b6ff5e0bf893049a939aec7c495870d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

22: 010: 622 Internet Technology and E-Business Dr. Peter R. Gillett Associate Professor Department of Accounting & Information Systems Rutgers Business School – Newark & New Brunswick Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 1

Outline n n n n The Story So Far. . . Why the Internet works so well? Internet Application Protocols Dell HTTP, SGML, HTML & XML Personal Web Pages Electronic Marketing The Story So Far. . . Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 2

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapters 1 -2: The revolutionary impact of the Internet & some links k. Chapter 3: Ubiquitous access k. Chapter 4: Analog v. digital k. Chapter 5: Digital data (Morse code) k. Chapter 6: Modulation-demodulation k. Chapter 7: Local area networks Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 3

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 8 -11: History of the Internet: u Many incompatible LANs u LANs incompatible with WANs u DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) u ARPANET (late 70 s) – backbone WAN u TCP/IP Open system è RFCs (Request for Comments) online è u 1982 Dr. Peter R Gillett Prototype Internet using TCP/IP 19 March 2018 4

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 8 -11: History of the Internet: u TCP/IP integrated into UNIX u NSF funds CSNET using TCP/IP u IAB (Internet Activities/Architecture Board) u IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) u NSFNET Mid-level Networks è NSF backbone è Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 5

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 8 -11: History of the Internet: u 1992: ANSNET u 1995: v. BNS u Internet 2 u Other networks: BITNET è FIDONET è JANET è EBONE è Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 6

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter u. Packet 12 -19: Underlying Technologies: switching è Label packets è Computer addressing è Variable size packets è Slow start – increasing transmission rates è TTL (Time To Live) u. Routers Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 7

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 12 -19: Underlying Technologies: u. Access è ISPs (Internet Service Providers) è Dial-Up/Modems è Cable modems è ADSL è Wireless Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 8

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter u. IP 12 -19: Underlying Technologies: (Internet Protocol) è Software on every (? ) machine è Datagrams: Internet packets è Dotted quad addresses u. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) è ACK è Resend è TTL Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 9
The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter u. DNS n 12 -19: Underlying Technologies: (Domain Name Servers) Other Protocols: k. HTTP k. SMTP k. POP 3 k. IMAP Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 10

The Story So Far. . . n Quality of Service k. Delay k. Jitter k. Bandwidth k. Reliability Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 11
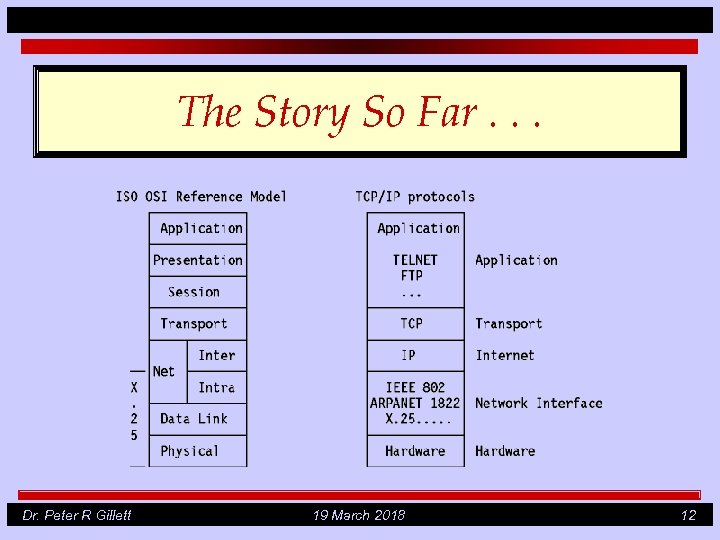
The Story So Far. . . Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 12

Why the Internet Works So Well n n n Today, typical computers are 1000 times faster than they were when TCP/IP was first used (around 1982) Switching technology is 2500% faster The Internet is a very complex system TCP/IP is well documented and it was well studied before it was put in action Dr. David Clark (Internet Architect from 1983 to 1989) said: “rough consensus and working code” Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 13

IP Provides Flexibility n Extremely flexible! n Makes NO assumptions about the underlying hardware Works on WANs and LANs Any speed networks Guaranteed no packet loss or just best effort Any media (level 1 or 2 of OSI model), such as fiber, twisted pair, cellular, etc. n n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 14
TCP Provides Reliability n n Adaptability of TCP allows it to manage IP datagrams across various media Compensates for differences in underlying network hardware k WANs can loose many packets, where LANs rarely do k Speed differences for different network links n Handles rapid changes in performance due to changing network loads Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 15

Long Term Research’s Role TCP/IP developed by dedicated and talented people n Researchers were allowed to experiment and look at fundamental problems n Researchers insisted each part work well before TCP/IP was released n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 16

Email, Bulletin Boards & Browsers n n Email is credited to Ray Tomlinson Economic Impact k Small and Large Companies k The earth’s distance shrunk again n Internet based communities k How to profit from them? k How to support them for business? k Extremely specialized k How do these impact professionals? Business people, physicians and lawyers? Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 17

Chat Rooms, Talk, etc. n What are the opportunities for Business? k Helping clients and potential clients k Competitive Information k Others? n Will Chat rooms evolve into interactive conference calls? k Do people want this? Is there good from some anonymity? k Business Issues k ATM networks, etc. Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 18
ftp and telnet n n n ftp: file transport protocol: predates the Internet back to the Arpanet days telnet: predates the present Internet as well, remote logins, MIT X Windows, etc. Purpose was to allow the use of remote resources ftp and telnet USE (sit on top of) TCP/IP The notion of time sharing! k Discussion, what exactly is this? k Classical examples, IBM VM, Unix, Multix Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 19
Industrial Interlude: Dell n The Dell Example k. Over $35 billion in sales expected this F Year (2003) k. Larger and larger portion of sales over the Internet n The Beginning: Mike Dell at Univ. of Texas k. The market he sold to k. The change in 1993 Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 20

Dell 30% to 40% growth rates n Some observations: n k. Dell’s initial market was the hobbyist k. Later, their market grew to business and home customers k. This change required re-engineering! k. The Web suited this well, & also fits the small computer shipping paradigm Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 21
Dell n n Compaq and the 1993 price war Dell lost $65 million, close to bankruptcy Response: fundamental change in business Re-engineering k Just-in-time manufacturing k Mass customization k Employees monitor their own productivity k Later: moved to customized electronic catalogues k Build web sites at Dell, for their large customers Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 22

HTTP n n Another protocol on top of TCP/IP How does it work? k Client/Server k Serves Web Pages u CGI bin, Common Gateway Interface, typical of Unix Servers u ASP: Active Server Pages, typical of Microsoft servers u Can dynamically, on demand, build varying pages to be served k Uses Dr. Peter R Gillett HTML for presentation 19 March 2018 23

HTML n History and place in industry k Hypertext named in the 1960 by T. Nelson in his book: “Literary Machines” k Scientists working on a generalized markup languages GMLs k ISO standardized SGML in 1986 u Mark up documents independent of computer hardware and software u Very exacting language: DOD, Assoc. American Publishers, Hewlett-Packard, Kodak, etc. , use SGML Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 24
SGML n Key Attributes and Advantages of SGML k Can last a long time due to standards of the ISO k Nonproprietary and software/hardware independence give it long lasting ability k Supports user defined tags n Disadvantages and difficulties k Expensive to set up and run k Expensive compared to HTML k Has a steep learning curve Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 25

HTML and XML n n n Both have their own DTDs (Document Type Definitions) T. Berners-Lee (and others? ) trimmed down SGML to create HTML only places and formats text! k Only static details, no “page state” is kept k Cannot interpret the meaning of parts of a page n n n XML (e. Xtensible Markup Language) XML is also based on SGML XML is designed to have some understanding of the semantics of data on a page Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 26

HTML’s Weakness n Lacking the ability to maintain the state of a visitor has lead to: k XML k Java. Script k Java applets, etc. k Visual Basic (as applied to the web) n Lacking the ability to understand details of its own data has given way to complex servers Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 27

XML See www. xml. com n XML both n k. Retains the state of a page or web surfer k“Understands” the content of a page Has metadata: information about data in a page n Helps automatic processing on web pages n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 28
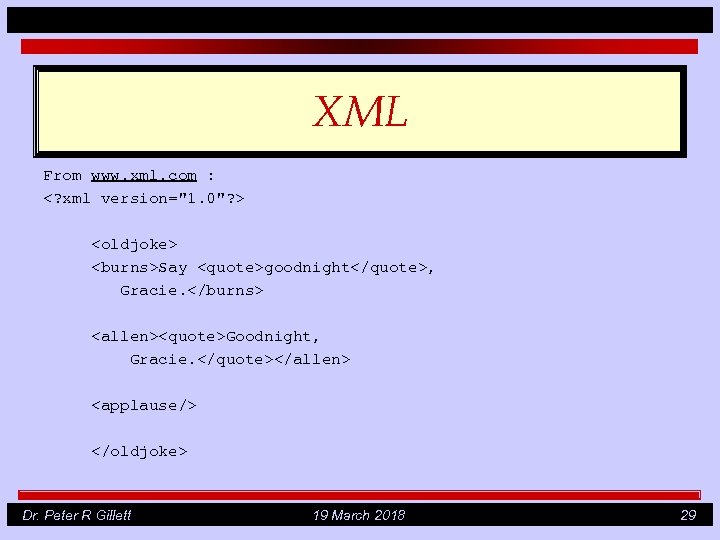
XML From www. xml. com : <? xml version="1. 0"? > <oldjoke> <burns>Say <quote>goodnight</quote>, Gracie. </burns> <allen><quote>Goodnight, Gracie. </quote></allen> <applause/> </oldjoke> Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 29

XML <!ELEMENT oldjoke (burns+, allen, applause? )> n Syntax: n k. X+ means one or more k. X means exactly one k. X? means perhaps one k. Similar to Regular Expression Syntax Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 30

HTML Basics <tag_name properties> Text to be Displayed </tag_name> n Example: <B> Wow! </B> n n Wow! Tags not case sensitive n Opening and closing tags, one sided tags: <P align=“right”> n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 31

HTML Basics n n n The main attraction: html links! <a href=“http: //www. rutgers. edu”> Visit Rutgers! </a> <a href=“http: //www. business. rutgers. edu”> RU Business! </a> <a href=“#ref_1”> Click Here to Go There </a> <a name=“ref_1”> !!! Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 32

HTML n n Check out: www. loc. gov/global/internet/html Also: www. w 3. org Current specification since 24 -Apr-1998 is 4. 0, revised 24 -Dec-1999 to 4. 01 Varying link structures k Linear k Trees k Other Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 33

Personal Web Pages n n n Various HTML editors MS Word, for example The public_html directory The file index. html Everything in public_html is viewable by the world! Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 34

Creating a Web Page n Create a subdirectory public_html: k md n public_html Enable public access: k chmod n n a+xr public_html Logout ftp the content of the “Homepage” directory to public_html k ftp. eden. ruters. edu k Login using your account name and password k cd public_html k put index. html k etc. n Test! Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 35
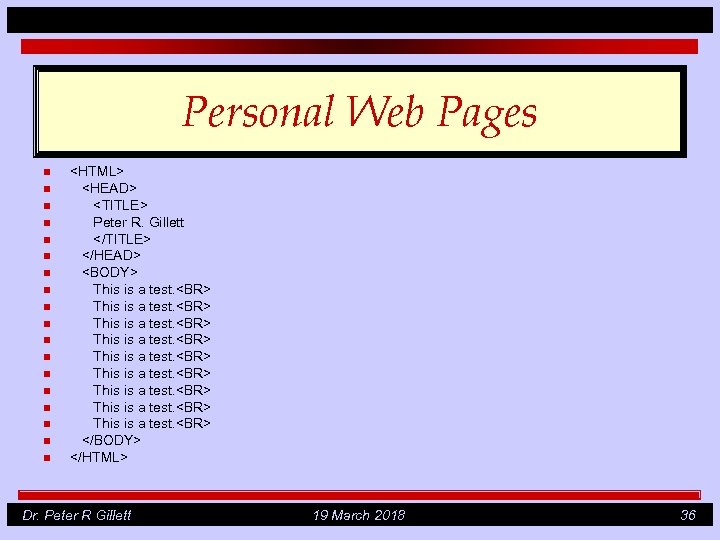
Personal Web Pages n n n n n <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE> Peter R. Gillett </TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> This is a test. <BR> This is a test. <BR> </BODY> </HTML> Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 36

Personal Web Pages http: //rucs. rutgers. edu/websupport. html n http: //www. nbcs. rutgers. edu/www. html n http: //www. eden. rutgers. edu/templatebody. html n http: //newarkwww. rutgers. edu/pubadmin/T PA/TPASpring 2000/webpages. PPT n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 37

Testing, testing and testing! n n n n Which web browsers Which versions of which web browsers? Loads - how many web pages served? Interactive speed on weak home computers Regression Testing Unit Testing Market Research Testing Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 38

Internets, Intranets and Extranets Internet: World-Wide WAN n Intranet: web-based private network n Extranet: intranet connecting business partners, certain customers or suppliers n Extranets and Wal-Mart's inventory management: letting the suppliers see the inventory moving off the shelves n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 39

A Start on E-Marketing n Two key issues of building web pages k. Marketing (Issue for most B 2 C and B 2 B) k. Logistics (Wal-Mart example) Profit = Revenue – Cost n Marketing focuses on Revenue n Logistics focuses on Costs n Both part of the same equation! n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 40

E-Marketing n Selling is hard: sell commodity X k. Makes potential buyers of X aware you are selling X k. Brand positioning of you with other vendors k. Sales strategy k. Make the Sale! n Flavors: relationship marketing, one-to-one marketing, mass marketing Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 41

What can the Internet Offer? n Mass marketing? Yes, but more! k Demographics of the Internet still pretty good k Make it easy for your customers to find you n Relationship marketing? Yes, k Use the Internet as another contact media k See the Dell example and my-yahoo: make customers dependant on you n One-to-one marketing? k Gigantic Dr. Peter R Gillett Advances! 19 March 2018 42
Some Details n New brand image media k k n n n Media of its own Enhancing other media Product comparison transparency Transaction costs/friction minimized Changing vendors costs/friction minimized (oops!) k How can we change this? Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 43

Internet One-to-One Marketing n Computers and Humans: complementary k In general what machines can do enhances what humans can do n Know your potential customer! k Who looked in my window? How much do they spend on shoes a year? k How many people that look in my window make a purchase? k Those days I have a red background do I sell more than when I have a green background? Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 44

Direct Marketing n Tools k Sign up! k Email marketing u Very low cost u Click a link and explore more offerings u Most direct marketing details translatable Coupons è Frequent-flyer miles (even easier) è u Other things? u Beware of spam! Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 45

Classical Purchase Model 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. There is a need for a solution Search for a solution, explicitly or implicitly Discovery or examination of different solutions Possible refinement of needs Evaluation of different solutions Purchase Possible service or follow up Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 46

Internet Effects on Purchase Model n n n How has the Internet effected this? Has every step been effected? Where are the traps and pitfalls? k Have n n you seen any traps and/or pitfalls? How could different firms use such models to enhance their web sites What is your web site’s goal? Web site strategies and planning WIIFM? Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 47
Choi et. al. ’s Cube of EC http: //uts. cc. utexas. edu/~soon/vita/sellingonline. html n X-axis: type of delivery agent: from physical to electronic (to virtual) n Y-axis: type of product: from physical to electronic (to virtual) n Z-axis: market processes: from physical to electronic (to virtual) n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 48

Lessons from Choi et. al. ’s Cube The New Economy n How extensive is it really? At least as seen through this cube? n Does the virtual dimension make any sense? n k. How can we exploit virtual information? What good do such models give us? n Where to next? n Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 49

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 20: Email u. Mailboxes u. Email addresses u. Client/Server! u. Mailing lists k. Chapter 21: Bulletin Boards/News u. Subscribing u. Netiquette Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 50

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k Chapter 22: Web Browsers u Gopherspace è Veronica Very Easy Rodent-Oriented Net-wide Index to Computerized Archives è u URLs k Chapter 25: Automated Web Search u Search Engines u Directories u String matching u Boolean Logic Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 51

The Story So Far. . . n Comer: k. Chapter 27: Faxes and FTP: u. Anonymous FTP u. Archie (database of FTP sites and their contents) k. Chapter 28: TELNET u. Remote Dr. Peter R Gillett access 19 March 2018 52

Class Projects n Personal Web Pages k. Will n be due March 5 Projects k. Will be group projects k. Produce a paper or demonstration relevant to the class u. Proposals due March 26 u. First Draft due April 16 u. Presentations and Final versions due April 30 Dr. Peter R Gillett 19 March 2018 53
b6ff5e0bf893049a939aec7c495870d6.ppt