000e3e025a6e4f2715afcd34f724b836.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 2007 -04 -12 Views on future wireless access from a Nordic and Baltic perspective Fredrik Florén Mobility Services Access Services & Technology
2007 -04 -12 Views on future wireless access from a Nordic and Baltic perspective Fredrik Florén Mobility Services Access Services & Technology
 Outline • • 2 Telia. Sonera Quick Guide Service Trends Emerging Technologies Heterogeneous Access Deploying a New Access Flat Rate and Qo. S Summary 2007 -04 -12
Outline • • 2 Telia. Sonera Quick Guide Service Trends Emerging Technologies Heterogeneous Access Deploying a New Access Flat Rate and Qo. S Summary 2007 -04 -12
 Telia. Sonera Quick Guide • • 3 Telia. Sonera is the leading telecommunications company in the Nordic and Baltic region Holds strong positions in mobile communications in Eurasia, Turkey and Russia. At the end of 2006 Telia. Sonera launched mobile services in Spain. 30. 2 million subscriptions, plus 65. 9 in associated companies 2007 -04 -12
Telia. Sonera Quick Guide • • 3 Telia. Sonera is the leading telecommunications company in the Nordic and Baltic region Holds strong positions in mobile communications in Eurasia, Turkey and Russia. At the end of 2006 Telia. Sonera launched mobile services in Spain. 30. 2 million subscriptions, plus 65. 9 in associated companies 2007 -04 -12
 2007 -04 -12 Service Trends
2007 -04 -12 Service Trends
 Service Trends • • • 5 More Talk - Voice will remain the killer application - Migration to mobile voice continues Information & Entertainment - Adapted and personalized content - Music downloads, TV, games, gambling, messaging, email - Access and manage your personal content from anywhere - Positioning Opportunity Driven Services (context) - Advertising on mobiles. Loyalty Programs. Benefits. Content paid with ad’s/banners - Context triggered services, e. g. , pushed offers/advertising from favorite stores when passing by. - User acceptance 2007 -04 -12
Service Trends • • • 5 More Talk - Voice will remain the killer application - Migration to mobile voice continues Information & Entertainment - Adapted and personalized content - Music downloads, TV, games, gambling, messaging, email - Access and manage your personal content from anywhere - Positioning Opportunity Driven Services (context) - Advertising on mobiles. Loyalty Programs. Benefits. Content paid with ad’s/banners - Context triggered services, e. g. , pushed offers/advertising from favorite stores when passing by. - User acceptance 2007 -04 -12
 Service Trends • • • 6 User Generated Services and Content - User creation and sharing (user generated content) - Chat forums, instant messaging, mobile TV The Mobile - Your Daily Companion - Mobile Identification, mobile wallet and “safebox” - Common calenders and location - Security – check home, summer house, boat Always best connected - Simplicity - High-speed Internet access (e. g. to the office) on the move, any where, any time - Best experience (automatic service and access configuration and best available access) - Content and services are created and adapted to the mobile channel and user preferences 2007 -04 -12
Service Trends • • • 6 User Generated Services and Content - User creation and sharing (user generated content) - Chat forums, instant messaging, mobile TV The Mobile - Your Daily Companion - Mobile Identification, mobile wallet and “safebox” - Common calenders and location - Security – check home, summer house, boat Always best connected - Simplicity - High-speed Internet access (e. g. to the office) on the move, any where, any time - Best experience (automatic service and access configuration and best available access) - Content and services are created and adapted to the mobile channel and user preferences 2007 -04 -12
 Data Traffic Trends • • • Data traffic volume increased (Sweden) - 300% during 2005 - 400% during 2006 - Large part over 3 G network SMS (Sweden) - 17 million during New Year’s weekend - 7. 2 million on Valentine’s day By 2020, ~2 -3 x existing spectrum will be required [1] ITU-R Report M. 2078 7 2007 -04 -12
Data Traffic Trends • • • Data traffic volume increased (Sweden) - 300% during 2005 - 400% during 2006 - Large part over 3 G network SMS (Sweden) - 17 million during New Year’s weekend - 7. 2 million on Valentine’s day By 2020, ~2 -3 x existing spectrum will be required [1] ITU-R Report M. 2078 7 2007 -04 -12
 2007 -04 -12 Emerging Technologies
2007 -04 -12 Emerging Technologies
 GERAN Evolution • • 9 Downlink - Dual carrier - Recieve diversity - Increased symbol rate - Higher order modulation - Turbo coding Uplink - Increased symbol rate - Higher order modulation - Turbo coding Latency improvements Duplex terminals 2007 -04 -12
GERAN Evolution • • 9 Downlink - Dual carrier - Recieve diversity - Increased symbol rate - Higher order modulation - Turbo coding Uplink - Increased symbol rate - Higher order modulation - Turbo coding Latency improvements Duplex terminals 2007 -04 -12
 HSPA Evolution • • 10 HSPA - HSDPA - HSUPA Receive Diversity Equalizer + Receive Diversity Enhanced packet data experience MIMO Higher-order modulation MBMS 2007 -04 -12
HSPA Evolution • • 10 HSPA - HSDPA - HSUPA Receive Diversity Equalizer + Receive Diversity Enhanced packet data experience MIMO Higher-order modulation MBMS 2007 -04 -12
 LTE • • • LTE spurred by - Wi. MAX mobile standard and poor PS performance of UMTS R 99 Low-latency, High data rate, Packet optimized Flexible bandwidth Possibility to use both existing and new frequency bands Reduced production cost Simplified architecture Mobility - Optimized for low speeds - Mobility up to 250 km/h Coverage - Focus on cell ranges up to 5 km - Up to 100 km should be possible Low complexity MBMS Ref: 3 GPP TR 25. 913, “Requirements for Evolved UTRA (E-UTRA) and Evolved UTRAN (E-UTRAN)” 11 2007 -04 -12
LTE • • • LTE spurred by - Wi. MAX mobile standard and poor PS performance of UMTS R 99 Low-latency, High data rate, Packet optimized Flexible bandwidth Possibility to use both existing and new frequency bands Reduced production cost Simplified architecture Mobility - Optimized for low speeds - Mobility up to 250 km/h Coverage - Focus on cell ranges up to 5 km - Up to 100 km should be possible Low complexity MBMS Ref: 3 GPP TR 25. 913, “Requirements for Evolved UTRA (E-UTRA) and Evolved UTRAN (E-UTRAN)” 11 2007 -04 -12
 LTE, cont’d • • • 12 OFDM(A)/SC-FDMA MIMO is baseline Requirements - 100 Mbps in DL, 50 Mbps in UL - 3 -4/2 -3 times DL/UL system capacity Rel-6 - 2 -3 times DL/UL Rel-6 user rates ”at cell border” Sites reused Requirements fulfilled? - Antenna configuration - HSPA enhancements - Choice of channel model Performance difference for LTE and HSPA Evolution? 2007 -04 -12
LTE, cont’d • • • 12 OFDM(A)/SC-FDMA MIMO is baseline Requirements - 100 Mbps in DL, 50 Mbps in UL - 3 -4/2 -3 times DL/UL system capacity Rel-6 - 2 -3 times DL/UL Rel-6 user rates ”at cell border” Sites reused Requirements fulfilled? - Antenna configuration - HSPA enhancements - Choice of channel model Performance difference for LTE and HSPA Evolution? 2007 -04 -12
 Mobile Wi. MAX • • • 13 Packet based, IP only OFDM(A) MIMO Peak rates (10 MHz) - 63 Mbps/23 Mbps in DL/UL Flexible bandwidth - First release: 5, 7, 8. 75, 10 MHz Deployable in multiple bands Mobility MBMS Qo. S support - Vo. IP, Streaming, Best effort TDD initially Standalone mode (c. f. , WLAN) 2007 -04 -12
Mobile Wi. MAX • • • 13 Packet based, IP only OFDM(A) MIMO Peak rates (10 MHz) - 63 Mbps/23 Mbps in DL/UL Flexible bandwidth - First release: 5, 7, 8. 75, 10 MHz Deployable in multiple bands Mobility MBMS Qo. S support - Vo. IP, Streaming, Best effort TDD initially Standalone mode (c. f. , WLAN) 2007 -04 -12
 802. 11 WLANs • • • 14 11 k Radio Resource Measurements 11 n High Throughput - 600 Mbps peak rate on 40 MHz channel - 11 n will deliver approximately 25 Mbps (peak 11 a data rate) on 55 meters distance from the AP in an office environment 11 r Fast BSS Transition 11 u Interworking with external networks 11 v Wireless Network Management 11 w Protected Management Frames 2007 -04 -12
802. 11 WLANs • • • 14 11 k Radio Resource Measurements 11 n High Throughput - 600 Mbps peak rate on 40 MHz channel - 11 n will deliver approximately 25 Mbps (peak 11 a data rate) on 55 meters distance from the AP in an office environment 11 r Fast BSS Transition 11 u Interworking with external networks 11 v Wireless Network Management 11 w Protected Management Frames 2007 -04 -12
 2007 -04 -12 Heterogeneous Access
2007 -04 -12 Heterogeneous Access
 Scenarios and Accesses • • • 16 Walk & Talk - GSM - LTE - Wi. MAX Sit & Work - WLAN - HSPA Evolution - LTE - Wi. MAX Stroll & Surf / Ride & Surf - EDGE/GERAN Evolution - HSPA Evolution - LTE - Wi. MAX - (DVB-h) 2007 -04 -12 • Stroll & Surf / Ride & Surf seem to be the main areas for mobile evolution • Both coverage and capacity required at reasonable cost Many (legacy) mobile and wireless systems will coexist Some accesses do the same thing Can one access do it all? • • •
Scenarios and Accesses • • • 16 Walk & Talk - GSM - LTE - Wi. MAX Sit & Work - WLAN - HSPA Evolution - LTE - Wi. MAX Stroll & Surf / Ride & Surf - EDGE/GERAN Evolution - HSPA Evolution - LTE - Wi. MAX - (DVB-h) 2007 -04 -12 • Stroll & Surf / Ride & Surf seem to be the main areas for mobile evolution • Both coverage and capacity required at reasonable cost Many (legacy) mobile and wireless systems will coexist Some accesses do the same thing Can one access do it all? • • •
 The radio pizza: Using heterogeneous access • Full taste to low cost – Optimise for coverage and capacity – Bread: IP core – Tomato: GSM – Cheese: GPRS – Salami: EDGE – Bacon: UMTS – Peppers: HSPA – Oregano: WLAN – Olives: Wi. MAX? – Onions: LTE? 17 2007 -04 -12 Combination of ingredients most important!
The radio pizza: Using heterogeneous access • Full taste to low cost – Optimise for coverage and capacity – Bread: IP core – Tomato: GSM – Cheese: GPRS – Salami: EDGE – Bacon: UMTS – Peppers: HSPA – Oregano: WLAN – Olives: Wi. MAX? – Onions: LTE? 17 2007 -04 -12 Combination of ingredients most important!
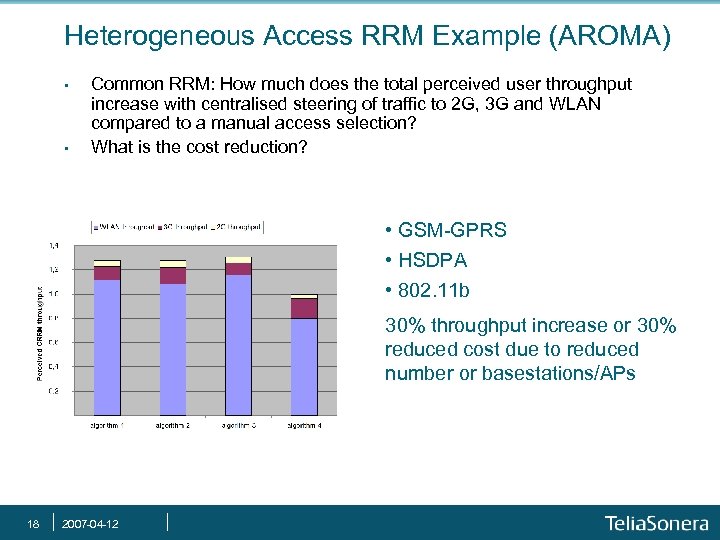 Heterogeneous Access RRM Example (AROMA) • • Common RRM: How much does the total perceived user throughput increase with centralised steering of traffic to 2 G, 3 G and WLAN compared to a manual access selection? What is the cost reduction? • GSM-GPRS • HSDPA • 802. 11 b 30% throughput increase or 30% reduced cost due to reduced number or basestations/APs 18 2007 -04 -12
Heterogeneous Access RRM Example (AROMA) • • Common RRM: How much does the total perceived user throughput increase with centralised steering of traffic to 2 G, 3 G and WLAN compared to a manual access selection? What is the cost reduction? • GSM-GPRS • HSDPA • 802. 11 b 30% throughput increase or 30% reduced cost due to reduced number or basestations/APs 18 2007 -04 -12
 Terminals • • 19 Many technologies will be available for multimode terminals - A few terminals may still be “all included”, but in general access technology support is based on the terminal category Walk & talk - Speech oriented technologies with additional data capabilities - GSM/GPRS/EDGE 5 -50 MB/month - UMTS/HSPA Stroll & surf - Data oriented technologies with additional speech capabilities - UMTS/HSPA 25 -250 MB/month - LTE - Wi. MAX Sit & work - Data only - HSPA - Wi. MAX 100 -1000 MB/month - LTE - WLAN 2007 -04 -12
Terminals • • 19 Many technologies will be available for multimode terminals - A few terminals may still be “all included”, but in general access technology support is based on the terminal category Walk & talk - Speech oriented technologies with additional data capabilities - GSM/GPRS/EDGE 5 -50 MB/month - UMTS/HSPA Stroll & surf - Data oriented technologies with additional speech capabilities - UMTS/HSPA 25 -250 MB/month - LTE - Wi. MAX Sit & work - Data only - HSPA - Wi. MAX 100 -1000 MB/month - LTE - WLAN 2007 -04 -12
 2007 -04 -12 Deploying a New Access
2007 -04 -12 Deploying a New Access
 A New System Should… • • • 21 Offer migration path by reuse of parts of the current infrastructure Support interworking with existing 3 G systems and non-3 GPP systems Support network sharing Offer migration to new architecture and co-existence with WCDMA radio Provide reduced OPEX - Avoid backhaul bottlenecks for high data rates - Robust operation and maintenance … and terminals must be available 2007 -04 -12
A New System Should… • • • 21 Offer migration path by reuse of parts of the current infrastructure Support interworking with existing 3 G systems and non-3 GPP systems Support network sharing Offer migration to new architecture and co-existence with WCDMA radio Provide reduced OPEX - Avoid backhaul bottlenecks for high data rates - Robust operation and maintenance … and terminals must be available 2007 -04 -12
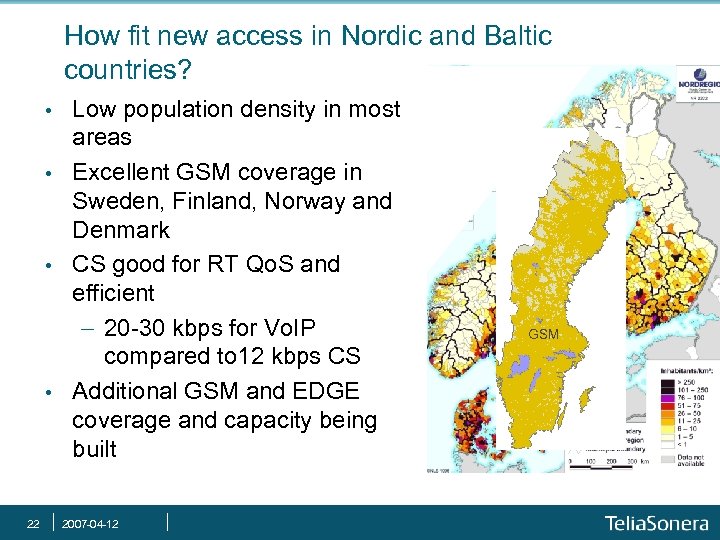 How fit new access in Nordic and Baltic countries? • • 22 Low population density in most areas Excellent GSM coverage in Sweden, Finland, Norway and Denmark CS good for RT Qo. S and efficient - 20 -30 kbps for Vo. IP compared to 12 kbps CS Additional GSM and EDGE coverage and capacity being built 2007 -04 -12 GSM
How fit new access in Nordic and Baltic countries? • • 22 Low population density in most areas Excellent GSM coverage in Sweden, Finland, Norway and Denmark CS good for RT Qo. S and efficient - 20 -30 kbps for Vo. IP compared to 12 kbps CS Additional GSM and EDGE coverage and capacity being built 2007 -04 -12 GSM
 How fit new access in Nordic and Baltic countries? • UMTS also good coverage - Large early investements due to licence - HSx. PA upgrades cost efficient • Telia. Sonera Home. Run WLAN complement for nomadic high data rate - Short range data/desktop use - WLAN cheap and available in all lap tops - WLANs continue to evolve • High fixed broadband penetration, typically around 50% Very high Internet usage and penetration; > 85% • 23 2007 -04 -12
How fit new access in Nordic and Baltic countries? • UMTS also good coverage - Large early investements due to licence - HSx. PA upgrades cost efficient • Telia. Sonera Home. Run WLAN complement for nomadic high data rate - Short range data/desktop use - WLAN cheap and available in all lap tops - WLANs continue to evolve • High fixed broadband penetration, typically around 50% Very high Internet usage and penetration; > 85% • 23 2007 -04 -12
 Risks with one size fits all • • • 24 Different requirements - Rural coverage, urban capacity, full mobility or nomadic usage - ”Half-good” at everything Basic requirements major cost driver - Terminal and base station output power - Signal processing Terminals will be late - Terminal availability crucial to success of system 2007 -04 -12
Risks with one size fits all • • • 24 Different requirements - Rural coverage, urban capacity, full mobility or nomadic usage - ”Half-good” at everything Basic requirements major cost driver - Terminal and base station output power - Signal processing Terminals will be late - Terminal availability crucial to success of system 2007 -04 -12
 Where to use a new access? • • 25 2. 6 GHz band - Licenses soon to be allocated - IMT-2000 - Technology neutrality 3. 4 -3. 6 GHz band - Used for FWA in many European countries - Technology neutrality - Fixed Wi. MAX network in Sweden (3. 5 GHz) 3. 6 -3. 8 GHz band - Used for FWA in some European countries - Licenses soon to be allocated in Sweden - Technology neutrality IMT-2000 Advanced - 400 MHz – 5 GHz 2007 -04 -12
Where to use a new access? • • 25 2. 6 GHz band - Licenses soon to be allocated - IMT-2000 - Technology neutrality 3. 4 -3. 6 GHz band - Used for FWA in many European countries - Technology neutrality - Fixed Wi. MAX network in Sweden (3. 5 GHz) 3. 6 -3. 8 GHz band - Used for FWA in some European countries - Licenses soon to be allocated in Sweden - Technology neutrality IMT-2000 Advanced - 400 MHz – 5 GHz 2007 -04 -12
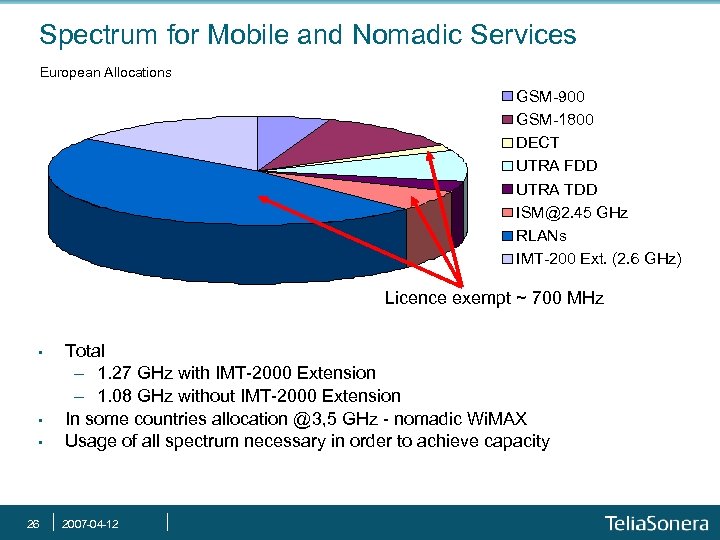 Spectrum for Mobile and Nomadic Services European Allocations GSM-900 GSM-1800 DECT UTRA FDD UTRA TDD ISM@2. 45 GHz RLANs IMT-200 Ext. (2. 6 GHz) Licence exempt ~ 700 MHz • • • 26 Total - 1. 27 GHz with IMT-2000 Extension - 1. 08 GHz without IMT-2000 Extension In some countries allocation @3, 5 GHz - nomadic Wi. MAX Usage of all spectrum necessary in order to achieve capacity 2007 -04 -12
Spectrum for Mobile and Nomadic Services European Allocations GSM-900 GSM-1800 DECT UTRA FDD UTRA TDD ISM@2. 45 GHz RLANs IMT-200 Ext. (2. 6 GHz) Licence exempt ~ 700 MHz • • • 26 Total - 1. 27 GHz with IMT-2000 Extension - 1. 08 GHz without IMT-2000 Extension In some countries allocation @3, 5 GHz - nomadic Wi. MAX Usage of all spectrum necessary in order to achieve capacity 2007 -04 -12
 2007 -04 -12 Flat Rate & Qo. S
2007 -04 -12 Flat Rate & Qo. S
 Flat rate and Qo. S • • Customers want flat rate Throughput varies significantly over cell What happens when capacity becomes limitation? How to charge without guaranteeing throughput? - Throughput guarantees - Different categories of users - Business vs. Private user • Services might rely on minimum throughput • Throughput guarantees needed Scheduler becomes increasingly important • 28 2007 -04 -12
Flat rate and Qo. S • • Customers want flat rate Throughput varies significantly over cell What happens when capacity becomes limitation? How to charge without guaranteeing throughput? - Throughput guarantees - Different categories of users - Business vs. Private user • Services might rely on minimum throughput • Throughput guarantees needed Scheduler becomes increasingly important • 28 2007 -04 -12
 Summary • • • 29 New services: ”Save time. Kill time” Demand for mobile data traffic shows strong increase New accesses and enhancements on the way Many accesses will co-exist Heterogeneous access is a cost-efficient way to achieve both coverage and capacity 2007 -04 -12
Summary • • • 29 New services: ”Save time. Kill time” Demand for mobile data traffic shows strong increase New accesses and enhancements on the way Many accesses will co-exist Heterogeneous access is a cost-efficient way to achieve both coverage and capacity 2007 -04 -12
 30 2007 -04 -12
30 2007 -04 -12
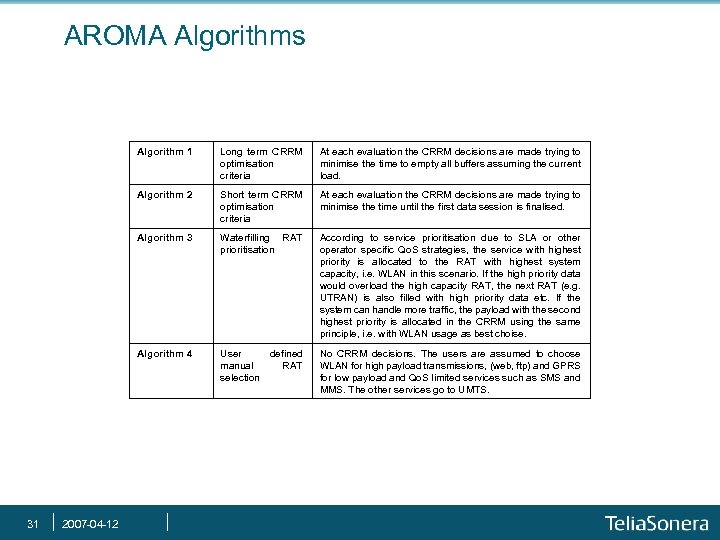 AROMA Algorithms Algorithm 1 Short term CRRM optimisation criteria At each evaluation the CRRM decisions are made trying to minimise the time until the first data session is finalised. Algorithm 3 Waterfilling RAT prioritisation According to service prioritisation due to SLA or other operator specific Qo. S strategies, the service with highest priority is allocated to the RAT with highest system capacity, i. e. WLAN in this scenario. If the high priority data would overload the high capacity RAT, the next RAT (e. g. UTRAN) is also filled with high priority data etc. If the system can handle more traffic, the payload with the second highest priority is allocated in the CRRM using the same principle, i. e. with WLAN usage as best choise. Algorithm 4 2007 -04 -12 At each evaluation the CRRM decisions are made trying to minimise the time to empty all buffers assuming the current load. Algorithm 2 31 Long term CRRM optimisation criteria User manual selection No CRRM decisions. The users are assumed to choose WLAN for high payload transmissions, (web, ftp) and GPRS for low payload and Qo. S limited services such as SMS and MMS. The other services go to UMTS. defined RAT
AROMA Algorithms Algorithm 1 Short term CRRM optimisation criteria At each evaluation the CRRM decisions are made trying to minimise the time until the first data session is finalised. Algorithm 3 Waterfilling RAT prioritisation According to service prioritisation due to SLA or other operator specific Qo. S strategies, the service with highest priority is allocated to the RAT with highest system capacity, i. e. WLAN in this scenario. If the high priority data would overload the high capacity RAT, the next RAT (e. g. UTRAN) is also filled with high priority data etc. If the system can handle more traffic, the payload with the second highest priority is allocated in the CRRM using the same principle, i. e. with WLAN usage as best choise. Algorithm 4 2007 -04 -12 At each evaluation the CRRM decisions are made trying to minimise the time to empty all buffers assuming the current load. Algorithm 2 31 Long term CRRM optimisation criteria User manual selection No CRRM decisions. The users are assumed to choose WLAN for high payload transmissions, (web, ftp) and GPRS for low payload and Qo. S limited services such as SMS and MMS. The other services go to UMTS. defined RAT


