952eec3b284b302f2d80b1443d094477.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 2010. 5. Jeong, Hyun-Cheol
2010. 5. Jeong, Hyun-Cheol
 Contents 1 DDo. S Attacks in Korea 2 Countermeasures against DDo. S Attacks in Korea 3 Conclusion 2
Contents 1 DDo. S Attacks in Korea 2 Countermeasures against DDo. S Attacks in Korea 3 Conclusion 2
 1 DDo. S Attacks in Korea • DDo. S Attack Trends • 7. 7 DDo. S Attack and Lessons 3
1 DDo. S Attacks in Korea • DDo. S Attack Trends • 7. 7 DDo. S Attack and Lessons 3
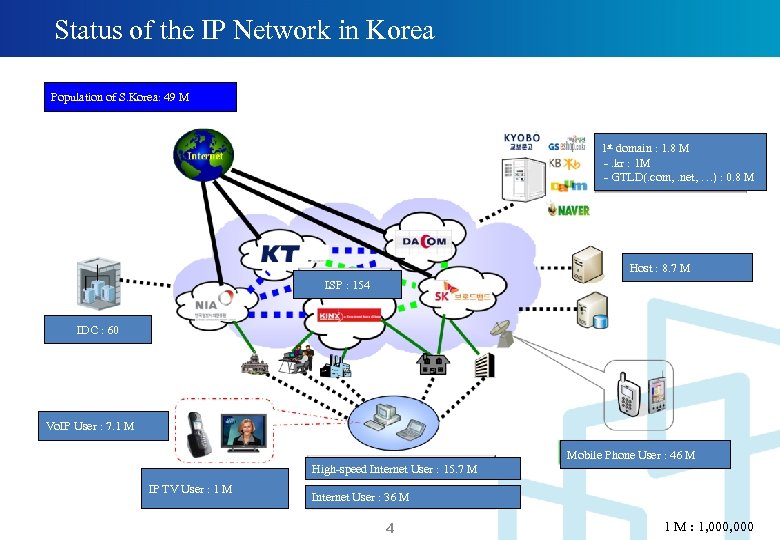 Status of the IP Network in Korea Population of S. Korea: 49 M 1 st domain : 1. 8 M -. kr : 1 M - GTLD(. com, . net, …) : 0. 8 M Host : 8. 7 M ISP : 154 IDC : 60 Vo. IP User : 7. 1 M Mobile Phone User : 46 M High-speed Internet User : 15. 7 M IP TV User : 1 M Internet User : 36 M 4 1 M : 1, 000
Status of the IP Network in Korea Population of S. Korea: 49 M 1 st domain : 1. 8 M -. kr : 1 M - GTLD(. com, . net, …) : 0. 8 M Host : 8. 7 M ISP : 154 IDC : 60 Vo. IP User : 7. 1 M Mobile Phone User : 46 M High-speed Internet User : 15. 7 M IP TV User : 1 M Internet User : 36 M 4 1 M : 1, 000
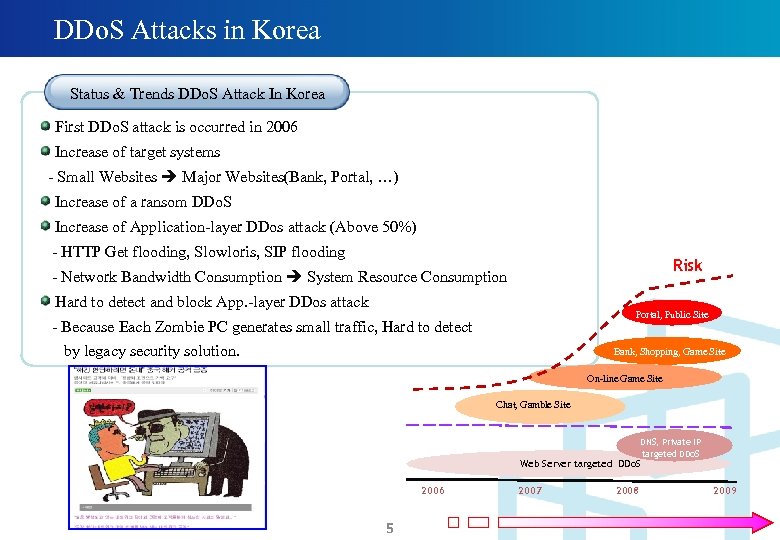 DDo. S Attacks in Korea Status & Trends DDo. S Attack In Korea First DDo. S attack is occurred in 2006 Increase of target systems - Small Websites Major Websites(Bank, Portal, …) Increase of a ransom DDo. S Increase of Application-layer DDos attack (Above 50%) - HTTP Get flooding, Slowloris, SIP flooding Risk - Network Bandwidth Consumption System Resource Consumption Hard to detect and block App. -layer DDos attack Portal, Public Site - Because Each Zombie PC generates small traffic, Hard to detect by legacy security solution. Bank, Shopping, Game Site On-line Game Site Chat, Gamble Site DNS, Private IP targeted DDo. S Web Server targeted DDo. S 2006 5 2007 2008 2009
DDo. S Attacks in Korea Status & Trends DDo. S Attack In Korea First DDo. S attack is occurred in 2006 Increase of target systems - Small Websites Major Websites(Bank, Portal, …) Increase of a ransom DDo. S Increase of Application-layer DDos attack (Above 50%) - HTTP Get flooding, Slowloris, SIP flooding Risk - Network Bandwidth Consumption System Resource Consumption Hard to detect and block App. -layer DDos attack Portal, Public Site - Because Each Zombie PC generates small traffic, Hard to detect by legacy security solution. Bank, Shopping, Game Site On-line Game Site Chat, Gamble Site DNS, Private IP targeted DDo. S Web Server targeted DDo. S 2006 5 2007 2008 2009
 7. 7 DDo. S Attack (1/3) Attack Time : Every 6 p. m. July 6. 2009 ~ July 9. 2009 Attack Targets : 22 Korean sites, 14 U. S sites - Korean sites : the Blue House, National Assembly, major portal & banking sites, … Estimated Damage : 3, 300 ~ 4, 950 million dollars (Src. : Hyundai Research Institute) 1 st Day Attack 6 PM, July 7 After DDo. S Destruct Hard disk 0 AM, July 10 2 nd Day Attack 3 rd Day Attack 6 PM, July 8 6 6 PM, July 9
7. 7 DDo. S Attack (1/3) Attack Time : Every 6 p. m. July 6. 2009 ~ July 9. 2009 Attack Targets : 22 Korean sites, 14 U. S sites - Korean sites : the Blue House, National Assembly, major portal & banking sites, … Estimated Damage : 3, 300 ~ 4, 950 million dollars (Src. : Hyundai Research Institute) 1 st Day Attack 6 PM, July 7 After DDo. S Destruct Hard disk 0 AM, July 10 2 nd Day Attack 3 rd Day Attack 6 PM, July 8 6 6 PM, July 9
 7. 7 DDo. S Attack (2/3) - Characteristics Very Large scale and Organized Attack - Zombies were infected from the famous Korean Web hard site which had been exploited - Lots of Zombie PCs (about 115, 000) were used in attack - Lots of Servers(about 400) were used in control the zombies Premeditated and Intelligent Attack - Attack started 6 PM that was coded in Malware(Logic Bomb) - Zombie’s Hard disk were destructed after DDo. S erase the attack evidence We could not know who the attacker were and why their intention were 7
7. 7 DDo. S Attack (2/3) - Characteristics Very Large scale and Organized Attack - Zombies were infected from the famous Korean Web hard site which had been exploited - Lots of Zombie PCs (about 115, 000) were used in attack - Lots of Servers(about 400) were used in control the zombies Premeditated and Intelligent Attack - Attack started 6 PM that was coded in Malware(Logic Bomb) - Zombie’s Hard disk were destructed after DDo. S erase the attack evidence We could not know who the attacker were and why their intention were 7
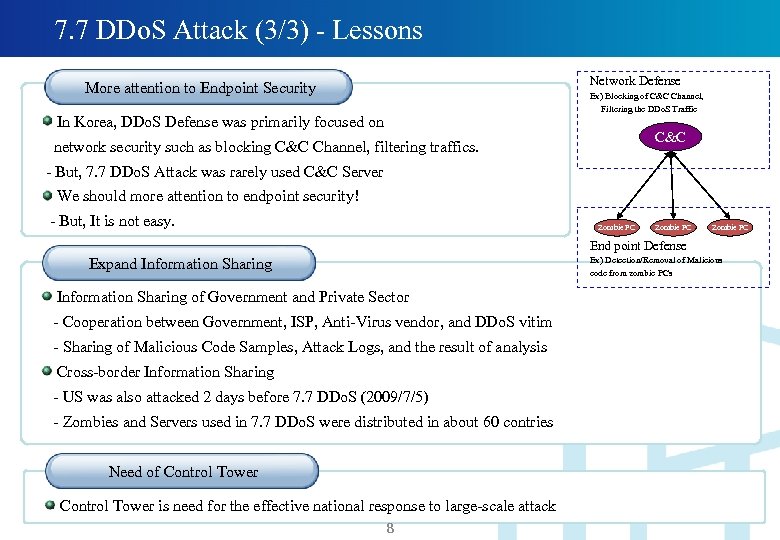 7. 7 DDo. S Attack (3/3) - Lessons Network Defense More attention to Endpoint Security Ex) Blocking of C&C Channel, Filtering the DDo. S Traffic In Korea, DDo. S Defense was primarily focused on C&C network security such as blocking C&C Channel, filtering traffics. - But, 7. 7 DDo. S Attack was rarely used C&C Server We should more attention to endpoint security! - But, It is not easy. Zombie PC End point Defense Expand Information Sharing Ex) Detection/Removal of Malicious code from zombie PCs Information Sharing of Government and Private Sector - Cooperation between Government, ISP, Anti-Virus vendor, and DDo. S vitim - Sharing of Malicious Code Samples, Attack Logs, and the result of analysis Cross-border Information Sharing - US was also attacked 2 days before 7. 7 DDo. S (2009/7/5) - Zombies and Servers used in 7. 7 DDo. S were distributed in about 60 contries Need of Control Tower 8 Control Tower is need for the effective national response to large-scale attack 8
7. 7 DDo. S Attack (3/3) - Lessons Network Defense More attention to Endpoint Security Ex) Blocking of C&C Channel, Filtering the DDo. S Traffic In Korea, DDo. S Defense was primarily focused on C&C network security such as blocking C&C Channel, filtering traffics. - But, 7. 7 DDo. S Attack was rarely used C&C Server We should more attention to endpoint security! - But, It is not easy. Zombie PC End point Defense Expand Information Sharing Ex) Detection/Removal of Malicious code from zombie PCs Information Sharing of Government and Private Sector - Cooperation between Government, ISP, Anti-Virus vendor, and DDo. S vitim - Sharing of Malicious Code Samples, Attack Logs, and the result of analysis Cross-border Information Sharing - US was also attacked 2 days before 7. 7 DDo. S (2009/7/5) - Zombies and Servers used in 7. 7 DDo. S were distributed in about 60 contries Need of Control Tower 8 Control Tower is need for the effective national response to large-scale attack 8
 2 Countermeasures against DDo. S Attacks in Korea • Operation of DNS Sinkhole Server • Improvement of Legal Framework • Development of Technologies 9
2 Countermeasures against DDo. S Attacks in Korea • Operation of DNS Sinkhole Server • Improvement of Legal Framework • Development of Technologies 9
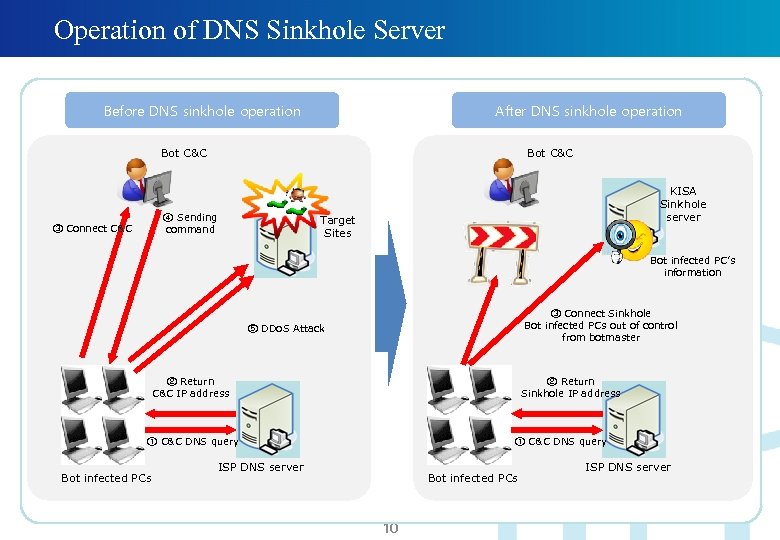 Operation of DNS Sinkhole Server Before DNS sinkhole operation After DNS sinkhole operation Bot C&C ④ Sending command ③ Connect C&C KISA Sinkhole server Target Sites Bot infected PC’s information ③ Connect Sinkhole Bot infected PCs out of control from botmaster ⑤ DDo. S Attack ② Return C&C IP address ② Return Sinkhole IP address ① C&C DNS query Bot infected PCs ① C&C DNS query ISP DNS server Bot infected PCs 10 ISP DNS server
Operation of DNS Sinkhole Server Before DNS sinkhole operation After DNS sinkhole operation Bot C&C ④ Sending command ③ Connect C&C KISA Sinkhole server Target Sites Bot infected PC’s information ③ Connect Sinkhole Bot infected PCs out of control from botmaster ⑤ DDo. S Attack ② Return C&C IP address ② Return Sinkhole IP address ① C&C DNS query Bot infected PCs ① C&C DNS query ISP DNS server Bot infected PCs 10 ISP DNS server
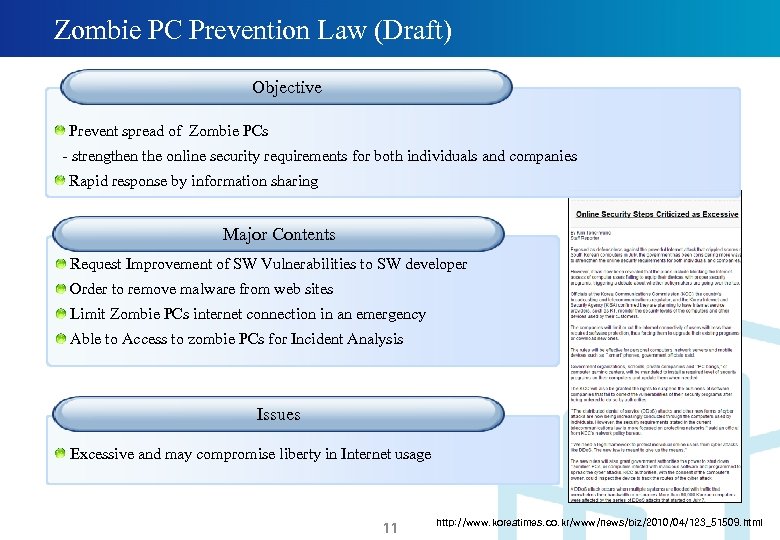 Zombie PC Prevention Law (Draft) Objective Prevent spread of Zombie PCs - strengthen the online security requirements for both individuals and companies Rapid response by information sharing Major Contents Request Improvement of SW Vulnerabilities to SW developer Order to remove malware from web sites Limit Zombie PCs internet connection in an emergency Able to Access to zombie PCs for Incident Analysis Issues Excessive and may compromise liberty in Internet usage 11 http: //www. koreatimes. co. kr/www/news/biz/2010/04/123_51509. html
Zombie PC Prevention Law (Draft) Objective Prevent spread of Zombie PCs - strengthen the online security requirements for both individuals and companies Rapid response by information sharing Major Contents Request Improvement of SW Vulnerabilities to SW developer Order to remove malware from web sites Limit Zombie PCs internet connection in an emergency Able to Access to zombie PCs for Incident Analysis Issues Excessive and may compromise liberty in Internet usage 11 http: //www. koreatimes. co. kr/www/news/biz/2010/04/123_51509. html
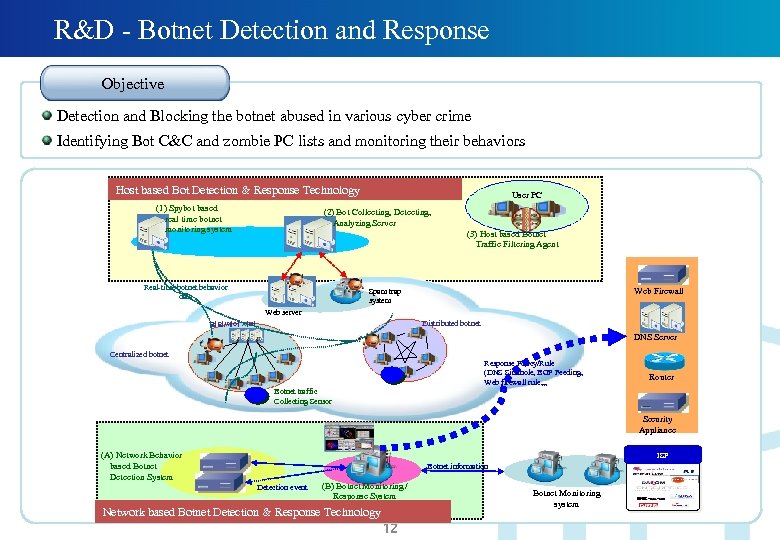 R&D - Botnet Detection and Response Objective Detection and Blocking the botnet abused in various cyber crime Identifying Bot C&C and zombie PC lists and monitoring their behaviors Host based Bot Detection & Response Technology (1) Spybot based real time botnet monitoring system User PC (2) Bot Collecting, Detecting, Analyzing Server (3) Host based Botnet Traffic Filtering Agent Real-time botnet behavior data Web Firewall Spam trap system Web server Distributed botnet 명령/제어 서버 DNS Server Centralized botnet Response Policy/Rule (DNS Sinkhole, BGP Feeding, Web firewall rule, , , Router Botnet traffic Collecting Sensor Security Appliance (A) Network Behavior based Botnet Detection System ISP Botnet information Detection event (B) Botnet Monitoring / Response System Network based Botnet Detection & Response Technology 12 Botnet Monitoring system
R&D - Botnet Detection and Response Objective Detection and Blocking the botnet abused in various cyber crime Identifying Bot C&C and zombie PC lists and monitoring their behaviors Host based Bot Detection & Response Technology (1) Spybot based real time botnet monitoring system User PC (2) Bot Collecting, Detecting, Analyzing Server (3) Host based Botnet Traffic Filtering Agent Real-time botnet behavior data Web Firewall Spam trap system Web server Distributed botnet 명령/제어 서버 DNS Server Centralized botnet Response Policy/Rule (DNS Sinkhole, BGP Feeding, Web firewall rule, , , Router Botnet traffic Collecting Sensor Security Appliance (A) Network Behavior based Botnet Detection System ISP Botnet information Detection event (B) Botnet Monitoring / Response System Network based Botnet Detection & Response Technology 12 Botnet Monitoring system
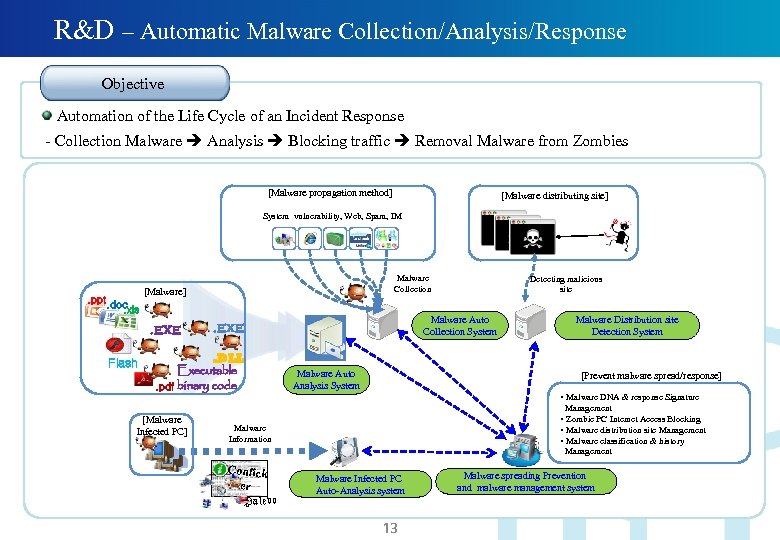 R&D – Automatic Malware Collection/Analysis/Response Objective Automation of the Life Cycle of an Incident Response - Collection Malware Analysis Blocking traffic Removal Malware from Zombies [Malware propagation method] [Malware distributing site] System vulnerability, Web, Spam, IM . ppt Malware Collection [Malware]. doc. xls . EXE Flash Malware Auto Collection System . EXE . DLL Executable. pdf binary code Detecting malicious site Malware Auto Analysis System Malware Distribution site Detection System [Prevent malware spread/response] • Malware DNA & response Signature Management [Malware Infected PC] • Zombie PC Internet Access Blocking • Malware distribution site Management • Malware classification & history Malware Information Management Confick er Palevo Malware Infected PC Auto-Analysis system 13 Malware spreading Prevention and malware management system
R&D – Automatic Malware Collection/Analysis/Response Objective Automation of the Life Cycle of an Incident Response - Collection Malware Analysis Blocking traffic Removal Malware from Zombies [Malware propagation method] [Malware distributing site] System vulnerability, Web, Spam, IM . ppt Malware Collection [Malware]. doc. xls . EXE Flash Malware Auto Collection System . EXE . DLL Executable. pdf binary code Detecting malicious site Malware Auto Analysis System Malware Distribution site Detection System [Prevent malware spread/response] • Malware DNA & response Signature Management [Malware Infected PC] • Zombie PC Internet Access Blocking • Malware distribution site Management • Malware classification & history Malware Information Management Confick er Palevo Malware Infected PC Auto-Analysis system 13 Malware spreading Prevention and malware management system
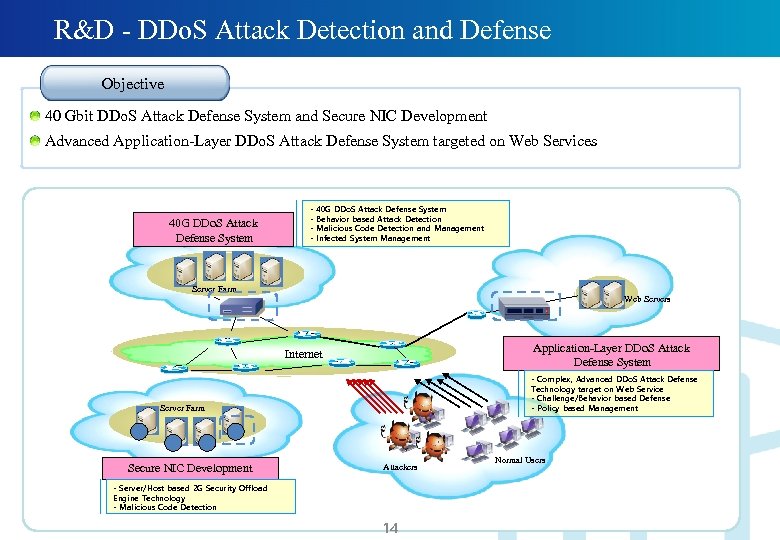 R&D - DDo. S Attack Detection and Defense Objective 40 Gbit DDo. S Attack Defense System and Secure NIC Development Advanced Application-Layer DDo. S Attack Defense System targeted on Web Services 40 G DDo. S Attack Defense System - 40 G DDo. S Attack Defense System Behavior based Attack Detection Malicious Code Detection and Management Infected System Management Server Farm Web Servers Application-Layer DDo. S Attack Defense System Internet - Complex, Advanced DDo. S Attack Defense Technology target on Web Service - Challenge/Behavior based Defense - Policy based Management Server Farm Secure NIC Development Attackers - Server/Host based 2 G Security Offload Engine Technology - Malicious Code Detection 14 Normal Users
R&D - DDo. S Attack Detection and Defense Objective 40 Gbit DDo. S Attack Defense System and Secure NIC Development Advanced Application-Layer DDo. S Attack Defense System targeted on Web Services 40 G DDo. S Attack Defense System - 40 G DDo. S Attack Defense System Behavior based Attack Detection Malicious Code Detection and Management Infected System Management Server Farm Web Servers Application-Layer DDo. S Attack Defense System Internet - Complex, Advanced DDo. S Attack Defense Technology target on Web Service - Challenge/Behavior based Defense - Policy based Management Server Farm Secure NIC Development Attackers - Server/Host based 2 G Security Offload Engine Technology - Malicious Code Detection 14 Normal Users
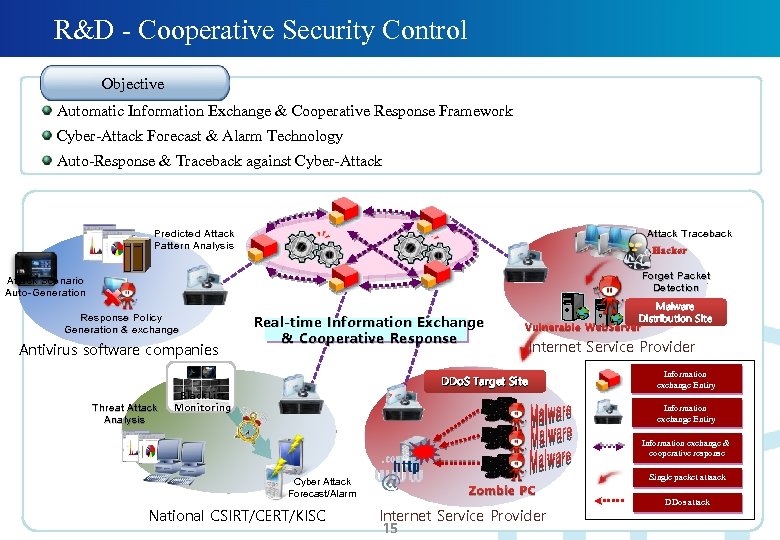 R&D - Cooperative Security Control Objective Automatic Information Exchange & Cooperative Response Framework Cyber-Attack Forecast & Alarm Technology Auto-Response & Traceback against Cyber-Attack Traceback Predicted Attack Pattern Analysis Hacker Forget Packet Detection Attack Scenario Auto-Generation Response Policy Generation & exchange Antivirus software companies Threat Attack Analysis Real-time Information Exchange & Cooperative Response Malware Distribution Site Vulnerable Web. Server Internet Service Provider DDo. S Target Site Black. List Monitoring Information exchange Entiry Information exchange & cooperative response Single packet attaack Cyber Attack Forecast/Alarm National CSIRT/CERT/KISC Zombie PC Internet Service Provider 15 DDos attack
R&D - Cooperative Security Control Objective Automatic Information Exchange & Cooperative Response Framework Cyber-Attack Forecast & Alarm Technology Auto-Response & Traceback against Cyber-Attack Traceback Predicted Attack Pattern Analysis Hacker Forget Packet Detection Attack Scenario Auto-Generation Response Policy Generation & exchange Antivirus software companies Threat Attack Analysis Real-time Information Exchange & Cooperative Response Malware Distribution Site Vulnerable Web. Server Internet Service Provider DDo. S Target Site Black. List Monitoring Information exchange Entiry Information exchange & cooperative response Single packet attaack Cyber Attack Forecast/Alarm National CSIRT/CERT/KISC Zombie PC Internet Service Provider 15 DDos attack
 Conclusion Information Sharing is the most important factor for success of effective prevention and response the incident. - For this purpose, We are improving the legal system and developing technology in Korea International Cooperation Cyber attacks occur in cross-border It is need that the consensus for - monitoring, keeping logs, information sharing, and cooperation against cross-border incidents Awareness It is the most difficult thing, but it is the most important for end-point security. We should improve not only the legal framework but also awareness. 16
Conclusion Information Sharing is the most important factor for success of effective prevention and response the incident. - For this purpose, We are improving the legal system and developing technology in Korea International Cooperation Cyber attacks occur in cross-border It is need that the consensus for - monitoring, keeping logs, information sharing, and cooperation against cross-border incidents Awareness It is the most difficult thing, but it is the most important for end-point security. We should improve not only the legal framework but also awareness. 16
 Thank you
Thank you


