4072f024d681013c7932044289f5c05e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 3. Data Communications 3. 2 Networking
3. Data Communications 3. 2 Networking
 Network Applications Fax, Voice, and Information Services Person to Person Communications Group Communications Exchanging Files
Network Applications Fax, Voice, and Information Services Person to Person Communications Group Communications Exchanging Files
 Fax, Voice and Information Services Fax-back services Voice mail On-line services
Fax, Voice and Information Services Fax-back services Voice mail On-line services
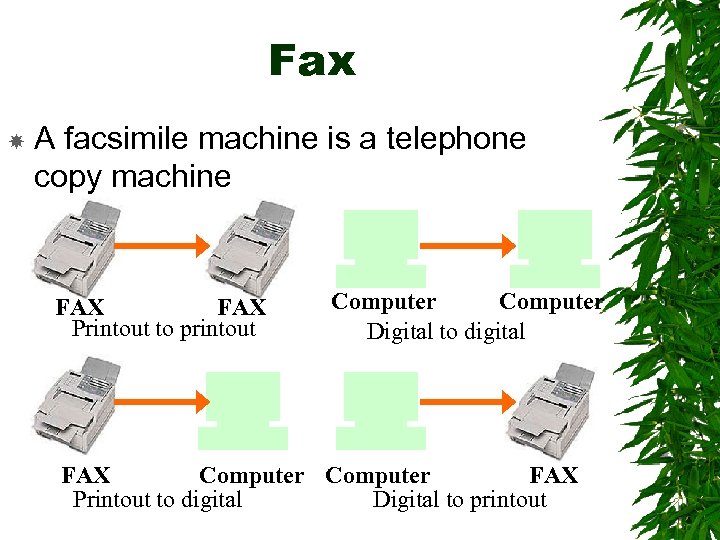 Fax A facsimile machine is a telephone copy machine FAX Printout to printout Computer Digital to digital FAX Computer FAX Printout to digital Digital to printout
Fax A facsimile machine is a telephone copy machine FAX Printout to printout Computer Digital to digital FAX Computer FAX Printout to digital Digital to printout
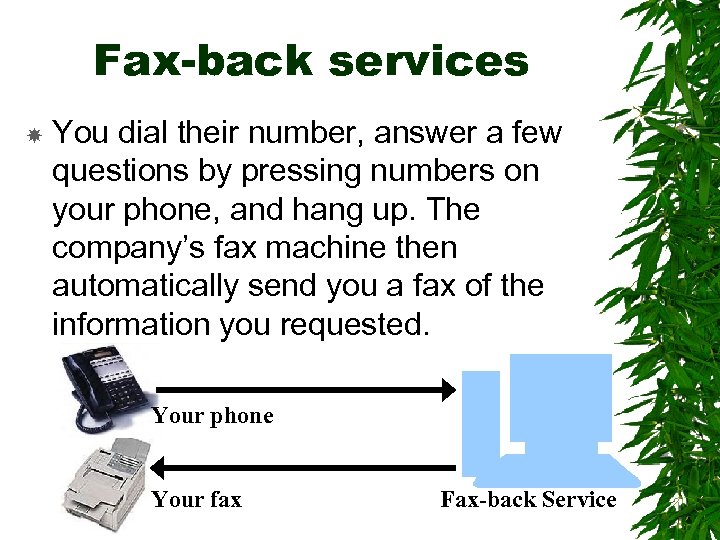 Fax-back services You dial their number, answer a few questions by pressing numbers on your phone, and hang up. The company’s fax machine then automatically send you a fax of the information you requested. Your phone Your fax Fax-back Service
Fax-back services You dial their number, answer a few questions by pressing numbers on your phone, and hang up. The company’s fax machine then automatically send you a fax of the information you requested. Your phone Your fax Fax-back Service
 Voice mail Automates phone answering and messaging Sophisticated systems have an automated attendant that routes you to the right person when you press the keys of a touch-tone phone Now, it’s even possible to leave video voice mail
Voice mail Automates phone answering and messaging Sophisticated systems have an automated attendant that routes you to the right person when you press the keys of a touch-tone phone Now, it’s even possible to leave video voice mail
 On-line services Networks were introduced at home through the large commercial information services such as Compu. Serve, AOL, and Microsoft Network. You can locate important information or exchange e-mail with other subscribers You can post messages on forums Type messages back and forth in chat mode
On-line services Networks were introduced at home through the large commercial information services such as Compu. Serve, AOL, and Microsoft Network. You can locate important information or exchange e-mail with other subscribers You can post messages on forums Type messages back and forth in chat mode
 Person to Person Communications Electronic mail E-mail makes it possible to have almost instantaneous communication Cost is low More convenient User name Domain name itchai@hotmail. com
Person to Person Communications Electronic mail E-mail makes it possible to have almost instantaneous communication Cost is low More convenient User name Domain name itchai@hotmail. com
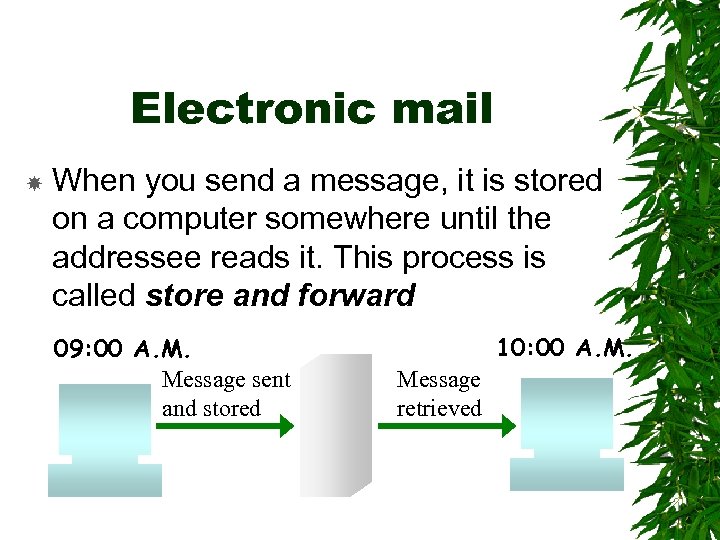 Electronic mail When you send a message, it is stored on a computer somewhere until the addressee reads it. This process is called store and forward 09: 00 A. M. Message sent and stored 10: 00 A. M. Message retrieved
Electronic mail When you send a message, it is stored on a computer somewhere until the addressee reads it. This process is called store and forward 09: 00 A. M. Message sent and stored 10: 00 A. M. Message retrieved
 Electronic mail E-mail software is used to write, read, and file messages E-mail software courtesy of Microsoft
Electronic mail E-mail software is used to write, read, and file messages E-mail software courtesy of Microsoft
 E-mail etiquette Don’t ever write and send nasty notes impulsively Don’t ever refer to third parties in an unflattering way Be careful of inflections, nuances, and sarcasm Don’t ever use your company’s name in personal postings outside the company Try to act as civilized as possible – and do unto others as you would have them do unto you
E-mail etiquette Don’t ever write and send nasty notes impulsively Don’t ever refer to third parties in an unflattering way Be careful of inflections, nuances, and sarcasm Don’t ever use your company’s name in personal postings outside the company Try to act as civilized as possible – and do unto others as you would have them do unto you
 Emoticons : -) means “I’m smiling”
Emoticons : -) means “I’m smiling” or
 Group Communications Newsgroup Mailing lists Internet relay chat (IRC) Network games Video conferencing
Group Communications Newsgroup Mailing lists Internet relay chat (IRC) Network games Video conferencing
 Newsgroup Usenet (Users Network) is a collection of thousands of ongoing topical discussions called newsgroup Also known as bulletin boards or discussion groups, newsgroups are used by people to share common interests Usenet is not a part of the Internet, or even a network of any kind It ’s a system for carrying on discussions that can be delivered in a number of ways, the Internet being just one of them
Newsgroup Usenet (Users Network) is a collection of thousands of ongoing topical discussions called newsgroup Also known as bulletin boards or discussion groups, newsgroups are used by people to share common interests Usenet is not a part of the Internet, or even a network of any kind It ’s a system for carrying on discussions that can be delivered in a number of ways, the Internet being just one of them
 Mailing lists use e-mail to keep groups informed on topics or events they wish to know about such as when a particular Web site has been updated As you get more involved with the Internet, you may find yourself the recipient of a mass-mailing called a spam
Mailing lists use e-mail to keep groups informed on topics or events they wish to know about such as when a particular Web site has been updated As you get more involved with the Internet, you may find yourself the recipient of a mass-mailing called a spam
 Internet relay chat (IRC) IRC allows you to chat with other users in real-time Any user with IRC software can go to an IRC computer called an IRC server, create a channel on some topic, and invite others to join in
Internet relay chat (IRC) IRC allows you to chat with other users in real-time Any user with IRC software can go to an IRC computer called an IRC server, create a channel on some topic, and invite others to join in
 Network games The first popular games were textbased The most popular are MUDs (multiuser dialogue) and their variants such as MOOs – object-oriented MOOs Graphical games are becoming more popular
Network games The first popular games were textbased The most popular are MUDs (multiuser dialogue) and their variants such as MOOs – object-oriented MOOs Graphical games are becoming more popular
 Network games hongkong. gameeast. com hk. games. yahoo. com www. microsoft. com/games/empires Igz 2. microsoft. com
Network games hongkong. gameeast. com hk. games. yahoo. com www. microsoft. com/games/empires Igz 2. microsoft. com
 Video conferencing Reduce travel to a minimum – Save time – Lower the cost
Video conferencing Reduce travel to a minimum – Save time – Lower the cost
 Exchanging Files Uploading and downloading ASCII and binary files Shared disks FTP on the Internet Binary files as e-mail attachments
Exchanging Files Uploading and downloading ASCII and binary files Shared disks FTP on the Internet Binary files as e-mail attachments
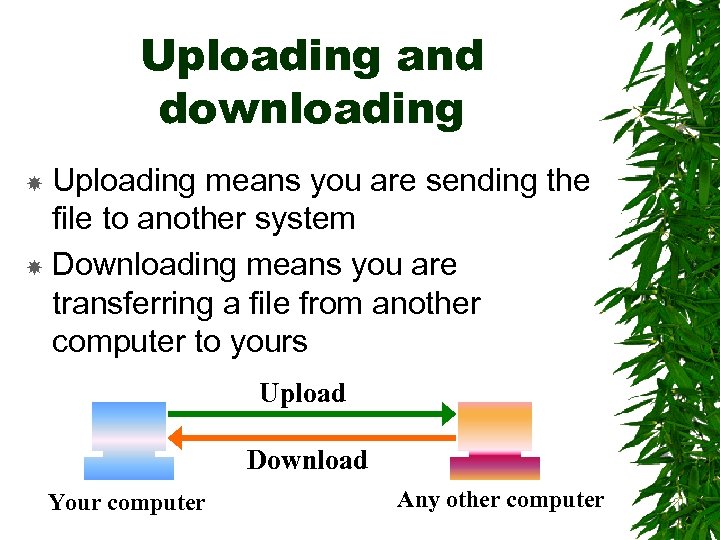 Uploading and downloading Uploading means you are sending the file to another system Downloading means you are transferring a file from another computer to yours Upload Download Your computer Any other computer
Uploading and downloading Uploading means you are sending the file to another system Downloading means you are transferring a file from another computer to yours Upload Download Your computer Any other computer
 ASCII files contain only a limited set of characters and have almost no formatting They are easy to transfer because of their simplicity
ASCII files contain only a limited set of characters and have almost no formatting They are easy to transfer because of their simplicity
 Binary files have lots of formatting and much of it is specific to the program that created the file A picture, a video, a word processing document, a spreadsheet, a database, an animation, or an executable program don’t transfer easily between the networks that use different protocols before being converted with a messy process
Binary files have lots of formatting and much of it is specific to the program that created the file A picture, a video, a word processing document, a spreadsheet, a database, an animation, or an executable program don’t transfer easily between the networks that use different protocols before being converted with a messy process
 Shared disks It’s as easy as moving or copying a file to a public folder. Friends or coworkers can then move it from there to one of their own folders Shared disk
Shared disks It’s as easy as moving or copying a file to a public folder. Friends or coworkers can then move it from there to one of their own folders Shared disk
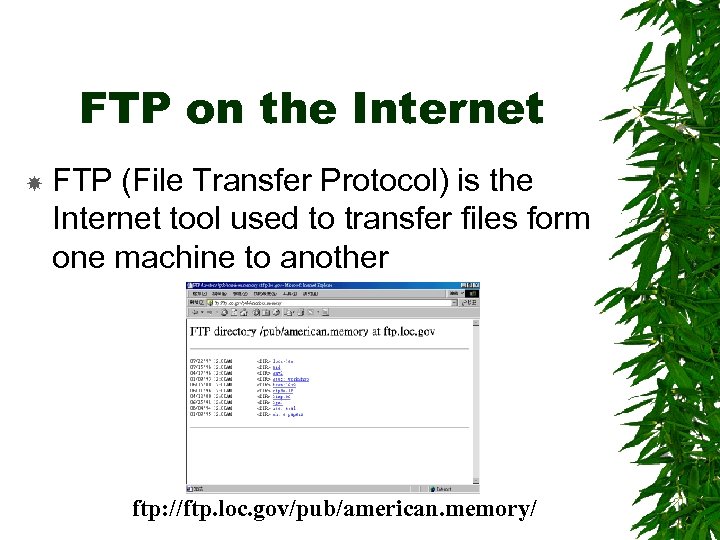 FTP on the Internet FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is the Internet tool used to transfer files form one machine to another ftp: //ftp. loc. gov/pub/american. memory/
FTP on the Internet FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is the Internet tool used to transfer files form one machine to another ftp: //ftp. loc. gov/pub/american. memory/
 FTP on the Internet Normally you would need a password to log onto the system However, using anonymous ftp, you can browse through computers that allow you to do so by using the name anonymous to log on
FTP on the Internet Normally you would need a password to log onto the system However, using anonymous ftp, you can browse through computers that allow you to do so by using the name anonymous to log on
 Binary files as e-mail attachments One of the most convenient ways to transfer files is as attachments to email messages If you are sending it across the Internet to a different network, the message will pass through other computes called gateway that may not be compatible
Binary files as e-mail attachments One of the most convenient ways to transfer files is as attachments to email messages If you are sending it across the Internet to a different network, the message will pass through other computes called gateway that may not be compatible
 Binary files as e-mail attachments Binary attachments may be corrupted Needed to use a program to convert them to an ASCII text file. This is called encoding The recipient muse a similar program to convert it from ASCII back to binary, decoding
Binary files as e-mail attachments Binary attachments may be corrupted Needed to use a program to convert them to an ASCII text file. This is called encoding The recipient muse a similar program to convert it from ASCII back to binary, decoding
 2 dominant encoding schemes in use UUcoding (binary to ASCII) and Uudecoding (ASCII to binary) – They were originally developed for UNIX-to. UNIX e-mailing MIME (multipurpose Internet Mail Extension) – Uses a form of encoding called “Base 64” which has been better designed to allow messages to pass through a network’s various e-mail gateways
2 dominant encoding schemes in use UUcoding (binary to ASCII) and Uudecoding (ASCII to binary) – They were originally developed for UNIX-to. UNIX e-mailing MIME (multipurpose Internet Mail Extension) – Uses a form of encoding called “Base 64” which has been better designed to allow messages to pass through a network’s various e-mail gateways
 Local Area Networks (LAN) Networks of computers within a small area are called LANs Network resources – – – The whole is greater than the sum of its parts E-mail Sharing peripherals Sharing files Groupware Network applications
Local Area Networks (LAN) Networks of computers within a small area are called LANs Network resources – – – The whole is greater than the sum of its parts E-mail Sharing peripherals Sharing files Groupware Network applications
 Network resources E-mail – The sending of messages to others on the network Sharing peripherals – Share expensive peripherals such as plotters, laser printers, and hard disk drives Sharing files – Share or exchange files with other users on the network
Network resources E-mail – The sending of messages to others on the network Sharing peripherals – Share expensive peripherals such as plotters, laser printers, and hard disk drives Sharing files – Share or exchange files with other users on the network
 Network resources Groupware – Groupware have been developed to make team or group activity easier – A typical groupware application is a common calendar on which anyone can make entries that others can see – Another is a document anyone can add to or change while others can see who is making the changes
Network resources Groupware – Groupware have been developed to make team or group activity easier – A typical groupware application is a common calendar on which anyone can make entries that others can see – Another is a document anyone can add to or change while others can see who is making the changes
 Network resources Network applications – The application rests on a computer somewhere on the network, not on your own machine – You transfer it to your system when you want to see it – A company has to fix or upgrade only one copy on the network – Often written in languages such as Java or Active. X for Internet
Network resources Network applications – The application rests on a computer somewhere on the network, not on your own machine – You transfer it to your system when you want to see it – A company has to fix or upgrade only one copy on the network – Often written in languages such as Java or Active. X for Internet
 Network users To use a network, you first log on with an ID and a password The ID is assigned by the network administrator The password is selected by you and can (and should) be changed frequently to improve security Normally you’ll find printers, hard disks, and other shared assets listed on your system’s dialog boxes even though they are located elsewhere on the network
Network users To use a network, you first log on with an ID and a password The ID is assigned by the network administrator The password is selected by you and can (and should) be changed frequently to improve security Normally you’ll find printers, hard disks, and other shared assets listed on your system’s dialog boxes even though they are located elsewhere on the network
 Network administrators Systems organized into a network are supervised by a network administrator/manager The network manager/administrator is responsible for: – – Setting up or enforcing network procedures Adding and removing users Assigning Ids and levels of access Troubleshooting problems should users arise and assisting both new and experienced users with problems
Network administrators Systems organized into a network are supervised by a network administrator/manager The network manager/administrator is responsible for: – – Setting up or enforcing network procedures Adding and removing users Assigning Ids and levels of access Troubleshooting problems should users arise and assisting both new and experienced users with problems
 Network administrators One user may be authorized access to correspondence files but denied access to financial analysis files Some users can be given just read-only access, whereas others can be allowed to enter and update the files
Network administrators One user may be authorized access to correspondence files but denied access to financial analysis files Some users can be given just read-only access, whereas others can be allowed to enter and update the files
 Passwords Don’t share your password with anyone Hard to guess. E. g. mix letters with numbers Don’t use a password that is your address, pet’s name, nickname, spouse’s name, telephone no. , or one that is obvious such as sequential numbers or letters Longer password, more secure. Six to eight characters is realistic Password is not visible on the computer screen when you enter it Password does not appear on printouts Don’t tape passwords to desks, walls, or terminals. Commit yours to memory
Passwords Don’t share your password with anyone Hard to guess. E. g. mix letters with numbers Don’t use a password that is your address, pet’s name, nickname, spouse’s name, telephone no. , or one that is obvious such as sequential numbers or letters Longer password, more secure. Six to eight characters is realistic Password is not visible on the computer screen when you enter it Password does not appear on printouts Don’t tape passwords to desks, walls, or terminals. Commit yours to memory
 Network’s Topologies Computers and other devices can be connected to form a LAN in several ways These connections are the network’s architecture or topology A network’s architecture is the way the data flows within the network, not to the way its parts are physically arranged in an office
Network’s Topologies Computers and other devices can be connected to form a LAN in several ways These connections are the network’s architecture or topology A network’s architecture is the way the data flows within the network, not to the way its parts are physically arranged in an office
 Basic network architecture/topology Node – A node is any piece of hardware on the system that can be addressed by a message from another node, that is, a computer, printer, fax, modem, or CD-ROM drive Hub – Nodes are connected to a hub / concentrator, whose purpose is to simplify the wiring of the nodes to each other and to route signals between the nodes
Basic network architecture/topology Node – A node is any piece of hardware on the system that can be addressed by a message from another node, that is, a computer, printer, fax, modem, or CD-ROM drive Hub – Nodes are connected to a hub / concentrator, whose purpose is to simplify the wiring of the nodes to each other and to route signals between the nodes
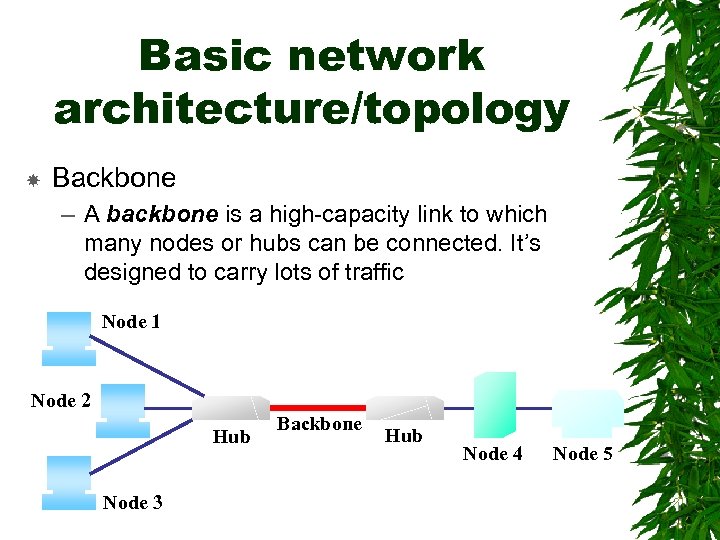 Basic network architecture/topology Backbone – A backbone is a high-capacity link to which many nodes or hubs can be connected. It’s designed to carry lots of traffic Node 1 Node 2 Hub Node 3 Backbone Hub Node 4 Node 5
Basic network architecture/topology Backbone – A backbone is a high-capacity link to which many nodes or hubs can be connected. It’s designed to carry lots of traffic Node 1 Node 2 Hub Node 3 Backbone Hub Node 4 Node 5
 Servers A server on a LAN is any computer that can be shared by other computers working on the LAN In many cases, the server has to be the most powerful computer on the network It is shared among so many users, or clients
Servers A server on a LAN is any computer that can be shared by other computers working on the LAN In many cases, the server has to be the most powerful computer on the network It is shared among so many users, or clients
 Clients Computers depend on the server for programs and data, or connections to other computers and devices
Clients Computers depend on the server for programs and data, or connections to other computers and devices
 File server Stores data files and some applications programs Large amounts of secondary storage in the form of hard disks, CD-ROM drives, tape drives, and other storage devices
File server Stores data files and some applications programs Large amounts of secondary storage in the form of hard disks, CD-ROM drives, tape drives, and other storage devices
 Print server Stores print jobs on a hard disk until they printer is ready to handle them
Print server Stores print jobs on a hard disk until they printer is ready to handle them
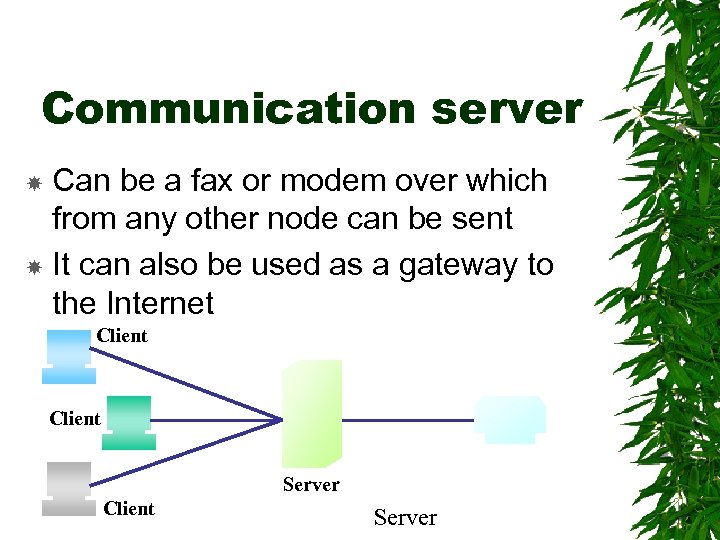 Communication server Can be a fax or modem over which from any other node can be sent It can also be used as a gateway to the Internet Client Server
Communication server Can be a fax or modem over which from any other node can be sent It can also be used as a gateway to the Internet Client Server
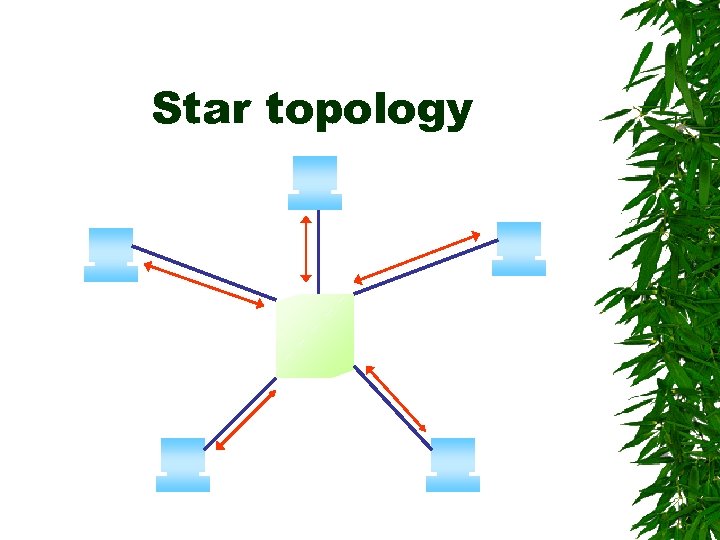
 Star topology Star topology has the nodes connected to a central, or host, computer or a central hub When one of the computers on the network sends signal, the host routes it to the node it’s addressed to There are no direct connections between the nodes on the network except through the host computer
Star topology Star topology has the nodes connected to a central, or host, computer or a central hub When one of the computers on the network sends signal, the host routes it to the node it’s addressed to There are no direct connections between the nodes on the network except through the host computer
 Star topology
Star topology
 Star topology Advantages: – Star topology are relatively easy to install and manage – it's easy to add and remove nodes – one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network Disadvantages: – they require more cabling than other topologies – bottlenecks can occur because all data must pass through the central hub – if the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable
Star topology Advantages: – Star topology are relatively easy to install and manage – it's easy to add and remove nodes – one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network Disadvantages: – they require more cabling than other topologies – bottlenecks can occur because all data must pass through the central hub – if the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable
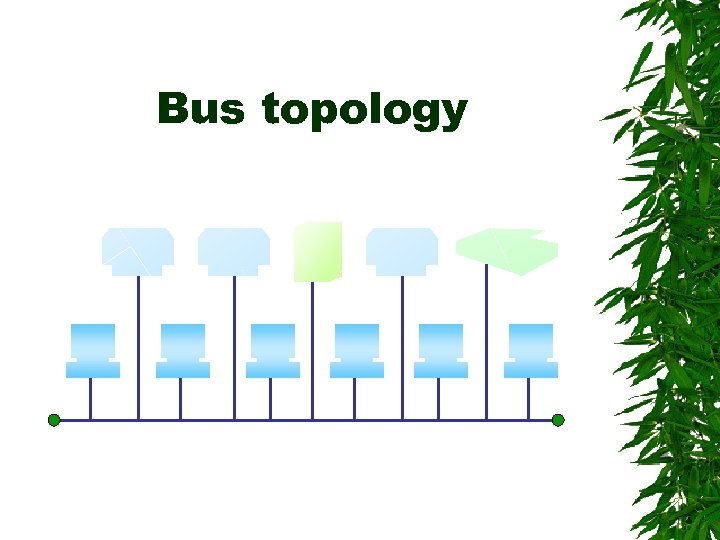
 Bus topology Bus, or linear, topology connects all nodes to a single bus / backbone, much as the components are organized within the computer A signal addressed to another node is sent to the bus All other nodes on the network examine the signal to see if it is addressed to one of them
Bus topology Bus, or linear, topology connects all nodes to a single bus / backbone, much as the components are organized within the computer A signal addressed to another node is sent to the bus All other nodes on the network examine the signal to see if it is addressed to one of them
 Bus topology Typically, wires connect each node to the network’s backbone, which is a fixed length of cable with terminators at both ends to stop reflections when signals hit the end
Bus topology Typically, wires connect each node to the network’s backbone, which is a fixed length of cable with terminators at both ends to stop reflections when signals hit the end
 Bus topology
Bus topology
 Bus topology Advantages: – are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks – one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network Disadvantages: – are relatively slow – Terminators are required to connect at the both ends
Bus topology Advantages: – are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks – one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network Disadvantages: – are relatively slow – Terminators are required to connect at the both ends
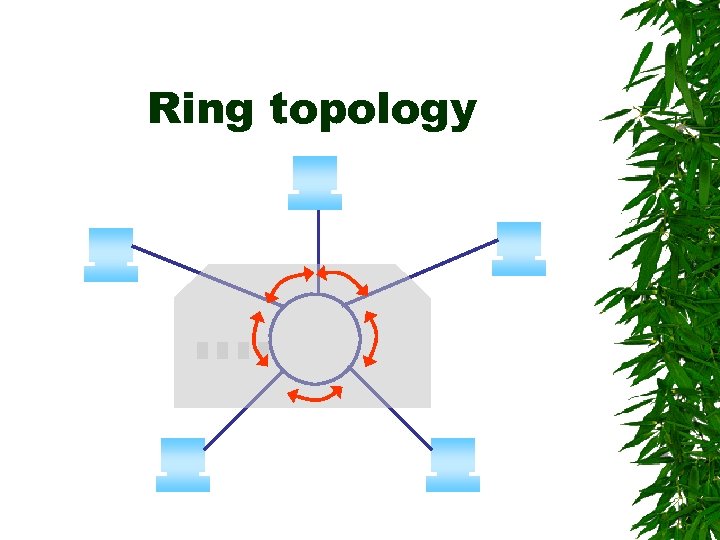
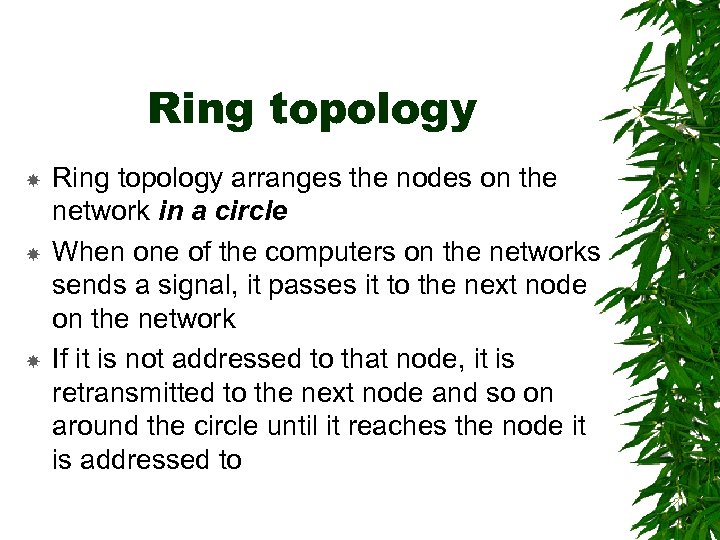 Ring topology Ring topology arranges the nodes on the network in a circle When one of the computers on the networks sends a signal, it passes it to the next node on the network If it is not addressed to that node, it is retransmitted to the next node and so on around the circle until it reaches the node it is addressed to
Ring topology Ring topology arranges the nodes on the network in a circle When one of the computers on the networks sends a signal, it passes it to the next node on the network If it is not addressed to that node, it is retransmitted to the next node and so on around the circle until it reaches the node it is addressed to
 Ring topology The connections between computers are not direct; instead, each computer attaches to a hub and the ring itself resides inside the hub
Ring topology The connections between computers are not direct; instead, each computer attaches to a hub and the ring itself resides inside the hub
 Ring topology
Ring topology
 Ring topology Advantage: – they can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it – offer high bandwidth and can span large distances Disadvantage: – are relatively expensive and difficult to install
Ring topology Advantage: – they can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it – offer high bandwidth and can span large distances Disadvantage: – are relatively expensive and difficult to install
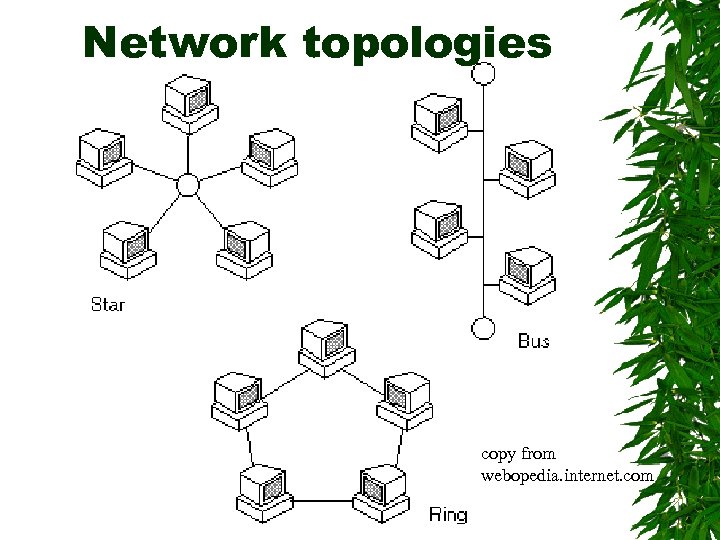 Network topologies copy from webopedia. internet. com
Network topologies copy from webopedia. internet. com
 Peer-to-peer networks Relatively easier and less expensive to set up and administer the networks Set up and run by users All computers are equals Data do not pass through a server You could be working on a spreadsheet on your computer while it was also routing print jobs from all of the other computers to your laser printer
Peer-to-peer networks Relatively easier and less expensive to set up and administer the networks Set up and run by users All computers are equals Data do not pass through a server You could be working on a spreadsheet on your computer while it was also routing print jobs from all of the other computers to your laser printer
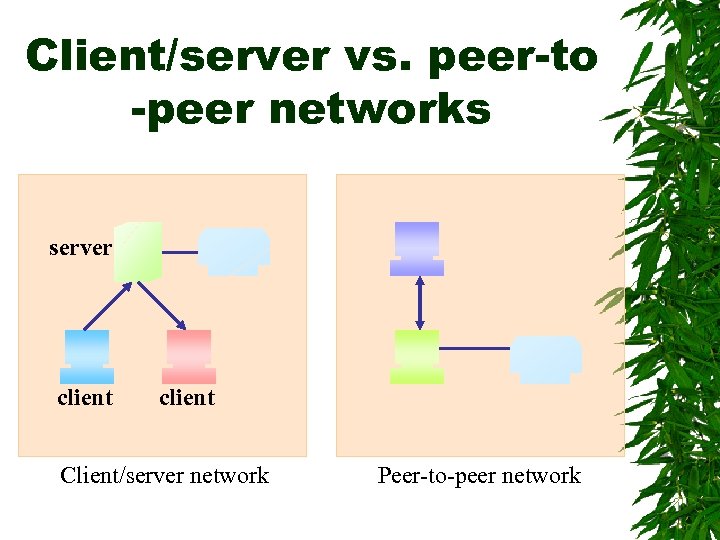 Client/server vs. peer-to -peer networks server client Client/server network Peer-to-peer network
Client/server vs. peer-to -peer networks server client Client/server network Peer-to-peer network
 Wireless LANs Connected by signals through the air instead of by wires The base station connected to the network broadcasts to individual computers They eliminate the need to run cabling through an old building The benefits of using wireless LANs: www. nokia. com/corporate/wlan/benefits. html (for business reference only) Other references: www. nokia. com/corporate/wlan/index. html
Wireless LANs Connected by signals through the air instead of by wires The base station connected to the network broadcasts to individual computers They eliminate the need to run cabling through an old building The benefits of using wireless LANs: www. nokia. com/corporate/wlan/benefits. html (for business reference only) Other references: www. nokia. com/corporate/wlan/index. html
 The System Network interface card (NIC) Physical links between devices – Twisted-pair wires (STP and UTP) – Coaxial cables – Fiber-optic cables Media access control (MAC) Ethernet Token ring
The System Network interface card (NIC) Physical links between devices – Twisted-pair wires (STP and UTP) – Coaxial cables – Fiber-optic cables Media access control (MAC) Ethernet Token ring
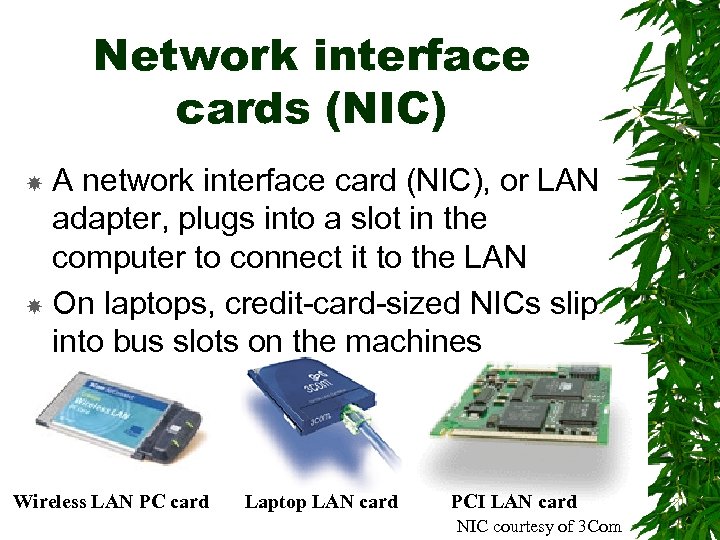 Network interface cards (NIC) A network interface card (NIC), or LAN adapter, plugs into a slot in the computer to connect it to the LAN On laptops, credit-card-sized NICs slip into bus slots on the machines Wireless LAN PC card Laptop LAN card PCI LAN card NIC courtesy of 3 Com
Network interface cards (NIC) A network interface card (NIC), or LAN adapter, plugs into a slot in the computer to connect it to the LAN On laptops, credit-card-sized NICs slip into bus slots on the machines Wireless LAN PC card Laptop LAN card PCI LAN card NIC courtesy of 3 Com
 Network interface cards An NIC serves a number of purposes: It makes the physical connection or bridge between the computer and the network It converts the parallel data on the computer’s bus into serial data for the network It boots or amplifies the signal’s strength so it can flow through the cables
Network interface cards An NIC serves a number of purposes: It makes the physical connection or bridge between the computer and the network It converts the parallel data on the computer’s bus into serial data for the network It boots or amplifies the signal’s strength so it can flow through the cables
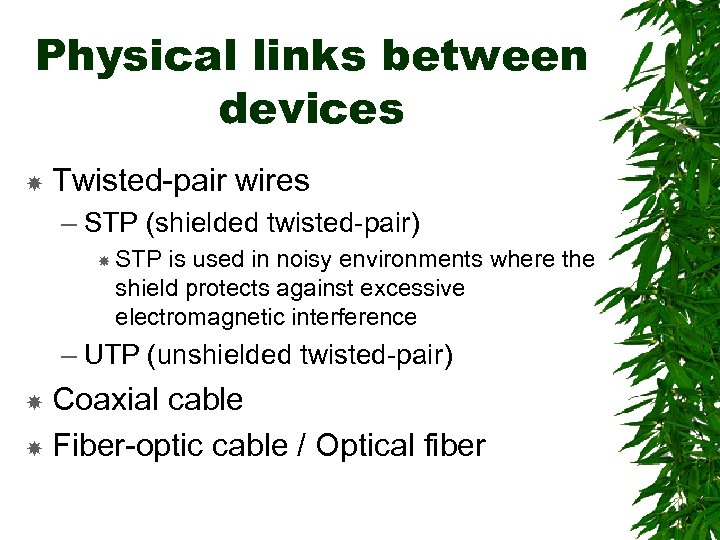 Physical links between devices Twisted-pair wires – STP (shielded twisted-pair) STP is used in noisy environments where the shield protects against excessive electromagnetic interference – UTP (unshielded twisted-pair) Coaxial cable Fiber-optic cable / Optical fiber
Physical links between devices Twisted-pair wires – STP (shielded twisted-pair) STP is used in noisy environments where the shield protects against excessive electromagnetic interference – UTP (unshielded twisted-pair) Coaxial cable Fiber-optic cable / Optical fiber
 Twisted-pair wires the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many business computers to the telephone company. two insulated copper wires are twisted around each other to reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires
Twisted-pair wires the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many business computers to the telephone company. two insulated copper wires are twisted around each other to reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires
 Twisted-pair wires Advantages: – Cheap – Easy to install Disadvantages: – Relatively slow – Tendency to pick up noise that can cause high error rates
Twisted-pair wires Advantages: – Cheap – Easy to install Disadvantages: – Relatively slow – Tendency to pick up noise that can cause high error rates
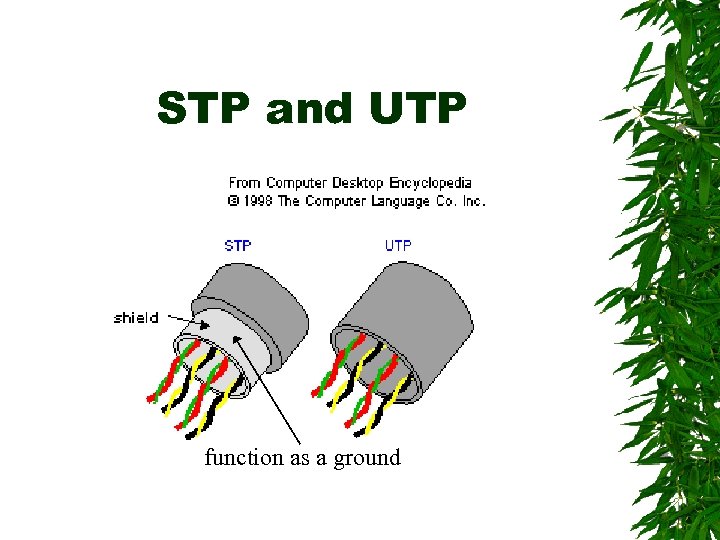 STP and UTP function as a ground
STP and UTP function as a ground
 Coaxial cables Like those in your cable TV system are layered with an inner wire surrounded by an insulating material that is, in turn, surrounded by a braided wire This braided wire shields the inner wire from any noise in the environment that can affect the quality of the transmission
Coaxial cables Like those in your cable TV system are layered with an inner wire surrounded by an insulating material that is, in turn, surrounded by a braided wire This braided wire shields the inner wire from any noise in the environment that can affect the quality of the transmission
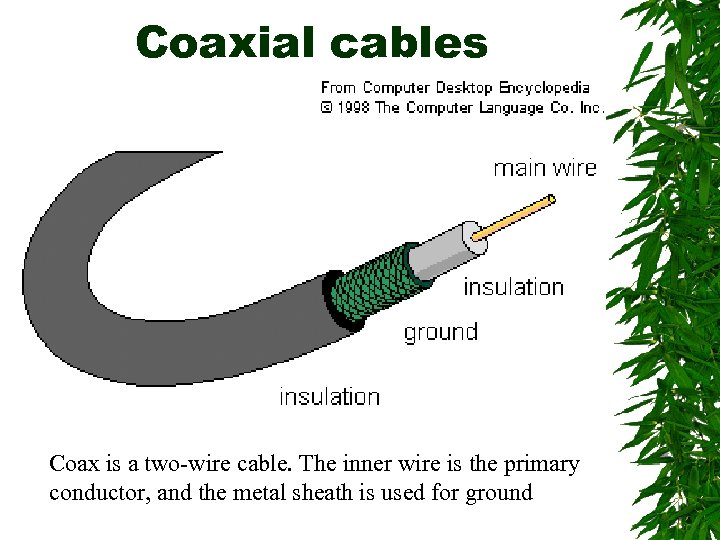 Coaxial cables Coax is a two-wire cable. The inner wire is the primary conductor, and the metal sheath is used for ground
Coaxial cables Coax is a two-wire cable. The inner wire is the primary conductor, and the metal sheath is used for ground
 Coaxial cables Reliable Have a wider bandwidth than twistedpair wires Much faster than twisted-pair wires
Coaxial cables Reliable Have a wider bandwidth than twistedpair wires Much faster than twisted-pair wires
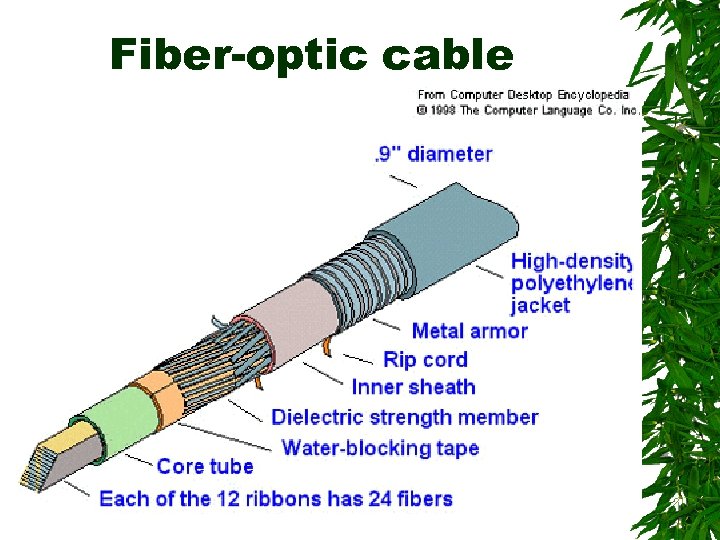
 Fiber-optic cable Are made of plastic or glass fibers the thickness of a human hair and covered with an opaque sheath that keeps light from entering or escaping The digital signals from a computer are used to code pulses of a light beam that carry information read at the receiving end A single hair-thin fiber is theoretically capable of supporting 100 trillion bits per second
Fiber-optic cable Are made of plastic or glass fibers the thickness of a human hair and covered with an opaque sheath that keeps light from entering or escaping The digital signals from a computer are used to code pulses of a light beam that carry information read at the receiving end A single hair-thin fiber is theoretically capable of supporting 100 trillion bits per second
 Fiber-optic cable Fast Reliable Light allow longer distances to be spanned without repeaters more secure, because taps in the line can be detected But more difficult to install
Fiber-optic cable Fast Reliable Light allow longer distances to be spanned without repeaters more secure, because taps in the line can be detected But more difficult to install
 Fiber-optic cable
Fiber-optic cable
 Fiber-optic cable Fiber versus copper
Fiber-optic cable Fiber versus copper
 Fiber-optic cable
Fiber-optic cable
 Media access control (MAC) A LAN needs an MAC scheme to prevent any overlapping signals The NIC determines the access method used by the network The two most popular access methods are Ethernet and token-ring
Media access control (MAC) A LAN needs an MAC scheme to prevent any overlapping signals The NIC determines the access method used by the network The two most popular access methods are Ethernet and token-ring
 Ethernet The first network access system was developed by Xerox in the 1970 s to link computers to laser printers Employs Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) All nodes listen to the traffic on the network and try to send data only when it’s quiet
Ethernet The first network access system was developed by Xerox in the 1970 s to link computers to laser printers Employs Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) All nodes listen to the traffic on the network and try to send data only when it’s quiet
 Ethernet If two nodes transmit at the same time, they detect the collision, and all nodes go quiet for a short, random period before attempting to resend the data Since the periods are random, one node will send first and gain control of the network
Ethernet If two nodes transmit at the same time, they detect the collision, and all nodes go quiet for a short, random period before attempting to resend the data Since the periods are random, one node will send first and gain control of the network
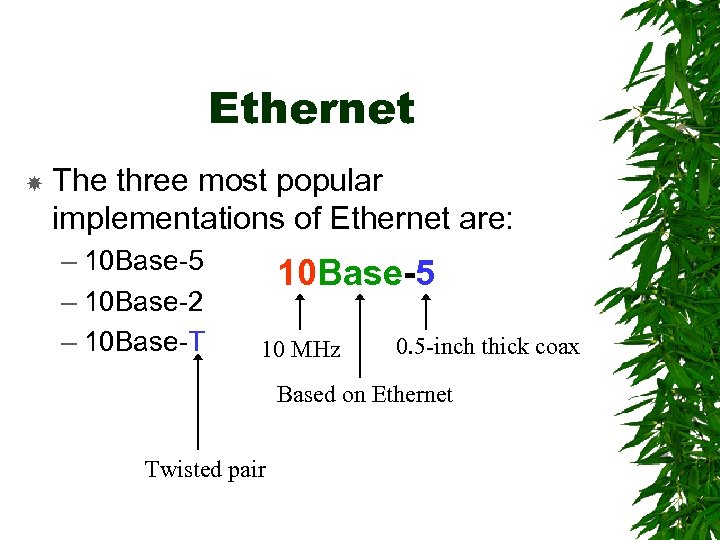 Ethernet The three most popular implementations of Ethernet are: – 10 Base-5 – 10 Base-2 – 10 Base-T 10 Base-5 10 MHz 0. 5 -inch thick coax Based on Ethernet Twisted pair
Ethernet The three most popular implementations of Ethernet are: – 10 Base-5 – 10 Base-2 – 10 Base-T 10 Base-5 10 MHz 0. 5 -inch thick coax Based on Ethernet Twisted pair
 Ethernet can use any of the network topologies, star, bus, or ring 10 Bae-5 and 10 Base-2 use a bus topology 10 Base-T uses a star topology
Ethernet can use any of the network topologies, star, bus, or ring 10 Bae-5 and 10 Base-2 use a bus topology 10 Base-T uses a star topology
 Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet delivers data at gigabit speeds making it possible to deliver multimedia applications over the network Fast Ethernet operating at 100 megahertz is being widely installed
Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet delivers data at gigabit speeds making it possible to deliver multimedia applications over the network Fast Ethernet operating at 100 megahertz is being widely installed
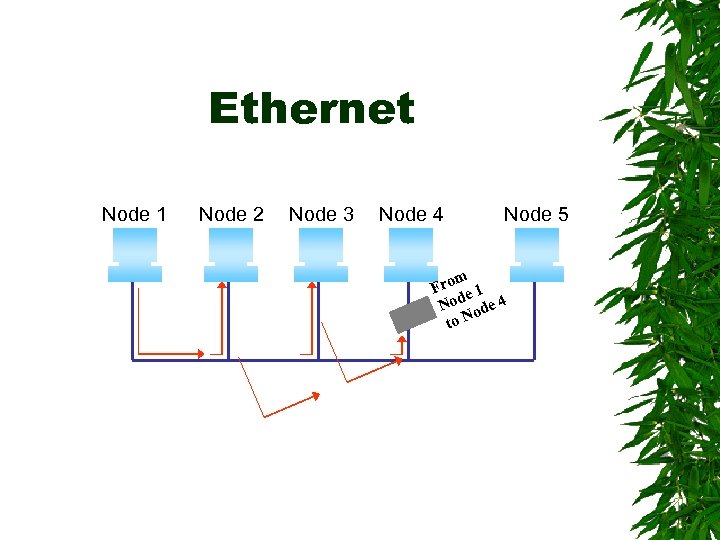 Ethernet Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 4 Node 5 m Fro e 1 Nod ode 4 to N
Ethernet Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 4 Node 5 m Fro e 1 Nod ode 4 to N
 Token ring networks are more orderly Nodes cannot address the network without first obtaining permission in the form of an electronic token that circulates around the network Token-ring networks use a ring topology STP or UTP wiring are used
Token ring networks are more orderly Nodes cannot address the network without first obtaining permission in the form of an electronic token that circulates around the network Token-ring networks use a ring topology STP or UTP wiring are used
 Token ring Advantages: – The sending node always gets confirmation that its data was received – It always guarantees that the next node on the network gets access when a transmission is complete
Token ring Advantages: – The sending node always gets confirmation that its data was received – It always guarantees that the next node on the network gets access when a transmission is complete
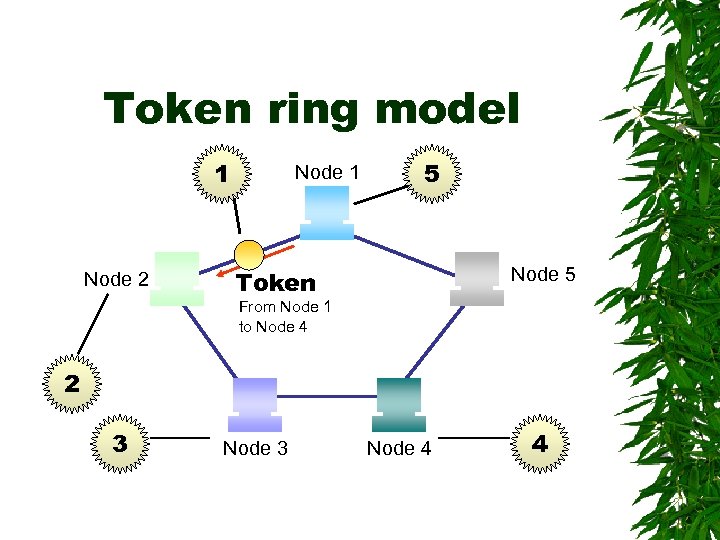 Token ring model 1 Node 2 Node 1 5 Node 5 Token From Node 1 to Node 4 2 3 Node 4 4
Token ring model 1 Node 2 Node 1 5 Node 5 Token From Node 1 to Node 4 2 3 Node 4 4
 Token ring model 1. A free token circulates through the network 2. A node wanting to send data grabs the token when it arrives, changes it to a message with an address to another node and resends it out onto the network 3. Each node in the network looks at the circulating message and if it’s not addressed to it, puts it back into circulation
Token ring model 1. A free token circulates through the network 2. A node wanting to send data grabs the token when it arrives, changes it to a message with an address to another node and resends it out onto the network 3. Each node in the network looks at the circulating message and if it’s not addressed to it, puts it back into circulation
 Token ring model 4. When the token reaches the node to which it was addressed, that node takes the message, attaches an acknowledgement of receipt and readdresses it to the sending node 5. When the sending node receives the token in acknowledgement, it puts the token back into circulation as a free token and the cycle repeats itself
Token ring model 4. When the token reaches the node to which it was addressed, that node takes the message, attaches an acknowledgement of receipt and readdresses it to the sending node 5. When the sending node receives the token in acknowledgement, it puts the token back into circulation as a free token and the cycle repeats itself
 Wide Area Networks (WANs) Metropolitan area networks (MANs) – – MANs are scattered around a metropolitan area Cellular phone networks are an example Wide area networks (WANs) – WANs are scattered over a larger geographic region
Wide Area Networks (WANs) Metropolitan area networks (MANs) – – MANs are scattered around a metropolitan area Cellular phone networks are an example Wide area networks (WANs) – WANs are scattered over a larger geographic region
 WAN Parts of the network may be connected by cables and other parts by microwave or satellite transmissions Typical WANs are those operated by the telephone companies The Internet is probably the widest of all networks in that it links not only LANs but also other WANs
WAN Parts of the network may be connected by cables and other parts by microwave or satellite transmissions Typical WANs are those operated by the telephone companies The Internet is probably the widest of all networks in that it links not only LANs but also other WANs
 Internet model
Internet model
 Intranets Corporations are building company wide intranets accessible only to their employees and other invited users Used for posting documents within an organization Used for linking software, databases, and hardware into a universal network Speak the same language Are fenced off from others on the Internet by firewalls
Intranets Corporations are building company wide intranets accessible only to their employees and other invited users Used for posting documents within an organization Used for linking software, databases, and hardware into a universal network Speak the same language Are fenced off from others on the Internet by firewalls
 Why are Intranets popular? The resources on the intranet are accessible to anyone, anywhere as long as they have a computer, a modem, and a password Complex data and applications can be used over the intranets with ease Learning to use an intranet is simple Costs are lower because so much software and so many connections are available from so many sources
Why are Intranets popular? The resources on the intranet are accessible to anyone, anywhere as long as they have a computer, a modem, and a password Complex data and applications can be used over the intranets with ease Learning to use an intranet is simple Costs are lower because so much software and so many connections are available from so many sources
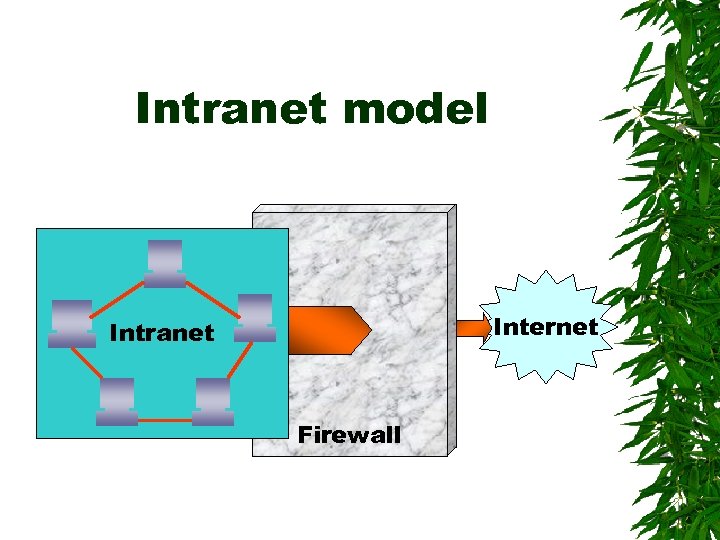 Intranet model Internet Intranet Firewall
Intranet model Internet Intranet Firewall
 Firewalls Prevent unauthorized users on the Internet from reaching the files and programs on the LAN When a computer connected to the outside Internet is also connected to an inside LAN, a firewall is installed between the Internet and the local network
Firewalls Prevent unauthorized users on the Internet from reaching the files and programs on the LAN When a computer connected to the outside Internet is also connected to an inside LAN, a firewall is installed between the Internet and the local network
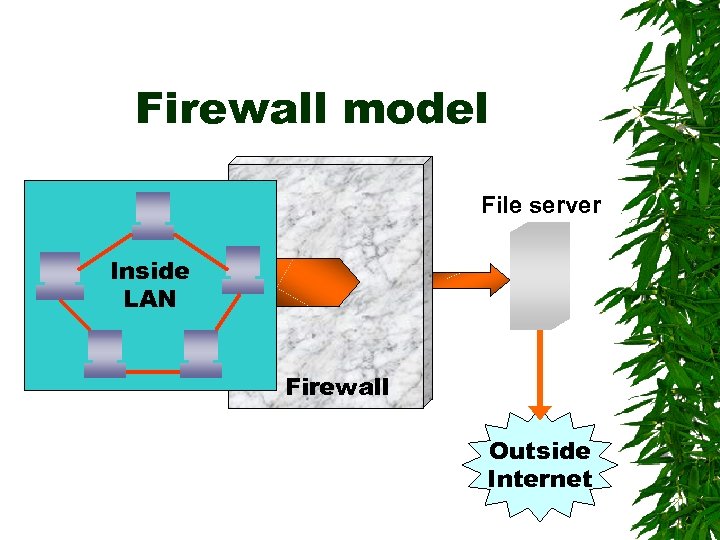 Firewall model File server Inside LAN Firewall Outside Internet
Firewall model File server Inside LAN Firewall Outside Internet
 Why firewalls? Data driven attacks Trojan horse DNS spoofing IP splicing/hijacking or session stealing Social engineering Viruses
Why firewalls? Data driven attacks Trojan horse DNS spoofing IP splicing/hijacking or session stealing Social engineering Viruses


