3eb2d9a397f31b05da3c2d284aebcace.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 2011 INAP Conference Workshop IV Updating the Assessment Criteria for National Technical Qualifications in Korea Authors: Seung-Il Na, Dong-yul Jung and Hye-kyung Lim Seoul National University Department of Vocational Education and Workforce Development jdy 83@snu. ac. kr
2011 INAP Conference Workshop IV Updating the Assessment Criteria for National Technical Qualifications in Korea Authors: Seung-Il Na, Dong-yul Jung and Hye-kyung Lim Seoul National University Department of Vocational Education and Workforce Development jdy 83@snu. ac. kr
 Contents I Introduction II Methods III Results IV Conclusions and Implications 1
Contents I Introduction II Methods III Results IV Conclusions and Implications 1
 I. Introduction National Technical Qualifications(NTQ) of Korea In 1973, enacting and declaring legal basics for NTQs ☞ Legal basic of NTQs: the National Technical Qualification Act Professional Engineer In 2007, introduce the sunset period Master Craftsman Engineer Industrial Engineer In 2010, operating 512 NTQs ☞ 481 NTQs in technical skills fields, 31 NTQs in service and clerical fields. ☞ 25 job areas, 114 sub job areas Craftsman Current Levels of NTQs in the technical skills fields Levels in service and clerical fields consist 1~3 or 1~2 2
I. Introduction National Technical Qualifications(NTQ) of Korea In 1973, enacting and declaring legal basics for NTQs ☞ Legal basic of NTQs: the National Technical Qualification Act Professional Engineer In 2007, introduce the sunset period Master Craftsman Engineer Industrial Engineer In 2010, operating 512 NTQs ☞ 481 NTQs in technical skills fields, 31 NTQs in service and clerical fields. ☞ 25 job areas, 114 sub job areas Craftsman Current Levels of NTQs in the technical skills fields Levels in service and clerical fields consist 1~3 or 1~2 2
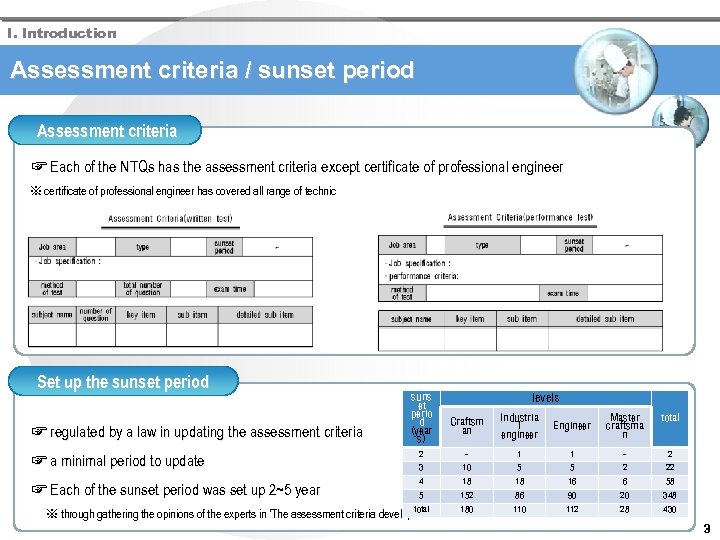 I. Introduction Assessment criteria / sunset period Assessment criteria ☞ Each of the NTQs has the assessment criteria except certificate of professional engineer ※ certificate of professional engineer has covered all range of technic Set up the sunset period ☞ regulated by a law in updating the assessment criteria suns et perio d (year s) levels Craftsm an Industria l engineer Engineer Master craftsma n total ☞ a minimal period to update 2 - 1 1 - 2 3 10 5 5 2 22 ☞ Each of the sunset period was set up 2~5 year 4 18 18 16 6 58 5 152 86 90 20 348 110 112 28 430 total 180 ※ through gathering the opinions of the experts in ‘The assessment criteria development committee’ 3
I. Introduction Assessment criteria / sunset period Assessment criteria ☞ Each of the NTQs has the assessment criteria except certificate of professional engineer ※ certificate of professional engineer has covered all range of technic Set up the sunset period ☞ regulated by a law in updating the assessment criteria suns et perio d (year s) levels Craftsm an Industria l engineer Engineer Master craftsma n total ☞ a minimal period to update 2 - 1 1 - 2 3 10 5 5 2 22 ☞ Each of the sunset period was set up 2~5 year 4 18 18 16 6 58 5 152 86 90 20 348 110 112 28 430 total 180 ※ through gathering the opinions of the experts in ‘The assessment criteria development committee’ 3
 I. Introduction Needs for Study The assessment criteria is played key role in NTQ ☞ The assessment criteria indicate the range of subject assessment ☞ regulation to develop assessment criteria for the enactment ☞ revision of the each qualification in accordance with the National Technical Qualifications Law Various efforts to updating the assessment criteria ☞ set up the sunset period in each assessment criteria to improve field suitability of the criteria ☞ the job analysis is carried out by field specialists in developing the assessment criteria, and since 2005 the employment of the NCS was expanded. circumstantial changes about NTQ ☞ It has been five years since the sunset period system was introduced ☞ the development of the NCS and its employment ☞ Technology has been changed Reviewing the status of using the assessment criteria/ Developing new update scheme for Assessment criteria 4
I. Introduction Needs for Study The assessment criteria is played key role in NTQ ☞ The assessment criteria indicate the range of subject assessment ☞ regulation to develop assessment criteria for the enactment ☞ revision of the each qualification in accordance with the National Technical Qualifications Law Various efforts to updating the assessment criteria ☞ set up the sunset period in each assessment criteria to improve field suitability of the criteria ☞ the job analysis is carried out by field specialists in developing the assessment criteria, and since 2005 the employment of the NCS was expanded. circumstantial changes about NTQ ☞ It has been five years since the sunset period system was introduced ☞ the development of the NCS and its employment ☞ Technology has been changed Reviewing the status of using the assessment criteria/ Developing new update scheme for Assessment criteria 4
 II. Methods Analysis ☞ literature review - precedent studies on the assessment criteria, policy documents and statistical resources ☞ interview - for figure out the actual condition - six staffs in HRD Korea(which was in charge of assessment), two specialists for developing the assessment criteria and two exam writers. ☞ survey - for find out the suitability of assessment criteria sunset period by types - complete enumeration(The assessment criteria development committee member) comprised of 52 groups in total with 10 members in each area Development ☞ developing the draft - prepared through the examinations of precedent studies and related law and through the result of current status analysis and investigation research ☞ examine the field suitability / applicability - three staffs in HRD Korea, two specialists for developing the assessment criteria and two exam writers. 5
II. Methods Analysis ☞ literature review - precedent studies on the assessment criteria, policy documents and statistical resources ☞ interview - for figure out the actual condition - six staffs in HRD Korea(which was in charge of assessment), two specialists for developing the assessment criteria and two exam writers. ☞ survey - for find out the suitability of assessment criteria sunset period by types - complete enumeration(The assessment criteria development committee member) comprised of 52 groups in total with 10 members in each area Development ☞ developing the draft - prepared through the examinations of precedent studies and related law and through the result of current status analysis and investigation research ☞ examine the field suitability / applicability - three staffs in HRD Korea, two specialists for developing the assessment criteria and two exam writers. 5
 III. Results Usage status of the Assessment criteria Development of Assesment Criteria Using the job analysis, resources from the NCS But, confusion of terms as the forms and names of item were different ex) C. A use the terms likes key item, sub item and detailed sub item J. A, NCS use the terms likes competency unit, competency unit element and key item respectively Development of the exam questions four or five times questions are made to be stocked in the item pool → the questions are selected and verified from the item pool to perform an examination Lack of the sufficient information about the level of difficult and field suitability for exam writer ※ 73. 7% of the exam writer is academic expert 6
III. Results Usage status of the Assessment criteria Development of Assesment Criteria Using the job analysis, resources from the NCS But, confusion of terms as the forms and names of item were different ex) C. A use the terms likes key item, sub item and detailed sub item J. A, NCS use the terms likes competency unit, competency unit element and key item respectively Development of the exam questions four or five times questions are made to be stocked in the item pool → the questions are selected and verified from the item pool to perform an examination Lack of the sufficient information about the level of difficult and field suitability for exam writer ※ 73. 7% of the exam writer is academic expert 6
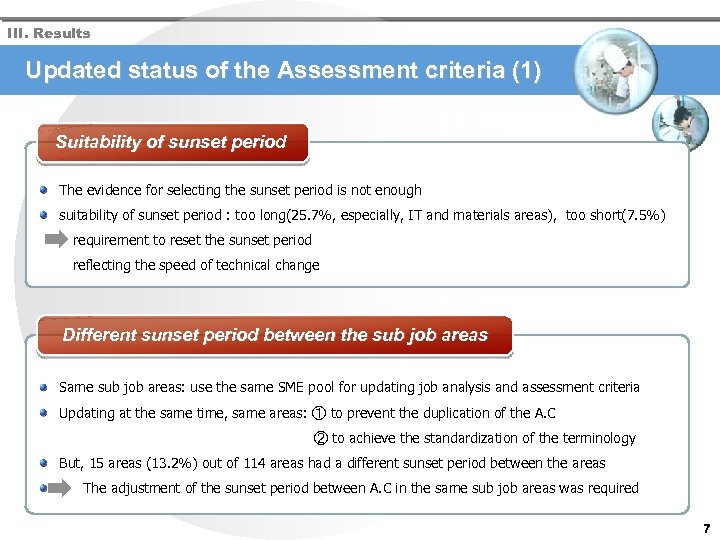 III. Results Updated status of the Assessment criteria (1) Suitability of sunset period The evidence for selecting the sunset period is not enough suitability of sunset period : too long(25. 7%, especially, IT and materials areas), too short(7. 5%) requirement to reset the sunset period reflecting the speed of technical change Different sunset period between the sub job areas Same sub job areas: use the same SME pool for updating job analysis and assessment criteria Updating at the same time, same areas: ① to prevent the duplication of the A. C ② to achieve the standardization of the terminology But, 15 areas (13. 2%) out of 114 areas had a different sunset period between the areas The adjustment of the sunset period between A. C in the same sub job areas was required 7
III. Results Updated status of the Assessment criteria (1) Suitability of sunset period The evidence for selecting the sunset period is not enough suitability of sunset period : too long(25. 7%, especially, IT and materials areas), too short(7. 5%) requirement to reset the sunset period reflecting the speed of technical change Different sunset period between the sub job areas Same sub job areas: use the same SME pool for updating job analysis and assessment criteria Updating at the same time, same areas: ① to prevent the duplication of the A. C ② to achieve the standardization of the terminology But, 15 areas (13. 2%) out of 114 areas had a different sunset period between the areas The adjustment of the sunset period between A. C in the same sub job areas was required 7
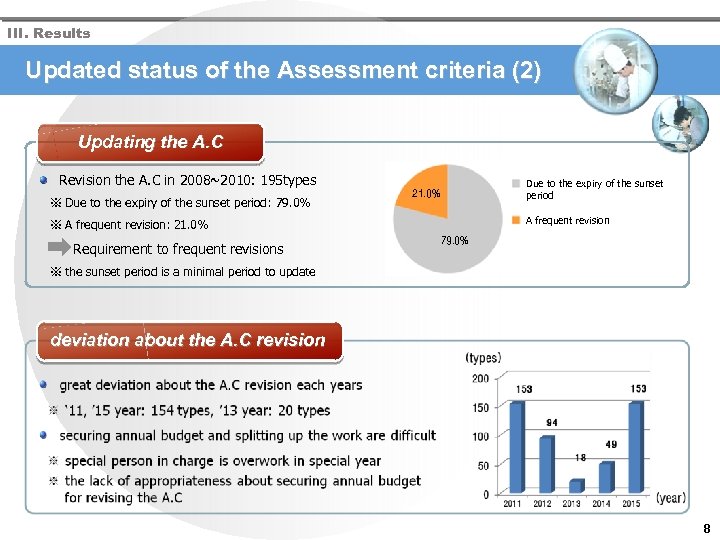 III. Results Updated status of the Assessment criteria (2) Updating the A. C Revision the A. C in 2008~2010: 195 types ※ Due to the expiry of the sunset period: 79. 0% Due to the expiry of the sunset period 21. 0% A frequent revision ※ A frequent revision: 21. 0% Requirement to frequent revisions 79. 0% ※ the sunset period is a minimal period to update deviation about the A. C revision 8
III. Results Updated status of the Assessment criteria (2) Updating the A. C Revision the A. C in 2008~2010: 195 types ※ Due to the expiry of the sunset period: 79. 0% Due to the expiry of the sunset period 21. 0% A frequent revision ※ A frequent revision: 21. 0% Requirement to frequent revisions 79. 0% ※ the sunset period is a minimal period to update deviation about the A. C revision 8
 III. Results Direction of improvement and new update scheme for Assessment criteria(1) Revision of the current A. C forms & name of items the rename of the name of items for use the NCS ※ ex) key item → competency unit Providing more information(about detailed sub items) to exam writers the level of difficulty, the level of importance and the level of frequency A scheme to apply the NCS(In updating the A. C ) reorganization of qualification types for using the NCS Revision the A. C using the assemble the NCS ※ Every field has its own standard in the future Reset the sunset period reset to reflect the speed of technical change, and the sunset period of the same type of sub job areas making revision plan (for revising Every year the same number (85~95 types) of the A. C) 9
III. Results Direction of improvement and new update scheme for Assessment criteria(1) Revision of the current A. C forms & name of items the rename of the name of items for use the NCS ※ ex) key item → competency unit Providing more information(about detailed sub items) to exam writers the level of difficulty, the level of importance and the level of frequency A scheme to apply the NCS(In updating the A. C ) reorganization of qualification types for using the NCS Revision the A. C using the assemble the NCS ※ Every field has its own standard in the future Reset the sunset period reset to reflect the speed of technical change, and the sunset period of the same type of sub job areas making revision plan (for revising Every year the same number (85~95 types) of the A. C) 9
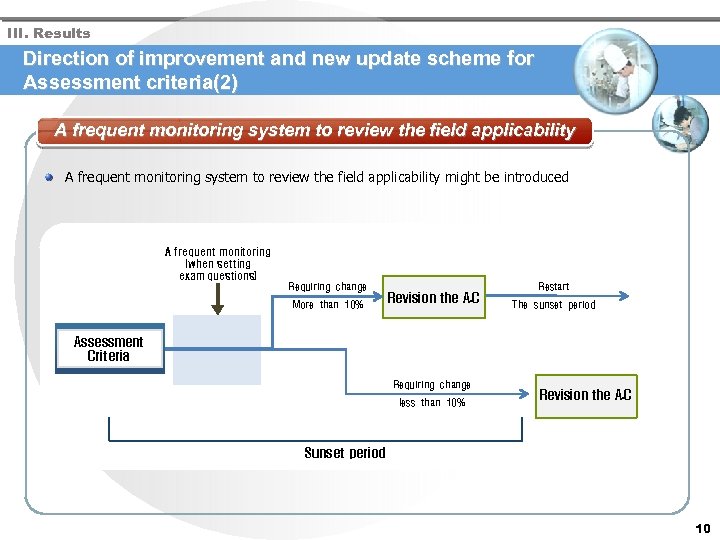 III. Results Direction of improvement and new update scheme for Assessment criteria(2) A frequent monitoring system to review the field applicability might be introduced A frequent monitoring (when setting exam questions) Requiring change More than 10% Revision the A. C Restart The sunset period Assessment Criteria 통계DB Requiring change less than 10% Revision the A. C Sunset period 10
III. Results Direction of improvement and new update scheme for Assessment criteria(2) A frequent monitoring system to review the field applicability might be introduced A frequent monitoring (when setting exam questions) Requiring change More than 10% Revision the A. C Restart The sunset period Assessment Criteria 통계DB Requiring change less than 10% Revision the A. C Sunset period 10
 IV. Conclusions & Implications Conclusions The A. C provide accurate information to users, and contain competency to be applicable to the field the A. C must be reviewed frequently and complemented reflecting newly developed technology But, less frequent revisions, updates were made obligatory after the expiry of the sunset period. Necessary to revise the form and items of A. C, reset the sunset period, adopt the frequent update system Implications to install a frequent monitoring system working together with the sunset period the NCS resources might be employed positively in the update 11
IV. Conclusions & Implications Conclusions The A. C provide accurate information to users, and contain competency to be applicable to the field the A. C must be reviewed frequently and complemented reflecting newly developed technology But, less frequent revisions, updates were made obligatory after the expiry of the sunset period. Necessary to revise the form and items of A. C, reset the sunset period, adopt the frequent update system Implications to install a frequent monitoring system working together with the sunset period the NCS resources might be employed positively in the update 11



