3.1 Characteristics of the global currency market 3.2


3.1 Characteristics of the global currency market 3.2 The reserve currency and exchange rate 3.3 Foreign exchange transactions Topic 3 - Global currency market
Definition of the global currency market Currency market - the market in which participants are able to buy, sell, exchange and speculate on currencies. A huge role in the development of the global currency market played: - System of fixed exchange rates (the Gold Standard + the Related system of regulated exchange rates ) System of floating exchange rates.
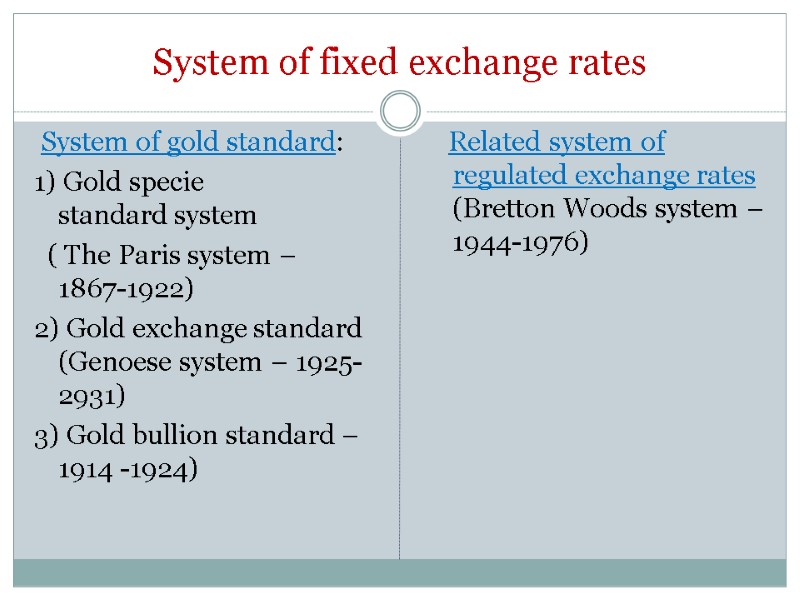
System of fixed exchange rates System of gold standard: 1) Gold specie standard system ( The Paris system – 1867-1922) 2) Gold exchange standard (Genoese system – 1925-2931) 3) Gold bullion standard –1914 -1924) Related system of regulated exchange rates (Bretton Woods system – 1944-1976)
Floating exchange rates ( Jamaican System) Floating exchange rates mean that currencies change in relative value all the time. The advantages of the Jamaican system, which was adopted in 1976. 1) The most important element of the Jamaican currency system is the displacement of gold from the International Settlements. 2) Central banks were able to carry out gold transactions at market prices, gold parties were canceled. 3) Displacement of gold accompanied by a nomination for the role of the SDR international reserve funds. 4) Countries are given a choice of exchange rate regime, and have been used mainly floating exchange rates, which are influenced by two basic conditions: purchasing power parity and the market supply and demand on world currency markets.

The reserve currency and exchange rate The money used in a country (euros, dollars, yen, tenge, etc.) – is its currency. Money in notes and coins is called cash. The following types of currencies: national currency - legal tender issued a nation's central bank or monetary authority on the territory its countries; foreign currency - legal tender of other countries, legally or illegally used in that country; freely convertible currency - the currency that is widely used to make payments for international transactions and actively bought and sold on the world market; hard currency - currency, which is characterized by a stable exchange rate movements; reserve currency - currency, in which countries hold their liquid international assets used to cover the negative balance of payments.

Exchange rate Exchange rate – is the price of a nation’s currency in terms of another currency. The following types of quotations exchange rates: direct quotation - a rate of one unit of foreign currency (base currency) expressed in national currency (the quote currency); indirect quotation - a rate of one unit of the national currency, expressed in a certain amount of foreign currency. cross-rate - the ratio between the two currencies, calculated on the basis of the course, each of them with respect to the leading third currency.

Exchange rate The nominal exchange rate – is rate between two currencies, when the price of units of national currency expressed in units of foreign currency. The real exchange rate - the nominal exchange rate, restated for the changes in the price level in the country and in the country to which the currency is quoted national currency.

Monetary policy Monetary policy - a set of measures in the field of monetary relations, undertaken in accordance with current and strategic goals of the country. State regulation of the exchange rate is carried out by: Currency interventions – are operations of the central banks in the currency markets for the purchase and sale of the national currency; Protectionist measures aimed at protecting its own economy, in which case the exchange rate. The devaluation of the currency - legal decline currency. Revaluation currency - legal increase currency.

14436-topic_3_-_gfm.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

