befc4841535c303a56599ebcfba23588.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 University-Enterprise cooperation for knowledge and skill requirements joint definition M. Carbonaro, GISIG, Genova, IT 25 th September 2014 0
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 University-Enterprise cooperation for knowledge and skill requirements joint definition M. Carbonaro, GISIG, Genova, IT 25 th September 2014 0
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 1 Foreword GISIG Association is a University – Enterprise Training partnership founded in 1992 within the former EC COMETT Programme. From more than 20 years we operate at European level for innovation and technology transfer on the GI field, grouping expertise from universities, companies and users to promote and develop joint projects.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 1 Foreword GISIG Association is a University – Enterprise Training partnership founded in 1992 within the former EC COMETT Programme. From more than 20 years we operate at European level for innovation and technology transfer on the GI field, grouping expertise from universities, companies and users to promote and develop joint projects.
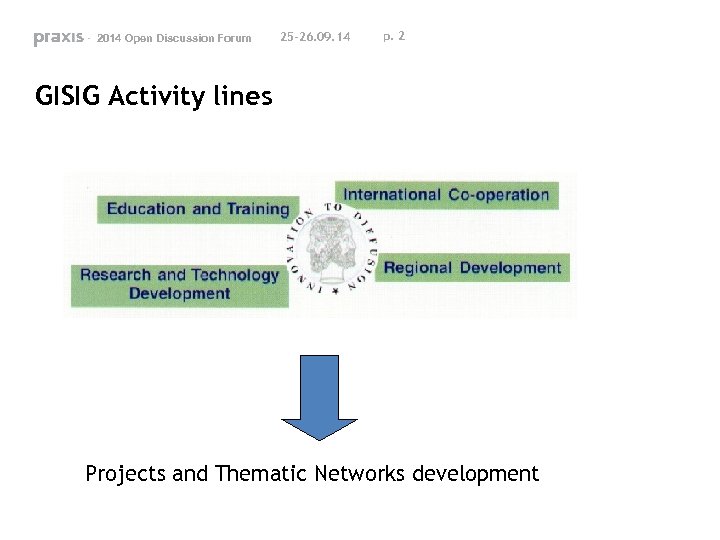 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 2 GISIG Activity lines Projects and Thematic Networks development
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 2 GISIG Activity lines Projects and Thematic Networks development
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 3 Education and Training Since 1992, for ten years we managed COMETT/Leonardo da Vinci grants for students/new graduates and staff needing practical experience and professional up-dating on geo-spatial technologies and related applications in specific thematic domains. We were pioneer to apply the EUROPASS Certificate to people on mobility. In parallel, we developed since the beginning training courses on GI application technologies. These activities evolved in a strong joint universityenterprise cooperation able to agree on shared definition of skills and competences requirements for new labour market needs in the GI field.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 3 Education and Training Since 1992, for ten years we managed COMETT/Leonardo da Vinci grants for students/new graduates and staff needing practical experience and professional up-dating on geo-spatial technologies and related applications in specific thematic domains. We were pioneer to apply the EUROPASS Certificate to people on mobility. In parallel, we developed since the beginning training courses on GI application technologies. These activities evolved in a strong joint universityenterprise cooperation able to agree on shared definition of skills and competences requirements for new labour market needs in the GI field.
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 4 LINKVIT Leveraging Inspire Knowledge into Vocational Innovative Training Leonardo da Vinci project Transfer of knowledge strand (IT) www. linkvit. eu
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 4 LINKVIT Leveraging Inspire Knowledge into Vocational Innovative Training Leonardo da Vinci project Transfer of knowledge strand (IT) www. linkvit. eu
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 5 Project aims • LINKVIT deals with “Digital Competence” as defined in the Key competences for Lifelong Learning- A European Framework. • Competences in geo-information are crucial in the new European context to be operational in the assignments of the INSPIRE Directive. • LINKVIT will aim at creating such competences through a set of training modules developed in different European initiatives.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 5 Project aims • LINKVIT deals with “Digital Competence” as defined in the Key competences for Lifelong Learning- A European Framework. • Competences in geo-information are crucial in the new European context to be operational in the assignments of the INSPIRE Directive. • LINKVIT will aim at creating such competences through a set of training modules developed in different European initiatives.
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 6 Project aims • LINKVIT aims to provide revised training material to support INSPIRE implementation • Start are the business processes supporting INSPIRE implementation • To cover the activities within those processes you need certain skills and knowledge • Define expert / job profiles for which learning paths are designed 6
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 6 Project aims • LINKVIT aims to provide revised training material to support INSPIRE implementation • Start are the business processes supporting INSPIRE implementation • To cover the activities within those processes you need certain skills and knowledge • Define expert / job profiles for which learning paths are designed 6
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 7 Target groups Already existing learning material is leveraged and reframed to provide end-user oriented modular learning to: • Employed people to be re-qualified on new competence required by INSPIRE • Postgraduates, for easier access to GI-labour market with a post-degree specialization • Professional profiles within public and private sector (technicians and decisions makers) 7
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 7 Target groups Already existing learning material is leveraged and reframed to provide end-user oriented modular learning to: • Employed people to be re-qualified on new competence required by INSPIRE • Postgraduates, for easier access to GI-labour market with a post-degree specialization • Professional profiles within public and private sector (technicians and decisions makers) 7
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 8 Learning Paths • How to define the Learning Paths? 1. Take into account the business processes and activities that should be covered. . . 2. Work from a more generic level towards a more detailed level (if necessary). . . 3. Based on the definition of what someone should be able to know and do. . . 4. To be fine-tuned for each individual when applied in practice. . .
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 8 Learning Paths • How to define the Learning Paths? 1. Take into account the business processes and activities that should be covered. . . 2. Work from a more generic level towards a more detailed level (if necessary). . . 3. Based on the definition of what someone should be able to know and do. . . 4. To be fine-tuned for each individual when applied in practice. . .
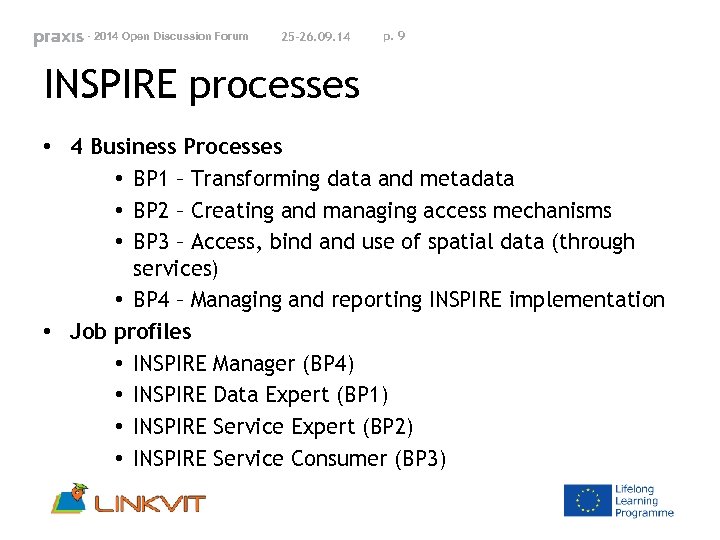 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 9 INSPIRE processes • 4 Business Processes • BP 1 – Transforming data and metadata • BP 2 – Creating and managing access mechanisms • BP 3 – Access, bind and use of spatial data (through services) • BP 4 – Managing and reporting INSPIRE implementation • Job profiles • INSPIRE Manager (BP 4) • INSPIRE Data Expert (BP 1) • INSPIRE Service Expert (BP 2) • INSPIRE Service Consumer (BP 3)
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 9 INSPIRE processes • 4 Business Processes • BP 1 – Transforming data and metadata • BP 2 – Creating and managing access mechanisms • BP 3 – Access, bind and use of spatial data (through services) • BP 4 – Managing and reporting INSPIRE implementation • Job profiles • INSPIRE Manager (BP 4) • INSPIRE Data Expert (BP 1) • INSPIRE Service Expert (BP 2) • INSPIRE Service Consumer (BP 3)
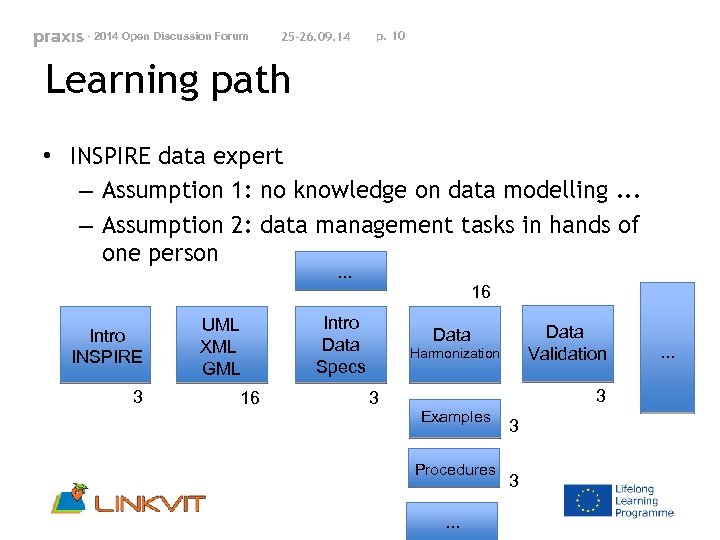 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 10 Learning path • INSPIRE data expert – Assumption 1: no knowledge on data modelling. . . – Assumption 2: data management tasks in hands of one person. . . Intro INSPIRE 3 UML XML GML 16 16 Intro Data Specs Data Validation Data Harmonization 3 3 Examples Procedures . . . 3 3 . . .
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 10 Learning path • INSPIRE data expert – Assumption 1: no knowledge on data modelling. . . – Assumption 2: data management tasks in hands of one person. . . Intro INSPIRE 3 UML XML GML 16 16 Intro Data Specs Data Validation Data Harmonization 3 3 Examples Procedures . . . 3 3 . . .
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 11 Geographic Information Need to Know (GI-N 2 K) • The GI-N 2 K project is built around a network of 31 partners ( 25 countries ) from the academic and non – academic sectors and partners from the GI industry (including Shell ), major GI associations and individual experts. • GI-N 2 K aims to answer the question on how the education and vocational training in the domain of GI S&T can match with the actual job requirements in the job market. • The project analyzes the current market demands with regard to the knowledge and skills and compare them with the current training offer in the GI S&T sector. The existing GI S&T Body of Knowledge is being used as a starting point, updated and brought in line with new technological developments, and with the European perspective in mind. ERASMUS Network
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 11 Geographic Information Need to Know (GI-N 2 K) • The GI-N 2 K project is built around a network of 31 partners ( 25 countries ) from the academic and non – academic sectors and partners from the GI industry (including Shell ), major GI associations and individual experts. • GI-N 2 K aims to answer the question on how the education and vocational training in the domain of GI S&T can match with the actual job requirements in the job market. • The project analyzes the current market demands with regard to the knowledge and skills and compare them with the current training offer in the GI S&T sector. The existing GI S&T Body of Knowledge is being used as a starting point, updated and brought in line with new technological developments, and with the European perspective in mind. ERASMUS Network
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 12 Geographic Information Need to Know (GI-N 2 K) • GI-N 2 K builds upon the existing Geographic Information Science and Technology Body of Knowledge (GI S&T Bo. K) that was developed by the American University Consortium for Geographic Information Science , published in 2006 by the Association of American Geographers. The ‘Bo. K’ will be updated and brought into line with the new technological developments and the European perspective ( e. g. importance of INSPIRE in Europe). • The renewed Bo. K will apply an ontological approach and will take the form of a dynamic e-platform (wiki-based format) including tools to use, explore the Bo. K, to define curricula , training opportunities and courses and to define job profiles. More info at www. gi-n 2 k. eu ERASMUS Network
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 12 Geographic Information Need to Know (GI-N 2 K) • GI-N 2 K builds upon the existing Geographic Information Science and Technology Body of Knowledge (GI S&T Bo. K) that was developed by the American University Consortium for Geographic Information Science , published in 2006 by the Association of American Geographers. The ‘Bo. K’ will be updated and brought into line with the new technological developments and the European perspective ( e. g. importance of INSPIRE in Europe). • The renewed Bo. K will apply an ontological approach and will take the form of a dynamic e-platform (wiki-based format) including tools to use, explore the Bo. K, to define curricula , training opportunities and courses and to define job profiles. More info at www. gi-n 2 k. eu ERASMUS Network
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 13 Assessment of training needs in the water sector
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 13 Assessment of training needs in the water sector
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 14 Assessment background ü has been carried out in the first project phase Objectives: ü to help the identification of the e. LEANOR training subjects ü to validate and further investigate existing training needs of water companies considered in the project ü to improve the training in the water sector through the optimisation and standardisation of the learning processes and pathways ü to reflect the main demands of skills by EU Directives (water protection, waste water treatment, water supply, storm water management)
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 14 Assessment background ü has been carried out in the first project phase Objectives: ü to help the identification of the e. LEANOR training subjects ü to validate and further investigate existing training needs of water companies considered in the project ü to improve the training in the water sector through the optimisation and standardisation of the learning processes and pathways ü to reflect the main demands of skills by EU Directives (water protection, waste water treatment, water supply, storm water management)
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 15 Steps The vocational training needs assessment covered following steps: ü Water business survey ü creation of a lists of Business Processes (BPs) and Job Profiles (JPs), ü validation of the lists by water professionals, ü assessment of a level of knowledge for each Job Profile, ü validation of the levels by water professionals, ü creation of a matrix mapping the training needs in relation with JPs and BPs.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 15 Steps The vocational training needs assessment covered following steps: ü Water business survey ü creation of a lists of Business Processes (BPs) and Job Profiles (JPs), ü validation of the lists by water professionals, ü assessment of a level of knowledge for each Job Profile, ü validation of the levels by water professionals, ü creation of a matrix mapping the training needs in relation with JPs and BPs.
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 16 Water business survey ü extension of the water domain is large ü in order to precise the different BP and the JP that derives from them, a better understanding of the water cycle was studied ü this understanding helped to choose the water uses to work on Industry Recreation Urban Water Uses Natural Environment Water Cycle Domains Aquaculture Energy Agriculture Transport/ Navigation Natural Hazards
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 16 Water business survey ü extension of the water domain is large ü in order to precise the different BP and the JP that derives from them, a better understanding of the water cycle was studied ü this understanding helped to choose the water uses to work on Industry Recreation Urban Water Uses Natural Environment Water Cycle Domains Aquaculture Energy Agriculture Transport/ Navigation Natural Hazards
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 17 Business Processes Frames of BP Asset Management Operation of Plants Works and Interventions Operation of Networks Measurements Water Resources Management Public Service Contract Management Environmental Monitoring Geographical Information 29 BPs within ü classification of urban water uses was done, by identifying the existing water business processes and jobs profiles ü Business Process (BP): Collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product (serve a particular goal) for a particular customer or customers. A process is thus a specific ordering of work activities across time and place, with a beginning, an end, and clearly defined inputs and outputs: a structure for action.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 17 Business Processes Frames of BP Asset Management Operation of Plants Works and Interventions Operation of Networks Measurements Water Resources Management Public Service Contract Management Environmental Monitoring Geographical Information 29 BPs within ü classification of urban water uses was done, by identifying the existing water business processes and jobs profiles ü Business Process (BP): Collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product (serve a particular goal) for a particular customer or customers. A process is thus a specific ordering of work activities across time and place, with a beginning, an end, and clearly defined inputs and outputs: a structure for action.
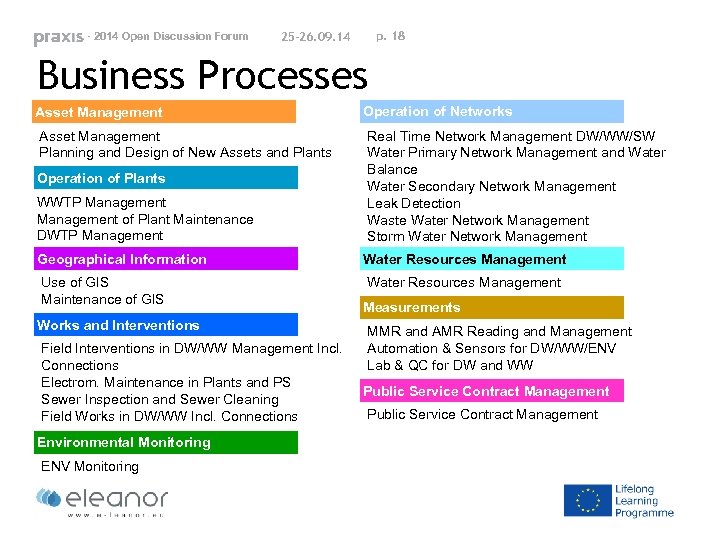 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum p. 18 25 -26. 09. 14 Business Processes Asset Management Planning and Design of New Assets and Plants Operation of Plants WWTP Management of Plant Maintenance DWTP Management Geographical Information Use of GIS Maintenance of GIS Works and Interventions Field Interventions in DW/WW Management Incl. Connections Electrom. Maintenance in Plants and PS Sewer Inspection and Sewer Cleaning Field Works in DW/WW Incl. Connections Environmental Monitoring ENV Monitoring Operation of Networks Real Time Network Management DW/WW/SW Water Primary Network Management and Water Balance Water Secondary Network Management Leak Detection Waste Water Network Management Storm Water Network Management Water Resources Management Measurements MMR and AMR Reading and Management Automation & Sensors for DW/WW/ENV Lab & QC for DW and WW Public Service Contract Management
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum p. 18 25 -26. 09. 14 Business Processes Asset Management Planning and Design of New Assets and Plants Operation of Plants WWTP Management of Plant Maintenance DWTP Management Geographical Information Use of GIS Maintenance of GIS Works and Interventions Field Interventions in DW/WW Management Incl. Connections Electrom. Maintenance in Plants and PS Sewer Inspection and Sewer Cleaning Field Works in DW/WW Incl. Connections Environmental Monitoring ENV Monitoring Operation of Networks Real Time Network Management DW/WW/SW Water Primary Network Management and Water Balance Water Secondary Network Management Leak Detection Waste Water Network Management Storm Water Network Management Water Resources Management Measurements MMR and AMR Reading and Management Automation & Sensors for DW/WW/ENV Lab & QC for DW and WW Public Service Contract Management
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 19 Job Profiles Frames of JP Management Waste Water Technical Support Engineers (TSE) Connection and Site Works Drinking Water Real Time Operations Automation Electromechanics and Pumps Measurements and Laboratory Projects ENV and Quality Certification Geographical Information 54 JP within ü classification of urban water uses was done, by identifying the existing water business processes and jobs profiles ü Job Profile (JP): The outline of the duties and tasked required of and performed by a person for a specific title/job.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 19 Job Profiles Frames of JP Management Waste Water Technical Support Engineers (TSE) Connection and Site Works Drinking Water Real Time Operations Automation Electromechanics and Pumps Measurements and Laboratory Projects ENV and Quality Certification Geographical Information 54 JP within ü classification of urban water uses was done, by identifying the existing water business processes and jobs profiles ü Job Profile (JP): The outline of the duties and tasked required of and performed by a person for a specific title/job.
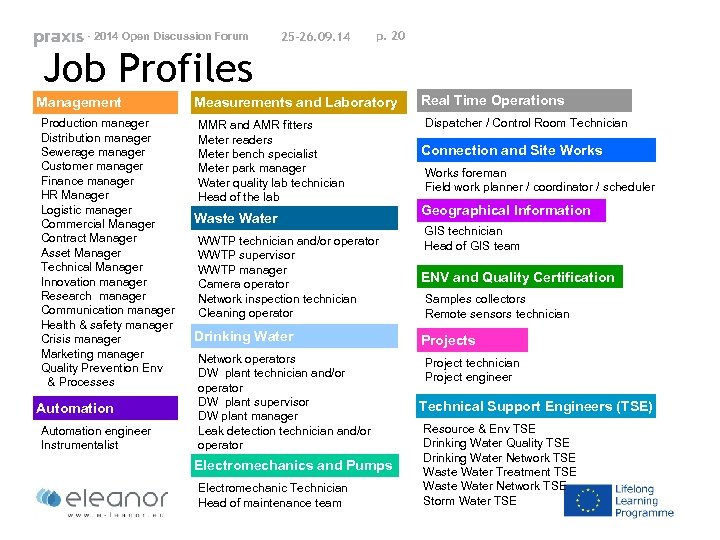 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 20 Job Profiles Management Production manager Distribution manager Sewerage manager Customer manager Finance manager HR Manager Logistic manager Commercial Manager Contract Manager Asset Manager Technical Manager Innovation manager Research manager Communication manager Health & safety manager Crisis manager Marketing manager Quality Prevention Env & Processes Automation engineer Instrumentalist Measurements and Laboratory MMR and AMR fitters Meter readers Meter bench specialist Meter park manager Water quality lab technician Head of the lab Waste Water WWTP technician and/or operator WWTP supervisor WWTP manager Camera operator Network inspection technician Cleaning operator Drinking Water Network operators DW plant technician and/or operator DW plant supervisor DW plant manager Leak detection technician and/or operator Electromechanics and Pumps Electromechanic Technician Head of maintenance team Real Time Operations Dispatcher / Control Room Technician Connection and Site Works foreman Field work planner / coordinator / scheduler Geographical Information GIS technician Head of GIS team ENV and Quality Certification Samples collectors Remote sensors technician Projects Project technician Project engineer Technical Support Engineers (TSE) Resource & Env TSE Drinking Water Quality TSE Drinking Water Network TSE Waste Water Treatment TSE Waste Water Network TSE Storm Water TSE
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 20 Job Profiles Management Production manager Distribution manager Sewerage manager Customer manager Finance manager HR Manager Logistic manager Commercial Manager Contract Manager Asset Manager Technical Manager Innovation manager Research manager Communication manager Health & safety manager Crisis manager Marketing manager Quality Prevention Env & Processes Automation engineer Instrumentalist Measurements and Laboratory MMR and AMR fitters Meter readers Meter bench specialist Meter park manager Water quality lab technician Head of the lab Waste Water WWTP technician and/or operator WWTP supervisor WWTP manager Camera operator Network inspection technician Cleaning operator Drinking Water Network operators DW plant technician and/or operator DW plant supervisor DW plant manager Leak detection technician and/or operator Electromechanics and Pumps Electromechanic Technician Head of maintenance team Real Time Operations Dispatcher / Control Room Technician Connection and Site Works foreman Field work planner / coordinator / scheduler Geographical Information GIS technician Head of GIS team ENV and Quality Certification Samples collectors Remote sensors technician Projects Project technician Project engineer Technical Support Engineers (TSE) Resource & Env TSE Drinking Water Quality TSE Drinking Water Network TSE Waste Water Treatment TSE Waste Water Network TSE Storm Water TSE
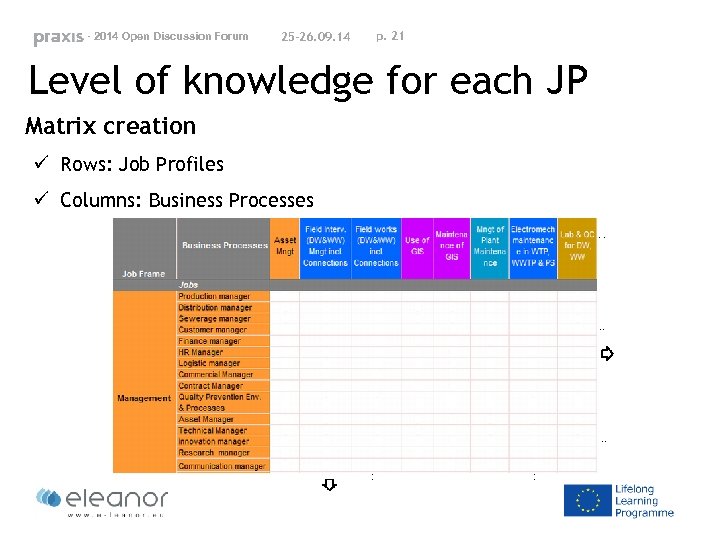 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 21 Level of knowledge for each JP Matrix creation ü Rows: Job Profiles ü Columns: Business Processes
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 21 Level of knowledge for each JP Matrix creation ü Rows: Job Profiles ü Columns: Business Processes
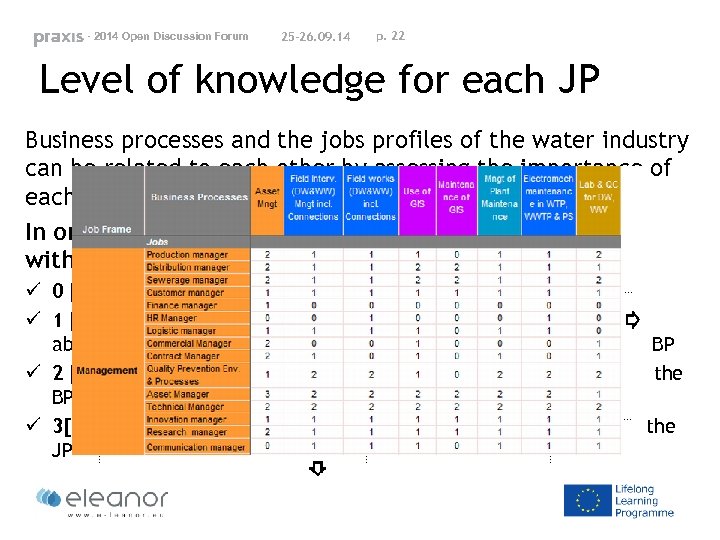 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 22 Level of knowledge for each JP Business processes and the jobs profiles of the water industry can be related to each other by assessing the importance of each BP in every JP In order to reflect this relation, the matrix was filled in with a scale from 0 to 3, indicating: ü 0 [not important]: No specific knowledge requested about this BP ü 1 [intermediate]: Minimal knowledge of the BP (general overview about the BP), but the JP requires a shallow knowledge about this BP ü 2 [important]: Knowledge of the global BP and activity in parts of the BP ü 3[very important]: In depth knowledge of the BP core activity of the JP and management of the BP
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 22 Level of knowledge for each JP Business processes and the jobs profiles of the water industry can be related to each other by assessing the importance of each BP in every JP In order to reflect this relation, the matrix was filled in with a scale from 0 to 3, indicating: ü 0 [not important]: No specific knowledge requested about this BP ü 1 [intermediate]: Minimal knowledge of the BP (general overview about the BP), but the JP requires a shallow knowledge about this BP ü 2 [important]: Knowledge of the global BP and activity in parts of the BP ü 3[very important]: In depth knowledge of the BP core activity of the JP and management of the BP
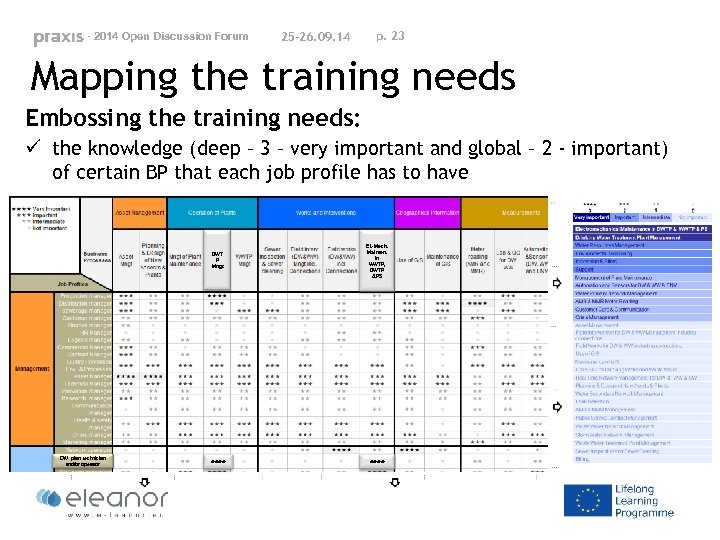 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 23 Mapping the training needs Embossing the training needs: ü the knowledge (deep – 3 – very important and global – 2 - important) of certain BP that each job profile has to have DWT P Mngt DW plant technician and/or operator El. -Mech. Mainten. In WWTP, DWTP &PS
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 23 Mapping the training needs Embossing the training needs: ü the knowledge (deep – 3 – very important and global – 2 - important) of certain BP that each job profile has to have DWT P Mngt DW plant technician and/or operator El. -Mech. Mainten. In WWTP, DWTP &PS
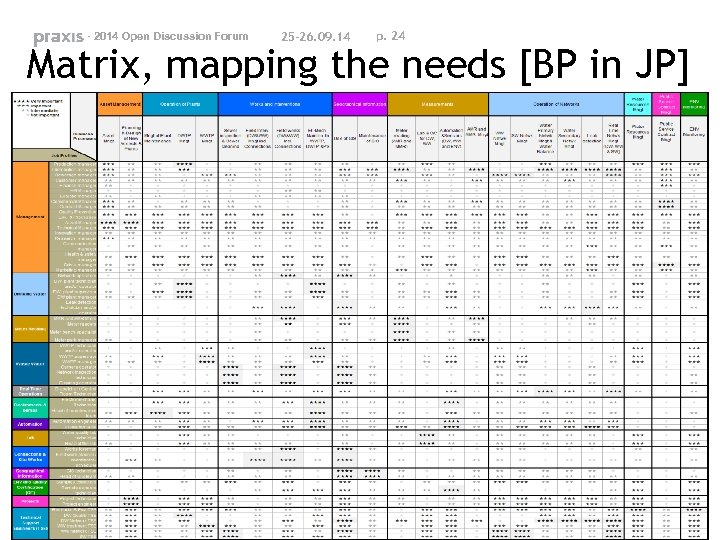 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 24 Matrix, mapping the needs [BP in JP]
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 24 Matrix, mapping the needs [BP in JP]
 - 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 25 Conclusions In the recent years the GI community is promoting several initiatives aimed at identifying the job market needs in terms of knowledge and skills for the new professional profiles arising from new regulatory as well as technological developments in the GIrelated fields. Those efforts will hopefully result in university-industry shared definition of competencies in specific professional domain, helping education and vocational training offer to match the actual job requirements, at the same time providing tools for competence certification and validation at EU level.
- 2014 Open Discussion Forum 25 -26. 09. 14 p. 25 Conclusions In the recent years the GI community is promoting several initiatives aimed at identifying the job market needs in terms of knowledge and skills for the new professional profiles arising from new regulatory as well as technological developments in the GIrelated fields. Those efforts will hopefully result in university-industry shared definition of competencies in specific professional domain, helping education and vocational training offer to match the actual job requirements, at the same time providing tools for competence certification and validation at EU level.



