8022d27a778b2ad56e0509c9b46372d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

2. WP 9 – Earth Observation Applications 1. Welcome and introduction (15 m) 2. WP 9 – Earth Observation Applications (50 m) 3. ESA and WP 9: infrastr, appl, TB 0/1 (50 m) 4. Demonstration of EO applications (45 m) 5. ESA and WP 9: scale up, effort, recovery plan (50 m) 6. Side ESA actions related to GRID (30 m) 7. Reviewer separate meeting (60 m) 8. Conclusions (30 m) ESA Data. Grid Review Frascati, 10 June 2002

Summary item 2 u WP 9 – Earth Observation Applications (50 m) n Data. Grid EO requirement (LF, 15 m) n Data. Grid WP 9 tasks, WP 9 Plan (JL, 15 m) ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 2
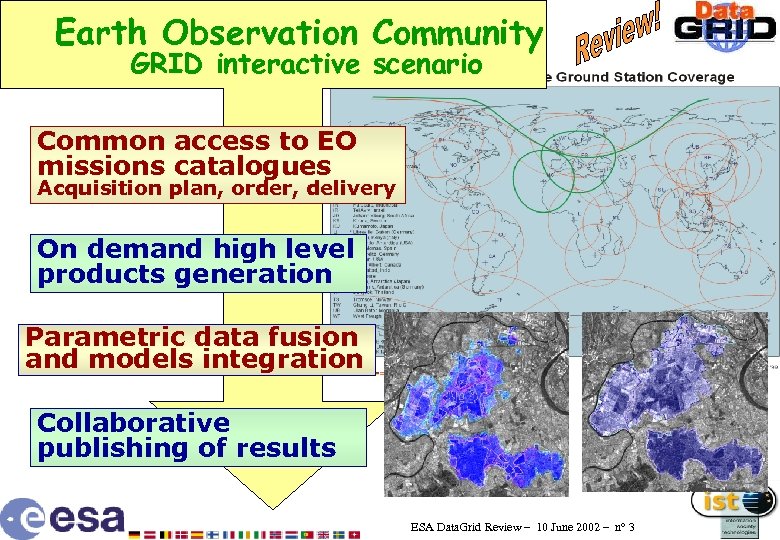
Earth Observation Community GRID interactive scenario Common access to EO missions catalogues Acquisition plan, order, delivery On demand high level products generation Parametric data fusion and models integration Collaborative publishing of results ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 3
EO and Network Computing data models: EO is more than “parallel task execution”!! u Distributed Computing n u High-Throughput Computing n u Generation of EO user products… Data-Intensive Computing n u Interferometry … On-Demand Computing n u Integration of data from various instruments and missions Archive data re-processing, climate modeling… Collaborative Computing n Ian Foster and Carl Kesselman, editors, “The Grid: Blueprint for a New Computing Infrastructure, ” Morgan Kaufmann, 1999 Scientists application interactions, Instrument cal/val … ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 4
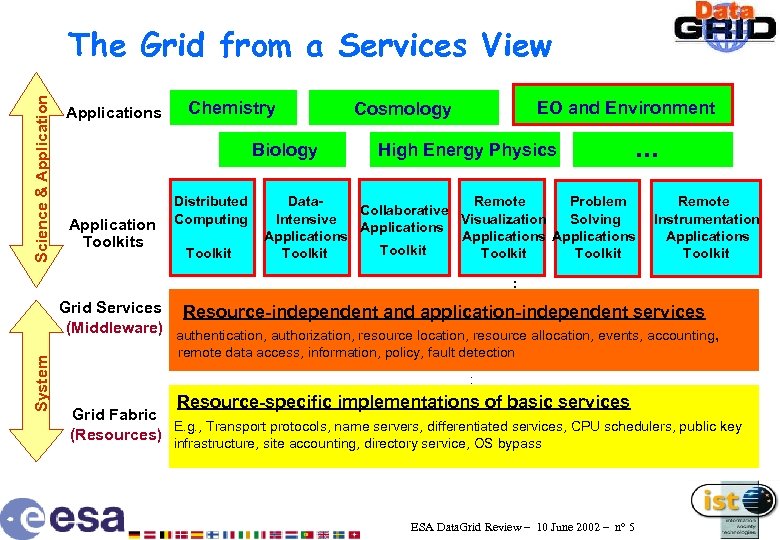
Science & Application The Grid from a Services View Applications Chemistry Biology Application Toolkits Distributed Computing Toolkit EO and Environment Cosmology High Energy Physics . . . Data. Remote Problem Collaborative Intensive Visualization Solving Applications Toolkit Remote Instrumentation Applications Toolkit : E. g. , System Grid Services Resource-independent and application-independent services (Middleware) authentication, authorization, resource location, resource allocation, events, accounting, remote data access, information, policy, fault detection : Resource-specific implementations of basic services Grid Fabric E. g. , Transport protocols, name servers, differentiated services, CPU schedulers, public key (Resources) infrastructure, site accounting, directory service, OS bypass ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 5
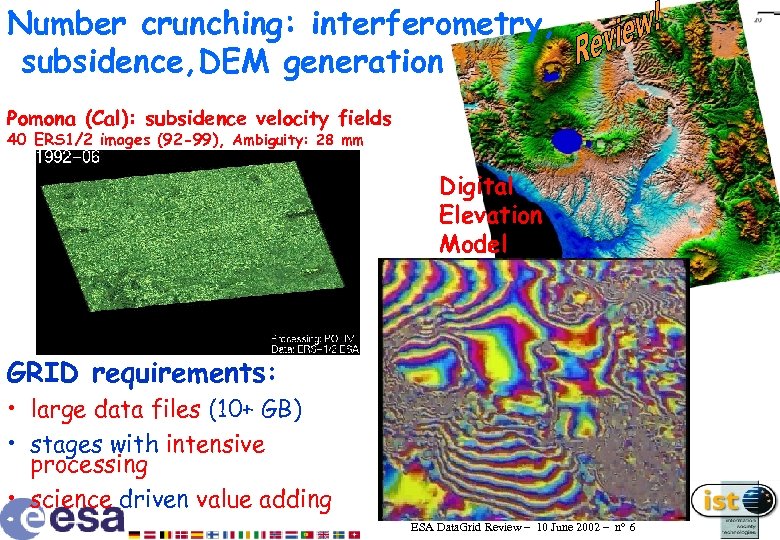
Number crunching: interferometry, subsidence, DEM generation Pomona (Cal): subsidence velocity fields 40 ERS 1/2 images (92 -99), Ambiguity: 28 mm Digital Elevation Model GRID requirements: • large data files (10+ GB) • stages with intensive processing • science driven value adding ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 6

Charter for Disaster Management • Provide a single access point to space systems to emergency & rescue organisations in case of disasters • Participating Space Agencies: CNES, CSA, ESA, ISRO, NOAA, … • Missions: RADARSAT; ERS, (Envisat); SPOT; IRS; NOAA, … ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 7
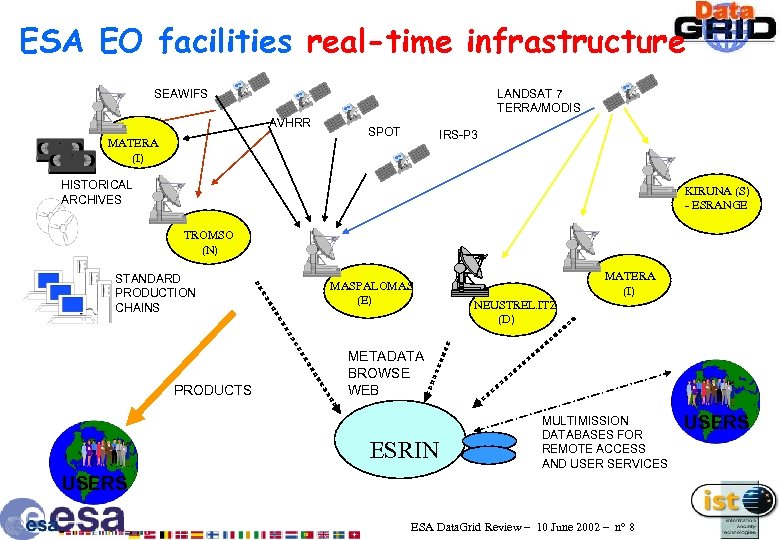
ESA EO facilities real-time infrastructure SEAWIFS LANDSAT 7 TERRA/MODIS AVHRR MATERA (I) SPOT IRS-P 3 HISTORICAL ARCHIVES KIRUNA (S) - ESRANGE TROMSO (N) STANDARD PRODUCTION CHAINS PRODUCTS MASPALOMAS (E) MATERA (I) NEUSTREL. ITZ (D) METADATA BROWSE WEB ESRIN MULTIMISSION DATABASES FOR REMOTE ACCESS AND USER SERVICES USERS ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 8 USERS
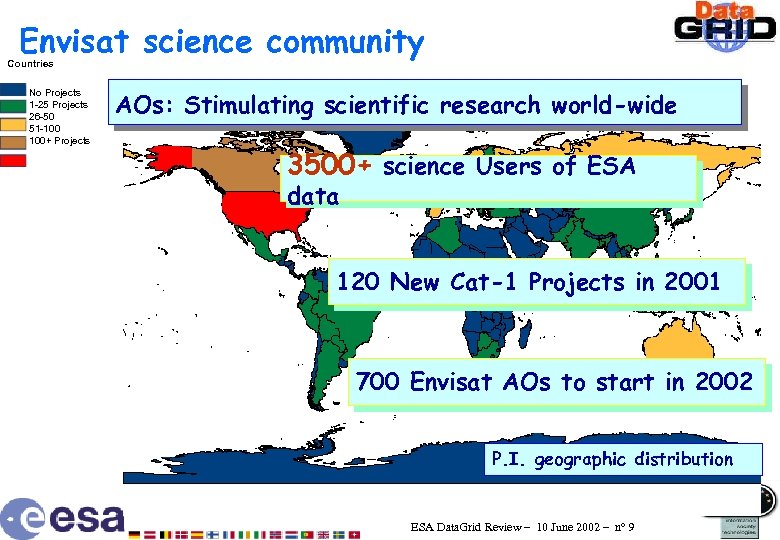
Envisat science community Countries No Projects 1 -25 Projects 26 -50 51 -100 100+ Projects AOs: Stimulating scientific research world-wide 3500+ science Users of ESA data 120 New Cat-1 Projects in 2001 700 Envisat AOs to start in 2002 P. I. geographic distribution ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 9
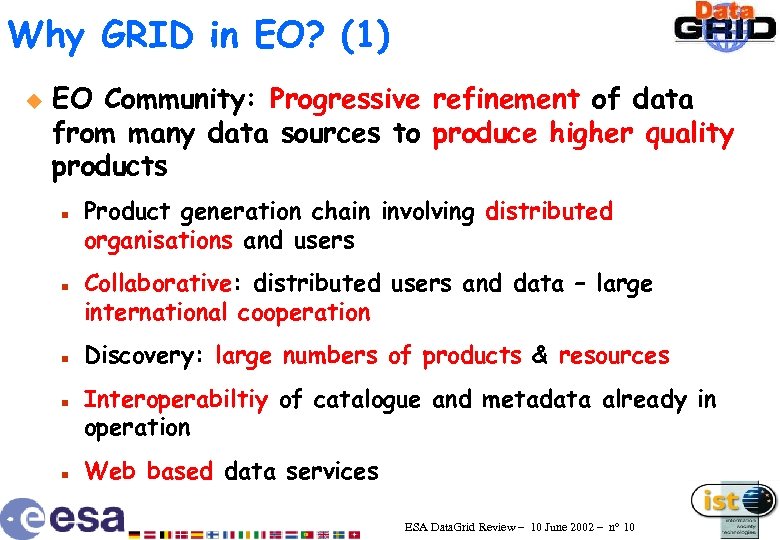
Why GRID in EO? (1) u EO Community: Progressive refinement of data from many data sources to produce higher quality products n n n Product generation chain involving distributed organisations and users Collaborative: distributed users and data – large international cooperation Discovery: large numbers of products & resources Interoperabiltiy of catalogue and metadata already in operation Web based data services ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 10
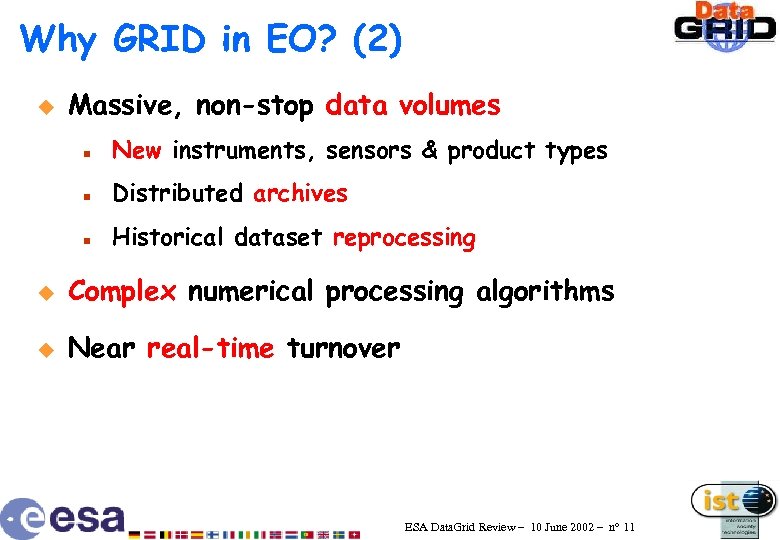
Why GRID in EO? (2) u Massive, non-stop data volumes n New instruments, sensors & product types n Distributed archives n Historical dataset reprocessing u Complex numerical processing algorithms u Near real-time turnover ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 11
Needed GRID technologies u Resource-independent and application-independent services (middleware) n n u u authentication, authorization, resource location, resource allocation, remote data access, accounting, security, quality of services, fault detection, real time services, … Specialized protocols, procedures, data standards, operational environments, interfaces to EO legacy systems… EO dedicated portal and user access… ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 12
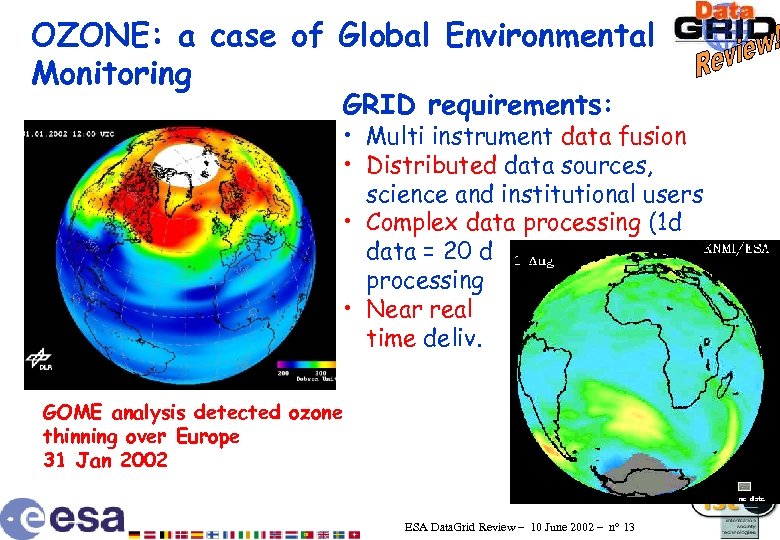
OZONE: a case of Global Environmental Monitoring GRID requirements: • Multi instrument data fusion • Distributed data sources, science and institutional users • Complex data processing (1 d data = 20 d processing • Near real time deliv. GOME analysis detected ozone thinning over Europe 31 Jan 2002 ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 13
Application of Data. Grid in EO u Focus on One EO application (Ozone) but explore: n n Develop generic components n Re-use components to add new applications n Integrate compatible technologies n u Interface to legacy and COTS systems n u Collaborative environment, parallel data processing, … Integrate other data types (new envisat instruments) Testing in “controlled” GRID environment (ESRINENEA) and in “wide-European” environment Feedback to Data. Grid developers and Architecture Group ESA Data. Grid Review – 10 June 2002 – n° 14
8022d27a778b2ad56e0509c9b46372d8.ppt