03a056ba842073e8e3a69847422d2da3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 2004 Developments in Aviation Forecast Guidance from the RUC Stan Benjamin Steve Weygandt NOAA / Forecast Systems Lab http: //ruc. fsl. noaa. gov NY Courtesy: ADDS/AWC/NOAA
2004 Developments in Aviation Forecast Guidance from the RUC Stan Benjamin Steve Weygandt NOAA / Forecast Systems Lab http: //ruc. fsl. noaa. gov NY Courtesy: ADDS/AWC/NOAA
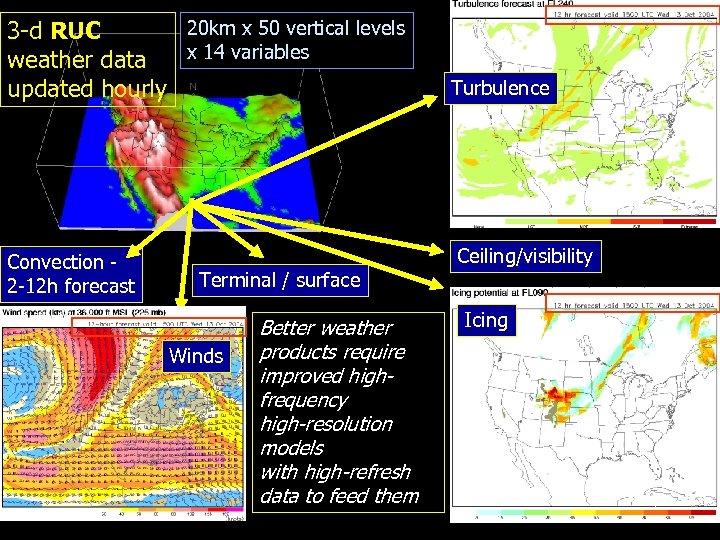 20 km x 50 vertical levels 3 -d RUC x 14 variables weather data updated hourly Convection 2 -12 h forecast Terminal / surface Winds Better weather products require improved highfrequency high-resolution models with high-refresh data to feed them Turbulence Ceiling/visibility Icing 2
20 km x 50 vertical levels 3 -d RUC x 14 variables weather data updated hourly Convection 2 -12 h forecast Terminal / surface Winds Better weather products require improved highfrequency high-resolution models with high-refresh data to feed them Turbulence Ceiling/visibility Icing 2
 RUC changes Impact on convection, ceiling/vis forecasts for aviation 2004 - 20 km RUC implementations completed – • April – RUC model - vertical advection of moisture better precip and clouds. More detailed land use/coastline. • September – RUC analysis – use boundary-layer depth in assimilation of surface/METAR obs better temp/dewpoint/CAPE/convection forecasts 2005 - 13 km RUC implementation planned • Real-time testing since spring (see http: //ruc. fsl. noaa. gov) 3
RUC changes Impact on convection, ceiling/vis forecasts for aviation 2004 - 20 km RUC implementations completed – • April – RUC model - vertical advection of moisture better precip and clouds. More detailed land use/coastline. • September – RUC analysis – use boundary-layer depth in assimilation of surface/METAR obs better temp/dewpoint/CAPE/convection forecasts 2005 - 13 km RUC implementation planned • Real-time testing since spring (see http: //ruc. fsl. noaa. gov) 3
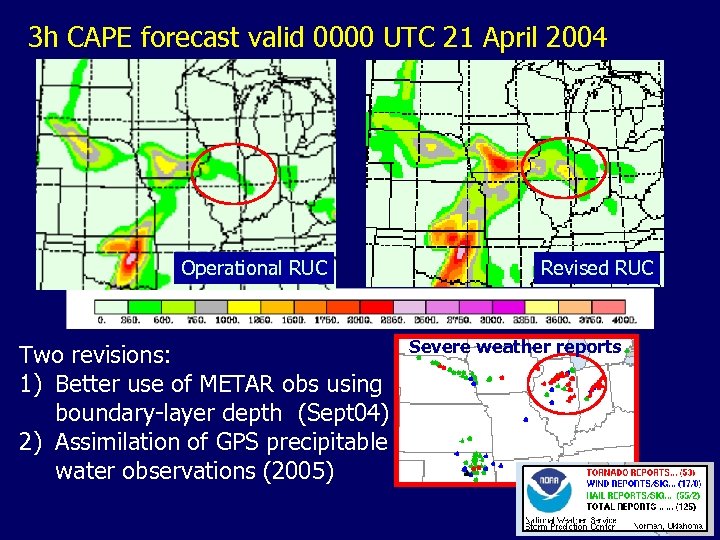 3 h CAPE forecast valid 0000 UTC 21 April 2004 Operational RUC Two revisions: 1) Better use of METAR obs using boundary-layer depth (Sept 04) 2) Assimilation of GPS precipitable water observations (2005) Revised RUC Severe weather reports 4
3 h CAPE forecast valid 0000 UTC 21 April 2004 Operational RUC Two revisions: 1) Better use of METAR obs using boundary-layer depth (Sept 04) 2) Assimilation of GPS precipitable water observations (2005) Revised RUC Severe weather reports 4
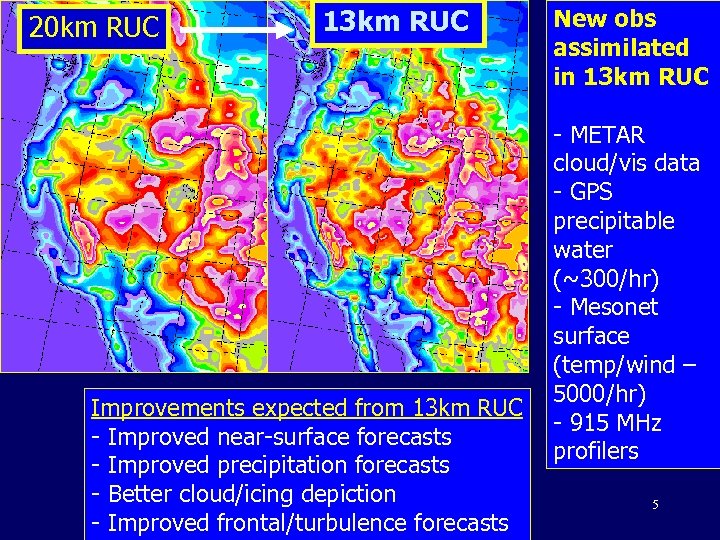 20 km RUC 13 km RUC Improvements expected from 13 km RUC - Improved near-surface forecasts - Improved precipitation forecasts - Better cloud/icing depiction - Improved frontal/turbulence forecasts New obs assimilated in 13 km RUC - METAR cloud/vis data - GPS precipitable water (~300/hr) - Mesonet surface (temp/wind – 5000/hr) - 915 MHz profilers 5
20 km RUC 13 km RUC Improvements expected from 13 km RUC - Improved near-surface forecasts - Improved precipitation forecasts - Better cloud/icing depiction - Improved frontal/turbulence forecasts New obs assimilated in 13 km RUC - METAR cloud/vis data - GPS precipitable water (~300/hr) - Mesonet surface (temp/wind – 5000/hr) - 915 MHz profilers 5
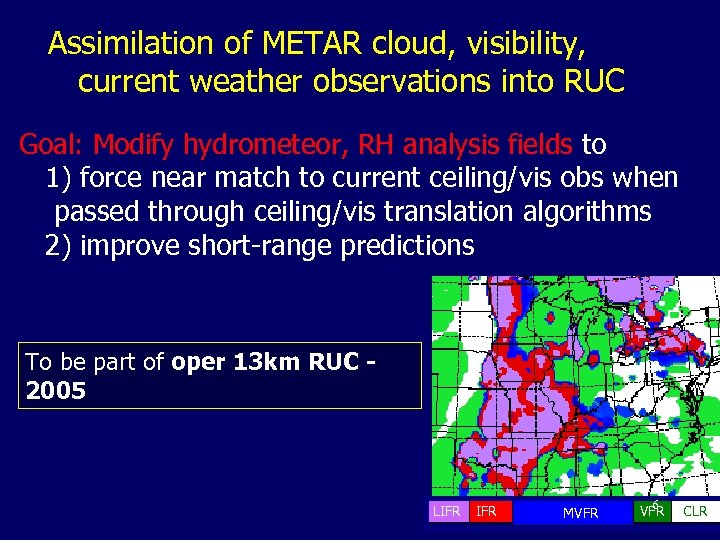 Assimilation of METAR cloud, visibility, current weather observations into RUC Goal: Modify hydrometeor, RH analysis fields to 1) force near match to current ceiling/vis obs when passed through ceiling/vis translation algorithms 2) improve short-range predictions To be part of oper 13 km RUC 2005 LIFR MVFR 6 VFR CLR
Assimilation of METAR cloud, visibility, current weather observations into RUC Goal: Modify hydrometeor, RH analysis fields to 1) force near match to current ceiling/vis obs when passed through ceiling/vis translation algorithms 2) improve short-range predictions To be part of oper 13 km RUC 2005 LIFR MVFR 6 VFR CLR
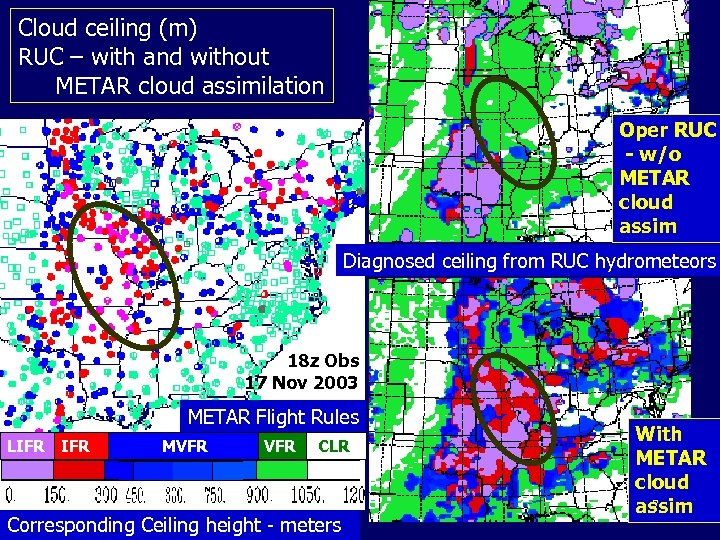 Cloud ceiling (m) RUC – with and without METAR cloud assimilation Oper RUC - w/o METAR cloud assim Diagnosed ceiling from RUC hydrometeors 18 z Obs 17 Nov 2003 METAR Flight Rules LIFR MVFR CLR Corresponding Ceiling height - meters With METAR cloud 7 assim
Cloud ceiling (m) RUC – with and without METAR cloud assimilation Oper RUC - w/o METAR cloud assim Diagnosed ceiling from RUC hydrometeors 18 z Obs 17 Nov 2003 METAR Flight Rules LIFR MVFR CLR Corresponding Ceiling height - meters With METAR cloud 7 assim
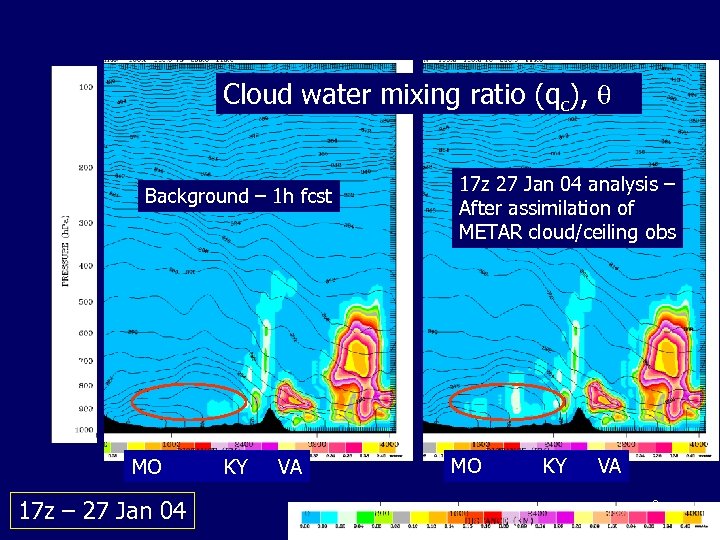 Cloud water mixing ratio (qc), Background – 1 h fcst MO 17 z – 27 Jan 04 KY VA 17 z 27 Jan 04 analysis – After assimilation of METAR cloud/ceiling obs MO KY VA 8
Cloud water mixing ratio (qc), Background – 1 h fcst MO 17 z – 27 Jan 04 KY VA 17 z 27 Jan 04 analysis – After assimilation of METAR cloud/ceiling obs MO KY VA 8
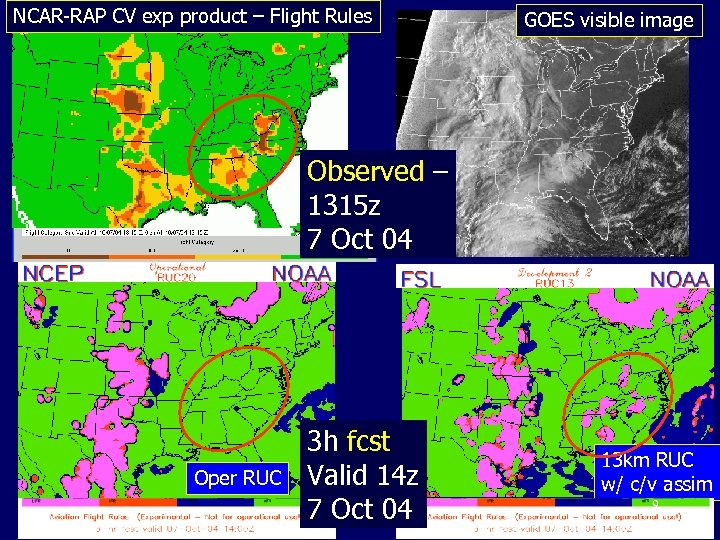 NCAR-RAP CV exp product – Flight Rules GOES visible image Observed – 1315 z 7 Oct 04 Oper RUC 3 h fcst Valid 14 z 7 Oct 04 13 km RUC w/ c/v assim 9
NCAR-RAP CV exp product – Flight Rules GOES visible image Observed – 1315 z 7 Oct 04 Oper RUC 3 h fcst Valid 14 z 7 Oct 04 13 km RUC w/ c/v assim 9
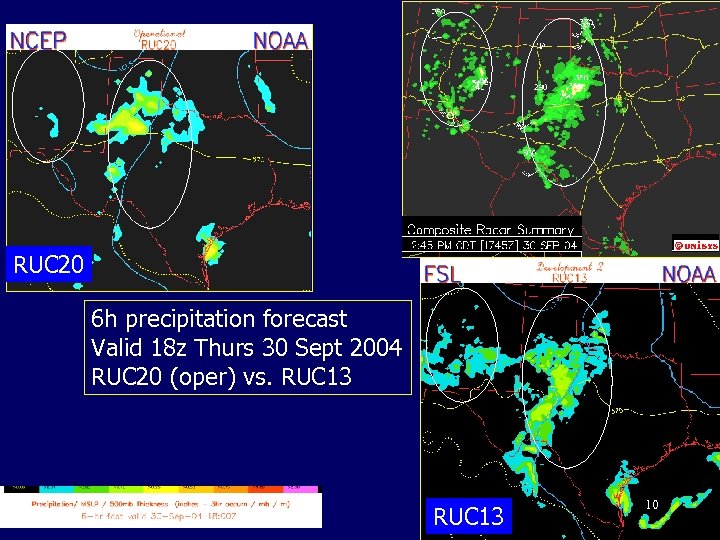 RUC 20 6 h precipitation forecast Valid 18 z Thurs 30 Sept 2004 RUC 20 (oper) vs. RUC 13 10
RUC 20 6 h precipitation forecast Valid 18 z Thurs 30 Sept 2004 RUC 20 (oper) vs. RUC 13 10
 RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF) • Ensemble-based thunderstorm likelihood product • • 2, 4, and 6 -h forecasts every two hours In-house testing 2003 and 2004 AWC evaluation planned for 2005 – use improved 13 km RUC EVENTUAL GOAL • Seamless 0 -6 h convective guidance product (ENCWF) • Guidance to forecasters, traffic flow managers, 11 automated decision support systems
RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF) • Ensemble-based thunderstorm likelihood product • • 2, 4, and 6 -h forecasts every two hours In-house testing 2003 and 2004 AWC evaluation planned for 2005 – use improved 13 km RUC EVENTUAL GOAL • Seamless 0 -6 h convective guidance product (ENCWF) • Guidance to forecasters, traffic flow managers, 11 automated decision support systems
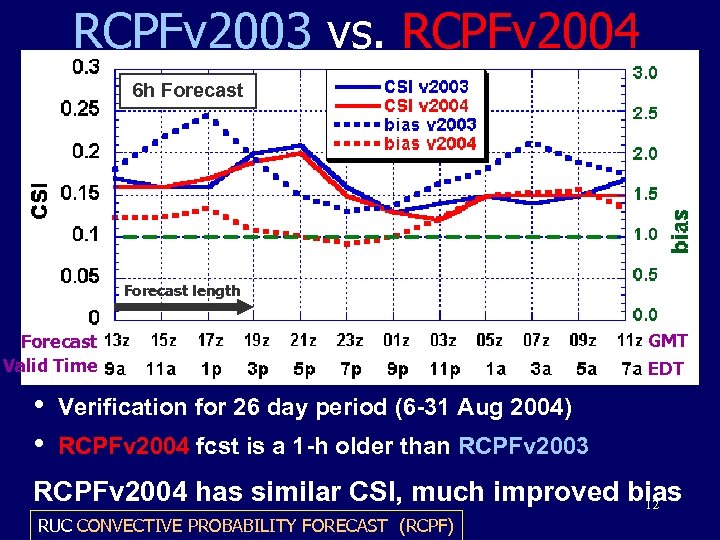 RCPFv 2003 vs. RCPFv 2004 6 h Forecast length Forecast Valid Time • • GMT EDT Verification for 26 day period (6 -31 Aug 2004) RCPFv 2004 fcst is a 1 -h older than RCPFv 2003 RCPFv 2004 has similar CSI, much improved bias 12 RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF)
RCPFv 2003 vs. RCPFv 2004 6 h Forecast length Forecast Valid Time • • GMT EDT Verification for 26 day period (6 -31 Aug 2004) RCPFv 2004 fcst is a 1 -h older than RCPFv 2003 RCPFv 2004 has similar CSI, much improved bias 12 RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF)
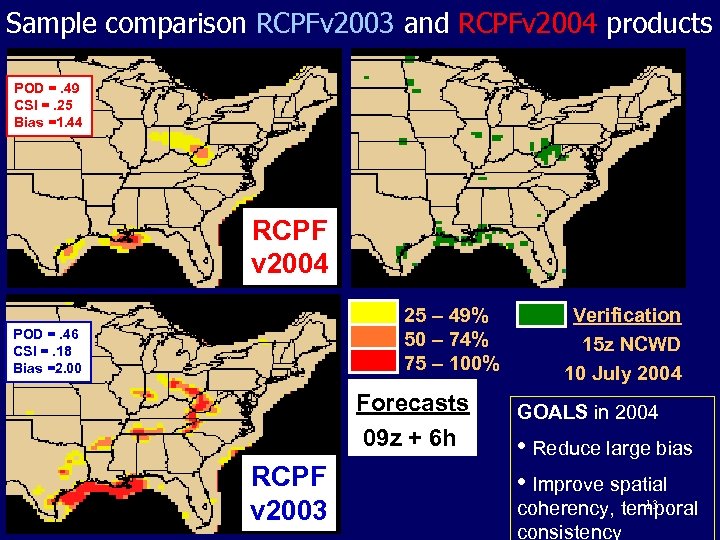 Sample comparison RCPFv 2003 and RCPFv 2004 products POD =. 49 CSI =. 25 Bias =1. 44 RCPF v 2004 25 – 49% 50 – 74% 75 – 100% POD =. 46 CSI =. 18 Bias =2. 00 Forecasts 09 z + 6 h RCPF v 2003 Verification 15 z NCWD 10 July 2004 GOALS in 2004 • Reduce large bias • Improve spatial 13 coherency, temporal consistency
Sample comparison RCPFv 2003 and RCPFv 2004 products POD =. 49 CSI =. 25 Bias =1. 44 RCPF v 2004 25 – 49% 50 – 74% 75 – 100% POD =. 46 CSI =. 18 Bias =2. 00 Forecasts 09 z + 6 h RCPF v 2003 Verification 15 z NCWD 10 July 2004 GOALS in 2004 • Reduce large bias • Improve spatial 13 coherency, temporal consistency
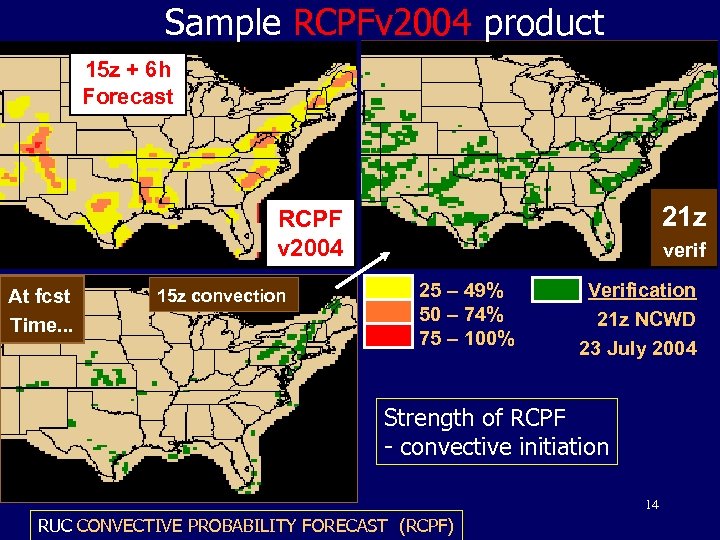 Sample RCPFv 2004 product 15 z + 6 h Forecast 21 z RCPF v 2004 At fcst Time. . . 15 z convection verif 25 – 49% 50 – 74% 75 – 100% Verification 21 z NCWD 23 July 2004 Strength of RCPF - convective initiation 14 RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF)
Sample RCPFv 2004 product 15 z + 6 h Forecast 21 z RCPF v 2004 At fcst Time. . . 15 z convection verif 25 – 49% 50 – 74% 75 – 100% Verification 21 z NCWD 23 July 2004 Strength of RCPF - convective initiation 14 RUC CONVECTIVE PROBABILITY FORECAST (RCPF)
 Backbone of improved aviation forecast products for winds, icing, turbulence, convection, TAFs = weather model forecasts updated at high frequency with latest observations Keys to improvement of RUC model aviation forecasts • Higher spatial resolution – better capture fine-scale weather hazards (13 km resolution) • Use new observations to initialize model – force more realism in model initial conditions (METAR ceil/vis obs, GPS moisture, mesonet) • Improved realism of physical processes in model – clouds, turbulence, land-surface (revised physics) 15
Backbone of improved aviation forecast products for winds, icing, turbulence, convection, TAFs = weather model forecasts updated at high frequency with latest observations Keys to improvement of RUC model aviation forecasts • Higher spatial resolution – better capture fine-scale weather hazards (13 km resolution) • Use new observations to initialize model – force more realism in model initial conditions (METAR ceil/vis obs, GPS moisture, mesonet) • Improved realism of physical processes in model – clouds, turbulence, land-surface (revised physics) 15


