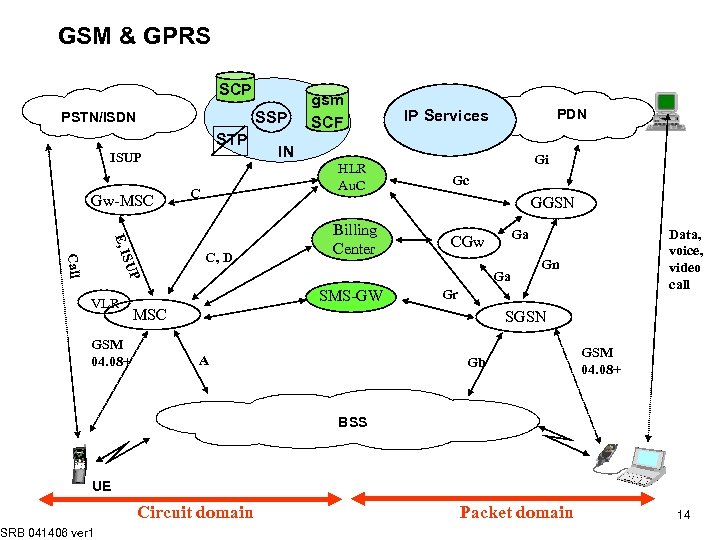 GSM & GPRS SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP ISUP Gw-MSC E, I SUP Call VLR GSM 04. 08+ gsm SCF IN HLR Au. C C PDN IP Services Gi Gc GGSN C, D Billing Center Ga SMS-GW Data, voice, video call Ga CGw Gn Gr MSC SGSN A Gb GSM 04. 08+ BSS UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain Packet domain 14
GSM & GPRS SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP ISUP Gw-MSC E, I SUP Call VLR GSM 04. 08+ gsm SCF IN HLR Au. C C PDN IP Services Gi Gc GGSN C, D Billing Center Ga SMS-GW Data, voice, video call Ga CGw Gn Gr MSC SGSN A Gb GSM 04. 08+ BSS UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain Packet domain 14
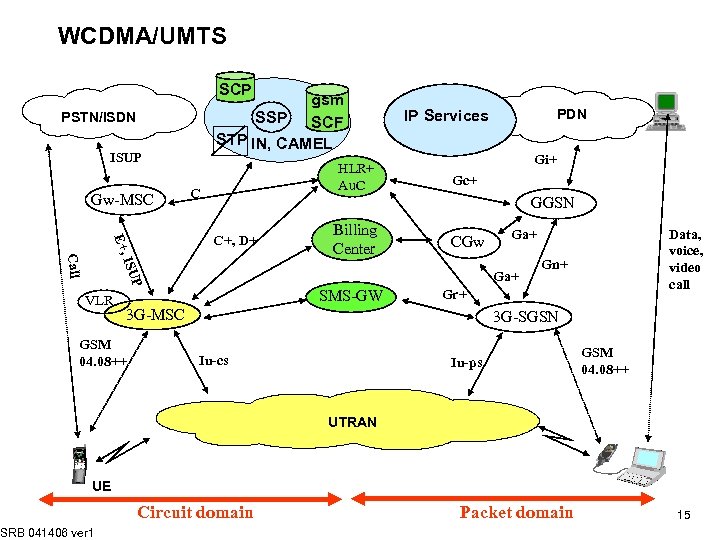 WCDMA/UMTS SCP gsm SSP SCF STP IN, CAMEL PSTN/ISDN ISUP Gw-MSC HLR+ Au. C C Gi+ Gc+ GGSN C+, D+ E+, Billing Center CGw ISU Call SMS-GW Gn+ Gr+ 3 G-MSC GSM 04. 08++ Data, voice, video call Ga+ P VLR PDN IP Services 3 G-SGSN Iu-cs Iu-ps GSM 04. 08++ UTRAN UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain Packet domain 15
WCDMA/UMTS SCP gsm SSP SCF STP IN, CAMEL PSTN/ISDN ISUP Gw-MSC HLR+ Au. C C Gi+ Gc+ GGSN C+, D+ E+, Billing Center CGw ISU Call SMS-GW Gn+ Gr+ 3 G-MSC GSM 04. 08++ Data, voice, video call Ga+ P VLR PDN IP Services 3 G-SGSN Iu-cs Iu-ps GSM 04. 08++ UTRAN UE SRB 041406 ver 1 Circuit domain Packet domain 15
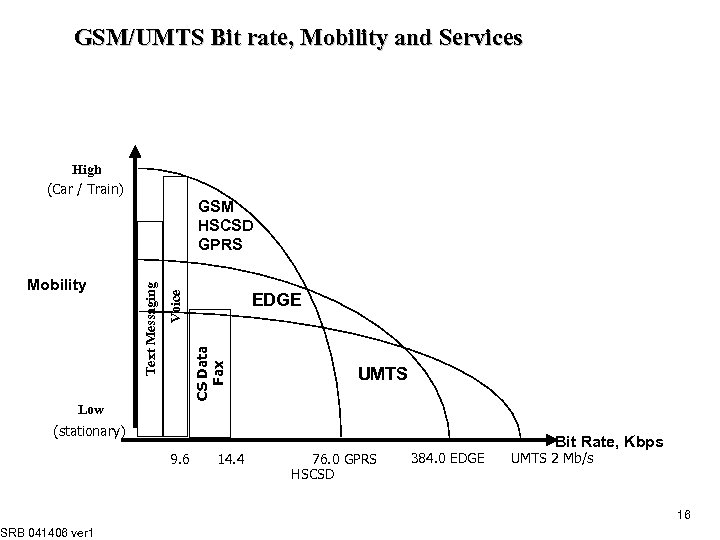 GSM/UMTS Bit rate, Mobility and Services High (Car / Train) EDGE CS Data Fax Voice Mobility Text Messaging GSM HSCSD GPRS UMTS Low (stationary) SRB 041406 ver 1 9. 6 14. 4 76. 0 GPRS HSCSD 384. 0 EDGE Bit Rate, Kbps UMTS 2 Mb/s 16
GSM/UMTS Bit rate, Mobility and Services High (Car / Train) EDGE CS Data Fax Voice Mobility Text Messaging GSM HSCSD GPRS UMTS Low (stationary) SRB 041406 ver 1 9. 6 14. 4 76. 0 GPRS HSCSD 384. 0 EDGE Bit Rate, Kbps UMTS 2 Mb/s 16
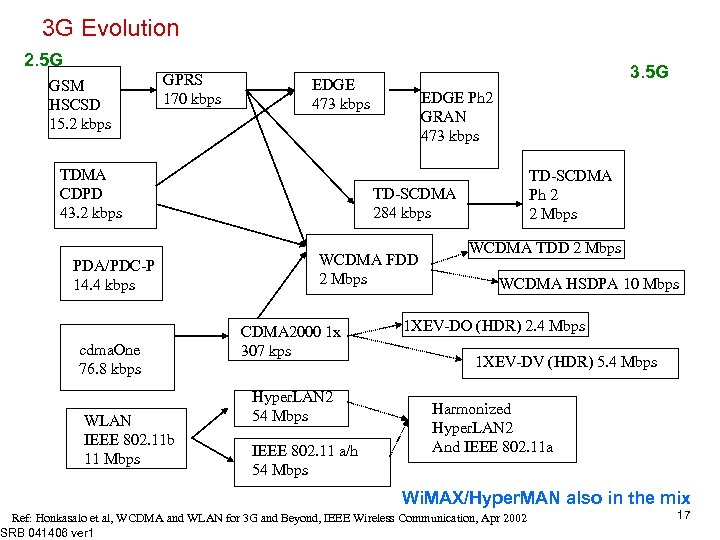 3 G Evolution 2. 5 G GSM HSCSD 15. 2 kbps GPRS 170 kbps TDMA CDPD 43. 2 kbps PDA/PDC-P 14. 4 kbps cdma. One 76. 8 kbps WLAN IEEE 802. 11 b 11 Mbps 3. 5 G EDGE 473 kbps EDGE Ph 2 GRAN 473 kbps TD-SCDMA Ph 2 2 Mbps TD-SCDMA 284 kbps WCDMA FDD 2 Mbps CDMA 2000 1 x 307 kps Hyper. LAN 2 54 Mbps IEEE 802. 11 a/h 54 Mbps WCDMA TDD 2 Mbps WCDMA HSDPA 10 Mbps 1 XEV-DO (HDR) 2. 4 Mbps 1 XEV-DV (HDR) 5. 4 Mbps Harmonized Hyper. LAN 2 And IEEE 802. 11 a Wi. MAX/Hyper. MAN also in the mix Ref: Honkasalo et al, WCDMA and WLAN for 3 G and Beyond, IEEE Wireless Communication, Apr 2002 SRB 041406 ver 1 17
3 G Evolution 2. 5 G GSM HSCSD 15. 2 kbps GPRS 170 kbps TDMA CDPD 43. 2 kbps PDA/PDC-P 14. 4 kbps cdma. One 76. 8 kbps WLAN IEEE 802. 11 b 11 Mbps 3. 5 G EDGE 473 kbps EDGE Ph 2 GRAN 473 kbps TD-SCDMA Ph 2 2 Mbps TD-SCDMA 284 kbps WCDMA FDD 2 Mbps CDMA 2000 1 x 307 kps Hyper. LAN 2 54 Mbps IEEE 802. 11 a/h 54 Mbps WCDMA TDD 2 Mbps WCDMA HSDPA 10 Mbps 1 XEV-DO (HDR) 2. 4 Mbps 1 XEV-DV (HDR) 5. 4 Mbps Harmonized Hyper. LAN 2 And IEEE 802. 11 a Wi. MAX/Hyper. MAN also in the mix Ref: Honkasalo et al, WCDMA and WLAN for 3 G and Beyond, IEEE Wireless Communication, Apr 2002 SRB 041406 ver 1 17
 Some Representative Current Wireless Options § 3 G Cellular (WCDMA) § § – Frequency Division Duplex (FDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in frequency – (“symmetric”) – Time Division Duplex (TDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in time – allows “asymmetric” traffic (adjust time slots in uplink and downlink) 3 G Cellular (CDMA 2000) Wi Fi – 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b; Hyper. LAN 2 – 2. 4 GHz band Wi. MAX – 802. 16 d (fixed); 802. 16 e (“portable”) – 5. 8 GHz band; 10 – 20 Mbps symmetrical BW Blue Tooth – RF based LAN technology; 20 -30 feet coverage – 2. 4 GHz band Darwin’s Theory of Evolution and Survival of the fittest SRB 041406 ver 1 18
Some Representative Current Wireless Options § 3 G Cellular (WCDMA) § § – Frequency Division Duplex (FDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in frequency – (“symmetric”) – Time Division Duplex (TDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in time – allows “asymmetric” traffic (adjust time slots in uplink and downlink) 3 G Cellular (CDMA 2000) Wi Fi – 802. 11 a and 802. 11 b; Hyper. LAN 2 – 2. 4 GHz band Wi. MAX – 802. 16 d (fixed); 802. 16 e (“portable”) – 5. 8 GHz band; 10 – 20 Mbps symmetrical BW Blue Tooth – RF based LAN technology; 20 -30 feet coverage – 2. 4 GHz band Darwin’s Theory of Evolution and Survival of the fittest SRB 041406 ver 1 18
 3 G WCDMA § § § § Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Domains, Protocols, and Channels Radio Resource Management Network Dimensioning and Optimization Quality of Service (Qo. S 0 and Location Services The favored twin sister of CDMA 2000 SRB 041406 ver 1 19
3 G WCDMA § § § § Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Domains, Protocols, and Channels Radio Resource Management Network Dimensioning and Optimization Quality of Service (Qo. S 0 and Location Services The favored twin sister of CDMA 2000 SRB 041406 ver 1 19
 Release 99 § § § Radio Bearer Negotiations Traffic Classes Complex Scrambling Speech Codec – (eight) Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR) Battery Life Transmission “spatial/antenna” diversity Compressed Mode – Measurements in multiple frequency – Use of transmission time reduction techniques # PDP Contexts per IP Address QPSK; coherent detection; Rake receiver Short and Long Spreading Codes Multicall – several simultaneous CS calls with dedicated bearers of independent traffic and performance characteristics Customized Application for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase 3 A lot to gobble SRB 041406 ver 1 20
Release 99 § § § Radio Bearer Negotiations Traffic Classes Complex Scrambling Speech Codec – (eight) Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR) Battery Life Transmission “spatial/antenna” diversity Compressed Mode – Measurements in multiple frequency – Use of transmission time reduction techniques # PDP Contexts per IP Address QPSK; coherent detection; Rake receiver Short and Long Spreading Codes Multicall – several simultaneous CS calls with dedicated bearers of independent traffic and performance characteristics Customized Application for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase 3 A lot to gobble SRB 041406 ver 1 20
 Release 4 § Bearer Independent Core Network § Tandem Free Operation (TFO), Transcoder Free Operation (Tr. FO), and Out of Band Transcoder Control (Oo. BTC) § § § Low Chip Rate TDD Operation Network Assisted Cell Change FDD Repeater Node. B Synchronization for TDD IPv 6 packet switched network supporting both real time and non-real time traffic – Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) replacing SS 7 § Home Subscriber Server (HSS) § MSC/VLR -> MSC server (mobility management) and MGW (Connection management subtasks) § Multimedia Message Service (MMS) environment SRB 041406 ver 1 21
Release 4 § Bearer Independent Core Network § Tandem Free Operation (TFO), Transcoder Free Operation (Tr. FO), and Out of Band Transcoder Control (Oo. BTC) § § § Low Chip Rate TDD Operation Network Assisted Cell Change FDD Repeater Node. B Synchronization for TDD IPv 6 packet switched network supporting both real time and non-real time traffic – Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) replacing SS 7 § Home Subscriber Server (HSS) § MSC/VLR -> MSC server (mobility management) and MGW (Connection management subtasks) § Multimedia Message Service (MMS) environment SRB 041406 ver 1 21
 Release 5 § § § § IP Transport in UTRAN High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) (upto 10 Mbps) Intra Domain Connection to Multiple CN Nodes (Iuflex) IP Multimedia CN Subsystem (IMS) “Guaranteed” End to End (E 2 E) Qo. S in the PS domain Global Text Telephony Support for Real Time Services in packet domain CAMEL Phase 4 SRB 041406 ver 1 22
Release 5 § § § § IP Transport in UTRAN High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) (upto 10 Mbps) Intra Domain Connection to Multiple CN Nodes (Iuflex) IP Multimedia CN Subsystem (IMS) “Guaranteed” End to End (E 2 E) Qo. S in the PS domain Global Text Telephony Support for Real Time Services in packet domain CAMEL Phase 4 SRB 041406 ver 1 22
 HSDPA § Peak Data rate > 10 Mbps § Same spectrum by both voice and data – Up to 12 spreading codes for High Speed DSCH (HS-DSCH) – Fast link Adaptation – Both code and time division for channel sharing § Transmission Time interval 2 ms § Hybrid Automatic Repeat re. Quest (HARQ) – Automatic optimizations to Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) § QPSK and 16 QAM modulation at 3. 84 Mhz symbol; spreading factor fixed to 16 § Incremental Redundancy or chase combining (CH) § New DPCCH 2 in uplink primarily for HARQ channel state info SRB 041406 ver 1 23
HSDPA § Peak Data rate > 10 Mbps § Same spectrum by both voice and data – Up to 12 spreading codes for High Speed DSCH (HS-DSCH) – Fast link Adaptation – Both code and time division for channel sharing § Transmission Time interval 2 ms § Hybrid Automatic Repeat re. Quest (HARQ) – Automatic optimizations to Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) § QPSK and 16 QAM modulation at 3. 84 Mhz symbol; spreading factor fixed to 16 § Incremental Redundancy or chase combining (CH) § New DPCCH 2 in uplink primarily for HARQ channel state info SRB 041406 ver 1 23
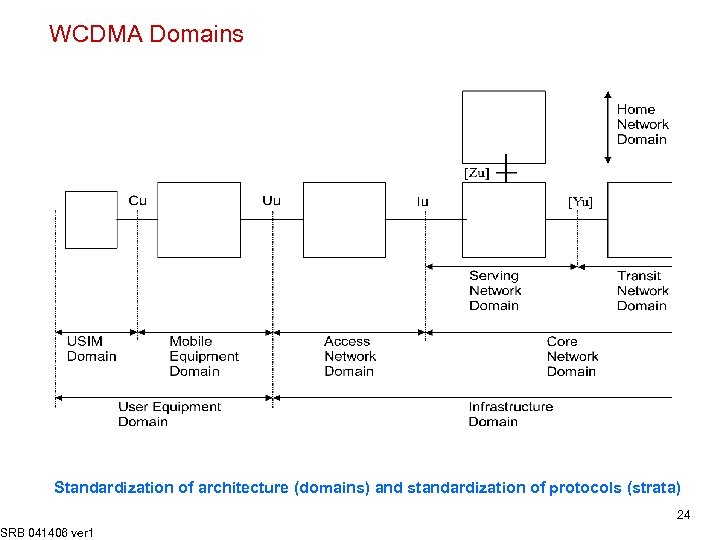 WCDMA Domains Standardization of architecture (domains) and standardization of protocols (strata) SRB 041406 ver 1 24
WCDMA Domains Standardization of architecture (domains) and standardization of protocols (strata) SRB 041406 ver 1 24
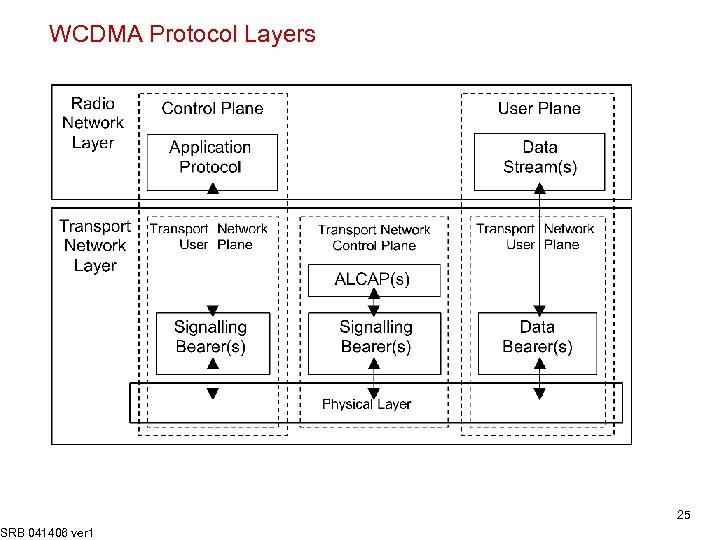 WCDMA Protocol Layers SRB 041406 ver 1 25
WCDMA Protocol Layers SRB 041406 ver 1 25
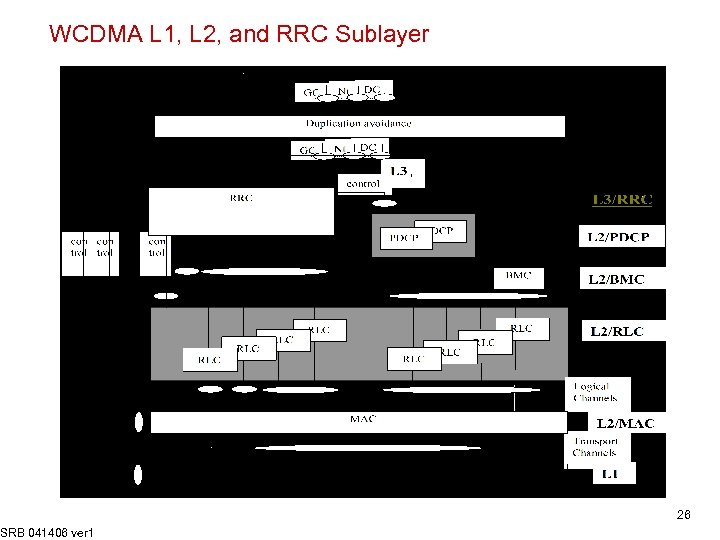 WCDMA L 1, L 2, and RRC Sublayer SRB 041406 ver 1 26
WCDMA L 1, L 2, and RRC Sublayer SRB 041406 ver 1 26
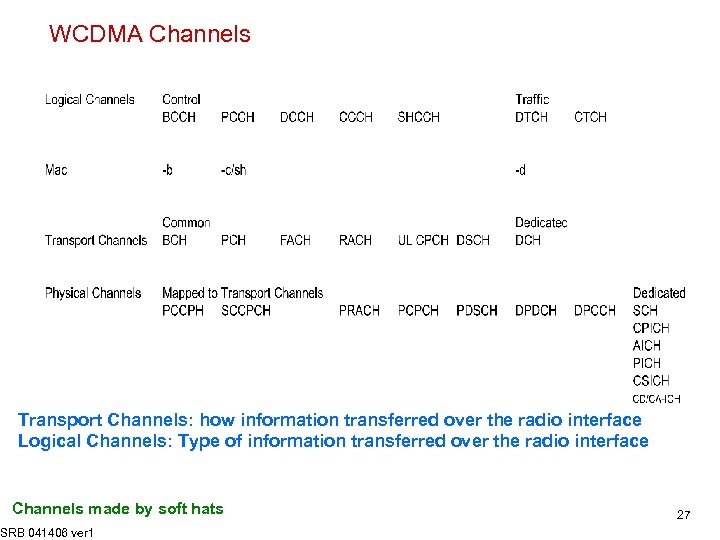 WCDMA Channels Transport Channels: how information transferred over the radio interface Logical Channels: Type of information transferred over the radio interface Channels made by soft hats SRB 041406 ver 1 27
WCDMA Channels Transport Channels: how information transferred over the radio interface Logical Channels: Type of information transferred over the radio interface Channels made by soft hats SRB 041406 ver 1 27
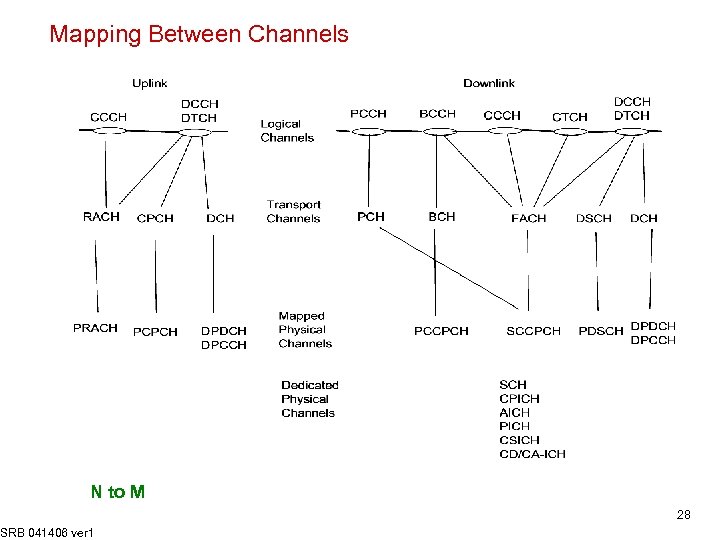 Mapping Between Channels N to M SRB 041406 ver 1 28
Mapping Between Channels N to M SRB 041406 ver 1 28
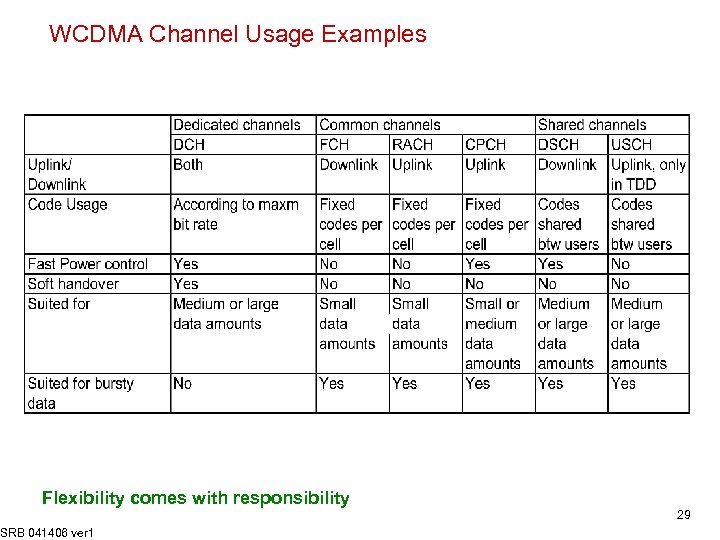 WCDMA Channel Usage Examples Flexibility comes with responsibility SRB 041406 ver 1 29
WCDMA Channel Usage Examples Flexibility comes with responsibility SRB 041406 ver 1 29
 Radio Resource Management § § § Power Control Handover Access Control Load and Congestion Control Packet Scheduling SRB 041406 ver 1 30
Radio Resource Management § § § Power Control Handover Access Control Load and Congestion Control Packet Scheduling SRB 041406 ver 1 30
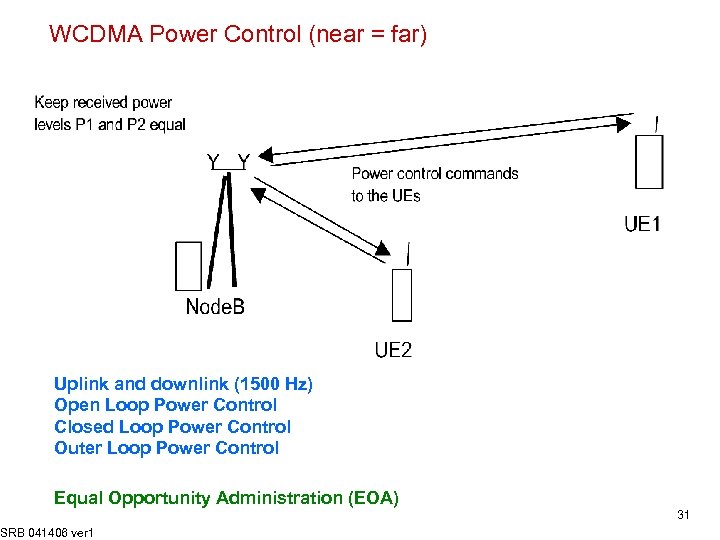 WCDMA Power Control (near = far) Uplink and downlink (1500 Hz) Open Loop Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Outer Loop Power Control Equal Opportunity Administration (EOA) SRB 041406 ver 1 31
WCDMA Power Control (near = far) Uplink and downlink (1500 Hz) Open Loop Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Outer Loop Power Control Equal Opportunity Administration (EOA) SRB 041406 ver 1 31
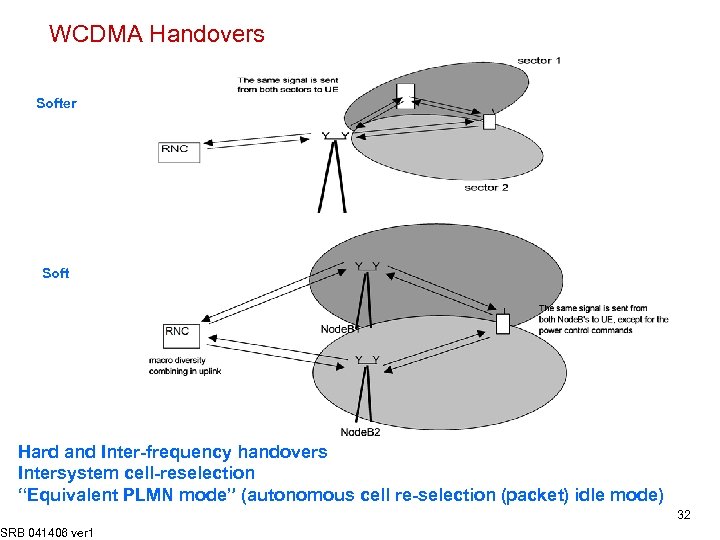 WCDMA Handovers Softer Soft Hard and Inter-frequency handovers Intersystem cell-reselection “Equivalent PLMN mode” (autonomous cell re-selection (packet) idle mode) SRB 041406 ver 1 32
WCDMA Handovers Softer Soft Hard and Inter-frequency handovers Intersystem cell-reselection “Equivalent PLMN mode” (autonomous cell re-selection (packet) idle mode) SRB 041406 ver 1 32
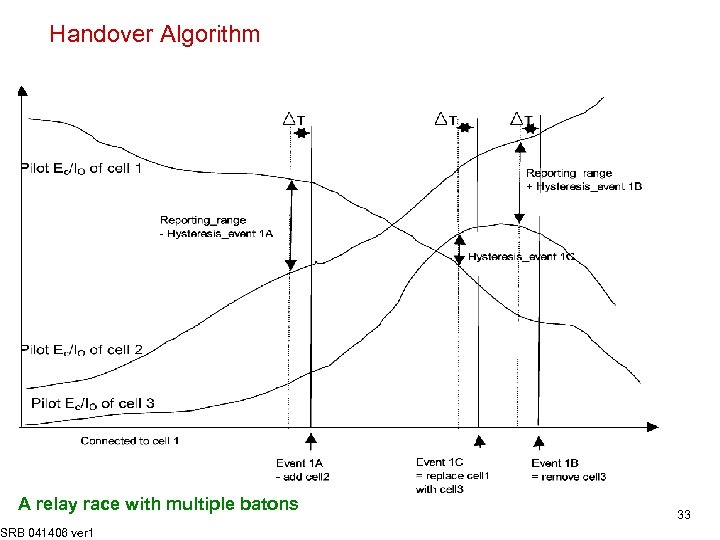 Handover Algorithm A relay race with multiple batons SRB 041406 ver 1 33
Handover Algorithm A relay race with multiple batons SRB 041406 ver 1 33
 Network Dimensioning and Optimization § Dimensioning Criteria – Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service § Dimensioning – Link budget, capacity (hard and soft) and load factor – Estimation of average interference power – Coverage end Outage probabilities § Optimization – Performance Requirements – Antenna adjustments, neighbor lists, scrambling codes Don’t force a round peg in a square hole SRB 041406 ver 1 34
Network Dimensioning and Optimization § Dimensioning Criteria – Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service § Dimensioning – Link budget, capacity (hard and soft) and load factor – Estimation of average interference power – Coverage end Outage probabilities § Optimization – Performance Requirements – Antenna adjustments, neighbor lists, scrambling codes Don’t force a round peg in a square hole SRB 041406 ver 1 34
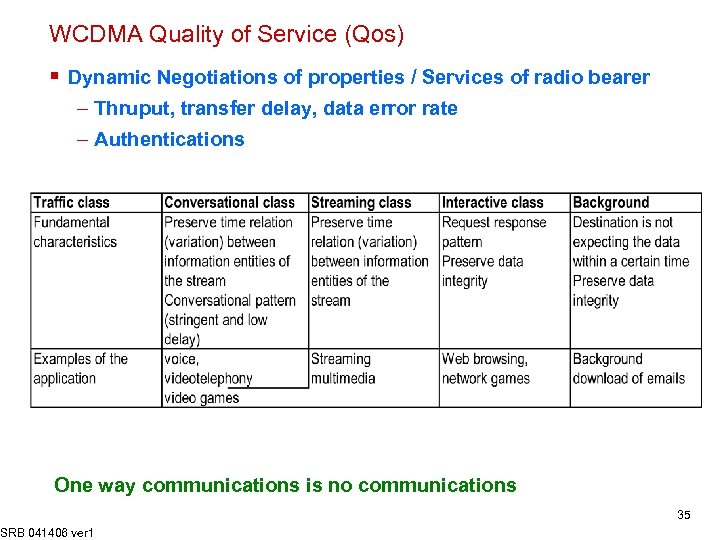 WCDMA Quality of Service (Qos) § Dynamic Negotiations of properties / Services of radio bearer – Thruput, transfer delay, data error rate – Authentications One way communications is no communications SRB 041406 ver 1 35
WCDMA Quality of Service (Qos) § Dynamic Negotiations of properties / Services of radio bearer – Thruput, transfer delay, data error rate – Authentications One way communications is no communications SRB 041406 ver 1 35
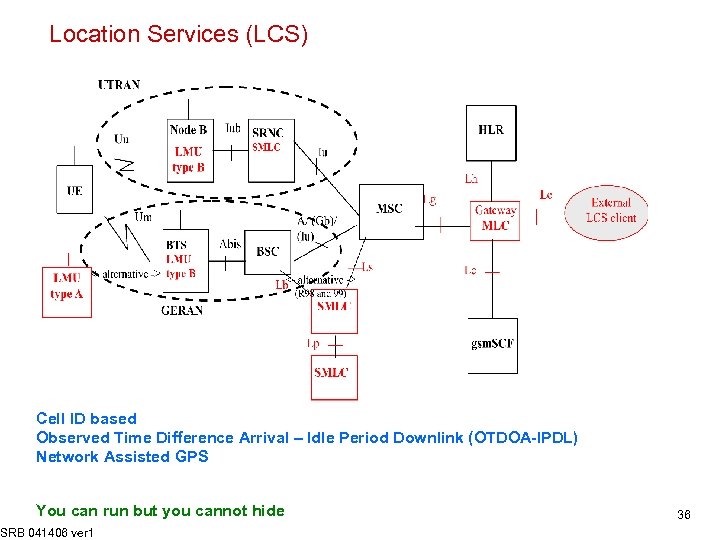 Location Services (LCS) Cell ID based Observed Time Difference Arrival – Idle Period Downlink (OTDOA-IPDL) Network Assisted GPS You can run but you cannot hide SRB 041406 ver 1 36
Location Services (LCS) Cell ID based Observed Time Difference Arrival – Idle Period Downlink (OTDOA-IPDL) Network Assisted GPS You can run but you cannot hide SRB 041406 ver 1 36
 Why Move Towards 4 G? § Limitation to meet expectations of applications like multimedia, full motion video, wireless teleconferencing – Wider Bandwidth § Difficult to move and interoperate due to different standards hampering global mobility and service portability § Primarily Cellular (WAN) with distinct LANs’; need a new integrated network § Limitations in applying recent advances in spectrally more efficient modulation schemes § Need all digital network to fully utilize IP and converged video and data Incessant human desire to reach the sky SRB 041406 ver 1 37
Why Move Towards 4 G? § Limitation to meet expectations of applications like multimedia, full motion video, wireless teleconferencing – Wider Bandwidth § Difficult to move and interoperate due to different standards hampering global mobility and service portability § Primarily Cellular (WAN) with distinct LANs’; need a new integrated network § Limitations in applying recent advances in spectrally more efficient modulation schemes § Need all digital network to fully utilize IP and converged video and data Incessant human desire to reach the sky SRB 041406 ver 1 37
 Where Do We Want to Go? § Seamless Roaming § Integrated “standard” Networks § Mobile Intelligent Internet Onwards to (Ultra) Wideband Wireless IP Networks We are no longer in Kansas, Toto SRB 041406 ver 1 38
Where Do We Want to Go? § Seamless Roaming § Integrated “standard” Networks § Mobile Intelligent Internet Onwards to (Ultra) Wideband Wireless IP Networks We are no longer in Kansas, Toto SRB 041406 ver 1 38
 Upcoming § 3. 5 G – Evolved radio Interface – IP based core network § 4 G – New Air Interface – Very high bit rate services – Convergence of Wireline, Wireless, and IP worlds And Now for Something Completely Different SRB 041406 ver 1 39
Upcoming § 3. 5 G – Evolved radio Interface – IP based core network § 4 G – New Air Interface – Very high bit rate services – Convergence of Wireline, Wireless, and IP worlds And Now for Something Completely Different SRB 041406 ver 1 39
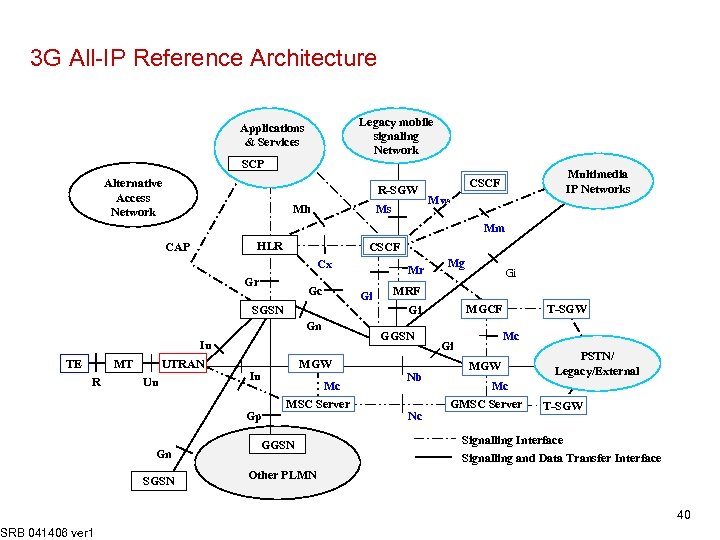 3 G All-IP Reference Architecture Legacy mobile signaling Network Applications & Services SCP Alternative Access Network R-SGW Mh Ms Multimedia IP Networks CSCF Mw Mm HSS HLR CAP CSCF Cx Gr Gc Gi Gn R SRB 041406 ver 1 UTRAN Uu Gp Gn SGSN MGW Iu Mc MSC Server GGSN Gi MRF GGSN Iu MT Mg MGCF Gi SGSN TE Mr Nb Nc T-SGW Mc Gi MGW PSTN/ Legacy/External Mc GMSC Server T-SGW Signalling Interface Signalling and Data Transfer Interface Other PLMN 40
3 G All-IP Reference Architecture Legacy mobile signaling Network Applications & Services SCP Alternative Access Network R-SGW Mh Ms Multimedia IP Networks CSCF Mw Mm HSS HLR CAP CSCF Cx Gr Gc Gi Gn R SRB 041406 ver 1 UTRAN Uu Gp Gn SGSN MGW Iu Mc MSC Server GGSN Gi MRF GGSN Iu MT Mg MGCF Gi SGSN TE Mr Nb Nc T-SGW Mc Gi MGW PSTN/ Legacy/External Mc GMSC Server T-SGW Signalling Interface Signalling and Data Transfer Interface Other PLMN 40
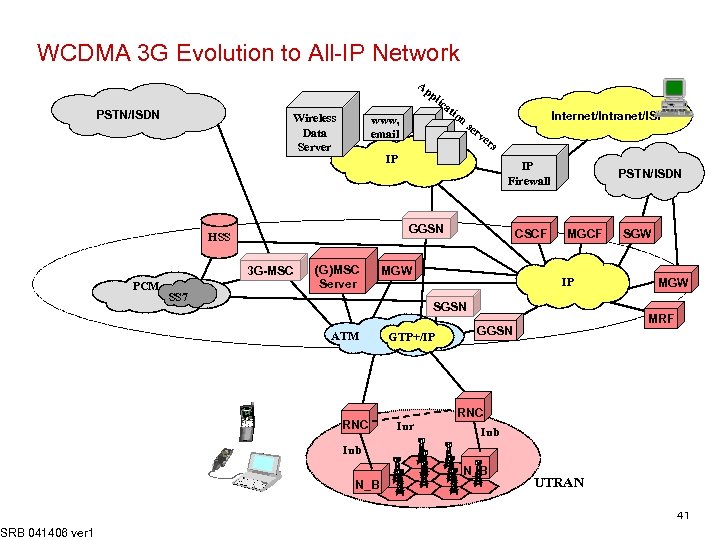 WCDMA 3 G Evolution to All-IP Network SRB 041406 ver 1 PSTN/ISDN Wireless Data Server www, email IP 3 G-MSC SS 7 Internet/Intranet/ISP IP Firewall GGSN HLR HSS Au. C PCM Ap pl ica tio n se rv er s (G)MSC Server CSCF MGW PSTN/ISDN MGCF IP SGSN ATM RNC GTP+/IP Iur SGW MRF GGSN RNC Iub N_B UTRAN 41
WCDMA 3 G Evolution to All-IP Network SRB 041406 ver 1 PSTN/ISDN Wireless Data Server www, email IP 3 G-MSC SS 7 Internet/Intranet/ISP IP Firewall GGSN HLR HSS Au. C PCM Ap pl ica tio n se rv er s (G)MSC Server CSCF MGW PSTN/ISDN MGCF IP SGSN ATM RNC GTP+/IP Iur SGW MRF GGSN RNC Iub N_B UTRAN 41
 3. 5 G Radio Network Evolution § High Data rate, low latency, packet optimized radio access § Support flexible bandwidth upto 20 MHz, new transmission § § § § schemes, advanced multi-antenna technologies, and signaling optimization Instantaneous peak DL 100 Mb/s and UP 50 Mb/S within 20 MHz spectrum Control plane latency of < 100 ms (camped to active) and < 50 ms (dormant to active) > 200 users per cell within 5 MHz spectrum Spectrum flexibility from 1. 25 MHz to 20 MHz Eliminate “dedicated” channels; avoid macro diversity in DL Migrate towards OFDM in DL and SC-FDMA in UL Support voice services in the packet domain Adaptive Modulation and Coding using Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) measurements SRB 041406 ver 1 42
3. 5 G Radio Network Evolution § High Data rate, low latency, packet optimized radio access § Support flexible bandwidth upto 20 MHz, new transmission § § § § schemes, advanced multi-antenna technologies, and signaling optimization Instantaneous peak DL 100 Mb/s and UP 50 Mb/S within 20 MHz spectrum Control plane latency of < 100 ms (camped to active) and < 50 ms (dormant to active) > 200 users per cell within 5 MHz spectrum Spectrum flexibility from 1. 25 MHz to 20 MHz Eliminate “dedicated” channels; avoid macro diversity in DL Migrate towards OFDM in DL and SC-FDMA in UL Support voice services in the packet domain Adaptive Modulation and Coding using Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) measurements SRB 041406 ver 1 42
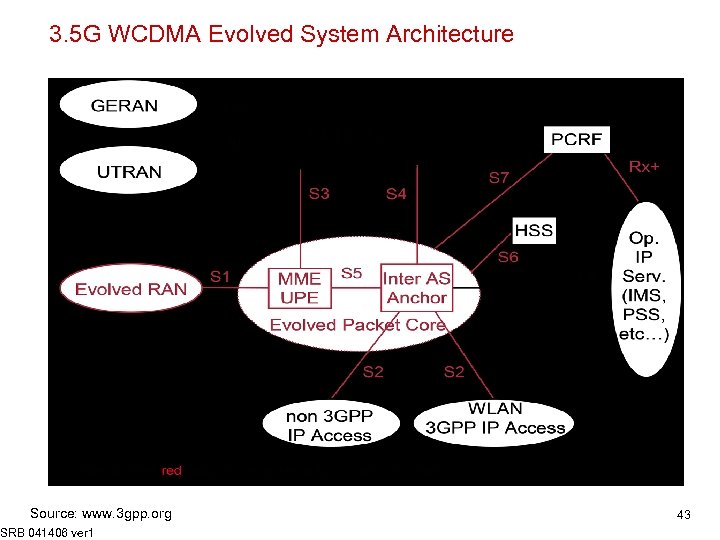 3. 5 G WCDMA Evolved System Architecture Source: www. 3 gpp. org SRB 041406 ver 1 43
3. 5 G WCDMA Evolved System Architecture Source: www. 3 gpp. org SRB 041406 ver 1 43
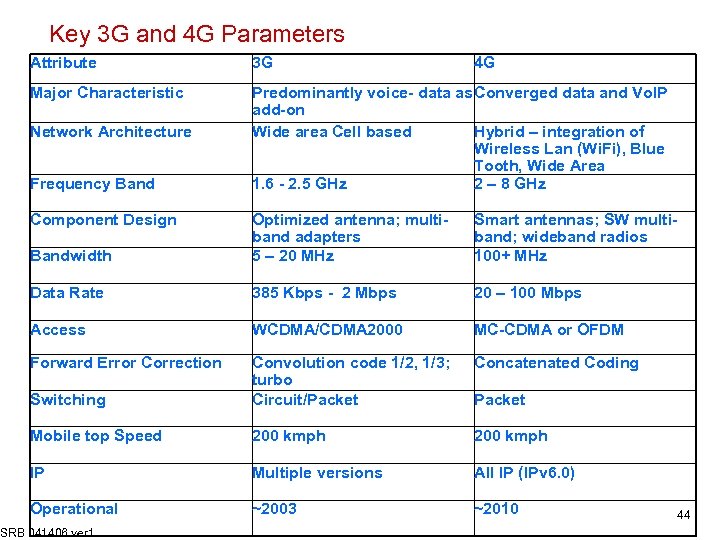 Key 3 G and 4 G Parameters Attribute 3 G Major Characteristic Predominantly voice- data as Converged data and Vo. IP add-on Wide area Cell based Hybrid – integration of Wireless Lan (Wi. Fi), Blue Tooth, Wide Area 1. 6 - 2. 5 GHz 2 – 8 GHz Network Architecture Frequency Band Component Design 4 G Bandwidth Optimized antenna; multiband adapters 5 – 20 MHz Smart antennas; SW multiband; wideband radios 100+ MHz Data Rate 385 Kbps - 2 Mbps 20 – 100 Mbps Access WCDMA/CDMA 2000 MC-CDMA or OFDM Forward Error Correction Concatenated Coding Switching Convolution code 1/2, 1/3; turbo Circuit/Packet Mobile top Speed 200 kmph IP Multiple versions All IP (IPv 6. 0) Operational ~2003 ~2010 SRB 041406 ver 1 Packet 44
Key 3 G and 4 G Parameters Attribute 3 G Major Characteristic Predominantly voice- data as Converged data and Vo. IP add-on Wide area Cell based Hybrid – integration of Wireless Lan (Wi. Fi), Blue Tooth, Wide Area 1. 6 - 2. 5 GHz 2 – 8 GHz Network Architecture Frequency Band Component Design 4 G Bandwidth Optimized antenna; multiband adapters 5 – 20 MHz Smart antennas; SW multiband; wideband radios 100+ MHz Data Rate 385 Kbps - 2 Mbps 20 – 100 Mbps Access WCDMA/CDMA 2000 MC-CDMA or OFDM Forward Error Correction Concatenated Coding Switching Convolution code 1/2, 1/3; turbo Circuit/Packet Mobile top Speed 200 kmph IP Multiple versions All IP (IPv 6. 0) Operational ~2003 ~2010 SRB 041406 ver 1 Packet 44
 Key 4 G Mobility Concepts § Mobile IP – Vo. IP – Ability to move around with the same IP address – IP tunnels – Intelligent Internet § Presence Awareness Technology – Knowing who is on line and where § Radio Router – Bringing IP to the base station § Smart Antennas – Unique spatial metric for each transmission Wireless IP <---> IP Wireless SRB 041406 ver 1 45
Key 4 G Mobility Concepts § Mobile IP – Vo. IP – Ability to move around with the same IP address – IP tunnels – Intelligent Internet § Presence Awareness Technology – Knowing who is on line and where § Radio Router – Bringing IP to the base station § Smart Antennas – Unique spatial metric for each transmission Wireless IP <---> IP Wireless SRB 041406 ver 1 45
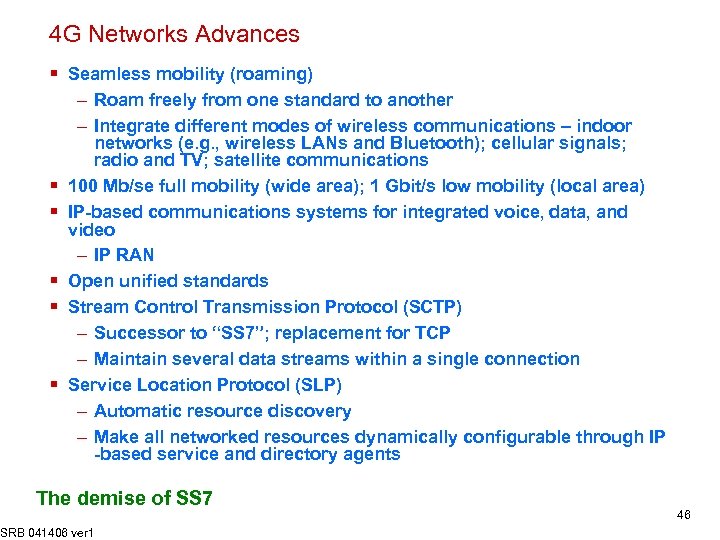 4 G Networks Advances § Seamless mobility (roaming) § § § – Roam freely from one standard to another – Integrate different modes of wireless communications – indoor networks (e. g. , wireless LANs and Bluetooth); cellular signals; radio and TV; satellite communications 100 Mb/se full mobility (wide area); 1 Gbit/s low mobility (local area) IP-based communications systems for integrated voice, data, and video – IP RAN Open unified standards Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) – Successor to “SS 7”; replacement for TCP – Maintain several data streams within a single connection Service Location Protocol (SLP) – Automatic resource discovery – Make all networked resources dynamically configurable through IP -based service and directory agents The demise of SS 7 SRB 041406 ver 1 46
4 G Networks Advances § Seamless mobility (roaming) § § § – Roam freely from one standard to another – Integrate different modes of wireless communications – indoor networks (e. g. , wireless LANs and Bluetooth); cellular signals; radio and TV; satellite communications 100 Mb/se full mobility (wide area); 1 Gbit/s low mobility (local area) IP-based communications systems for integrated voice, data, and video – IP RAN Open unified standards Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) – Successor to “SS 7”; replacement for TCP – Maintain several data streams within a single connection Service Location Protocol (SLP) – Automatic resource discovery – Make all networked resources dynamically configurable through IP -based service and directory agents The demise of SS 7 SRB 041406 ver 1 46
 4 G Networks Advances – cont’d § Diameter – Successor to “Radius” – Unified authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) § Integrated LAN card and Subscriber Identity Modules (SIMs) § HSS – Unified Subscriber Information § Application developers, Service providers, and content creators Expand beyond the circle SRB 041406 ver 1 47
4 G Networks Advances – cont’d § Diameter – Successor to “Radius” – Unified authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) § Integrated LAN card and Subscriber Identity Modules (SIMs) § HSS – Unified Subscriber Information § Application developers, Service providers, and content creators Expand beyond the circle SRB 041406 ver 1 47
 Key Challenges § Spectral Efficiencies – Challenge Shannon’s fundamental law of data communications (BW, Sig/No) – Hardware Frequency Synthesis techniques esp. for Frequency Hop (FH) systems – Traffic characteristics management (burstiness, directionality) § Multi Carrier Modulation (MCM) – Baseband process using parallel equal bandwidth subchannels – MC-CDMA; OFDM – Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK); Multilevel Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (M-QAM); Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) – Add cyclic extension or guard band to data – Challenges of Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) and Peak to Average Ratio (PAVR) No pain, no gain SRB 041406 ver 1 48
Key Challenges § Spectral Efficiencies – Challenge Shannon’s fundamental law of data communications (BW, Sig/No) – Hardware Frequency Synthesis techniques esp. for Frequency Hop (FH) systems – Traffic characteristics management (burstiness, directionality) § Multi Carrier Modulation (MCM) – Baseband process using parallel equal bandwidth subchannels – MC-CDMA; OFDM – Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK); Multilevel Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (M-QAM); Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) – Add cyclic extension or guard band to data – Challenges of Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) and Peak to Average Ratio (PAVR) No pain, no gain SRB 041406 ver 1 48
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 1 § Signal Processing and optimizations – Handling extremely large number of users – Synchronous and asynchronous transmissions – Orthogonality / correlation of large number of codes – Spectrum Pollution – Multi path re-enforcement / interference – Multi User Detection (MUD) and Adaptive Interference suppression techniques (ISI and MAI) SRB 041406 ver 1 49
Key Challenges - cont’d - 1 § Signal Processing and optimizations – Handling extremely large number of users – Synchronous and asynchronous transmissions – Orthogonality / correlation of large number of codes – Spectrum Pollution – Multi path re-enforcement / interference – Multi User Detection (MUD) and Adaptive Interference suppression techniques (ISI and MAI) SRB 041406 ver 1 49
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 2 § Extremely Fast Arithmetic (esp. multiplication) – N Dimensional vector spaces – IFFT, FFT – Advanced DSP’s for parsing and processing data § Smart / Intelligent Antennas – Dynamically adjust beam pattern based on CQI – Switched beam Antennas; adaptive arrays – Coverage limitations due to high frequencies (> 5 GHz) Manage Entropy SRB 041406 ver 1 50
Key Challenges - cont’d - 2 § Extremely Fast Arithmetic (esp. multiplication) – N Dimensional vector spaces – IFFT, FFT – Advanced DSP’s for parsing and processing data § Smart / Intelligent Antennas – Dynamically adjust beam pattern based on CQI – Switched beam Antennas; adaptive arrays – Coverage limitations due to high frequencies (> 5 GHz) Manage Entropy SRB 041406 ver 1 50
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 3 § More Efficient and Sensitive Transreceiver Designs – Noise figure, gain, group delay, bandwidth, sensitivity, tunable filters, spurious rejection, power consumption – Frequency Reuse; linearity techniques – Tight closed Loop power control – Dynamic Frequency selection and packet assignments – Multi band, wide band, and flexible radios – Error Correction Coding – “Perfect” Synchronization / phase alignment between Xmitter and Receiver • Clock recovery algorithms (e. g. , as times-two, zero crossing) – Adaptive digitization of speech and multi media signals SRB 041406 ver 1 • A/D and D/A transformations 51
Key Challenges - cont’d - 3 § More Efficient and Sensitive Transreceiver Designs – Noise figure, gain, group delay, bandwidth, sensitivity, tunable filters, spurious rejection, power consumption – Frequency Reuse; linearity techniques – Tight closed Loop power control – Dynamic Frequency selection and packet assignments – Multi band, wide band, and flexible radios – Error Correction Coding – “Perfect” Synchronization / phase alignment between Xmitter and Receiver • Clock recovery algorithms (e. g. , as times-two, zero crossing) – Adaptive digitization of speech and multi media signals SRB 041406 ver 1 • A/D and D/A transformations 51
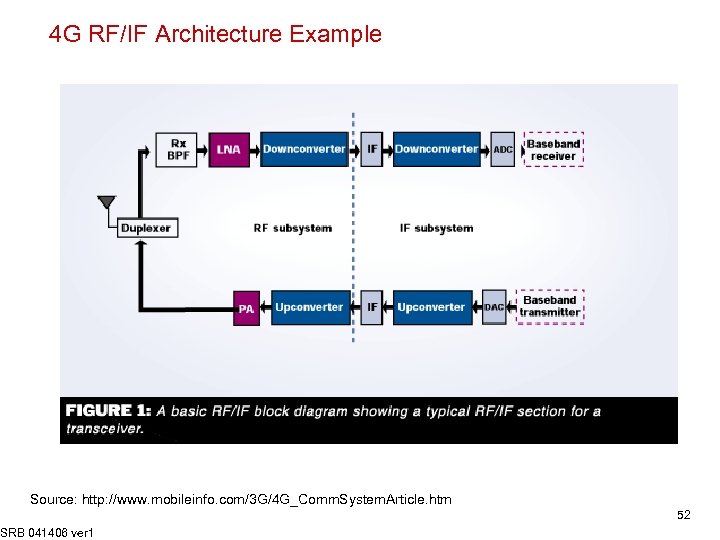 4 G RF/IF Architecture Example Source: http: //www. mobileinfo. com/3 G/4 G_Comm. System. Article. htm SRB 041406 ver 1 52
4 G RF/IF Architecture Example Source: http: //www. mobileinfo. com/3 G/4 G_Comm. System. Article. htm SRB 041406 ver 1 52
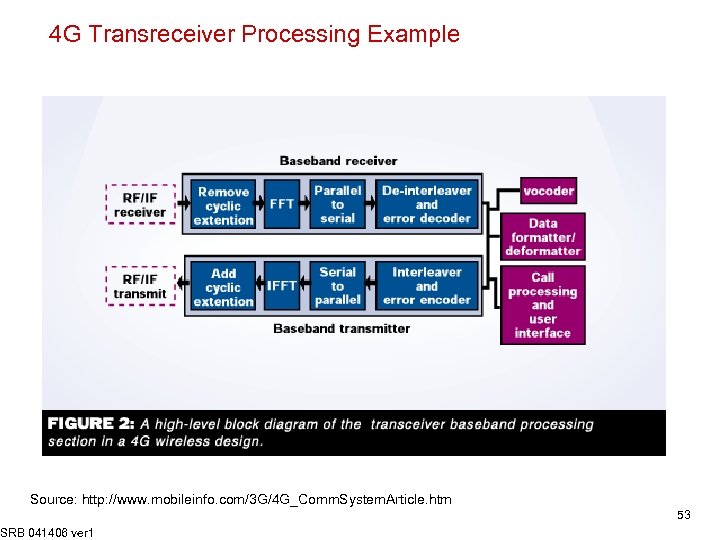 4 G Transreceiver Processing Example Source: http: //www. mobileinfo. com/3 G/4 G_Comm. System. Article. htm SRB 041406 ver 1 53
4 G Transreceiver Processing Example Source: http: //www. mobileinfo. com/3 G/4 G_Comm. System. Article. htm SRB 041406 ver 1 53
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 4 § All IP Network – Tunneling and Firewalls – Fast Handoff control, authentication, realtime location tracking, distributed policy management – Media Gateways for handling packet switched traffic • Trasnscoders, echo cancellations, media conversions Planetary Interoperability § Integration across different topologies – Multi Disciplinary Cooperation WPAN WWAN WLAN IP WMAN There is packet at the end of the tunnel SRB 041406 ver 1 + 54
Key Challenges - cont’d - 4 § All IP Network – Tunneling and Firewalls – Fast Handoff control, authentication, realtime location tracking, distributed policy management – Media Gateways for handling packet switched traffic • Trasnscoders, echo cancellations, media conversions Planetary Interoperability § Integration across different topologies – Multi Disciplinary Cooperation WPAN WWAN WLAN IP WMAN There is packet at the end of the tunnel SRB 041406 ver 1 + 54
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 5 § Distribute intelligence to the edges – Very Smart User equipment; away from “network Centric” architecture – Access routers – Miniaturization esp User Equipment § Security and Levels of Quality of Service (Qo. S) – Encryption Protocols; Security and “trust of information” – Different rates, error profiles, latencies, burstiness – Dynamic optimization of scarce resources § Advanced Used interactions / presentation – Improved User interfaces – advanced Speech recognition and synthesis – Flexible displays SRB 041406 ver 1 55
Key Challenges - cont’d - 5 § Distribute intelligence to the edges – Very Smart User equipment; away from “network Centric” architecture – Access routers – Miniaturization esp User Equipment § Security and Levels of Quality of Service (Qo. S) – Encryption Protocols; Security and “trust of information” – Different rates, error profiles, latencies, burstiness – Dynamic optimization of scarce resources § Advanced Used interactions / presentation – Improved User interfaces – advanced Speech recognition and synthesis – Flexible displays SRB 041406 ver 1 55
 Key Challenges - cont’d - 6 § Web AI service / Interactive Intelligent Programs – Smart applications in the web; intelligent agents – Web Adaptiveness – global database schemes, global error corrective feedback, logic layer protocol, learning algorithms – Symbolic manipulation – Derive specifically targeted knowledge from diverse information sources § Standardizations and Regulatory – Modulation techniques, switching schemes, roaming – Spectrum – Cooperation/coordination among global Spectrum Regulators SRB 041406 ver 1 56
Key Challenges - cont’d - 6 § Web AI service / Interactive Intelligent Programs – Smart applications in the web; intelligent agents – Web Adaptiveness – global database schemes, global error corrective feedback, logic layer protocol, learning algorithms – Symbolic manipulation – Derive specifically targeted knowledge from diverse information sources § Standardizations and Regulatory – Modulation techniques, switching schemes, roaming – Spectrum – Cooperation/coordination among global Spectrum Regulators SRB 041406 ver 1 56
 4 G Forums § Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF) in Europe § Next-Generation Internet (NGI) – Led by and focused on US Fed Agencies (Do. D, Do. E, NASA, NIH etc. ) – High Performance networks: v. BNS (NSF), NREN (NASA), DREN (Do. D), ESnet (Do. E), § Internet 2 – US Universities Initiated – Focus on Gigabit/sec Points of Presence (giga. Po. Ps) SRB 041406 ver 1 57
4 G Forums § Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF) in Europe § Next-Generation Internet (NGI) – Led by and focused on US Fed Agencies (Do. D, Do. E, NASA, NIH etc. ) – High Performance networks: v. BNS (NSF), NREN (NASA), DREN (Do. D), ESnet (Do. E), § Internet 2 – US Universities Initiated – Focus on Gigabit/sec Points of Presence (giga. Po. Ps) SRB 041406 ver 1 57
 Summary § Mobile Intelligent Internet and multi media applications § Seamless Roaming, substantially high and selectable user bandwidth, customized Qo. S, Intelligent and responsive user interface § Mobile IP, Radio Routers, smart Antennas § Continued advances and challenges from 1 G -> 4 G – Modulation techniques, transreceiver advances, fast manipulations, user interfaces, IP tunelling and firewalls – Spectrum usage, regulatory decisions, “one” standard, authentication and security, multi disciplinary co-operation § Packing so much intelligence in smaller and smaller physical space, esp. User Equipment (UE) IP + WPAN + WLAN + WMAN + WWAN + any other stragglers = 4 G IP in the sky with diamonds SRB 041406 ver 1 58
Summary § Mobile Intelligent Internet and multi media applications § Seamless Roaming, substantially high and selectable user bandwidth, customized Qo. S, Intelligent and responsive user interface § Mobile IP, Radio Routers, smart Antennas § Continued advances and challenges from 1 G -> 4 G – Modulation techniques, transreceiver advances, fast manipulations, user interfaces, IP tunelling and firewalls – Spectrum usage, regulatory decisions, “one” standard, authentication and security, multi disciplinary co-operation § Packing so much intelligence in smaller and smaller physical space, esp. User Equipment (UE) IP + WPAN + WLAN + WMAN + WWAN + any other stragglers = 4 G IP in the sky with diamonds SRB 041406 ver 1 58
 SRB 041406 ver 1 Back-up 59
SRB 041406 ver 1 Back-up 59
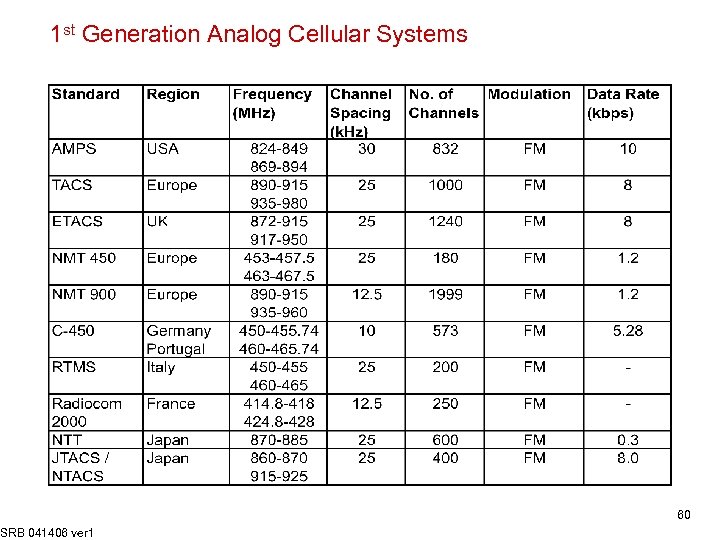 1 st Generation Analog Cellular Systems SRB 041406 ver 1 60
1 st Generation Analog Cellular Systems SRB 041406 ver 1 60
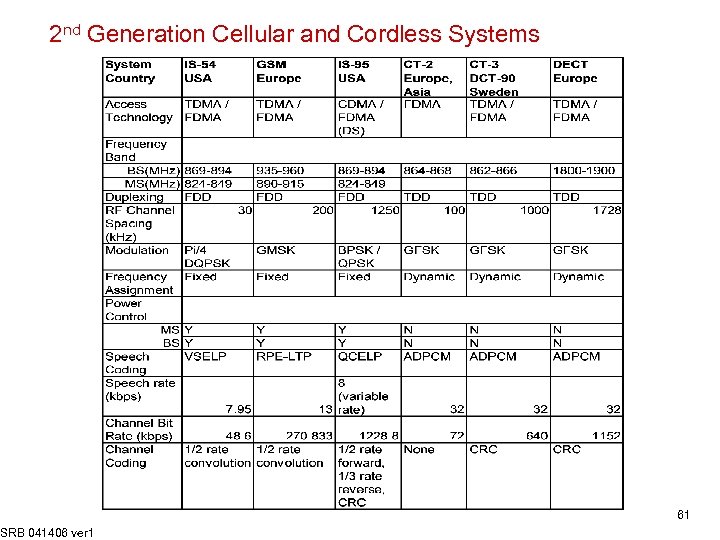 2 nd Generation Cellular and Cordless Systems SRB 041406 ver 1 61
2 nd Generation Cellular and Cordless Systems SRB 041406 ver 1 61
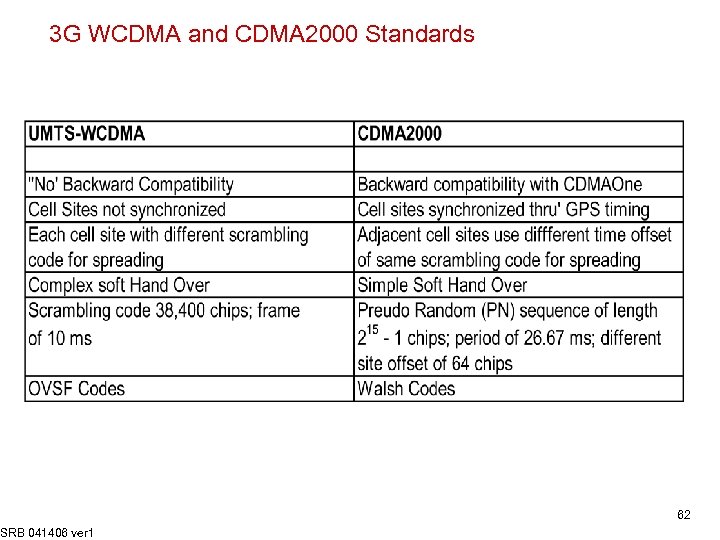 3 G WCDMA and CDMA 2000 Standards SRB 041406 ver 1 62
3 G WCDMA and CDMA 2000 Standards SRB 041406 ver 1 62
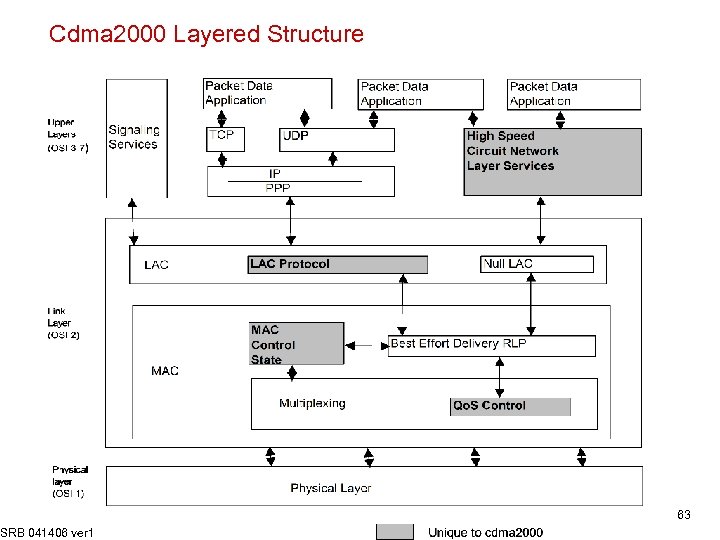 Cdma 2000 Layered Structure SRB 041406 ver 1 63
Cdma 2000 Layered Structure SRB 041406 ver 1 63
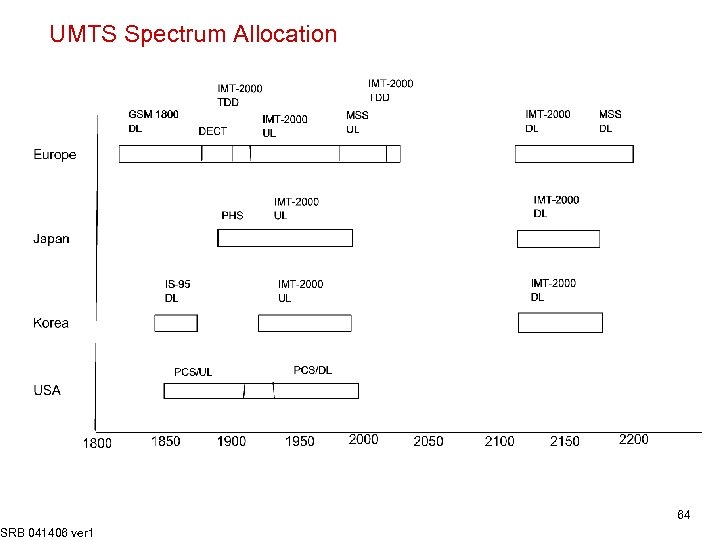 UMTS Spectrum Allocation SRB 041406 ver 1 64
UMTS Spectrum Allocation SRB 041406 ver 1 64
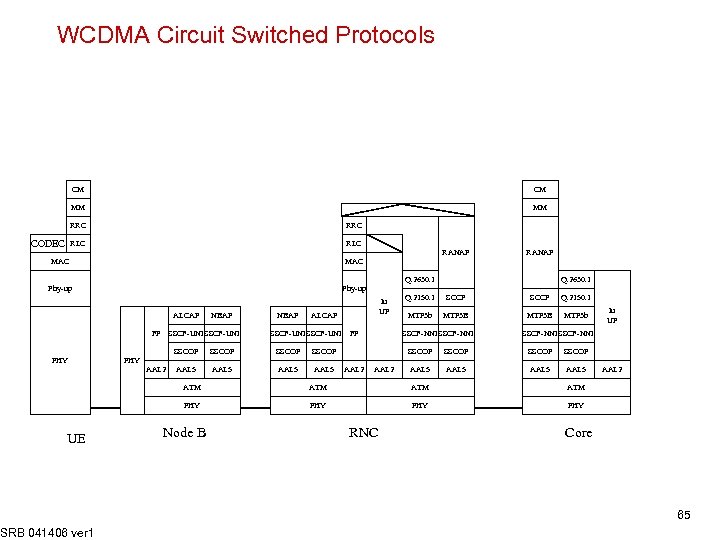 WCDMA Circuit Switched Protocols CM CM MM MM RRC RLC CODEC RRC RLC RANAP MAC Phy-up Q. 2630. 1 ALCAP NBAP FP SSCF-UNI NBAP ALCAP SSCF-UNI FP SSCOP PHY Iu UP SSCOP AAL 5 Q. 2150. 1 SCCP Q. 2150. 1 MTP 3 b MTP 3 B MTP 3 b SSCF-NNI SSCOP AAL 5 Q. 2630. 1 SSCF-NNI SSCOP AAL 5 PHY AAL 2 ATM SRB 041406 ver 1 ATM PHY AAL 2 ATM PHY UE Iu UP PHY Node B RNC Core 65
WCDMA Circuit Switched Protocols CM CM MM MM RRC RLC CODEC RRC RLC RANAP MAC Phy-up Q. 2630. 1 ALCAP NBAP FP SSCF-UNI NBAP ALCAP SSCF-UNI FP SSCOP PHY Iu UP SSCOP AAL 5 Q. 2150. 1 SCCP Q. 2150. 1 MTP 3 b MTP 3 B MTP 3 b SSCF-NNI SSCOP AAL 5 Q. 2630. 1 SSCF-NNI SSCOP AAL 5 PHY AAL 2 ATM SRB 041406 ver 1 ATM PHY AAL 2 ATM PHY UE Iu UP PHY Node B RNC Core 65
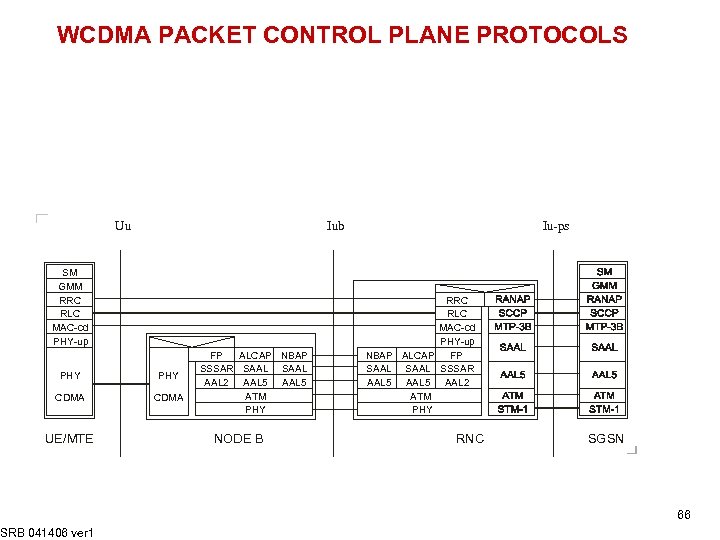 WCDMA PACKET CONTROL PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub SM GMM RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up PHY CDMA UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver 1 FP ALCAP NBAP SSSAR SAAL AAL 2 AAL 5 ATM PHY NODE B Iu-ps RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up NBAP ALCAP FP SAAL SSSAR AAL 5 AAL 2 ATM PHY RNC SGSN 66
WCDMA PACKET CONTROL PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub SM GMM RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up PHY CDMA UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver 1 FP ALCAP NBAP SSSAR SAAL AAL 2 AAL 5 ATM PHY NODE B Iu-ps RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up NBAP ALCAP FP SAAL SSSAR AAL 5 AAL 2 ATM PHY RNC SGSN 66
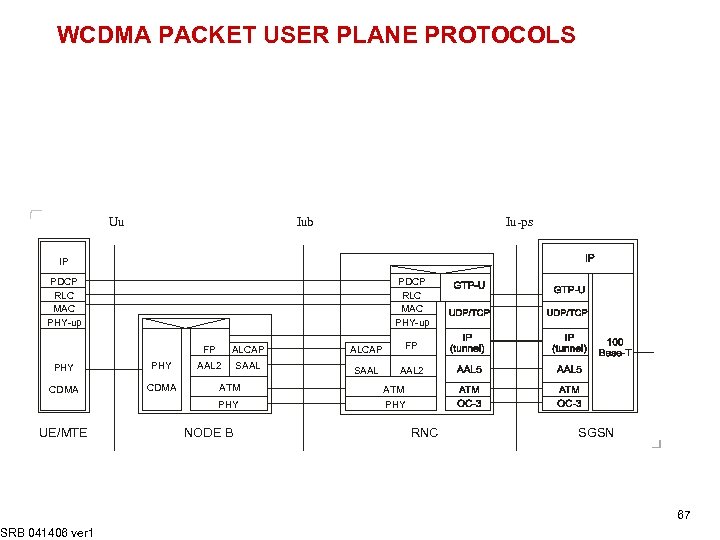 WCDMA PACKET USER PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub Iu-ps IP PDCP RLC MAC PHY-up FP PHY CDMA ALCAP FP AAL 2 SAAL AAL 2 ATM PHY UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver 1 NODE B ATM PHY RNC SGSN 67
WCDMA PACKET USER PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub Iu-ps IP PDCP RLC MAC PHY-up FP PHY CDMA ALCAP FP AAL 2 SAAL AAL 2 ATM PHY UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver 1 NODE B ATM PHY RNC SGSN 67
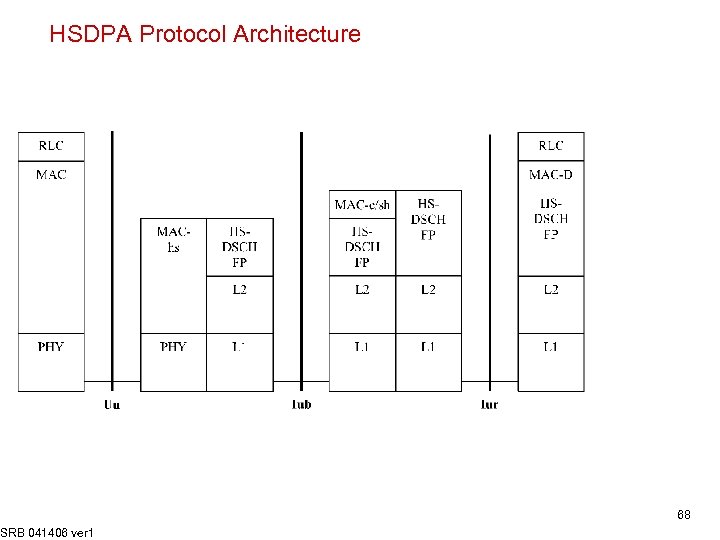 HSDPA Protocol Architecture SRB 041406 ver 1 68
HSDPA Protocol Architecture SRB 041406 ver 1 68
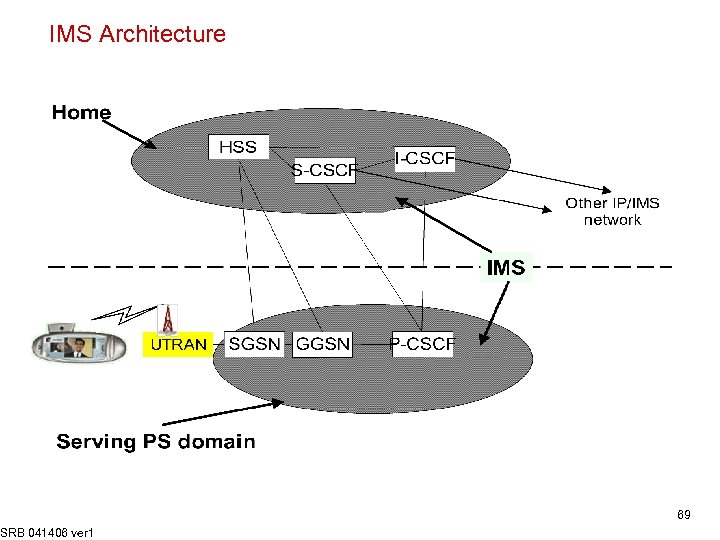 IMS Architecture SRB 041406 ver 1 69
IMS Architecture SRB 041406 ver 1 69
 Standards IEEE 802. 11 a and b: Wireless LAN (Wi. Fi) IEEE 802. 15: Wireless PAN (Bluetooth) IEEE 802. 16 d and e: Wireless MAN (Wi. MAX) IS-41: Inter-systems operation (TIA/EIA-41) IS-54: 1 st Gen (US) TDMA; 6 users per 30 KHz channel IS-88: CDMA IS-91: Analog Callular air interface IS-93: Wireless to PSTN Interface IS-95: TIA for CDMA (US) (Cdmaone) IS-124: Call detail and billing record IS-136: 2 nd Genr TDMA (TDMA control channel) IS-637: CDMA Short Message Service (SMS) IS-756: TIA for Wireless Network Portability (WNP) IS-2000: cdma 2000 air interface (follow on to TIA/EIA 95 -B) SRB 041406 ver 1 70
Standards IEEE 802. 11 a and b: Wireless LAN (Wi. Fi) IEEE 802. 15: Wireless PAN (Bluetooth) IEEE 802. 16 d and e: Wireless MAN (Wi. MAX) IS-41: Inter-systems operation (TIA/EIA-41) IS-54: 1 st Gen (US) TDMA; 6 users per 30 KHz channel IS-88: CDMA IS-91: Analog Callular air interface IS-93: Wireless to PSTN Interface IS-95: TIA for CDMA (US) (Cdmaone) IS-124: Call detail and billing record IS-136: 2 nd Genr TDMA (TDMA control channel) IS-637: CDMA Short Message Service (SMS) IS-756: TIA for Wireless Network Portability (WNP) IS-2000: cdma 2000 air interface (follow on to TIA/EIA 95 -B) SRB 041406 ver 1 70
 Glossary 3 GPP: 3 G Partnership Project AAA: Authentication, Authorization, Accounting AMR: Adaptive Multi Rate (Speech Codec) ANSI: American National Standards Institute ARIB: Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (Japan) BRAN: Broadband Radio Access Network (HYPERLAN 2) 2. 5 Mbps CAMEL: Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access CWTS: China Wireless Telecommunications Standards group (China) ECMA: European Computer Manufacturers Association EDGE: Enhanced Data for GSM Evolution ETSI: European Telecommunications Standards Institute FDD: Frequency Division Duplex FDMA: Frequency Division Multiple Access GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node GMSC: Gateway MSC GPRS: General Packet Radio Service GSM: Global System for Mobile communication GTP: GPRS Tunneling Protocol HIPERLAN: High Performance Radio Local Area Network HLR: Home Location Register HSCSD: High Speed Circuit Switched Data HYPERLAN: High Performance Radio Access network IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity SRB 041406 ver 1 IMT: International Mobile Telecommunications ITU: International Telecommunications Union OVSF: Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor PDN: Public Data Network PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network Qo. S: Quality of Service RAB: Radio Access Bearer RNC: Radio Network Controller RRC: Radio Resource Control SGSN: Servicing GPRS Support Node SIM: Subscriber Identity Module TDD: Time Division Duplex TDMA: Time Division Multiple Access TTA: Telecommunications Technology Association (Korea) TTC: Telecommunications Technology Commission (Japan) UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UTRAN: UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network Vo. IP: Voice over Internet Protocol WCDMA: Wideband Code Division Multiple Access WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network WPAN: Wireless Personal Area Network WWAN: Wireless Wide Area Network 71
Glossary 3 GPP: 3 G Partnership Project AAA: Authentication, Authorization, Accounting AMR: Adaptive Multi Rate (Speech Codec) ANSI: American National Standards Institute ARIB: Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (Japan) BRAN: Broadband Radio Access Network (HYPERLAN 2) 2. 5 Mbps CAMEL: Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access CWTS: China Wireless Telecommunications Standards group (China) ECMA: European Computer Manufacturers Association EDGE: Enhanced Data for GSM Evolution ETSI: European Telecommunications Standards Institute FDD: Frequency Division Duplex FDMA: Frequency Division Multiple Access GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node GMSC: Gateway MSC GPRS: General Packet Radio Service GSM: Global System for Mobile communication GTP: GPRS Tunneling Protocol HIPERLAN: High Performance Radio Local Area Network HLR: Home Location Register HSCSD: High Speed Circuit Switched Data HYPERLAN: High Performance Radio Access network IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity SRB 041406 ver 1 IMT: International Mobile Telecommunications ITU: International Telecommunications Union OVSF: Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor PDN: Public Data Network PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network Qo. S: Quality of Service RAB: Radio Access Bearer RNC: Radio Network Controller RRC: Radio Resource Control SGSN: Servicing GPRS Support Node SIM: Subscriber Identity Module TDD: Time Division Duplex TDMA: Time Division Multiple Access TTA: Telecommunications Technology Association (Korea) TTC: Telecommunications Technology Commission (Japan) UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UTRAN: UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network Vo. IP: Voice over Internet Protocol WCDMA: Wideband Code Division Multiple Access WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network WPAN: Wireless Personal Area Network WWAN: Wireless Wide Area Network 71
 References 1. www. 3 gpp. org 2. WCDMA for UMTS, Ed. : H. Holma and A. Toskala, John Wiley, 2001 3. UMTS - Mobile Communications for the Future, Ed. F. Muratore, John Wiley, 2001 4. WCDMA: Towards IP Mobility and Mobile Internet, Eds E. Djanpera and R. Prasad, Artech House, 2001 5. IS-95 CDMA and CDMA 2000, V. K. Garg, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2002 6. IP Telephony, O. Hersent, D. Gurle Et, and J-P Petit, Addison-Wesley, 2000 7. www. mobileinfo. com SRB 041406 ver 1 72
References 1. www. 3 gpp. org 2. WCDMA for UMTS, Ed. : H. Holma and A. Toskala, John Wiley, 2001 3. UMTS - Mobile Communications for the Future, Ed. F. Muratore, John Wiley, 2001 4. WCDMA: Towards IP Mobility and Mobile Internet, Eds E. Djanpera and R. Prasad, Artech House, 2001 5. IS-95 CDMA and CDMA 2000, V. K. Garg, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2002 6. IP Telephony, O. Hersent, D. Gurle Et, and J-P Petit, Addison-Wesley, 2000 7. www. mobileinfo. com SRB 041406 ver 1 72


