e6f3c6be1a9382542f9536d04252bca4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 2010 EA Conference Reference Architecture Track Terry Hagle, Office of Do. D CIO/AS&I 703 -607 -0235 terry. hagle@osd. mil
2010 EA Conference Reference Architecture Track Terry Hagle, Office of Do. D CIO/AS&I 703 -607 -0235 terry. hagle@osd. mil
 Agenda Ø Enterprise Reference Architecture Cell (ERAC) Overview – Terry Hagle Ø Reference Architecture (RA)– Steve Ring – Principles – Technical Positions – Patterns Ø Enterprise-wide Access to Network and Collaboration Services (EANCS) RA – Norm Minekime Ø Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture (IEA) – Al Mazyck – Purpose/Background – Content – Application of the Do. D IEA • Example EANCS RA – Compliance with the Do. D IEA • Example EANCS RA 2
Agenda Ø Enterprise Reference Architecture Cell (ERAC) Overview – Terry Hagle Ø Reference Architecture (RA)– Steve Ring – Principles – Technical Positions – Patterns Ø Enterprise-wide Access to Network and Collaboration Services (EANCS) RA – Norm Minekime Ø Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture (IEA) – Al Mazyck – Purpose/Background – Content – Application of the Do. D IEA • Example EANCS RA – Compliance with the Do. D IEA • Example EANCS RA 2
 ERAC OVERVIEW 3
ERAC OVERVIEW 3
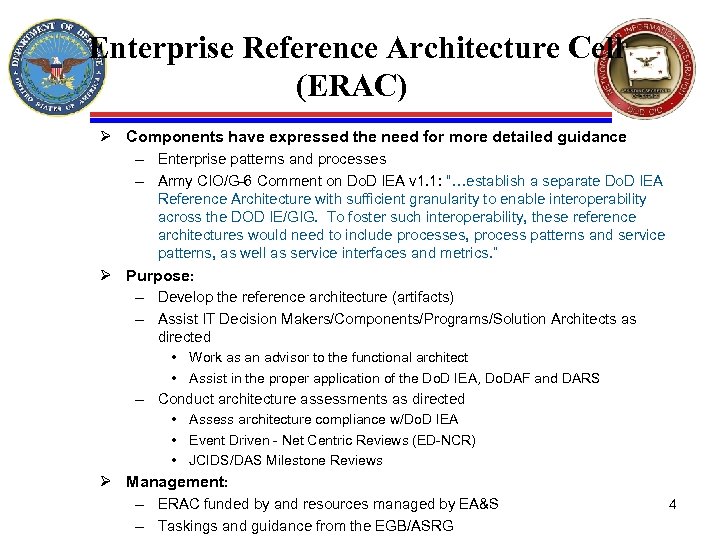 Enterprise Reference Architecture Cell (ERAC) Ø Components have expressed the need for more detailed guidance – Enterprise patterns and processes – Army CIO/G-6 Comment on Do. D IEA v 1. 1: “…establish a separate Do. D IEA Reference Architecture with sufficient granularity to enable interoperability across the DOD IE/GIG. To foster such interoperability, these reference architectures would need to include processes, process patterns and service patterns, as well as service interfaces and metrics. ” Ø Purpose: – Develop the reference architecture (artifacts) – Assist IT Decision Makers/Components/Programs/Solution Architects as directed • Work as an advisor to the functional architect • Assist in the proper application of the Do. D IEA, Do. DAF and DARS – Conduct architecture assessments as directed • Assess architecture compliance w/Do. D IEA • Event Driven - Net Centric Reviews (ED-NCR) • JCIDS/DAS Milestone Reviews Ø Management: – ERAC funded by and resources managed by EA&S – Taskings and guidance from the EGB/ASRG 4
Enterprise Reference Architecture Cell (ERAC) Ø Components have expressed the need for more detailed guidance – Enterprise patterns and processes – Army CIO/G-6 Comment on Do. D IEA v 1. 1: “…establish a separate Do. D IEA Reference Architecture with sufficient granularity to enable interoperability across the DOD IE/GIG. To foster such interoperability, these reference architectures would need to include processes, process patterns and service patterns, as well as service interfaces and metrics. ” Ø Purpose: – Develop the reference architecture (artifacts) – Assist IT Decision Makers/Components/Programs/Solution Architects as directed • Work as an advisor to the functional architect • Assist in the proper application of the Do. D IEA, Do. DAF and DARS – Conduct architecture assessments as directed • Assess architecture compliance w/Do. D IEA • Event Driven - Net Centric Reviews (ED-NCR) • JCIDS/DAS Milestone Reviews Ø Management: – ERAC funded by and resources managed by EA&S – Taskings and guidance from the EGB/ASRG 4
 Enterprise Reference Architecture Mission Statement Ø The intent of Reference Architecture is to: Normalize the institutional understanding of capabilities at the enterprise level and provide a common set of principles, patterns, and technical positions for use within the Do. D to guide development of Enterprise, Segment, or Solution architectures. Ø Development of a Reference Architecture is a process that results in the required content 5
Enterprise Reference Architecture Mission Statement Ø The intent of Reference Architecture is to: Normalize the institutional understanding of capabilities at the enterprise level and provide a common set of principles, patterns, and technical positions for use within the Do. D to guide development of Enterprise, Segment, or Solution architectures. Ø Development of a Reference Architecture is a process that results in the required content 5
 Reference Architecture Description Ø Five components of a Reference Architecture: – Strategic Purpose • Describes the context, scope, goals, purpose, and intended use of the RA – Principles • – • • High-level statements about the IT environment that tie back to business goals Incorporate values, organizational culture, and business goals Drive Technical Positions (and Patterns) Technical Positions • Statements that provide technical guidance (standards, technologies, etc) for use with each major architectural component or service – Patterns/Templates • • Diagrams that address the distribution of systems functions and how they relate topologically Models that show relationships between components specified by the Technical Positions – Vocabulary Ø Reference Architecture Description 6
Reference Architecture Description Ø Five components of a Reference Architecture: – Strategic Purpose • Describes the context, scope, goals, purpose, and intended use of the RA – Principles • – • • High-level statements about the IT environment that tie back to business goals Incorporate values, organizational culture, and business goals Drive Technical Positions (and Patterns) Technical Positions • Statements that provide technical guidance (standards, technologies, etc) for use with each major architectural component or service – Patterns/Templates • • Diagrams that address the distribution of systems functions and how they relate topologically Models that show relationships between components specified by the Technical Positions – Vocabulary Ø Reference Architecture Description 6
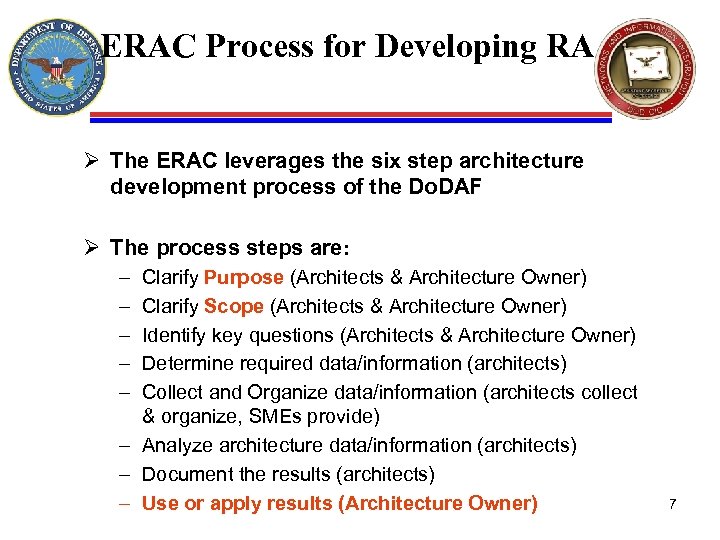 ERAC Process for Developing RA Ø The ERAC leverages the six step architecture development process of the Do. DAF Ø The process steps are: – – – Clarify Purpose (Architects & Architecture Owner) Clarify Scope (Architects & Architecture Owner) Identify key questions (Architects & Architecture Owner) Determine required data/information (architects) Collect and Organize data/information (architects collect & organize, SMEs provide) – Analyze architecture data/information (architects) – Document the results (architects) – Use or apply results (Architecture Owner) 7
ERAC Process for Developing RA Ø The ERAC leverages the six step architecture development process of the Do. DAF Ø The process steps are: – – – Clarify Purpose (Architects & Architecture Owner) Clarify Scope (Architects & Architecture Owner) Identify key questions (Architects & Architecture Owner) Determine required data/information (architects) Collect and Organize data/information (architects collect & organize, SMEs provide) – Analyze architecture data/information (architects) – Document the results (architects) – Use or apply results (Architecture Owner) 7
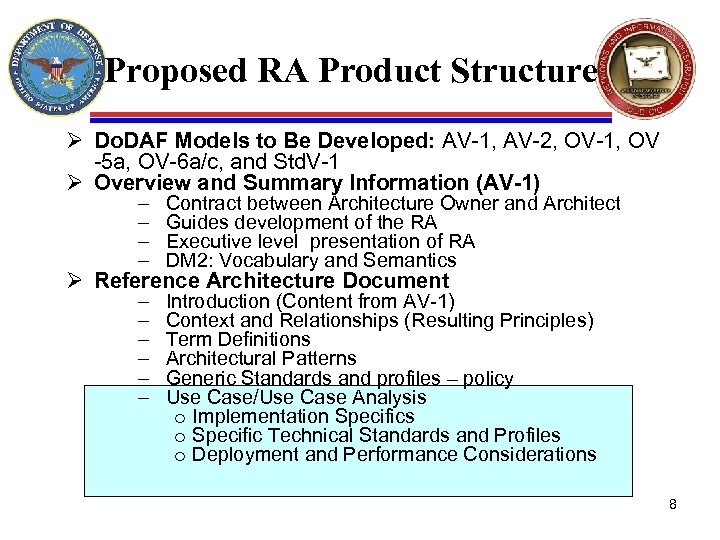 Proposed RA Product Structure Ø Do. DAF Models to Be Developed: AV-1, AV-2, OV-1, OV -5 a, OV-6 a/c, and Std. V-1 Ø Overview and Summary Information (AV-1) – – Contract between Architecture Owner and Architect Guides development of the RA Executive level presentation of RA DM 2: Vocabulary and Semantics – – – Introduction (Content from AV-1) Context and Relationships (Resulting Principles) Term Definitions Architectural Patterns Generic Standards and profiles – policy Use Case/Use Case Analysis o Implementation Specifics o Specific Technical Standards and Profiles o Deployment and Performance Considerations Ø Reference Architecture Document 8
Proposed RA Product Structure Ø Do. DAF Models to Be Developed: AV-1, AV-2, OV-1, OV -5 a, OV-6 a/c, and Std. V-1 Ø Overview and Summary Information (AV-1) – – Contract between Architecture Owner and Architect Guides development of the RA Executive level presentation of RA DM 2: Vocabulary and Semantics – – – Introduction (Content from AV-1) Context and Relationships (Resulting Principles) Term Definitions Architectural Patterns Generic Standards and profiles – policy Use Case/Use Case Analysis o Implementation Specifics o Specific Technical Standards and Profiles o Deployment and Performance Considerations Ø Reference Architecture Document 8
 Do. D IEA Website http: //cio-nii. defense. gov/sites/diea/ 9
Do. D IEA Website http: //cio-nii. defense. gov/sites/diea/ 9
 REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE 10
REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE 10
 Purpose Ø Do. D CIO intends to use Reference Architecture as a means to provide Department-wide Guidance for architectures and solutions Ø Reference Architecture, as currently used within Do. D… Is defined at different levels of detail and abstraction (from specific to generalized) with… Has little agreement and much confusion Has multiple meanings relative to the context of the environment Ø To support the Do. D CIO intent, a common definition of Reference Architecture is needed that… Provides policy and direction to the Do. D enterprise (commands, services, agencies) that guides and constrains architectures and solutions Can be equally applied across the wide spectrum of Do. D environments Ø IT/ Business and Service (SOA) domains Ø Warfighter domains 11
Purpose Ø Do. D CIO intends to use Reference Architecture as a means to provide Department-wide Guidance for architectures and solutions Ø Reference Architecture, as currently used within Do. D… Is defined at different levels of detail and abstraction (from specific to generalized) with… Has little agreement and much confusion Has multiple meanings relative to the context of the environment Ø To support the Do. D CIO intent, a common definition of Reference Architecture is needed that… Provides policy and direction to the Do. D enterprise (commands, services, agencies) that guides and constrains architectures and solutions Can be equally applied across the wide spectrum of Do. D environments Ø IT/ Business and Service (SOA) domains Ø Warfighter domains 11
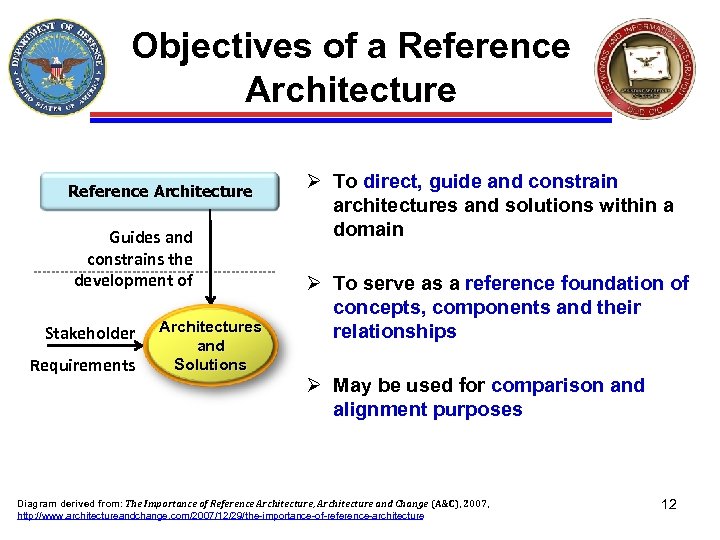 Objectives of a Reference Architecture Guides and constrains the development of Stakeholder Requirements Architectures and Solutions Ø To direct, guide and constrain architectures and solutions within a domain Ø To serve as a reference foundation of concepts, components and their relationships Ø May be used for comparison and alignment purposes Diagram derived from: The Importance of Reference Architecture, Architecture and Change (A&C), 2007, http: //www. architectureandchange. com/2007/12/29/the-importance-of-reference-architecture 12
Objectives of a Reference Architecture Guides and constrains the development of Stakeholder Requirements Architectures and Solutions Ø To direct, guide and constrain architectures and solutions within a domain Ø To serve as a reference foundation of concepts, components and their relationships Ø May be used for comparison and alignment purposes Diagram derived from: The Importance of Reference Architecture, Architecture and Change (A&C), 2007, http: //www. architectureandchange. com/2007/12/29/the-importance-of-reference-architecture 12
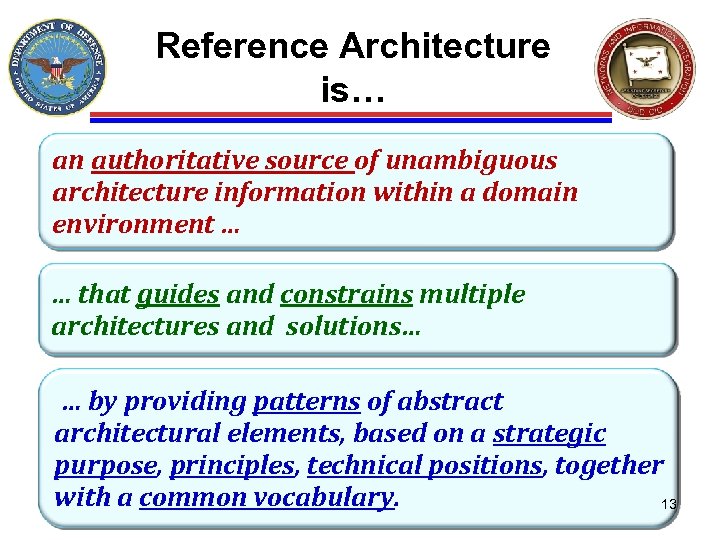 Reference Architecture is… an authoritative source of unambiguous architecture information within a domain environment … … that guides and constrains multiple architectures and solutions… … by providing patterns of abstract architectural elements, based on a strategic purpose, principles, technical positions, together with a common vocabulary. 13
Reference Architecture is… an authoritative source of unambiguous architecture information within a domain environment … … that guides and constrains multiple architectures and solutions… … by providing patterns of abstract architectural elements, based on a strategic purpose, principles, technical positions, together with a common vocabulary. 13
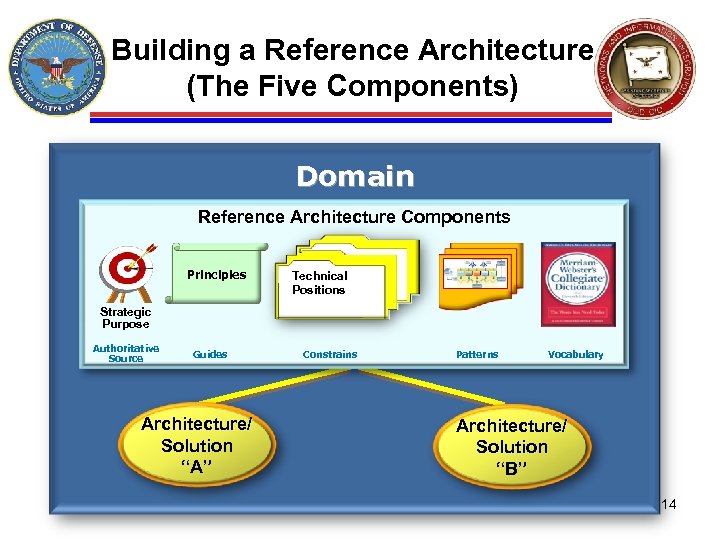 Building a Reference Architecture (The Five Components) Domain Reference Architecture Components Principles Technical Positions Strategic Purpose Authoritative Source Guides Architecture/ Solution “A” Constrains Patterns Vocabulary Architecture/ Solution “B” 14
Building a Reference Architecture (The Five Components) Domain Reference Architecture Components Principles Technical Positions Strategic Purpose Authoritative Source Guides Architecture/ Solution “A” Constrains Patterns Vocabulary Architecture/ Solution “B” 14
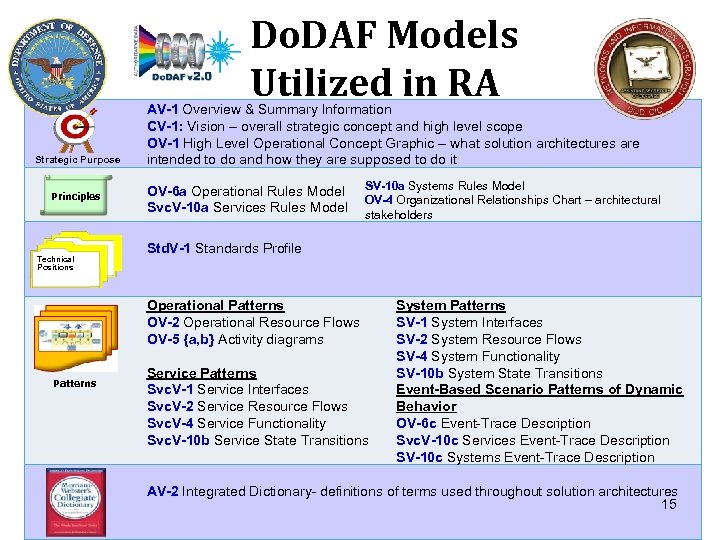 Do. DAF Models Utilized in RA Strategic Purpose Principles Technical Positions AV-1 Overview & Summary Information CV-1: Vision – overall strategic concept and high level scope OV-1 High Level Operational Concept Graphic – what solution architectures are intended to do and how they are supposed to do it OV-6 a Operational Rules Model Svc. V-10 a Services Rules Model SV-10 a Systems Rules Model OV-4 Organizational Relationships Chart – architectural stakeholders Std. V-1 Standards Profile Operational Patterns OV-2 Operational Resource Flows OV-5 {a, b} Activity diagrams Patterns Service Patterns Svc. V-1 Service Interfaces Svc. V-2 Service Resource Flows Svc. V-4 Service Functionality Svc. V-10 b Service State Transitions System Patterns SV-1 System Interfaces SV-2 System Resource Flows SV-4 System Functionality SV-10 b System State Transitions Event-Based Scenario Patterns of Dynamic Behavior OV-6 c Event-Trace Description Svc. V-10 c Services Event-Trace Description SV-10 c Systems Event-Trace Description AV-2 Integrated Dictionary- definitions of terms used throughout solution architectures 15
Do. DAF Models Utilized in RA Strategic Purpose Principles Technical Positions AV-1 Overview & Summary Information CV-1: Vision – overall strategic concept and high level scope OV-1 High Level Operational Concept Graphic – what solution architectures are intended to do and how they are supposed to do it OV-6 a Operational Rules Model Svc. V-10 a Services Rules Model SV-10 a Systems Rules Model OV-4 Organizational Relationships Chart – architectural stakeholders Std. V-1 Standards Profile Operational Patterns OV-2 Operational Resource Flows OV-5 {a, b} Activity diagrams Patterns Service Patterns Svc. V-1 Service Interfaces Svc. V-2 Service Resource Flows Svc. V-4 Service Functionality Svc. V-10 b Service State Transitions System Patterns SV-1 System Interfaces SV-2 System Resource Flows SV-4 System Functionality SV-10 b System State Transitions Event-Based Scenario Patterns of Dynamic Behavior OV-6 c Event-Trace Description Svc. V-10 c Services Event-Trace Description SV-10 c Systems Event-Trace Description AV-2 Integrated Dictionary- definitions of terms used throughout solution architectures 15
 Benefits Ø Authoritative source of architecture information within a problem space that guides and constrains architectures and solutions Ø Simplifies and standardizes solutions for complex problems by providing common repeatable patterns Ø Provides early, focused guidance at a sufficient level of abstraction and detail before concrete implementation decisions are known Ø A tool to ensure interoperable architectures and solutions based on common guidance 16
Benefits Ø Authoritative source of architecture information within a problem space that guides and constrains architectures and solutions Ø Simplifies and standardizes solutions for complex problems by providing common repeatable patterns Ø Provides early, focused guidance at a sufficient level of abstraction and detail before concrete implementation decisions are known Ø A tool to ensure interoperable architectures and solutions based on common guidance 16
 First Usage: EANCS Reference Architecture Ø Supports development of EANCS implementation guidance and solution architectures Ø “…focuses on that portion of the characteristic dealing with global authentication, authorization and access control to globally accessible resources. It is intended to guide the development of solution architectures and support the development of specific implementation guidance for achieving this capability. ” 17
First Usage: EANCS Reference Architecture Ø Supports development of EANCS implementation guidance and solution architectures Ø “…focuses on that portion of the characteristic dealing with global authentication, authorization and access control to globally accessible resources. It is intended to guide the development of solution architectures and support the development of specific implementation guidance for achieving this capability. ” 17
 Enterprise-wide Access to Networks and Collaboration Services (EANCS) Reference Architecture (RA) 18
Enterprise-wide Access to Networks and Collaboration Services (EANCS) Reference Architecture (RA) 18
 EANCS RA Background Ø Operational Requirements – GIG 2. 0 Operational Reference Architecture (ORA) describes requirement for “Global Authentication, Access Control, and Directory Services” – Vice Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff (VCJCS) directed ability to “go anywhere [in Do. D], login, and be productive” Ø EANCS RA to address these requirements by: – Providing basis for implementation guidance/roadmap for Enterprise Services Security Foundation (ESSF) – Describing Authentication and Authorization and Access Control to networks (NIPRNet and SIPRNet) and designated Enterprise Services (e. g. , Enterprise Directory Service, Enterprise e-mail, DCO, Intelink) – Supporting implementation of an initial authentication and access control capability in 6 to 9 months for Enterprise User Initiative – Leveraging: • Common credentials for authentication (PKI/CAC for NIPR, PKI/hard-token for SIPR) • Authoritative identity attributes for authorization and access control (Attribute-Based Access Control) 19
EANCS RA Background Ø Operational Requirements – GIG 2. 0 Operational Reference Architecture (ORA) describes requirement for “Global Authentication, Access Control, and Directory Services” – Vice Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff (VCJCS) directed ability to “go anywhere [in Do. D], login, and be productive” Ø EANCS RA to address these requirements by: – Providing basis for implementation guidance/roadmap for Enterprise Services Security Foundation (ESSF) – Describing Authentication and Authorization and Access Control to networks (NIPRNet and SIPRNet) and designated Enterprise Services (e. g. , Enterprise Directory Service, Enterprise e-mail, DCO, Intelink) – Supporting implementation of an initial authentication and access control capability in 6 to 9 months for Enterprise User Initiative – Leveraging: • Common credentials for authentication (PKI/CAC for NIPR, PKI/hard-token for SIPR) • Authoritative identity attributes for authorization and access control (Attribute-Based Access Control) 19
 EANCS RA Purpose and Scope Ø Purpose – Gain Department-wide consensus on requirements for authenticating users and authorizing user access to Do. D Information Enterprise (IE) and, more specifically, to representative collaborative services, to include portals and enterprise e-mail – Describe architectural patterns to guide, standardize, and enable the most rapid and cost-effective implementations of an authentication and authorization capability in support of secure information sharing across Do. D Ø Scope – “To Be” Architectural Description – Document requirements, activities, and information for authentication and authorization and access control – Document “standard/common” authentication and authorization and access control processes 20
EANCS RA Purpose and Scope Ø Purpose – Gain Department-wide consensus on requirements for authenticating users and authorizing user access to Do. D Information Enterprise (IE) and, more specifically, to representative collaborative services, to include portals and enterprise e-mail – Describe architectural patterns to guide, standardize, and enable the most rapid and cost-effective implementations of an authentication and authorization capability in support of secure information sharing across Do. D Ø Scope – “To Be” Architectural Description – Document requirements, activities, and information for authentication and authorization and access control – Document “standard/common” authentication and authorization and access control processes 20
 EANCS RA Development Approach Ø Architecture Owner organized Working Group (WG) – Composed of SMEs from ASD (NII)/CIO, Military Services, Joint Staff/J 6, Defense Manpower Data Center (DMDC), Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA), and National Security Agency (NSA) – Team members represented their stakeholder organizations Ø Architecture Owner worked with ERAC to establish RA purpose, perspective, and scope Ø WG developed Concept of Operations (CONOPS) for context Ø WG provided necessary architecture data/information – Existing documents served as knowledge baseline – SME knowledge and experience provided rest of information Ø ERAC organized collected data into Do. DAF-compliant RA description Ø WG approved RA content (Dec 2009) Ø Submitted to Architecture and Standards Review Group (ASRG) for approval and federation into Do. D EA 21
EANCS RA Development Approach Ø Architecture Owner organized Working Group (WG) – Composed of SMEs from ASD (NII)/CIO, Military Services, Joint Staff/J 6, Defense Manpower Data Center (DMDC), Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA), and National Security Agency (NSA) – Team members represented their stakeholder organizations Ø Architecture Owner worked with ERAC to establish RA purpose, perspective, and scope Ø WG developed Concept of Operations (CONOPS) for context Ø WG provided necessary architecture data/information – Existing documents served as knowledge baseline – SME knowledge and experience provided rest of information Ø ERAC organized collected data into Do. DAF-compliant RA description Ø WG approved RA content (Dec 2009) Ø Submitted to Architecture and Standards Review Group (ASRG) for approval and federation into Do. D EA 21
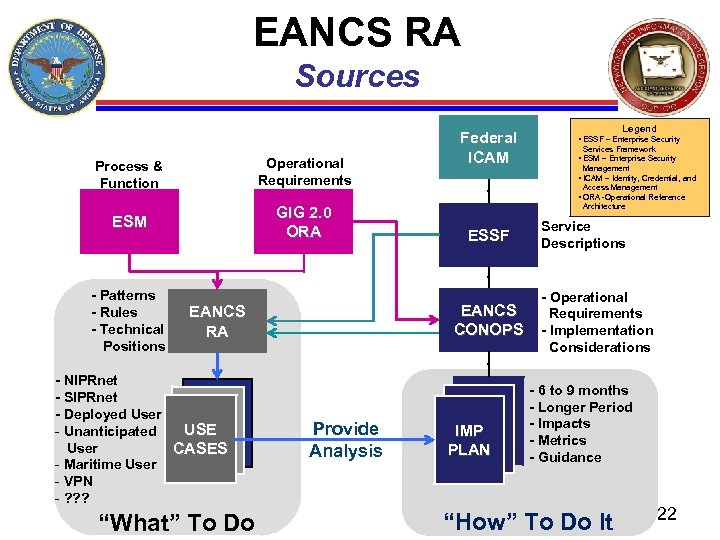 EANCS RA Sources Operational Requirements Process & Function Federal ICAM Legend • ESSF – Enterprise Security Services Framework • ESM – Enterprise Security Management • ICAM – Identity, Credential, and Access Management • ORA -Operational Reference GIG 2. 0 ORA ESM - Patterns - Rules - Technical Positions “What” To Do ESSF EANCS CONOPS EANCS RA - NIPRnet - SIPRnet - Deployed User USE - Unanticipated User CASES - Maritime User - VPN - ? ? ? Architecture Provide Analysis IMP PLAN Service Descriptions - Operational Requirements - Implementation Considerations - 6 to 9 months - Longer Period - Impacts - Metrics - Guidance “How” To Do It 22
EANCS RA Sources Operational Requirements Process & Function Federal ICAM Legend • ESSF – Enterprise Security Services Framework • ESM – Enterprise Security Management • ICAM – Identity, Credential, and Access Management • ORA -Operational Reference GIG 2. 0 ORA ESM - Patterns - Rules - Technical Positions “What” To Do ESSF EANCS CONOPS EANCS RA - NIPRnet - SIPRnet - Deployed User USE - Unanticipated User CASES - Maritime User - VPN - ? ? ? Architecture Provide Analysis IMP PLAN Service Descriptions - Operational Requirements - Implementation Considerations - 6 to 9 months - Longer Period - Impacts - Metrics - Guidance “How” To Do It 22
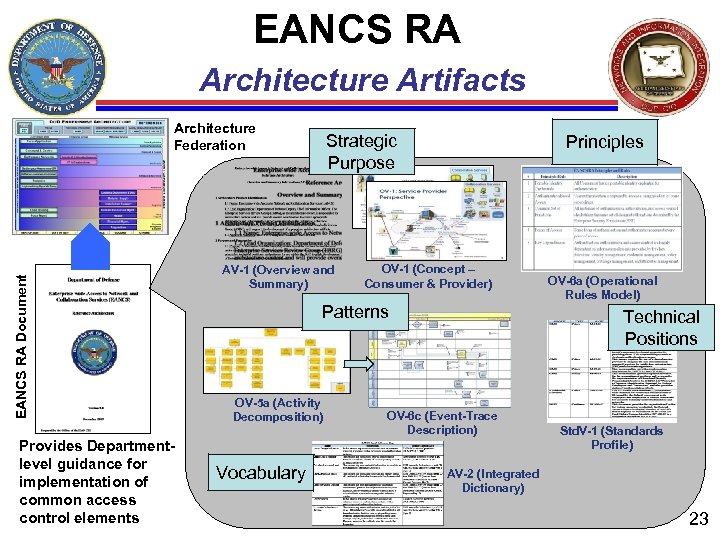 EANCS RA Architecture Artifacts EANCS RA Document Architecture Federation Provides Departmentlevel guidance for implementation of common access control elements Strategic Purpose AV-1 (Overview and Summary) Principles OV-1 (Concept – Consumer & Provider) Patterns OV-5 a (Activity Decomposition) Vocabulary OV-6 a (Operational Rules Model) Technical Positions OV-6 c (Event-Trace Description) Std. V-1 (Standards Profile) AV-2 (Integrated Dictionary) 23
EANCS RA Architecture Artifacts EANCS RA Document Architecture Federation Provides Departmentlevel guidance for implementation of common access control elements Strategic Purpose AV-1 (Overview and Summary) Principles OV-1 (Concept – Consumer & Provider) Patterns OV-5 a (Activity Decomposition) Vocabulary OV-6 a (Operational Rules Model) Technical Positions OV-6 c (Event-Trace Description) Std. V-1 (Standards Profile) AV-2 (Integrated Dictionary) 23
 Compliance with Do. D IEA Ø Development of RA guided by Department’s Net-centric vision “to function as one unified Do. D Enterprise, creating an information advantage” for Do. D, its people, and its mission partners, as described in Do. D IEA Ø Alignment with Do. D IEA “built-in” during RA development IAW Do. D IEA Appendix D Ø Compliance with Do. D IEA documented in IAW Do. D IEA Appendix E 24
Compliance with Do. D IEA Ø Development of RA guided by Department’s Net-centric vision “to function as one unified Do. D Enterprise, creating an information advantage” for Do. D, its people, and its mission partners, as described in Do. D IEA Ø Alignment with Do. D IEA “built-in” during RA development IAW Do. D IEA Appendix D Ø Compliance with Do. D IEA documented in IAW Do. D IEA Appendix E 24
 Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture (IEA) 25
Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture (IEA) 25
 Purpose Ø Unify the concepts embedded in the Do. D’s netcentric strategies into a common vision Ø Drive common solutions and promote consistency Ø Describe the integrated Defense Information Enterprise and the rules for information assets and resources that enable it Ø Foster alignment of Do. D architectures with the enterprise net-centric vision Do. D Net-centric Vision To function as one unified Do. D Enterprise, creating an information advantage for our people and mission partners by providing: A rich information sharing environment in which data and services are visible, accessible, understandable, and trusted across the enterprise. An available and protected network infrastructure (the GIG) that enables responsive information-centric operations using dynamic and interoperable communications and computing capabilities. 26
Purpose Ø Unify the concepts embedded in the Do. D’s netcentric strategies into a common vision Ø Drive common solutions and promote consistency Ø Describe the integrated Defense Information Enterprise and the rules for information assets and resources that enable it Ø Foster alignment of Do. D architectures with the enterprise net-centric vision Do. D Net-centric Vision To function as one unified Do. D Enterprise, creating an information advantage for our people and mission partners by providing: A rich information sharing environment in which data and services are visible, accessible, understandable, and trusted across the enterprise. An available and protected network infrastructure (the GIG) that enables responsive information-centric operations using dynamic and interoperable communications and computing capabilities. 26
 Background Ø Major Net-Centric Strategies • Data (9 May 2003) • Spectrum Management (3 Aug 2006) • Services (4 May 2007) • Net. Ops (February 2008) • Information Assurance (26 April 2006) • Communications/Transport • Computing Infrastructure (September 2007) • Information Sharing (4 May 2007) Ø Do. D IEA v 1. 0 (Approved 11 April 2008) – Established five priority areas for realizing net-centric goals – Provided key principles, rules, and activities for priority areas – Positioned as a tool to guide the net-centric transformation of the Information Enterprise (IE) Ø Do. D IEA v 1. 1 (Approved 27 May 2009) – Describes a process for applying the Do. D IEA content (App D) – Describes compliance areas and criteria (App E) – Provides activity mapping between the Do. D IEA and the NCOW RM (App F) 27
Background Ø Major Net-Centric Strategies • Data (9 May 2003) • Spectrum Management (3 Aug 2006) • Services (4 May 2007) • Net. Ops (February 2008) • Information Assurance (26 April 2006) • Communications/Transport • Computing Infrastructure (September 2007) • Information Sharing (4 May 2007) Ø Do. D IEA v 1. 0 (Approved 11 April 2008) – Established five priority areas for realizing net-centric goals – Provided key principles, rules, and activities for priority areas – Positioned as a tool to guide the net-centric transformation of the Information Enterprise (IE) Ø Do. D IEA v 1. 1 (Approved 27 May 2009) – Describes a process for applying the Do. D IEA content (App D) – Describes compliance areas and criteria (App E) – Provides activity mapping between the Do. D IEA and the NCOW RM (App F) 27
 Audience & Intended Use Ø IT Architects – Align architecture with the Do. D IEA – Apply Do. D IEA content (rules, activities, etc) to guide and constrain information enterprise solutions Ø Managers of IT Programs (PM, PEO, etc. ) – Use the Do. D IEA to support program design, development, and implementation – Through solution architectures properly aligned with the Do. D IEA Ø IT Decision-Makers (CPM, IRB, CIO, etc. ) – Use the Do. D IEA to support investment decisions – Through enterprise and solution architectures properly aligned with the Do. D IEA 28
Audience & Intended Use Ø IT Architects – Align architecture with the Do. D IEA – Apply Do. D IEA content (rules, activities, etc) to guide and constrain information enterprise solutions Ø Managers of IT Programs (PM, PEO, etc. ) – Use the Do. D IEA to support program design, development, and implementation – Through solution architectures properly aligned with the Do. D IEA Ø IT Decision-Makers (CPM, IRB, CIO, etc. ) – Use the Do. D IEA to support investment decisions – Through enterprise and solution architectures properly aligned with the Do. D IEA 28
 Do. D IEA v 1. 2 (Draft) Ø Adds Do. D EA Compliance Requirements (Appendix G) – Compliance with Do. D IEA – Compliance with Capability and Component EAs – Compliance with the DISR D ra ft – Compliance with Mandatory Core and Shared Designated Do. D Enterprise Services (ES) – Architecture Registration Requirements Ø Provides a table of Mandatory Core and Shared Designated Do. D ES Ø Adds content to the Rules, App D, and App E to maintain consistency with App G 29
Do. D IEA v 1. 2 (Draft) Ø Adds Do. D EA Compliance Requirements (Appendix G) – Compliance with Do. D IEA – Compliance with Capability and Component EAs – Compliance with the DISR D ra ft – Compliance with Mandatory Core and Shared Designated Do. D Enterprise Services (ES) – Architecture Registration Requirements Ø Provides a table of Mandatory Core and Shared Designated Do. D ES Ø Adds content to the Rules, App D, and App E to maintain consistency with App G 29
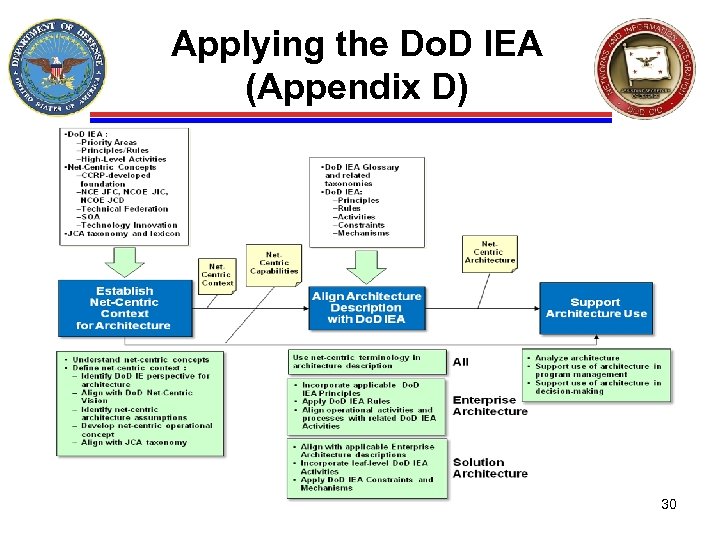 Applying the Do. D IEA (Appendix D) 30
Applying the Do. D IEA (Appendix D) 30
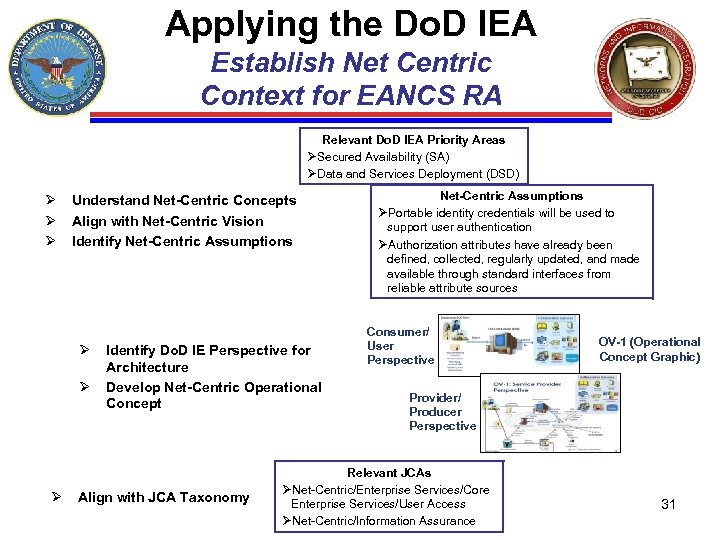 Applying the Do. D IEA Establish Net Centric Context for EANCS RA Relevant Do. D IEA Priority Areas ØSecured Availability (SA) ØData and Services Deployment (DSD) Ø Ø Ø Understand Net-Centric Concepts Align with Net-Centric Vision Identify Net-Centric Assumptions Ø Ø Ø Identify Do. D IE Perspective for Architecture Develop Net-Centric Operational Concept Align with JCA Taxonomy Net-Centric Assumptions ØPortable identity credentials will be used to support user authentication ØAuthorization attributes have already been defined, collected, regularly updated, and made available through standard interfaces from reliable attribute sources Consumer/ User Perspective OV-1 (Operational Concept Graphic) Provider/ Producer Perspective Relevant JCAs ØNet-Centric/Enterprise Services/Core Enterprise Services/User Access ØNet-Centric/Information Assurance 31
Applying the Do. D IEA Establish Net Centric Context for EANCS RA Relevant Do. D IEA Priority Areas ØSecured Availability (SA) ØData and Services Deployment (DSD) Ø Ø Ø Understand Net-Centric Concepts Align with Net-Centric Vision Identify Net-Centric Assumptions Ø Ø Ø Identify Do. D IE Perspective for Architecture Develop Net-Centric Operational Concept Align with JCA Taxonomy Net-Centric Assumptions ØPortable identity credentials will be used to support user authentication ØAuthorization attributes have already been defined, collected, regularly updated, and made available through standard interfaces from reliable attribute sources Consumer/ User Perspective OV-1 (Operational Concept Graphic) Provider/ Producer Perspective Relevant JCAs ØNet-Centric/Enterprise Services/Core Enterprise Services/User Access ØNet-Centric/Information Assurance 31
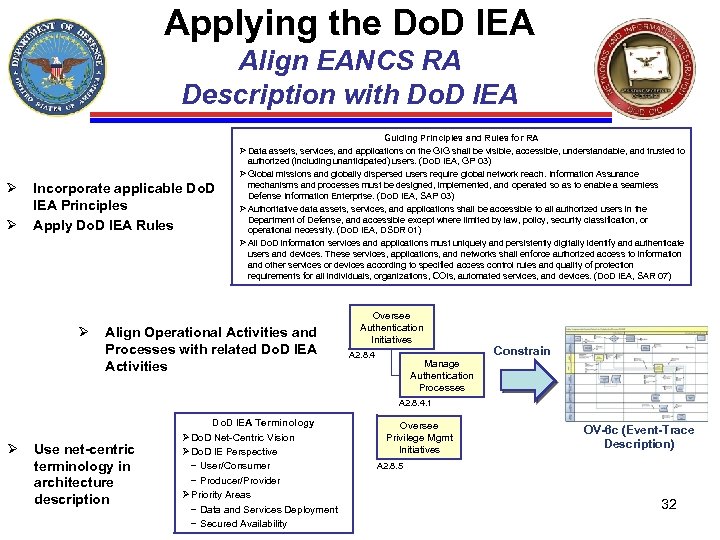 Applying the Do. D IEA Align EANCS RA Description with Do. D IEA Guiding Principles and Rules for RA Ø Data assets, services, and applications on the GIG shall be visible, accessible, understandable, and trusted to authorized (including unanticipated) users. (Do. D IEA, GP 03) Ø Global missions and globally dispersed users require global network reach. Information Assurance Ø Ø Incorporate applicable Do. D IEA Principles Apply Do. D IEA Rules Ø mechanisms and processes must be designed, implemented, and operated so as to enable a seamless Defense Information Enterprise. (Do. D IEA, SAP 03) Ø Authoritative data assets, services, and applications shall be accessible to all authorized users in the Department of Defense, and accessible except where limited by law, policy, security classification, or operational necessity. (Do. D IEA, DSDR 01) Ø All Do. D information services and applications must uniquely and persistently digitally identify and authenticate users and devices. These services, applications, and networks shall enforce authorized access to information and other services or devices according to specified access control rules and quality of protection requirements for all individuals, organizations, COIs, automated services, and devices. (Do. D IEA, SAR 07) Align Operational Activities and Processes with related Do. D IEA Activities Oversee Authentication Initiatives A 2. 8. 4 Constrain Manage Authentication Processes A 2. 8. 4. 1 Ø Use net-centric terminology in architecture description Do. D IEA Terminology Ø Do. D Net-Centric Vision Ø Do. D IE Perspective – User/Consumer – Producer/Provider Ø Priority Areas – Data and Services Deployment – Secured Availability Oversee Privilege Mgmt Initiatives OV-6 c (Event-Trace Description) A 2. 8. 5 32
Applying the Do. D IEA Align EANCS RA Description with Do. D IEA Guiding Principles and Rules for RA Ø Data assets, services, and applications on the GIG shall be visible, accessible, understandable, and trusted to authorized (including unanticipated) users. (Do. D IEA, GP 03) Ø Global missions and globally dispersed users require global network reach. Information Assurance Ø Ø Incorporate applicable Do. D IEA Principles Apply Do. D IEA Rules Ø mechanisms and processes must be designed, implemented, and operated so as to enable a seamless Defense Information Enterprise. (Do. D IEA, SAP 03) Ø Authoritative data assets, services, and applications shall be accessible to all authorized users in the Department of Defense, and accessible except where limited by law, policy, security classification, or operational necessity. (Do. D IEA, DSDR 01) Ø All Do. D information services and applications must uniquely and persistently digitally identify and authenticate users and devices. These services, applications, and networks shall enforce authorized access to information and other services or devices according to specified access control rules and quality of protection requirements for all individuals, organizations, COIs, automated services, and devices. (Do. D IEA, SAR 07) Align Operational Activities and Processes with related Do. D IEA Activities Oversee Authentication Initiatives A 2. 8. 4 Constrain Manage Authentication Processes A 2. 8. 4. 1 Ø Use net-centric terminology in architecture description Do. D IEA Terminology Ø Do. D Net-Centric Vision Ø Do. D IE Perspective – User/Consumer – Producer/Provider Ø Priority Areas – Data and Services Deployment – Secured Availability Oversee Privilege Mgmt Initiatives OV-6 c (Event-Trace Description) A 2. 8. 5 32
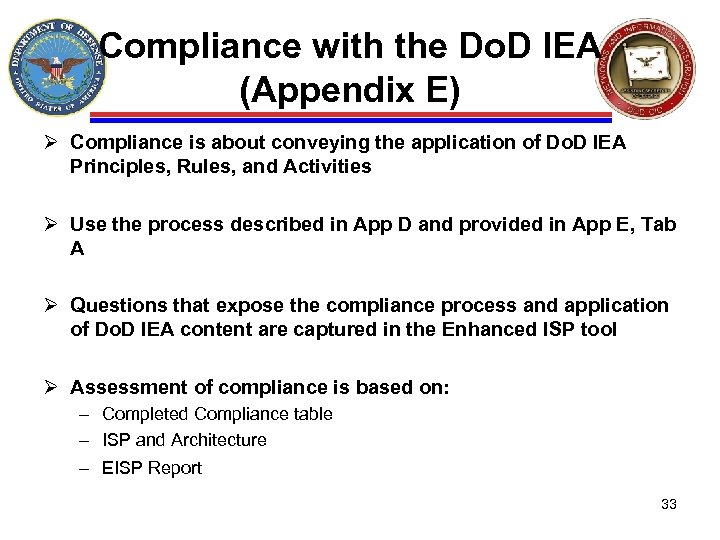 Compliance with the Do. D IEA (Appendix E) Ø Compliance is about conveying the application of Do. D IEA Principles, Rules, and Activities Ø Use the process described in App D and provided in App E, Tab A Ø Questions that expose the compliance process and application of Do. D IEA content are captured in the Enhanced ISP tool Ø Assessment of compliance is based on: – Completed Compliance table – ISP and Architecture – EISP Report 33
Compliance with the Do. D IEA (Appendix E) Ø Compliance is about conveying the application of Do. D IEA Principles, Rules, and Activities Ø Use the process described in App D and provided in App E, Tab A Ø Questions that expose the compliance process and application of Do. D IEA content are captured in the Enhanced ISP tool Ø Assessment of compliance is based on: – Completed Compliance table – ISP and Architecture – EISP Report 33
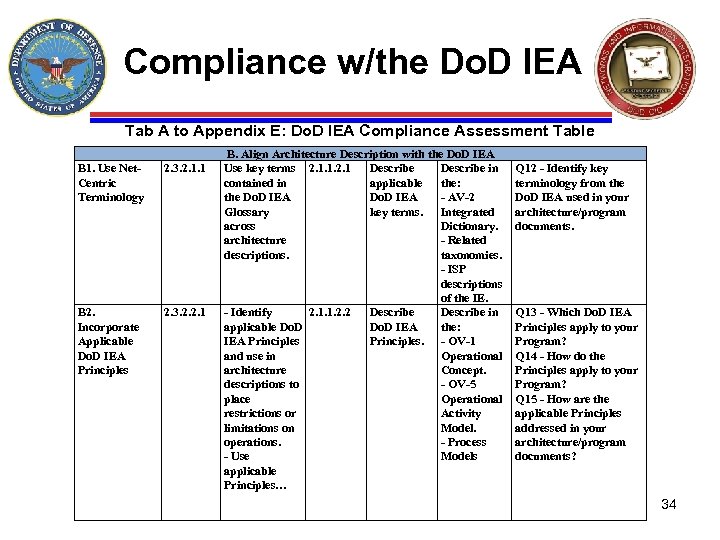 Compliance w/the Do. D IEA Tab A to Appendix E: Do. D IEA Compliance Assessment Table B 1. Use Net. Centric Terminology 2. 3. 2. 1. 1 B 2. Incorporate Applicable Do. D IEA Principles 2. 3. 2. 2. 1 B. Align Architecture Description with the Do. D IEA Use key terms 2. 1. 1. 2. 1 Describe in contained in applicable the: the Do. D IEA - AV-2 Glossary key terms. Integrated across Dictionary. architecture - Related descriptions. taxonomies. - ISP descriptions of the IE. - Identify 2. 1. 1. 2. 2 Describe in applicable Do. D IEA the: IEA Principles. - OV-1 and use in Operational architecture Concept. descriptions to - OV-5 place Operational restrictions or Activity limitations on Model. operations. - Process - Use Models applicable Principles… Q 12 - Identify key terminology from the Do. D IEA used in your architecture/program documents. Q 13 - Which Do. D IEA Principles apply to your Program? Q 14 - How do the Principles apply to your Program? Q 15 - How are the applicable Principles addressed in your architecture/program documents? 34
Compliance w/the Do. D IEA Tab A to Appendix E: Do. D IEA Compliance Assessment Table B 1. Use Net. Centric Terminology 2. 3. 2. 1. 1 B 2. Incorporate Applicable Do. D IEA Principles 2. 3. 2. 2. 1 B. Align Architecture Description with the Do. D IEA Use key terms 2. 1. 1. 2. 1 Describe in contained in applicable the: the Do. D IEA - AV-2 Glossary key terms. Integrated across Dictionary. architecture - Related descriptions. taxonomies. - ISP descriptions of the IE. - Identify 2. 1. 1. 2. 2 Describe in applicable Do. D IEA the: IEA Principles. - OV-1 and use in Operational architecture Concept. descriptions to - OV-5 place Operational restrictions or Activity limitations on Model. operations. - Process - Use Models applicable Principles… Q 12 - Identify key terminology from the Do. D IEA used in your architecture/program documents. Q 13 - Which Do. D IEA Principles apply to your Program? Q 14 - How do the Principles apply to your Program? Q 15 - How are the applicable Principles addressed in your architecture/program documents? 34
 Compliance with the Do. D IEA EANCS RA Example Ø Incorporated description of key alignment aspects into RA document – Added section describing RA alignment with JCAs and Do. D IEA Priority Areas – Added text descriptions of how process patterns align with Do. D IEA activities into pattern discussions Ø Filled out Tab A Compliance Matrix for RA Ø Developed e. ISP excerpt for RA – Used “Guidance for Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture in EISP 2. 0” to identify and locate Do. D IEA questions to be answered – Incorporated information and text from RA document – Generated compliance matrix using Xml 2 PDF 2007 application and ISP_Do. D_IEA_Compliance_Table style sheet 35
Compliance with the Do. D IEA EANCS RA Example Ø Incorporated description of key alignment aspects into RA document – Added section describing RA alignment with JCAs and Do. D IEA Priority Areas – Added text descriptions of how process patterns align with Do. D IEA activities into pattern discussions Ø Filled out Tab A Compliance Matrix for RA Ø Developed e. ISP excerpt for RA – Used “Guidance for Do. D Information Enterprise Architecture in EISP 2. 0” to identify and locate Do. D IEA questions to be answered – Incorporated information and text from RA document – Generated compliance matrix using Xml 2 PDF 2007 application and ISP_Do. D_IEA_Compliance_Table style sheet 35
 Initiatives and Projects Ø Reference Architecture Description – Comment Adjudication for ASRG Approval Ø Do. D IEA – Comment Adjudication (v 1. 2) for DCIO Approval – Work on future versions of the Do. D IEA Ø EANCS RA – Delivered to owner; now in FAC/ASRG approval process Ø Document Process for Developing RA – Describe the process used to develop the EANCS RA Ø FEA BRM Extension – Extend Do. D LOBs for the FEA BRM – Recommended changes provided to OMB FEA for action 36
Initiatives and Projects Ø Reference Architecture Description – Comment Adjudication for ASRG Approval Ø Do. D IEA – Comment Adjudication (v 1. 2) for DCIO Approval – Work on future versions of the Do. D IEA Ø EANCS RA – Delivered to owner; now in FAC/ASRG approval process Ø Document Process for Developing RA – Describe the process used to develop the EANCS RA Ø FEA BRM Extension – Extend Do. D LOBs for the FEA BRM – Recommended changes provided to OMB FEA for action 36
 Do. D IEA Site: http: //cio-nii. defense. gov/sites/diea/ Questions? 37
Do. D IEA Site: http: //cio-nii. defense. gov/sites/diea/ Questions? 37
 BACKUP SLIDES 38
BACKUP SLIDES 38
 Information Enterprise Services and Infrastructure Architecture 3/19/2018
Information Enterprise Services and Infrastructure Architecture 3/19/2018
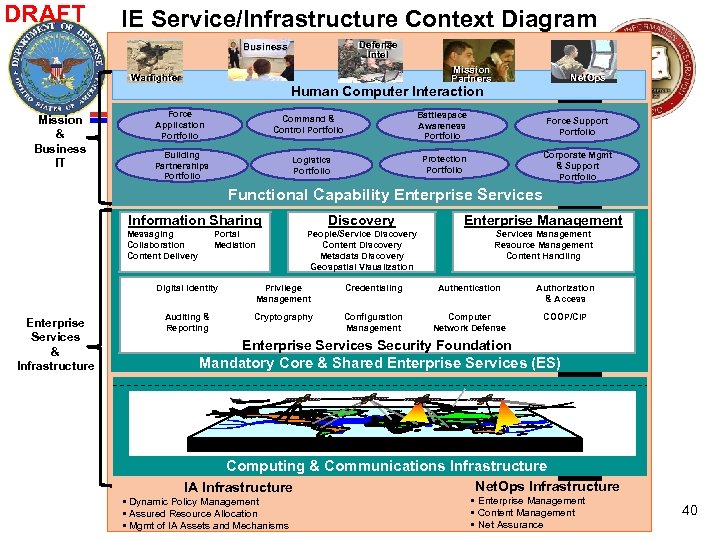 DRAFT IE Service/Infrastructure Context Diagram Defense Intel Business Mission Partners Warfighter Mission & Business IT Net. Ops Human Computer Interaction Force Application Portfolio Battlespace Awareness Portfolio Building Partnerships Portfolio Logistics Portfolio Force Support Portfolio Protection Portfolio Command & Control Portfolio Corporate Mgmt & Support Portfolio Functional Capability Enterprise Services Information Sharing Messaging Collaboration Content Delivery Discovery Enterprise Management People/Service Discovery Content Discovery Metadata Discovery Geospatial Visualization Portal Mediation Services Management Resource Management Content Handling Digital Identity Enterprise Services & Infrastructure Privilege Management Credentialing Authentication Authorization & Access Auditing & Reporting Cryptography Configuration Management Computer Network Defense COOP/CIP Enterprise Services Security Foundation Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services (ES) Computing & Communications Infrastructure IA Infrastructure • Dynamic Policy Management • Assured Resource Allocation • Mgmt of IA Assets and Mechanisms Net. Ops Infrastructure • Enterprise Management • Content Management • Net Assurance 40
DRAFT IE Service/Infrastructure Context Diagram Defense Intel Business Mission Partners Warfighter Mission & Business IT Net. Ops Human Computer Interaction Force Application Portfolio Battlespace Awareness Portfolio Building Partnerships Portfolio Logistics Portfolio Force Support Portfolio Protection Portfolio Command & Control Portfolio Corporate Mgmt & Support Portfolio Functional Capability Enterprise Services Information Sharing Messaging Collaboration Content Delivery Discovery Enterprise Management People/Service Discovery Content Discovery Metadata Discovery Geospatial Visualization Portal Mediation Services Management Resource Management Content Handling Digital Identity Enterprise Services & Infrastructure Privilege Management Credentialing Authentication Authorization & Access Auditing & Reporting Cryptography Configuration Management Computer Network Defense COOP/CIP Enterprise Services Security Foundation Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services (ES) Computing & Communications Infrastructure IA Infrastructure • Dynamic Policy Management • Assured Resource Allocation • Mgmt of IA Assets and Mechanisms Net. Ops Infrastructure • Enterprise Management • Content Management • Net Assurance 40
 Use Enterprise Services Framework to Organize and Focus ES Efforts Enterprise Services Security Foundation (ESSF) 41
Use Enterprise Services Framework to Organize and Focus ES Efforts Enterprise Services Security Foundation (ESSF) 41
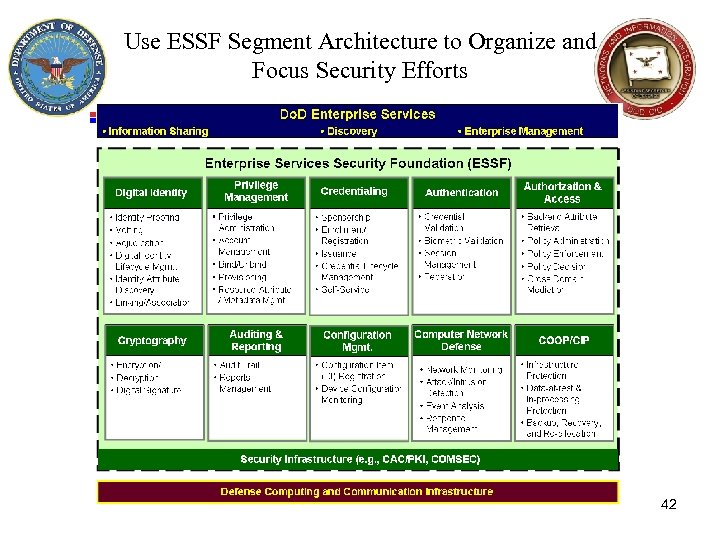 Use ESSF Segment Architecture to Organize and Focus Security Efforts 42
Use ESSF Segment Architecture to Organize and Focus Security Efforts 42
 Development Approach Ø Describe the components of the context diagram Ø Build use cases based on GIG 2. 0 Attributes to establish relationships between its functional components (Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services) – – – Global Authentication, Access Control, and Directory Services Information and Services From The Edge Joint Infrastructure Common Policies and Standards Unity of Command Ø Analyze use cases through identification, sequencing, and prioritization of functional components to develop key or foundational Services first Ø Apply analysis to prioritize and manage: – Reference Architecture Development (Principles, Technical Positions, Patterns) – Sequence and Monitor Initiatives, Projects, and Programs – Identify Issues, Gaps, and Shortfalls 43
Development Approach Ø Describe the components of the context diagram Ø Build use cases based on GIG 2. 0 Attributes to establish relationships between its functional components (Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services) – – – Global Authentication, Access Control, and Directory Services Information and Services From The Edge Joint Infrastructure Common Policies and Standards Unity of Command Ø Analyze use cases through identification, sequencing, and prioritization of functional components to develop key or foundational Services first Ø Apply analysis to prioritize and manage: – Reference Architecture Development (Principles, Technical Positions, Patterns) – Sequence and Monitor Initiatives, Projects, and Programs – Identify Issues, Gaps, and Shortfalls 43
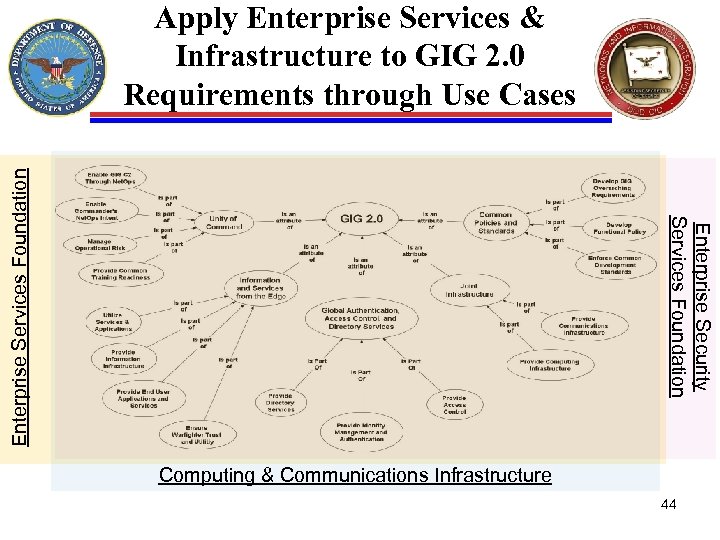 Enterprise Security Services Foundation Enterprise Services Foundation Apply Enterprise Services & Infrastructure to GIG 2. 0 Requirements through Use Cases Computing & Communications Infrastructure 44
Enterprise Security Services Foundation Enterprise Services Foundation Apply Enterprise Services & Infrastructure to GIG 2. 0 Requirements through Use Cases Computing & Communications Infrastructure 44
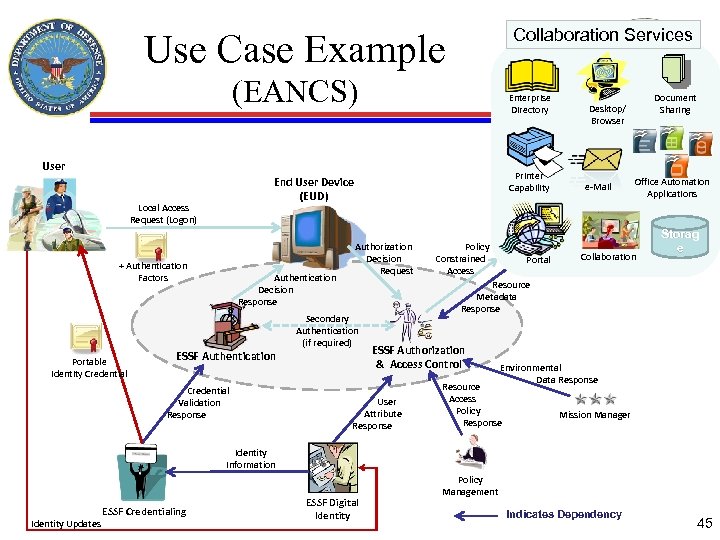 Collaboration Services Use Case Example (EANCS) Enterprise Directory User Local Access Request (Logon) + Authentication Factors Portable Identity Credential Printer Capability End User Device (EUD) Authentication Decision Response ESSF Authentication Credential Validation Response Authorization Decision Request Secondary Authentication (if required) Policy Constrained Access Portal Document Sharing Desktop/ Browser e-Mail Office Automation Applications Collaboration Storag e Resource Metadata Response ESSF Authorization & Access Control User Attribute Response Environmental Data Response Resource Access Policy Response Mission Manager Identity Information Identity Updates ESSF Credentialing ESSF Digital Identity Policy Management Indicates Dependency 45
Collaboration Services Use Case Example (EANCS) Enterprise Directory User Local Access Request (Logon) + Authentication Factors Portable Identity Credential Printer Capability End User Device (EUD) Authentication Decision Response ESSF Authentication Credential Validation Response Authorization Decision Request Secondary Authentication (if required) Policy Constrained Access Portal Document Sharing Desktop/ Browser e-Mail Office Automation Applications Collaboration Storag e Resource Metadata Response ESSF Authorization & Access Control User Attribute Response Environmental Data Response Resource Access Policy Response Mission Manager Identity Information Identity Updates ESSF Credentialing ESSF Digital Identity Policy Management Indicates Dependency 45
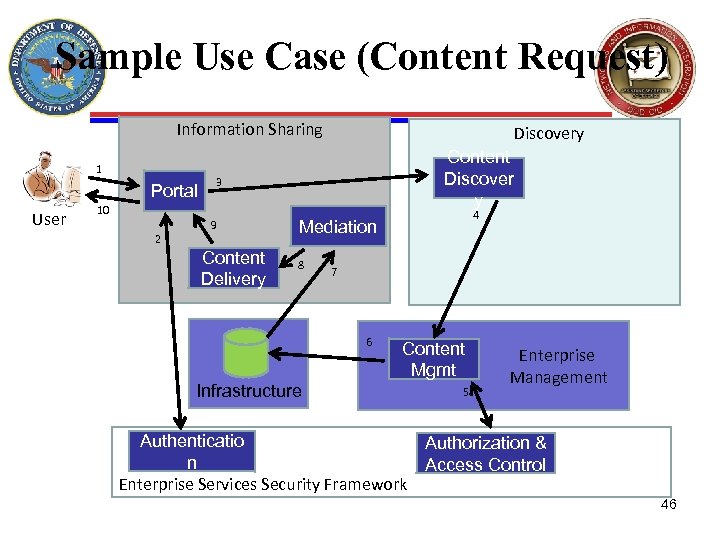 Sample Use Case (Content Request) Information Sharing 1 Portal User Content Discover y 3 10 2 Discovery 9 Content Delivery 4 Mediation 8 7 6 Infrastructure Content Mgmt 5 Enterprise Management Authenticatio Authorization & n Access Control Enterprise Services Security Framework 46
Sample Use Case (Content Request) Information Sharing 1 Portal User Content Discover y 3 10 2 Discovery 9 Content Delivery 4 Mediation 8 7 6 Infrastructure Content Mgmt 5 Enterprise Management Authenticatio Authorization & n Access Control Enterprise Services Security Framework 46
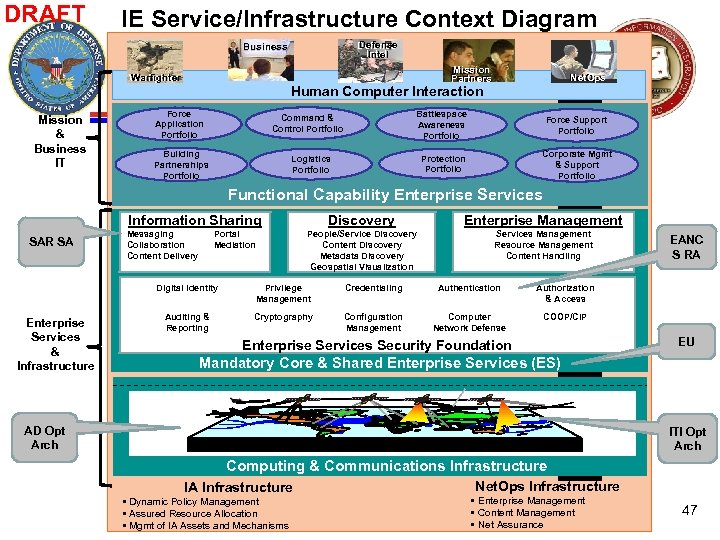 DRAFT IE Service/Infrastructure Context Diagram Defense Intel Business Mission Partners Warfighter Mission & Business IT Net. Ops Human Computer Interaction Force Application Portfolio Battlespace Awareness Portfolio Building Partnerships Portfolio Force Support Portfolio Protection Portfolio Command & Control Portfolio Corporate Mgmt & Support Portfolio Logistics Portfolio Functional Capability Enterprise Services Information Sharing SAR SA Messaging Collaboration Content Delivery Discovery Enterprise Management People/Service Discovery Content Discovery Metadata Discovery Geospatial Visualization Portal Mediation Services Management Resource Management Content Handling Digital Identity Enterprise Services & Infrastructure Privilege Management Credentialing Authentication Authorization & Access Auditing & Reporting Cryptography Configuration Management Computer Network Defense EANC S RA COOP/CIP Enterprise Services Security Foundation EU Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services (ES) AD Opt Arch ITI Opt Arch Computing & Communications Infrastructure IA Infrastructure • Dynamic Policy Management • Assured Resource Allocation • Mgmt of IA Assets and Mechanisms Net. Ops Infrastructure • Enterprise Management • Content Management • Net Assurance 47
DRAFT IE Service/Infrastructure Context Diagram Defense Intel Business Mission Partners Warfighter Mission & Business IT Net. Ops Human Computer Interaction Force Application Portfolio Battlespace Awareness Portfolio Building Partnerships Portfolio Force Support Portfolio Protection Portfolio Command & Control Portfolio Corporate Mgmt & Support Portfolio Logistics Portfolio Functional Capability Enterprise Services Information Sharing SAR SA Messaging Collaboration Content Delivery Discovery Enterprise Management People/Service Discovery Content Discovery Metadata Discovery Geospatial Visualization Portal Mediation Services Management Resource Management Content Handling Digital Identity Enterprise Services & Infrastructure Privilege Management Credentialing Authentication Authorization & Access Auditing & Reporting Cryptography Configuration Management Computer Network Defense EANC S RA COOP/CIP Enterprise Services Security Foundation EU Mandatory Core & Shared Enterprise Services (ES) AD Opt Arch ITI Opt Arch Computing & Communications Infrastructure IA Infrastructure • Dynamic Policy Management • Assured Resource Allocation • Mgmt of IA Assets and Mechanisms Net. Ops Infrastructure • Enterprise Management • Content Management • Net Assurance 47


