9647f9b922766d96b6e0b2e1d770a8fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 2011 -2012 Special Education Paraprofessional After-School Training Series Supplementary Aids and Services: What Paraprofessionals Need to Know Jennifer Goldbloom, Pa. TTAN March 14, 2012 www. pattan. net Pennsylvania Training and Technical Assistance Network
2011 -2012 Special Education Paraprofessional After-School Training Series Supplementary Aids and Services: What Paraprofessionals Need to Know Jennifer Goldbloom, Pa. TTAN March 14, 2012 www. pattan. net Pennsylvania Training and Technical Assistance Network
 Pa. TTAN’s Mission The mission of the Pennsylvania Training and Technical Assistance Network (Pa. TTAN) is to support the efforts and initiatives of the Bureau of Special Education, and to build the capacity of local educational agencies to serve students who receive special education services.
Pa. TTAN’s Mission The mission of the Pennsylvania Training and Technical Assistance Network (Pa. TTAN) is to support the efforts and initiatives of the Bureau of Special Education, and to build the capacity of local educational agencies to serve students who receive special education services.
 District, IU, Preschool Agency Policy Your local district or agency’s policies regarding paraprofessional job descriptions, duties, and responsibilities provide the final word!
District, IU, Preschool Agency Policy Your local district or agency’s policies regarding paraprofessional job descriptions, duties, and responsibilities provide the final word!
 PDE’s Commitment to Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) Our goal for each child is to ensure Individualized Education Program (IEP) teams begin with the general education setting with the use of Supplementary Aids and Services before considering a more restrictive environment.
PDE’s Commitment to Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) Our goal for each child is to ensure Individualized Education Program (IEP) teams begin with the general education setting with the use of Supplementary Aids and Services before considering a more restrictive environment.
 Agenda • Legal Foundations for Providing Supplementary Aids and Services • Defining and Using Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) • The Purpose and Use of the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit • Considering Sa. S for students: Wrap up activity
Agenda • Legal Foundations for Providing Supplementary Aids and Services • Defining and Using Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) • The Purpose and Use of the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit • Considering Sa. S for students: Wrap up activity
 Learner Outcomes Participants will: • Explain the legal foundation for use of supplementary aids and services in schools • Describe the types of supplementary aids and services used to support students with disabilities as learners and participants in their educational program • Discuss the purposes of the Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) Consideration Toolkit • Identify the paraprofessional’s role in supporting students through the use of supplementary aids and services.
Learner Outcomes Participants will: • Explain the legal foundation for use of supplementary aids and services in schools • Describe the types of supplementary aids and services used to support students with disabilities as learners and participants in their educational program • Discuss the purposes of the Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) Consideration Toolkit • Identify the paraprofessional’s role in supporting students through the use of supplementary aids and services.
 Before we begin… SAS Sa. S • Standards Aligned System • http: //pdesas. org/ • Standards • Assessment • Curriculum framework • Instruction • Materials • Safe and supportive schools • Supplementary Aids and Services • Supports provided to students • Collaborative • Instructional • Physical • Social-behavioral
Before we begin… SAS Sa. S • Standards Aligned System • http: //pdesas. org/ • Standards • Assessment • Curriculum framework • Instruction • Materials • Safe and supportive schools • Supplementary Aids and Services • Supports provided to students • Collaborative • Instructional • Physical • Social-behavioral
 LEGAL FOUNDATIONS FOR PROVIDING SUPPLEMENTARY AIDS AND SERVICES
LEGAL FOUNDATIONS FOR PROVIDING SUPPLEMENTARY AIDS AND SERVICES
 IDEA on LRE Least Restrictive Environment “To the maximum extent appropriate, children with disabilities, including children in public or private institutions or other care facilities, are educated with children who are not disabled, and special classes, separate schooling or other removal of children with disabilities from the regular education environment occurs only when the nature or severity of the disability of a child is such that education in regular classes with the use of supplementary aids and services cannot be achieved satisfactorily. ” 9 IDEA sec. 612 (5)(A)
IDEA on LRE Least Restrictive Environment “To the maximum extent appropriate, children with disabilities, including children in public or private institutions or other care facilities, are educated with children who are not disabled, and special classes, separate schooling or other removal of children with disabilities from the regular education environment occurs only when the nature or severity of the disability of a child is such that education in regular classes with the use of supplementary aids and services cannot be achieved satisfactorily. ” 9 IDEA sec. 612 (5)(A)
 IDEA on Placement (b) The child’s placement – (1) Is determined annually; (2) Is based on the child’s IEP; and (3) Is as close as possible to the child’s home; (c) Unless the IEP of a child with a disability requires some other arrangement, the child is educated in the school that he or she would attend if nondisabled; 10
IDEA on Placement (b) The child’s placement – (1) Is determined annually; (2) Is based on the child’s IEP; and (3) Is as close as possible to the child’s home; (c) Unless the IEP of a child with a disability requires some other arrangement, the child is educated in the school that he or she would attend if nondisabled; 10
 IDEA on Placement (d) In selecting the LRE, consideration is given to any potential harmful effect on the child or on the quality of services that he or she needs; and (e) A child with a disability is not removed from education in age appropriate regular classrooms solely because of needed modifications in the general education curriculum [§ 300. 116]
IDEA on Placement (d) In selecting the LRE, consideration is given to any potential harmful effect on the child or on the quality of services that he or she needs; and (e) A child with a disability is not removed from education in age appropriate regular classrooms solely because of needed modifications in the general education curriculum [§ 300. 116]
 Student Placement • First consideration is the general education classroom with supplementary aids and services • All general educators expect to have students with the full range of disabilities in their classrooms for meaningful portions of the day • All students are welcome members of the classroom 12
Student Placement • First consideration is the general education classroom with supplementary aids and services • All general educators expect to have students with the full range of disabilities in their classrooms for meaningful portions of the day • All students are welcome members of the classroom 12
 IDEA on IEPs Sa. S The IEP for each child with a disability includes “A statement of the special education and related services and supplementary aids and services, based on peer-reviewed research to the extent practicable, to be provided to the child, or on behalf of the child, and a statement of the program modifications or supports for school personnel that will be provided for the child to …attain annual goals, be involved in and make progress in the general education curriculum…. To be educated and participate with other children with disabilities and nondisabled children in the activities described in this section; [§ 300. 320(4)]. 13
IDEA on IEPs Sa. S The IEP for each child with a disability includes “A statement of the special education and related services and supplementary aids and services, based on peer-reviewed research to the extent practicable, to be provided to the child, or on behalf of the child, and a statement of the program modifications or supports for school personnel that will be provided for the child to …attain annual goals, be involved in and make progress in the general education curriculum…. To be educated and participate with other children with disabilities and nondisabled children in the activities described in this section; [§ 300. 320(4)]. 13
 Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) IDEA Defines Sa. S: The term ‘supplementary aids and services' means aids, services, and other supports that are provided in regular education classes and other education -related settings, and in extracurricular and nonacademic settings, to enable children with disabilities to be educated with nondisabled children to the maximum extent appropriate” [§ 300. 42] 14
Supplementary Aids and Services (Sa. S) IDEA Defines Sa. S: The term ‘supplementary aids and services' means aids, services, and other supports that are provided in regular education classes and other education -related settings, and in extracurricular and nonacademic settings, to enable children with disabilities to be educated with nondisabled children to the maximum extent appropriate” [§ 300. 42] 14
 Student Needs Question #1 • What supplementary aids and services were considered? • What supplementary aids and services were rejected? • Explain why the supplementary aids and services will or will not enable the student to make progress on the goals and objectives (if applicable) in this IEP in the general education class. *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English 15
Student Needs Question #1 • What supplementary aids and services were considered? • What supplementary aids and services were rejected? • Explain why the supplementary aids and services will or will not enable the student to make progress on the goals and objectives (if applicable) in this IEP in the general education class. *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English 15
 Student Needs Question #2 • What benefits are provided in the regular education class with supplementary aids and services versus the benefits provided in the special education class? *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English 16
Student Needs Question #2 • What benefits are provided in the regular education class with supplementary aids and services versus the benefits provided in the special education class? *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English 16
 Student Needs Question #3 • What potentially beneficial effects and/or harmful effects might be expected on the student with disabilities or the other students in the class, even with supplementary aids and services? Question #4 • To what extent, if any, will the student participate with non-disabled peers in extracurricular activities or other nonacademic activities? *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 17 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English
Student Needs Question #3 • What potentially beneficial effects and/or harmful effects might be expected on the student with disabilities or the other students in the class, even with supplementary aids and services? Question #4 • To what extent, if any, will the student participate with non-disabled peers in extracurricular activities or other nonacademic activities? *See Annotated IEP for additional details: http: //www. pattan. net/category/Legal/Forms/Browse/Single/? id=4 db 2885 acd 6 17 9 f 9 c 443540000&bor=ag=School%20 Age%20 Annotated**l=English
 LRE BEC • For more information on legal foundations, refer to the LRE BEC and the Sa. S Fact Sheet
LRE BEC • For more information on legal foundations, refer to the LRE BEC and the Sa. S Fact Sheet
 Check for Understanding 1. The goal of providing Sa. S is to: a. give students a head start. b. make sure the paraprofessional knows what to do. c. enable students to be instructed along with their peers. d. have paraprofessionals do everything for students.
Check for Understanding 1. The goal of providing Sa. S is to: a. give students a head start. b. make sure the paraprofessional knows what to do. c. enable students to be instructed along with their peers. d. have paraprofessionals do everything for students.
 Check for Understanding 2. IEP teams need to consider Sa. S for a student so the student can be a. be included in general education to the maximum extent. b. be removed to another class. c. get teachers and paraprofessionals working together. d. get assistive technology.
Check for Understanding 2. IEP teams need to consider Sa. S for a student so the student can be a. be included in general education to the maximum extent. b. be removed to another class. c. get teachers and paraprofessionals working together. d. get assistive technology.
 DEFINING AND USING SUPPLEMENTARY AIDS AND SERVICES
DEFINING AND USING SUPPLEMENTARY AIDS AND SERVICES
 Consider Your Student • Think of a student you work with who has an IEP • Write down some of the supports this student receives
Consider Your Student • Think of a student you work with who has an IEP • Write down some of the supports this student receives
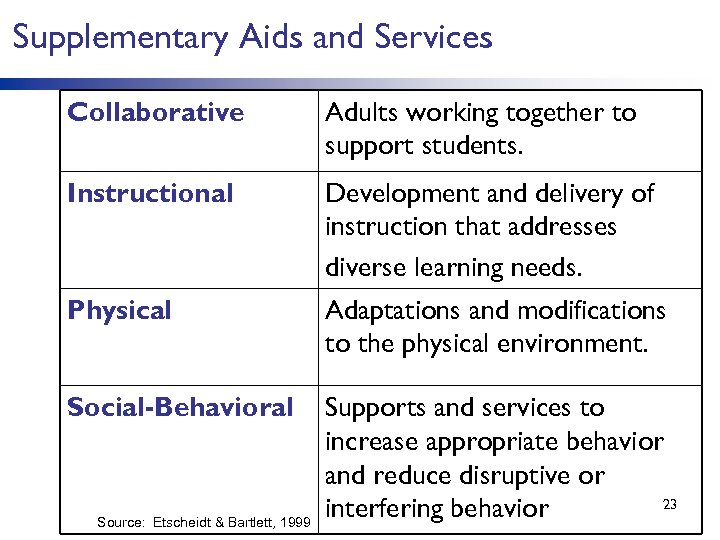 Supplementary Aids and Services Collaborative Adults working together to support students. Instructional Development and delivery of instruction that addresses diverse learning needs. Physical Adaptations and modifications to the physical environment. Social-Behavioral Supports and services to increase appropriate behavior and reduce disruptive or 23 interfering behavior Source: Etscheidt & Bartlett, 1999
Supplementary Aids and Services Collaborative Adults working together to support students. Instructional Development and delivery of instruction that addresses diverse learning needs. Physical Adaptations and modifications to the physical environment. Social-Behavioral Supports and services to increase appropriate behavior and reduce disruptive or 23 interfering behavior Source: Etscheidt & Bartlett, 1999
 Sa. S: Collaborative Examples • Communication among adults • Professional development related to collaboration • Scheduled time for co-planning and team meetings • Co-teaching; classroom consultation • Scheduled opportunities for parental collaboration 24
Sa. S: Collaborative Examples • Communication among adults • Professional development related to collaboration • Scheduled time for co-planning and team meetings • Co-teaching; classroom consultation • Scheduled opportunities for parental collaboration 24
 Collaborative Ideas • Assistance/support teams • Individual student support teams • Home-school communication • Study buddies (teacher assigned pairs of students) • Mentor teachers (coaching/guided support)
Collaborative Ideas • Assistance/support teams • Individual student support teams • Home-school communication • Study buddies (teacher assigned pairs of students) • Mentor teachers (coaching/guided support)
 Sa. S: Instructional Examples • • • Using a keyboard/portable device Instruction in keyboarding skills Providing guided notes Using scaffolding to plan for written work Providing visual cues Modifying curricular goals 26
Sa. S: Instructional Examples • • • Using a keyboard/portable device Instruction in keyboarding skills Providing guided notes Using scaffolding to plan for written work Providing visual cues Modifying curricular goals 26
 Instructional Ideas • • • Using special paper or writing tools Color-coding mathematical symbols Highlighting reading materials/directions Providing graphic organizers/note-taking tools Students can respond in different modes Providing instruction on and utilizing guided notes
Instructional Ideas • • • Using special paper or writing tools Color-coding mathematical symbols Highlighting reading materials/directions Providing graphic organizers/note-taking tools Students can respond in different modes Providing instruction on and utilizing guided notes
 Sa. S: Physical Examples • Arrange furniture differently or provide specialized furniture • Adjust sensory characteristics of environment (e. g. , temperature, sound) • Provide access to specific areas of classroom or other settings outside of classroom • Allow for water bottle or sensory object during instruction 28
Sa. S: Physical Examples • Arrange furniture differently or provide specialized furniture • Adjust sensory characteristics of environment (e. g. , temperature, sound) • Provide access to specific areas of classroom or other settings outside of classroom • Allow for water bottle or sensory object during instruction 28
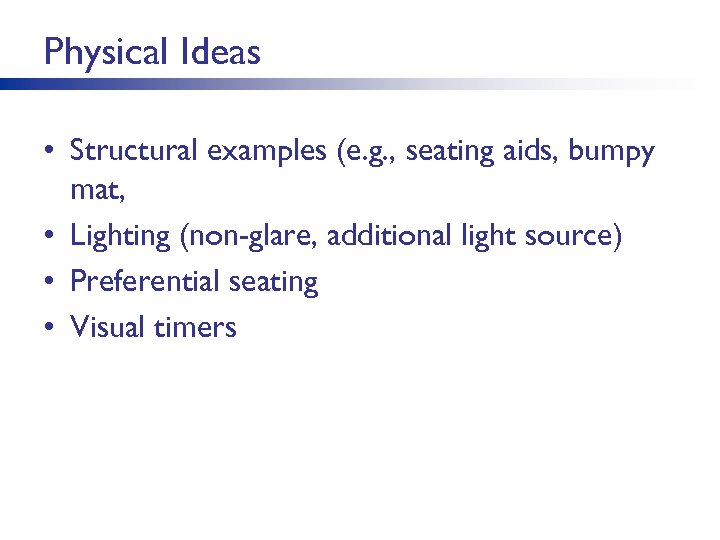 Physical Ideas • Structural examples (e. g. , seating aids, bumpy mat, • Lighting (non-glare, additional light source) • Preferential seating • Visual timers
Physical Ideas • Structural examples (e. g. , seating aids, bumpy mat, • Lighting (non-glare, additional light source) • Preferential seating • Visual timers
 Sa. S: Social-Behavioral Examples • • • Modify rules or expectations Peer supports (e. g. , facilitating friendships) Individualized behavioral support plan Social skills training Counseling supports 30
Sa. S: Social-Behavioral Examples • • • Modify rules or expectations Peer supports (e. g. , facilitating friendships) Individualized behavioral support plan Social skills training Counseling supports 30
 Social-Behavioral Ideas • Cooperative learning strategies • Instruction in communication skills • Home-school communication • Consistent system of rewards • Preparation for transitions • Private prompt for redirection • Self-regulation strategies instruction
Social-Behavioral Ideas • Cooperative learning strategies • Instruction in communication skills • Home-school communication • Consistent system of rewards • Preparation for transitions • Private prompt for redirection • Self-regulation strategies instruction
 Sa. S: Role of the IEP Team • The IEP team determines supplementary aids and services necessary for each child to receive specially designed instruction in the least restrictive environment. • Placement determination must be the final component of the IEP development process. • The IEP team decides the educational placement for an individual student. Basic Education Circulars (PA Code) 32
Sa. S: Role of the IEP Team • The IEP team determines supplementary aids and services necessary for each child to receive specially designed instruction in the least restrictive environment. • Placement determination must be the final component of the IEP development process. • The IEP team decides the educational placement for an individual student. Basic Education Circulars (PA Code) 32
 Paraprofessional’s Role • • • Implementing planned program of Sa. S supports Collecting data Providing input to the team Facilitating supports Promoting use of natural supports Fading adult support
Paraprofessional’s Role • • • Implementing planned program of Sa. S supports Collecting data Providing input to the team Facilitating supports Promoting use of natural supports Fading adult support
 Check for Understanding 3. The four categories of Sa. S are: a. AT, para support, hand-over-hand, consequences. b. collaborative, instructional, physical, socialbehavioral c. communication, behavioral, personnel, facilitation d. classroom arrangement, paras, sensory input, antecedents.
Check for Understanding 3. The four categories of Sa. S are: a. AT, para support, hand-over-hand, consequences. b. collaborative, instructional, physical, socialbehavioral c. communication, behavioral, personnel, facilitation d. classroom arrangement, paras, sensory input, antecedents.
 Check for Understanding The paraprofessional’s role is to a. provide input to the team. b. implement the planned supports. c. decide which supports to implement. d. both a and b. e. both a and c.
Check for Understanding The paraprofessional’s role is to a. provide input to the team. b. implement the planned supports. c. decide which supports to implement. d. both a and b. e. both a and c.
 THE PURPOSE AND USE OF THE SAS CONSIDERATION TOOLKIT
THE PURPOSE AND USE OF THE SAS CONSIDERATION TOOLKIT

 What is the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit? A student-specific process in which a trained facilitator assists the IEP team to: • Identify student strengths and interests • Describe the general education setting(s); • Compare and identify potential barriers to participation and learning for the student in the general education setting(s); and, • Brainstorm supplementary aids and services that will support the student’s learning and participation in general education setting(s). 38
What is the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit? A student-specific process in which a trained facilitator assists the IEP team to: • Identify student strengths and interests • Describe the general education setting(s); • Compare and identify potential barriers to participation and learning for the student in the general education setting(s); and, • Brainstorm supplementary aids and services that will support the student’s learning and participation in general education setting(s). 38
 Why use the Sa. S Toolkit? Sa. S Consideration Toolkit is used by teams for: • planning and placement decision-making • problem-solving for supports within a new general education curricular area; • comprehensive planning for transition to a new school building, grade or other instructional setting. 39
Why use the Sa. S Toolkit? Sa. S Consideration Toolkit is used by teams for: • planning and placement decision-making • problem-solving for supports within a new general education curricular area; • comprehensive planning for transition to a new school building, grade or other instructional setting. 39
 A Multi-Step Process • Identify Student Strengths and Needs • Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s) • Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction • Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barriers • Identify Viable Alternatives for Implementation 40
A Multi-Step Process • Identify Student Strengths and Needs • Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s) • Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction • Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barriers • Identify Viable Alternatives for Implementation 40
 Components of the Toolkit A: Introduction and Preparation for Use -Overview of the Sa. S consideration process, describing who does what at each step. B: Student Profile: Summary of Strengths, Needs, and Learning Characteristics Helps the team organize student information in a format designed to facilitate instructional planning and problem-solving to support inclusive placements. 41
Components of the Toolkit A: Introduction and Preparation for Use -Overview of the Sa. S consideration process, describing who does what at each step. B: Student Profile: Summary of Strengths, Needs, and Learning Characteristics Helps the team organize student information in a format designed to facilitate instructional planning and problem-solving to support inclusive placements. 41
 Components of the Toolkit C: The Supplementary Aids and Services Consideration Tool Teams then complete this four-step process that results in the identification of student-specific, environmentally-referenced supplementary aids and services. 42
Components of the Toolkit C: The Supplementary Aids and Services Consideration Tool Teams then complete this four-step process that results in the identification of student-specific, environmentally-referenced supplementary aids and services. 42
 Components of the Toolkit D: Supplementary Aids and Services Self-Check As teams move through the Sa. S consideration process, this self-assessment tool is a means of ensuring that all steps of the process have been completed with fidelity. 43
Components of the Toolkit D: Supplementary Aids and Services Self-Check As teams move through the Sa. S consideration process, this self-assessment tool is a means of ensuring that all steps of the process have been completed with fidelity. 43
 Recommended Implementation Sequence • Second page of each toolkit component highlights: – Task – Suggested personnel – Which component/ section 44
Recommended Implementation Sequence • Second page of each toolkit component highlights: – Task – Suggested personnel – Which component/ section 44
 Supplementary Aids and Services Consideration Toolkit - Component C • What are the demands of the general education setting? • What are potential barriers to learning and participation? • What are our ideas for Sa. S to bridge the barriers? 45
Supplementary Aids and Services Consideration Toolkit - Component C • What are the demands of the general education setting? • What are potential barriers to learning and participation? • What are our ideas for Sa. S to bridge the barriers? 45
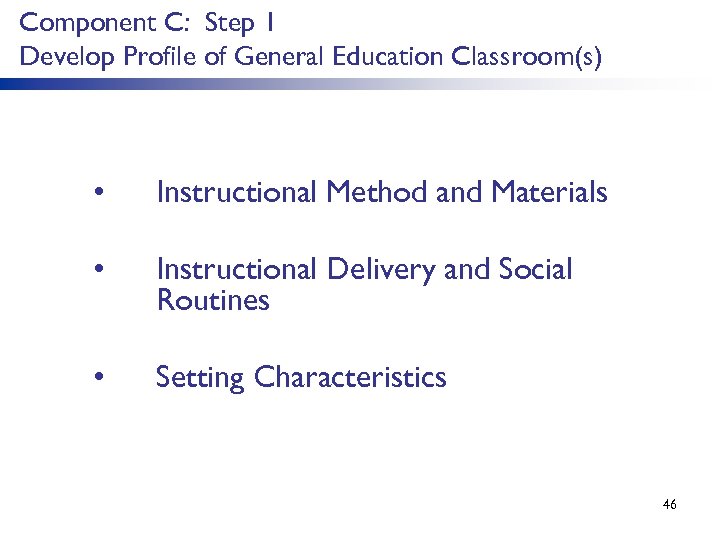 Component C: Step 1 Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s) • Instructional Method and Materials • Instructional Delivery and Social Routines • Setting Characteristics 46
Component C: Step 1 Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s) • Instructional Method and Materials • Instructional Delivery and Social Routines • Setting Characteristics 46
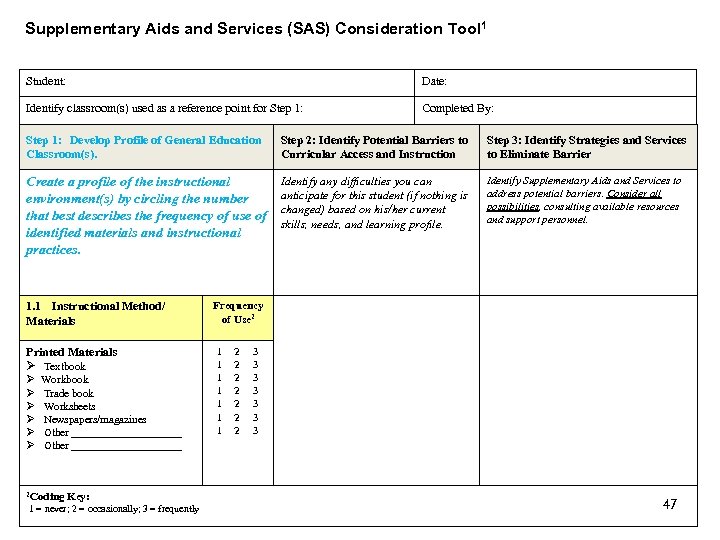 Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s). Step 2: Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barrier Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile. Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 47
Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s). Step 2: Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barrier Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile. Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 47
 Component C: Step 2 Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction – – – Student skills Student learning characteristics Priority needs in the context of general education classroom. *Completed by all team members 48
Component C: Step 2 Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction – – – Student skills Student learning characteristics Priority needs in the context of general education classroom. *Completed by all team members 48
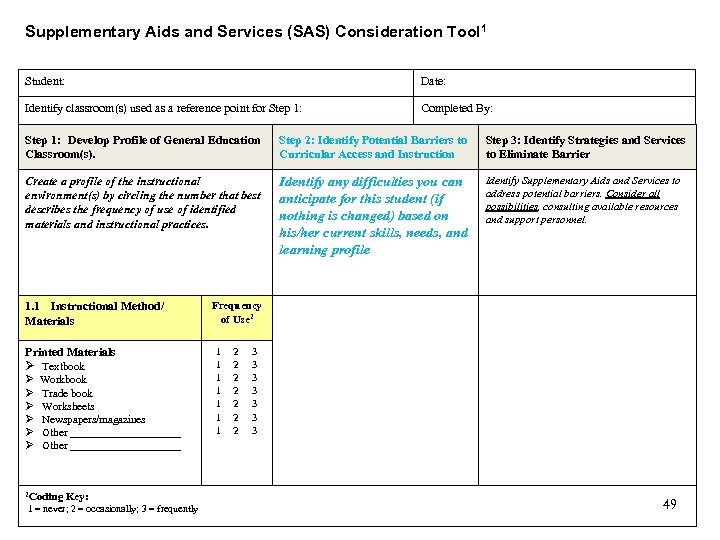 Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s). Step 2: Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barrier Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 49
Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Develop Profile of General Education Classroom(s). Step 2: Identify Potential Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barrier Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 49
 Component C: Step 3 Identify Strategies and Service to Eliminate Barriers • Support strategies should maximize participation and reduce instructional barriers • Use student strengths to address barriers *Completed by all team members 50
Component C: Step 3 Identify Strategies and Service to Eliminate Barriers • Support strategies should maximize participation and reduce instructional barriers • Use student strengths to address barriers *Completed by all team members 50
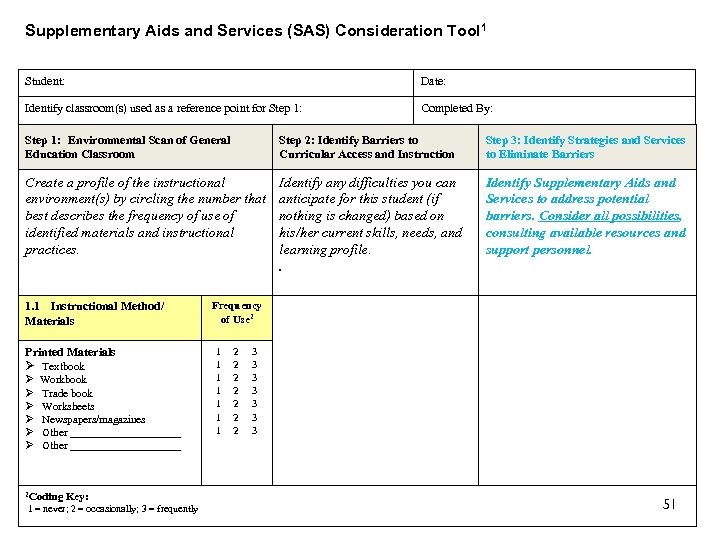 Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Environmental Scan of General Education Classroom Step 2: Identify Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barriers Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile. . Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 51
Supplementary Aids and Services (SAS) Consideration Tool 1 Student: Date: Identify classroom(s) used as a reference point for Step 1: Completed By: Step 1: Environmental Scan of General Education Classroom Step 2: Identify Barriers to Curricular Access and Instruction Step 3: Identify Strategies and Services to Eliminate Barriers Create a profile of the instructional environment(s) by circling the number that best describes the frequency of use of identified materials and instructional practices. Identify any difficulties you can anticipate for this student (if nothing is changed) based on his/her current skills, needs, and learning profile. . Identify Supplementary Aids and Services to address potential barriers. Consider all possibilities, consulting available resources and support personnel. 1. 1 Instructional Method/ Materials Printed Materials Textbook Workbook Trade book Worksheets Newspapers/magazines Other ____________________ 2 Coding Key: 1 = never; 2 = occasionally; 3 = frequently Frequency of Use 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 51
 Component C: Step 4 Identify Viable Alternatives for Implementation • What does the student need to be successful? • What do the adults need in order to be able to support the student? • How will we get there? *Completed by all team members 52
Component C: Step 4 Identify Viable Alternatives for Implementation • What does the student need to be successful? • What do the adults need in order to be able to support the student? • How will we get there? *Completed by all team members 52
 Component D Self-Check For IEP Teams • A self-assessment tool for teams to use as they move through the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit 53
Component D Self-Check For IEP Teams • A self-assessment tool for teams to use as they move through the Sa. S Consideration Toolkit 53
 Points to Remember • Sa. S Fact Sheet and Consideration Toolkit help structure team planning regarding Sa. S considerations • Assists team in developing supports to meet the needs of the student 54
Points to Remember • Sa. S Fact Sheet and Consideration Toolkit help structure team planning regarding Sa. S considerations • Assists team in developing supports to meet the needs of the student 54
 Points to Remember Participation of all team members is critical to the process. • Families bring deep knowledge of student • Teachers bring knowledge of the curricular and instructional demands • Special education teachers bring knowledge of Sa. S • Paraprofessionals bring knowledge of how the student learns and what is challenging for the student • Administrators facilitate implementation of plan and are aware of school level resources 55
Points to Remember Participation of all team members is critical to the process. • Families bring deep knowledge of student • Teachers bring knowledge of the curricular and instructional demands • Special education teachers bring knowledge of Sa. S • Paraprofessionals bring knowledge of how the student learns and what is challenging for the student • Administrators facilitate implementation of plan and are aware of school level resources 55
 Considering Sa. S for Students Activity • Review the scenario. • Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
Considering Sa. S for Students Activity • Review the scenario. • Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
 Student A - 5 th Grade Student Receiving Learning Support Strengths: • using computers & technology • long term memory • remembering strategies • generates creative ideas • works well in structured small groups with peers • likes animals, arts and crafts & movies Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • reading and math skills below grade level • difficulty interpreting subtle communication from peers and adults • anxiety with changes in routine • putting ideas into writing with correct grammar and spelling
Student A - 5 th Grade Student Receiving Learning Support Strengths: • using computers & technology • long term memory • remembering strategies • generates creative ideas • works well in structured small groups with peers • likes animals, arts and crafts & movies Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • reading and math skills below grade level • difficulty interpreting subtle communication from peers and adults • anxiety with changes in routine • putting ideas into writing with correct grammar and spelling
 Student A - 5 th Grade Student Receiving Learning Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
Student A - 5 th Grade Student Receiving Learning Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
 Student B – 6 th Grade Student Receiving Emotional and Learning Support Strengths: • role playing/dramatic acting • sense of humor/sarcastic • likes to be physically active • likes to play games, but very competitive • likes to help adults • likes talking on phone Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • forgets to bring materials home from school to complete assignments • difficulty accepting limits (e. g. being told no) • difficulty establishing relationships with peers because always wants to be right • can bully other kids to try to get her own way • poor reading comprehension skills (can read fluently)
Student B – 6 th Grade Student Receiving Emotional and Learning Support Strengths: • role playing/dramatic acting • sense of humor/sarcastic • likes to be physically active • likes to play games, but very competitive • likes to help adults • likes talking on phone Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • forgets to bring materials home from school to complete assignments • difficulty accepting limits (e. g. being told no) • difficulty establishing relationships with peers because always wants to be right • can bully other kids to try to get her own way • poor reading comprehension skills (can read fluently)
 Student B – 6 th Grade Student Receiving Emotional and Learning Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
Student B – 6 th Grade Student Receiving Emotional and Learning Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
 Student C – 9 th Grade Student Receiving Life Skills Support Strengths: • follows verbal directions well • loves music and fashion • gets along with familiar peers in school • wants to have a job • uses computer for leisure and academics • likes to take photos Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • asks for clarification for all tasks • needs a lot of reminders to stay on task • limited receptive vocabulary • speech can be hard to understand due to articulation issues • lack of family support/collaboration with school • limited experience with academic instruction in earlier grades
Student C – 9 th Grade Student Receiving Life Skills Support Strengths: • follows verbal directions well • loves music and fashion • gets along with familiar peers in school • wants to have a job • uses computer for leisure and academics • likes to take photos Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • asks for clarification for all tasks • needs a lot of reminders to stay on task • limited receptive vocabulary • speech can be hard to understand due to articulation issues • lack of family support/collaboration with school • limited experience with academic instruction in earlier grades
 Student C – 9 th Grade Student Receiving Life Skills Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
Student C – 9 th Grade Student Receiving Life Skills Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
 Student D – 2 nd Grade Student Receiving Multiple Disabilities Support Strengths: • uses combination of gestures, vocalizations and electronic, programmable communication device to express wants, needs and exchange information with others • highly motivated to learn • enjoys interacting with both peers and adults • math skills are close to grade level • uses power wheelchair Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • difficult to assess learning because of communication challenges • reads sight words; beginning to decode • physical limitations regarding fine motor activities • challenges with computer access • needs wait time to respond to prompts • tries to please adults by giving the answer he thinks they want rather than thinking it through • personal care needs require him to miss chunks of instructional time
Student D – 2 nd Grade Student Receiving Multiple Disabilities Support Strengths: • uses combination of gestures, vocalizations and electronic, programmable communication device to express wants, needs and exchange information with others • highly motivated to learn • enjoys interacting with both peers and adults • math skills are close to grade level • uses power wheelchair Barriers to participation and learning in general education classes: • difficult to assess learning because of communication challenges • reads sight words; beginning to decode • physical limitations regarding fine motor activities • challenges with computer access • needs wait time to respond to prompts • tries to please adults by giving the answer he thinks they want rather than thinking it through • personal care needs require him to miss chunks of instructional time
 Student D – 2 nd Grade Student Receiving Multiple Disabilities Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
Student D – 2 nd Grade Student Receiving Multiple Disabilities Support Choose the combination of supports you think would best meet the needs of this student to access instruction and make educational progress.
 References • Center for Applied Special Technology (CAST). http: //www. cast. org/teachingeverystudent/ • Etscheidt, S. K. , & Bartlett, L. (1999). The IDEA Amendments: A four-step approach for determining supplementary aids and services. Exceptional Children, 65(2), 163 -174. 65
References • Center for Applied Special Technology (CAST). http: //www. cast. org/teachingeverystudent/ • Etscheidt, S. K. , & Bartlett, L. (1999). The IDEA Amendments: A four-step approach for determining supplementary aids and services. Exceptional Children, 65(2), 163 -174. 65
 Final reminder • If you registered individually for this session through Pa. TTAN’s coursewhere system, a certificate of attendance should be available for you to download from the Pa. TTAN website’s transcript section within about a month.
Final reminder • If you registered individually for this session through Pa. TTAN’s coursewhere system, a certificate of attendance should be available for you to download from the Pa. TTAN website’s transcript section within about a month.
 Contact Information www. pattan. net Jennifer Goldbloom jgoldbloom@pattan. net Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Tom Corbett, Governor Pennsylvania Department of Education Ronald J. Tomalis, Secretary Dr. Carolyn Dumaresq, Deputy Secretary Office for Elementary and Secondary Education John J. Tommasini, Director Bureau of Special Education Patricia Hozella, Assistant Director Bureau of Special Education
Contact Information www. pattan. net Jennifer Goldbloom jgoldbloom@pattan. net Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Tom Corbett, Governor Pennsylvania Department of Education Ronald J. Tomalis, Secretary Dr. Carolyn Dumaresq, Deputy Secretary Office for Elementary and Secondary Education John J. Tommasini, Director Bureau of Special Education Patricia Hozella, Assistant Director Bureau of Special Education


