f60ef8d42ffd6350f9475cf98d20ed67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 © 2007 Thomson South-Western
© 2007 Thomson South-Western
 CONTROLS ON PRICES Controls on Prices are enacted when … – policymakers believe the market price is unfair to buyers or sellers © 2007 Thomson South-Western
CONTROLS ON PRICES Controls on Prices are enacted when … – policymakers believe the market price is unfair to buyers or sellers © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 CONTROLS ON PRICES • Price Ceiling – A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
CONTROLS ON PRICES • Price Ceiling – A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
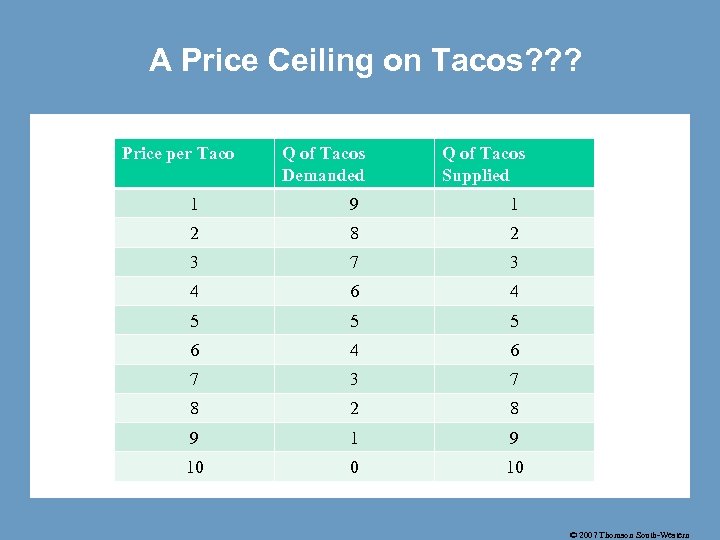 A Price Ceiling on Tacos? ? ? Price per Taco Q of Tacos Demanded Q of Tacos Supplied 1 9 1 2 8 2 3 7 3 4 6 4 5 5 5 6 4 6 7 3 7 8 2 8 9 10 0 10 © 2007 Thomson South-Western
A Price Ceiling on Tacos? ? ? Price per Taco Q of Tacos Demanded Q of Tacos Supplied 1 9 1 2 8 2 3 7 3 4 6 4 5 5 5 6 4 6 7 3 7 8 2 8 9 10 0 10 © 2007 Thomson South-Western
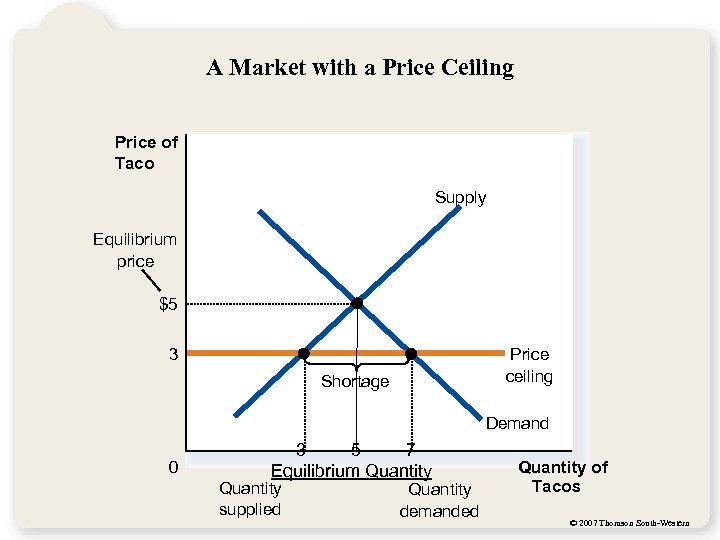 A Market with a Price Ceiling Price of Taco Supply Equilibrium price $5 3 Price ceiling Shortage Demand 0 3 5 7 Equilibrium Quantity supplied Quantity demanded Quantity of Tacos © 2007 Thomson South-Western
A Market with a Price Ceiling Price of Taco Supply Equilibrium price $5 3 Price ceiling Shortage Demand 0 3 5 7 Equilibrium Quantity supplied Quantity demanded Quantity of Tacos © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Effects of a Price Ceiling • Shortages • QD > QS • Inefficient allocation to consumers • Missed opportunities • Wasted resources Opportunity cost of looking for a taco • Inefficiently low quality • Taco suppliers ‘cut corners’ on quality • Black Market • Goods bought and sold illegally © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Effects of a Price Ceiling • Shortages • QD > QS • Inefficient allocation to consumers • Missed opportunities • Wasted resources Opportunity cost of looking for a taco • Inefficiently low quality • Taco suppliers ‘cut corners’ on quality • Black Market • Goods bought and sold illegally © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 CASE STUDY: Lines at the Gas Pump • In 1973, OPEC raised the price of crude oil in world markets. Crude oil is the major input in gasoline, so the higher oil prices reduced the supply of gasoline. • What was responsible for the long gas lines? • Economists blame government regulations that limited the price oil companies could charge for gasoline. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
CASE STUDY: Lines at the Gas Pump • In 1973, OPEC raised the price of crude oil in world markets. Crude oil is the major input in gasoline, so the higher oil prices reduced the supply of gasoline. • What was responsible for the long gas lines? • Economists blame government regulations that limited the price oil companies could charge for gasoline. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
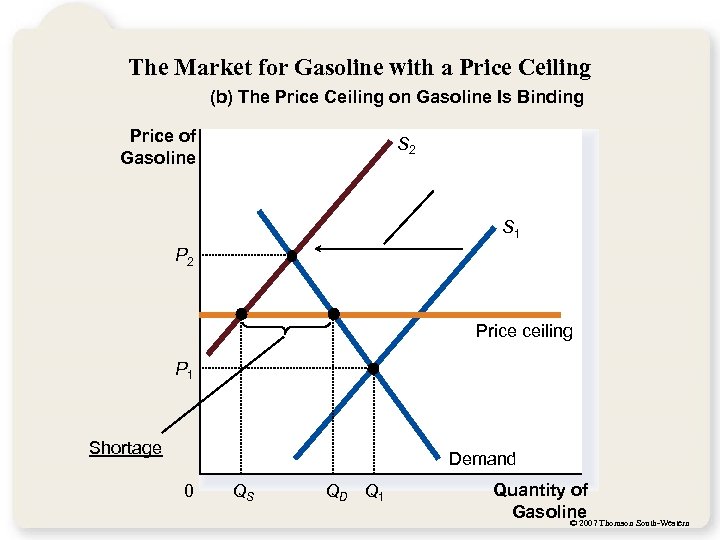 The Market for Gasoline with a Price Ceiling (b) The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Binding Price of Gasoline S 2 S 1 P 2 Price ceiling P 1 Shortage Demand 0 QS QD Q 1 Quantity of Gasoline Thomson South-Western © 2007
The Market for Gasoline with a Price Ceiling (b) The Price Ceiling on Gasoline Is Binding Price of Gasoline S 2 S 1 P 2 Price ceiling P 1 Shortage Demand 0 QS QD Q 1 Quantity of Gasoline Thomson South-Western © 2007
 CONTROLS ON PRICES • Price Floor – A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
CONTROLS ON PRICES • Price Floor – A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
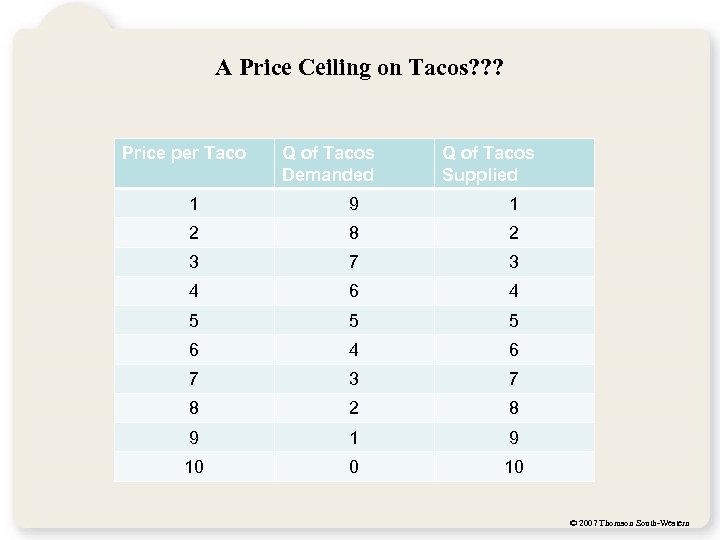 A Price Ceiling on Tacos? ? ? Price per Taco Q of Tacos Demanded Q of Tacos Supplied 1 9 1 2 8 2 3 7 3 4 6 4 5 5 5 6 4 6 7 3 7 8 2 8 9 10 0 10 © 2007 Thomson South-Western
A Price Ceiling on Tacos? ? ? Price per Taco Q of Tacos Demanded Q of Tacos Supplied 1 9 1 2 8 2 3 7 3 4 6 4 5 5 5 6 4 6 7 3 7 8 2 8 9 10 0 10 © 2007 Thomson South-Western
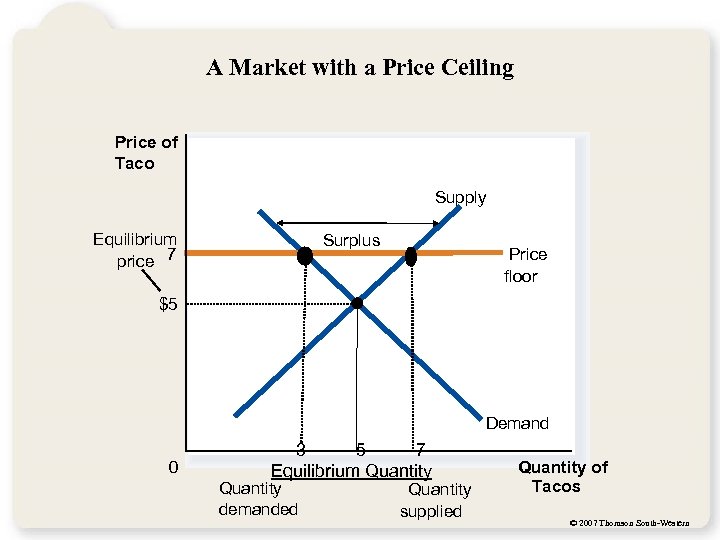 A Market with a Price Ceiling Price of Taco Supply Equilibrium price 7 Surplus Price floor $5 Demand 0 3 5 7 Equilibrium Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Quantity of Tacos © 2007 Thomson South-Western
A Market with a Price Ceiling Price of Taco Supply Equilibrium price 7 Surplus Price floor $5 Demand 0 3 5 7 Equilibrium Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Quantity of Tacos © 2007 Thomson South-Western
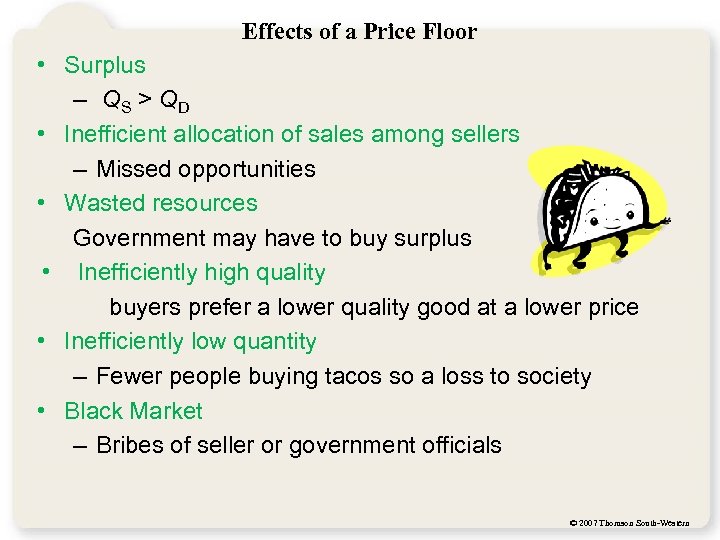 Effects of a Price Floor • Surplus – QS > QD • Inefficient allocation of sales among sellers – Missed opportunities • Wasted resources Government may have to buy surplus • Inefficiently high quality buyers prefer a lower quality good at a lower price • Inefficiently low quantity – Fewer people buying tacos so a loss to society • Black Market – Bribes of seller or government officials © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Effects of a Price Floor • Surplus – QS > QD • Inefficient allocation of sales among sellers – Missed opportunities • Wasted resources Government may have to buy surplus • Inefficiently high quality buyers prefer a lower quality good at a lower price • Inefficiently low quantity – Fewer people buying tacos so a loss to society • Black Market – Bribes of seller or government officials © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 CASE STUDY: The Minimum Wage • An important example of a price floor is the minimum wage. • Minimum wage laws dictate the lowest price possible for labor that any employer may pay. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
CASE STUDY: The Minimum Wage • An important example of a price floor is the minimum wage. • Minimum wage laws dictate the lowest price possible for labor that any employer may pay. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
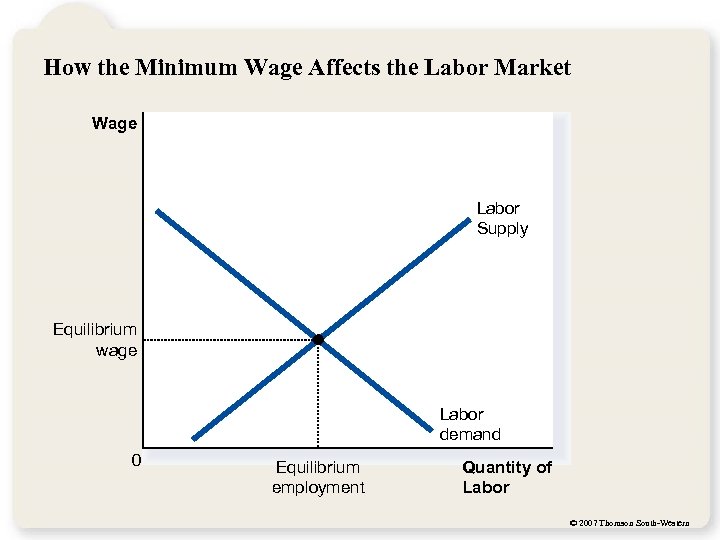 How the Minimum Wage Affects the Labor Market Wage Labor Supply Equilibrium wage Labor demand 0 Equilibrium employment Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
How the Minimum Wage Affects the Labor Market Wage Labor Supply Equilibrium wage Labor demand 0 Equilibrium employment Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
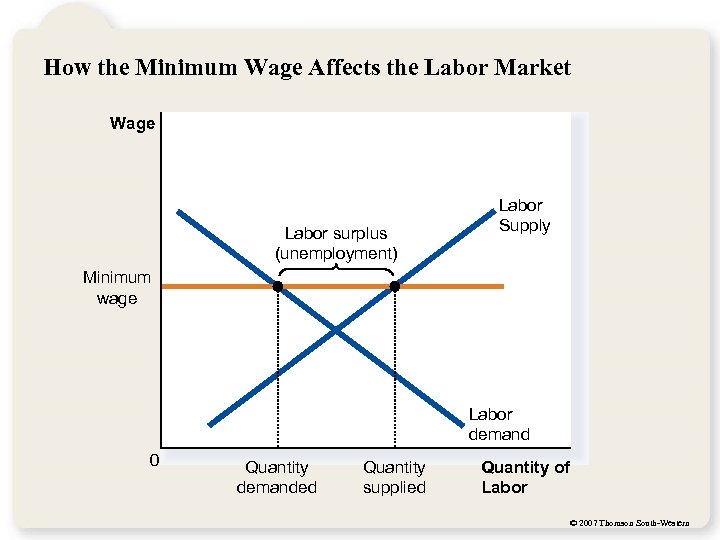 How the Minimum Wage Affects the Labor Market Wage Labor surplus (unemployment) Labor Supply Minimum wage Labor demand 0 Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
How the Minimum Wage Affects the Labor Market Wage Labor surplus (unemployment) Labor Supply Minimum wage Labor demand 0 Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Quantity Controls - Quotas A quota is … • an upper limit on the quantity of some good that can be bought or sold. • usually controlled by a license © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Quantity Controls - Quotas A quota is … • an upper limit on the quantity of some good that can be bought or sold. • usually controlled by a license © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Example: Ocean Caught Salmon Market What controls how many each salmon boat may catch? Licenses are allocated. Total quota limit reached = ocean caught salmon season is OVER!!! © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Example: Ocean Caught Salmon Market What controls how many each salmon boat may catch? Licenses are allocated. Total quota limit reached = ocean caught salmon season is OVER!!! © 2007 Thomson South-Western
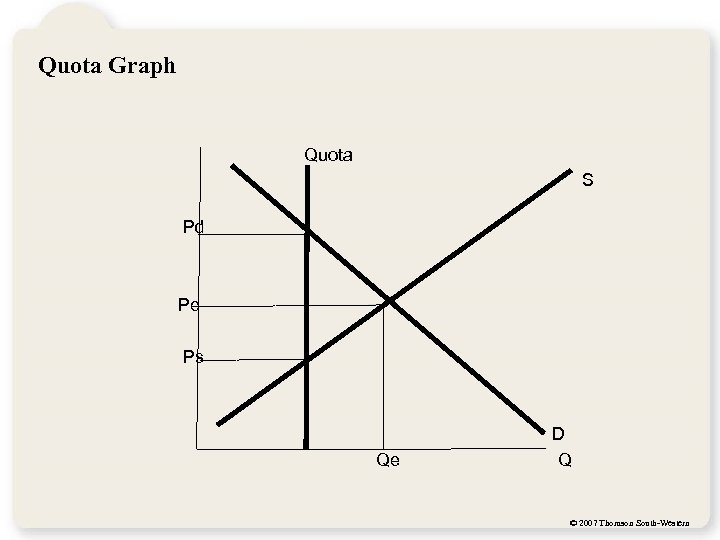 Quota Graph Quota S Pd Pe Ps Qe D Q © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Quota Graph Quota S Pd Pe Ps Qe D Q © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Costs of Quantity Controls • Inefficiency – missed opportunities • Incentives for illegal activities - poaching © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Costs of Quantity Controls • Inefficiency – missed opportunities • Incentives for illegal activities - poaching © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 TAXES • Governments levy taxes to raise revenue for public projects. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
TAXES • Governments levy taxes to raise revenue for public projects. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 How Taxes on Buyers (and Sellers) Affect Market Outcomes • Taxes discourage market activity. • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
How Taxes on Buyers (and Sellers) Affect Market Outcomes • Taxes discourage market activity. • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 How Taxes on Buyers Affect Market Outcomes • Elasticity and tax incidence • Tax incidence is the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a market. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
How Taxes on Buyers Affect Market Outcomes • Elasticity and tax incidence • Tax incidence is the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a market. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 How Taxes on Buyers Affect Market Outcomes • Elasticity and Tax Incidence • Tax incidence is the study of who bears the burden of a tax. • Taxes result in a change in market equilibrium. • Buyers pay more and sellers receive less, regardless of whom the tax is levied on. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
How Taxes on Buyers Affect Market Outcomes • Elasticity and Tax Incidence • Tax incidence is the study of who bears the burden of a tax. • Taxes result in a change in market equilibrium. • Buyers pay more and sellers receive less, regardless of whom the tax is levied on. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
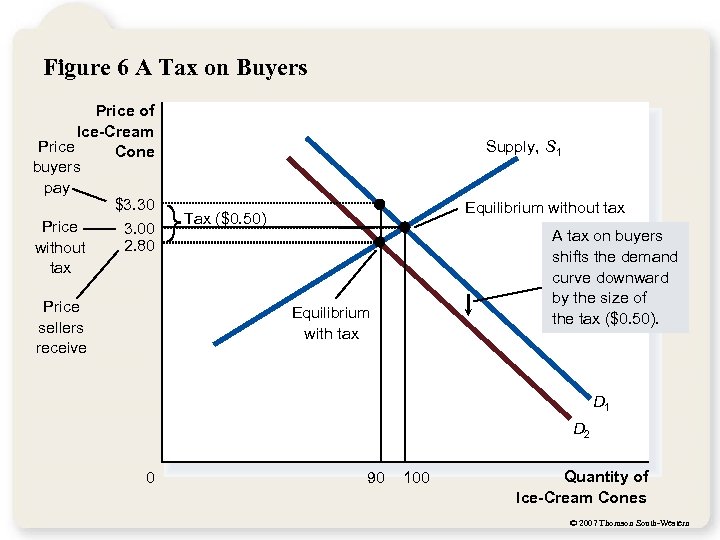 Figure 6 A Tax on Buyers Price of Ice-Cream Price Cone buyers pay $3. 30 Price 3. 00 2. 80 without tax Price sellers receive Supply, S 1 Equilibrium without tax Tax ($0. 50) A tax on buyers shifts the demand curve downward by the size of the tax ($0. 50). Equilibrium with tax D 1 D 2 0 90 100 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Figure 6 A Tax on Buyers Price of Ice-Cream Price Cone buyers pay $3. 30 Price 3. 00 2. 80 without tax Price sellers receive Supply, S 1 Equilibrium without tax Tax ($0. 50) A tax on buyers shifts the demand curve downward by the size of the tax ($0. 50). Equilibrium with tax D 1 D 2 0 90 100 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones © 2007 Thomson South-Western
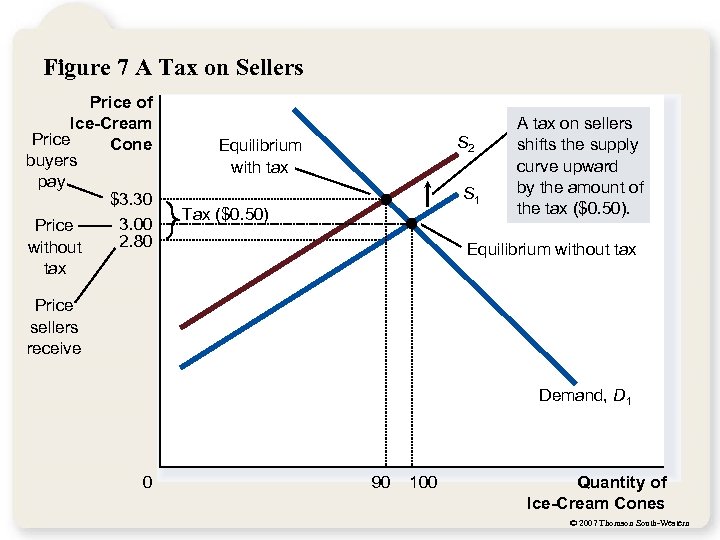 Figure 7 A Tax on Sellers Price of Ice-Cream Price Cone buyers pay $3. 30 3. 00 Price 2. 80 without tax S 2 Equilibrium with tax S 1 Tax ($0. 50) A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve upward by the amount of the tax ($0. 50). Equilibrium without tax Price sellers receive Demand, D 1 0 90 100 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Figure 7 A Tax on Sellers Price of Ice-Cream Price Cone buyers pay $3. 30 3. 00 Price 2. 80 without tax S 2 Equilibrium with tax S 1 Tax ($0. 50) A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve upward by the amount of the tax ($0. 50). Equilibrium without tax Price sellers receive Demand, D 1 0 90 100 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Elasticity and Tax Incidence • What was the impact of tax? • Taxes discourage market activity. • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Elasticity and Tax Incidence • What was the impact of tax? • Taxes discourage market activity. • When a good is taxed, the quantity sold is smaller. • Buyers and sellers share the tax burden. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
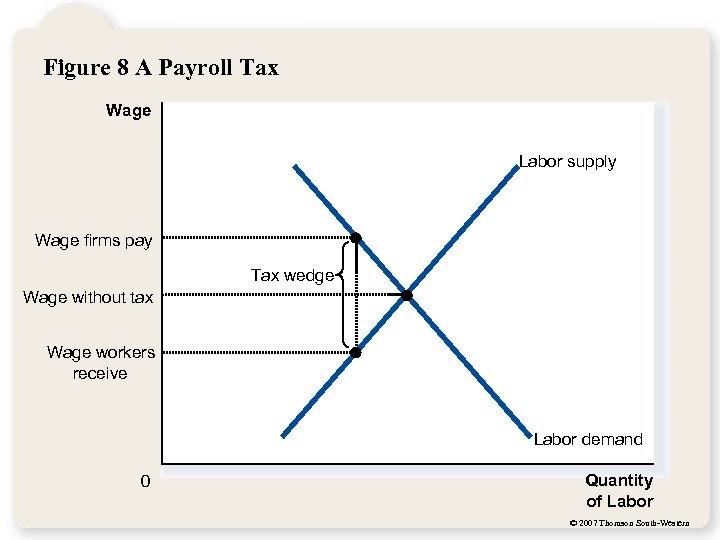 Figure 8 A Payroll Tax Wage Labor supply Wage firms pay Tax wedge Wage without tax Wage workers receive Labor demand 0 Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Figure 8 A Payroll Tax Wage Labor supply Wage firms pay Tax wedge Wage without tax Wage workers receive Labor demand 0 Quantity of Labor © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Elasticity and Tax Incidence • In what proportions is the burden of the tax divided? • How do the effects of taxes on sellers compare to those levied on buyers? • The answers to these questions depend on the elasticity of demand the elasticity of supply. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Elasticity and Tax Incidence • In what proportions is the burden of the tax divided? • How do the effects of taxes on sellers compare to those levied on buyers? • The answers to these questions depend on the elasticity of demand the elasticity of supply. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
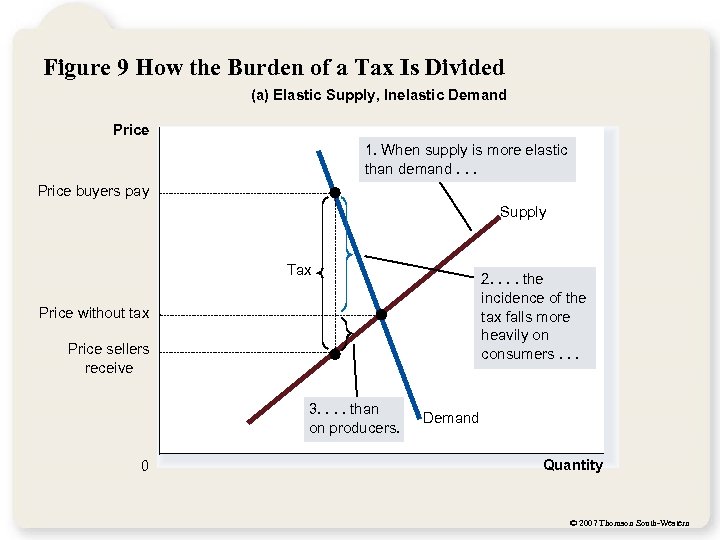 Figure 9 How the Burden of a Tax Is Divided (a) Elastic Supply, Inelastic Demand Price 1. When supply is more elastic than demand. . . Price buyers pay Supply Tax 2. . the incidence of the tax falls more heavily on consumers. . . Price without tax Price sellers receive 3. . than on producers. 0 Demand Quantity © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Figure 9 How the Burden of a Tax Is Divided (a) Elastic Supply, Inelastic Demand Price 1. When supply is more elastic than demand. . . Price buyers pay Supply Tax 2. . the incidence of the tax falls more heavily on consumers. . . Price without tax Price sellers receive 3. . than on producers. 0 Demand Quantity © 2007 Thomson South-Western
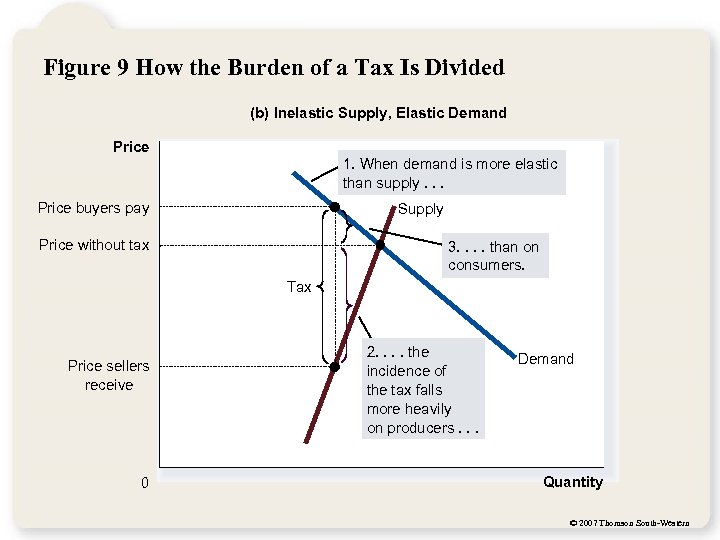 Figure 9 How the Burden of a Tax Is Divided (b) Inelastic Supply, Elastic Demand Price 1. When demand is more elastic than supply. . . Price buyers pay Supply Price without tax 3. . than on consumers. Tax Price sellers receive 0 2. . the incidence of the tax falls more heavily on producers. . . Demand Quantity © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Figure 9 How the Burden of a Tax Is Divided (b) Inelastic Supply, Elastic Demand Price 1. When demand is more elastic than supply. . . Price buyers pay Supply Price without tax 3. . than on consumers. Tax Price sellers receive 0 2. . the incidence of the tax falls more heavily on producers. . . Demand Quantity © 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Elasticity and Tax Incidence So, how is the burden of the tax divided? The burden of a tax falls more heavily on the side of the market that is less elastic. © 2007 Thomson South-Western
Elasticity and Tax Incidence So, how is the burden of the tax divided? The burden of a tax falls more heavily on the side of the market that is less elastic. © 2007 Thomson South-Western


