3f3cd1fae9777b0a249812bdbc4e27d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 120
 3 -1 The Unification of Germany
3 -1 The Unification of Germany
 Moving Toward a Unified Germany • Between 1807 and 1812 Napoleon took lands from Germans, dissolved the Holy Roman Empire, and put German states into the Rhine confederation
Moving Toward a Unified Germany • Between 1807 and 1812 Napoleon took lands from Germans, dissolved the Holy Roman Empire, and put German states into the Rhine confederation
 • He freed serfs, made trade easier and abolished rules against Jews • Some Germans fought to free their lands and demanded a unified German state • The Congress of Vienna created the German Confederation and put Austria in charge • 1830 the Zollverein dismantled trade barriers between German states
• He freed serfs, made trade easier and abolished rules against Jews • Some Germans fought to free their lands and demanded a unified German state • The Congress of Vienna created the German Confederation and put Austria in charge • 1830 the Zollverein dismantled trade barriers between German states
 Standard • W. 13 Summarize the causes, course, and consequences of unification in Italy and Germany including the role of Giuseppe Garibaldi and Otto von Bismarck.
Standard • W. 13 Summarize the causes, course, and consequences of unification in Italy and Germany including the role of Giuseppe Garibaldi and Otto von Bismarck.
 Objective • A. Identify Otto Von Bismarck and William I
Objective • A. Identify Otto Von Bismarck and William I
 Bismarck Becomes the Architect of German Unity • Otto von Bismarck came from the Junker class (conservative landowners) • He became chancellor in 1862 • Realpolitik- realistic politics
Bismarck Becomes the Architect of German Unity • Otto von Bismarck came from the Junker class (conservative landowners) • He became chancellor in 1862 • Realpolitik- realistic politics
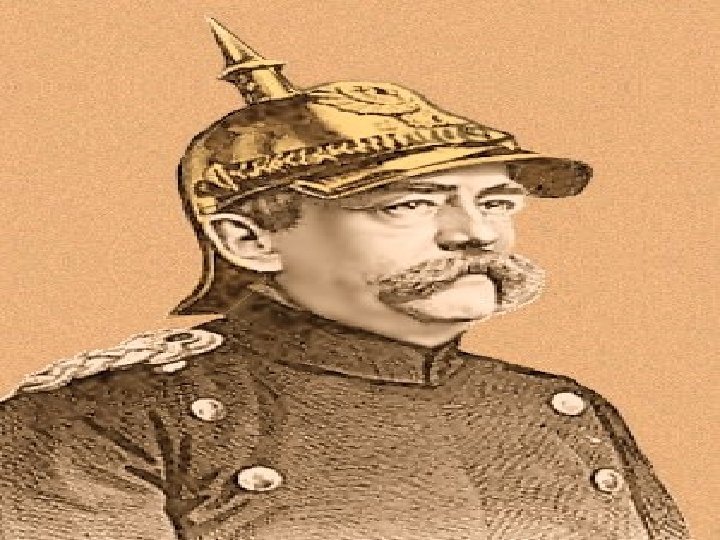
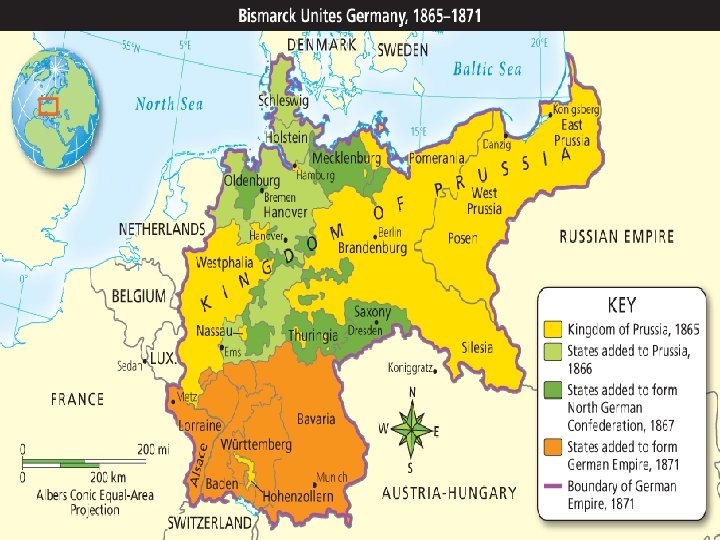

 • In 1864 he signed an alliance with Austria • He then invented an excuse to attack Austria and annexed several more German states • He dissolved the Austrian-led German Confederation and created a new confederation dominated by Prussia • They defeated France in a quick war
• In 1864 he signed an alliance with Austria • He then invented an excuse to attack Austria and annexed several more German states • He dissolved the Austrian-led German Confederation and created a new confederation dominated by Prussia • They defeated France in a quick war
 Objective • B. Define Kaiser
Objective • B. Define Kaiser
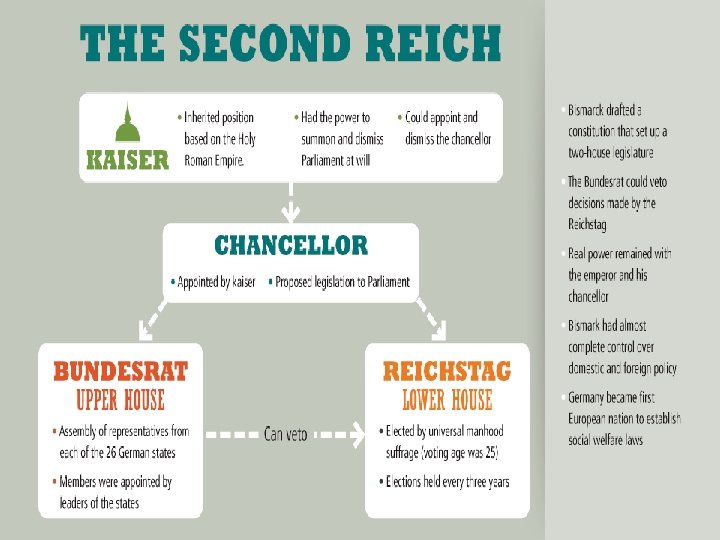
 The German Empire • After the victories over Austria and France William I was persuaded to take the role of Kaiser • Kaiser= emperor • January 1871 was the start of the Second Reich (empire) • He set up a 2 house legislature
The German Empire • After the victories over Austria and France William I was persuaded to take the role of Kaiser • Kaiser= emperor • January 1871 was the start of the Second Reich (empire) • He set up a 2 house legislature
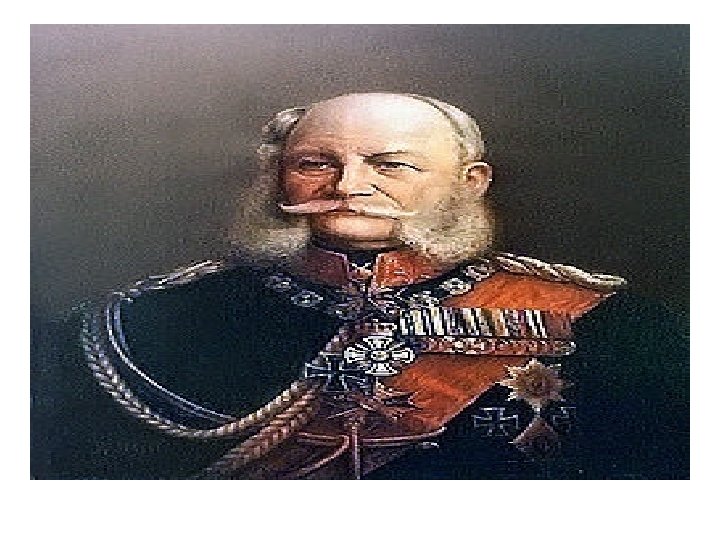

 Objective • C. Identify the different houses of German Parliament
Objective • C. Identify the different houses of German Parliament
 • Bundesrat- upper house appointed by rulers • Reichstag- lower house voted in by people • Bundestrat could veto the Reichstag
• Bundesrat- upper house appointed by rulers • Reichstag- lower house voted in by people • Bundestrat could veto the Reichstag
 Objective • D. Describe what led to Germany becoming the new industrial giant in Europe
Objective • D. Describe what led to Germany becoming the new industrial giant in Europe
 Germany Becomes an Industrial Giant • When Germany defeated France in 1871 it symbolized a shift in the balance of power in Europe • Germany became the industrial giant of Europe because of it’s large amounts of coal and Iron • It also had an educated workforce that grew from 41 million in 1871 to 67 mil in 1914
Germany Becomes an Industrial Giant • When Germany defeated France in 1871 it symbolized a shift in the balance of power in Europe • Germany became the industrial giant of Europe because of it’s large amounts of coal and Iron • It also had an educated workforce that grew from 41 million in 1871 to 67 mil in 1914
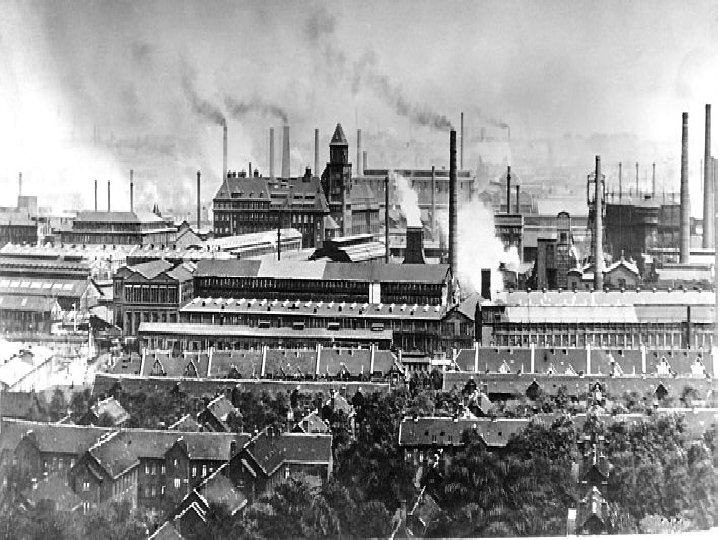


 • They supported research in their universities and hired many scientist • When a world wide recession hit in the late 1800’s they raised tariffs to protect their own businesses
• They supported research in their universities and hired many scientist • When a world wide recession hit in the late 1800’s they raised tariffs to protect their own businesses
 The Iron Chancellor • He tried to crush all local loyalties that were not to the German state such as the Catholic Church and socialist • He implemented Kulturkampf – battle for civilization • He made people get married in civil services instead of religious
The Iron Chancellor • He tried to crush all local loyalties that were not to the German state such as the Catholic Church and socialist • He implemented Kulturkampf – battle for civilization • He made people get married in civil services instead of religious
 • Bismarck was fearful that the Social Democratic Party would convince workers to revolt • He dissolved their groups, shut down their meetings and shut down their newspapers • He tried to entice workers to his side by making laws to protect them
• Bismarck was fearful that the Social Democratic Party would convince workers to revolt • He dissolved their groups, shut down their meetings and shut down their newspapers • He tried to entice workers to his side by making laws to protect them
 • By the 1890’s, Germans had health and accident insurance • They also had retirement benefits • By 1912 the Reichstag had more socialist then any other
• By the 1890’s, Germans had health and accident insurance • They also had retirement benefits • By 1912 the Reichstag had more socialist then any other
 • Unification of Germany video
• Unification of Germany video
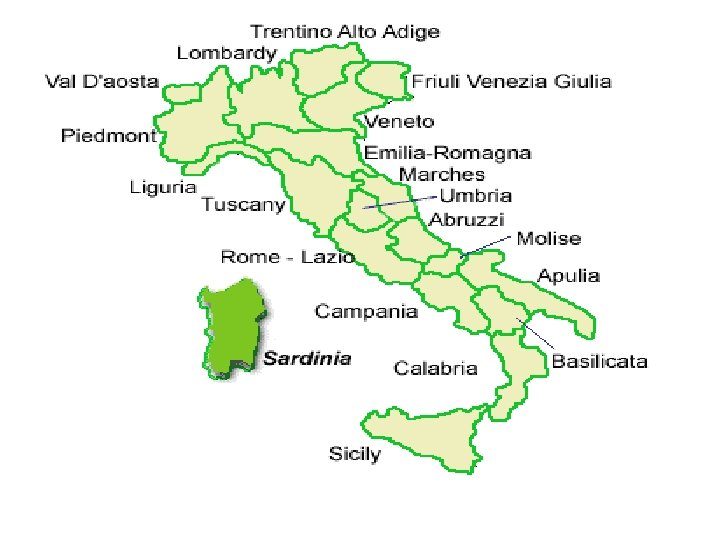
 3 -2 Unifying Italy
3 -2 Unifying Italy
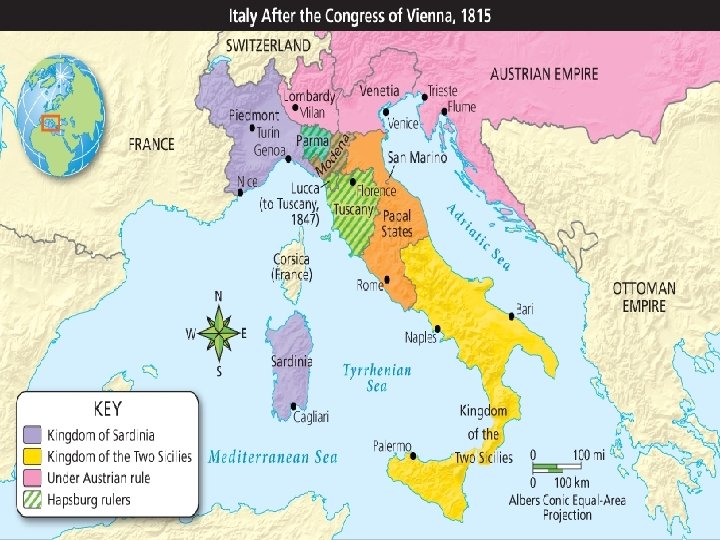
 Obstacles to Italian Unity • Years of warfare had led people to have a sense of belonging to regions • The congress ignored this and put Austria in charge of Northern Italy, and a French ruler in charge of Naples and Sicily
Obstacles to Italian Unity • Years of warfare had led people to have a sense of belonging to regions • The congress ignored this and put Austria in charge of Northern Italy, and a French ruler in charge of Naples and Sicily
 Objective • E. Identify Victor Emanuel II, Count Cavour, and Garibaldi
Objective • E. Identify Victor Emanuel II, Count Cavour, and Garibaldi
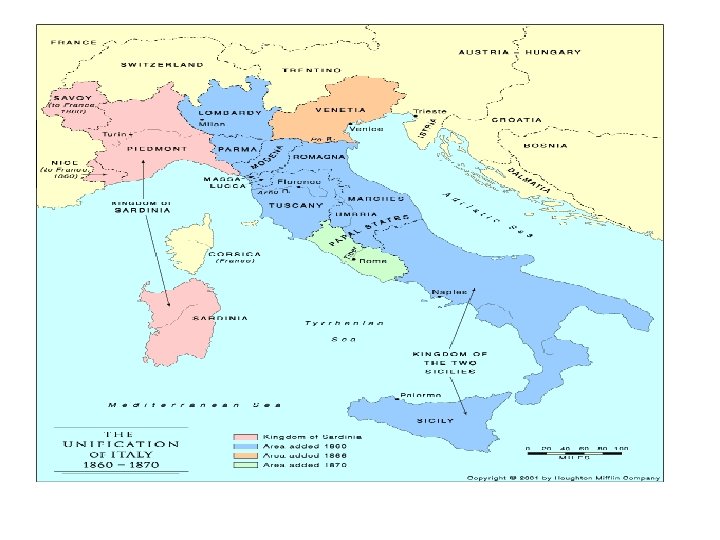
 The Struggle for Italy • In 1848, the Risorgimento, passed to Sardinia. • Their king was Victor Emmanuel II and he wanted to increase his power • In 1852 Count Cavour became prime minister • He was a believer in Realpolitik and his first order was to reform their economy
The Struggle for Italy • In 1848, the Risorgimento, passed to Sardinia. • Their king was Victor Emmanuel II and he wanted to increase his power • In 1852 Count Cavour became prime minister • He was a believer in Realpolitik and his first order was to reform their economy
 • His long term goal was to end Austria’s power and take Lombardy and Venetia • In 1855 Sardinia aided Britain and France in the Crimean War • Napoleon III promised to aid Sardinia if they went to war with Austria
• His long term goal was to end Austria’s power and take Lombardy and Venetia • In 1855 Sardinia aided Britain and France in the Crimean War • Napoleon III promised to aid Sardinia if they went to war with Austria
 • Garibaldi raised a 1000 volunteers and aided by Cavour won Sicily • In 1861 Garibaldi turned over the southern states and Victor Emanuel II was crowned king of Italy • Later in 1861 Italy acquired Venetia in the Austro-Prussian war • 1870 They acquired Rome after the Franco-Prussian war
• Garibaldi raised a 1000 volunteers and aided by Cavour won Sicily • In 1861 Garibaldi turned over the southern states and Victor Emanuel II was crowned king of Italy • Later in 1861 Italy acquired Venetia in the Austro-Prussian war • 1870 They acquired Rome after the Franco-Prussian war
 • Garibaldi
• Garibaldi
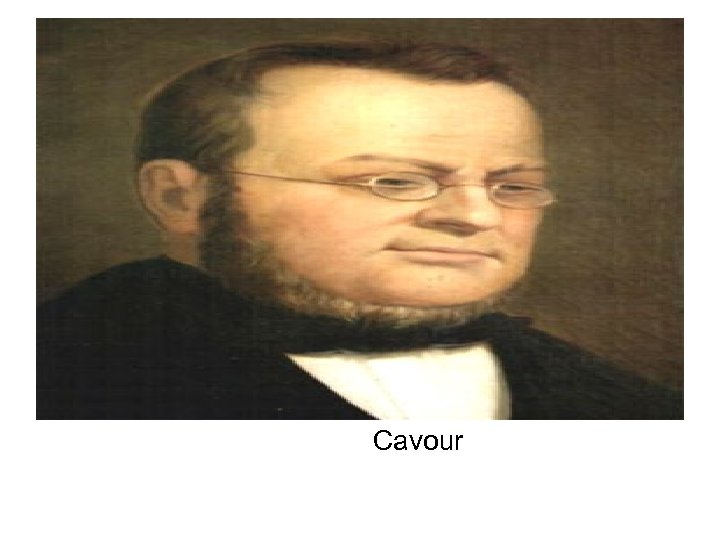 Cavour
Cavour
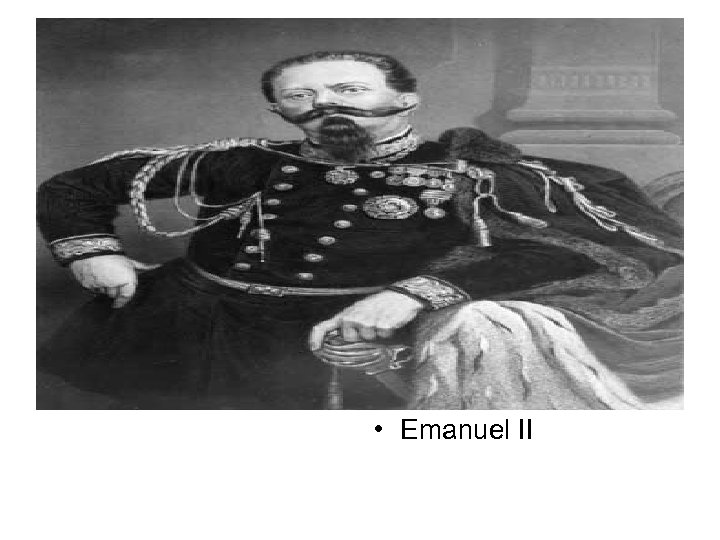 • Emanuel II
• Emanuel II
 Challenges Facing the New Nation • There was not a sense of unity and regional rivalries made it difficult to get national issues resolved • The North was richer and had more cities then the South • Pope’s saw themselves as prisoners in the Vatican and urged priest not to cooperate with the government
Challenges Facing the New Nation • There was not a sense of unity and regional rivalries made it difficult to get national issues resolved • The North was richer and had more cities then the South • Pope’s saw themselves as prisoners in the Vatican and urged priest not to cooperate with the government

 • The upper house was appointed by the king and could veto the lower house • Socialists organized strikes while anarchists turned to sabotage • After the 1900’s the economy improved with industries starting in the north
• The upper house was appointed by the king and could veto the lower house • Socialists organized strikes while anarchists turned to sabotage • After the 1900’s the economy improved with industries starting in the north

 • Unification of Italy video
• Unification of Italy video
 3 -3 The New Imperialism
3 -3 The New Imperialism
 Objective • F. Define imperialism
Objective • F. Define imperialism
 • Imperialism Crash Course
• Imperialism Crash Course
 The New Imperialism and its Causes • Imperialism- domination of the political, economic, or cultural life of another country • beginning in the 1870 s, Europeans brought much of the world under their control • Manufacturers needed over seas resources such as rubber, petroleum, manganese for steel and palm oil for machines
The New Imperialism and its Causes • Imperialism- domination of the political, economic, or cultural life of another country • beginning in the 1870 s, Europeans brought much of the world under their control • Manufacturers needed over seas resources such as rubber, petroleum, manganese for steel and palm oil for machines
 • They also needed new markets to sell factory goods • Now that merchant and naval vessels need coal for steam they needed bases all around the world
• They also needed new markets to sell factory goods • Now that merchant and naval vessels need coal for steam they needed bases all around the world
 Standard • Compare the progression of imperialistic claims on the African continent using historical maps.
Standard • Compare the progression of imperialistic claims on the African continent using historical maps.
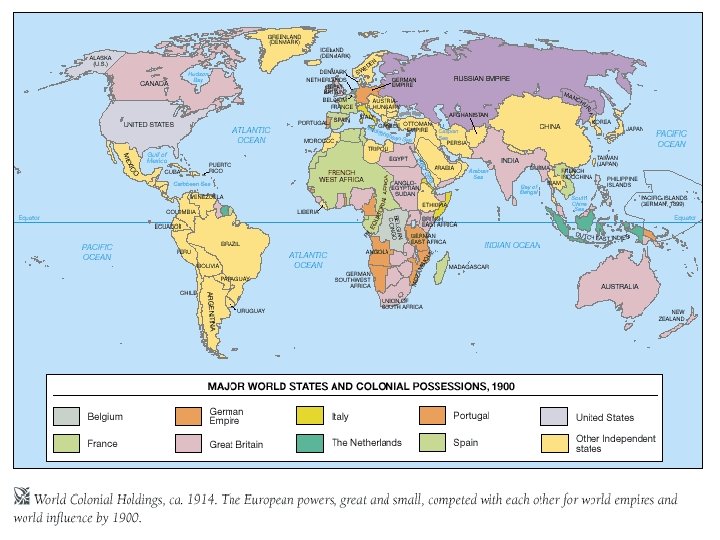
 Objectives • G. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of Western and nonwestern nations
Objectives • G. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of Western and nonwestern nations
 Western Imperialism Spreads Rapidly • 1. Weakness of Non-Western States • Older civilizations (Ottoman, Middle East, India, Quing China) were in decline • There were many wars between African peoples and their new states were weak
Western Imperialism Spreads Rapidly • 1. Weakness of Non-Western States • Older civilizations (Ottoman, Middle East, India, Quing China) were in decline • There were many wars between African peoples and their new states were weak
 • 2. Western Advantages • They had strong economies, armies and well organized governments • Superior Technology and medicine • Probably the biggest factor was machine guns, repeating rifles, and steam ship warships
• 2. Western Advantages • They had strong economies, armies and well organized governments • Superior Technology and medicine • Probably the biggest factor was machine guns, repeating rifles, and steam ship warships

 • Western educated Africans and Asians fought back by building Nationalism • In the west itself some people said Imperialism was immoral and a tool for the rich
• Western educated Africans and Asians fought back by building Nationalism • In the west itself some people said Imperialism was immoral and a tool for the rich
 Objective • H. Describe different forms of colonial rule
Objective • H. Describe different forms of colonial rule
 Forms of Imperial Rule • France and Britain developed colonies • France tried to impose their culture on their colonies while Britain used indirect rule • In a protectorate, local rulers were left in place but had to do what their European leaders told them • A sphere of influence was when one country took trading privileges with a specific area
Forms of Imperial Rule • France and Britain developed colonies • France tried to impose their culture on their colonies while Britain used indirect rule • In a protectorate, local rulers were left in place but had to do what their European leaders told them • A sphere of influence was when one country took trading privileges with a specific area
 The Effects of Imperialism • They introduced European legal systems that relied on abstract principles of right and wrong. • Where mineral resources were lacking, colonial powers developed cash crops, such as rubber, cotton, palm oil, and peanuts. • Colonist were heavily taxed, to pay for the cost to the European countries
The Effects of Imperialism • They introduced European legal systems that relied on abstract principles of right and wrong. • Where mineral resources were lacking, colonial powers developed cash crops, such as rubber, cotton, palm oil, and peanuts. • Colonist were heavily taxed, to pay for the cost to the European countries
 • Christian missionaries worked hard to win converts
• Christian missionaries worked hard to win converts
 3 -4 Latin American Nations Win Independence
3 -4 Latin American Nations Win Independence
 Standard • W. 22 Cite evidence from text to describe the movements led by Emiliano Zapata, Francisco Madero, Pancho Villa, and Venustiano Carranza in Mexico stemming from the desire for land reform and democratic participation. (G, H, P)
Standard • W. 22 Cite evidence from text to describe the movements led by Emiliano Zapata, Francisco Madero, Pancho Villa, and Venustiano Carranza in Mexico stemming from the desire for land reform and democratic participation. (G, H, P)
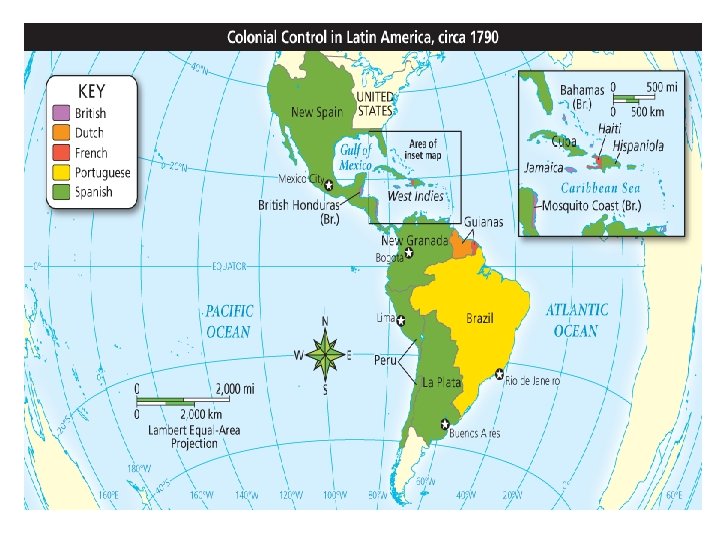
 Objective • I. Define peninsulares, creoles, mestizos, and mulattoes
Objective • I. Define peninsulares, creoles, mestizos, and mulattoes
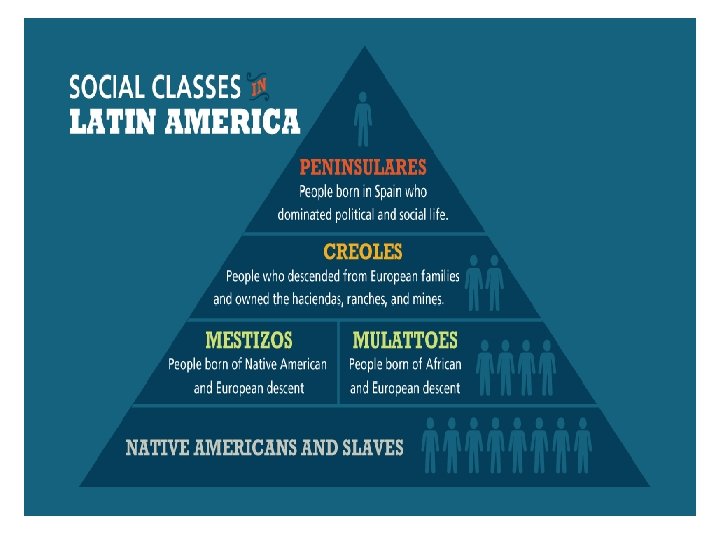
 Sources of Discontent • Peninsulares- Spanish born men that were the only ones who could hold top jobs in govt or the church • Creoles- European descended men who owned the haciendas and mines and resented their second class status • Mestizos- Native American and European and Mulattoes- African and European that were angry about being denied status and wealth
Sources of Discontent • Peninsulares- Spanish born men that were the only ones who could hold top jobs in govt or the church • Creoles- European descended men who owned the haciendas and mines and resented their second class status • Mestizos- Native American and European and Mulattoes- African and European that were angry about being denied status and wealth
 Objective • J. Identify Simon Bolivar
Objective • J. Identify Simon Bolivar
 • Simón Bolívar (a few slides from now)
• Simón Bolívar (a few slides from now)
 objective • K. Identify Toussaint L’Ouverture • L. Describe the events of the Haitian slave revolt
objective • K. Identify Toussaint L’Ouverture • L. Describe the events of the Haitian slave revolt
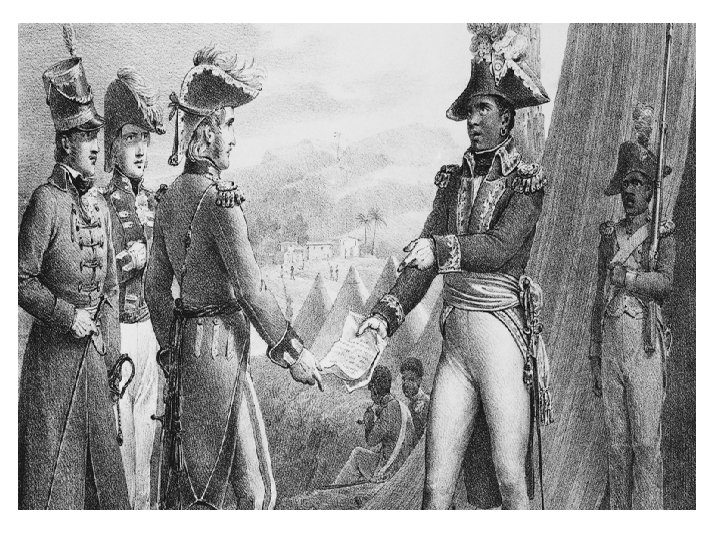
 Haiti Fights for Freedom • Haiti was France's most prized possession in the Caribbean in the 1700’s • The French owned sugar plantations with about 500, 000 slaves • There were also about 25, 000 mulattoes • In 1791 the slave revolt began, and Toussaint L’Ouverture was their leader
Haiti Fights for Freedom • Haiti was France's most prized possession in the Caribbean in the 1700’s • The French owned sugar plantations with about 500, 000 slaves • There were also about 25, 000 mulattoes • In 1791 the slave revolt began, and Toussaint L’Ouverture was their leader
 • In 1798 the slaves were freed but Haiti remained a French colony • In 1802, Napoleon invaded Haiti to reclaim it • In 1804, Haiti declared their independence and in 1820 became a republic
• In 1798 the slaves were freed but Haiti remained a French colony • In 1802, Napoleon invaded Haiti to reclaim it • In 1804, Haiti declared their independence and in 1820 became a republic
 Independence for Mexico and Central America
Independence for Mexico and Central America
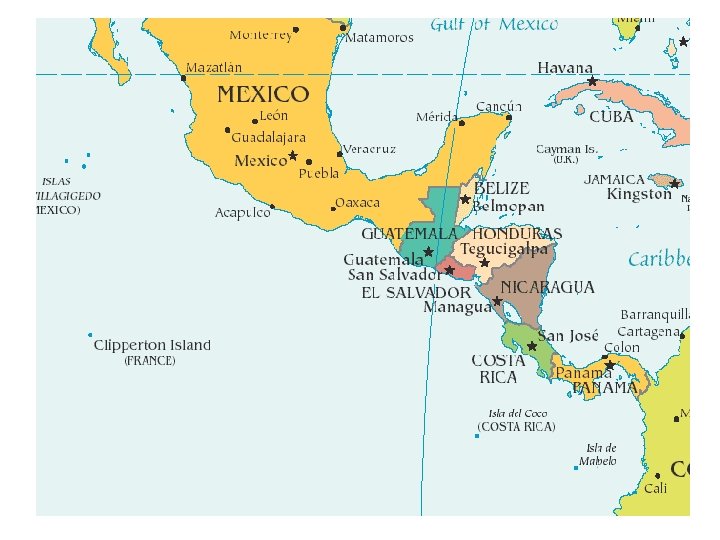
 • In 1810, Father Miguel Hidalgo called for freedom for Mexico • Jose Morelos kept the movement going for 4 years before he was captured and shot • • In Spain in 1820, liberals forced the king to issue a constitution
• In 1810, Father Miguel Hidalgo called for freedom for Mexico • Jose Morelos kept the movement going for 4 years before he was captured and shot • • In Spain in 1820, liberals forced the king to issue a constitution
 Discontent Sparks Revolts in South America • • In 1810, Bolívar led an uprising that established a republic in his native Venezuela • José de San Martín • Bolivar tried to unite the lands he had liberated into a single nation, called Gran Colombia
Discontent Sparks Revolts in South America • • In 1810, Bolívar led an uprising that established a republic in his native Venezuela • José de San Martín • Bolivar tried to unite the lands he had liberated into a single nation, called Gran Colombia
 3 -5 India Becomes a British Colony
3 -5 India Becomes a British Colony
 Standard • Explain the transfer in 1858 of government to Great Britain on the Indian Subcontinent following the Sepoy Rebellion.
Standard • Explain the transfer in 1858 of government to Great Britain on the Indian Subcontinent following the Sepoy Rebellion.
 Objective • M. Identify the British East India company • N. Describe the events that led to the Sepoy rebellion
Objective • M. Identify the British East India company • N. Describe the events that led to the Sepoy rebellion
 The British East India Company • In the mid 1800’s, the British East India company controlled 3/5 of India • The British encouraged competition between rival princes • The main goal of the company was to make money, but they did improve roads, and preserve peace
The British East India Company • In the mid 1800’s, the British East India company controlled 3/5 of India • The British encouraged competition between rival princes • The main goal of the company was to make money, but they did improve roads, and preserve peace
 The Writers Building in Calcutta, India, was designed in 1777 by the British. Over the years, many extensions were added to this important administrative office for the British East India Company .
The Writers Building in Calcutta, India, was designed in 1777 by the British. Over the years, many extensions were added to this important administrative office for the British East India Company .
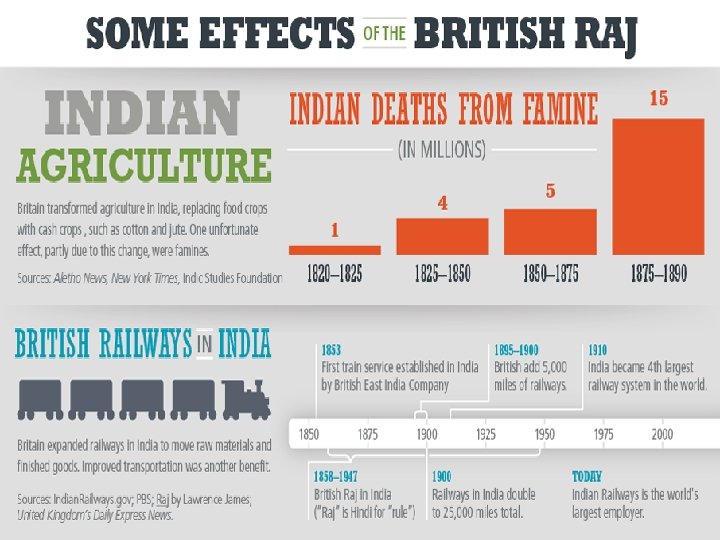
 • The British introduced Western education • They worked to end slavery and the caste system • They put a end to sati- when a widow is expected to kill herself to be with her husband • In 1850’s they angered Indians because they required sepoys (Indian Soldiers) to serve anywhere
• The British introduced Western education • They worked to end slavery and the caste system • They put a end to sati- when a widow is expected to kill herself to be with her husband • In 1850’s they angered Indians because they required sepoys (Indian Soldiers) to serve anywhere
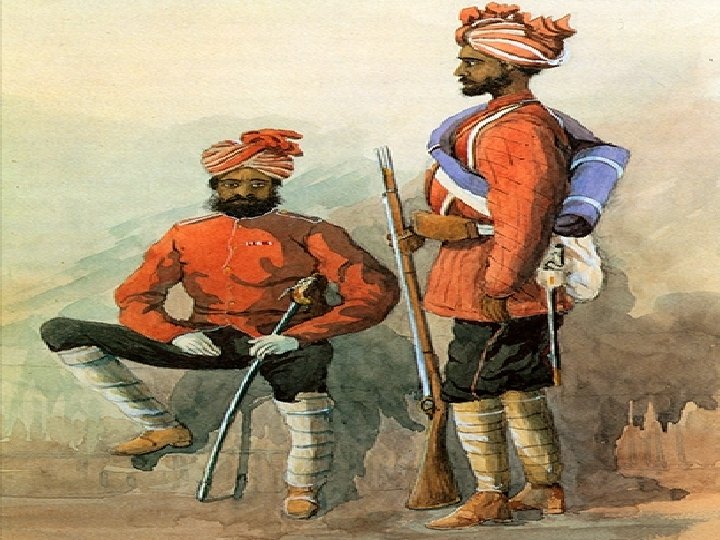

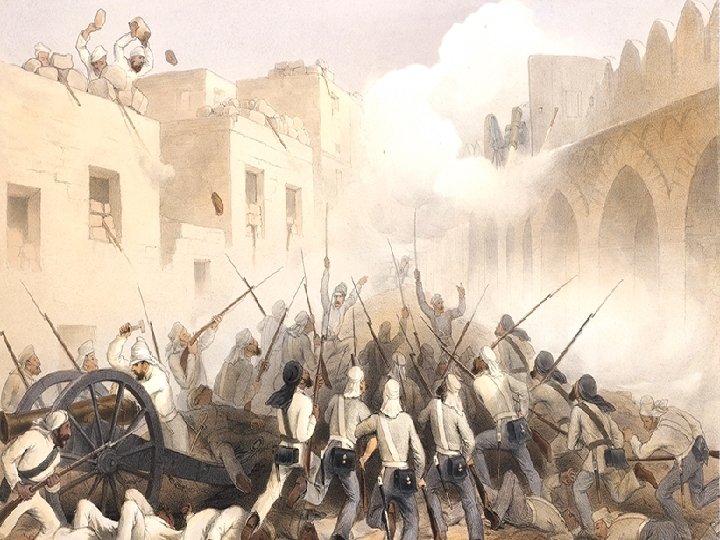
 • They also passed a law allowing Hindu widows to remarry • Many sepoys revolted and claimed the last Mughal empire leader as their leader • In 1858, Britain took India out of control of the company and put it under the British crown.
• They also passed a law allowing Hindu widows to remarry • Many sepoys revolted and claimed the last Mughal empire leader as their leader • In 1858, Britain took India out of control of the company and put it under the British crown.

 India Under British Rule • In India, a British Viceroy ruled in place of the Queen • The British introduced better medicine and food production which led to a population boom • • Clearing new farmlands led to massive deforestation
India Under British Rule • In India, a British Viceroy ruled in place of the Queen • The British introduced better medicine and food production which led to a population boom • • Clearing new farmlands led to massive deforestation
 Diverse Views on Culture • Some Indians wanted to change to western ways while others thought the answers to change lay in their Hindu or Muslim beliefs • Ram Mohun Roy combined the 2 thoughts and is known as the father of Indian nationalism
Diverse Views on Culture • Some Indians wanted to change to western ways while others thought the answers to change lay in their Hindu or Muslim beliefs • Ram Mohun Roy combined the 2 thoughts and is known as the father of Indian nationalism

 The Growth of Indian Nationalism • In the late 1800’s, western educated Indians were spearheading a nationalist movement • In 1885, they created the Indian National Congress • In 1906, the Muslim league was founded to protect Muslim rights.
The Growth of Indian Nationalism • In the late 1800’s, western educated Indians were spearheading a nationalist movement • In 1885, they created the Indian National Congress • In 1906, the Muslim league was founded to protect Muslim rights.
 3 -6 China and the West
3 -6 China and the West
 Standard • Explain the growing influence of the West in China, the Boxer Rebellion, Sun Yatsen, and the Xinhai Revolution.
Standard • Explain the growing influence of the West in China, the Boxer Rebellion, Sun Yatsen, and the Xinhai Revolution.
 Economic Interest in China • China sold silk, porcelain and tea for gold and silver • China had a trade surplus- exporting more then they imported • Europe had a trade deficit- importing more then they exported
Economic Interest in China • China sold silk, porcelain and tea for gold and silver • China had a trade surplus- exporting more then they imported • Europe had a trade deficit- importing more then they exported
 Chinese merchants examine goods, including porcelain, which was highly prized by European buyers.
Chinese merchants examine goods, including porcelain, which was highly prized by European buyers.
 Objective • O. Describe the events that led to and occurred during the opium war
Objective • O. Describe the events that led to and occurred during the opium war
 • By the late 1700’s China was on the decline and western powers were superior with their military • The British started to make a lot of money trading opium for tea • China outlawed the drug and executed drug dealers • In 1839, the British beat the Chinese in the Opium war
• By the late 1700’s China was on the decline and western powers were superior with their military • The British started to make a lot of money trading opium for tea • China outlawed the drug and executed drug dealers • In 1839, the British beat the Chinese in the Opium war
 • • 1842 was the treaty of Nanjing Britain got paid a large indemnity Britain took Hong Kong British citizens extraterritoriality
• • 1842 was the treaty of Nanjing Britain got paid a large indemnity Britain took Hong Kong British citizens extraterritoriality
 The antiquated Chinese fleet was outmatched by larger, more technologically advanced British warships during the Opium War.
The antiquated Chinese fleet was outmatched by larger, more technologically advanced British warships during the Opium War.
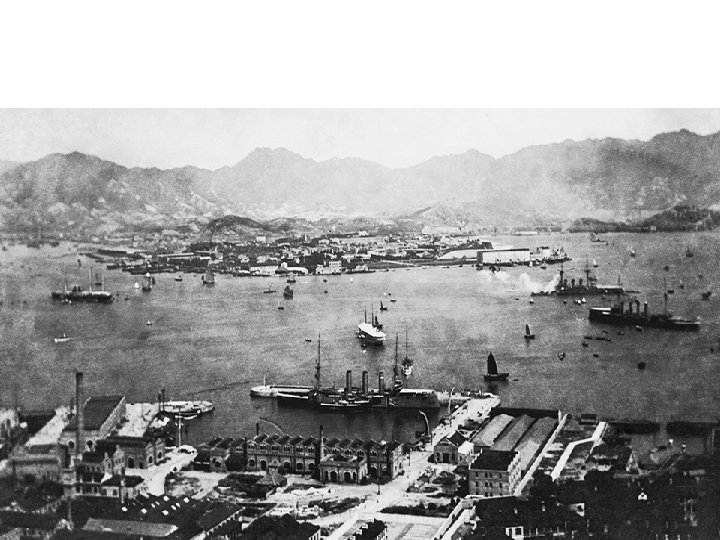 The harbor in Hong Kong was already a busy shipping hub by 1900 .
The harbor in Hong Kong was already a busy shipping hub by 1900 .
 The Taiping Rebellion and a Weakened China • 1800 s Qing dynasty was in decline • Taiping rebellion 1850 -1864 was probably the most devastating revolt in history • When it was all over it was estimated to have killed 20 -30 million • The Qing dynasty almost collapsed and Russia took northern China lands
The Taiping Rebellion and a Weakened China • 1800 s Qing dynasty was in decline • Taiping rebellion 1850 -1864 was probably the most devastating revolt in history • When it was all over it was estimated to have killed 20 -30 million • The Qing dynasty almost collapsed and Russia took northern China lands
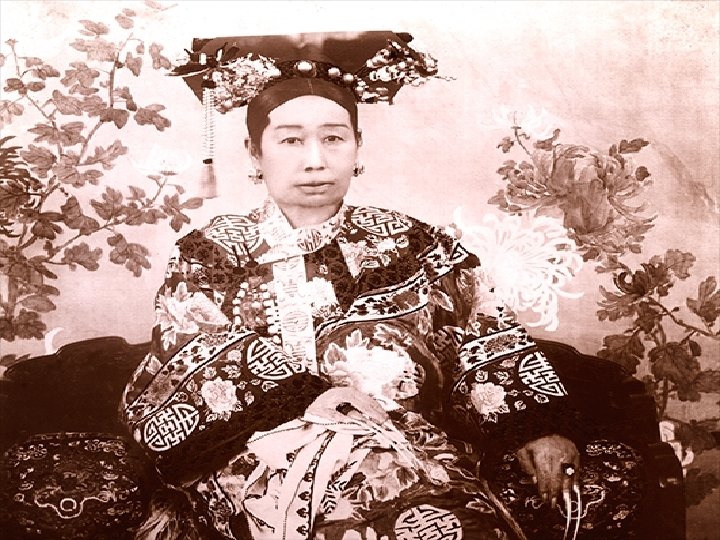
 Reform Efforts in China • Mid 1800 s the Chinese were split on whether they should take western reforms • By the late 1800 s the empress Ci Xi had gained power and surrounded herself with advisors committed to Confucian traditions
Reform Efforts in China • Mid 1800 s the Chinese were split on whether they should take western reforms • By the late 1800 s the empress Ci Xi had gained power and surrounded herself with advisors committed to Confucian traditions

 Objective • P. Define sphere of influence
Objective • P. Define sphere of influence
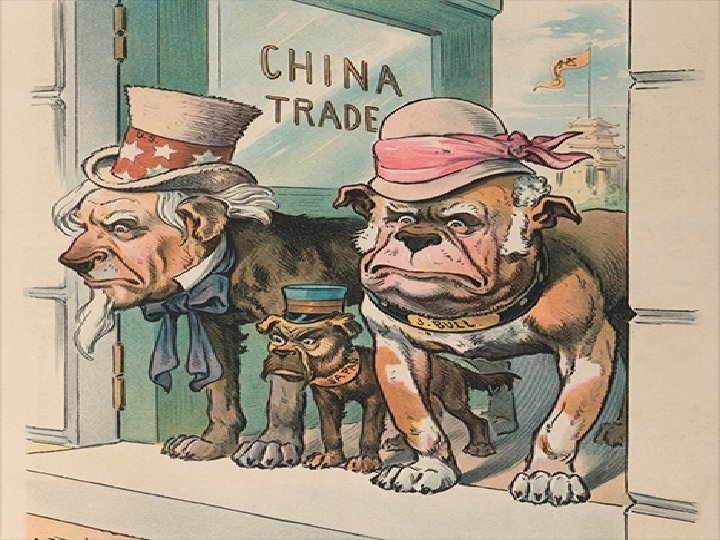
 • In 1894 the Chinese lost the Sino Japanese war and lost the island of Taiwan • The European powers carved out their own sphere of influence and the U. S. called for an open door policy • A new emperor, Guang Xu, started the 100 days of reform
• In 1894 the Chinese lost the Sino Japanese war and lost the island of Taiwan • The European powers carved out their own sphere of influence and the U. S. called for an open door policy • A new emperor, Guang Xu, started the 100 days of reform
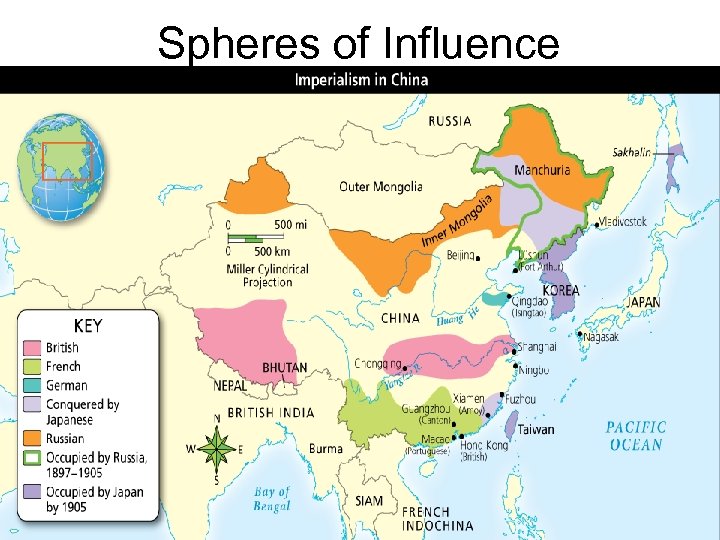 Spheres of Influence
Spheres of Influence

 • Conservatives rallied against it and he was imprisoned
• Conservatives rallied against it and he was imprisoned
 Objective • Q. Describe the events of the boxer rebellion
Objective • Q. Describe the events of the boxer rebellion
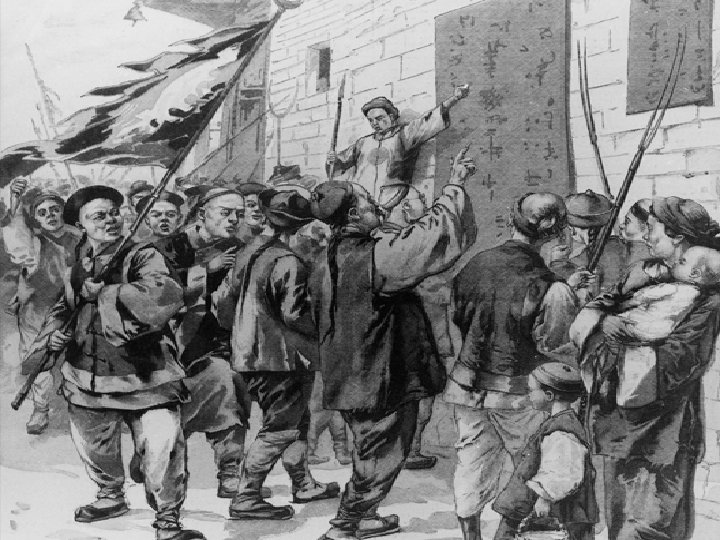
 The Fall of the Qing Dynasty • In 1899, the boxer uprising occurred • A secret society of Chinese called the Righteous Harmonious Fist attacked foreigners across the country • They expanded mining, shipping, railroads, banking and exports of cash crops
The Fall of the Qing Dynasty • In 1899, the boxer uprising occurred • A secret society of Chinese called the Righteous Harmonious Fist attacked foreigners across the country • They expanded mining, shipping, railroads, banking and exports of cash crops

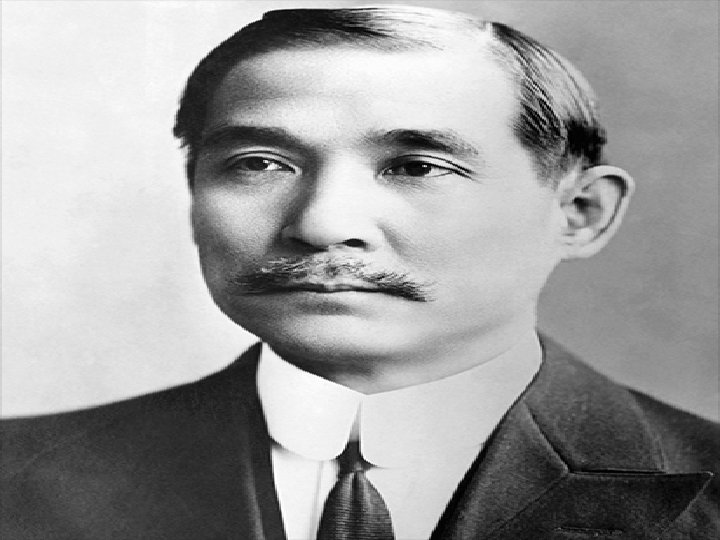
 Objective • R. Identify Sun Yixian
Objective • R. Identify Sun Yixian
 • Sun Yixian was a passionate spokesperson for China and in 1911 was named the first president of the New Chinese Republic
• Sun Yixian was a passionate spokesperson for China and in 1911 was named the first president of the New Chinese Republic

 • Crash course Asian response to Imperialism
• Crash course Asian response to Imperialism
 3 -7 • American Expansion
3 -7 • American Expansion
 Standard • Describe American imperialism in the Philippines and the Philippine-American War led by Emilio Aguinaldo.
Standard • Describe American imperialism in the Philippines and the Philippine-American War led by Emilio Aguinaldo.
 Objective • S. Identify Emilio Aquinaldo
Objective • S. Identify Emilio Aquinaldo
 America and its new lands 3. Philippines- Filipinos revolted against American rule led by Emilio Aquinaldo – Americans forced Filipinos into concentration camps until revolt was suppressed (three years) – America loses 4, 000 troops and $400 million as Philippines becomes a protectorate – Receives freedom after WWII
America and its new lands 3. Philippines- Filipinos revolted against American rule led by Emilio Aquinaldo – Americans forced Filipinos into concentration camps until revolt was suppressed (three years) – America loses 4, 000 troops and $400 million as Philippines becomes a protectorate – Receives freedom after WWII
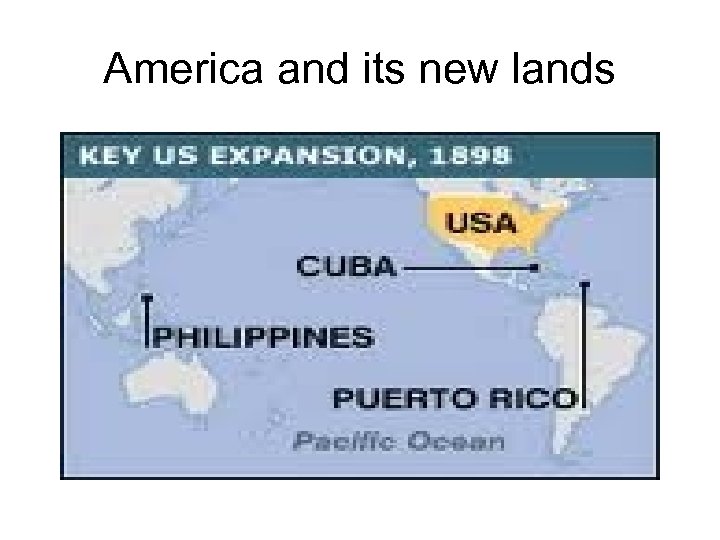 America and its new lands
America and its new lands
 • Crash Course American Imperialism
• Crash Course American Imperialism


