b99ef03217461ade6f39521e8f70e272.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 105
 3/16/2018 Chemistry Unit C 1 – Chemistry in our World Ed. Excel
3/16/2018 Chemistry Unit C 1 – Chemistry in our World Ed. Excel
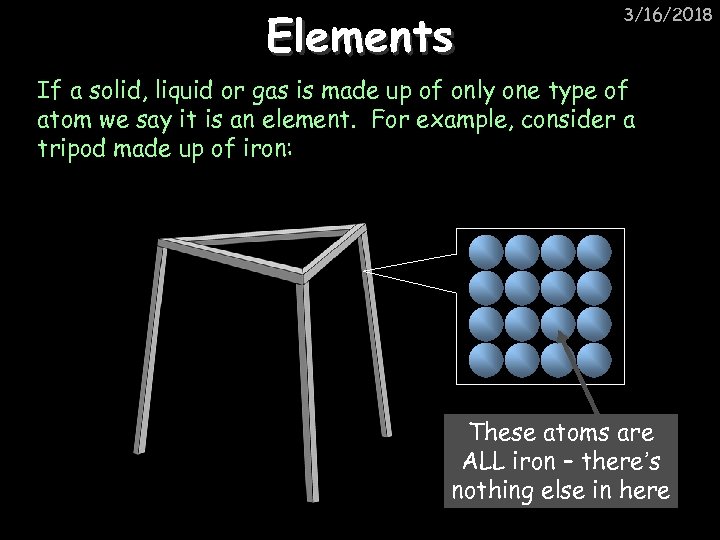 Elements 3/16/2018 If a solid, liquid or gas is made up of only one type of atom we say it is an element. For example, consider a tripod made up of iron: These atoms are ALL iron – there’s nothing else in here
Elements 3/16/2018 If a solid, liquid or gas is made up of only one type of atom we say it is an element. For example, consider a tripod made up of iron: These atoms are ALL iron – there’s nothing else in here
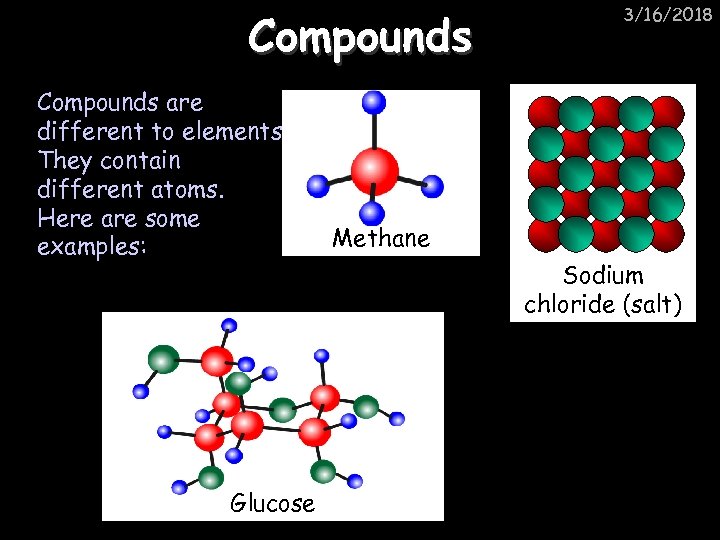 Compounds are different to elements. They contain different atoms. Here are some examples: Glucose 3/16/2018 Methane Sodium chloride (salt)
Compounds are different to elements. They contain different atoms. Here are some examples: Glucose 3/16/2018 Methane Sodium chloride (salt)
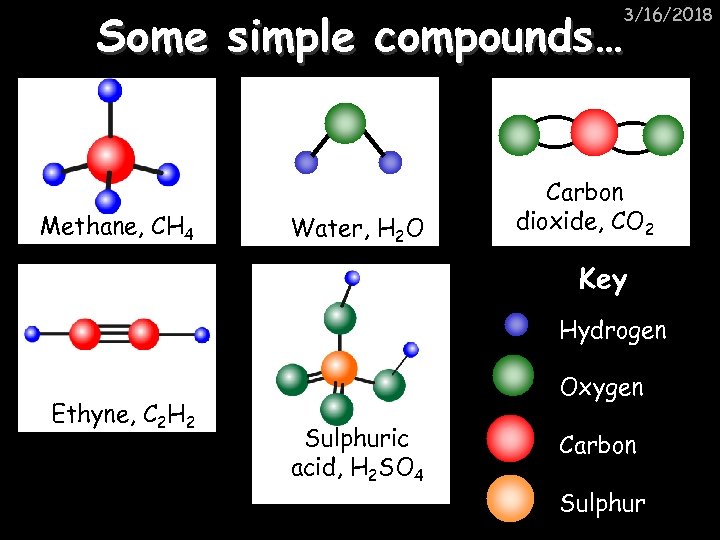 3/16/2018 Some simple compounds… Methane, CH 4 Water, H 2 O Carbon dioxide, CO 2 Key Hydrogen Ethyne, C 2 H 2 Oxygen Sulphuric acid, H 2 SO 4 Carbon Sulphur
3/16/2018 Some simple compounds… Methane, CH 4 Water, H 2 O Carbon dioxide, CO 2 Key Hydrogen Ethyne, C 2 H 2 Oxygen Sulphuric acid, H 2 SO 4 Carbon Sulphur
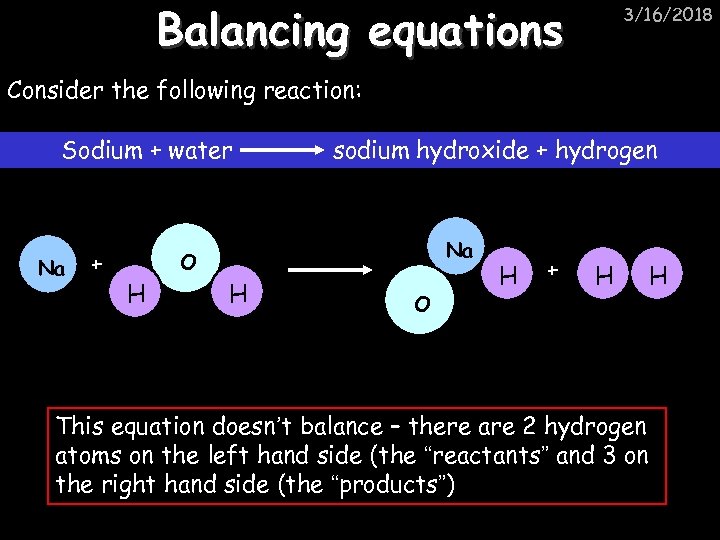 Balancing equations 3/16/2018 Consider the following reaction: Sodium + water Na + sodium hydroxide + hydrogen Na O H H O H + H This equation doesn’t balance – there are 2 hydrogen atoms on the left hand side (the “reactants” and 3 on the right hand side (the “products”) H
Balancing equations 3/16/2018 Consider the following reaction: Sodium + water Na + sodium hydroxide + hydrogen Na O H H O H + H This equation doesn’t balance – there are 2 hydrogen atoms on the left hand side (the “reactants” and 3 on the right hand side (the “products”) H
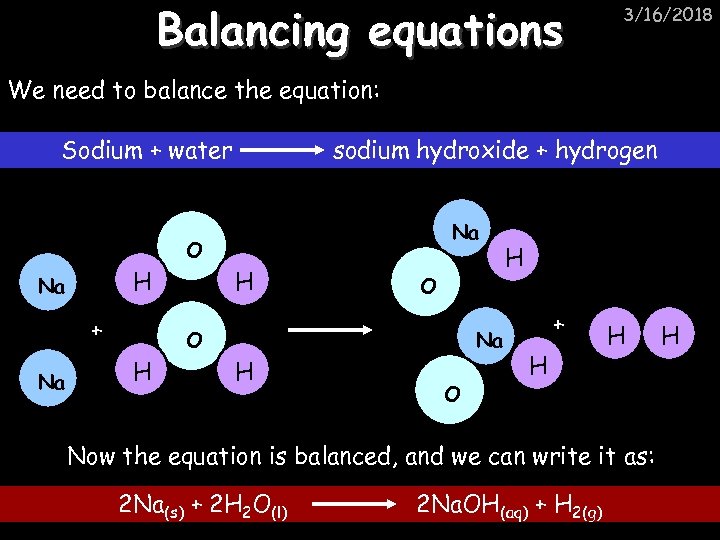 Balancing equations 3/16/2018 We need to balance the equation: Sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen Na O H Na + Na H O O H Na H O H + H H Now the equation is balanced, and we can write it as: 2 Na(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) 2 Na. OH(aq) + H 2(g) H
Balancing equations 3/16/2018 We need to balance the equation: Sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen Na O H Na + Na H O O H Na H O H + H H Now the equation is balanced, and we can write it as: 2 Na(s) + 2 H 2 O(l) 2 Na. OH(aq) + H 2(g) H
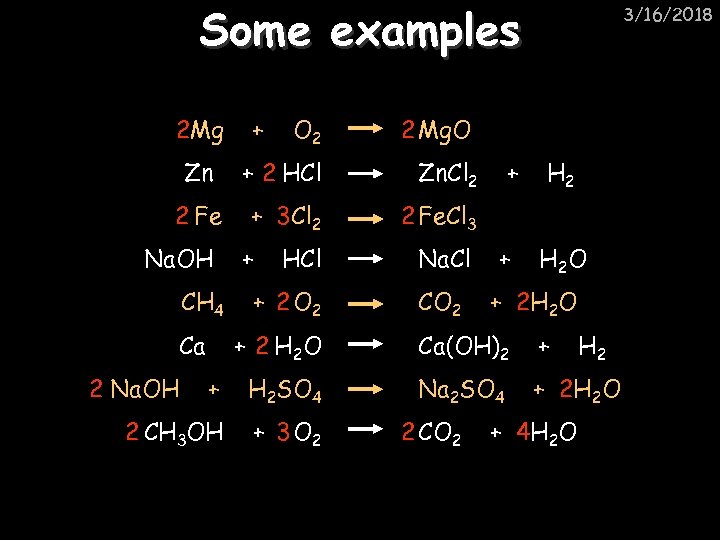 Some examples 2 Mg O 2 2 Mg. O Zn + 2 HCl Zn. Cl 2 2 Fe + 3 Cl 2 2 Fe. Cl 3 Na. OH CH 4 Ca + 3/16/2018 + HCl + 2 O 2 Na. Cl CO 2 + + H 2 O + 2 H 2 O + 2 H 2 O Ca(OH)2 + + H 2 SO 4 Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O 2 CH 3 OH + 3 O 2 2 Na. OH 2 CO 2 + 4 H 2 O H 2
Some examples 2 Mg O 2 2 Mg. O Zn + 2 HCl Zn. Cl 2 2 Fe + 3 Cl 2 2 Fe. Cl 3 Na. OH CH 4 Ca + 3/16/2018 + HCl + 2 O 2 Na. Cl CO 2 + + H 2 O + 2 H 2 O + 2 H 2 O Ca(OH)2 + + H 2 SO 4 Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O 2 CH 3 OH + 3 O 2 2 Na. OH 2 CO 2 + 4 H 2 O H 2
 Hazard signs to learn… Acid Corrosive h Irritant Toxic i Harmful 3/16/2018 Oxidising
Hazard signs to learn… Acid Corrosive h Irritant Toxic i Harmful 3/16/2018 Oxidising
 3/16/2018 Topic 1 – The Earth’s Sea and Atmosphere
3/16/2018 Topic 1 – The Earth’s Sea and Atmosphere
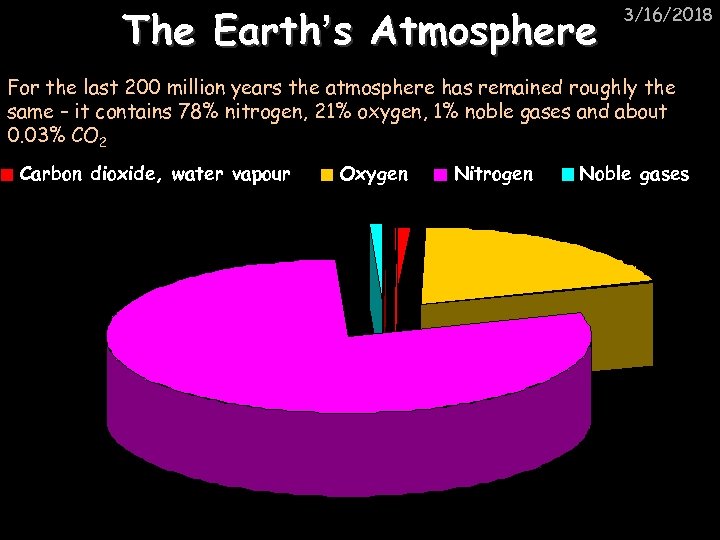 The Earth’s Atmosphere 3/16/2018 For the last 200 million years the atmosphere has remained roughly the same – it contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% noble gases and about 0. 03% CO 2 Carbon dioxide, water vapour Oxygen Nitrogen Noble gases
The Earth’s Atmosphere 3/16/2018 For the last 200 million years the atmosphere has remained roughly the same – it contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% noble gases and about 0. 03% CO 2 Carbon dioxide, water vapour Oxygen Nitrogen Noble gases
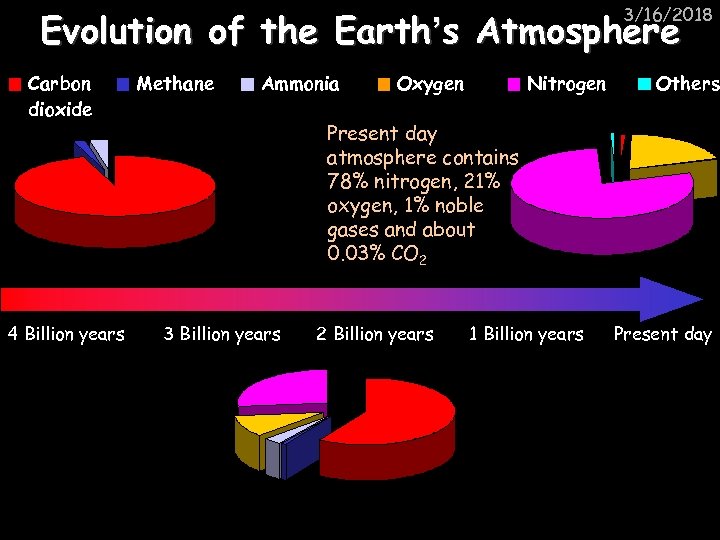 3/16/2018 Evolution of the Earth’s Atmosphere Carbon dioxide 4 Billion years Methane Ammonia Oxygen Nitrogen Others Present day atmosphere contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% noble gases and about 0. 03% CO 2 3 Billion years 2 Billion years 1 Billion years Present day
3/16/2018 Evolution of the Earth’s Atmosphere Carbon dioxide 4 Billion years Methane Ammonia Oxygen Nitrogen Others Present day atmosphere contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% noble gases and about 0. 03% CO 2 3 Billion years 2 Billion years 1 Billion years Present day
 3/16/2018 Evolution of the Earth’s Atmosphere Volcanic activity releases CO 2, methane, ammonia and water vapour into the atmosphere. The water vapour condenses to form oceans. 4 Billion years 3 Billion years Some of the oxygen is converted into ozone. The ozone layer blocks out harmful ultra-violet rays which allows for the development of new life. 2 Billion years 1 Billion years Green plants evolve which take in CO 2 and give out oxygen by photosynthesis, increasing the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere. Carbon from CO 2 becomes locked up in sedimentary rocks as carbonates and fossil fuels and is dissolved into the sea. Methane and ammonia react with the oxygen and nitrogen is released. Present day
3/16/2018 Evolution of the Earth’s Atmosphere Volcanic activity releases CO 2, methane, ammonia and water vapour into the atmosphere. The water vapour condenses to form oceans. 4 Billion years 3 Billion years Some of the oxygen is converted into ozone. The ozone layer blocks out harmful ultra-violet rays which allows for the development of new life. 2 Billion years 1 Billion years Green plants evolve which take in CO 2 and give out oxygen by photosynthesis, increasing the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere. Carbon from CO 2 becomes locked up in sedimentary rocks as carbonates and fossil fuels and is dissolved into the sea. Methane and ammonia react with the oxygen and nitrogen is released. Present day
 Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere 3/16/2018 The amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere is affected by 3 things: 1) Geological activity moves carbonate rocks deep into the Earth and they release _______ into the atmosphere during volcanic activity. 2) Human activity - When fossil fuels are burned the carbon contained in them reacts with _____ to form CO 2. Furthermore, deforestation means that less _____ are around to take in CO 2. 3) Increased CO 2 in the atmosphere causes a reaction between it and _______. These reactions do not remove ALL of the new CO 2 so the greenhouse effect is still getting _______! Words – oxygen, seawater, carbon dioxide, worse, trees
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere 3/16/2018 The amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere is affected by 3 things: 1) Geological activity moves carbonate rocks deep into the Earth and they release _______ into the atmosphere during volcanic activity. 2) Human activity - When fossil fuels are burned the carbon contained in them reacts with _____ to form CO 2. Furthermore, deforestation means that less _____ are around to take in CO 2. 3) Increased CO 2 in the atmosphere causes a reaction between it and _______. These reactions do not remove ALL of the new CO 2 so the greenhouse effect is still getting _______! Words – oxygen, seawater, carbon dioxide, worse, trees
 Topic 2 – Materials from the Earth 3/16/2018
Topic 2 – Materials from the Earth 3/16/2018
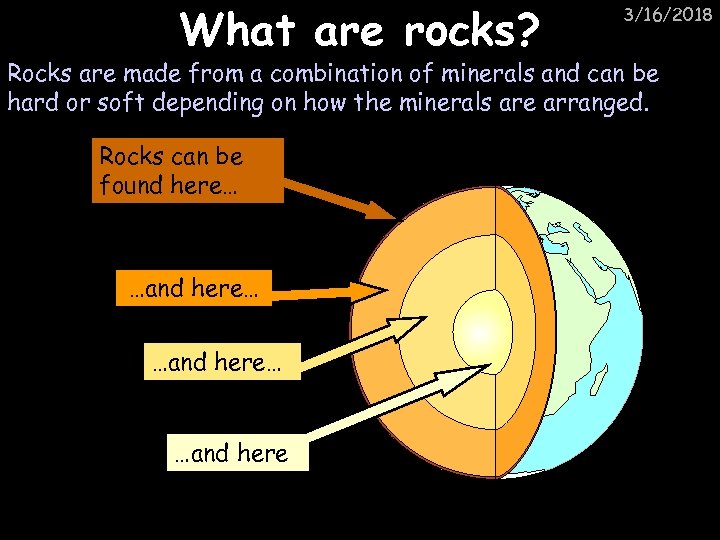 What are rocks? 3/16/2018 Rocks are made from a combination of minerals and can be hard or soft depending on how the minerals are arranged. Rocks can be found here… …and here
What are rocks? 3/16/2018 Rocks are made from a combination of minerals and can be hard or soft depending on how the minerals are arranged. Rocks can be found here… …and here
 Sedimentary rocks 3/16/2018 Limestone Sandstone Chalk Conglomerate
Sedimentary rocks 3/16/2018 Limestone Sandstone Chalk Conglomerate
 Sedimentary rocks 3/16/2018 How sedimentary rocks are formed: 1) Weathering 2) Transportation 3) Deposition 4) Burial
Sedimentary rocks 3/16/2018 How sedimentary rocks are formed: 1) Weathering 2) Transportation 3) Deposition 4) Burial
 Metamorphic rocks Quartzite Slate Marble (made from chalk or limestone) 3/16/2018
Metamorphic rocks Quartzite Slate Marble (made from chalk or limestone) 3/16/2018
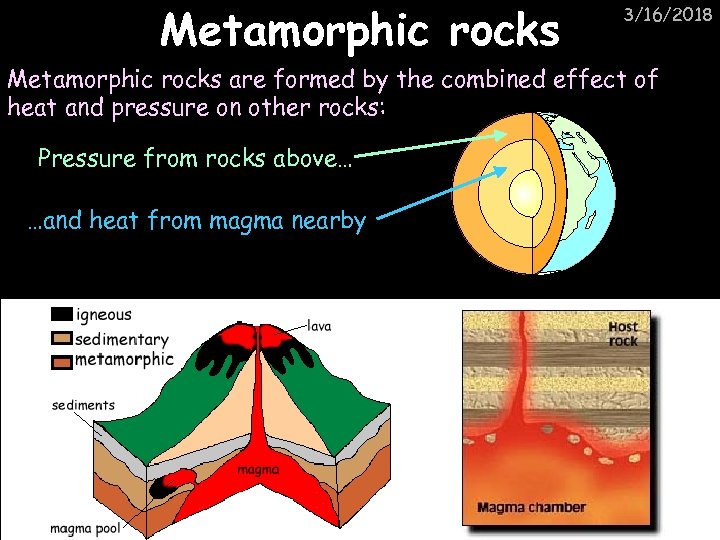 Metamorphic rocks 3/16/2018 Metamorphic rocks are formed by the combined effect of heat and pressure on other rocks: Pressure from rocks above… …and heat from magma nearby
Metamorphic rocks 3/16/2018 Metamorphic rocks are formed by the combined effect of heat and pressure on other rocks: Pressure from rocks above… …and heat from magma nearby
 Igneous rocks Granite Pumice 3/16/2018 Obsidian
Igneous rocks Granite Pumice 3/16/2018 Obsidian
 Igneous Rock 3/16/2018 Granite – a slow cooling rock with big crystals and rich in silica Rhyolite – a fast cooling rock with small crystals and rich in silica Basalt – a fast cooling rock with small crystals and rich in iron Gabbro – a slow cooling rock with big crystals and rich in iron
Igneous Rock 3/16/2018 Granite – a slow cooling rock with big crystals and rich in silica Rhyolite – a fast cooling rock with small crystals and rich in silica Basalt – a fast cooling rock with small crystals and rich in iron Gabbro – a slow cooling rock with big crystals and rich in iron
 Igneous rocks 3/16/2018 Igneous rocks are formed when lava or magma cools down and solidifies If the lava or magma cools QUICKLY it has SMALL crystals If the lava or magma cools SLOWLY it has BIG crystals
Igneous rocks 3/16/2018 Igneous rocks are formed when lava or magma cools down and solidifies If the lava or magma cools QUICKLY it has SMALL crystals If the lava or magma cools SLOWLY it has BIG crystals
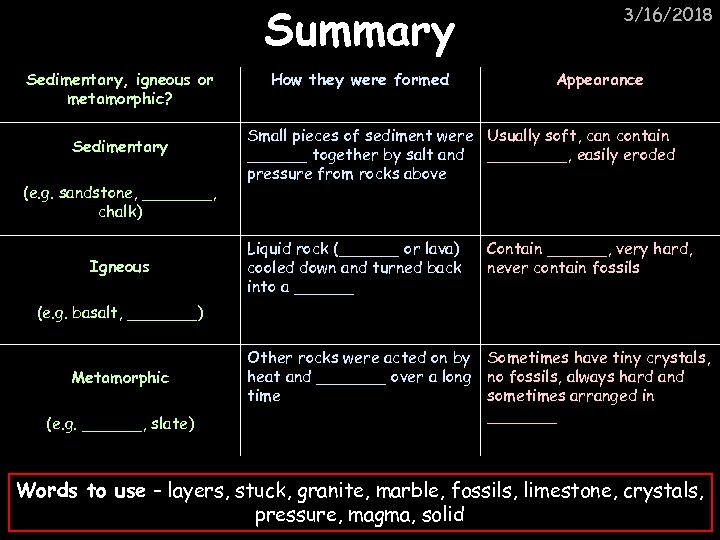 Summary Sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic? Sedimentary (e. g. sandstone, _______, chalk) Igneous How they were formed 3/16/2018 Appearance Small pieces of sediment were Usually soft, can contain ______ together by salt and ____, easily eroded pressure from rocks above Liquid rock (______ or lava) cooled down and turned back into a ______ Contain ______, very hard, never contain fossils Other rocks were acted on by heat and _______ over a long time Sometimes have tiny crystals, no fossils, always hard and sometimes arranged in _______ (e. g. basalt, _______) Metamorphic (e. g. ______, slate) Words to use – layers, stuck, granite, marble, fossils, limestone, crystals, pressure, magma, solid
Summary Sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic? Sedimentary (e. g. sandstone, _______, chalk) Igneous How they were formed 3/16/2018 Appearance Small pieces of sediment were Usually soft, can contain ______ together by salt and ____, easily eroded pressure from rocks above Liquid rock (______ or lava) cooled down and turned back into a ______ Contain ______, very hard, never contain fossils Other rocks were acted on by heat and _______ over a long time Sometimes have tiny crystals, no fossils, always hard and sometimes arranged in _______ (e. g. basalt, _______) Metamorphic (e. g. ______, slate) Words to use – layers, stuck, granite, marble, fossils, limestone, crystals, pressure, magma, solid
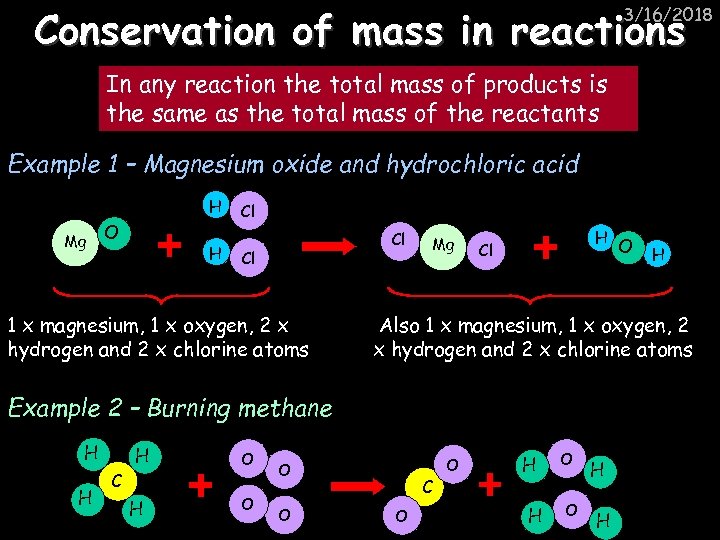 Conservation of mass in reactions 3/16/2018 In any reaction the total mass of products is the same as the total mass of the reactants Example 1 – Magnesium oxide and hydrochloric acid H Mg O H Cl Cl Cl 1 x magnesium, 1 x oxygen, 2 x hydrogen and 2 x chlorine atoms Mg H Cl H H C H O O H Also 1 x magnesium, 1 x oxygen, 2 x hydrogen and 2 x chlorine atoms Example 2 – Burning methane H O C O O H H
Conservation of mass in reactions 3/16/2018 In any reaction the total mass of products is the same as the total mass of the reactants Example 1 – Magnesium oxide and hydrochloric acid H Mg O H Cl Cl Cl 1 x magnesium, 1 x oxygen, 2 x hydrogen and 2 x chlorine atoms Mg H Cl H H C H O O H Also 1 x magnesium, 1 x oxygen, 2 x hydrogen and 2 x chlorine atoms Example 2 – Burning methane H O C O O H H
 Calcium Carbonate 3/16/2018 Calcium carbonate is a common chemical in the Earth and we’ve already come across it in a number of forms: Limestone Chalk Marble (made from chalk or limestone)
Calcium Carbonate 3/16/2018 Calcium carbonate is a common chemical in the Earth and we’ve already come across it in a number of forms: Limestone Chalk Marble (made from chalk or limestone)
 Limestone View video of limestone being quarried 3/16/2018
Limestone View video of limestone being quarried 3/16/2018
 Limestone 3/16/2018 Limestone is a _____ rock made up of mainly calcium carbonate. It’s cheap and easy to obtain. Some uses: 1) Building materials – limestone can be quarried and cut into blocks to be used in _______. However, it is badly affected by ____. 2) Glass making – glass is made by mixing limestone with _____ and soda: Limestone + sand + soda glass 3) Cement making – limestone can be “roasted” in a rotary kiln to produce dry cement. It’s then mixed with sand gravel to make _______. Words – sand, building, sedimentary, concrete, acid rain
Limestone 3/16/2018 Limestone is a _____ rock made up of mainly calcium carbonate. It’s cheap and easy to obtain. Some uses: 1) Building materials – limestone can be quarried and cut into blocks to be used in _______. However, it is badly affected by ____. 2) Glass making – glass is made by mixing limestone with _____ and soda: Limestone + sand + soda glass 3) Cement making – limestone can be “roasted” in a rotary kiln to produce dry cement. It’s then mixed with sand gravel to make _______. Words – sand, building, sedimentary, concrete, acid rain
 3/16/2018 Pros and Cons of quarrying limestone Reasons why quarrying limestone is a good idea Reasons why quarrying limestone is a bad idea
3/16/2018 Pros and Cons of quarrying limestone Reasons why quarrying limestone is a good idea Reasons why quarrying limestone is a bad idea
 Limestone 3/16/2018 Limestone has a number of uses when it undergoes chemical reactions. There are two reactions to know: 1) Firstly, a THERMAL _________ reaction is used to break the calcium carbonate down into calcium ______ and __________: Calcium carbonate HEAT calcium oxide + carbon dioxide 2) _____ is then added to produce calcium _____: Calcium oxide WATER calcium hydroxide Words – hydroxide, decomposition, carbon dioxide, water, oxide
Limestone 3/16/2018 Limestone has a number of uses when it undergoes chemical reactions. There are two reactions to know: 1) Firstly, a THERMAL _________ reaction is used to break the calcium carbonate down into calcium ______ and __________: Calcium carbonate HEAT calcium oxide + carbon dioxide 2) _____ is then added to produce calcium _____: Calcium oxide WATER calcium hydroxide Words – hydroxide, decomposition, carbon dioxide, water, oxide
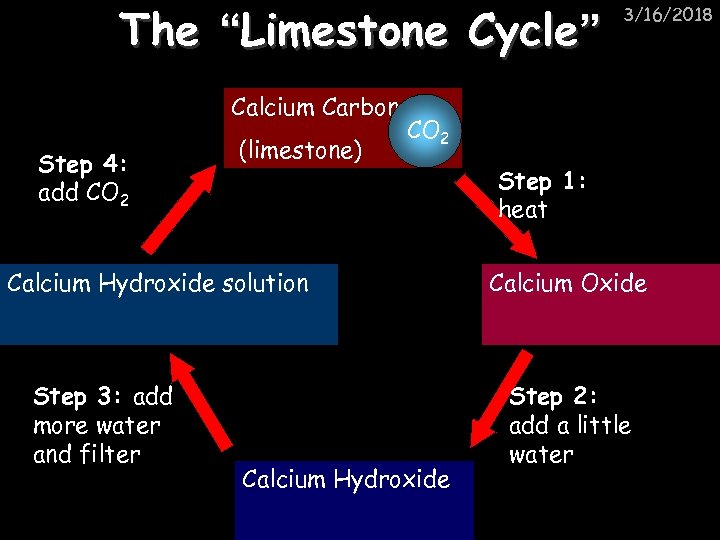 The “Limestone Cycle” Step 4: add CO 2 Calcium Carbonate CO 2 (limestone) Calcium Hydroxide solution Step 3: add more water and filter Calcium Hydroxide 3/16/2018 Step 1: heat Calcium Oxide Step 2: add a little water
The “Limestone Cycle” Step 4: add CO 2 Calcium Carbonate CO 2 (limestone) Calcium Hydroxide solution Step 3: add more water and filter Calcium Hydroxide 3/16/2018 Step 1: heat Calcium Oxide Step 2: add a little water
 Uses of these Calcium compounds 3/16/2018 Calcium carbonate (limestone), calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide have a number of uses: 1) Neutralising acidic soil – calcium carbonate, calcium hydroxide and calcium oxide are _______ and can be used to ____ soil acidity to help ______ growth. 2) Removing pollutants – calcium carbonate can be used as a “_______” to remove acidic gases from a coalfired power station’s waste products, helping prevent _____. Words – acid rain, alkaline, plant, scrubber, neutralise
Uses of these Calcium compounds 3/16/2018 Calcium carbonate (limestone), calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide have a number of uses: 1) Neutralising acidic soil – calcium carbonate, calcium hydroxide and calcium oxide are _______ and can be used to ____ soil acidity to help ______ growth. 2) Removing pollutants – calcium carbonate can be used as a “_______” to remove acidic gases from a coalfired power station’s waste products, helping prevent _____. Words – acid rain, alkaline, plant, scrubber, neutralise
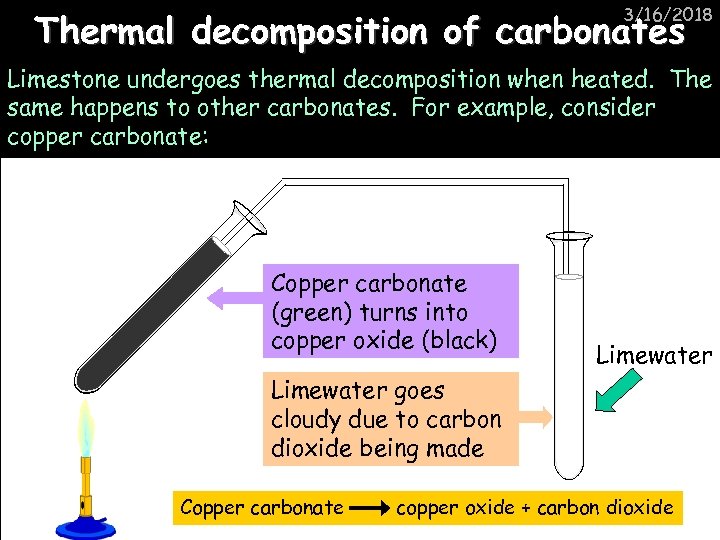 3/16/2018 Thermal decomposition of carbonates Limestone undergoes thermal decomposition when heated. The same happens to other carbonates. For example, consider copper carbonate: Copper carbonate (green) turns into copper oxide (black) Limewater goes cloudy due to carbon dioxide being made Copper carbonate copper oxide + carbon dioxide
3/16/2018 Thermal decomposition of carbonates Limestone undergoes thermal decomposition when heated. The same happens to other carbonates. For example, consider copper carbonate: Copper carbonate (green) turns into copper oxide (black) Limewater goes cloudy due to carbon dioxide being made Copper carbonate copper oxide + carbon dioxide
 Topic 3 – Acids 3/16/2018
Topic 3 – Acids 3/16/2018
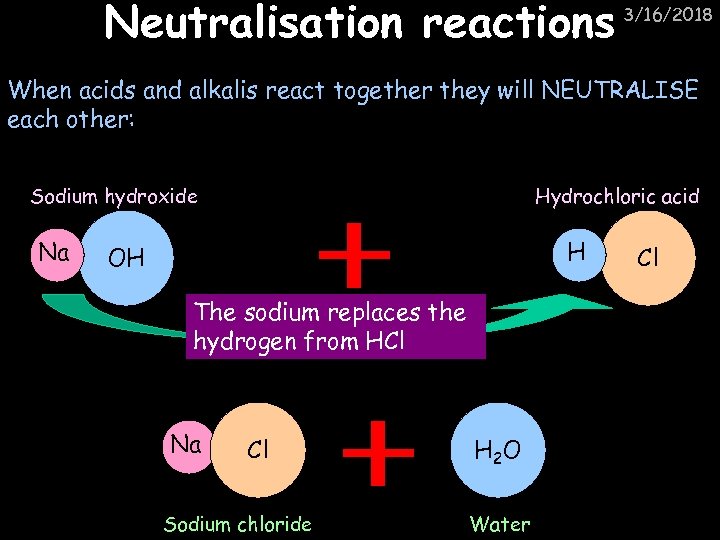 Neutralisation reactions 3/16/2018 When acids and alkalis react together they will NEUTRALISE each other: Sodium hydroxide Na Hydrochloric acid H OH The sodium replaces the hydrogen from HCl Na Cl Sodium chloride H 2 O Water Cl
Neutralisation reactions 3/16/2018 When acids and alkalis react together they will NEUTRALISE each other: Sodium hydroxide Na Hydrochloric acid H OH The sodium replaces the hydrogen from HCl Na Cl Sodium chloride H 2 O Water Cl
 Neutralisation experiment 3/16/2018 In this experiment we mixed sodium hydroxide (an _____) and hydrochloric acid together and they ____ each other. The equation for this reaction is… Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride + water A ____ was formed during the reaction, and we could have separated this by _____ the solution. The salt that we formed depended on the acid: • Hydrochloric acid will make a CHLORIDE • Nitric acid will make a _____ • Sulphuric acid will make a _____ Words – nitrate, neutralised, alkali, sulphate, salt, evaporating
Neutralisation experiment 3/16/2018 In this experiment we mixed sodium hydroxide (an _____) and hydrochloric acid together and they ____ each other. The equation for this reaction is… Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride + water A ____ was formed during the reaction, and we could have separated this by _____ the solution. The salt that we formed depended on the acid: • Hydrochloric acid will make a CHLORIDE • Nitric acid will make a _____ • Sulphuric acid will make a _____ Words – nitrate, neutralised, alkali, sulphate, salt, evaporating
 Stomach Acid 3/16/2018 Hydrochloric acid is used in the stomach to help _______ and to kill ______. If we eat too many “rich” foods our stomachs create too much ____ – this is called ______. This acid needs to be neutralised by taking indigestion tablets. Indigestion tablets contain substances such as _______ that neutralise excess stomach acid. Words – digestion, indigestion, acid, alkalis, bacteria
Stomach Acid 3/16/2018 Hydrochloric acid is used in the stomach to help _______ and to kill ______. If we eat too many “rich” foods our stomachs create too much ____ – this is called ______. This acid needs to be neutralised by taking indigestion tablets. Indigestion tablets contain substances such as _______ that neutralise excess stomach acid. Words – digestion, indigestion, acid, alkalis, bacteria
 Neutralisation reactions 3/16/2018 A neutralisation reaction occurs when an acid reacts with an alkali. An alkali is a metal oxide or metal hydroxide dissolved in water. ACID + ALKALI Na O H H Cl SALT + WATER Cl Na Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium hydroxide + sulphuric acid 4) Magnesium hydroxide + sulphuric acid H O H
Neutralisation reactions 3/16/2018 A neutralisation reaction occurs when an acid reacts with an alkali. An alkali is a metal oxide or metal hydroxide dissolved in water. ACID + ALKALI Na O H H Cl SALT + WATER Cl Na Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium hydroxide + sulphuric acid 4) Magnesium hydroxide + sulphuric acid H O H
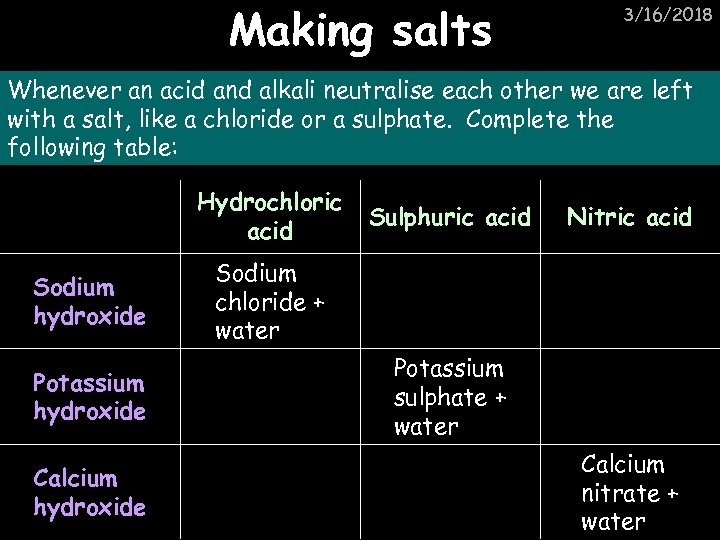 Making salts 3/16/2018 Whenever an acid and alkali neutralise each other we are left with a salt, like a chloride or a sulphate. Complete the following table: Hydrochloric acid Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide Calcium hydroxide Sulphuric acid Nitric acid Sodium chloride + water Potassium sulphate + water Calcium nitrate + water
Making salts 3/16/2018 Whenever an acid and alkali neutralise each other we are left with a salt, like a chloride or a sulphate. Complete the following table: Hydrochloric acid Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide Calcium hydroxide Sulphuric acid Nitric acid Sodium chloride + water Potassium sulphate + water Calcium nitrate + water
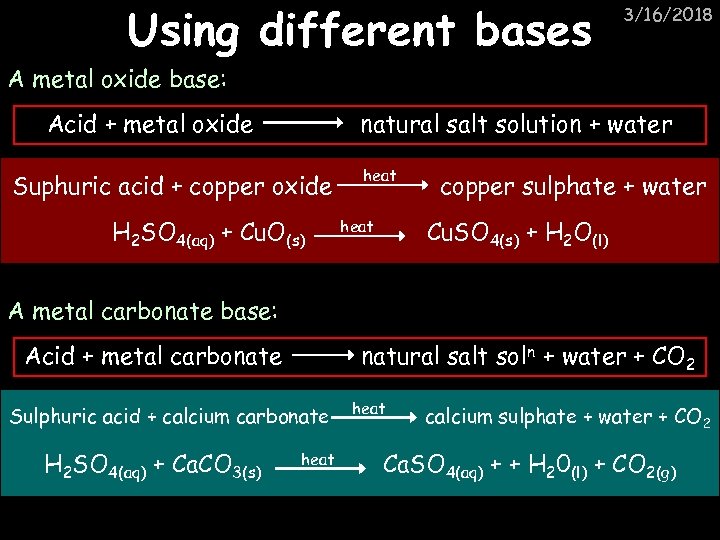 Using different bases 3/16/2018 A metal oxide base: Acid + metal oxide natural salt solution + water Suphuric acid + copper oxide H 2 SO 4(aq) + Cu. O(s) heat copper sulphate + water Cu. SO 4(s) + H 2 O(l) heat A metal carbonate base: Acid + metal carbonate natural salt sol n + water + CO 2 Sulphuric acid + calcium carbonate H 2 SO 4(aq) + Ca. CO 3(s) heat calcium sulphate + water + CO 2 Ca. SO 4(aq) + + H 20(l) + CO 2(g)
Using different bases 3/16/2018 A metal oxide base: Acid + metal oxide natural salt solution + water Suphuric acid + copper oxide H 2 SO 4(aq) + Cu. O(s) heat copper sulphate + water Cu. SO 4(s) + H 2 O(l) heat A metal carbonate base: Acid + metal carbonate natural salt sol n + water + CO 2 Sulphuric acid + calcium carbonate H 2 SO 4(aq) + Ca. CO 3(s) heat calcium sulphate + water + CO 2 Ca. SO 4(aq) + + H 20(l) + CO 2(g)
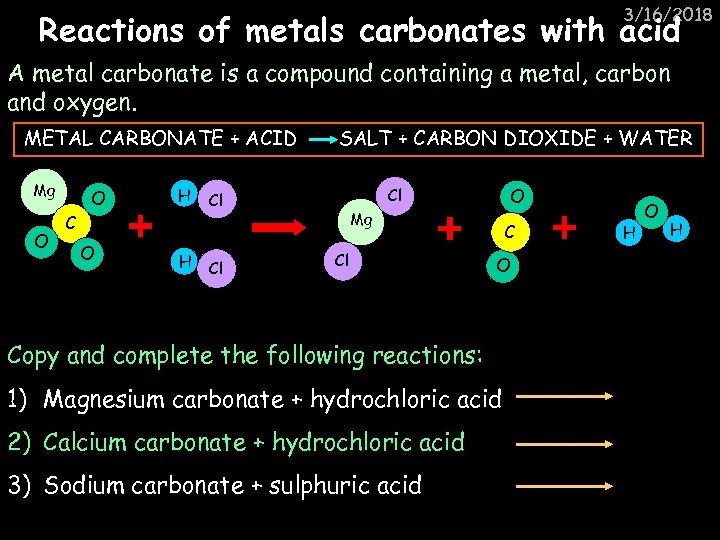 3/16/2018 Reactions of metals carbonates with acid A metal carbonate is a compound containing a metal, carbon and oxygen. METAL CARBONATE + ACID Mg O O H C O H SALT + CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER Cl O Cl Cl Mg Cl C O Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Magnesium carbonate + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium carbonate + sulphuric acid H O H
3/16/2018 Reactions of metals carbonates with acid A metal carbonate is a compound containing a metal, carbon and oxygen. METAL CARBONATE + ACID Mg O O H C O H SALT + CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER Cl O Cl Cl Mg Cl C O Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Magnesium carbonate + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium carbonate + sulphuric acid H O H
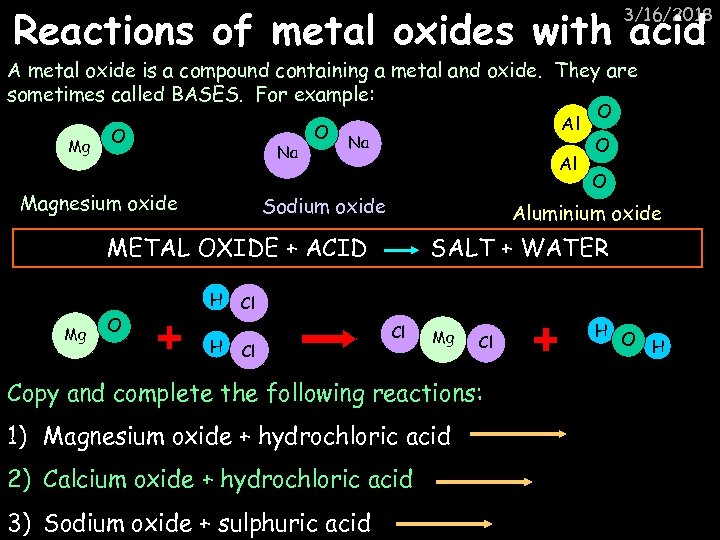 Reactions of metal oxides with acid 3/16/2018 A metal oxide is a compound containing a metal and oxide. They are sometimes called BASES. For example: Mg O Na Magnesium oxide O Al Na Al Sodium oxide Mg O H O O Aluminium oxide METAL OXIDE + ACID H O SALT + WATER Cl Cl Cl Mg Cl Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Magnesium oxide + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium oxide + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium oxide + sulphuric acid H O H
Reactions of metal oxides with acid 3/16/2018 A metal oxide is a compound containing a metal and oxide. They are sometimes called BASES. For example: Mg O Na Magnesium oxide O Al Na Al Sodium oxide Mg O H O O Aluminium oxide METAL OXIDE + ACID H O SALT + WATER Cl Cl Cl Mg Cl Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Magnesium oxide + hydrochloric acid 2) Calcium oxide + hydrochloric acid 3) Sodium oxide + sulphuric acid H O H
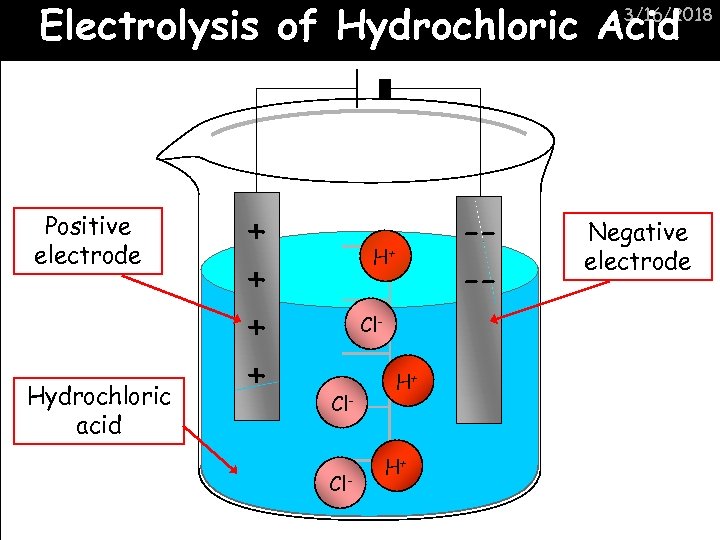 Electrolysis of Hydrochloric Acid 3/16/2018 Positive electrode Hydrochloric acid + + --- H+ Cl- Cl- H+ H+ Negative electrode
Electrolysis of Hydrochloric Acid 3/16/2018 Positive electrode Hydrochloric acid + + --- H+ Cl- Cl- H+ H+ Negative electrode
 Testing for Hydrogen “POP” 3/16/2018
Testing for Hydrogen “POP” 3/16/2018
 Testing for Chlorine 3/16/2018 Chlorine “bleaches” damp indicator paper. It is also a toxic gas so don’t breathe it! This leads to problems when it comes to large-scale manufacture of chlorine gas.
Testing for Chlorine 3/16/2018 Chlorine “bleaches” damp indicator paper. It is also a toxic gas so don’t breathe it! This leads to problems when it comes to large-scale manufacture of chlorine gas.
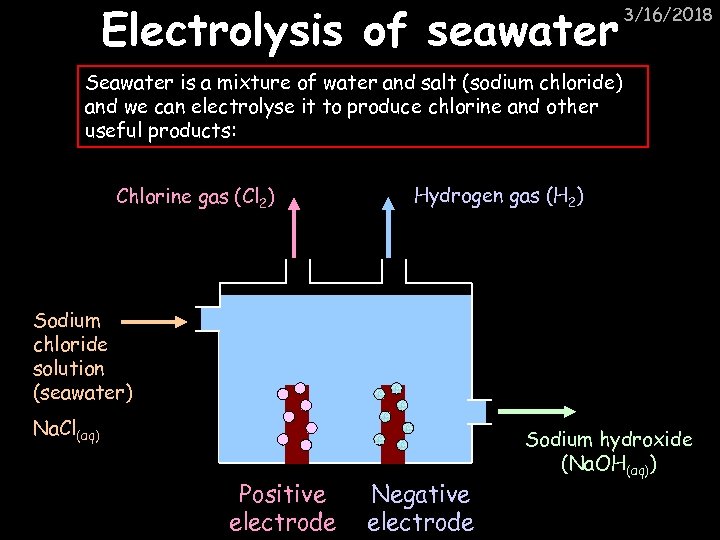 Electrolysis of seawater 3/16/2018 Seawater is a mixture of water and salt (sodium chloride) and we can electrolyse it to produce chlorine and other useful products: Chlorine gas (Cl 2) Hydrogen gas (H 2) Sodium chloride solution (seawater) Na. Cl(aq) Positive electrode Negative electrode Sodium hydroxide (Na. OH(aq))
Electrolysis of seawater 3/16/2018 Seawater is a mixture of water and salt (sodium chloride) and we can electrolyse it to produce chlorine and other useful products: Chlorine gas (Cl 2) Hydrogen gas (H 2) Sodium chloride solution (seawater) Na. Cl(aq) Positive electrode Negative electrode Sodium hydroxide (Na. OH(aq))
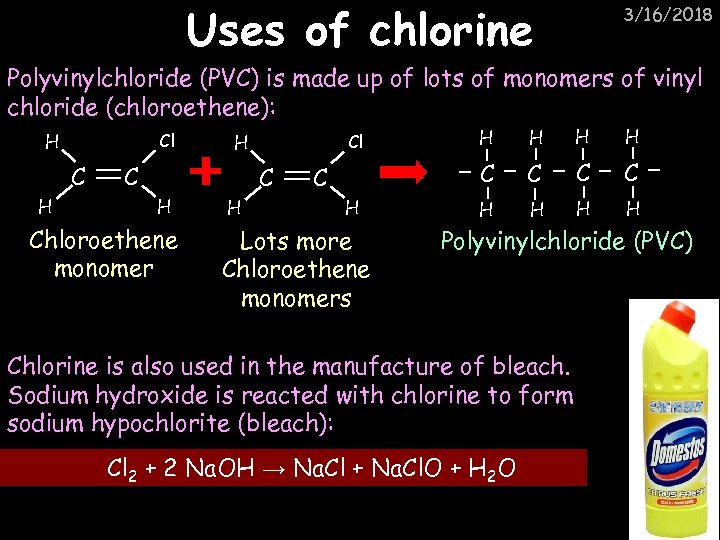 Uses of chlorine 3/16/2018 Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is made up of lots of monomers of vinyl chloride (chloroethene): Cl H C H Chloroethene monomer C H Lots more Chloroethene monomers H H C Cl H C C C H H Polyvinylchloride (PVC) Chlorine is also used in the manufacture of bleach. Sodium hydroxide is reacted with chlorine to form sodium hypochlorite (bleach): Cl 2 + 2 Na. OH → Na. Cl + Na. Cl. O + H 2 O
Uses of chlorine 3/16/2018 Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is made up of lots of monomers of vinyl chloride (chloroethene): Cl H C H Chloroethene monomer C H Lots more Chloroethene monomers H H C Cl H C C C H H Polyvinylchloride (PVC) Chlorine is also used in the manufacture of bleach. Sodium hydroxide is reacted with chlorine to form sodium hypochlorite (bleach): Cl 2 + 2 Na. OH → Na. Cl + Na. Cl. O + H 2 O
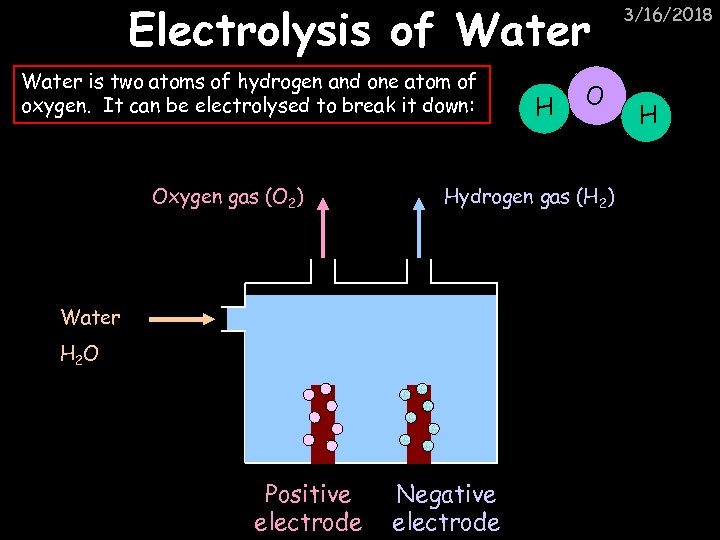 Electrolysis of Water is two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. It can be electrolysed to break it down: Oxygen gas (O 2) O Hydrogen gas (H 2) Water H 2 O Positive electrode H Negative electrode 3/16/2018 H
Electrolysis of Water is two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. It can be electrolysed to break it down: Oxygen gas (O 2) O Hydrogen gas (H 2) Water H 2 O Positive electrode H Negative electrode 3/16/2018 H
 Testing for Oxygen will relight a glowing splint 3/16/2018
Testing for Oxygen will relight a glowing splint 3/16/2018
 3/16/2018 Topic 4 – Obtaining and Using Metals
3/16/2018 Topic 4 – Obtaining and Using Metals
 Extracting Metals 3/16/2018 Some definitions: A METAL ORE is a mineral or mixture of minerals from which it is “economically viable” to extract some metal. Most ores contain METAL OXIDES (e. g. rust = iron oxide). To “extract” a metal from a metal oxide we need to REDUCE the oxygen. This is called a REDUCTION reaction. To put it simply: Iron ore Iron Oxide “Reduce” the oxygen to make iron
Extracting Metals 3/16/2018 Some definitions: A METAL ORE is a mineral or mixture of minerals from which it is “economically viable” to extract some metal. Most ores contain METAL OXIDES (e. g. rust = iron oxide). To “extract” a metal from a metal oxide we need to REDUCE the oxygen. This is called a REDUCTION reaction. To put it simply: Iron ore Iron Oxide “Reduce” the oxygen to make iron
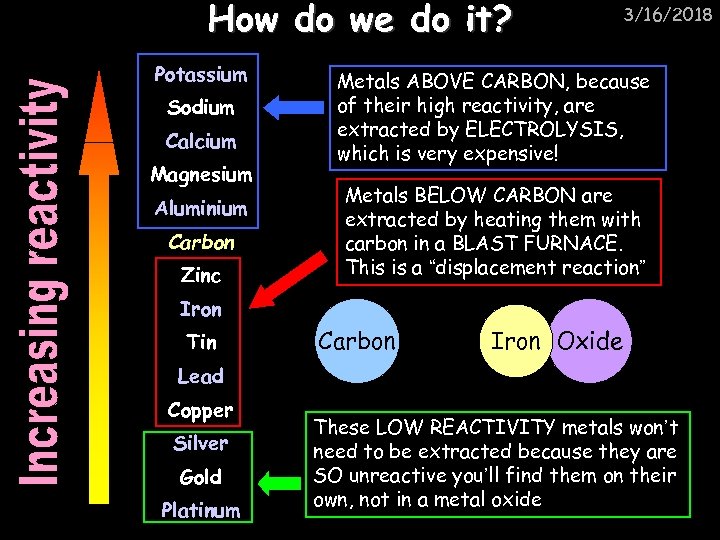 How do we do it? Potassium Sodium Calcium Magnesium Aluminium Carbon Zinc 3/16/2018 Metals ABOVE CARBON, because of their high reactivity, are extracted by ELECTROLYSIS, which is very expensive! Metals BELOW CARBON are extracted by heating them with carbon in a BLAST FURNACE. This is a “displacement reaction” Iron Tin Carbon Iron Oxide Lead Copper Silver Gold Platinum These LOW REACTIVITY metals won’t need to be extracted because they are SO unreactive you’ll find them on their own, not in a metal oxide
How do we do it? Potassium Sodium Calcium Magnesium Aluminium Carbon Zinc 3/16/2018 Metals ABOVE CARBON, because of their high reactivity, are extracted by ELECTROLYSIS, which is very expensive! Metals BELOW CARBON are extracted by heating them with carbon in a BLAST FURNACE. This is a “displacement reaction” Iron Tin Carbon Iron Oxide Lead Copper Silver Gold Platinum These LOW REACTIVITY metals won’t need to be extracted because they are SO unreactive you’ll find them on their own, not in a metal oxide
 Extracting metals 3/16/2018 1) What is an ore? 2) In what form are metals usually found in the Earth? 3) How do you get a metal out of a metal oxide? 4) What is this type of reaction called? Type of metal High reactivity (i. e anything above carbon) Middle reactivity (i. e. anything below carbon) Low reactivity Extraction process Examples
Extracting metals 3/16/2018 1) What is an ore? 2) In what form are metals usually found in the Earth? 3) How do you get a metal out of a metal oxide? 4) What is this type of reaction called? Type of metal High reactivity (i. e anything above carbon) Middle reactivity (i. e. anything below carbon) Low reactivity Extraction process Examples
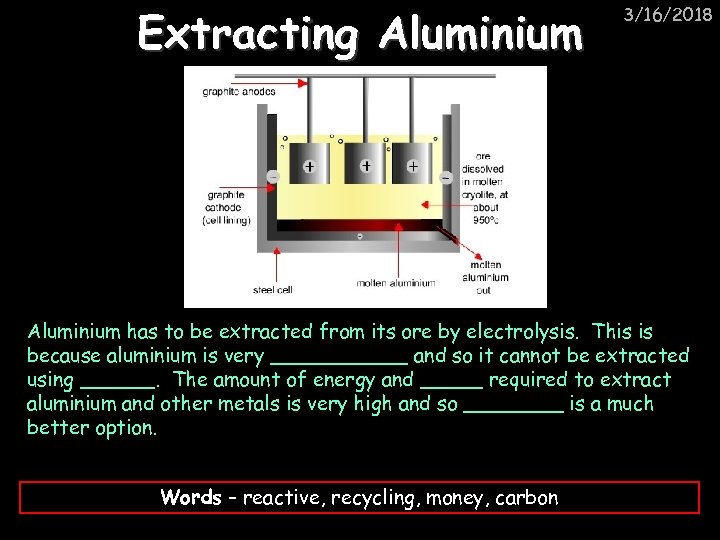 Extracting Aluminium 3/16/2018 Aluminium has to be extracted from its ore by electrolysis. This is because aluminium is very ______ and so it cannot be extracted using ______. The amount of energy and _____ required to extract aluminium and other metals is very high and so ____ is a much better option. Words – reactive, recycling, money, carbon
Extracting Aluminium 3/16/2018 Aluminium has to be extracted from its ore by electrolysis. This is because aluminium is very ______ and so it cannot be extracted using ______. The amount of energy and _____ required to extract aluminium and other metals is very high and so ____ is a much better option. Words – reactive, recycling, money, carbon
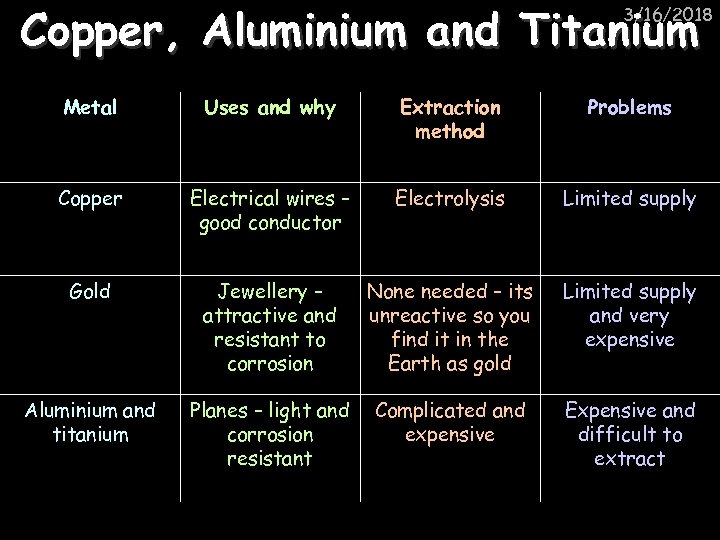 Copper, Aluminium and Titanium 3/16/2018 Metal Uses and why Extraction method Problems Copper Electrical wires – good conductor Electrolysis Limited supply Gold Jewellery – attractive and resistant to corrosion None needed – its unreactive so you find it in the Earth as gold Limited supply and very expensive Aluminium and titanium Planes – light and corrosion resistant Complicated and expensive Expensive and difficult to extract
Copper, Aluminium and Titanium 3/16/2018 Metal Uses and why Extraction method Problems Copper Electrical wires – good conductor Electrolysis Limited supply Gold Jewellery – attractive and resistant to corrosion None needed – its unreactive so you find it in the Earth as gold Limited supply and very expensive Aluminium and titanium Planes – light and corrosion resistant Complicated and expensive Expensive and difficult to extract
 Using impurities to strengthen Iron 3/16/2018 In pure iron all impurities are removed. This makes the iron soft: Adding 1% impurities makes the iron much stronger:
Using impurities to strengthen Iron 3/16/2018 In pure iron all impurities are removed. This makes the iron soft: Adding 1% impurities makes the iron much stronger:
 Alloys 3/16/2018 Steel is an “alloy” – i. e. a mixture of metals. Here are other alloys: Gold mixed with copper Aluminium mixed with magnesium and copper Aluminiun mixed with chromium
Alloys 3/16/2018 Steel is an “alloy” – i. e. a mixture of metals. Here are other alloys: Gold mixed with copper Aluminium mixed with magnesium and copper Aluminiun mixed with chromium
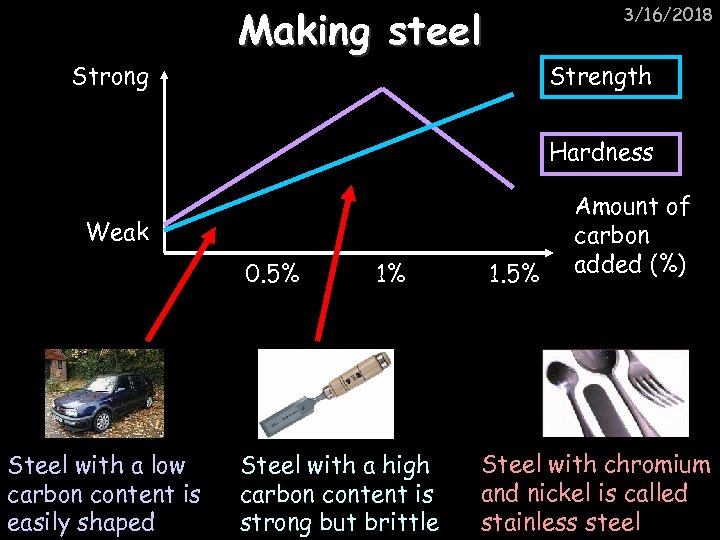 Strong Making steel 3/16/2018 Strength Hardness Weak 0. 5% Steel with a low carbon content is easily shaped 1% Steel with a high carbon content is strong but brittle 1. 5% Amount of carbon added (%) Steel with chromium and nickel is called stainless steel
Strong Making steel 3/16/2018 Strength Hardness Weak 0. 5% Steel with a low carbon content is easily shaped 1% Steel with a high carbon content is strong but brittle 1. 5% Amount of carbon added (%) Steel with chromium and nickel is called stainless steel
 Smart Alloys 3/16/2018 A “smart alloy” is one that can “remember” its original state after being bent or stretched. These glasses are made from a “smart” material – if they are bent they will return to their original shape. They could be made from an alloy called “nitinol” (an alloy of nickel and titanium) which can be bent but then returned to its original shape simply by heating to its “transformation temperature”.
Smart Alloys 3/16/2018 A “smart alloy” is one that can “remember” its original state after being bent or stretched. These glasses are made from a “smart” material – if they are bent they will return to their original shape. They could be made from an alloy called “nitinol” (an alloy of nickel and titanium) which can be bent but then returned to its original shape simply by heating to its “transformation temperature”.
 Gold alloys 3/16/2018 Gold can be mixed with other metals to make alloys with different properties. For example: 24 -Carat gold 9 -Carat gold “Pure gold” – 99. 99% of the atoms in this bar are gold atoms (fineness off 999. 9). Pure and malleable but soft. “ 9 carat gold” – around 9/24 ths of the atoms in these earrings are gold atoms. Harder than pure gold but less malleable.
Gold alloys 3/16/2018 Gold can be mixed with other metals to make alloys with different properties. For example: 24 -Carat gold 9 -Carat gold “Pure gold” – 99. 99% of the atoms in this bar are gold atoms (fineness off 999. 9). Pure and malleable but soft. “ 9 carat gold” – around 9/24 ths of the atoms in these earrings are gold atoms. Harder than pure gold but less malleable.
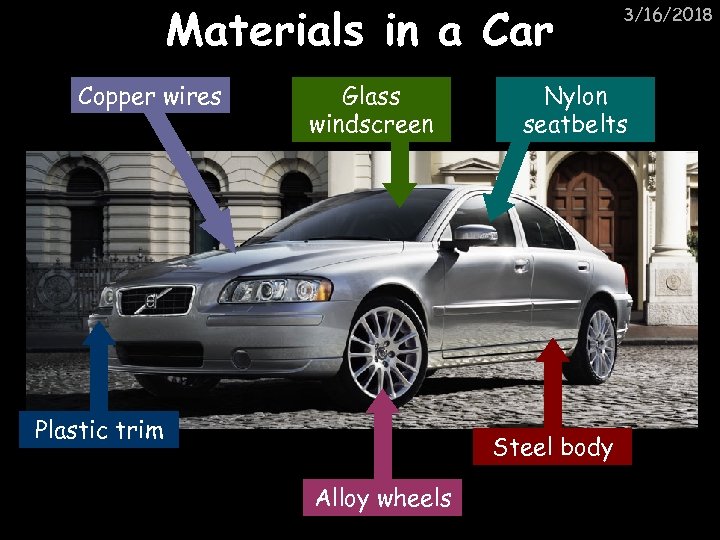 Materials in a Car Copper wires Glass windscreen Plastic trim Nylon seatbelts Steel body Alloy wheels 3/16/2018
Materials in a Car Copper wires Glass windscreen Plastic trim Nylon seatbelts Steel body Alloy wheels 3/16/2018
 Iron or aluminium? 3/16/2018 Aluminium: Does not corrode Less dense so it’s lighter Iron: Cheaper than aluminium Magnetic so easily recycled Most cars are made from steel (an alloy of carbon) From 2015 95% of a car will have to be made from recycled material. What are the advantages of this?
Iron or aluminium? 3/16/2018 Aluminium: Does not corrode Less dense so it’s lighter Iron: Cheaper than aluminium Magnetic so easily recycled Most cars are made from steel (an alloy of carbon) From 2015 95% of a car will have to be made from recycled material. What are the advantages of this?
 Recycling 3/16/2018 Why recycle metals? 1) Less space will be needed for landfill sites 2) Recycled metals only need about 1/10 th of the energy to produce compared to producing new metals 3) Recycling saves on raw materials 4) Less excavation and mining costs
Recycling 3/16/2018 Why recycle metals? 1) Less space will be needed for landfill sites 2) Recycled metals only need about 1/10 th of the energy to produce compared to producing new metals 3) Recycling saves on raw materials 4) Less excavation and mining costs
 Rusting 3/16/2018 Rust is a hydrated form of iron oxide. It is formed when iron and/or steel combines with oxygen and water in an oxidation reaction: Iron + oxygen + water hydrated iron (III) oxide
Rusting 3/16/2018 Rust is a hydrated form of iron oxide. It is formed when iron and/or steel combines with oxygen and water in an oxidation reaction: Iron + oxygen + water hydrated iron (III) oxide
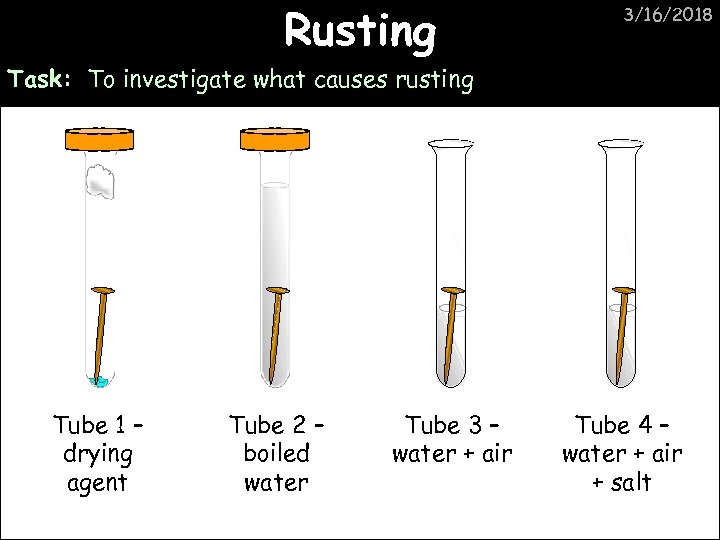 Rusting 3/16/2018 Task: To investigate what causes rusting Tube 1 – drying agent Tube 2 – boiled water Tube 3 – water + air Tube 4 – water + air + salt
Rusting 3/16/2018 Task: To investigate what causes rusting Tube 1 – drying agent Tube 2 – boiled water Tube 3 – water + air Tube 4 – water + air + salt
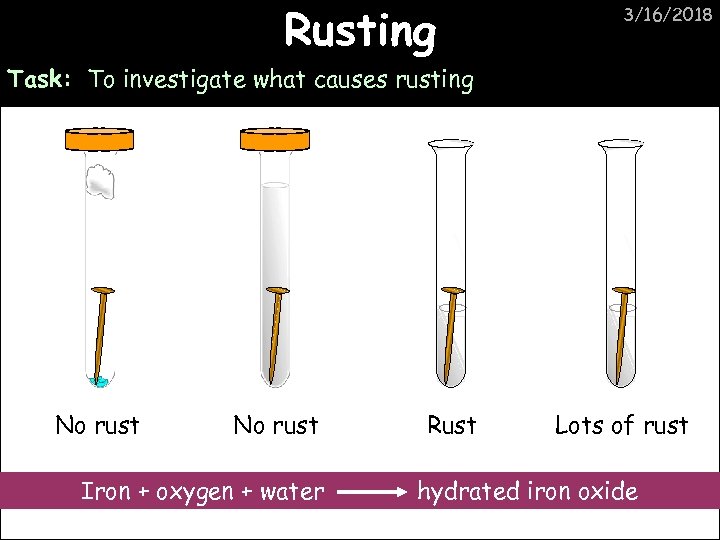 Rusting 3/16/2018 Task: To investigate what causes rusting No rust Iron + oxygen + water Rust Lots of rust hydrated iron oxide
Rusting 3/16/2018 Task: To investigate what causes rusting No rust Iron + oxygen + water Rust Lots of rust hydrated iron oxide
 More on Redox Reactions 3/16/2018 Basically, during a redox reaction electrons are either lost or gained: The Golden Rule: OILRIG Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons) Reduction Is Gain (of electrons) For example: Fe Fe 2+ 2 Cl- Cl 2 Fe 2+ Fe Cl 2 2 Cl- These reactions both involve the loss of electrons – they are Oxidation reactions These reactions both involve the gain of electrons – they are Reduction reactions
More on Redox Reactions 3/16/2018 Basically, during a redox reaction electrons are either lost or gained: The Golden Rule: OILRIG Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons) Reduction Is Gain (of electrons) For example: Fe Fe 2+ 2 Cl- Cl 2 Fe 2+ Fe Cl 2 2 Cl- These reactions both involve the loss of electrons – they are Oxidation reactions These reactions both involve the gain of electrons – they are Reduction reactions
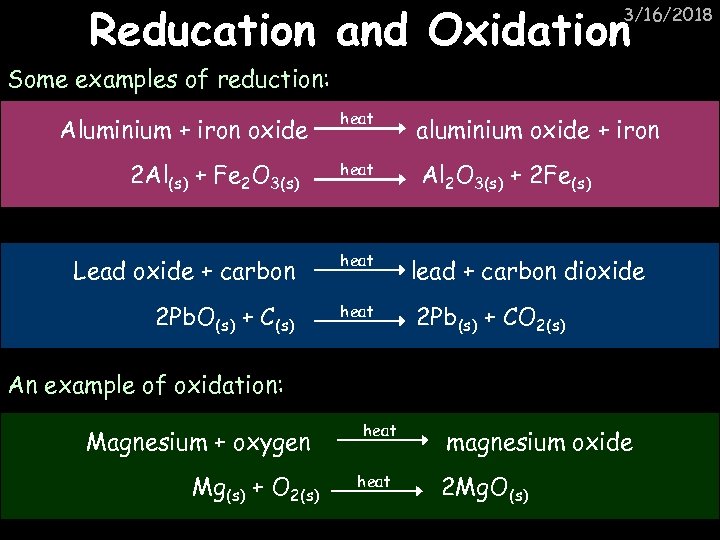 Reducation and Oxidation 3/16/2018 Some examples of reduction: heat aluminium oxide + iron 2 Al(s) + Fe 2 O 3(s) heat Al 2 O 3(s) + 2 Fe(s) Lead oxide + carbon heat 2 Pb. O(s) + C(s) heat Aluminium + iron oxide lead + carbon dioxide 2 Pb(s) + CO 2(s) An example of oxidation: Magnesium + oxygen Mg(s) + O 2(s) heat magnesium oxide 2 Mg. O(s)
Reducation and Oxidation 3/16/2018 Some examples of reduction: heat aluminium oxide + iron 2 Al(s) + Fe 2 O 3(s) heat Al 2 O 3(s) + 2 Fe(s) Lead oxide + carbon heat 2 Pb. O(s) + C(s) heat Aluminium + iron oxide lead + carbon dioxide 2 Pb(s) + CO 2(s) An example of oxidation: Magnesium + oxygen Mg(s) + O 2(s) heat magnesium oxide 2 Mg. O(s)
 Topic 5 – Fuels 3/16/2018
Topic 5 – Fuels 3/16/2018
 Fuels 3/16/2018 Fuels are substances that can be used to release useful amounts of energy when they burn, e. g. Wood Oil Gas Coal These fuels are called “fossil fuels” and are described as being “non-renewable”.
Fuels 3/16/2018 Fuels are substances that can be used to release useful amounts of energy when they burn, e. g. Wood Oil Gas Coal These fuels are called “fossil fuels” and are described as being “non-renewable”.
 Crude Oil 3/16/2018
Crude Oil 3/16/2018
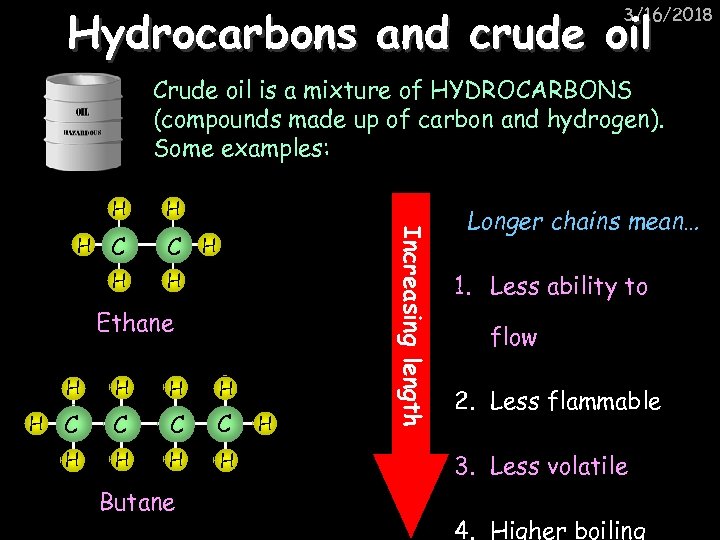 Hydrocarbons and crude oil 3/16/2018 Crude oil is a mixture of HYDROCARBONS (compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen). Some examples: C C H H H Ethane H H H C C H H Butane H Increasing length H Longer chains mean… 1. Less ability to flow 2. Less flammable 3. Less volatile 4. Higher boiling
Hydrocarbons and crude oil 3/16/2018 Crude oil is a mixture of HYDROCARBONS (compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen). Some examples: C C H H H Ethane H H H C C H H Butane H Increasing length H Longer chains mean… 1. Less ability to flow 2. Less flammable 3. Less volatile 4. Higher boiling
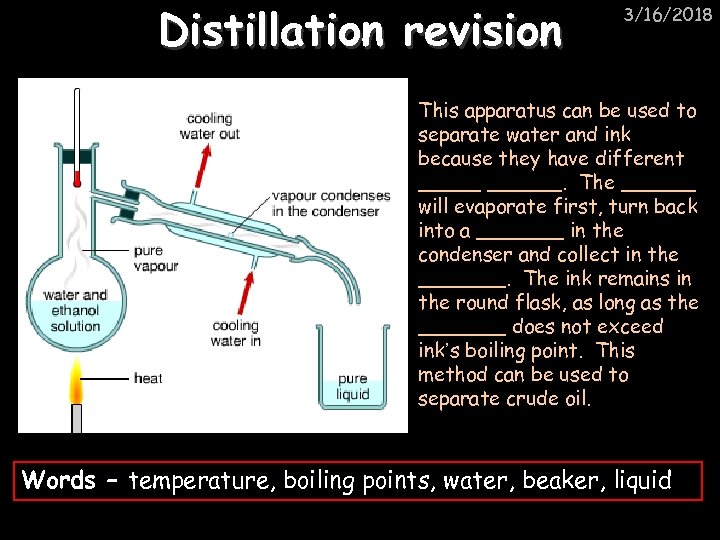 Distillation revision 3/16/2018 This apparatus can be used to separate water and ink because they have different ______. The ______ will evaporate first, turn back into a _______ in the condenser and collect in the _______. The ink remains in the round flask, as long as the _______ does not exceed ink’s boiling point. This method can be used to separate crude oil. Words – temperature, boiling points, water, beaker, liquid
Distillation revision 3/16/2018 This apparatus can be used to separate water and ink because they have different ______. The ______ will evaporate first, turn back into a _______ in the condenser and collect in the _______. The ink remains in the round flask, as long as the _______ does not exceed ink’s boiling point. This method can be used to separate crude oil. Words – temperature, boiling points, water, beaker, liquid
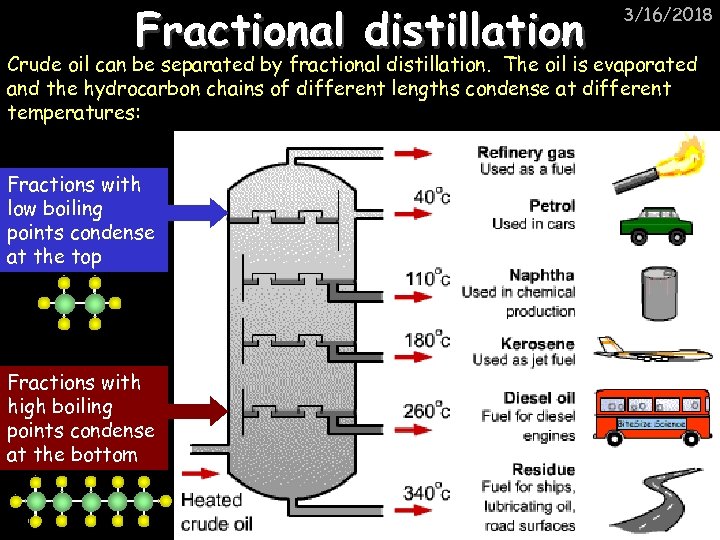 Fractional distillation 3/16/2018 Crude oil can be separated by fractional distillation. The oil is evaporated and the hydrocarbon chains of different lengths condense at different temperatures: Fractions with low boiling points condense at the top Fractions with high boiling points condense at the bottom
Fractional distillation 3/16/2018 Crude oil can be separated by fractional distillation. The oil is evaporated and the hydrocarbon chains of different lengths condense at different temperatures: Fractions with low boiling points condense at the top Fractions with high boiling points condense at the bottom
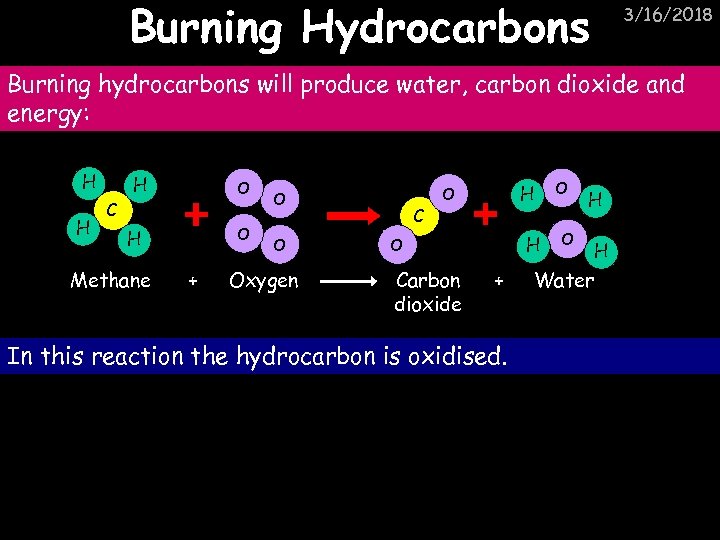 Burning Hydrocarbons 3/16/2018 Burning hydrocarbons will produce water, carbon dioxide and energy: H H H O C O H Methane + O O Oxygen C H O Carbon dioxide + In this reaction the hydrocarbon is oxidised. O O H H Water
Burning Hydrocarbons 3/16/2018 Burning hydrocarbons will produce water, carbon dioxide and energy: H H H O C O H Methane + O O Oxygen C H O Carbon dioxide + In this reaction the hydrocarbon is oxidised. O O H H Water
 Testing for Carbon Dioxide 3/16/2018 Gas Limewater turns milky/cloudy
Testing for Carbon Dioxide 3/16/2018 Gas Limewater turns milky/cloudy
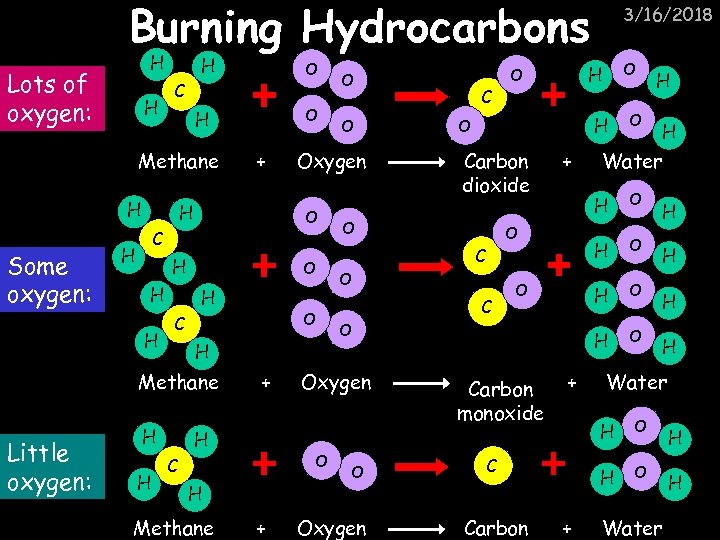 Burning Hydrocarbons H Lots of oxygen: H H C H + H H O H H Methane H H O C + H H Methane + O C H Carbon dioxide + C Carbon monoxide + O O H H O H + H Water H C Carbon O H O H Water H O Oxygen O H O C O O H O Oxygen O C H Little oxygen: O H Methane Some oxygen: O 3/16/2018 O Water H H
Burning Hydrocarbons H Lots of oxygen: H H C H + H H O H H Methane H H O C + H H Methane + O C H Carbon dioxide + C Carbon monoxide + O O H H O H + H Water H C Carbon O H O H Water H O Oxygen O H O C O O H O Oxygen O C H Little oxygen: O H Methane Some oxygen: O 3/16/2018 O Water H H
 Why Carbon Monoxide is Dangerous 3/16/2018 Basically, carbon monoxide “sticks” to red blood cells instead of oxygen, causing anybody inhaling it to essentially suffocate: CO 1) Carbon Monoxide is breathed in 2) The molecule “sticks” to red blood cells instead of oxygen 3) The red blood cells transport the “carboxyhaemoglobin” molecule to the rest of the body and the body’s cells are starved of the oxygen needed for respiration. Carbon monoxide is odourless, colourless and non-irritating so it’s very difficult to detect!
Why Carbon Monoxide is Dangerous 3/16/2018 Basically, carbon monoxide “sticks” to red blood cells instead of oxygen, causing anybody inhaling it to essentially suffocate: CO 1) Carbon Monoxide is breathed in 2) The molecule “sticks” to red blood cells instead of oxygen 3) The red blood cells transport the “carboxyhaemoglobin” molecule to the rest of the body and the body’s cells are starved of the oxygen needed for respiration. Carbon monoxide is odourless, colourless and non-irritating so it’s very difficult to detect!
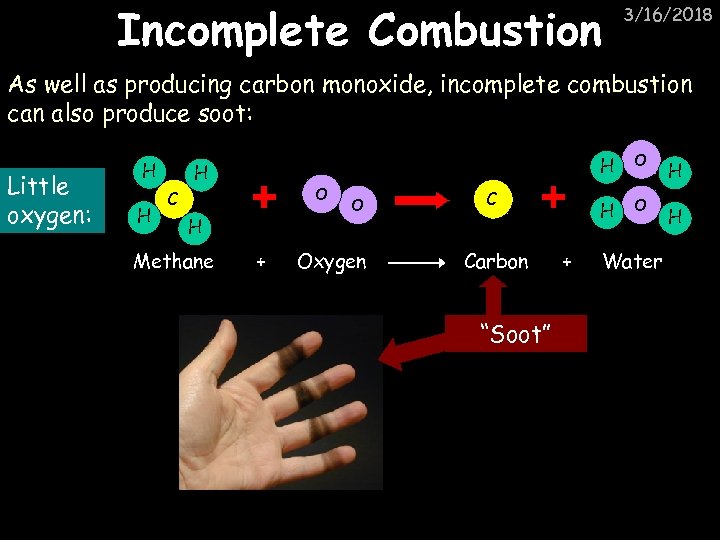 Incomplete Combustion 3/16/2018 As well as producing carbon monoxide, incomplete combustion can also produce soot: Little oxygen: H H O C H Methane + O Oxygen H C Carbon “Soot” + O O Water H H
Incomplete Combustion 3/16/2018 As well as producing carbon monoxide, incomplete combustion can also produce soot: Little oxygen: H H O C H Methane + O Oxygen H C Carbon “Soot” + O O Water H H
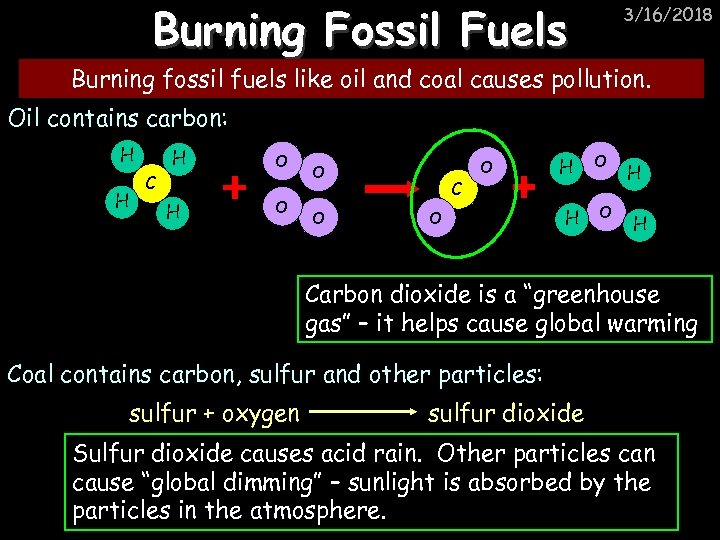 Burning Fossil Fuels 3/16/2018 Burning fossil fuels like oil and coal causes pollution. Oil contains carbon: H H H C H O O C O O H H Carbon dioxide is a “greenhouse gas” – it helps cause global warming Coal contains carbon, sulfur and other particles: sulfur + oxygen sulfur dioxide Sulfur dioxide causes acid rain. Other particles can cause “global dimming” – sunlight is absorbed by the particles in the atmosphere.
Burning Fossil Fuels 3/16/2018 Burning fossil fuels like oil and coal causes pollution. Oil contains carbon: H H H C H O O C O O H H Carbon dioxide is a “greenhouse gas” – it helps cause global warming Coal contains carbon, sulfur and other particles: sulfur + oxygen sulfur dioxide Sulfur dioxide causes acid rain. Other particles can cause “global dimming” – sunlight is absorbed by the particles in the atmosphere.
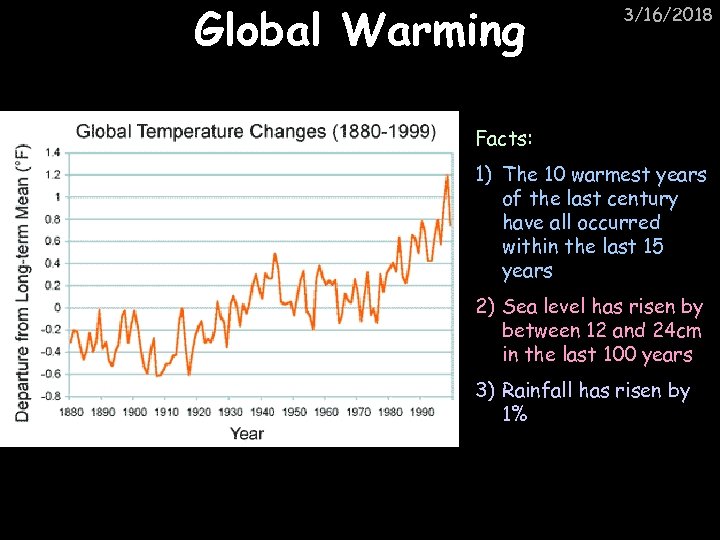 Global Warming 3/16/2018 Facts: 1) The 10 warmest years of the last century have all occurred within the last 15 years 2) Sea level has risen by between 12 and 24 cm in the last 100 years 3) Rainfall has risen by 1%
Global Warming 3/16/2018 Facts: 1) The 10 warmest years of the last century have all occurred within the last 15 years 2) Sea level has risen by between 12 and 24 cm in the last 100 years 3) Rainfall has risen by 1%
 The Greenhouse Effect We get heat from the sun: 3/16/2018 A lot of this heat is _______ back into space. However, most of it is kept inside the Earth by a layer of gases that prevent the heat escaping by _______ and then re-radiating it back again. This is called the _____ Effect. It has always been around, but is currently being made worse due to: 1) Burning (releasing CO 2) 2) _____ (removing trees that remove CO 2) 3) Increased micro organism activity (from rotting ______) 4) Cattle and rice fields (they both produce _______) These changes will cause GLOBAL WARMING and RISING SEA LEVELS Words – methane, radiated, absorbing, deforestation, waste, greenhouse
The Greenhouse Effect We get heat from the sun: 3/16/2018 A lot of this heat is _______ back into space. However, most of it is kept inside the Earth by a layer of gases that prevent the heat escaping by _______ and then re-radiating it back again. This is called the _____ Effect. It has always been around, but is currently being made worse due to: 1) Burning (releasing CO 2) 2) _____ (removing trees that remove CO 2) 3) Increased micro organism activity (from rotting ______) 4) Cattle and rice fields (they both produce _______) These changes will cause GLOBAL WARMING and RISING SEA LEVELS Words – methane, radiated, absorbing, deforestation, waste, greenhouse
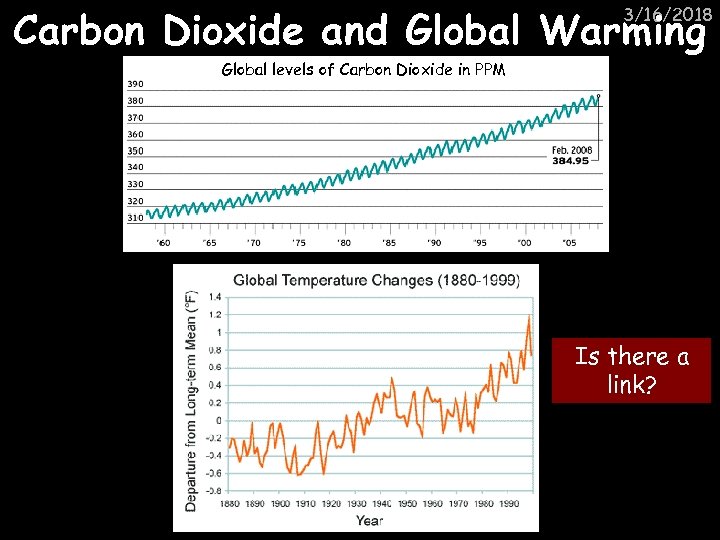 Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming 3/16/2018 Global levels of Carbon Dioxide in PPM Is there a link?
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming 3/16/2018 Global levels of Carbon Dioxide in PPM Is there a link?
 3/16/2018 Reducing the amount of Carbon Dioxide Scientists are trying to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through a number of possibilities: 1) “Iron seeding” – this is the process where iron is intentionally put in seawater to help produce more phytoplankton which then increases photosynthetic activity, therefore reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere. Aerial view of phytoplankton near Argentina 2) Converting CO 2 into hydrocarbons – carbon dioxide can be converted into hydrocarbons and then stored in the Earth by putting it in such places as old oil fields or coal beds.
3/16/2018 Reducing the amount of Carbon Dioxide Scientists are trying to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through a number of possibilities: 1) “Iron seeding” – this is the process where iron is intentionally put in seawater to help produce more phytoplankton which then increases photosynthetic activity, therefore reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere. Aerial view of phytoplankton near Argentina 2) Converting CO 2 into hydrocarbons – carbon dioxide can be converted into hydrocarbons and then stored in the Earth by putting it in such places as old oil fields or coal beds.
 Reducing Pollution from vehicles 3/16/2018 A number of suggestions: 1) Buy a new, smaller, cleaner car 2) Buy a “hybrid” car 3) Convert your car to run on biodiesel 4) Make sure your car has a catalytic converter: Carbon monoxide + oxygen Nitrogen monoxide + carbon monoxide 5) Use the train or a bus! carbon dioxide nitrogen + carbon monoxide
Reducing Pollution from vehicles 3/16/2018 A number of suggestions: 1) Buy a new, smaller, cleaner car 2) Buy a “hybrid” car 3) Convert your car to run on biodiesel 4) Make sure your car has a catalytic converter: Carbon monoxide + oxygen Nitrogen monoxide + carbon monoxide 5) Use the train or a bus! carbon dioxide nitrogen + carbon monoxide
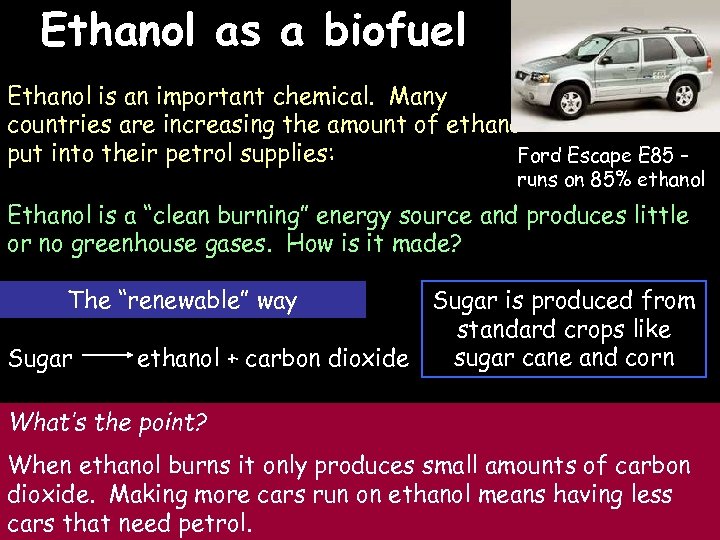 Ethanol as a biofuel 3/16/2018 Ethanol is an important chemical. Many countries are increasing the amount of ethanol put into their petrol supplies: Ford Escape E 85 – runs on 85% ethanol Ethanol is a “clean burning” energy source and produces little or no greenhouse gases. How is it made? The “renewable” way Sugar is produced from standard crops like sugar cane and corn ethanol + carbon dioxide What’s the point? When ethanol burns it only produces small amounts of carbon dioxide. Making more cars run on ethanol means having less cars that need petrol.
Ethanol as a biofuel 3/16/2018 Ethanol is an important chemical. Many countries are increasing the amount of ethanol put into their petrol supplies: Ford Escape E 85 – runs on 85% ethanol Ethanol is a “clean burning” energy source and produces little or no greenhouse gases. How is it made? The “renewable” way Sugar is produced from standard crops like sugar cane and corn ethanol + carbon dioxide What’s the point? When ethanol burns it only produces small amounts of carbon dioxide. Making more cars run on ethanol means having less cars that need petrol.
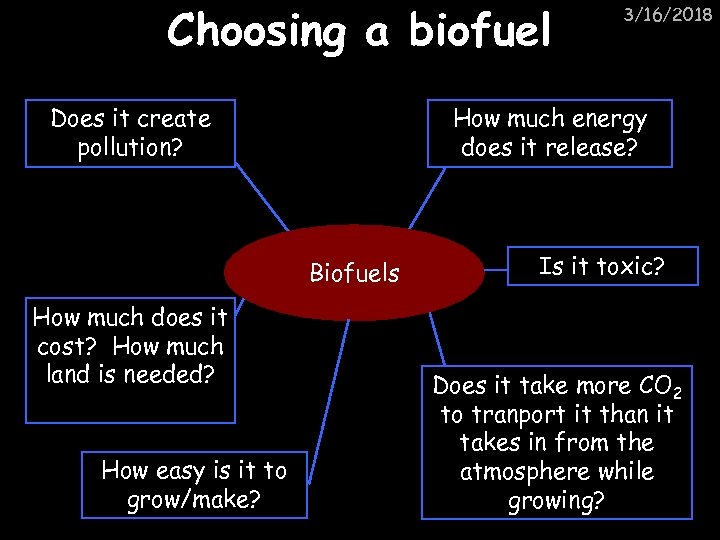 Choosing a biofuel Does it create pollution? How much energy does it release? Biofuels How much does it cost? How much land is needed? How easy is it to grow/make? 3/16/2018 Is it toxic? Does it take more CO 2 to tranport it than it takes in from the atmosphere while growing?
Choosing a biofuel Does it create pollution? How much energy does it release? Biofuels How much does it cost? How much land is needed? How easy is it to grow/make? 3/16/2018 Is it toxic? Does it take more CO 2 to tranport it than it takes in from the atmosphere while growing?
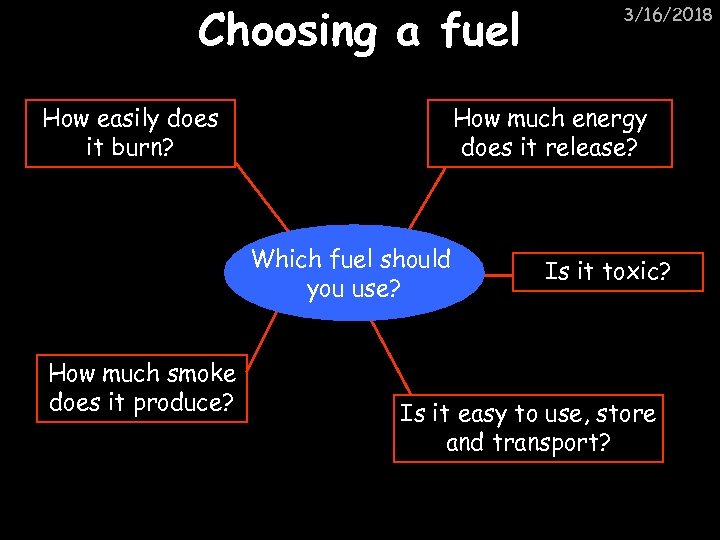 Choosing a fuel How easily does it burn? How much energy does it release? Which fuel should you use? How much smoke does it produce? 3/16/2018 Is it toxic? Is it easy to use, store and transport?
Choosing a fuel How easily does it burn? How much energy does it release? Which fuel should you use? How much smoke does it produce? 3/16/2018 Is it toxic? Is it easy to use, store and transport?
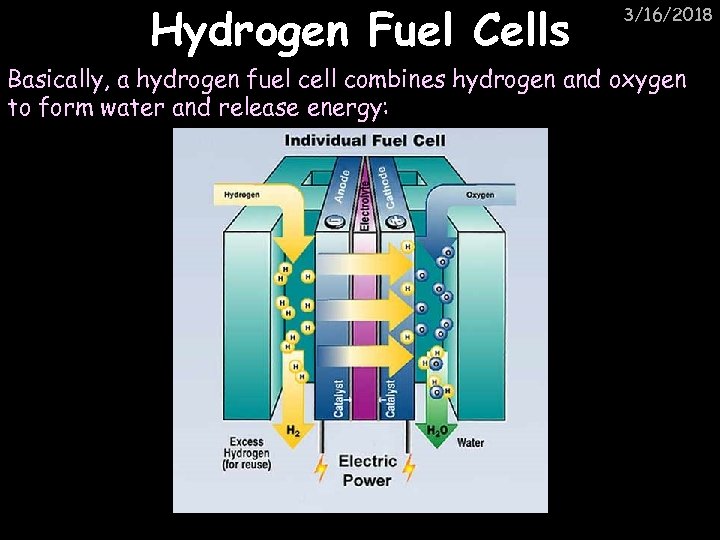 Hydrogen Fuel Cells 3/16/2018 Basically, a hydrogen fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to form water and release energy:
Hydrogen Fuel Cells 3/16/2018 Basically, a hydrogen fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to form water and release energy:
 Hydrogen Fuel Cells Advantages of fuel cells 3/16/2018 Advantages of petrol Hydrogen fuel cells vs Petrol
Hydrogen Fuel Cells Advantages of fuel cells 3/16/2018 Advantages of petrol Hydrogen fuel cells vs Petrol
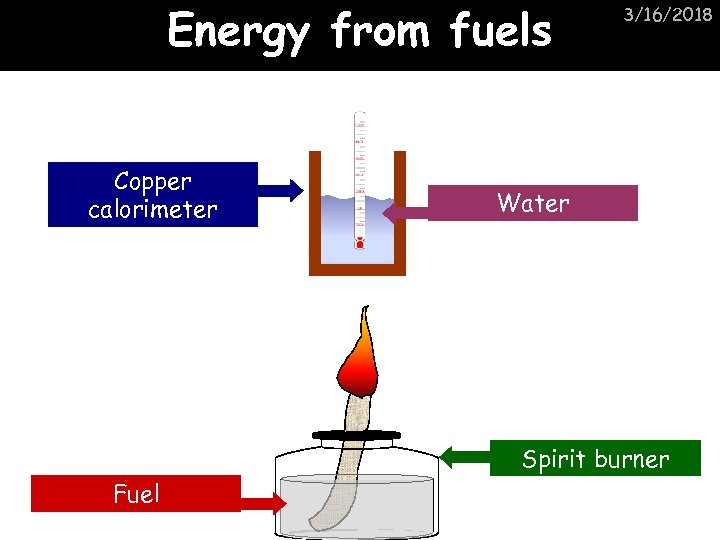 Energy from fuels Copper calorimeter 3/16/2018 Water Spirit burner Fuel
Energy from fuels Copper calorimeter 3/16/2018 Water Spirit burner Fuel
 Where fossil fuels come from 3/16/2018 Petrol, kerosene and diesel oil are non-renewable fossil fuels that come from crude oil. Methane is a non-renewable fossil fuel found in natural gas.
Where fossil fuels come from 3/16/2018 Petrol, kerosene and diesel oil are non-renewable fossil fuels that come from crude oil. Methane is a non-renewable fossil fuel found in natural gas.
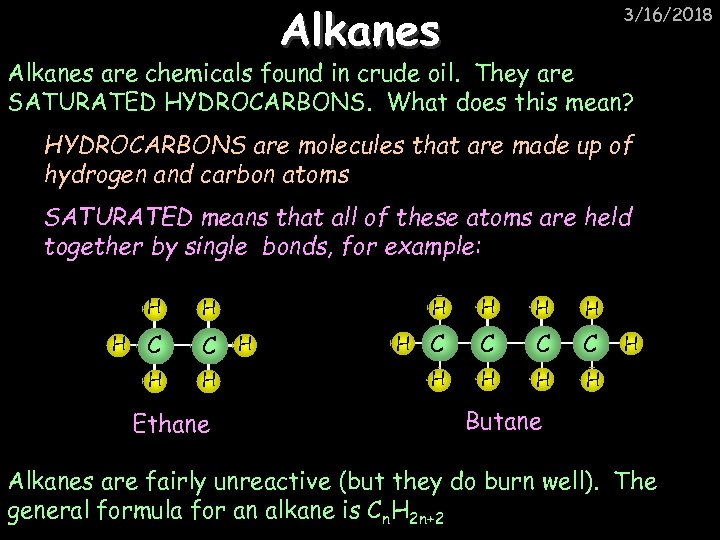 Alkanes 3/16/2018 Alkanes are chemicals found in crude oil. They are SATURATED HYDROCARBONS. What does this mean? HYDROCARBONS are molecules that are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms SATURATED means that all of these atoms are held together by single bonds, for example: H C C H H Ethane H H H C C H H H Butane Alkanes are fairly unreactive (but they do burn well). The general formula for an alkane is Cn. H 2 n+2
Alkanes 3/16/2018 Alkanes are chemicals found in crude oil. They are SATURATED HYDROCARBONS. What does this mean? HYDROCARBONS are molecules that are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms SATURATED means that all of these atoms are held together by single bonds, for example: H C C H H Ethane H H H C C H H H Butane Alkanes are fairly unreactive (but they do burn well). The general formula for an alkane is Cn. H 2 n+2
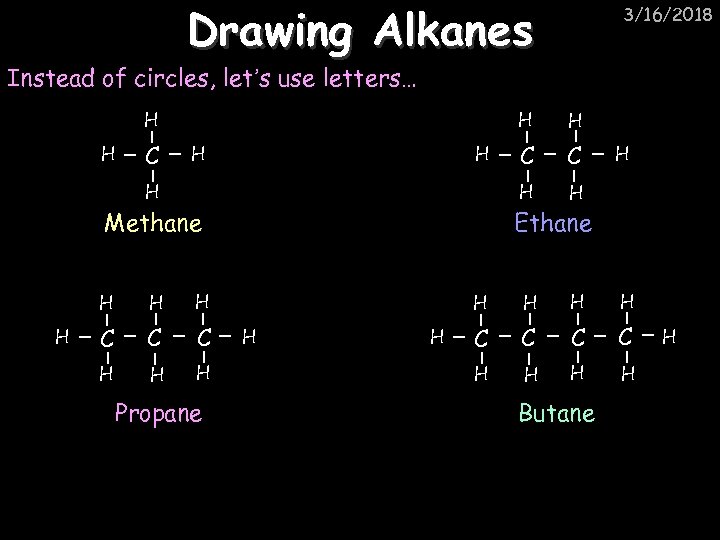 Drawing Alkanes 3/16/2018 Instead of circles, let’s use letters… H H C H H H Methane H H H C C H H H Propane C C H H Ethane H H C H H H H C C H H Butane H
Drawing Alkanes 3/16/2018 Instead of circles, let’s use letters… H H C H H H Methane H H H C C H H H Propane C C H H Ethane H H C H H H H C C H H Butane H
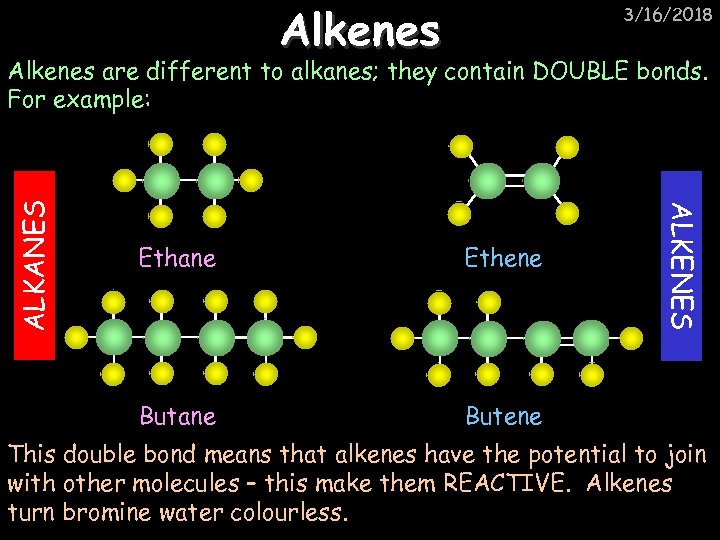 Alkenes 3/16/2018 Ethane Ethene Butane ALKENES ALKANES Alkenes are different to alkanes; they contain DOUBLE bonds. For example: Butene This double bond means that alkenes have the potential to join with other molecules – this make them REACTIVE. Alkenes turn bromine water colourless.
Alkenes 3/16/2018 Ethane Ethene Butane ALKENES ALKANES Alkenes are different to alkanes; they contain DOUBLE bonds. For example: Butene This double bond means that alkenes have the potential to join with other molecules – this make them REACTIVE. Alkenes turn bromine water colourless.
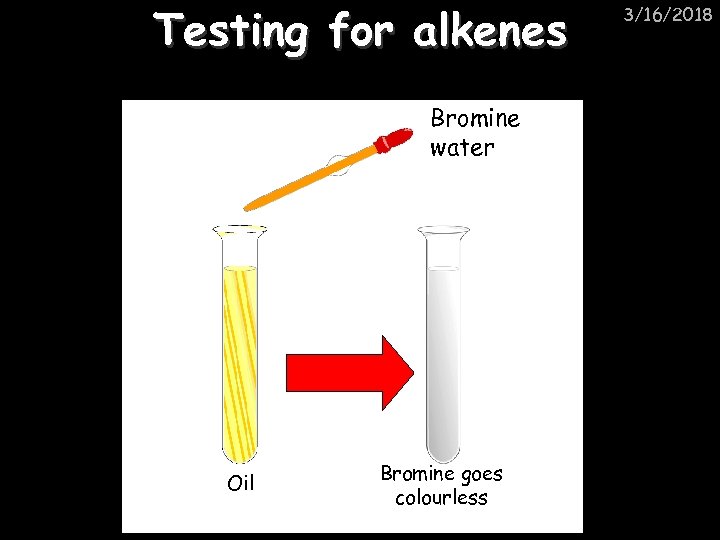 Testing for alkenes Bromine water Oil Bromine goes colourless 3/16/2018
Testing for alkenes Bromine water Oil Bromine goes colourless 3/16/2018
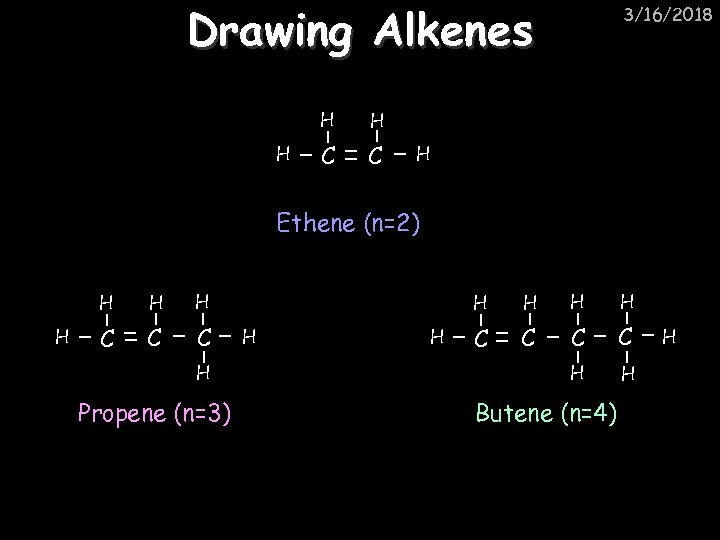 Drawing Alkenes H H H C C 3/16/2018 H Ethene (n=2) H H C C C H Propene (n=3) H H H C C H H Butene (n=4) H
Drawing Alkenes H H H C C 3/16/2018 H Ethene (n=2) H H C C C H Propene (n=3) H H H C C H H Butene (n=4) H
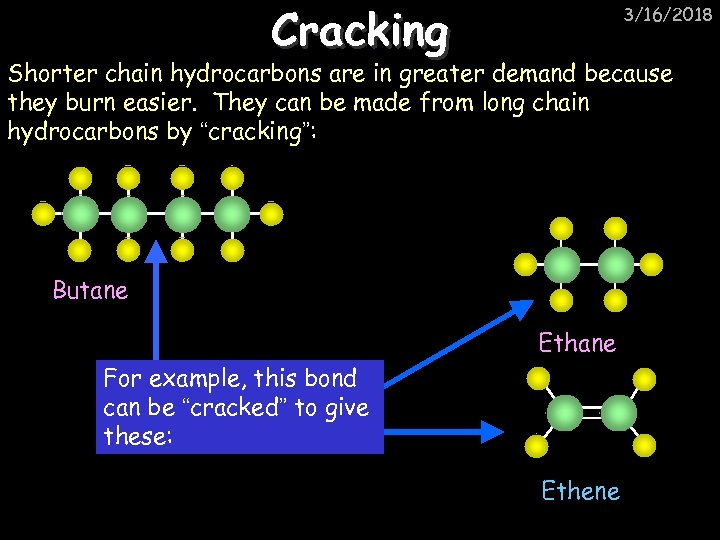 Cracking 3/16/2018 Shorter chain hydrocarbons are in greater demand because they burn easier. They can be made from long chain hydrocarbons by “cracking”: Butane Ethane For example, this bond can be “cracked” to give these: Ethene
Cracking 3/16/2018 Shorter chain hydrocarbons are in greater demand because they burn easier. They can be made from long chain hydrocarbons by “cracking”: Butane Ethane For example, this bond can be “cracked” to give these: Ethene
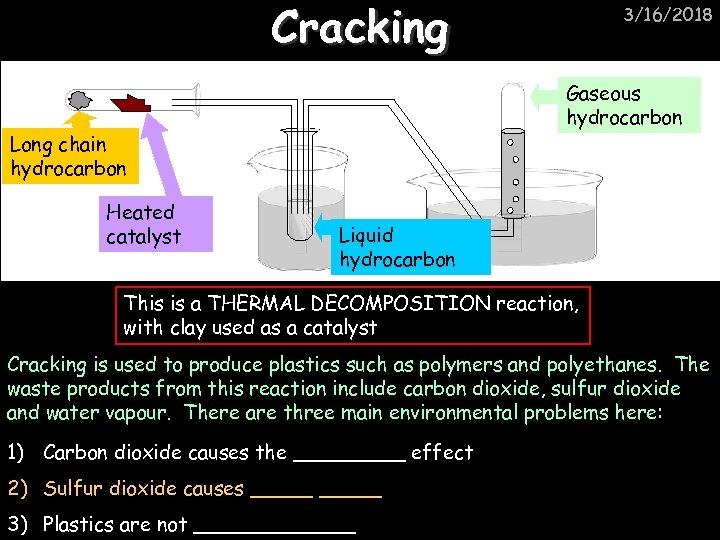 Cracking Gaseous hydrocarbon Long chain hydrocarbon Heated catalyst 3/16/2018 Liquid hydrocarbon This is a THERMAL DECOMPOSITION reaction, with clay used as a catalyst Cracking is used to produce plastics such as polymers and polyethanes. The waste products from this reaction include carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and water vapour. There are three main environmental problems here: 1) Carbon dioxide causes the _____ effect 2) Sulfur dioxide causes _____ 3) Plastics are not _______
Cracking Gaseous hydrocarbon Long chain hydrocarbon Heated catalyst 3/16/2018 Liquid hydrocarbon This is a THERMAL DECOMPOSITION reaction, with clay used as a catalyst Cracking is used to produce plastics such as polymers and polyethanes. The waste products from this reaction include carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and water vapour. There are three main environmental problems here: 1) Carbon dioxide causes the _____ effect 2) Sulfur dioxide causes _____ 3) Plastics are not _______
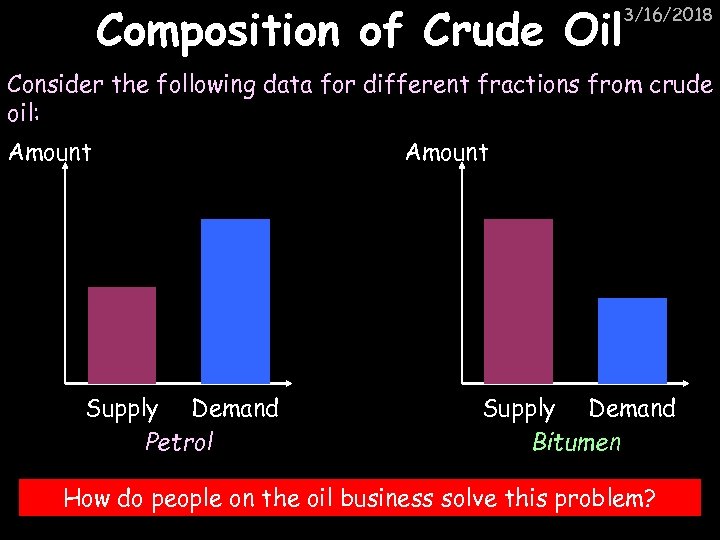 Composition of Crude Oil 3/16/2018 Consider the following data for different fractions from crude oil: Amount Supply Demand Petrol Amount Supply Demand Bitumen How do people on the oil business solve this problem?
Composition of Crude Oil 3/16/2018 Consider the following data for different fractions from crude oil: Amount Supply Demand Petrol Amount Supply Demand Bitumen How do people on the oil business solve this problem?
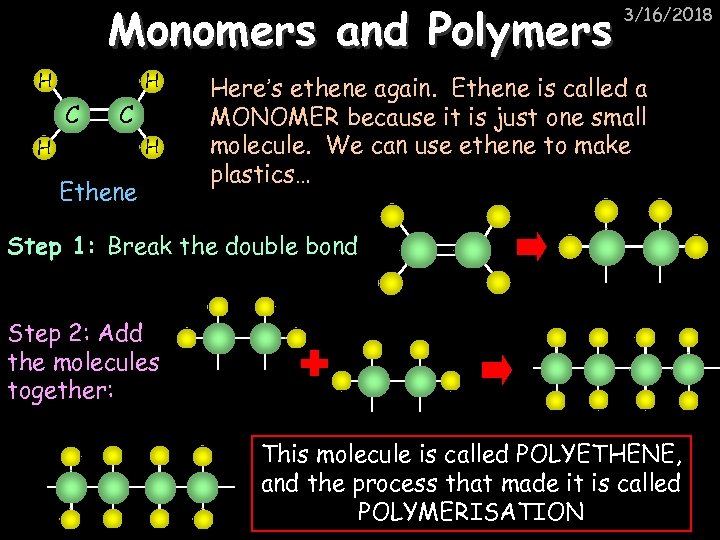 Monomers and Polymers H H C C H H Ethene 3/16/2018 Here’s ethene again. Ethene is called a MONOMER because it is just one small molecule. We can use ethene to make plastics… Step 1: Break the double bond Step 2: Add the molecules together: This molecule is called POLYETHENE, and the process that made it is called POLYMERISATION
Monomers and Polymers H H C C H H Ethene 3/16/2018 Here’s ethene again. Ethene is called a MONOMER because it is just one small molecule. We can use ethene to make plastics… Step 1: Break the double bond Step 2: Add the molecules together: This molecule is called POLYETHENE, and the process that made it is called POLYMERISATION
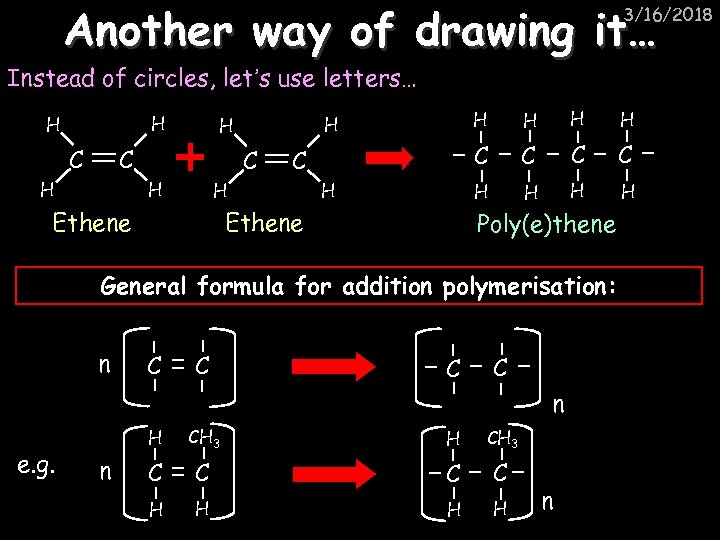 Another way of drawing it… 3/16/2018 Instead of circles, let’s use letters… H H C C H Ethene H H C C C H H H C C H Ethene H H H Poly(e)thene General formula for addition polymerisation: n C C n e. g. H n CH 3 H CH 3 C C H H n
Another way of drawing it… 3/16/2018 Instead of circles, let’s use letters… H H C C H Ethene H H C C C H H H C C H Ethene H H H Poly(e)thene General formula for addition polymerisation: n C C n e. g. H n CH 3 H CH 3 C C H H n
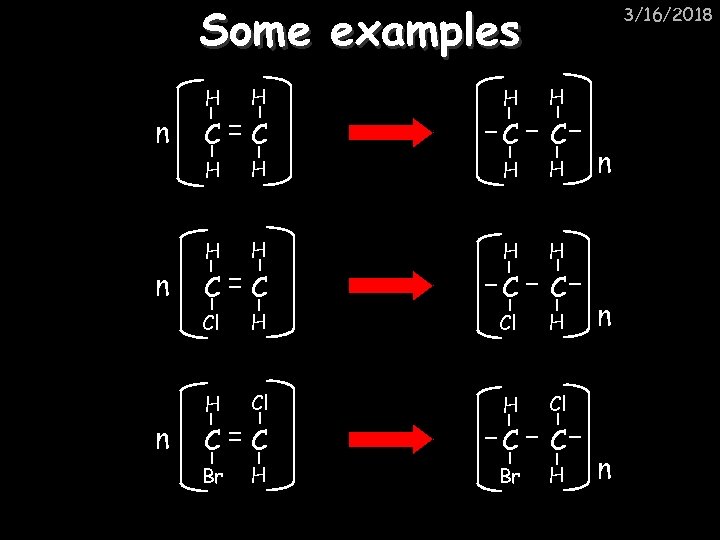 Some examples 3/16/2018 H C C H H H C C Cl H H n H Cl C C Br H n n n
Some examples 3/16/2018 H C C H H H C C Cl H H n H Cl C C Br H n n n
 Uses of addition polymers 3/16/2018 Poly(ethene) Poly(propene) Poly(styrene) Poly(chloroethene), PVC
Uses of addition polymers 3/16/2018 Poly(ethene) Poly(propene) Poly(styrene) Poly(chloroethene), PVC
 Disposal of plastics 3/16/2018 1) Landfill sites - most plastics do not _____ which means that landfill sites are quickly filled up. Research is being carried out on _____ plastics. 2) Burning – this releases carbon dioxide which causes the ____ effect, as well as other ____ gases. 3) _______ – the best option, but difficult because of the different types of plastic Words – recycling, greenhouse, decompose, biodegradable, poisonous
Disposal of plastics 3/16/2018 1) Landfill sites - most plastics do not _____ which means that landfill sites are quickly filled up. Research is being carried out on _____ plastics. 2) Burning – this releases carbon dioxide which causes the ____ effect, as well as other ____ gases. 3) _______ – the best option, but difficult because of the different types of plastic Words – recycling, greenhouse, decompose, biodegradable, poisonous
 Biodegradable carrier bags 3/16/2018 This carrier bag has been made with flax fibre from industrial waste.
Biodegradable carrier bags 3/16/2018 This carrier bag has been made with flax fibre from industrial waste.


