bea629efcd31d7dd87e261962303a359.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 3 -1 Chapter Seven Understanding Local Customers MKT 568 Global Marketing Management Dr. Fred Miller
3 -1 Chapter Seven Understanding Local Customers MKT 568 Global Marketing Management Dr. Fred Miller
 Sample Essay Question Herbal. Soft produces organic, herbal lotions for both women and men. It wishes to build upon its successful entry into European markets by introducing its products into the Middle East. To do so, it must learn how lotions are used in the region, how they are perceived by consumers and how the firm’s current packages and brands would be perceived. Recommend a marketing research program to Herbal. Soft that: 1) includes one project from each of the three major types of marketing research, and 2) explains the value for each project for selecting the best marketing strategy. Identify and describe two common problems with survey research, explaining how you would address each problem.
Sample Essay Question Herbal. Soft produces organic, herbal lotions for both women and men. It wishes to build upon its successful entry into European markets by introducing its products into the Middle East. To do so, it must learn how lotions are used in the region, how they are perceived by consumers and how the firm’s current packages and brands would be perceived. Recommend a marketing research program to Herbal. Soft that: 1) includes one project from each of the three major types of marketing research, and 2) explains the value for each project for selecting the best marketing strategy. Identify and describe two common problems with survey research, explaining how you would address each problem.
 Culture and Buyer Behavior Marketing and materialism cultural impact of marketing efforts, resistance to materialism permanent & relative income, conspicuous consumption Product Meaning Core benefits related to product preferences Universal Traits of Consumption goal orientation, purposeful behavior often in response to hidden motivators
Culture and Buyer Behavior Marketing and materialism cultural impact of marketing efforts, resistance to materialism permanent & relative income, conspicuous consumption Product Meaning Core benefits related to product preferences Universal Traits of Consumption goal orientation, purposeful behavior often in response to hidden motivators
 Local Buyer Research The research process Types of research Exploratory - focus groups, interviews, open-ended questions Descriptive – consumer & trade surveys, observation Causal – laboratory, controlled testing Problems in international marketing research Measurement equivalence – construct, translation, calibration, score Misunderstanding due to language problems (back translation) Inference problems due to sampling frame difficulties Administration problems in conducting fieldwork
Local Buyer Research The research process Types of research Exploratory - focus groups, interviews, open-ended questions Descriptive – consumer & trade surveys, observation Causal – laboratory, controlled testing Problems in international marketing research Measurement equivalence – construct, translation, calibration, score Misunderstanding due to language problems (back translation) Inference problems due to sampling frame difficulties Administration problems in conducting fieldwork
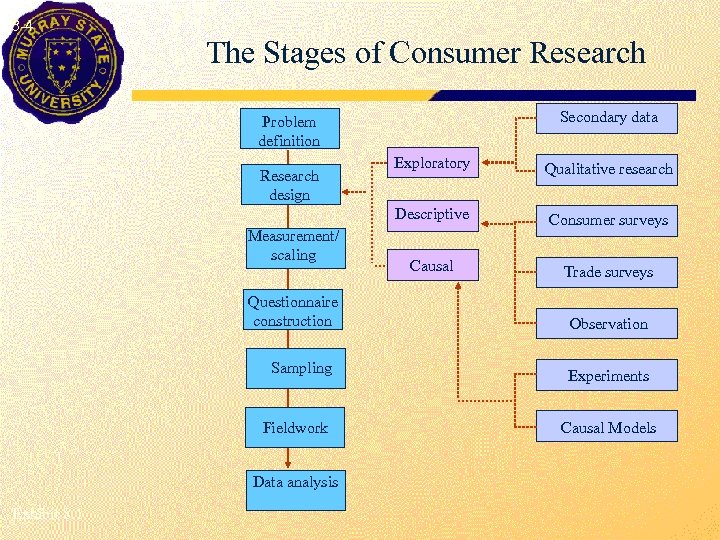 8 -4 The Stages of Consumer Research Secondary data Problem definition Measurement/ scaling Questionnaire construction Sampling Fieldwork Data analysis Exhibit 8. 1 Exploratory Qualitative research Descriptive Research design Consumer surveys Causal Trade surveys Observation Experiments Causal Models
8 -4 The Stages of Consumer Research Secondary data Problem definition Measurement/ scaling Questionnaire construction Sampling Fieldwork Data analysis Exhibit 8. 1 Exploratory Qualitative research Descriptive Research design Consumer surveys Causal Trade surveys Observation Experiments Causal Models
 Exploratory Research for Beer How many people are in attendance at a small wedding? How many people are in attendance at a large wedding? Are alcoholic beverages served at weddings? Is wine or champagne served at weddings? Are distilled spirits served at weddings? Is beer served at weddings?
Exploratory Research for Beer How many people are in attendance at a small wedding? How many people are in attendance at a large wedding? Are alcoholic beverages served at weddings? Is wine or champagne served at weddings? Are distilled spirits served at weddings? Is beer served at weddings?
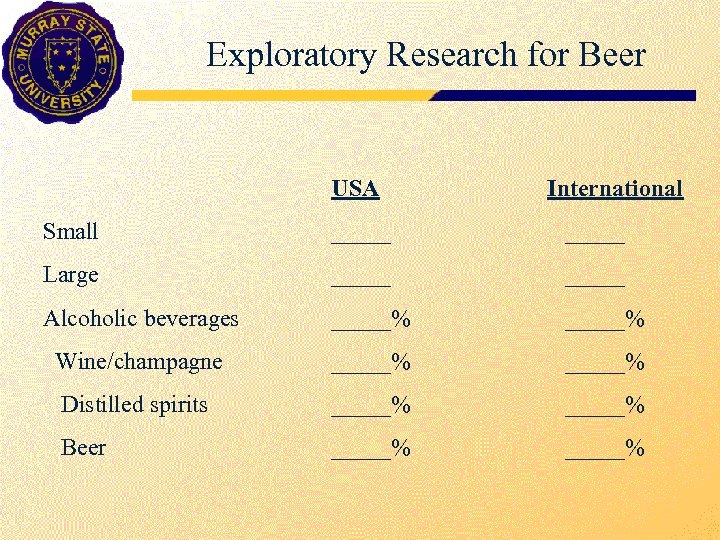 Exploratory Research for Beer USA International Small _____ Large _____ Alcoholic beverages _____% Wine/champagne _____% Distilled spirits _____% Beer _____%
Exploratory Research for Beer USA International Small _____ Large _____ Alcoholic beverages _____% Wine/champagne _____% Distilled spirits _____% Beer _____%
 Causal Research for Beer For each product package you see, write down; The name of the brand The type of product An adjective describing the product, i. e. refreshing, strong, tasty, sparkling, nasty, weak
Causal Research for Beer For each product package you see, write down; The name of the brand The type of product An adjective describing the product, i. e. refreshing, strong, tasty, sparkling, nasty, weak

 Recognition by Time and Angle For each product package you see, write down; The name of the brand The type of product An adjective describing the product, i. e. refreshing, strong, tasty, sparkling, nasty, weak
Recognition by Time and Angle For each product package you see, write down; The name of the brand The type of product An adjective describing the product, i. e. refreshing, strong, tasty, sparkling, nasty, weak
 Descriptive Research for Beer Taste By what criteria Price On a piece of paper, write a number Import do you decide between 1 and 9 inclusive. Brewer hip (7) square (1) to what brand of clueless to with it bad to baaaad Calories/carbs stinks to awesome, beer to buy? it sucks to wicked, killer, Popularity gnarly, the bomb five minutes ago to now Taste – malty (1) to dry (7) (1 = Unimportant, 7= Important) to Brands Price – overpriced to value priced Evaluate Import – domestic to import Brewer – major to micro Calories/carbs – high to low Popularity – unpopular to popular TLLT to TNBT
Descriptive Research for Beer Taste By what criteria Price On a piece of paper, write a number Import do you decide between 1 and 9 inclusive. Brewer hip (7) square (1) to what brand of clueless to with it bad to baaaad Calories/carbs stinks to awesome, beer to buy? it sucks to wicked, killer, Popularity gnarly, the bomb five minutes ago to now Taste – malty (1) to dry (7) (1 = Unimportant, 7= Important) to Brands Price – overpriced to value priced Evaluate Import – domestic to import Brewer – major to micro Calories/carbs – high to low Popularity – unpopular to popular TLLT to TNBT
 Types of Marketing Research Classify each of the following research projects as exploratory, descriptive or causal. Lab tests of package recognition Statistical surveys of consumers Focus groups with target consumers Testing brain wave responses to brand logos An open-ended written survey Observation of shopping patterns Interviews with select target consumers Statistical surveys of intermediaries
Types of Marketing Research Classify each of the following research projects as exploratory, descriptive or causal. Lab tests of package recognition Statistical surveys of consumers Focus groups with target consumers Testing brain wave responses to brand logos An open-ended written survey Observation of shopping patterns Interviews with select target consumers Statistical surveys of intermediaries
 Local Buyer Research The research process Types of research Exploratory - focus groups Descriptive – consumer & trade surveys, observation Causal – laboratory, controlled Problems in international marketing research Measurement equivalence – construct, translation, calibration, score Misunderstanding due to language problems (back translation) Inference problems due to sampling frame difficulties Administration problems in conducting fieldwork
Local Buyer Research The research process Types of research Exploratory - focus groups Descriptive – consumer & trade surveys, observation Causal – laboratory, controlled Problems in international marketing research Measurement equivalence – construct, translation, calibration, score Misunderstanding due to language problems (back translation) Inference problems due to sampling frame difficulties Administration problems in conducting fieldwork
 Buyer Decision Making Core benefits of products may vary Evaluation - multi-attribute models compensatory (lead markets), hierarchical (following markets) Choice social forces, motivation to comply, social norms satisfaction related to expectations and previous experience
Buyer Decision Making Core benefits of products may vary Evaluation - multi-attribute models compensatory (lead markets), hierarchical (following markets) Choice social forces, motivation to comply, social norms satisfaction related to expectations and previous experience
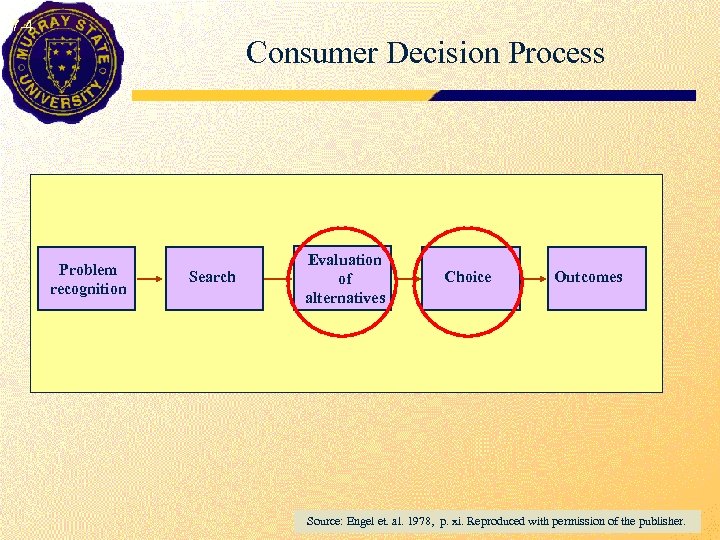 7 -4 Consumer Decision Process Problem recognition Search Evaluation of alternatives Choice Outcomes Source: Engel et. al. 1978, p. xi. Reproduced with permission of the publisher.
7 -4 Consumer Decision Process Problem recognition Search Evaluation of alternatives Choice Outcomes Source: Engel et. al. 1978, p. xi. Reproduced with permission of the publisher.
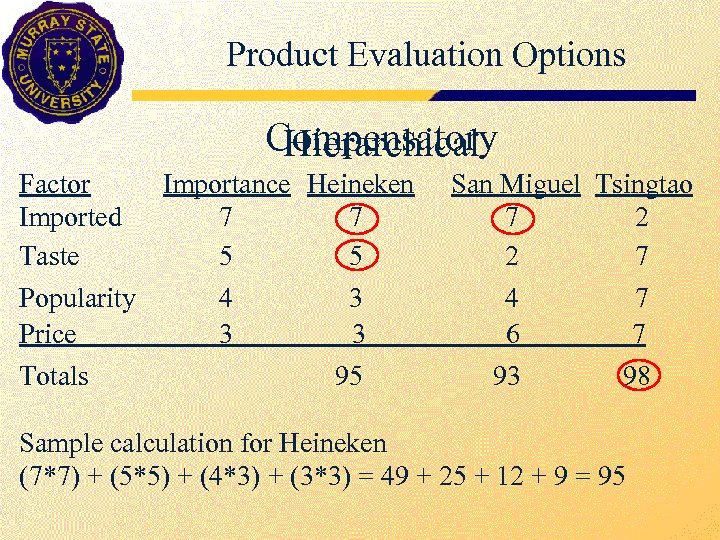 Product Evaluation Options Compensatory Hierarchical Factor Imported Taste Importance Heineken San Miguel Tsingtao 7 7 2 5 5 2 7 Popularity 4 3 4 7 Price 3 6 7 Totals 95 93 98 Sample calculation for Heineken (7*7) + (5*5) + (4*3) + (3*3) = 49 + 25 + 12 + 9 = 95
Product Evaluation Options Compensatory Hierarchical Factor Imported Taste Importance Heineken San Miguel Tsingtao 7 7 2 5 5 2 7 Popularity 4 3 4 7 Price 3 6 7 Totals 95 93 98 Sample calculation for Heineken (7*7) + (5*5) + (4*3) + (3*3) = 49 + 25 + 12 + 9 = 95
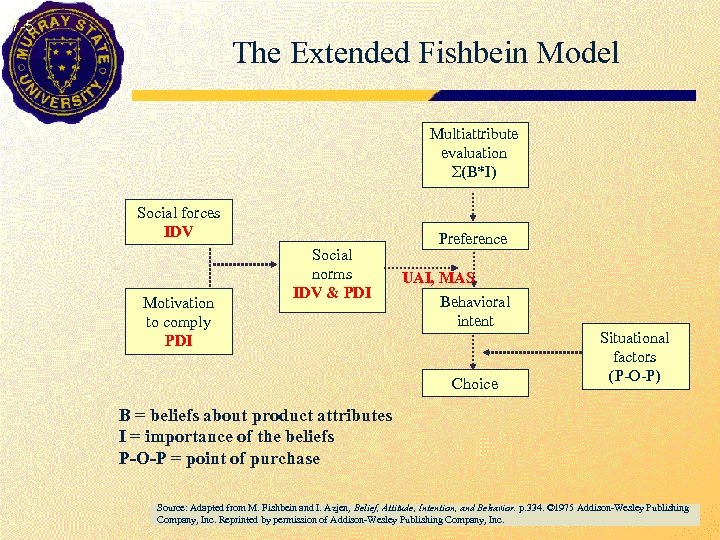 7 -5 The Extended Fishbein Model Multiattribute evaluation Σ(B*I) Social forces IDV Motivation to comply PDI Social norms IDV & PDI Preference UAI, MAS Behavioral intent Choice Situational factors (P-O-P) B = beliefs about product attributes I = importance of the beliefs P-O-P = point of purchase Source: Adapted from M. Fishbein and I. Azjen, Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior. p. 334. © 1975 Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. Reprinted by permission of Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
7 -5 The Extended Fishbein Model Multiattribute evaluation Σ(B*I) Social forces IDV Motivation to comply PDI Social norms IDV & PDI Preference UAI, MAS Behavioral intent Choice Situational factors (P-O-P) B = beliefs about product attributes I = importance of the beliefs P-O-P = point of purchase Source: Adapted from M. Fishbein and I. Azjen, Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior. p. 334. © 1975 Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. Reprinted by permission of Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
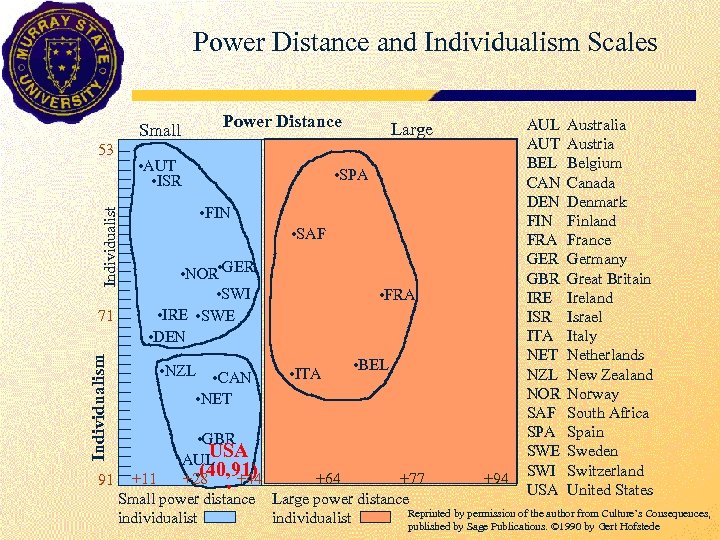 Power Distance and Individualism Scales Power Distance Small Individualist 53 Individualism 71 • AUT • ISR Large • SPA • FIN • SAF • NOR • GER • SWI • IRE • SWE • DEN • NZL • CAN • NET • FRA • ITA • BEL AUL Australia AUT Austria BEL Belgium CAN Canada DEN Denmark FIN Finland FRA France GER Germany GBR Great Britain IRE Ireland ISR Israel ITA Italy NET Netherlands NZL New Zealand NOR Norway SAF South Africa SPA Spain SWE Sweden SWI Switzerland USA United States • GBR USA AUL • (40, 91) +28 • +44 +64 +77 +94 91 +11 Small power distance Large power distance Reprinted by permission of the author from Culture’s Consequences, individualist published by Sage Publications. © 1990 by Gert Hofstede
Power Distance and Individualism Scales Power Distance Small Individualist 53 Individualism 71 • AUT • ISR Large • SPA • FIN • SAF • NOR • GER • SWI • IRE • SWE • DEN • NZL • CAN • NET • FRA • ITA • BEL AUL Australia AUT Austria BEL Belgium CAN Canada DEN Denmark FIN Finland FRA France GER Germany GBR Great Britain IRE Ireland ISR Israel ITA Italy NET Netherlands NZL New Zealand NOR Norway SAF South Africa SPA Spain SWE Sweden SWI Switzerland USA United States • GBR USA AUL • (40, 91) +28 • +44 +64 +77 +94 91 +11 Small power distance Large power distance Reprinted by permission of the author from Culture’s Consequences, individualist published by Sage Publications. © 1990 by Gert Hofstede
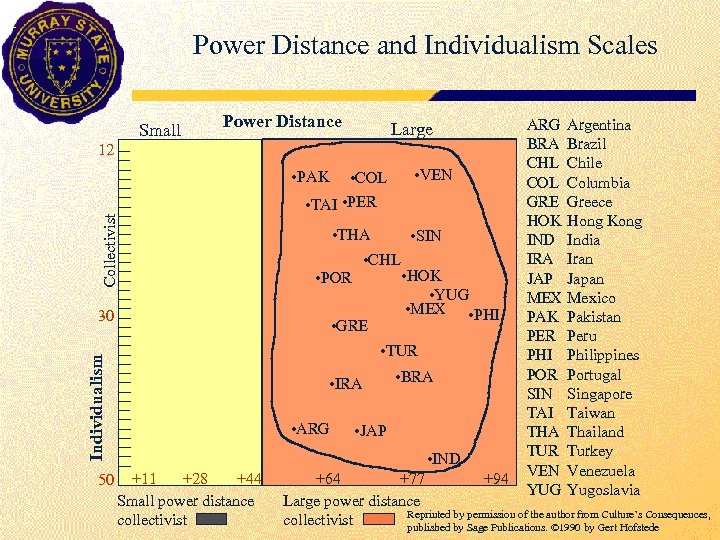 - Power Distance and Individualism Scales Small Power Distance Large 12 • VEN • PAK Collectivist • COL • TAI • PER • THA • GRE • HOK • YUG • MEX • PHI • TUR Individualism 50 • CHL • POR 30 • SIN • IRA • ARG • BRA • JAP • IND +11 +28 +44 Small power distance collectivist ARG Argentina BRA Brazil CHL Chile COL Columbia GRE Greece HOK Hong Kong IND India IRA Iran JAP Japan MEX Mexico PAK Pakistan PER Peru PHI Philippines POR Portugal SIN Singapore TAI Taiwan THA Thailand TUR Turkey VEN Venezuela YUG Yugoslavia +64 +77 +94 Large power distance Reprinted by permission of the author from Culture’s Consequences, collectivist published by Sage Publications. © 1990 by Gert Hofstede
- Power Distance and Individualism Scales Small Power Distance Large 12 • VEN • PAK Collectivist • COL • TAI • PER • THA • GRE • HOK • YUG • MEX • PHI • TUR Individualism 50 • CHL • POR 30 • SIN • IRA • ARG • BRA • JAP • IND +11 +28 +44 Small power distance collectivist ARG Argentina BRA Brazil CHL Chile COL Columbia GRE Greece HOK Hong Kong IND India IRA Iran JAP Japan MEX Mexico PAK Pakistan PER Peru PHI Philippines POR Portugal SIN Singapore TAI Taiwan THA Thailand TUR Turkey VEN Venezuela YUG Yugoslavia +64 +77 +94 Large power distance Reprinted by permission of the author from Culture’s Consequences, collectivist published by Sage Publications. © 1990 by Gert Hofstede
 Culture and Industrial Buyers Complexity of buying situation raw materials to turnkey facilties National and organizational culture factors power distance, risk avoidance, organizational influence Industrial buying process Relationship marketing take buyer’s view, transparency, relationship growth, proactive Japanese and Swedish networks
Culture and Industrial Buyers Complexity of buying situation raw materials to turnkey facilties National and organizational culture factors power distance, risk avoidance, organizational influence Industrial buying process Relationship marketing take buyer’s view, transparency, relationship growth, proactive Japanese and Swedish networks
 3 -1 Chapter Seven Understanding Local Customers MKT 568 Global Marketing Management Dr. Fred Miller
3 -1 Chapter Seven Understanding Local Customers MKT 568 Global Marketing Management Dr. Fred Miller
 What do you think? If you were Anheuser Busch, how would your Budweiser ads in the Super Bowl differ from those in the World Cup final game relative to Target audience? Ad scheduling? Message? Media?
What do you think? If you were Anheuser Busch, how would your Budweiser ads in the Super Bowl differ from those in the World Cup final game relative to Target audience? Ad scheduling? Message? Media?

 Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Chapter How does market research help identify differing consumer preferences in international markets? How do consumer buying behaviors differ in international markets? How do industrial buying behaviors differ in international markets?
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
 Currency Problem: Part 1 The current SF/$US spot rate is (1) 1. 3655 The value of the contract is SF (2) 122, 895 1. 3655 * 90, 000 = 122, 895
Currency Problem: Part 1 The current SF/$US spot rate is (1) 1. 3655 The value of the contract is SF (2) 122, 895 1. 3655 * 90, 000 = 122, 895
 Currency Problem: Part 2 After 30 days, the spot rate is 1. 4233 SF/$US The dollar has (3)strengthened to the SF, resulting in a (4) loss on the transaction of (5) $3, 655. 122, 895 / 1. 4233 = 86, 345 90, 000 – 86, 345 = 3, 655
Currency Problem: Part 2 After 30 days, the spot rate is 1. 4233 SF/$US The dollar has (3)strengthened to the SF, resulting in a (4) loss on the transaction of (5) $3, 655. 122, 895 / 1. 4233 = 86, 345 90, 000 – 86, 345 = 3, 655
 A Strengthened $US to SF is: Bad for Good for US exporters Swiss importers Swiss visitors to US US importers Swiss exporters US visitors to Switzerland A Weakened $US to SF reverses these outcomes.
A Strengthened $US to SF is: Bad for Good for US exporters Swiss importers Swiss visitors to US US importers Swiss exporters US visitors to Switzerland A Weakened $US to SF reverses these outcomes.
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
 Currency Problem: Part 3 30 day forward agreement rate is (6) 1. 3606 and produces a (7) loss of (8) $579. 122, 895 *. 99 = 121, 666 / 1. 3606 = 89, 421 90, 000 - 89, 421 = 579
Currency Problem: Part 3 30 day forward agreement rate is (6) 1. 3606 and produces a (7) loss of (8) $579. 122, 895 *. 99 = 121, 666 / 1. 3606 = 89, 421 90, 000 - 89, 421 = 579
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
 Currency Problem: Part 4 To hedge this position with a futures contract, you should (9) sell (10) one contract(s) at a unit price of (11). 7366 and a total price of (12) $ 92, 075. SF 125, 000 *. 7366 = $ 92, 075
Currency Problem: Part 4 To hedge this position with a futures contract, you should (9) sell (10) one contract(s) at a unit price of (11). 7366 and a total price of (12) $ 92, 075. SF 125, 000 *. 7366 = $ 92, 075
 Currency Futures Trading
Currency Futures Trading
 Currency Futures Trading
Currency Futures Trading
 Currency Futures Trading Buy or Sell Buy Sell Number of Contracts Seven 1 * 125, 000 = $125, 000 5 * 125, 000 = $625, 000 Ninety Price (last digit) Two . 0001 * 125, 000 = $12. 50. 0005 * 125, 000 = $62. 50 Seven
Currency Futures Trading Buy or Sell Buy Sell Number of Contracts Seven 1 * 125, 000 = $125, 000 5 * 125, 000 = $625, 000 Ninety Price (last digit) Two . 0001 * 125, 000 = $12. 50. 0005 * 125, 000 = $62. 50 Seven
 Futures Contract: Coffee Farmer, Nestle’s We are in the coffee business and want to lock in a guaranteed price to lessen our risk and facilitate planning. FC Farmer: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Nestle’s: We will buy 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Spot $5. 00 Jan 5 Mar 15
Futures Contract: Coffee Farmer, Nestle’s We are in the coffee business and want to lock in a guaranteed price to lessen our risk and facilitate planning. FC Farmer: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Nestle’s: We will buy 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Spot $5. 00 Jan 5 Mar 15
 Futures Contract: Speculator I don’t grow or own any coffee, but I believe coffee prices will be lower on March 15 and want to profit from that fall. FC Spot Speculator: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb $5. 00 Jan 5 $4. 00 = $100 ▲ $6. 00 = $100 ▼ Mar 15
Futures Contract: Speculator I don’t grow or own any coffee, but I believe coffee prices will be lower on March 15 and want to profit from that fall. FC Spot Speculator: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb $5. 00 Jan 5 $4. 00 = $100 ▲ $6. 00 = $100 ▼ Mar 15
 Futures Contract: Speculator I don’t grow or own any coffee, but I believe coffee prices will go down and want to profit from that fall. FC 1 Speculator: I will sell 100 X lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb FC 2 Spot ($5 -4) * 100 = $100 ▲ Speculator: I will buy 100 X lbs of coffee on March 15 for $4. 00 per lb $5. 00 Jan 5 $4. 00 Feb 4 Mar 15
Futures Contract: Speculator I don’t grow or own any coffee, but I believe coffee prices will go down and want to profit from that fall. FC 1 Speculator: I will sell 100 X lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb FC 2 Spot ($5 -4) * 100 = $100 ▲ Speculator: I will buy 100 X lbs of coffee on March 15 for $4. 00 per lb $5. 00 Jan 5 $4. 00 Feb 4 Mar 15
 Hedging with Futures Contract Transaction 5 Jan Futures Contract is offset by $490 EITHER 4 Feb $490 4 Feb OR $500
Hedging with Futures Contract Transaction 5 Jan Futures Contract is offset by $490 EITHER 4 Feb $490 4 Feb OR $500
 Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
Global Marketing Decisions in this Exercise How can exchange rate fluctuation affect the profitability of export sales? How can this risk be hedged with forward agreements? How can this risk be hedged with futures contracts? Which method is best for this situation?
 Hedging Methods Choices Forward Agreement Futures Contract Variable amount Fixed amount Flexible time Fixed time Financial institution Futures market Fee/commission/discount Account/commission Best for transactions Best for positions
Hedging Methods Choices Forward Agreement Futures Contract Variable amount Fixed amount Flexible time Fixed time Financial institution Futures market Fee/commission/discount Account/commission Best for transactions Best for positions
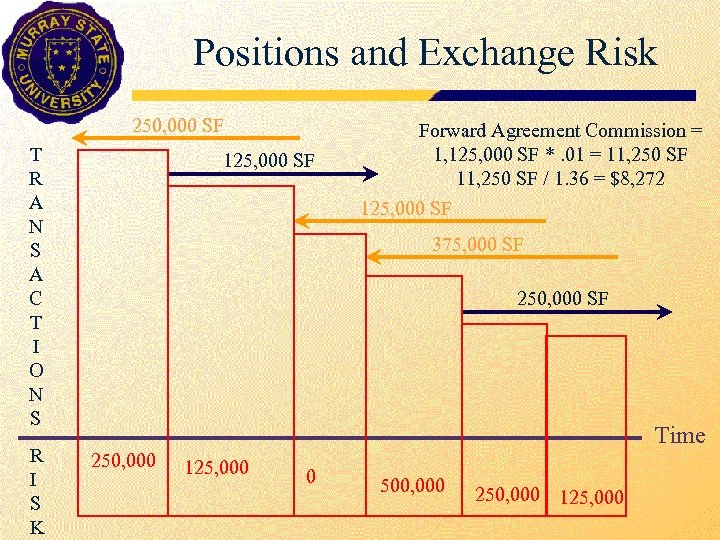 Positions and Exchange Risk 250, 000 SF T R A N S A C T I O N S R I S K 125, 000 SF Forward Agreement Commission = 1, 125, 000 SF *. 01 = 11, 250 SF / 1. 36 = $8, 272 125, 000 SF 375, 000 SF 250, 000 SF Time 250, 000 125, 000 0 500, 000 250, 000 125, 000
Positions and Exchange Risk 250, 000 SF T R A N S A C T I O N S R I S K 125, 000 SF Forward Agreement Commission = 1, 125, 000 SF *. 01 = 11, 250 SF / 1. 36 = $8, 272 125, 000 SF 375, 000 SF 250, 000 SF Time 250, 000 125, 000 0 500, 000 250, 000 125, 000
 WSJ Online Quote
WSJ Online Quote
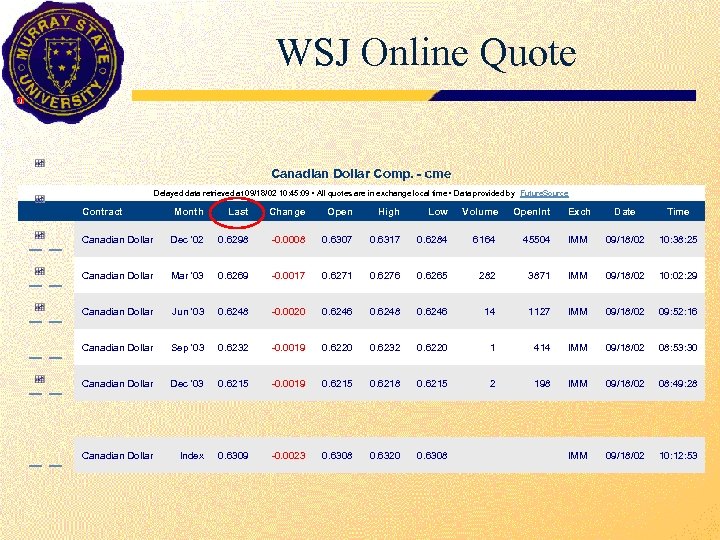 WSJ Online Quote Canadian Dollar Comp. - cme Delayed data retrieved at 09/18/02 10: 45: 09 • All quotes are in exchange local time • Data provided by Future. Source Contract Month Last Change Open High Low Volume Open. Int Exch Date Time Canadian Dollar Dec '02 0. 6298 -0. 0008 0. 6307 0. 6317 0. 6284 6164 45504 IMM 09/18/02 10: 38: 25 Canadian Dollar Mar '03 0. 6269 -0. 0017 0. 6271 0. 6276 0. 6265 282 3871 IMM 09/18/02 10: 02: 29 Canadian Dollar Jun '03 0. 6248 -0. 0020 0. 6246 0. 6248 0. 6246 14 1127 IMM 09/18/02 09: 52: 16 Canadian Dollar Sep '03 0. 6232 -0. 0019 0. 6220 0. 6232 0. 6220 1 414 IMM 09/18/02 08: 53: 30 Canadian Dollar Dec '03 0. 6215 -0. 0019 0. 6215 0. 6218 0. 6215 2 198 IMM 09/18/02 08: 49: 28 Canadian Dollar Index 0. 6309 -0. 0023 0. 6308 0. 6320 0. 6308 IMM 09/18/02 10: 12: 53
WSJ Online Quote Canadian Dollar Comp. - cme Delayed data retrieved at 09/18/02 10: 45: 09 • All quotes are in exchange local time • Data provided by Future. Source Contract Month Last Change Open High Low Volume Open. Int Exch Date Time Canadian Dollar Dec '02 0. 6298 -0. 0008 0. 6307 0. 6317 0. 6284 6164 45504 IMM 09/18/02 10: 38: 25 Canadian Dollar Mar '03 0. 6269 -0. 0017 0. 6271 0. 6276 0. 6265 282 3871 IMM 09/18/02 10: 02: 29 Canadian Dollar Jun '03 0. 6248 -0. 0020 0. 6246 0. 6248 0. 6246 14 1127 IMM 09/18/02 09: 52: 16 Canadian Dollar Sep '03 0. 6232 -0. 0019 0. 6220 0. 6232 0. 6220 1 414 IMM 09/18/02 08: 53: 30 Canadian Dollar Dec '03 0. 6215 -0. 0019 0. 6215 0. 6218 0. 6215 2 198 IMM 09/18/02 08: 49: 28 Canadian Dollar Index 0. 6309 -0. 0023 0. 6308 0. 6320 0. 6308 IMM 09/18/02 10: 12: 53
 Hedging with Sports Bets I sell you a shipment of Dunker bobble heads for $50, 000. Attached to the payment is a receipt for a $25, 000 bet on MSU vs WKU in Saturday’s game. How much money will I get if MSU wins? $75, 000 How much money will I get if WKU wins? $25, 000 I want to guarantee the $50, 000 contract price, so I make a second $25, 000 bet on WKU to win the game. How much money will I get if MSU wins? $50, 000 $25, 000 win on MSU bet, $25, 000 loss on WKU offset, keep $50, 000 payment How much money will I get if WKU wins? $50, 000 $25, 000 loss on MSU bet, $25, 000 win on WKU offset, keep $50, 000 payment
Hedging with Sports Bets I sell you a shipment of Dunker bobble heads for $50, 000. Attached to the payment is a receipt for a $25, 000 bet on MSU vs WKU in Saturday’s game. How much money will I get if MSU wins? $75, 000 How much money will I get if WKU wins? $25, 000 I want to guarantee the $50, 000 contract price, so I make a second $25, 000 bet on WKU to win the game. How much money will I get if MSU wins? $50, 000 $25, 000 win on MSU bet, $25, 000 loss on WKU offset, keep $50, 000 payment How much money will I get if WKU wins? $50, 000 $25, 000 loss on MSU bet, $25, 000 win on WKU offset, keep $50, 000 payment
 Futures Contract Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75 Buy or Sell: Sell Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75
Futures Contract Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75 Buy or Sell: Sell Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75
 Futures Contract Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00 Buy or Sell: Sell Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00
Futures Contract Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00 Buy or Sell: Sell Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00
 Liquidating Futures Contracts 11: 30 Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00 Buy or Sell: Sell 11: 40 Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Exit Market, Leaving $. 25 Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75
Liquidating Futures Contracts 11: 30 Buy or Sell: Buy Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $1. 00 Buy or Sell: Sell 11: 40 Date & Time: 13 Feb, 12: 15 PM Exit Market, Leaving $. 25 Commodity: One 12 oz Coca Cola Price: $0. 75
 Chinese Management & Modern China Videos Explain the role of the following in traditional Chinese management style and practices Family relationships and quanxi Harmony and loyalty Respect for superiors and creativity What can Chinese managers most productively learn from Western management styles? What can Western managers most productively learn from Chinese management styles? How has economic reform affected state owned firms, private enterprises and rural farmers in China?
Chinese Management & Modern China Videos Explain the role of the following in traditional Chinese management style and practices Family relationships and quanxi Harmony and loyalty Respect for superiors and creativity What can Chinese managers most productively learn from Western management styles? What can Western managers most productively learn from Chinese management styles? How has economic reform affected state owned firms, private enterprises and rural farmers in China?
 Going International Video How important is the concept of culture in understanding the behavior of people from different countries? Use examples from the video to illustrate your answers. What is the difference between “cultural awareness” and “cultural stereotyping? ” How can managers benefit from the former without suffering from the latter? According to the video (use examples), how do the world’s cultures vary in each of the following dimensions? Time Space Sanitary habits Communication style
Going International Video How important is the concept of culture in understanding the behavior of people from different countries? Use examples from the video to illustrate your answers. What is the difference between “cultural awareness” and “cultural stereotyping? ” How can managers benefit from the former without suffering from the latter? According to the video (use examples), how do the world’s cultures vary in each of the following dimensions? Time Space Sanitary habits Communication style
 Understanding Culture Academic approaches How are cultures organized? What do they value? History Anthropology Geography Humanities University Studies courses Professional/pragmatic approaches How should managers operate in multiple cultures? Social and professional values Social and professional behavior Intercultural communication and negotiation Multicultural interpersonal interaction International business, management, marketing courses
Understanding Culture Academic approaches How are cultures organized? What do they value? History Anthropology Geography Humanities University Studies courses Professional/pragmatic approaches How should managers operate in multiple cultures? Social and professional values Social and professional behavior Intercultural communication and negotiation Multicultural interpersonal interaction International business, management, marketing courses
 Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values? What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values? What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
 Legacy of China Video Identify and describe three major religious/philosophical traditions which form the foundation of Chinese civilization. Explain how traditional Chinese cuisine, medicine, calligraphy and artistic traditions reflect the values of these three traditions. What historical events in the last 150 years have caused the Chinese people to lose faith in these traditions? With what results for modern China?
Legacy of China Video Identify and describe three major religious/philosophical traditions which form the foundation of Chinese civilization. Explain how traditional Chinese cuisine, medicine, calligraphy and artistic traditions reflect the values of these three traditions. What historical events in the last 150 years have caused the Chinese people to lose faith in these traditions? With what results for modern China?
 Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values? What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values? What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
 Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism Daoism Buddhism
Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism Daoism Buddhism
 Confucian Rectification of Names silver weed coffee valley
Confucian Rectification of Names silver weed coffee valley
 “Things can not be accomplished. ” artificial flower arrangement urn flower(s) silver
“Things can not be accomplished. ” artificial flower arrangement urn flower(s) silver
 “Ceremonies will not flourish. ” Our Father Who art in Heaven Your uncle who was in Shangrila An ostrich eats motorcycles
“Ceremonies will not flourish. ” Our Father Who art in Heaven Your uncle who was in Shangrila An ostrich eats motorcycles
 Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know
Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know
 The World According to Daoism Being Ugliness Active Soft Hard Beauty Passive Non-being
The World According to Daoism Being Ugliness Active Soft Hard Beauty Passive Non-being
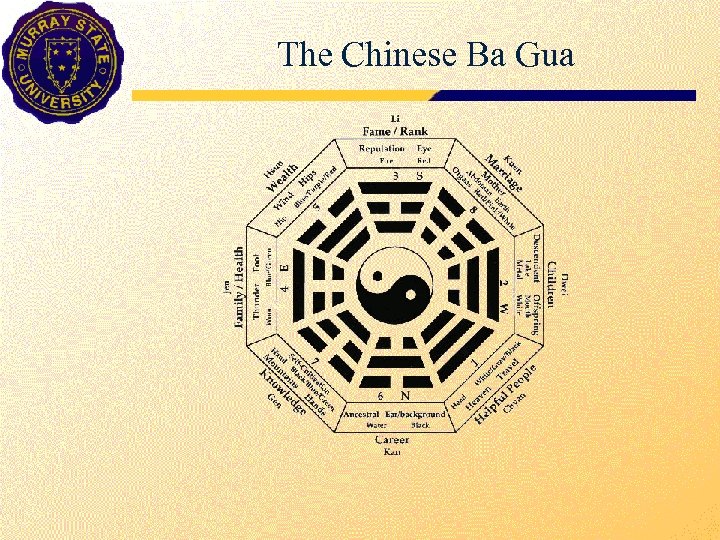 The Chinese Ba Gua
The Chinese Ba Gua
 Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know Daoism – Yes, but not ultimately so
Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know Daoism – Yes, but not ultimately so
 Treatise of the Golden Lion
Treatise of the Golden Lion
 Treatise of the Golden Lion
Treatise of the Golden Lion
 Treatise of the Golden Lion
Treatise of the Golden Lion
 Treatise of the Golden Lion
Treatise of the Golden Lion
 Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know Daoism – Yes, but not ultimately so Buddhism – No, and it is folly to believe it is These three traditions are part of one truth!
Unity within diversity: Religion in China Is the world perceived by the senses real? Confucianism – Yes, it is all we can know Daoism – Yes, but not ultimately so Buddhism – No, and it is folly to believe it is These three traditions are part of one truth!
 Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
Researching History, Religion and Culture What are your country’s major historical events and their impact? What are your country’s major religious traditions and their values What are your country’s major linguistic and ethnic groups? What is their importance?
 Negatives of Modern Cosmology The Earth is not the center of the universe The sun is not the center of the universe Our galaxy is not the center of the universe Our type of matter is not the dominant constituent of the Universe (dark matter is) Our Universe (seen and unseen) is not the only Universe Our physics is not the only physics. There might exist separate universes with completely different physics. Source: Mark Davis, Professor of Astronomy and Physics, Cal Berkeley
Negatives of Modern Cosmology The Earth is not the center of the universe The sun is not the center of the universe Our galaxy is not the center of the universe Our type of matter is not the dominant constituent of the Universe (dark matter is) Our Universe (seen and unseen) is not the only Universe Our physics is not the only physics. There might exist separate universes with completely different physics. Source: Mark Davis, Professor of Astronomy and Physics, Cal Berkeley
 Futures Contract: Hedger I will receive SF on Feb 5 and, therefore run a risk that the value of the SF will fall. I want to limit that risk with an instrument that will profit if the SF falls. FC 1 Speculator: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Speculator: I will buy 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $4. 00 per lb FC 2 Spot ($5 -4) * 100 = $100 ▲ $5. 00 $4. 00 Jan 5 Feb 5 Mar 15
Futures Contract: Hedger I will receive SF on Feb 5 and, therefore run a risk that the value of the SF will fall. I want to limit that risk with an instrument that will profit if the SF falls. FC 1 Speculator: I will sell 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $5. 00 per lb Speculator: I will buy 100 lbs of coffee on March 15 for $4. 00 per lb FC 2 Spot ($5 -4) * 100 = $100 ▲ $5. 00 $4. 00 Jan 5 Feb 5 Mar 15


