473c90edebe92b77c1a7ccead4f77a42.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

2 Operations Strategy in a Global Environment Power. Point presentation to accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10 e Principles of Operations Management, 8 e Power. Point slides by Jeff Heyl © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -1
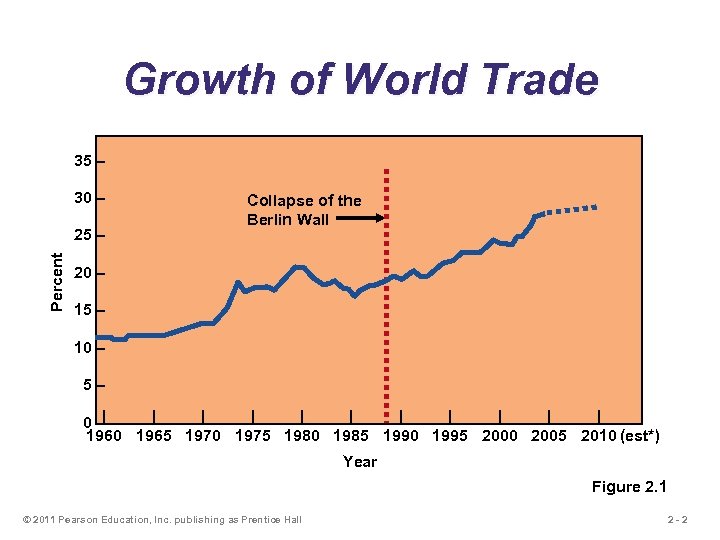
Growth of World Trade 35 – 30 – Percent 25 – Collapse of the Berlin Wall 20 – 15 – 10 – 5– | | | | | 0 –| 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 (est*) Year Figure 2. 1 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -2
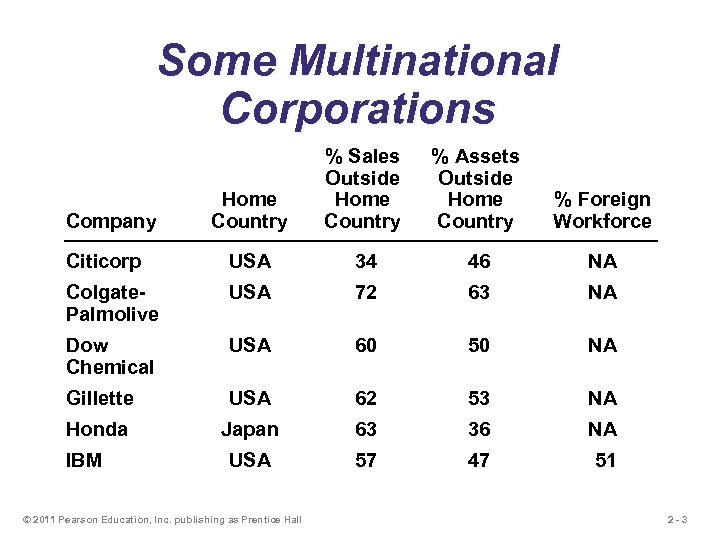
Some Multinational Corporations Home Country % Sales Outside Home Country % Assets Outside Home Country % Foreign Workforce Citicorp USA 34 46 NA Colgate. Palmolive USA 72 63 NA Dow Chemical USA 60 50 NA Gillette USA 62 53 NA Honda Japan 63 36 NA USA 57 47 51 Company IBM © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -3
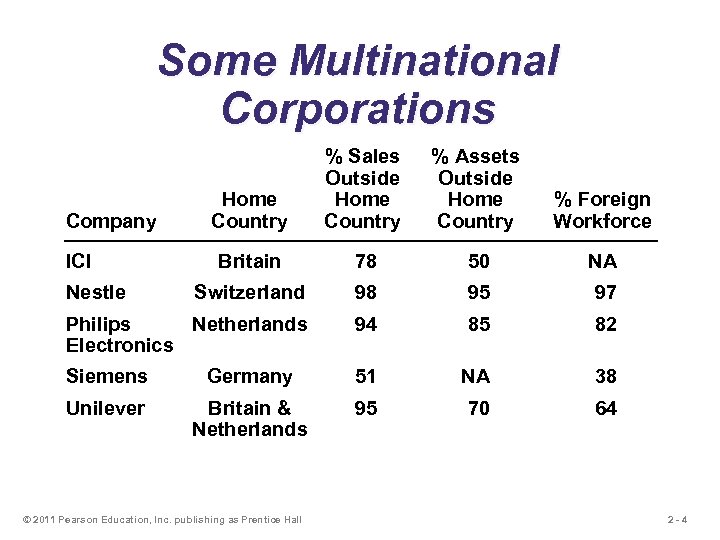
Some Multinational Corporations Home Country % Sales Outside Home Country % Assets Outside Home Country % Foreign Workforce Britain 78 50 NA Switzerland 98 95 97 Philips Netherlands Electronics 94 85 82 Siemens Germany 51 NA 38 Unilever Britain & Netherlands 95 70 64 Company ICI Nestle © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -4

Reasons to Globalize Tangible 1. Reduce costs (labor, taxes, tariffs, etc. ) Reasons 2. Improve supply chain 3. Provide better goods and services 4. Understand markets Intangible 5. Learn to improve operations Reasons 6. Attract and retain global talent © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -5

Developing Missions and Strategies Mission statements tell an organization where it is going The Strategy tells the organization how to get there © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -6
Mission u Mission - where are you going? u Organization’s purpose for being u Answers ‘What do we provide society? ’ u Provides boundaries and focus © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -7

Hard Rock Cafe Our Mission: To spread the spirit of Rock ’n’ Roll by delivering an exceptional entertainment and dining experience. We are committed to being an important, contributing member of our community and offering the Hard Rock family a fun, healthy, and nurturing work environment while ensuring our long-term success. Figure 2. 2 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -8

Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children provides state-of-the-art, family centered healthcare focused on restoring the joy of childhood in an environment of compassion, healing, and hope. Figure 2. 2 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 -9
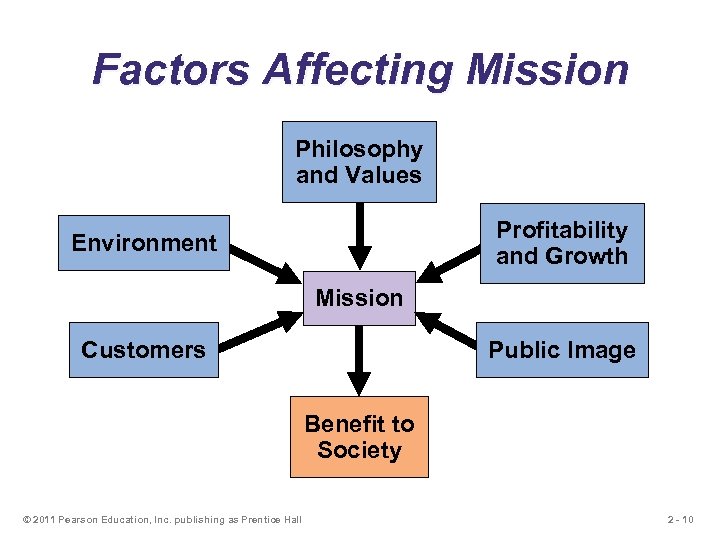
Factors Affecting Mission Philosophy and Values Profitability and Growth Environment Mission Customers Public Image Benefit to Society © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 10

Sample Missions Sample Company Mission To manufacture and service an innovative, growing, and profitable worldwide microwave communications business that exceeds our customers’ expectations. Sample Operations Management Mission To produce products consistent with the company’s mission as the worldwide low-cost manufacturer. Figure 2. 3 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 11
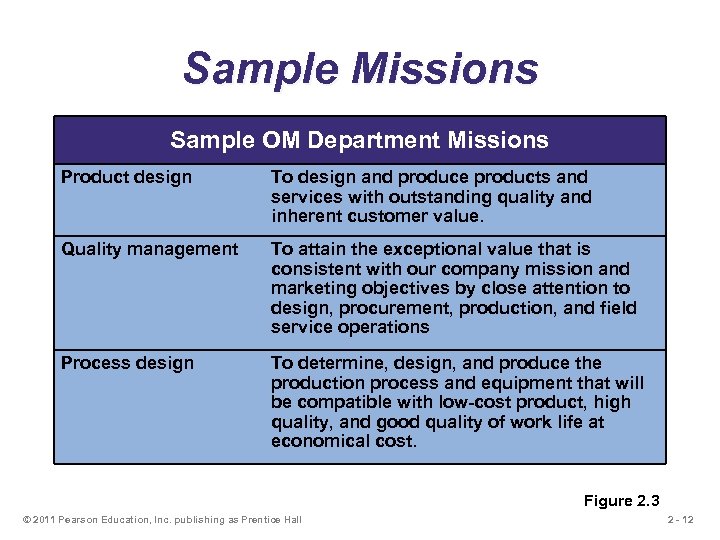
Sample Missions Sample OM Department Missions Product design To design and produce products and services with outstanding quality and inherent customer value. Quality management To attain the exceptional value that is consistent with our company mission and marketing objectives by close attention to design, procurement, production, and field service operations Process design To determine, design, and produce the production process and equipment that will be compatible with low-cost product, high quality, and good quality of work life at economical cost. Figure 2. 3 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 12
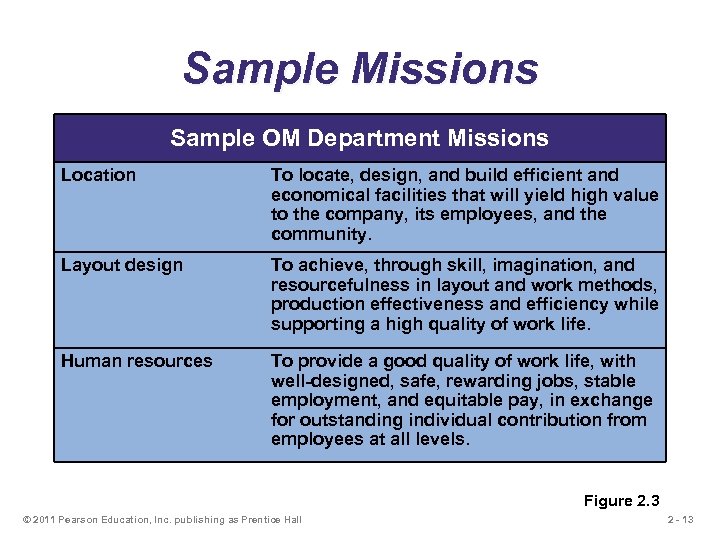
Sample Missions Sample OM Department Missions Location To locate, design, and build efficient and economical facilities that will yield high value to the company, its employees, and the community. Layout design To achieve, through skill, imagination, and resourcefulness in layout and work methods, production effectiveness and efficiency while supporting a high quality of work life. Human resources To provide a good quality of work life, with well-designed, safe, rewarding jobs, stable employment, and equitable pay, in exchange for outstanding individual contribution from employees at all levels. Figure 2. 3 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 13
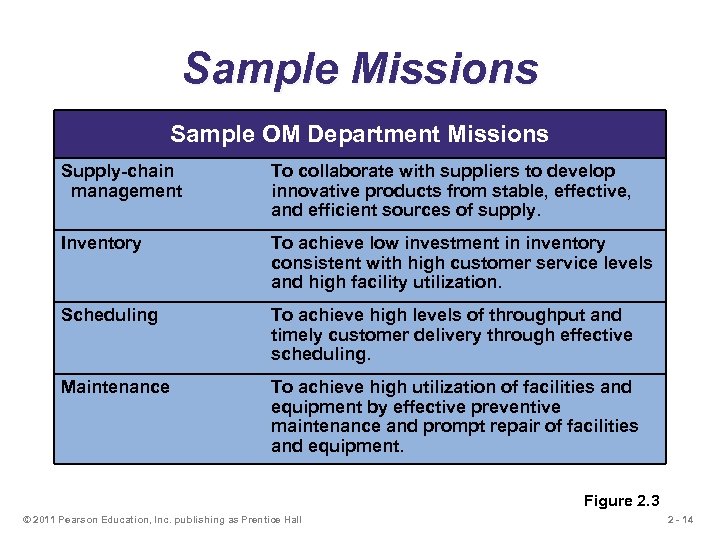
Sample Missions Sample OM Department Missions Supply-chain management To collaborate with suppliers to develop innovative products from stable, effective, and efficient sources of supply. Inventory To achieve low investment in inventory consistent with high customer service levels and high facility utilization. Scheduling To achieve high levels of throughput and timely customer delivery through effective scheduling. Maintenance To achieve high utilization of facilities and equipment by effective preventive maintenance and prompt repair of facilities and equipment. Figure 2. 3 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 14
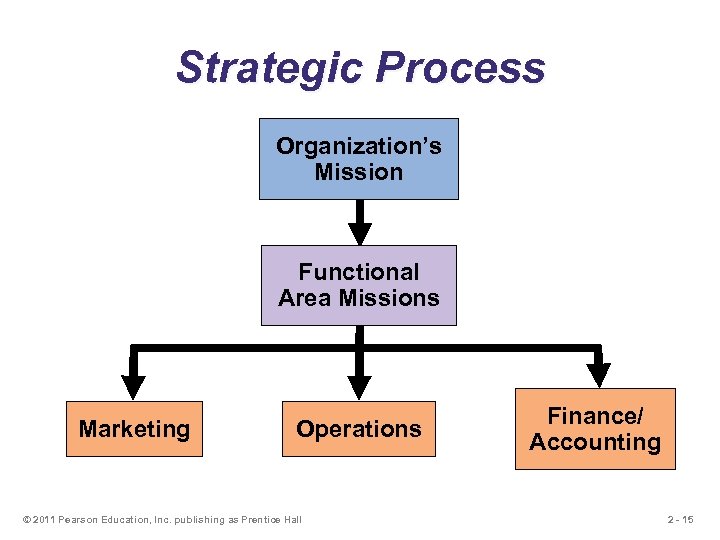
Strategic Process Organization’s Mission Functional Area Missions Marketing Operations © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Finance/ Accounting 2 - 15

Strategy u Action plan to achieve mission u Functional areas have strategies u Strategies exploit opportunities and strengths, neutralize threats, and avoid weaknesses © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 16

Strategies for Competitive Advantage u Differentiation – better, or at least different u Cost leadership – cheaper u Response – rapid response © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 17

Competing on Differentiation Uniqueness can go beyond both the physical characteristics and service attributes to encompass everything that impacts customer’s perception of value u Safeskin gloves – leading edge products u Walt Disney Magic Kingdom – experience differentiation u Hard Rock Cafe – dining experience © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 18

Competing on Cost Provide the maximum value as perceived by customer. Does not imply low quality. u Southwest Airlines – secondary airports, no frills service, efficient utilization of equipment u Wal-Mart – small overhead, shrinkage, distribution costs u Franz Colruyt – no bags, low light, no music, doors on freezers © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 19

Competing on Response u Flexibility is matching market changes in design innovation and volumes u A way of life at Hewlett-Packard u Reliability is meeting schedules u German machine industry u Timeliness is quickness in design, production, and delivery u Johnson Electric, Pizza Hut, Motorola © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 20
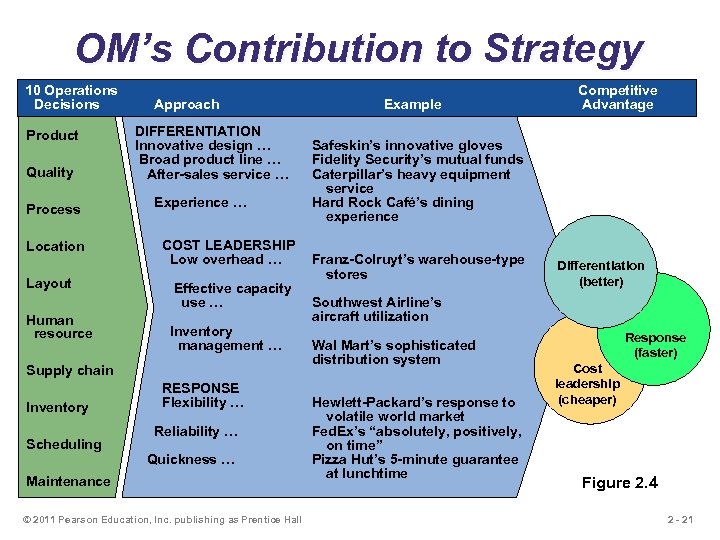
OM’s Contribution to Strategy 10 Operations Decisions Product Quality Process Location Layout Human resource Approach DIFFERENTIATION Innovative design … Broad product line … After-sales service … Experience … COST LEADERSHIP Low overhead … Effective capacity use … Inventory management … Supply chain Inventory Scheduling RESPONSE Flexibility … Reliability … Quickness … Maintenance © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Example Competitive Advantage Safeskin’s innovative gloves Fidelity Security’s mutual funds Caterpillar’s heavy equipment service Hard Rock Café’s dining experience Franz-Colruyt’s warehouse-type stores Differentiation (better) Southwest Airline’s aircraft utilization Wal Mart’s sophisticated distribution system Hewlett-Packard’s response to volatile world market Fed. Ex’s “absolutely, positively, on time” Pizza Hut’s 5 -minute guarantee at lunchtime Response (faster) Cost leadership (cheaper) Figure 2. 4 2 - 21
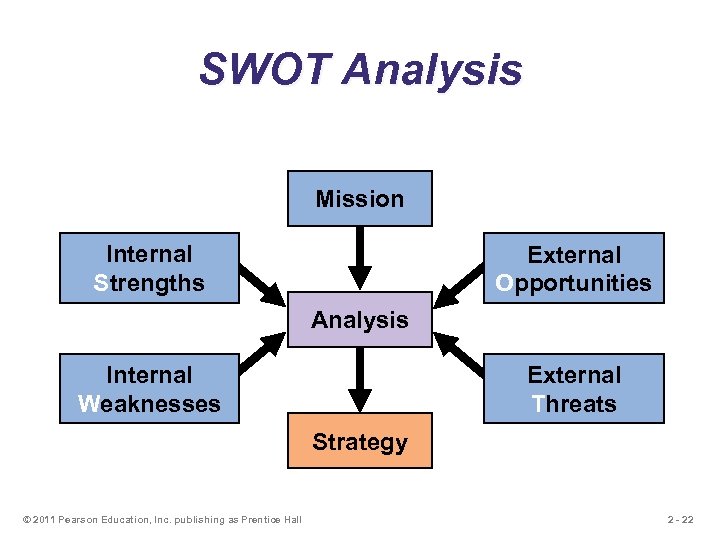
SWOT Analysis Mission Internal Strengths External Opportunities Analysis Internal Weaknesses External Threats Strategy © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 22
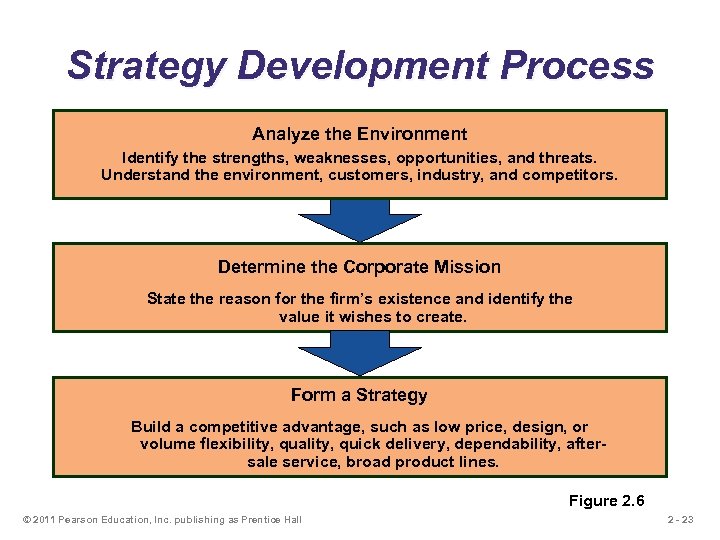
Strategy Development Process Analyze the Environment Identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understand the environment, customers, industry, and competitors. Determine the Corporate Mission State the reason for the firm’s existence and identify the value it wishes to create. Form a Strategy Build a competitive advantage, such as low price, design, or volume flexibility, quality, quick delivery, dependability, aftersale service, broad product lines. Figure 2. 6 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 23

Strategy Development and Implementation u Identify key success factors u Build and staff the organization u Integrate OM with other activities The operations manager’s job is to implement an OM strategy, provide competitive advantage, and increase productivity © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 24
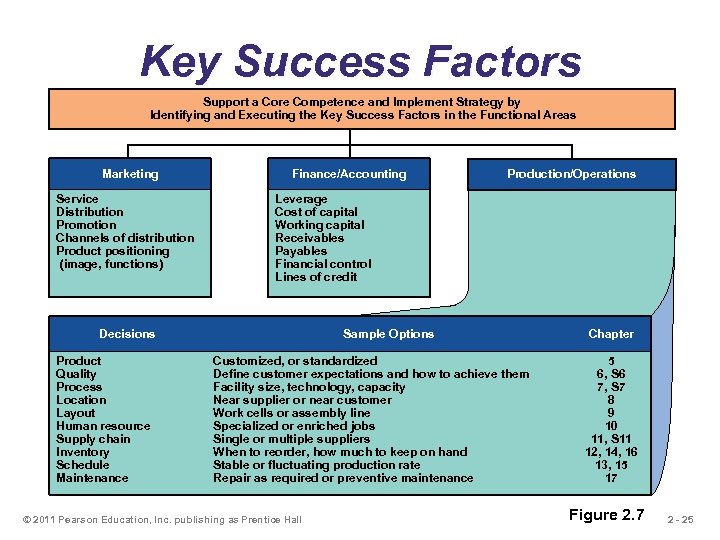
Key Success Factors Support a Core Competence and Implement Strategy by Identifying and Executing the Key Success Factors in the Functional Areas Marketing Service Distribution Promotion Channels of distribution Product positioning (image, functions) Finance/Accounting Leverage Cost of capital Working capital Receivables Payables Financial control Lines of credit Decisions Product Quality Process Location Layout Human resource Supply chain Inventory Schedule Maintenance Production/Operations Sample Options Customized, or standardized Define customer expectations and how to achieve them Facility size, technology, capacity Near supplier or near customer Work cells or assembly line Specialized or enriched jobs Single or multiple suppliers When to reorder, how much to keep on hand Stable or fluctuating production rate Repair as required or preventive maintenance © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 5 6, S 6 7, S 7 8 9 10 11, S 11 12, 14, 16 13, 15 17 Figure 2. 7 2 - 25
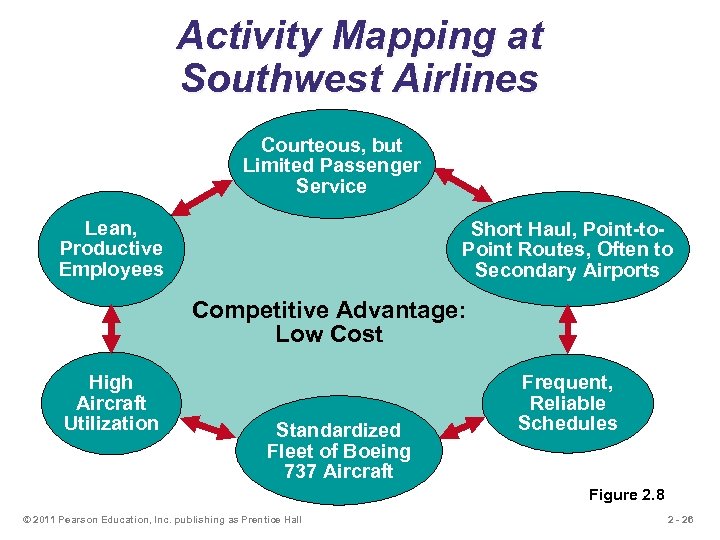
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Competitive Advantage: Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 26
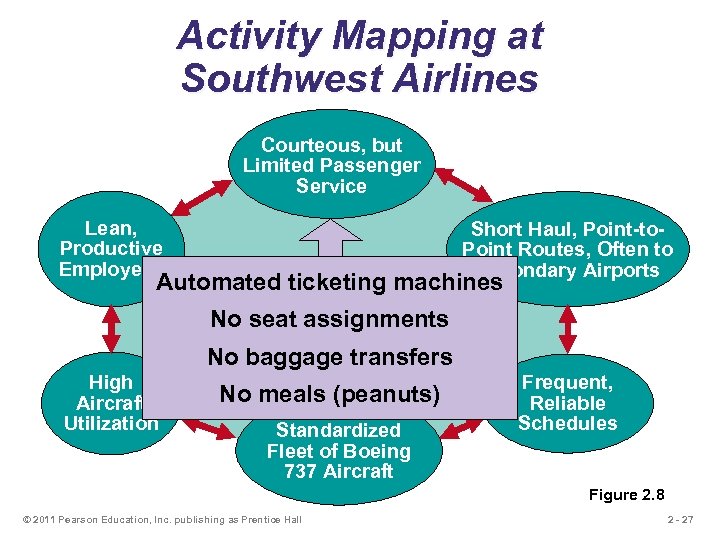
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Automated ticketing machines Competitive Advantage: No seat assignments Low Cost No baggage transfers High Aircraft Utilization No meals (peanuts) Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 27
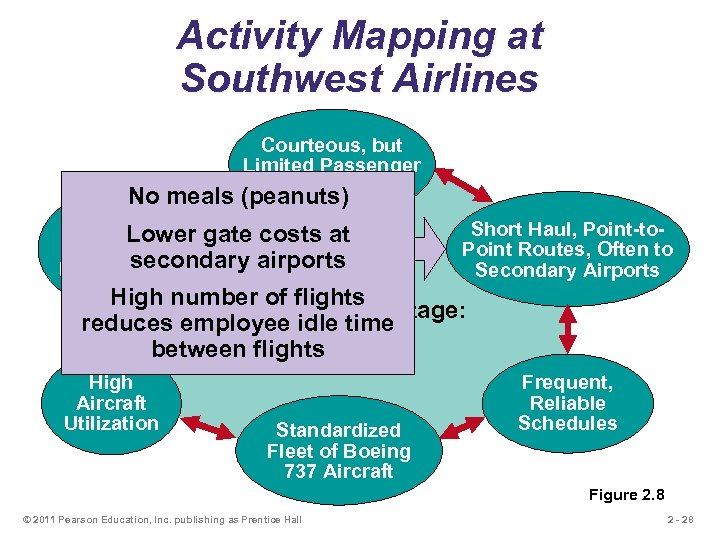
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service No meals (peanuts) Lean, Lower gate costs at Productive secondary airports Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports High number of flights Competitive Advantage: reduces employee idle time Low Cost between flights High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 28
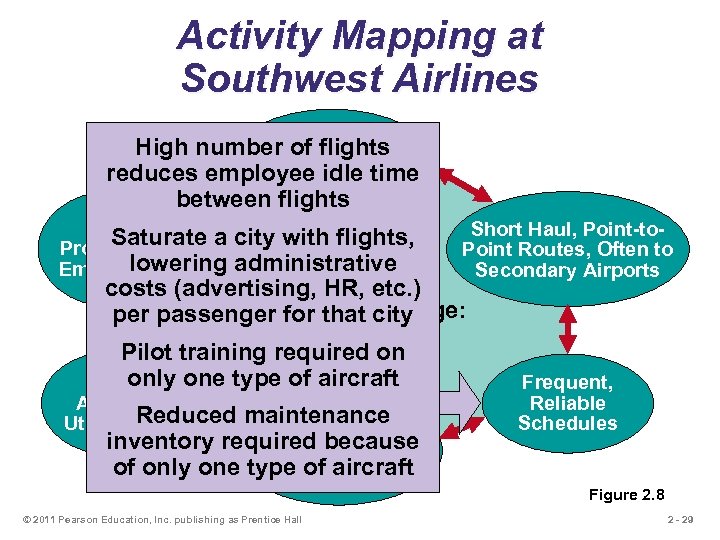
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but High number of flights Limited idle time reduces employee Passenger Service between flights Lean, Saturate a Productive lowering Employees Short Haul, Point-tocity with flights, Point Routes, Often to administrative Secondary Airports costs (advertising, HR, etc. ) Competitive Advantage: per passenger for that city Low Cost Pilot training required on only one type of aircraft High Frequent, Aircraft Reduced Utilization maintenance Standardized inventory required of Boeing Fleet because of only one type of. Aircraft 737 aircraft Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 29
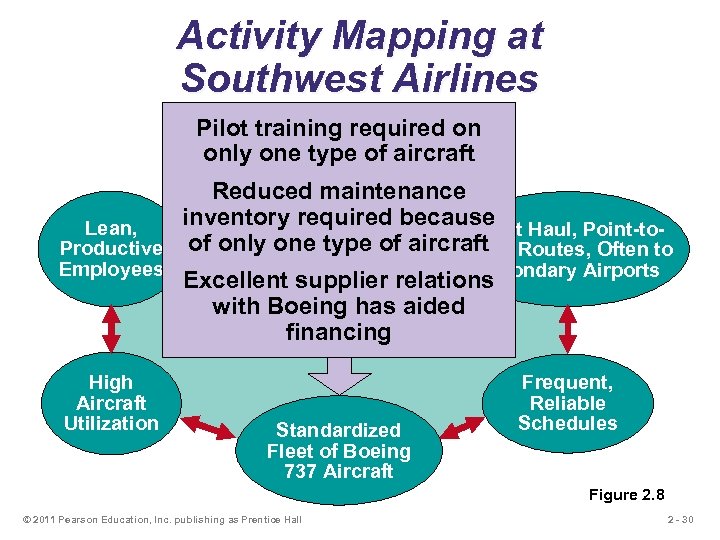
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Pilot training required on Courteous, but only one type of aircraft Limited Passenger Service Reduced maintenance inventory required because Haul, Point-to. Lean, Short of only one type of aircraft Routes, Often to Productive Point Employees Secondary Airports Excellent supplier relations with Boeing has aided Competitive Advantage: financing Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 30
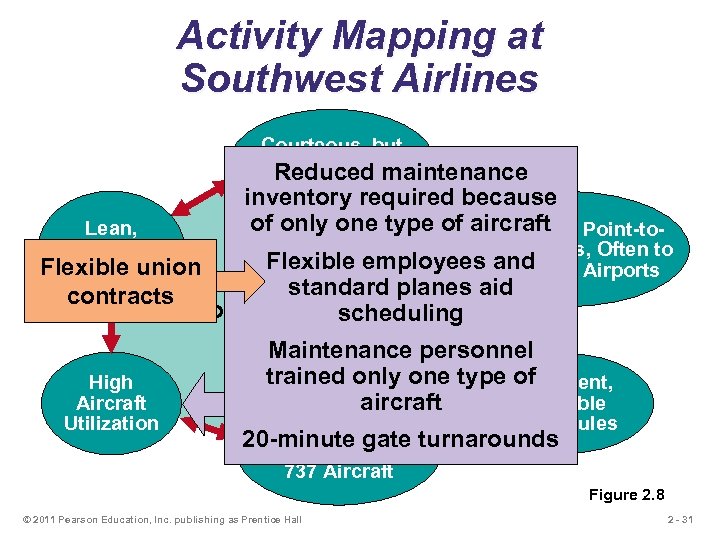
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Reduced maintenance Service Lean, Productive Flexible union Employees inventory required because of only one type of aircraft Point-to. Short Haul, Point Routes, Often to Flexible employees and Secondary Airports standard planes aid contracts Competitive Advantage: scheduling Low Cost Maintenance personnel trained only one type of High Frequent, Aircraft Reliable aircraft Utilization Standardized 20 -minute gate Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Schedules turnarounds Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 31
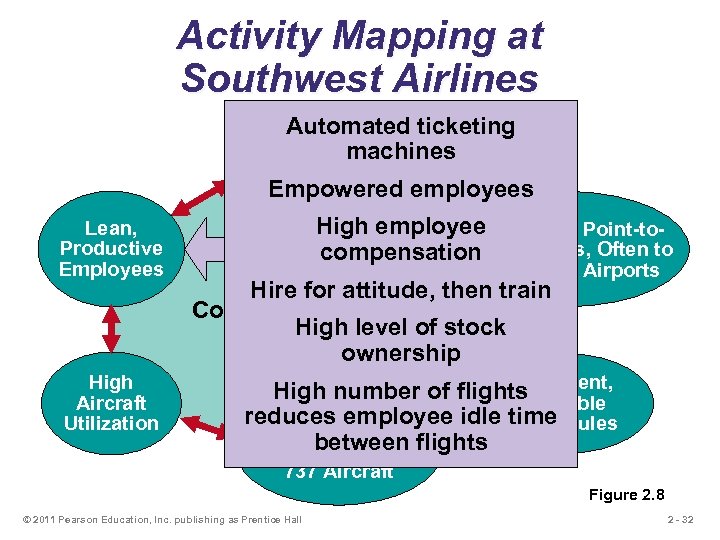
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Automated ticketing Courteous, but machines Limited Passenger Service Empowered employees Lean, Productive Employees High Aircraft Utilization High employee Short Haul, Point-to. Point compensation Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Hire for attitude, then train Competitive Advantage: High level Low Cost of stock ownership Frequent, High number of flights Reliable reduces employee idle time Schedules Standardized Fleetbetween flights of Boeing 737 Aircraft Figure 2. 8 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 32
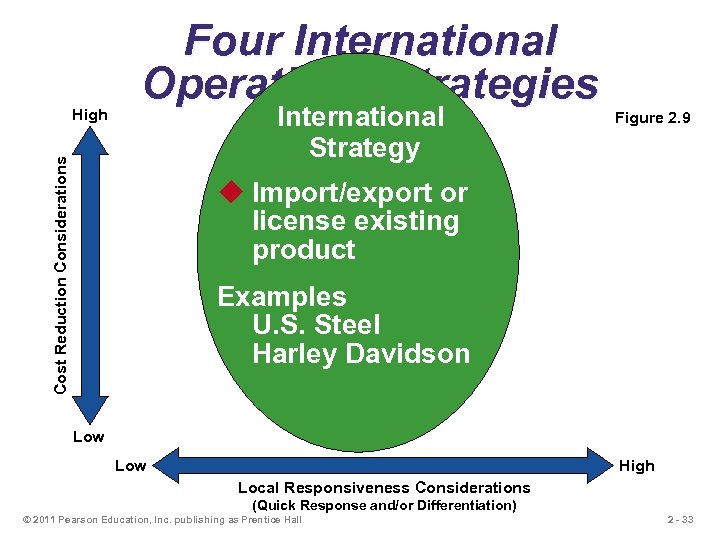
International Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations High Four International Operations Strategies Figure 2. 9 u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 33
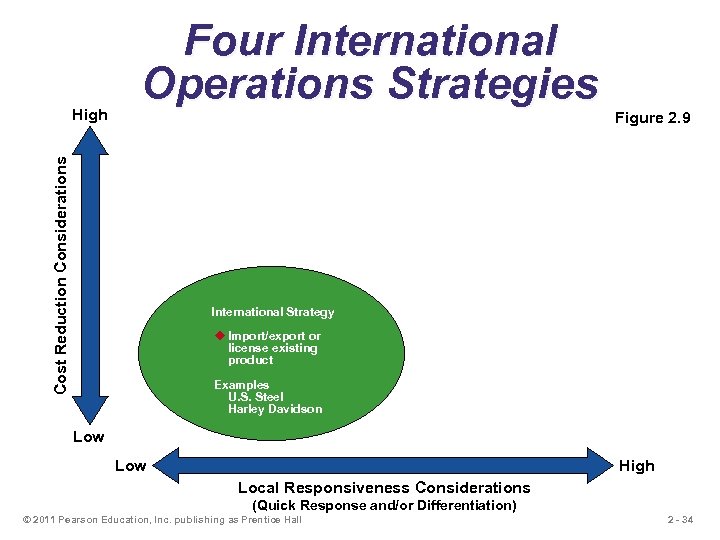
Cost Reduction Considerations High Four International Operations Strategies Figure 2. 9 International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 34
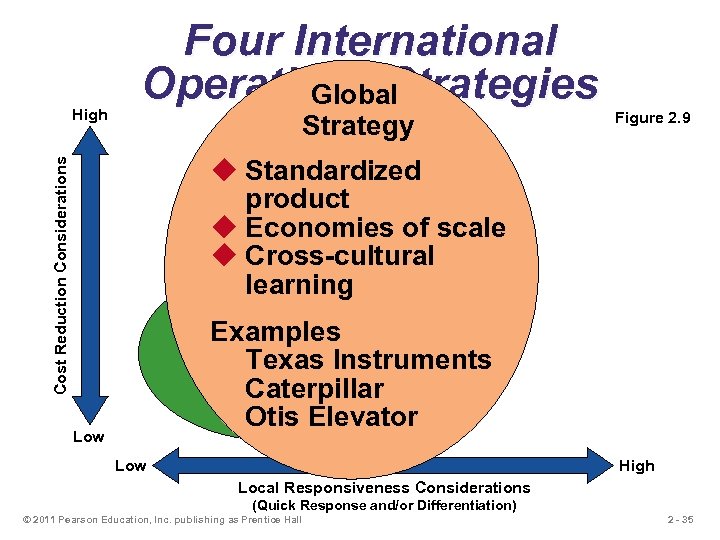
High Four International Operations Strategies Global Strategy Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning International Strategy u Import/export or Examples license existing product Texas Instruments Examples Caterpillar U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Otis Elevator Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 35
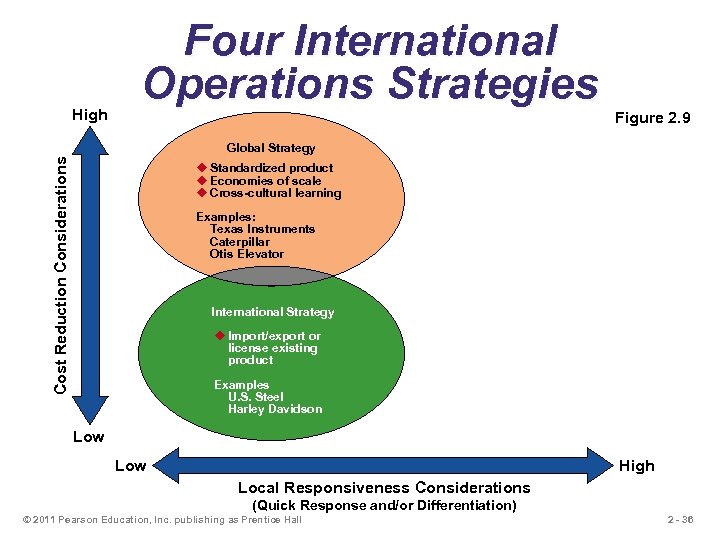
High Four International Operations Strategies Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 36
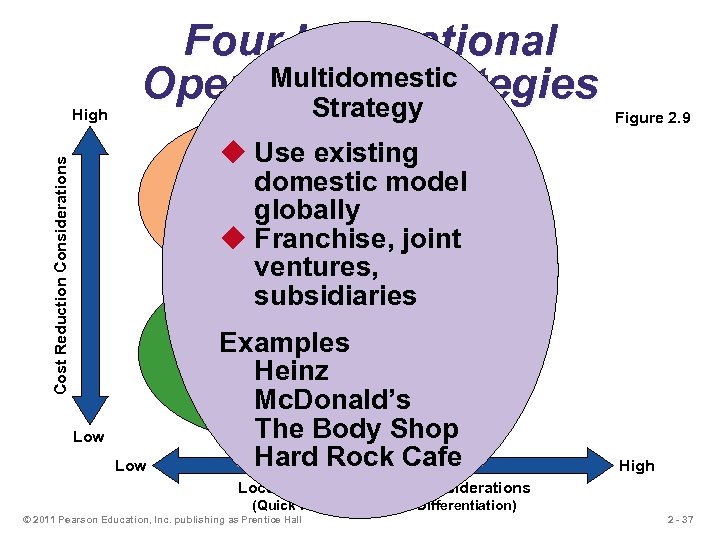
High Four International Multidomestic Operations Strategies Strategy Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Use existing u Standardized product u Economies of scale domestic model u Cross-cultural learning Examples: globally Texas Instruments Caterpillar u Franchise, joint Otis Elevator ventures, subsidiaries International Strategy Examples Heinz Examples U. S. Steel Mc. Donald’s Harley Davidson The Body Shop Hard Rock Cafe u Import/export or license existing product Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 37
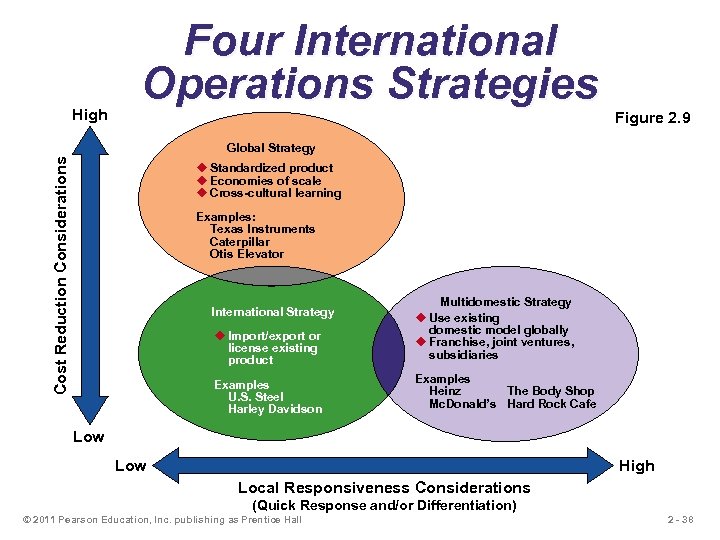
High Four International Operations Strategies Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 38
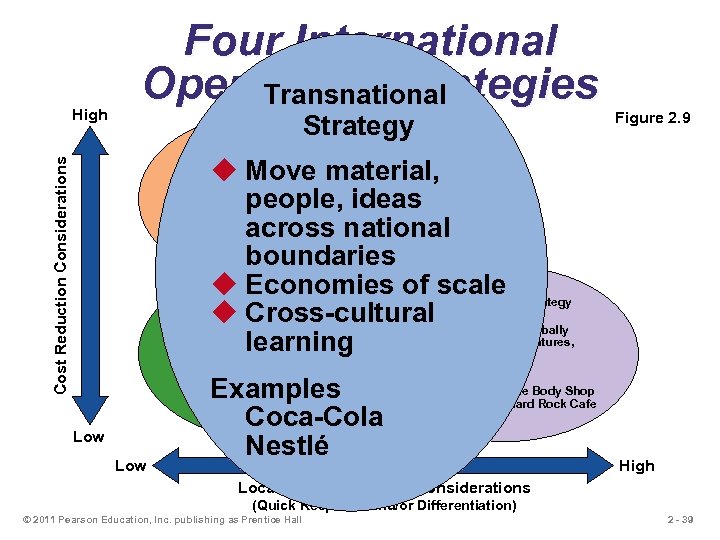
High Four International Operations Strategies Transnational Strategy Figure 2. 9 Global Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations u Move material, people, ideas Examples: Texas across national Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator boundaries u Economies of scale Strategy Multidomestic International Strategy u Use u Cross-cultural existing globally domestic model u Import/export or u Franchise, joint ventures, learning license existing subsidiaries product u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 39
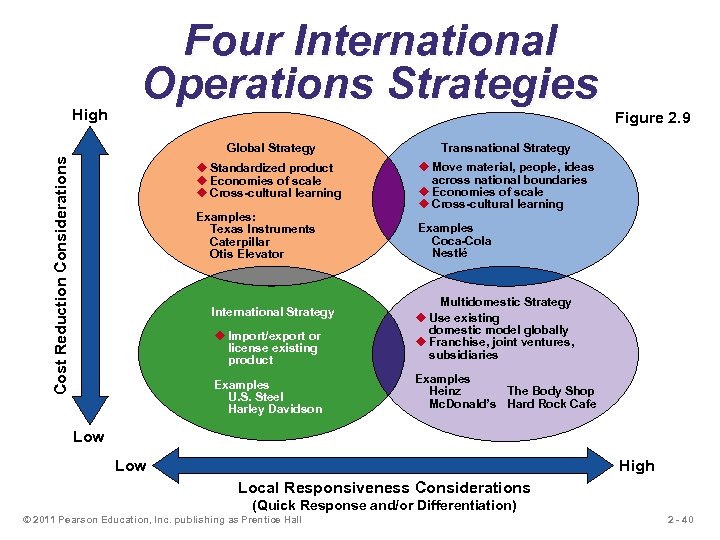
High Four International Operations Strategies Transnational Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy Figure 2. 9 u Move material, people, ideas across national boundaries u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 2 - 40
473c90edebe92b77c1a7ccead4f77a42.ppt