9bde60bdc1a6c3a83d21bc62e3f34ff2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

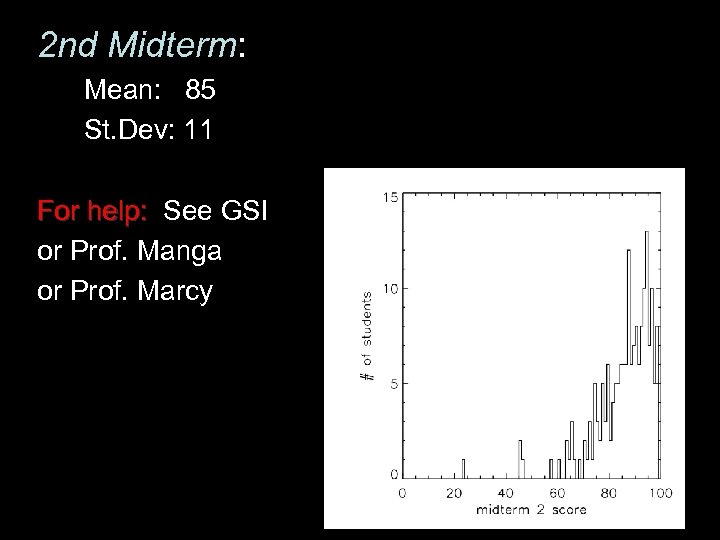 2 nd Midterm: Mean: 85 St. Dev: 11 For help: See GSI For help: or Prof. Manga or Prof. Marcy
2 nd Midterm: Mean: 85 St. Dev: 11 For help: See GSI For help: or Prof. Manga or Prof. Marcy
 2 nd Midterm: Common Mistakes 1. Greenhouse Effect: • CO 2 absorbs IR light (not UV). • 2. Geological activity on Jupiter’s moons is due to their composition of ice: Allows melting at low temperatures in the outer solar system. Volcanism and tectonics possible.
2 nd Midterm: Common Mistakes 1. Greenhouse Effect: • CO 2 absorbs IR light (not UV). • 2. Geological activity on Jupiter’s moons is due to their composition of ice: Allows melting at low temperatures in the outer solar system. Volcanism and tectonics possible.
 Announcements • Homework due a week from Friday: • Chapter 13 on Planets Around Other Stars Homework counts 50% of grade; Drop lowest score. • Final Exam - comprehensive: May 20 @ 8 am: 237 Hearst Gym • Telescope Observations: Saturn, Mars, Orion Nebula. Observing Starts: 8 pm ! Star Chart with 3 obs of Mars: Due May 1.
Announcements • Homework due a week from Friday: • Chapter 13 on Planets Around Other Stars Homework counts 50% of grade; Drop lowest score. • Final Exam - comprehensive: May 20 @ 8 am: 237 Hearst Gym • Telescope Observations: Saturn, Mars, Orion Nebula. Observing Starts: 8 pm ! Star Chart with 3 obs of Mars: Due May 1.
 "The Dawn of Creation: The First Two Billion Years" A Special Lecture by Steven Beckwith Wednesday, April 23, 5: 30 pm Chevron Auditorium - International House Extra Credit: 3 points for half-page summary of talk
"The Dawn of Creation: The First Two Billion Years" A Special Lecture by Steven Beckwith Wednesday, April 23, 5: 30 pm Chevron Auditorium - International House Extra Credit: 3 points for half-page summary of talk
 Are there Other Planetary Systems ? Are any of them like our Solar System ?
Are there Other Planetary Systems ? Are any of them like our Solar System ?
 February 5, 1996
February 5, 1996
 Now Exiting our Solar System to … . . . Now Leaving. The Solar System. Galaxy. our Milky Way. . . .
Now Exiting our Solar System to … . . . Now Leaving. The Solar System. Galaxy. our Milky Way. . . .
 Democritus: Greek philosopher (460 - 370 BC). “ There are innumerable worlds of different sizes. These worlds are at irregular distances, more in one direction and less in another, and some are flourishing, others declining. Here they come into being, there they die, and they are destroyed by collision with one another. Some of the worlds have no animal or vegetable life nor any water. “
Democritus: Greek philosopher (460 - 370 BC). “ There are innumerable worlds of different sizes. These worlds are at irregular distances, more in one direction and less in another, and some are flourishing, others declining. Here they come into being, there they die, and they are destroyed by collision with one another. Some of the worlds have no animal or vegetable life nor any water. “
 Epicurus (341 -270 B. C. ) Greek philosopher in Athens where he opened a school of philosophy “There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. . . we must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world…”
Epicurus (341 -270 B. C. ) Greek philosopher in Athens where he opened a school of philosophy “There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. . . we must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world…”
 http: //www. gospelcom. net/chi/DAILYF/2002/02/daily-02 -17 -2002. shtml Giordano Bruno 1584 Wrote; ‘ De l'infinito, universo e mondi (The Infinity, the Universe and Its Worlds) • Bruno was enthusiastic about the Copernican theory that the planets circle the sun and he believed there are many other planets around other stars, some of them with life. Giordano Bruno lost the thread of truth and the Roman Church burned him for it. Burned at the Stake February 17, 1600 By Catholic Church
http: //www. gospelcom. net/chi/DAILYF/2002/02/daily-02 -17 -2002. shtml Giordano Bruno 1584 Wrote; ‘ De l'infinito, universo e mondi (The Infinity, the Universe and Its Worlds) • Bruno was enthusiastic about the Copernican theory that the planets circle the sun and he believed there are many other planets around other stars, some of them with life. Giordano Bruno lost the thread of truth and the Roman Church burned him for it. Burned at the Stake February 17, 1600 By Catholic Church
 Stars are a billion times brighter…
Stars are a billion times brighter…
 …than the planet hidden in the glare. Detecting Earths: Like detecting a firefly next to a nuclear explosion
…than the planet hidden in the glare. Detecting Earths: Like detecting a firefly next to a nuclear explosion

 Planet Detection The Wobble of a Star: Gravitational pull by the planet Star moves slower, due to conservation of momentum: mass x velocity MSTAR VSTAR = Mplanet Vplanet
Planet Detection The Wobble of a Star: Gravitational pull by the planet Star moves slower, due to conservation of momentum: mass x velocity MSTAR VSTAR = Mplanet Vplanet

 Wobble Velocity 1/2 m. PLVPL 2 = G m. PLMStar / r VPL ~ 10 km/s Momentum: ( ) V VStar = MPL MSTAR PL VSTAR ~ 10 m/s x (MPL /MJUP)
Wobble Velocity 1/2 m. PLVPL 2 = G m. PLMStar / r VPL ~ 10 km/s Momentum: ( ) V VStar = MPL MSTAR PL VSTAR ~ 10 m/s x (MPL /MJUP)
 Detecting a Star’s Wobble: Doppler Effect Spectrum starlight Detecting the wobble of a Star, pulled around by its planet.
Detecting a Star’s Wobble: Doppler Effect Spectrum starlight Detecting the wobble of a Star, pulled around by its planet.
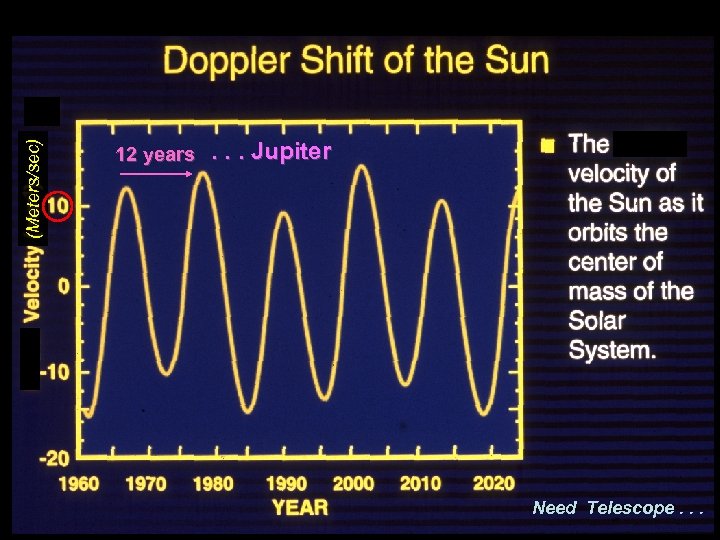 (Meters/sec) 12 years . . . Jupiter Need Telescope. . .
(Meters/sec) 12 years . . . Jupiter Need Telescope. . .


 Starlight From Telescope High Resolution ``Echelle” Spectrometer Echelle Spectrometer CCD Echelle Grating Collimator
Starlight From Telescope High Resolution ``Echelle” Spectrometer Echelle Spectrometer CCD Echelle Grating Collimator
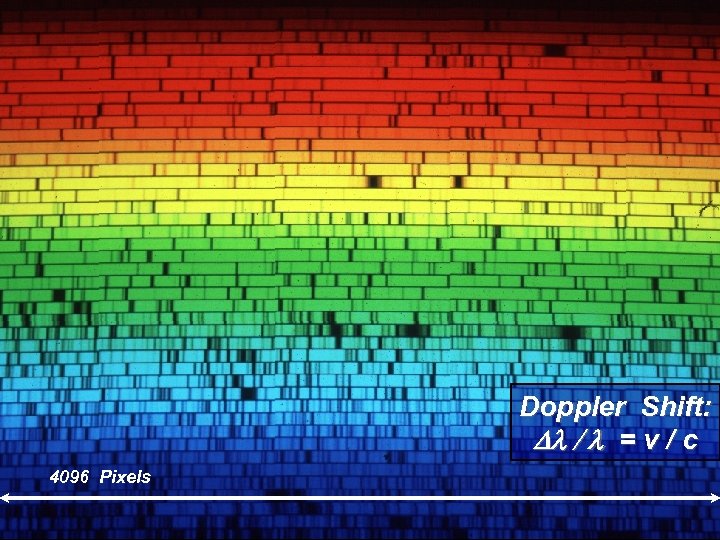 Spectrum of Star: Doppler Effect Doppler Shift: Dl / l = v / c 4096 Pixels
Spectrum of Star: Doppler Effect Doppler Shift: Dl / l = v / c 4096 Pixels
 Claim of First Detected Extrasolar Planet: 51 Pegasi Orbital Period = 4. 2 days ! Absurd Michel Mayor & Didier Queloz 51 Peg
Claim of First Detected Extrasolar Planet: 51 Pegasi Orbital Period = 4. 2 days ! Absurd Michel Mayor & Didier Queloz 51 Peg
 One week Later. . . 4 Nights at Lick Observatory October 11, 1995
One week Later. . . 4 Nights at Lick Observatory October 11, 1995


 Determination of Orbital Distance from Star to Planet Period = 4. 2 days Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Units: P in years, a in AU Solve for a: a = 0. 05 AU Proximity: Temp = 1500 C
Determination of Orbital Distance from Star to Planet Period = 4. 2 days Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Units: P in years, a in AU Solve for a: a = 0. 05 AU Proximity: Temp = 1500 C
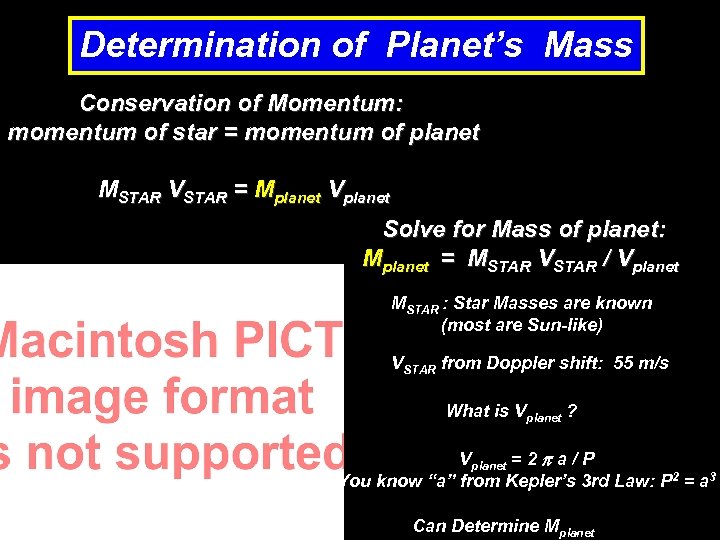 Determination of Planet’s Mass Conservation of Momentum: momentum of star = momentum of planet MSTAR VSTAR = Mplanet Vplanet Solve for Mass of planet: Mplanet = MSTAR VSTAR / Vplanet MSTAR : Star Masses are known (most are Sun-like) VSTAR from Doppler shift: 55 m/s What is Vplanet ? Vplanet = 2 a / P You know “a” from Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Can Determine Mplanet
Determination of Planet’s Mass Conservation of Momentum: momentum of star = momentum of planet MSTAR VSTAR = Mplanet Vplanet Solve for Mass of planet: Mplanet = MSTAR VSTAR / Vplanet MSTAR : Star Masses are known (most are Sun-like) VSTAR from Doppler shift: 55 m/s What is Vplanet ? Vplanet = 2 a / P You know “a” from Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Can Determine Mplanet

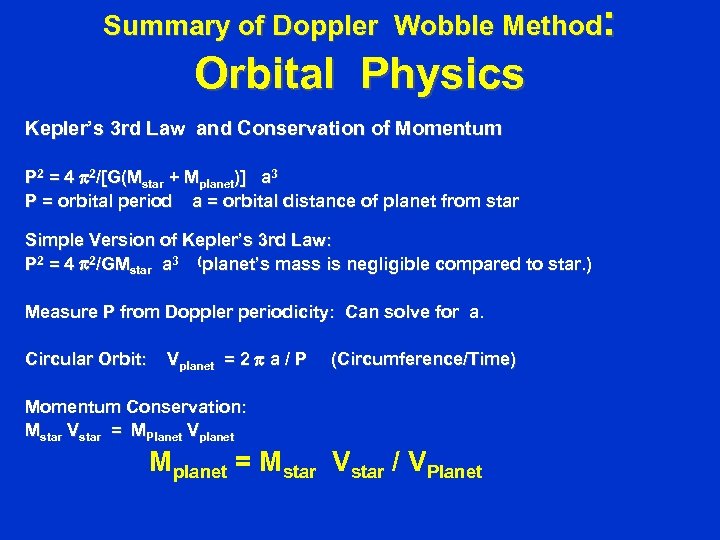 Summary of Doppler Wobble Method: Orbital Physics Kepler’s 3 rd Law and Conservation of Momentum P 2 = 4 p 2/[G(Mstar + Mplanet)] a 3 P = orbital period a = orbital distance of planet from star Simple Version of Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = 4 p 2/GMstar a 3 (planet’s mass is negligible compared to star. ) Measure P from Doppler periodicity: Can solve for a. Circular Orbit: Vplanet = 2 p a / P (Circumference/Time) Momentum Conservation: Mstar Vstar = MPlanet Vplanet Mplanet = Mstar Vstar / VPlanet
Summary of Doppler Wobble Method: Orbital Physics Kepler’s 3 rd Law and Conservation of Momentum P 2 = 4 p 2/[G(Mstar + Mplanet)] a 3 P = orbital period a = orbital distance of planet from star Simple Version of Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = 4 p 2/GMstar a 3 (planet’s mass is negligible compared to star. ) Measure P from Doppler periodicity: Can solve for a. Circular Orbit: Vplanet = 2 p a / P (Circumference/Time) Momentum Conservation: Mstar Vstar = MPlanet Vplanet Mplanet = Mstar Vstar / VPlanet
 Doppler Wobble Method: Unknown Orbital Inclination Tilt of Planet’s Orbital Plane: Unknown • Edge-on Orbit: Full Doppler Effect • Face-on Orbit: No Doppler Effect • General Tilt Angle: True Wobble speed is greater than Doppler indicates True planet mass is GREATER than the mass found by the Doppler method. (25% greater on Avg. ) We measure M sin i
Doppler Wobble Method: Unknown Orbital Inclination Tilt of Planet’s Orbital Plane: Unknown • Edge-on Orbit: Full Doppler Effect • Face-on Orbit: No Doppler Effect • General Tilt Angle: True Wobble speed is greater than Doppler indicates True planet mass is GREATER than the mass found by the Doppler method. (25% greater on Avg. ) We measure M sin i

 51 Pegasi First Extrasolar Planet Period = 4. 2 days Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Units: P in years, a in AU Solve for a: a = 0. 05 AU Proximity: Temp = 1500 C
51 Pegasi First Extrasolar Planet Period = 4. 2 days Kepler’s 3 rd Law: P 2 = a 3 Units: P in years, a in AU Solve for a: a = 0. 05 AU Proximity: Temp = 1500 C
 16 Cygni B Mass = 1. 7 MJUP Not Sinusoidal (Min) Orbit Period 2. 2 yr Velocity Wobble
16 Cygni B Mass = 1. 7 MJUP Not Sinusoidal (Min) Orbit Period 2. 2 yr Velocity Wobble
 Velocity
Velocity
 Orbit of Planet around 16 Cygni
Orbit of Planet around 16 Cygni
 16 Cygni: Planet & Moon
16 Cygni: Planet & Moon
 Life on Gas Giant Planets ? Earth-Like Moon Floaters
Life on Gas Giant Planets ? Earth-Like Moon Floaters
 Eccentric Orbit ! of Planet around 16 Cygni
Eccentric Orbit ! of Planet around 16 Cygni
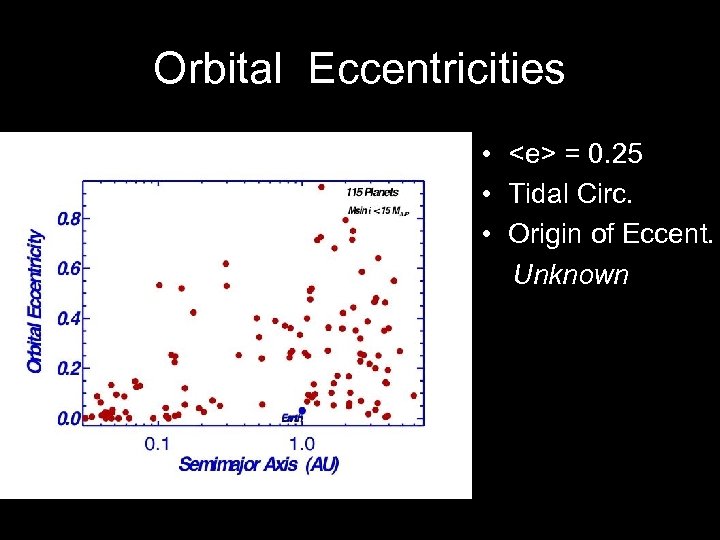 Orbital Eccentricities •
Orbital Eccentricities •
 Origin of Eccentricities Planet - Planet Gravitational Interactions
Origin of Eccentricities Planet - Planet Gravitational Interactions


 Mass = 0. 62 MJUP 70 Days
Mass = 0. 62 MJUP 70 Days
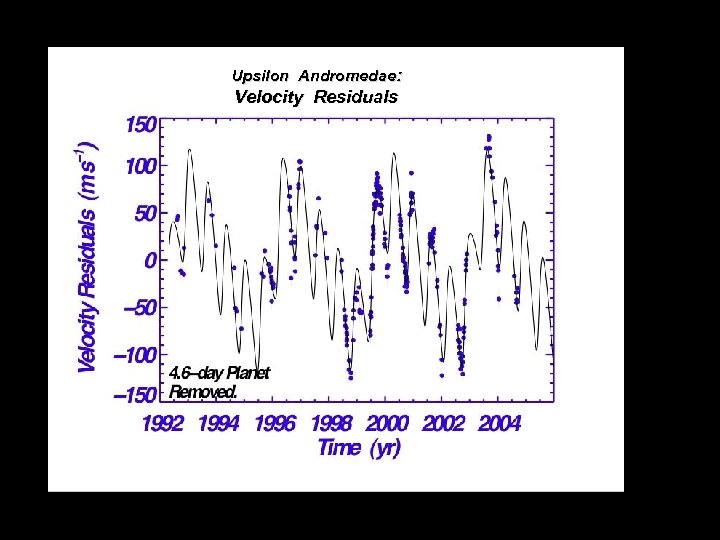 Upsilon Andromedae: Velocity Residuals
Upsilon Andromedae: Velocity Residuals
 . Upsilon andromedae: . triple planet system Planets have No Names. 2 MJUP. . 0. 6 MJUP . 4 MJup. .
. Upsilon andromedae: . triple planet system Planets have No Names. 2 MJUP. . 0. 6 MJUP . 4 MJup. .
 Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae


