269a9c9901ebdbf70348584304e1d3b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 2008 GT STRUDL Users Group Meeting & Training Seminar Soil-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Composite Structure on a Backfill Hilltop WSRC-STI-2008 -00269 Rev 0 Lisa Anderson, Bechtel National, Inc. Jay Amin, Washington Savannah River Co. June 25, 2008 6/25/2008 1
2008 GT STRUDL Users Group Meeting & Training Seminar Soil-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Composite Structure on a Backfill Hilltop WSRC-STI-2008 -00269 Rev 0 Lisa Anderson, Bechtel National, Inc. Jay Amin, Washington Savannah River Co. June 25, 2008 6/25/2008 1
 Overview Scope of Analysis Building Description Analysis Conclusions 6/25/2008 2
Overview Scope of Analysis Building Description Analysis Conclusions 6/25/2008 2
 Scope of Analysis 6/25/2008 3
Scope of Analysis 6/25/2008 3
 Scope of Analysis Assess feasibility of adding new process to this complex n n n 6/25/2008 Building complex constructed in 1980’s Not designed to resist current seismic loads or wind loads Lateral load path is not well defined 4
Scope of Analysis Assess feasibility of adding new process to this complex n n n 6/25/2008 Building complex constructed in 1980’s Not designed to resist current seismic loads or wind loads Lateral load path is not well defined 4
 Scope of Analysis Evaluate the structures for n n n Normal operating dead and live loads PC-3 seismic loads* PC-2 wind loads* administrative controls will stop process prior to tornado events n II/I concerns* *DOE Standard 1020 6/25/2008 5
Scope of Analysis Evaluate the structures for n n n Normal operating dead and live loads PC-3 seismic loads* PC-2 wind loads* administrative controls will stop process prior to tornado events n II/I concerns* *DOE Standard 1020 6/25/2008 5
 Building Description 6/25/2008 6
Building Description 6/25/2008 6
 Building Complex Split up for analysis n n n 6/25/2008 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room (Concrete) Enclosure Building (Steel) Benzene Stripper Building (Composite) 7
Building Complex Split up for analysis n n n 6/25/2008 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room (Concrete) Enclosure Building (Steel) Benzene Stripper Building (Composite) 7
 Building Complex 6/25/2008 8
Building Complex 6/25/2008 8
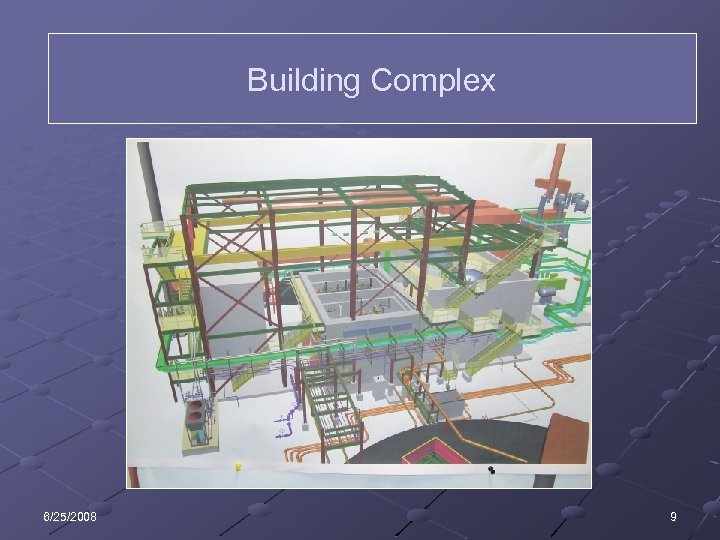 Building Complex 6/25/2008 9
Building Complex 6/25/2008 9
 Analysis 6/25/2008 10
Analysis 6/25/2008 10
 Finite Element Models Create finite element models in GT STRUDL using a model builder program n Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Convert Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room to SASSI House Model STRUSASSI n n 6/25/2008 Enclosure Building Benzene Stripper Building 11
Finite Element Models Create finite element models in GT STRUDL using a model builder program n Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Convert Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room to SASSI House Model STRUSASSI n n 6/25/2008 Enclosure Building Benzene Stripper Building 11
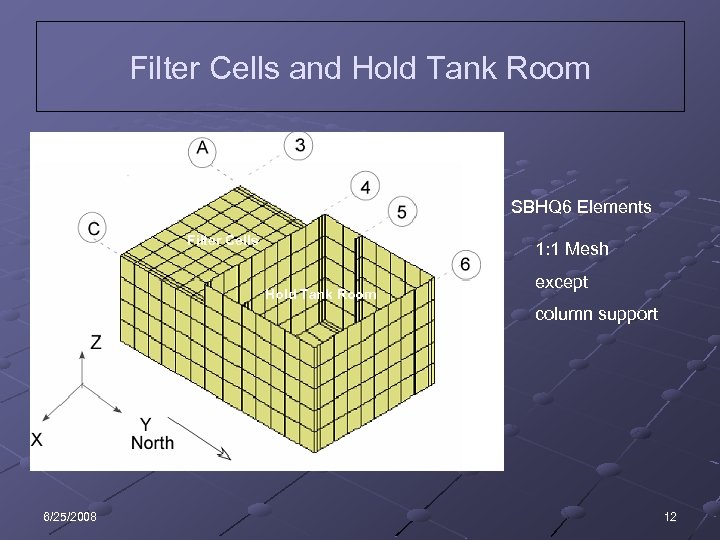 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room SBHQ 6 Elements Filter Cells 1: 1 Mesh Hold Tank Room except column support 6/25/2008 12
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room SBHQ 6 Elements Filter Cells 1: 1 Mesh Hold Tank Room except column support 6/25/2008 12
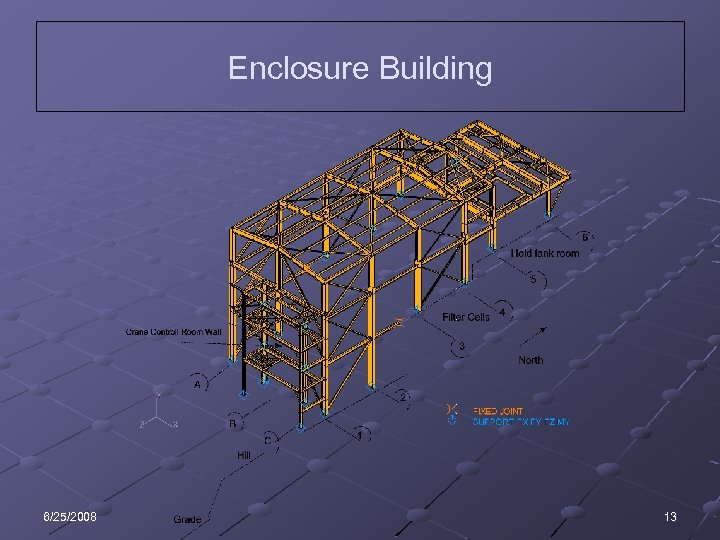 Enclosure Building 6/25/2008 13
Enclosure Building 6/25/2008 13
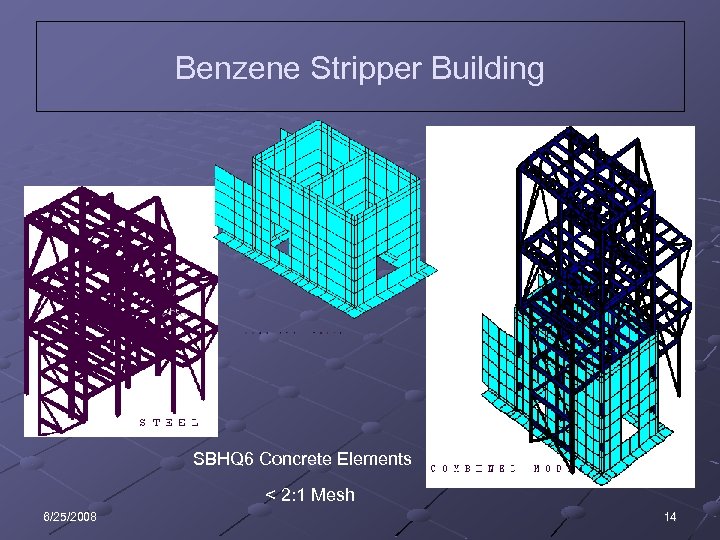 Benzene Stripper Building SBHQ 6 Concrete Elements < 2: 1 Mesh 6/25/2008 14
Benzene Stripper Building SBHQ 6 Concrete Elements < 2: 1 Mesh 6/25/2008 14
 General Site Analysis Generation of time histories Amplified for hilltop Free-field soil analysis 6/25/2008 15
General Site Analysis Generation of time histories Amplified for hilltop Free-field soil analysis 6/25/2008 15
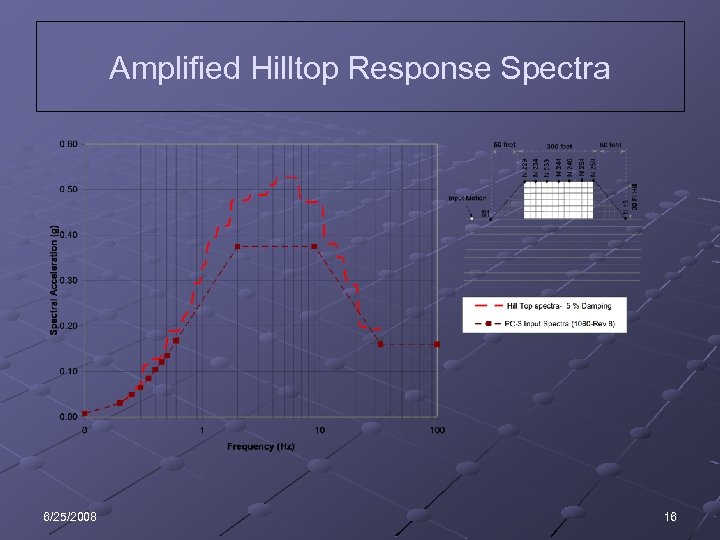 Amplified Hilltop Response Spectra 6/25/2008 16
Amplified Hilltop Response Spectra 6/25/2008 16
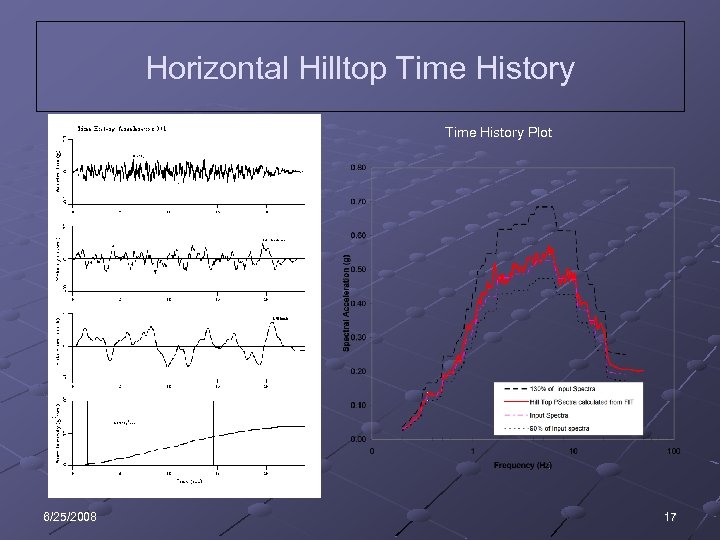 Horizontal Hilltop Time History Plot 6/25/2008 17
Horizontal Hilltop Time History Plot 6/25/2008 17
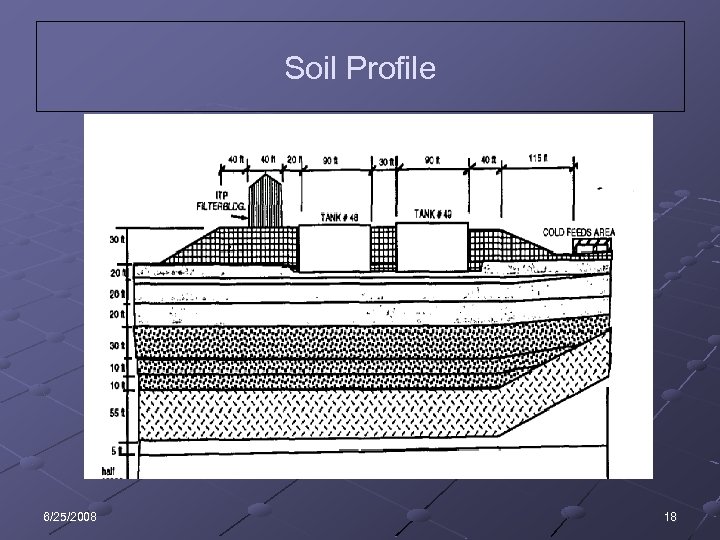 Soil Profile 6/25/2008 18
Soil Profile 6/25/2008 18
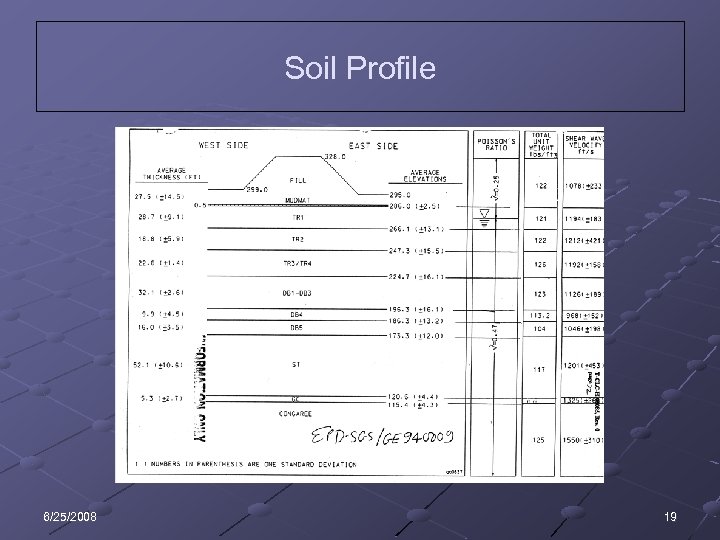 Soil Profile 6/25/2008 19
Soil Profile 6/25/2008 19
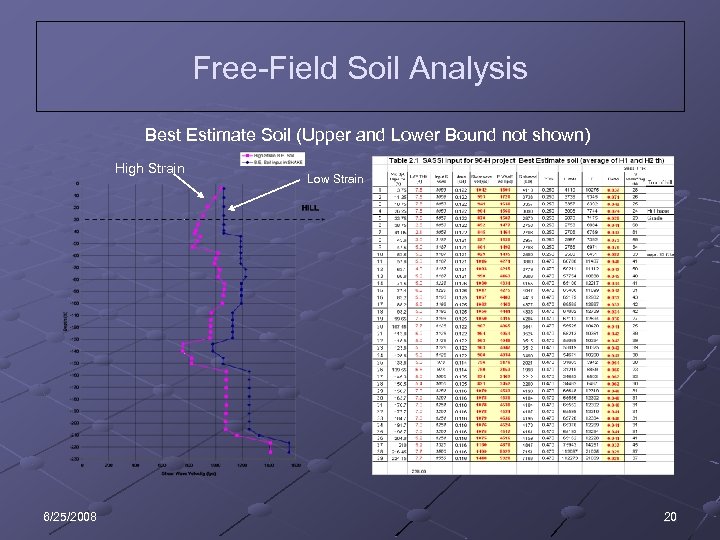 Free-Field Soil Analysis Best Estimate Soil (Upper and Lower Bound not shown) High Strain 6/25/2008 Low Strain 20
Free-Field Soil Analysis Best Estimate Soil (Upper and Lower Bound not shown) High Strain 6/25/2008 Low Strain 20
 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Analysis Perform Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) on the Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room SASSI model n n 6/25/2008 Obtain response at connection points of Enclosure Building Apply response to FEM of Enclosure Building and Benzene Stripper Building 21
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Analysis Perform Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) on the Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room SASSI model n n 6/25/2008 Obtain response at connection points of Enclosure Building Apply response to FEM of Enclosure Building and Benzene Stripper Building 21
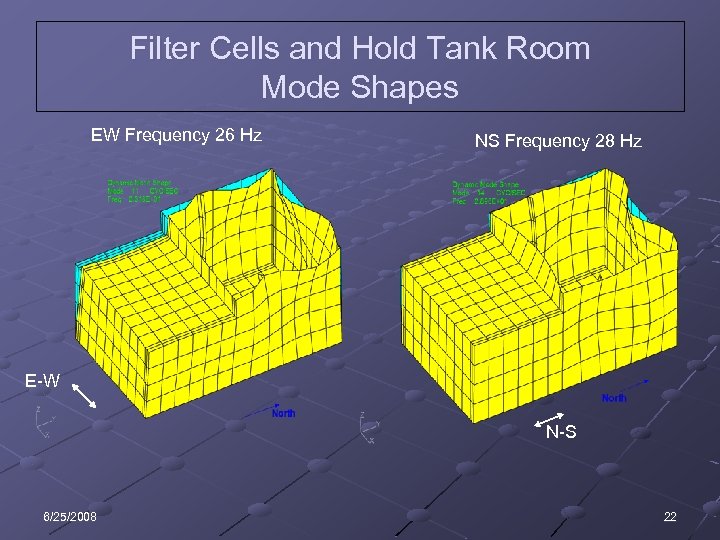 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Mode Shapes EW Frequency 26 Hz NS Frequency 28 Hz E-W N-S 6/25/2008 22
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Mode Shapes EW Frequency 26 Hz NS Frequency 28 Hz E-W N-S 6/25/2008 22
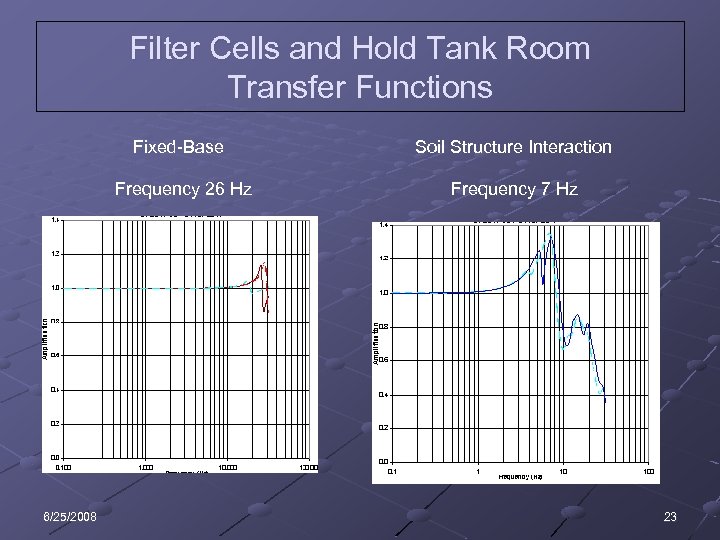 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Transfer Functions Fixed-Base Frequency 26 Hz 6/25/2008 Soil Structure Interaction Frequency 7 Hz 23
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Transfer Functions Fixed-Base Frequency 26 Hz 6/25/2008 Soil Structure Interaction Frequency 7 Hz 23
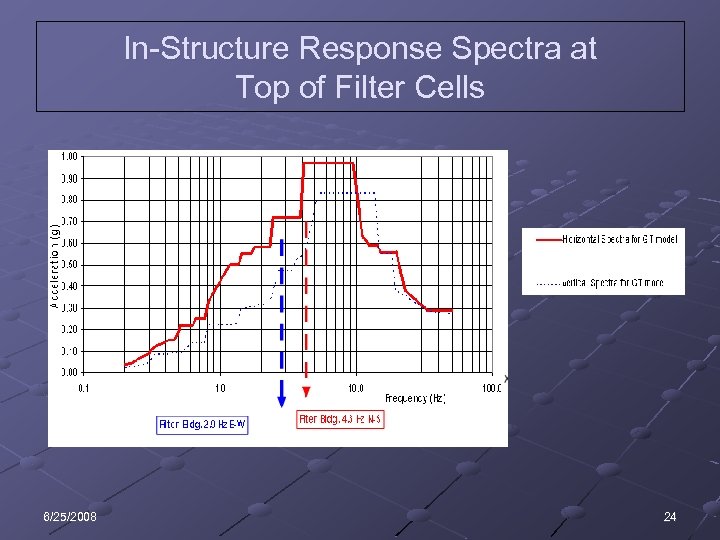 In-Structure Response Spectra at Top of Filter Cells 6/25/2008 24
In-Structure Response Spectra at Top of Filter Cells 6/25/2008 24
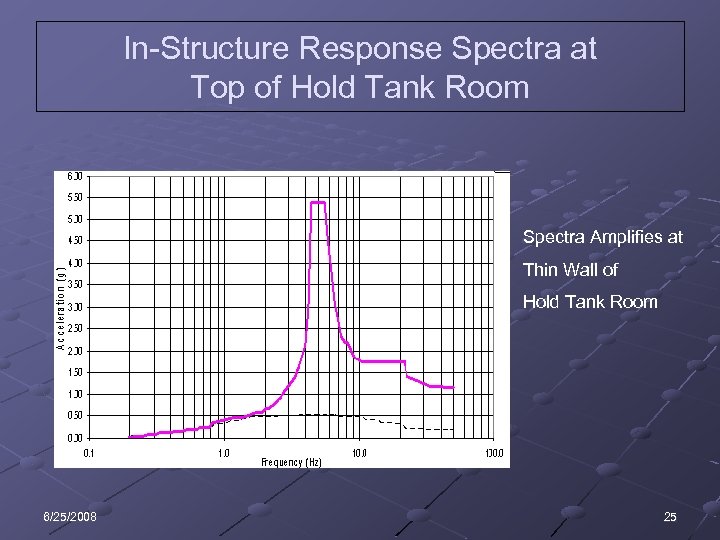 In-Structure Response Spectra at Top of Hold Tank Room Spectra Amplifies at Thin Wall of Hold Tank Room 6/25/2008 25
In-Structure Response Spectra at Top of Hold Tank Room Spectra Amplifies at Thin Wall of Hold Tank Room 6/25/2008 25
 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Analysis Perform SSI on the House model n Obtain zero-period accelerations at each node Apply as equivalent static loads in GT STRUDL Run GT STRUDL stiffness analysis n n Apply section cuts to obtain demands Compute capacities based on existing conditions Shear wall demand to capacity spreadsheet macro n 6/25/2008 Report demand to capacity ratios 26
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Analysis Perform SSI on the House model n Obtain zero-period accelerations at each node Apply as equivalent static loads in GT STRUDL Run GT STRUDL stiffness analysis n n Apply section cuts to obtain demands Compute capacities based on existing conditions Shear wall demand to capacity spreadsheet macro n 6/25/2008 Report demand to capacity ratios 26
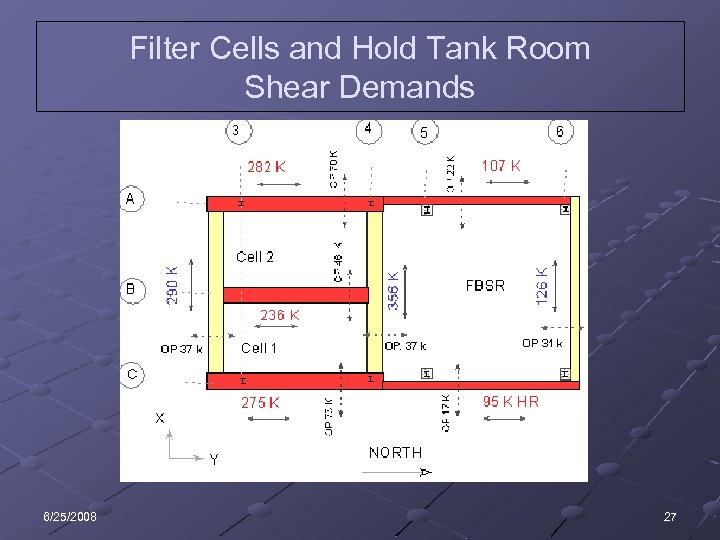 Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Shear Demands 6/25/2008 27
Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Shear Demands 6/25/2008 27
 Enclosure Building Analysis Run GT STRUDL response spectra analysis n n 6/25/2008 Using the soil-structure interaction input motion Check ASD 9 code Check ASCE 7 -05 wind loads Report demand to capacity ratios 28
Enclosure Building Analysis Run GT STRUDL response spectra analysis n n 6/25/2008 Using the soil-structure interaction input motion Check ASD 9 code Check ASCE 7 -05 wind loads Report demand to capacity ratios 28
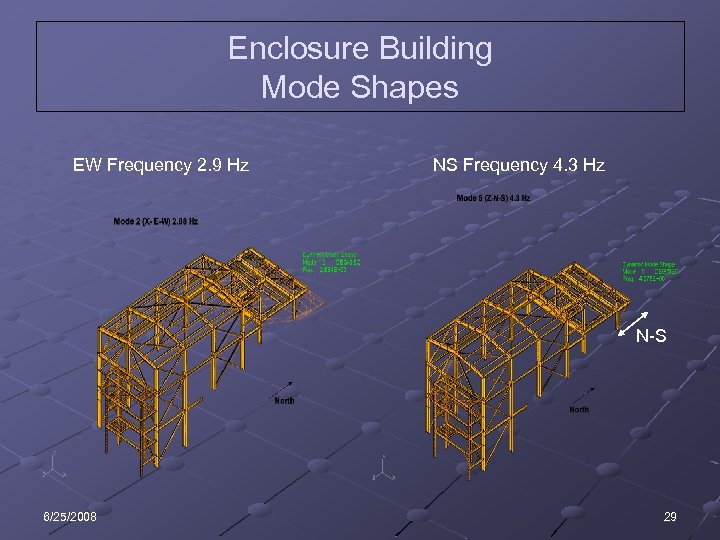 Enclosure Building Mode Shapes EW Frequency 2. 9 Hz NS Frequency 4. 3 Hz N-S 6/25/2008 29
Enclosure Building Mode Shapes EW Frequency 2. 9 Hz NS Frequency 4. 3 Hz N-S 6/25/2008 29
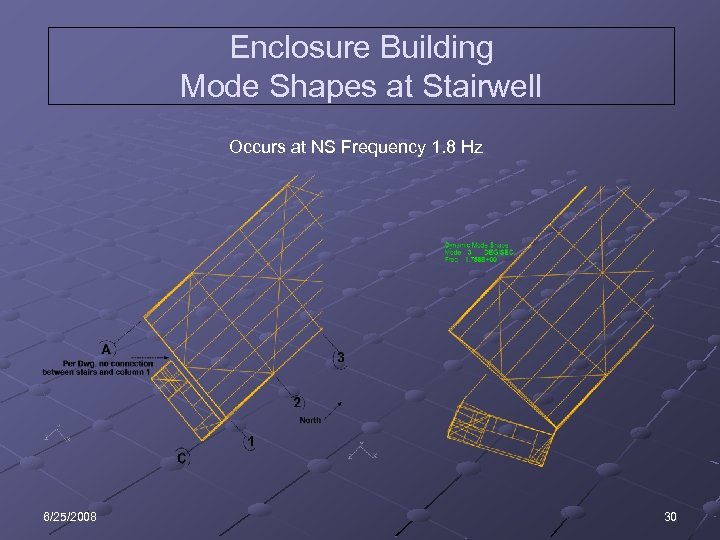 Enclosure Building Mode Shapes at Stairwell Occurs at NS Frequency 1. 8 Hz 6/25/2008 30
Enclosure Building Mode Shapes at Stairwell Occurs at NS Frequency 1. 8 Hz 6/25/2008 30
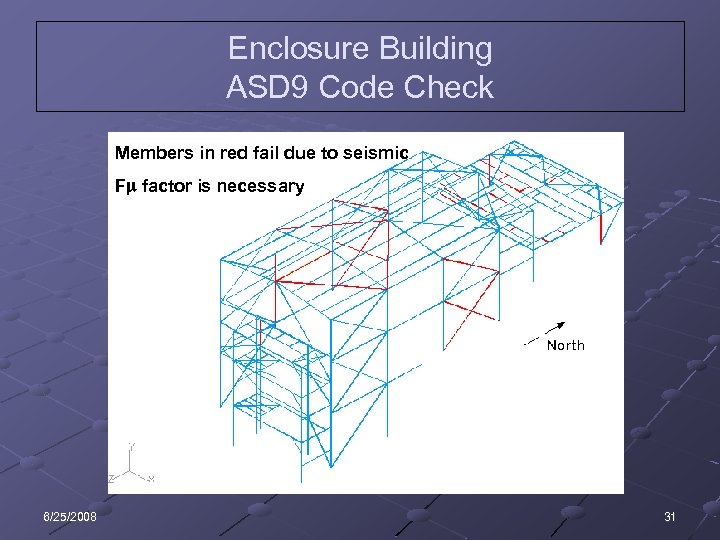 Enclosure Building ASD 9 Code Check Members in red fail due to seismic F factor is necessary 6/25/2008 31
Enclosure Building ASD 9 Code Check Members in red fail due to seismic F factor is necessary 6/25/2008 31
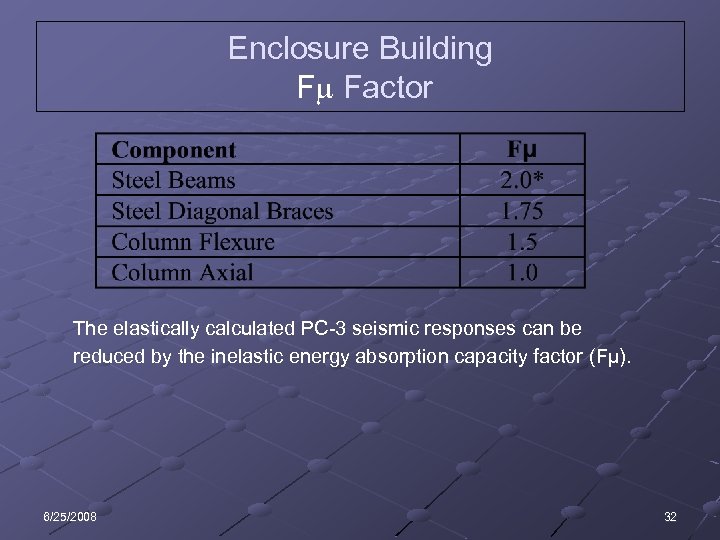 Enclosure Building F Factor The elastically calculated PC-3 seismic responses can be reduced by the inelastic energy absorption capacity factor (Fμ). 6/25/2008 32
Enclosure Building F Factor The elastically calculated PC-3 seismic responses can be reduced by the inelastic energy absorption capacity factor (Fμ). 6/25/2008 32
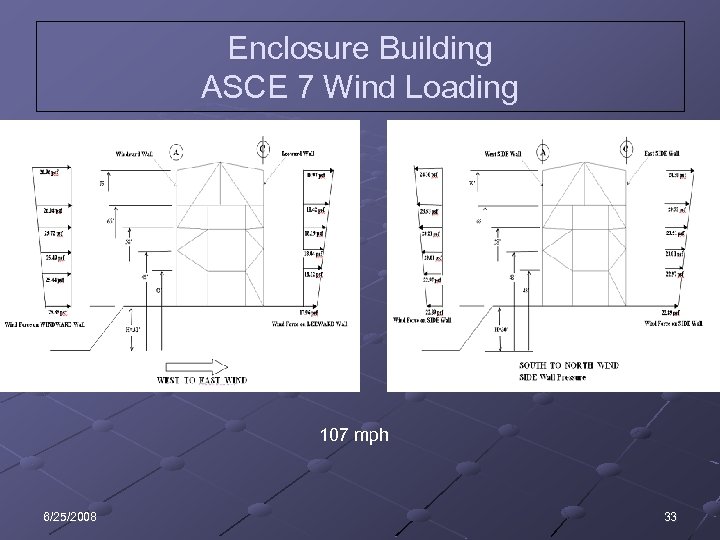 Enclosure Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 107 mph 6/25/2008 33
Enclosure Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 107 mph 6/25/2008 33
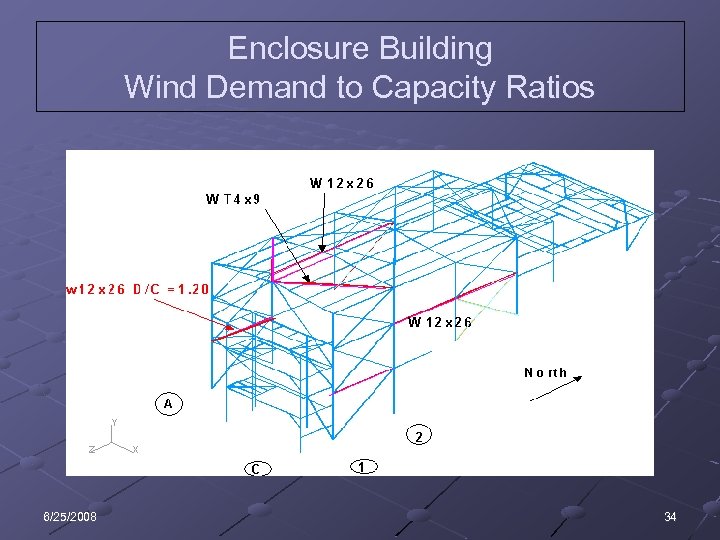 Enclosure Building Wind Demand to Capacity Ratios 6/25/2008 34
Enclosure Building Wind Demand to Capacity Ratios 6/25/2008 34
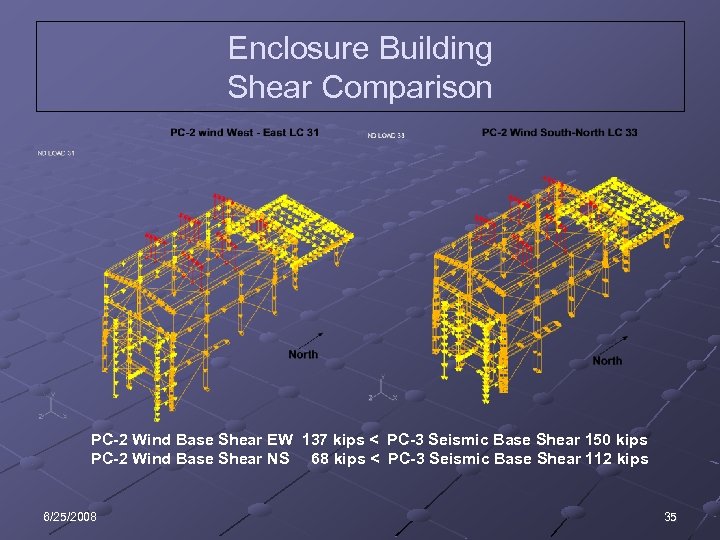 Enclosure Building Shear Comparison PC-2 Wind Base Shear EW 137 kips < PC-3 Seismic Base Shear 150 kips PC-2 Wind Base Shear NS 68 kips < PC-3 Seismic Base Shear 112 kips 6/25/2008 35
Enclosure Building Shear Comparison PC-2 Wind Base Shear EW 137 kips < PC-3 Seismic Base Shear 150 kips PC-2 Wind Base Shear NS 68 kips < PC-3 Seismic Base Shear 112 kips 6/25/2008 35
 Benzene Stripper Building Analysis Run GT STRUDL response spectra analysis n n n Using the soil-structure interaction input motion Including ASCE 7 -05 wind Check ASD 9 code Report demand to capacity ratios Apply section cuts to obtain concrete demands Compute capacities based on existing conditions Shear wall demand to capacity spreadsheet macro n 6/25/2008 Report demand to capacity ratios 36
Benzene Stripper Building Analysis Run GT STRUDL response spectra analysis n n n Using the soil-structure interaction input motion Including ASCE 7 -05 wind Check ASD 9 code Report demand to capacity ratios Apply section cuts to obtain concrete demands Compute capacities based on existing conditions Shear wall demand to capacity spreadsheet macro n 6/25/2008 Report demand to capacity ratios 36
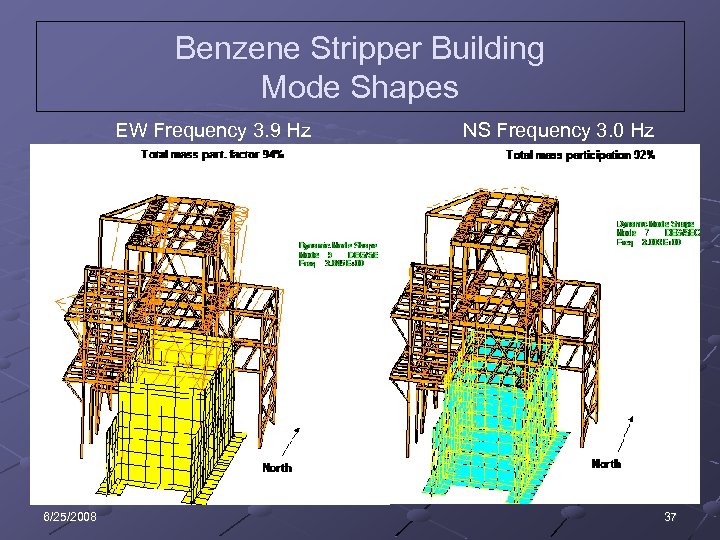 Benzene Stripper Building Mode Shapes EW Frequency 3. 9 Hz 6/25/2008 NS Frequency 3. 0 Hz 37
Benzene Stripper Building Mode Shapes EW Frequency 3. 9 Hz 6/25/2008 NS Frequency 3. 0 Hz 37
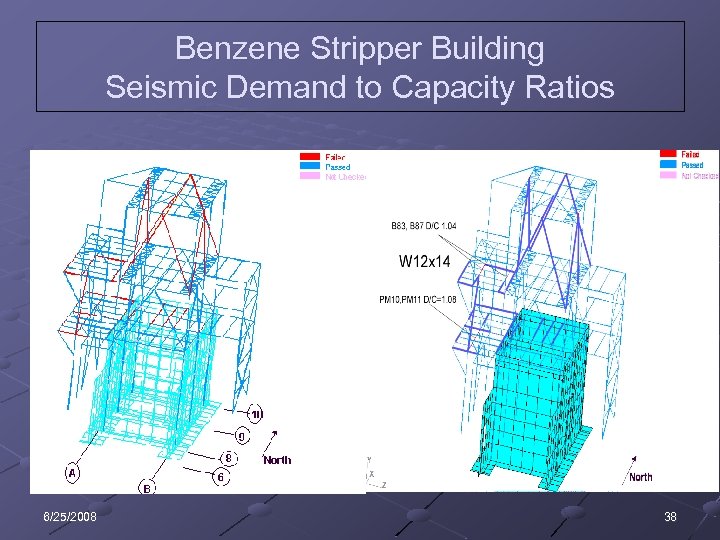 Benzene Stripper Building Seismic Demand to Capacity Ratios 6/25/2008 38
Benzene Stripper Building Seismic Demand to Capacity Ratios 6/25/2008 38
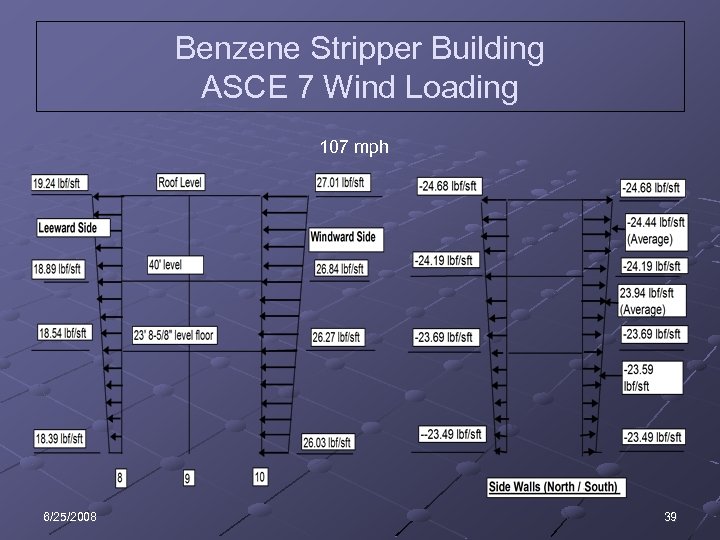 Benzene Stripper Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 107 mph 6/25/2008 39
Benzene Stripper Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 107 mph 6/25/2008 39
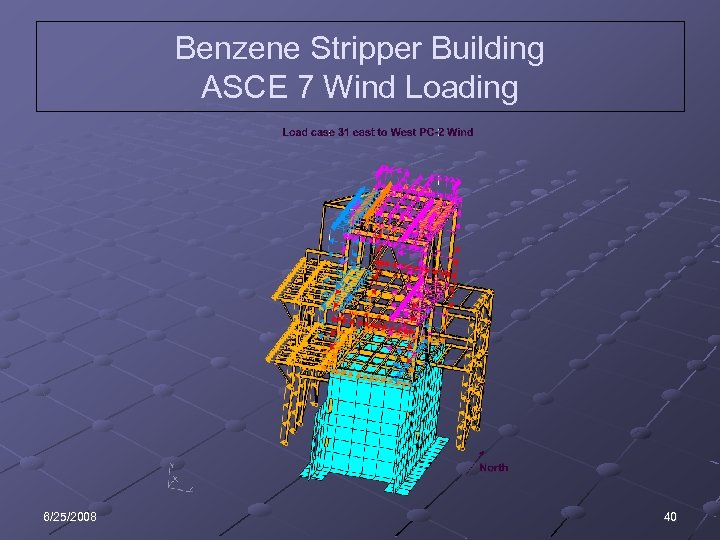 Benzene Stripper Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 6/25/2008 40
Benzene Stripper Building ASCE 7 Wind Loading 6/25/2008 40
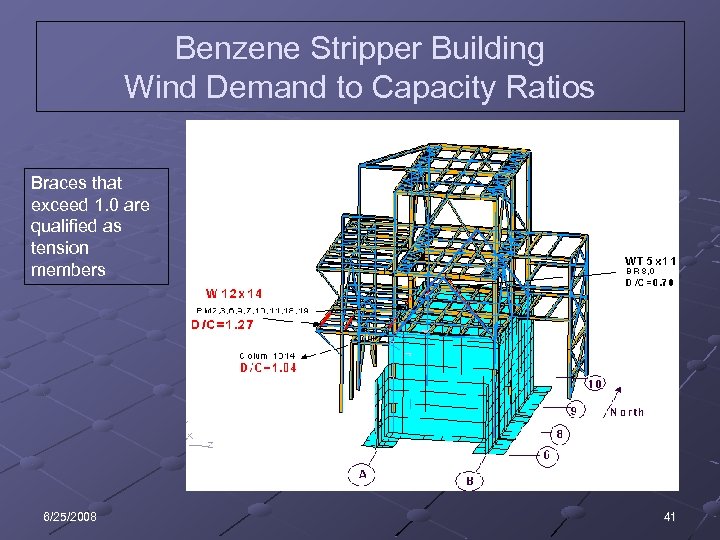 Benzene Stripper Building Wind Demand to Capacity Ratios Braces that exceed 1. 0 are qualified as tension members 6/25/2008 41
Benzene Stripper Building Wind Demand to Capacity Ratios Braces that exceed 1. 0 are qualified as tension members 6/25/2008 41
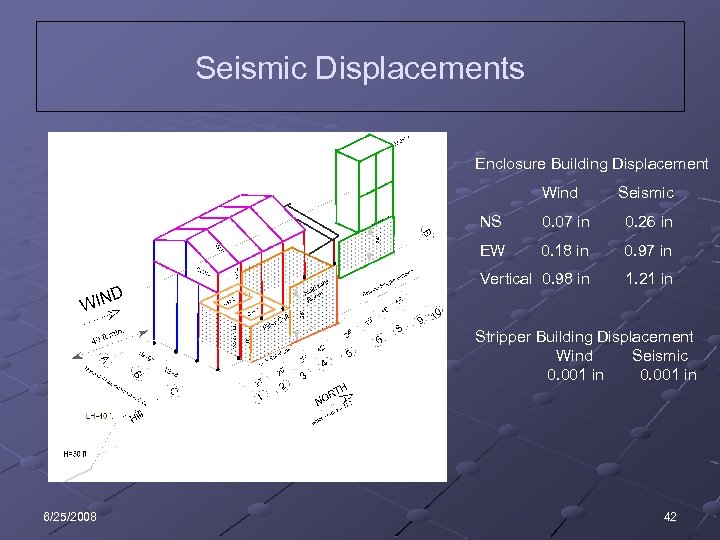 Seismic Displacements Enclosure Building Displacement Enclosure Wind Seismic NS 0. 18 in 0. 97 in Vertical 0. 98 in 6/25/2008 0. 26 in EW North 0. 07 in 1. 21 in Stripper Building Displacement Wind Seismic 0. 001 in 42
Seismic Displacements Enclosure Building Displacement Enclosure Wind Seismic NS 0. 18 in 0. 97 in Vertical 0. 98 in 6/25/2008 0. 26 in EW North 0. 07 in 1. 21 in Stripper Building Displacement Wind Seismic 0. 001 in 42
 Conclusions 6/25/2008 43
Conclusions 6/25/2008 43
 Conclusions Adequate for PC-3 seismic and PC-2 wind loads n n n Enclosure Building Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Benzene Stripper Building No pounding occurs 6/25/2008 44
Conclusions Adequate for PC-3 seismic and PC-2 wind loads n n n Enclosure Building Filter Cells and Hold Tank Room Benzene Stripper Building No pounding occurs 6/25/2008 44
 Questions? 6/25/2008 45
Questions? 6/25/2008 45


