d5426a3fb7be0110d87419fbbd731758.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 2007. 10. 15 Korea Power Exchange
2007. 10. 15 Korea Power Exchange
 Korean Electric Industry Overview(1) v No Inter-Connection - Isolated electric power system v Highly dependent on foreign energy resources (Gas, Oil) - Imported fuels 97% v Rapid growth in electricity demand (about 6. 8%/year) - Recent 5 years (’ 01~’ 05) - about 9. 7% (’ 91~’ 00) v Peak Electricity Demand - 62, 285 MW(Aug. 21, 2007) v Total Generating Capacity - 67, 196 MW(August, 2007) 1
Korean Electric Industry Overview(1) v No Inter-Connection - Isolated electric power system v Highly dependent on foreign energy resources (Gas, Oil) - Imported fuels 97% v Rapid growth in electricity demand (about 6. 8%/year) - Recent 5 years (’ 01~’ 05) - about 9. 7% (’ 91~’ 00) v Peak Electricity Demand - 62, 285 MW(Aug. 21, 2007) v Total Generating Capacity - 67, 196 MW(August, 2007) 1
 Korean Electric Industry Overview(2) q Area of South Korea : 99, 601 km 2 q GDP : 897. 4 Billion USD(’ 06, 12 th Largest in the World) q Population: 49 million (Seoul Metro. Area : 24 mil. ’ 07) q Electric Power Industry Overview v 17. 62 million customers (December, ‘ 06) v 832 Generating Units (July, ‘ 07) v 765 k. V/345 k. V/154 k. V/(66 k. V), DC 180 k. V v Installed Capacity : 67, 196 MW (August, ‘ 07) v Electricity Consumption per Capita: 7, 191 k. Wh(‘ 06) 2 2
Korean Electric Industry Overview(2) q Area of South Korea : 99, 601 km 2 q GDP : 897. 4 Billion USD(’ 06, 12 th Largest in the World) q Population: 49 million (Seoul Metro. Area : 24 mil. ’ 07) q Electric Power Industry Overview v 17. 62 million customers (December, ‘ 06) v 832 Generating Units (July, ‘ 07) v 765 k. V/345 k. V/154 k. V/(66 k. V), DC 180 k. V v Installed Capacity : 67, 196 MW (August, ‘ 07) v Electricity Consumption per Capita: 7, 191 k. Wh(‘ 06) 2 2
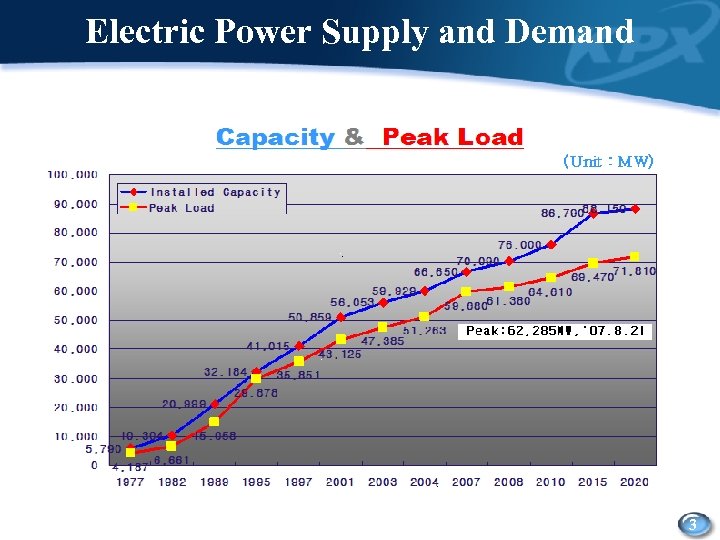 Electric Power Supply and Demand 3
Electric Power Supply and Demand 3
 Generation Capacity in South Korea By Generating Fuels Oil Hydro 8. 8% Nuclear 8. 2% 67, 196 MW 26. 4% KHNP 18, 250 (27. 2%) (as of 2007. 10, MW, %) CC, LNG 26. 9% Coal 29. 7% Private 762 (11. 3%) 5 Genco’s 41, 330 (61. 5%) By Genco’s 4 4
Generation Capacity in South Korea By Generating Fuels Oil Hydro 8. 8% Nuclear 8. 2% 67, 196 MW 26. 4% KHNP 18, 250 (27. 2%) (as of 2007. 10, MW, %) CC, LNG 26. 9% Coal 29. 7% Private 762 (11. 3%) 5 Genco’s 41, 330 (61. 5%) By Genco’s 4 4
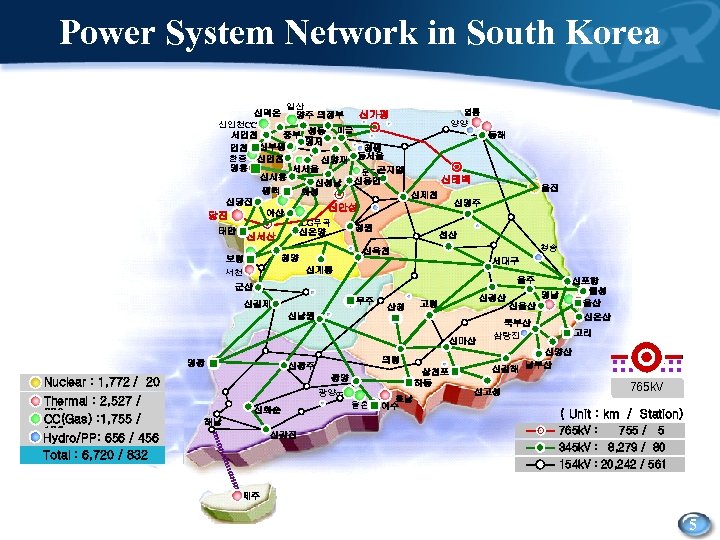 Power System Network in South Korea 일산 영동 신덕은 신가평 양주 의정부 양양 신인천CC 중부 성동 미금 서인천 동해 영서 청평 인천 신부평 한종 신인천 신양재 동서울 영흥 서서울 분당곤지암 신시흥 신태백 신성남 신용인 평택 화성 신제천 신당진 신영주 신안성 아산 당진 LG부곡 청원 태안 신온양 선산 신서산 청송 신옥천 청양 보령 서천 서대구 신계룡 울주 군산 무주 신김제 신남원 산청 신경산 고령 신마산 영광 의령 신광주 삼천포 하동 광양 Nuclear : 1, 772 / 20 Thermal : 2, 527 / 220 CC(Gas) : 1, 755 / 136 Hydro/PP: 656 / 456 Total : 6, 720 / 832 울진 광양cc 신화순 해남 율촌 호남 여수 신포항 월성 울산 영남 신울산 신온산 북부산 삼랑진 고리 신양산 신김해 남부산 765 k. V 345 k. V 해저케이블 154 k. V 신고성 ( Unit : km / Station) 765 k. V : 755 / 5 345 k. V : 신강진 8, 279 / 80 154 k. V : 20, 242 / 561 제주 5
Power System Network in South Korea 일산 영동 신덕은 신가평 양주 의정부 양양 신인천CC 중부 성동 미금 서인천 동해 영서 청평 인천 신부평 한종 신인천 신양재 동서울 영흥 서서울 분당곤지암 신시흥 신태백 신성남 신용인 평택 화성 신제천 신당진 신영주 신안성 아산 당진 LG부곡 청원 태안 신온양 선산 신서산 청송 신옥천 청양 보령 서천 서대구 신계룡 울주 군산 무주 신김제 신남원 산청 신경산 고령 신마산 영광 의령 신광주 삼천포 하동 광양 Nuclear : 1, 772 / 20 Thermal : 2, 527 / 220 CC(Gas) : 1, 755 / 136 Hydro/PP: 656 / 456 Total : 6, 720 / 832 울진 광양cc 신화순 해남 율촌 호남 여수 신포항 월성 울산 영남 신울산 신온산 북부산 삼랑진 고리 신양산 신김해 남부산 765 k. V 345 k. V 해저케이블 154 k. V 신고성 ( Unit : km / Station) 765 k. V : 755 / 5 345 k. V : 신강진 8, 279 / 80 154 k. V : 20, 242 / 561 제주 5
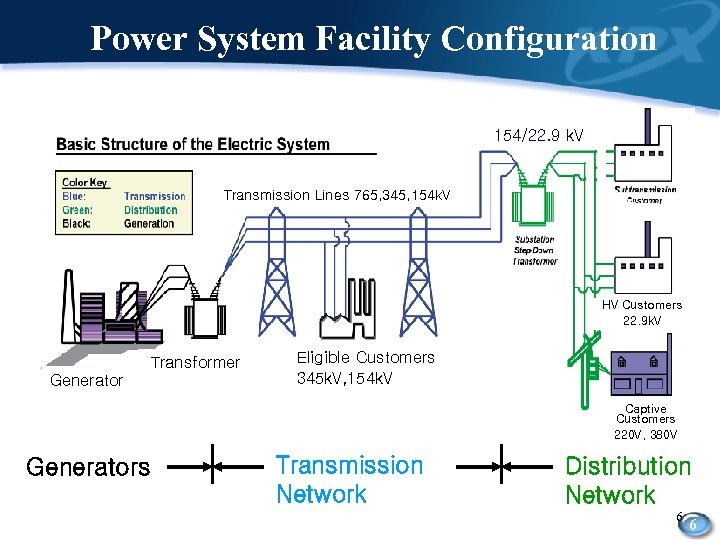 Power System Facility Configuration 154/22. 9 k. V Transmission Lines 765, 345, 154 k. V HV Customers 22. 9 k. V Transformer Generator Eligible Customers 345 k. V, 154 k. V Captive Customers 220 V, 380 V Generators Transmission Network Distribution Network 6 6
Power System Facility Configuration 154/22. 9 k. V Transmission Lines 765, 345, 154 k. V HV Customers 22. 9 k. V Transformer Generator Eligible Customers 345 k. V, 154 k. V Captive Customers 220 V, 380 V Generators Transmission Network Distribution Network 6 6
 Electric industry liberalization in South Korea v Industry structure before the liberalization start in 1999 – KEPCO monopolized 94% of installed generation capacity of 47, 053 MW, and 100% of transmission & distribution (Government owned utility) – A small number of IPP’s sold electricity to KEPCO, a single buyer. – Tariff based on usage (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, agricultural) v Objectives of the liberalization – To enhance the efficiency of the electricity supply industry – To effectively finance new generation capacity – To increase consumer benefits and improve service quality v Guiding Principles of Electricity Industry liberalization – – Unbundling of electricity business into Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Supply Mandatory Pool Regulatory Body Independent System & Market Operator 7 7
Electric industry liberalization in South Korea v Industry structure before the liberalization start in 1999 – KEPCO monopolized 94% of installed generation capacity of 47, 053 MW, and 100% of transmission & distribution (Government owned utility) – A small number of IPP’s sold electricity to KEPCO, a single buyer. – Tariff based on usage (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, agricultural) v Objectives of the liberalization – To enhance the efficiency of the electricity supply industry – To effectively finance new generation capacity – To increase consumer benefits and improve service quality v Guiding Principles of Electricity Industry liberalization – – Unbundling of electricity business into Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Supply Mandatory Pool Regulatory Body Independent System & Market Operator 7 7
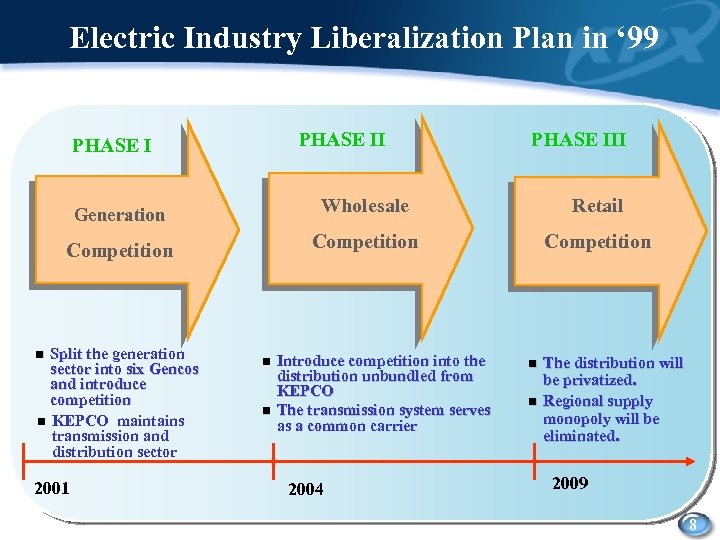 Electric Industry Liberalization Plan in ‘ 99 PHASE III Generation Wholesale Retail Competition Split the generation sector into six Gencos and introduce competition n KEPCO maintains transmission and distribution sector n 2001 n n Introduce competition into the distribution unbundled from KEPCO The transmission system serves as a common carrier 2004 n n The distribution will be privatized. Regional supply monopoly will be eliminated. 2009 8
Electric Industry Liberalization Plan in ‘ 99 PHASE III Generation Wholesale Retail Competition Split the generation sector into six Gencos and introduce competition n KEPCO maintains transmission and distribution sector n 2001 n n Introduce competition into the distribution unbundled from KEPCO The transmission system serves as a common carrier 2004 n n The distribution will be privatized. Regional supply monopoly will be eliminated. 2009 8
 What has been done thus far in South Korea v Liberalization process to date – – 1999. 01 “The basic plan for restructuring of the electric power industry” unveiled 2000. 12 Necessary Legislations were enacted 2001. 04 KOREC and KPX established, 6 Genco’s were spun off 2004. 06 Distribution Spin-off suspended by Biz, Labor & Government • • Impact of Electricity Market crisis in U. S. (California) Concern about Price Volatility and Unstable Supply in the future Wholesale Market – 2006. 09 Transformed Regional Distribution & Sales Branches of KEPCO into 9 Independent Business Divisions and Internal Competition among them v Current State and Effects of the Liberalization – – – Cost-Based Pool Model is being continued Genco’s and Distribution & Sales divisions are Not yet privatized Investments are not effectively on time Managerial efficiency in the Generation Sector has been improved Power System Quality has been improved than before 9
What has been done thus far in South Korea v Liberalization process to date – – 1999. 01 “The basic plan for restructuring of the electric power industry” unveiled 2000. 12 Necessary Legislations were enacted 2001. 04 KOREC and KPX established, 6 Genco’s were spun off 2004. 06 Distribution Spin-off suspended by Biz, Labor & Government • • Impact of Electricity Market crisis in U. S. (California) Concern about Price Volatility and Unstable Supply in the future Wholesale Market – 2006. 09 Transformed Regional Distribution & Sales Branches of KEPCO into 9 Independent Business Divisions and Internal Competition among them v Current State and Effects of the Liberalization – – – Cost-Based Pool Model is being continued Genco’s and Distribution & Sales divisions are Not yet privatized Investments are not effectively on time Managerial efficiency in the Generation Sector has been improved Power System Quality has been improved than before 9
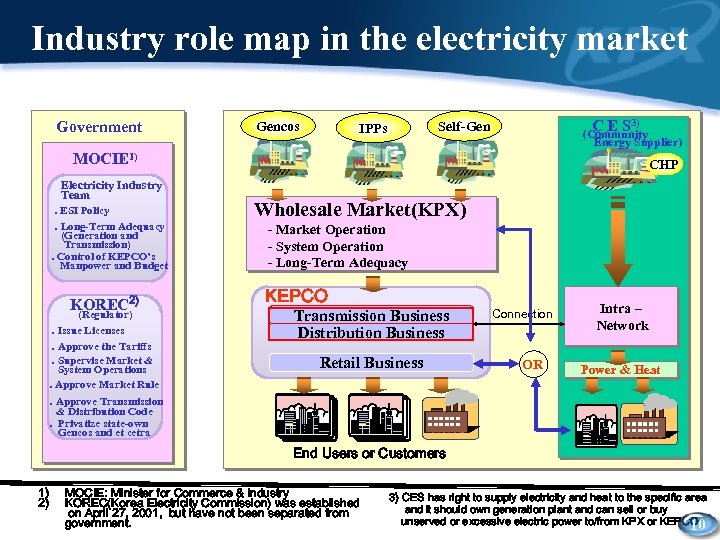 Industry role map in the electricity market Government Gencos C E S 3) Self-Gen IPPs (Community Energy Supplier) MOCIE 1) Electricity Industry Team. ESI Policy. Long-Term Adequacy (Generation and Transmission). Control of KEPCO’s Manpower and Budget KOREC 2) (Regulator). Issue Licenses. Approve the Tariffs. Supervise Market & System Operations. Approve Market Rule CHP Wholesale Market(KPX) - Market Operation - System Operation - Long-Term Adequacy KEPCO Transmission Business Distribution Business Retail Business Connection OR Intra – Network Power & Heat . Approve Transmission & Distribution Code. Privatize state-own Gencos and et cetra End Users or Customers 1) 2) MOCIE: Minister for Commerce & Industry KOREC(Korea Electricity Commission) was established on April 27, 2001, but have not been separated from government. 3) CES has right to supply electricity and heat to the specific area and it should own generation plant and can sell or buy unserved or excessive electric power to/from KPX or KEPCO 10
Industry role map in the electricity market Government Gencos C E S 3) Self-Gen IPPs (Community Energy Supplier) MOCIE 1) Electricity Industry Team. ESI Policy. Long-Term Adequacy (Generation and Transmission). Control of KEPCO’s Manpower and Budget KOREC 2) (Regulator). Issue Licenses. Approve the Tariffs. Supervise Market & System Operations. Approve Market Rule CHP Wholesale Market(KPX) - Market Operation - System Operation - Long-Term Adequacy KEPCO Transmission Business Distribution Business Retail Business Connection OR Intra – Network Power & Heat . Approve Transmission & Distribution Code. Privatize state-own Gencos and et cetra End Users or Customers 1) 2) MOCIE: Minister for Commerce & Industry KOREC(Korea Electricity Commission) was established on April 27, 2001, but have not been separated from government. 3) CES has right to supply electricity and heat to the specific area and it should own generation plant and can sell or buy unserved or excessive electric power to/from KPX or KEPCO 10
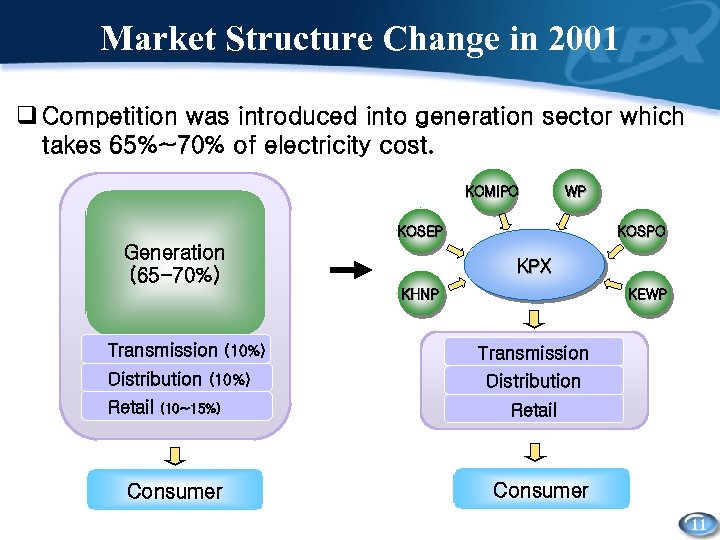 Market Structure Change in 2001 q Competition was introduced into generation sector which takes 65%~70% of electricity cost. KOMIPO WP KOSEP Generation (65 -70%) KOSPO KPX KHNP Transmission (10%) Distribution (10%) Retail (10~15%) Consumer KEWP Transmission Distribution Retail Consumer 11
Market Structure Change in 2001 q Competition was introduced into generation sector which takes 65%~70% of electricity cost. KOMIPO WP KOSEP Generation (65 -70%) KOSPO KPX KHNP Transmission (10%) Distribution (10%) Retail (10~15%) Consumer KEWP Transmission Distribution Retail Consumer 11
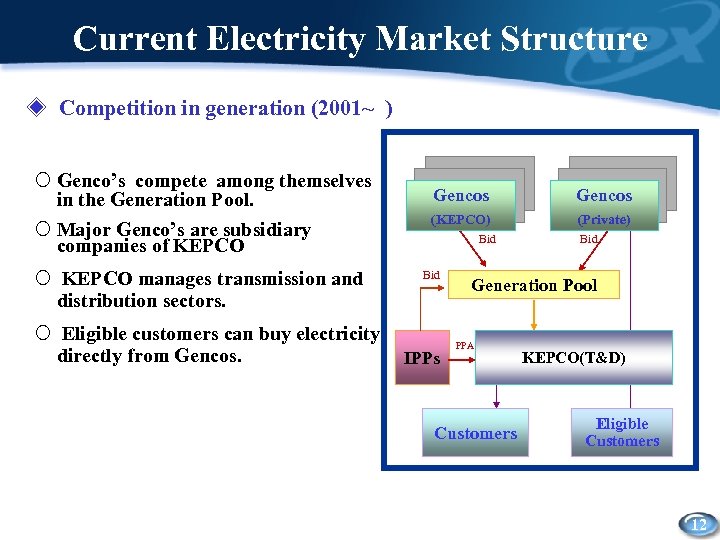 Current Electricity Market Structure ◈ Competition in generation (2001~ ) ¡ Genco’s compete among themselves in the Generation Pool. ¡ Major Genco’s are subsidiary companies of KEPCO ¡ KEPCO manages transmission and distribution sectors. ¡ Eligible customers can buy electricity directly from Gencos (KEPCO) (Private) Bid IPPs Bid Generation Pool PPA Customers KEPCO(T&D) Eligible Customers 12
Current Electricity Market Structure ◈ Competition in generation (2001~ ) ¡ Genco’s compete among themselves in the Generation Pool. ¡ Major Genco’s are subsidiary companies of KEPCO ¡ KEPCO manages transmission and distribution sectors. ¡ Eligible customers can buy electricity directly from Gencos (KEPCO) (Private) Bid IPPs Bid Generation Pool PPA Customers KEPCO(T&D) Eligible Customers 12
 Key Features of the Market(1) q All generators and retailers should trade electricity through the market. v Generators bid into the pool with their available capacity of each generator and each trading daily v KEPCO is the only purchaser in the market v Eligible Customers are allowed to buy electricity directly from the pool(2003. 1) v Some PPA holders do not participate in the market q Dispatch schedule is made by the predetermined costs of each generator. v Generation Cost Evaluation Committee(GCEC) determines the variable costs of each generator. v GCEC evaluates the construction cost and fixed costs of each generator. 13 13
Key Features of the Market(1) q All generators and retailers should trade electricity through the market. v Generators bid into the pool with their available capacity of each generator and each trading daily v KEPCO is the only purchaser in the market v Eligible Customers are allowed to buy electricity directly from the pool(2003. 1) v Some PPA holders do not participate in the market q Dispatch schedule is made by the predetermined costs of each generator. v Generation Cost Evaluation Committee(GCEC) determines the variable costs of each generator. v GCEC evaluates the construction cost and fixed costs of each generator. 13 13
 Key Features of the Market(2) q Generators are paid by system marginal price(SMP) plus capacity payment v SMP reflects actual production costs(start-up, no-load, incremental cost) of the latest generator brought into operation v CP is paid to all generators offering, whether or not dispatched q CP ensures capital costs recovery and underpins further investments 14 14
Key Features of the Market(2) q Generators are paid by system marginal price(SMP) plus capacity payment v SMP reflects actual production costs(start-up, no-load, incremental cost) of the latest generator brought into operation v CP is paid to all generators offering, whether or not dispatched q CP ensures capital costs recovery and underpins further investments 14 14
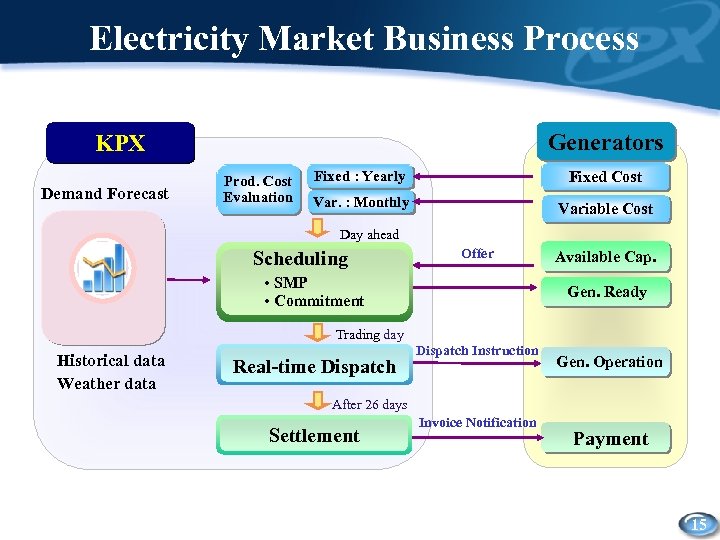 Electricity Market Business Process Generators KPX Demand Forecast Prod. Cost Evaluation Fixed Cost Fixed : Yearly Var. : Monthly Submit Variable Cost Offer Available Cap. Notify Gen. Ready Day ahead Scheduling • SMP • Commitment Trading day Historical data Weather data Real-time Dispatch Instruction Gen. Operation After 26 days Settlement Invoice Notification Payment 15
Electricity Market Business Process Generators KPX Demand Forecast Prod. Cost Evaluation Fixed Cost Fixed : Yearly Var. : Monthly Submit Variable Cost Offer Available Cap. Notify Gen. Ready Day ahead Scheduling • SMP • Commitment Trading day Historical data Weather data Real-time Dispatch Instruction Gen. Operation After 26 days Settlement Invoice Notification Payment 15
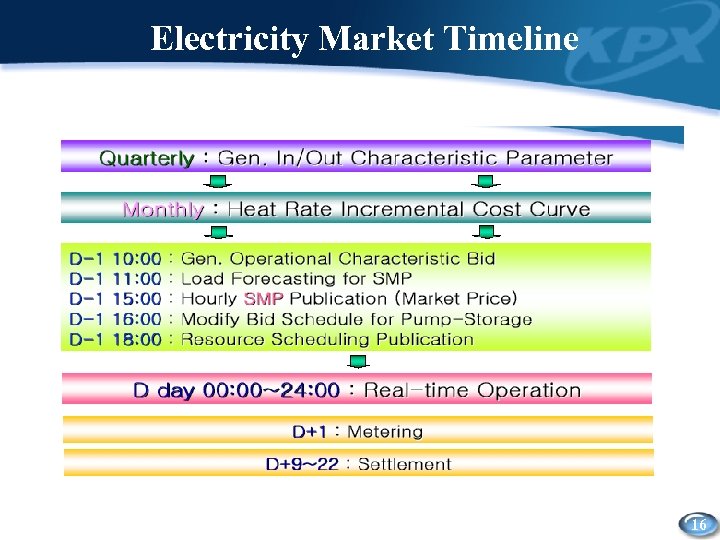 Electricity Market Timeline 16
Electricity Market Timeline 16
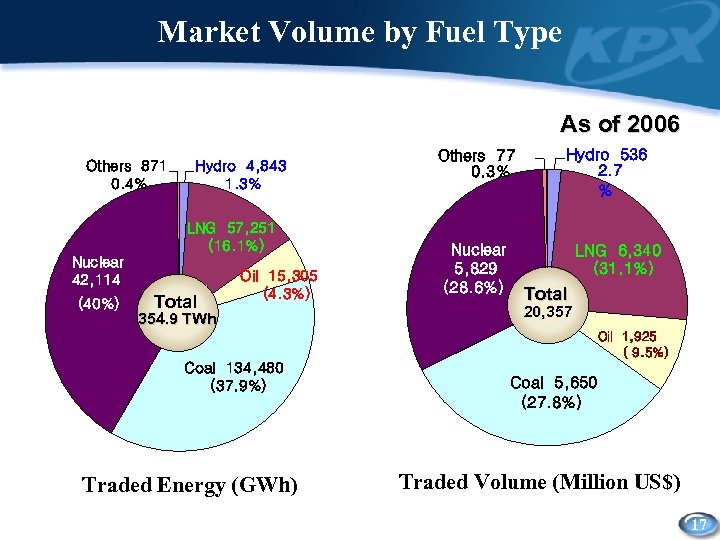 Market Volume by Fuel Type As of 2006 Others 871 0. 4% Hydro 4, 843 1. 3% LNG 57, 251 (16. 1%) Nuclear 42, 114 (40%) Total Oil 15, 305 (4. 3%) 354. 9 TWh Others 77 0. 3% Nuclear 5, 829 (28. 6%) Hydro 536 2. 7 % LNG 6, 340 (31. 1%) Total 20, 357 18, 924 Bwon Oil 1, 925 ( 9. 5%) Coal 134, 480 (37. 9%) Traded Energy (GWh) Coal 5, 650 (27. 8%) Traded Volume (Million US$) 17
Market Volume by Fuel Type As of 2006 Others 871 0. 4% Hydro 4, 843 1. 3% LNG 57, 251 (16. 1%) Nuclear 42, 114 (40%) Total Oil 15, 305 (4. 3%) 354. 9 TWh Others 77 0. 3% Nuclear 5, 829 (28. 6%) Hydro 536 2. 7 % LNG 6, 340 (31. 1%) Total 20, 357 18, 924 Bwon Oil 1, 925 ( 9. 5%) Coal 134, 480 (37. 9%) Traded Energy (GWh) Coal 5, 650 (27. 8%) Traded Volume (Million US$) 17
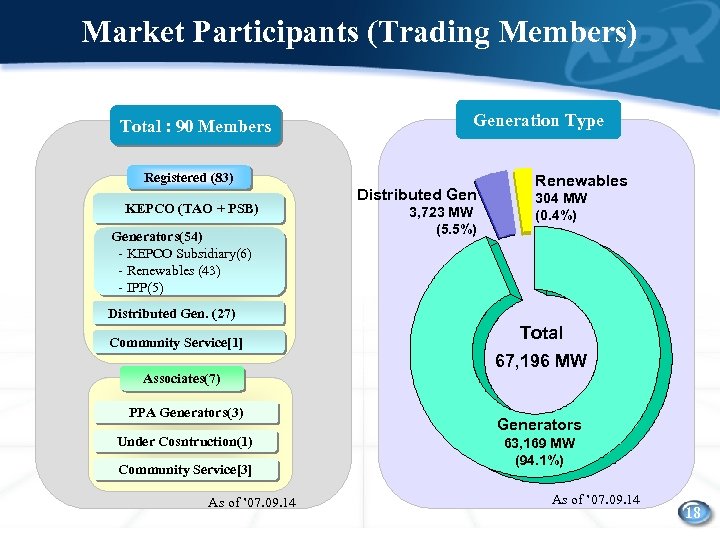 Market Participants (Trading Members) Total : 90 Members Generation Type Registered (83) KEPCO (TAO + PSB) Generators(54) - KEPCO Subsidiary(6) - Renewables (43) - IPP(5) Distributed Gen 3, 723 MW (5. 5%) Renewables 304 MW (0. 4%) Distributed Gen. (27) Community Service[1] Total 67, 196 MW Associates(7) PPA Generators(3) Under Cosntruction(1) Community Service[3] As of ’ 07. 09. 14 Generators 63, 169 MW (94. 1%) As of ’ 07. 09. 14 18
Market Participants (Trading Members) Total : 90 Members Generation Type Registered (83) KEPCO (TAO + PSB) Generators(54) - KEPCO Subsidiary(6) - Renewables (43) - IPP(5) Distributed Gen 3, 723 MW (5. 5%) Renewables 304 MW (0. 4%) Distributed Gen. (27) Community Service[1] Total 67, 196 MW Associates(7) PPA Generators(3) Under Cosntruction(1) Community Service[3] As of ’ 07. 09. 14 Generators 63, 169 MW (94. 1%) As of ’ 07. 09. 14 18
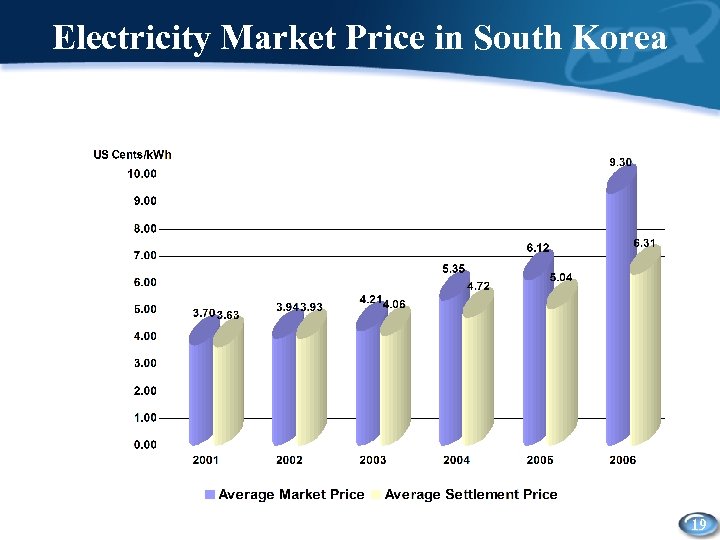 Electricity Market Price in South Korea 19
Electricity Market Price in South Korea 19
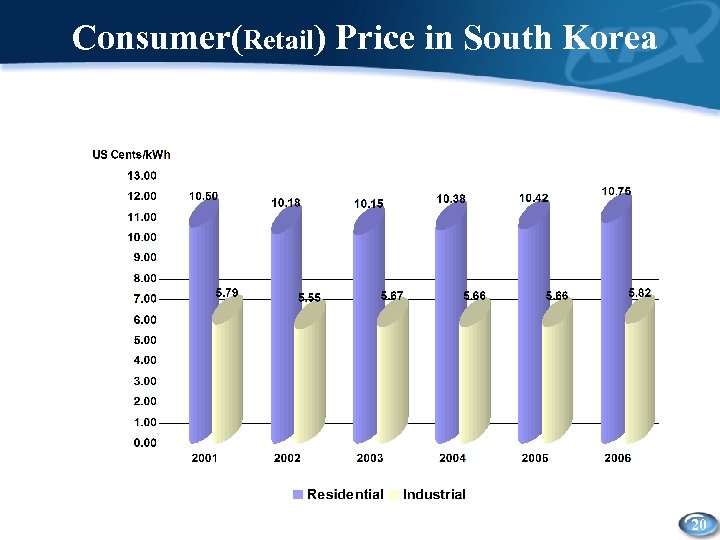 Consumer(Retail) Price in South Korea 20
Consumer(Retail) Price in South Korea 20
 Issues in the Korean electricity Market § Electric industry liberalization program has been stopped for long time o Phase 1 model(Cost Based Pool) has been maintained for more than 6 years o CBP was designed for simplicity and quick implementation during the transitory period (need some amendments to be a sustainable market) § CBP has revealed the limitation as a temporary system lacking of detailed provisions in the market design o o Low efficiency due to the dual market structure (Base & Non-base load markets) Lack of locational signal in consideration of transmission losses Possibility of over-investment with inappropriate capacity payment Lack of incentives to save fuel costs § Extensive improvement works in market rules and trading arrangements were carried out in 2006 to make a sustainable electricity market 21
Issues in the Korean electricity Market § Electric industry liberalization program has been stopped for long time o Phase 1 model(Cost Based Pool) has been maintained for more than 6 years o CBP was designed for simplicity and quick implementation during the transitory period (need some amendments to be a sustainable market) § CBP has revealed the limitation as a temporary system lacking of detailed provisions in the market design o o Low efficiency due to the dual market structure (Base & Non-base load markets) Lack of locational signal in consideration of transmission losses Possibility of over-investment with inappropriate capacity payment Lack of incentives to save fuel costs § Extensive improvement works in market rules and trading arrangements were carried out in 2006 to make a sustainable electricity market 21
 Recent Changes in Market Settlement q Energy Payment o Marginal Loss Factors are applied to price setting and settlement o Adjusted settlement price for the Base-load (Nuclear, Coal) Energy • Settlement prices of baseload power plants are negotiated with parties, based on the advice of an independent committee to protect Korean electricity consumers q Ancillary Services Payment o Regulation reserve services are compensated for their contribution q Capacity Payment o To further refine the signal, the payment amount is weighted to reflect the value of capacity across the year and the locations o Locational(Seoul Metropolitan/ Non-Metropolitan/ Jeju-island) and seasonal (Peak/Medium/Off-peak) reserve requirements are applied 22
Recent Changes in Market Settlement q Energy Payment o Marginal Loss Factors are applied to price setting and settlement o Adjusted settlement price for the Base-load (Nuclear, Coal) Energy • Settlement prices of baseload power plants are negotiated with parties, based on the advice of an independent committee to protect Korean electricity consumers q Ancillary Services Payment o Regulation reserve services are compensated for their contribution q Capacity Payment o To further refine the signal, the payment amount is weighted to reflect the value of capacity across the year and the locations o Locational(Seoul Metropolitan/ Non-Metropolitan/ Jeju-island) and seasonal (Peak/Medium/Off-peak) reserve requirements are applied 22
 Issues to be challenged in the future q Introducing bilateral contracts in Energy Market • Bilateral purchasing agreements between the generating companies and KEPCO(Vesting Contract, Off-Take Contract) q Zonal Pricing in Energy Market q Ex-post pricing for real-time market • Multi-settlement with Day-ahead market and real-time only q Ancillary Service settlement • By Whom and how much should AS payment be paid? q Real time cost offer or/and limited price bidding q Forward Capacity Market 23
Issues to be challenged in the future q Introducing bilateral contracts in Energy Market • Bilateral purchasing agreements between the generating companies and KEPCO(Vesting Contract, Off-Take Contract) q Zonal Pricing in Energy Market q Ex-post pricing for real-time market • Multi-settlement with Day-ahead market and real-time only q Ancillary Service settlement • By Whom and how much should AS payment be paid? q Real time cost offer or/and limited price bidding q Forward Capacity Market 23
 Thank You! Byung Kyo Choi Tel: 82 -2 -3456 -6504, choibk@kpx. or. kr
Thank You! Byung Kyo Choi Tel: 82 -2 -3456 -6504, choibk@kpx. or. kr


