4f4120b97eadae8ed63087ac9827ab8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China R&D: Life Line for pharmaceutical companies: A GM perspective • • • Joseph Cho CEO, Astellas Pharma China Vice Chairman, RDPAC
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China R&D: Life Line for pharmaceutical companies: A GM perspective • • • Joseph Cho CEO, Astellas Pharma China Vice Chairman, RDPAC
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Disclaimer • This is not a thorough research report by a consultant. • This is the personal perspective of a General managers with 33 years of working experience in the pharma industry – 20 years in Taiwan (sales, marketing, drug registration, clinical trial, business development) – 13 years in Hong Kong and mainland China – 20 years of working and engagement in industry groups in Taiwan (IRPMA), Hong Kong (HKAPI) and China (RDPAC). • Some thought exchanged with government officials and experts in the industry and acadmics. • Information supported by colleagues in the company, friends in IMS, colleagues in RDPAC and lessons from top management and colleagues in Astellas Pharma Group
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Disclaimer • This is not a thorough research report by a consultant. • This is the personal perspective of a General managers with 33 years of working experience in the pharma industry – 20 years in Taiwan (sales, marketing, drug registration, clinical trial, business development) – 13 years in Hong Kong and mainland China – 20 years of working and engagement in industry groups in Taiwan (IRPMA), Hong Kong (HKAPI) and China (RDPAC). • Some thought exchanged with government officials and experts in the industry and acadmics. • Information supported by colleagues in the company, friends in IMS, colleagues in RDPAC and lessons from top management and colleagues in Astellas Pharma Group
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Protection of IPR: Essential for financing drug R&D
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Protection of IPR: Essential for financing drug R&D
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Increasing R&D cost ratio in pharma and Bio industry 出所:医薬産業政策研究所(2003)「財務データからみた製薬企業の 10年」 リサーチペーパーシリーズ N0.13
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Increasing R&D cost ratio in pharma and Bio industry 出所:医薬産業政策研究所(2003)「財務データからみた製薬企業の 10年」 リサーチペーパーシリーズ N0.13
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Characteristics of patent for pharmaceuticals Pharmaceuticals Automobile, Electronics appliances Substance Formulat ion patent Drug Substance patent formulat ions a product is composed of hundreds and thousand of patent、impact of a single patent limited. Existence of a patent may not hinder the develop of other patents formulat ion One Basic patent(substance) High royalty fee Giving up of new drug development due to patent infringement
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Characteristics of patent for pharmaceuticals Pharmaceuticals Automobile, Electronics appliances Substance Formulat ion patent Drug Substance patent formulat ions a product is composed of hundreds and thousand of patent、impact of a single patent limited. Existence of a patent may not hinder the develop of other patents formulat ion One Basic patent(substance) High royalty fee Giving up of new drug development due to patent infringement
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China develop ment) Clinical Pre-clinical trial 5~ 10 Y 3~ 5 Y Drug discovery Screening 2~ 3 Y RA approval Apply Candidate compounds Mode of action, Clinical trial AMDE P 1→P 2→P 3 pharmacokinetics, Efficacy and safety Pharmaco dynamics in human formulation PK PD regulatory No. of compounds 500, 000~ 1000, 000 compounds Library 5, 000~ 10, 000 compounds Synthesized 5~ 10 compunds 1 compo und 10, 000 Developed compounds Product Cost of JY 80 Billion/1 NCE launch Investigation Optimizing total 10~ 20 Y
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China develop ment) Clinical Pre-clinical trial 5~ 10 Y 3~ 5 Y Drug discovery Screening 2~ 3 Y RA approval Apply Candidate compounds Mode of action, Clinical trial AMDE P 1→P 2→P 3 pharmacokinetics, Efficacy and safety Pharmaco dynamics in human formulation PK PD regulatory No. of compounds 500, 000~ 1000, 000 compounds Library 5, 000~ 10, 000 compounds Synthesized 5~ 10 compunds 1 compo und 10, 000 Developed compounds Product Cost of JY 80 Billion/1 NCE launch Investigation Optimizing total 10~ 20 Y
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Animal studies Formul ation Clinical trials P 1→P 2→P 3 CMC 2~ 3 Y review 10~ 15 years for R&D approval Basic Optimizing research Invention research 5~ 10 Y Application 3~ 5 Y 2~ 3 Y Launch of generics Clinical Review Exclusive period screening Pre-clinical Launching of NCE Discovery 10~ 15 Y α Patent application ※α= extended IPR Patent 20 Yr+α(Max. 5 Yr) =exclusivity(Max. 25 Yr)
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Animal studies Formul ation Clinical trials P 1→P 2→P 3 CMC 2~ 3 Y review 10~ 15 years for R&D approval Basic Optimizing research Invention research 5~ 10 Y Application 3~ 5 Y 2~ 3 Y Launch of generics Clinical Review Exclusive period screening Pre-clinical Launching of NCE Discovery 10~ 15 Y α Patent application ※α= extended IPR Patent 20 Yr+α(Max. 5 Yr) =exclusivity(Max. 25 Yr)
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Specific Challenges in China pharma market for innovative drugs - market access • In China, import or manufacture approval does not mean market accessible. – – – Pricing approval in provinces/cities Listing into formulary of target hospitals Winning in hospital bidding/price negotiations Reimbursement by health insurance Distribution to retail outlets • Reduction of 5 -7 years of real patent life • Generics may be launched prior to original products • Ensuring sufficient market exclusive period vital for R&D investment return • Early entry to the market essential
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Specific Challenges in China pharma market for innovative drugs - market access • In China, import or manufacture approval does not mean market accessible. – – – Pricing approval in provinces/cities Listing into formulary of target hospitals Winning in hospital bidding/price negotiations Reimbursement by health insurance Distribution to retail outlets • Reduction of 5 -7 years of real patent life • Generics may be launched prior to original products • Ensuring sufficient market exclusive period vital for R&D investment return • Early entry to the market essential
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China How important is R&D? • Emergence of a company. – If you have a break through new drugs. • Rapid Growth of the Company – If you have a series of successful new product launch. • Can keeping the company alive – When IPR of main products subsides. • Change of healthcare practice – The case with H 2 blockers for gastro-tectomy • If R&D flops : – – • Likely lay off, change of company, jobs and positions for many people, Loss of investment, Death of patients and Company no long exist: as shown next few slides
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China How important is R&D? • Emergence of a company. – If you have a break through new drugs. • Rapid Growth of the Company – If you have a series of successful new product launch. • Can keeping the company alive – When IPR of main products subsides. • Change of healthcare practice – The case with H 2 blockers for gastro-tectomy • If R&D flops : – – • Likely lay off, change of company, jobs and positions for many people, Loss of investment, Death of patients and Company no long exist: as shown next few slides
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Relationship between R&D investment and No. of new drugs launched 上 市 新 薬 数 ■ Mega ◆ 30 Japan Major ● R 2 0. 8328 R= 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 10, 000 ※新薬数は新規化合物 20, 000 30, 000 40, 000 R&D expense (US $Million) 50, 000 60, 000
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Relationship between R&D investment and No. of new drugs launched 上 市 新 薬 数 ■ Mega ◆ 30 Japan Major ● R 2 0. 8328 R= 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 10, 000 ※新薬数は新規化合物 20, 000 30, 000 40, 000 R&D expense (US $Million) 50, 000 60, 000
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China EU companies:Merger、scale up、restructure COG reduction、R&D increase、S&M increase
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China EU companies:Merger、scale up、restructure COG reduction、R&D increase、S&M increase
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 Glaxo Wellcome 95合併 SK Beckman 89合併 Glaxo Smith. Kline Wellcome 00 合併 Smith. Kline Beecham 93 医薬品事業部門分離独立 ICI Rhone-Poulenc Rorer 90 買収 W. H. Rorer Hoechst 68 Astra Zeneca acquisition of a majority holding Marion Roussel-Uclaf 89 Merrell Dow Ciba-Geigy 95買収 Roche Genentech Aventis 04買収 Marion Merrell Dow Sandoz 90 資本参加 99 合併 Hoechst 95 買収 Sanofi SI Synthelabo Ciba-Geigy 70合併 Astra. Zeneca 99 合併 Fisons 94 Sanofi Prescription drug部門 Sterling JR Geigy 02 03 04 94買収 Syntex 96 合併 Sanofiー aventis Sanofi-Synthelabo 99合併 Novartis 97 買収 Boehringer Mannheim Novartis 02 買収 Chugai Roche
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 Glaxo Wellcome 95合併 SK Beckman 89合併 Glaxo Smith. Kline Wellcome 00 合併 Smith. Kline Beecham 93 医薬品事業部門分離独立 ICI Rhone-Poulenc Rorer 90 買収 W. H. Rorer Hoechst 68 Astra Zeneca acquisition of a majority holding Marion Roussel-Uclaf 89 Merrell Dow Ciba-Geigy 95買収 Roche Genentech Aventis 04買収 Marion Merrell Dow Sandoz 90 資本参加 99 合併 Hoechst 95 買収 Sanofi SI Synthelabo Ciba-Geigy 70合併 Astra. Zeneca 99 合併 Fisons 94 Sanofi Prescription drug部門 Sterling JR Geigy 02 03 04 94買収 Syntex 96 合併 Sanofiー aventis Sanofi-Synthelabo 99合併 Novartis 97 買収 Boehringer Mannheim Novartis 02 買収 Chugai Roche
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key Acquisitions in 2008~2009 in the industry
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key Acquisitions in 2008~2009 in the industry
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key Acquisition cases in Jan. ~Feb. 2010 in the industry Time acquiring Corp. Target Corp. ) ( bil. USD Strategy
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key Acquisition cases in Jan. ~Feb. 2010 in the industry Time acquiring Corp. Target Corp. ) ( bil. USD Strategy
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading MNC’s portfolio by development status Most of leading MNCs have a big discover products base. Source: Thomason Pharma
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading MNC’s portfolio by development status Most of leading MNCs have a big discover products base. Source: Thomason Pharma
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Some thoughts about drug discovery
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Some thoughts about drug discovery
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 科 学 技 術 革 新 2 nd golden period First Golden Period Pharmacology Receptor Ion Channel Enzyme Organic Chemistry Naturals Pioneer technology Genomics Biotechnology Recombined Genes Cell fusion Antibody Epoch making New drugs Vaccines Gene-chips Insulin(DM) Growth hormone Patent Expiry Β antagonist( Angina・ Hypertension) α Antagonist( Hypertension・ BPH) H 2 Antagonist( Pepti-ucler) Ca antagonsit( Hypertension・ Angina) ACE inhibitor( Hypertension・ Cardiac Failure) Aspirin HMG-Co. A reductase( Hyperlipidemia) (Rheumatoid Arthritis) 新 薬 誕 生 1800 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 (年) - 薬理学会公開講座「夢のくすり、今のくすり」1998年.京都市 -
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 科 学 技 術 革 新 2 nd golden period First Golden Period Pharmacology Receptor Ion Channel Enzyme Organic Chemistry Naturals Pioneer technology Genomics Biotechnology Recombined Genes Cell fusion Antibody Epoch making New drugs Vaccines Gene-chips Insulin(DM) Growth hormone Patent Expiry Β antagonist( Angina・ Hypertension) α Antagonist( Hypertension・ BPH) H 2 Antagonist( Pepti-ucler) Ca antagonsit( Hypertension・ Angina) ACE inhibitor( Hypertension・ Cardiac Failure) Aspirin HMG-Co. A reductase( Hyperlipidemia) (Rheumatoid Arthritis) 新 薬 誕 生 1800 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 (年) - 薬理学会公開講座「夢のくすり、今のくすり」1998年.京都市 -
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key steps to new drug discovery 発想 (Inspiration) New treatment inspired by identified mechanism of diseases -information from papers, patients, healthcare professionals. Establishment of physical reactions and life syndromes of target diseases. Establishment of Methodology for screening (Discovery ) - Papers and laboratory observations Creation of new drugs via new technology (organic chemistry, Bio-technology, Antibody, Vaccines) (Invention) -Team works of multi-disciplines in life science 発見 発明 Innovation
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Key steps to new drug discovery 発想 (Inspiration) New treatment inspired by identified mechanism of diseases -information from papers, patients, healthcare professionals. Establishment of physical reactions and life syndromes of target diseases. Establishment of Methodology for screening (Discovery ) - Papers and laboratory observations Creation of new drugs via new technology (organic chemistry, Bio-technology, Antibody, Vaccines) (Invention) -Team works of multi-disciplines in life science 発見 発明 Innovation
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China • New challenges for drug discovery: The diseases, the causes and life styles Why some diseases occurs – – – • In some ethnics In some ages In a gender In a geographic location In some weather conditions In some occupations What are the causes – Extrinsic – Intrinsic • • What is the prognosis for different types of patients? How long will the disease last and how long does it takes to recover? The role of new drugs in the healing process. How to diagnose How to prevent from occurring? How change of life styles affect the treatment The recurrence and the causes. Can we prevent it from occurring? How to test anti-bodies, biologics for human use in animals? Scaling up of new biologics and genomic product?
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China • New challenges for drug discovery: The diseases, the causes and life styles Why some diseases occurs – – – • In some ethnics In some ages In a gender In a geographic location In some weather conditions In some occupations What are the causes – Extrinsic – Intrinsic • • What is the prognosis for different types of patients? How long will the disease last and how long does it takes to recover? The role of new drugs in the healing process. How to diagnose How to prevent from occurring? How change of life styles affect the treatment The recurrence and the causes. Can we prevent it from occurring? How to test anti-bodies, biologics for human use in animals? Scaling up of new biologics and genomic product?
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The relationship between the level of satisfaction with medical treatment and the level of contribution that medication makes to treatment (Japan) 100 Contribution of medication to treatment (%) Hypertension Peptic ulcer 90 80 70 60 Angina Pectoris Gout Diabetes mellitus Hyperlipidemia Tuberculosis Asthma Arrhythmia Chlamydia infection Allergic rhinitis Candidiasis Herpes virus infection Epilepsy Myocardial Dermatophytosis Anxiety Leukemia infarction MRSA infection Depression Prostate hyperplasia Schizophrenia Prostate cancer Parkinson’s disease SLE Glaucoma Low back pain Atopic dermatitis Irritable bowel syndrome Pressure sores Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Rheumatoid arthritis. Autonomic 40 Endometriosis Transplantation AIDS ataxia. Osteoporosis Nephrosis syndrome Occlusive peripheral arterial disease Cerebral infarction Hemorrhagic stroke Stress urinary incontinence Hepatitis C 30 Urinary Breast cancer Diabetic neuropathy Fibroid Chronic glomerulonephritis Osteoarthritis incontinence Spondylosis Cataracts Diabetic nephropathy Uterine cancer Hepatitis B 20 Cirrhosis Diabetic retinopathy Chronic pelvic pain Neuromuscular disturbance and Chronic renal failure Stomach cancer Lung cancer myopathy Liver cancer Colon cancer Multiple sclerosis 10 Alzheimer’s disease Senile dementia 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 50 90 Satisfaction is relatively high for diseases in the PCP market Diseases mainly taken care of by PCPs Note: Questionnaire for Japanese doctors ( : 15/10/1999 -22/12/1999; postal survey; 128 responses; ) Source: Japan Human Science Foundation: 2000 report on survey into basic technology in Japan, “Outlook on medical needs in 2010”; internal Astellas data; BCG analysis; Level of satisfaction with medical 100 treatment (%)
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The relationship between the level of satisfaction with medical treatment and the level of contribution that medication makes to treatment (Japan) 100 Contribution of medication to treatment (%) Hypertension Peptic ulcer 90 80 70 60 Angina Pectoris Gout Diabetes mellitus Hyperlipidemia Tuberculosis Asthma Arrhythmia Chlamydia infection Allergic rhinitis Candidiasis Herpes virus infection Epilepsy Myocardial Dermatophytosis Anxiety Leukemia infarction MRSA infection Depression Prostate hyperplasia Schizophrenia Prostate cancer Parkinson’s disease SLE Glaucoma Low back pain Atopic dermatitis Irritable bowel syndrome Pressure sores Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Rheumatoid arthritis. Autonomic 40 Endometriosis Transplantation AIDS ataxia. Osteoporosis Nephrosis syndrome Occlusive peripheral arterial disease Cerebral infarction Hemorrhagic stroke Stress urinary incontinence Hepatitis C 30 Urinary Breast cancer Diabetic neuropathy Fibroid Chronic glomerulonephritis Osteoarthritis incontinence Spondylosis Cataracts Diabetic nephropathy Uterine cancer Hepatitis B 20 Cirrhosis Diabetic retinopathy Chronic pelvic pain Neuromuscular disturbance and Chronic renal failure Stomach cancer Lung cancer myopathy Liver cancer Colon cancer Multiple sclerosis 10 Alzheimer’s disease Senile dementia 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 50 90 Satisfaction is relatively high for diseases in the PCP market Diseases mainly taken care of by PCPs Note: Questionnaire for Japanese doctors ( : 15/10/1999 -22/12/1999; postal survey; 128 responses; ) Source: Japan Human Science Foundation: 2000 report on survey into basic technology in Japan, “Outlook on medical needs in 2010”; internal Astellas data; BCG analysis; Level of satisfaction with medical 100 treatment (%)
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China New challenges of clinical research for unmet needs • More aging population with many underlying diseases who use many drugs. • Difficulty in conduct clinical trials for infants. • Diagnostic method and parameters not established. • Need to provide long term efficacy and safety. • Not just for efficacy and safety, need to justify the value with health-economic models, accepted by the payers and, healthcare professionals and patients. • How to justify value to quality of life and extension of life expectancy not in years. • Early engagement in clinical trial design of marketing for proper positioning of the new drug
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China New challenges of clinical research for unmet needs • More aging population with many underlying diseases who use many drugs. • Difficulty in conduct clinical trials for infants. • Diagnostic method and parameters not established. • Need to provide long term efficacy and safety. • Not just for efficacy and safety, need to justify the value with health-economic models, accepted by the payers and, healthcare professionals and patients. • How to justify value to quality of life and extension of life expectancy not in years. • Early engagement in clinical trial design of marketing for proper positioning of the new drug
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 6 phases of failed clinical development project • • • Enthusiasm Disillusionment Panic Search for guilty Punishment for the innocent Praise and honors fir non-participants
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China 6 phases of failed clinical development project • • • Enthusiasm Disillusionment Panic Search for guilty Punishment for the innocent Praise and honors fir non-participants
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The Global Scenario Envisioned by Astellas Ø Progress of policies to control health expenditure Ø New healthcare reforms in EU, USA and Japan all focusing in cost containment. Ø Who should pay for the drug and technology innovation? Government? Insurance? Patient? Ø Decrease in market growth rate Ø Market growth in EU, Japan and USA decreased to 5% of below, except pharmerging markets led by China. Ø Increased complexity of the market Ø Many diseases cared by primary care professionals are getting satisfactory treatment by medicines while good remedies for chronic diseases, CNS, DM, RA and diseases related to auto-immune system remains few.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The Global Scenario Envisioned by Astellas Ø Progress of policies to control health expenditure Ø New healthcare reforms in EU, USA and Japan all focusing in cost containment. Ø Who should pay for the drug and technology innovation? Government? Insurance? Patient? Ø Decrease in market growth rate Ø Market growth in EU, Japan and USA decreased to 5% of below, except pharmerging markets led by China. Ø Increased complexity of the market Ø Many diseases cared by primary care professionals are getting satisfactory treatment by medicines while good remedies for chronic diseases, CNS, DM, RA and diseases related to auto-immune system remains few.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The total number of blockbusters produced by the top 10 drug companies, the number of blockbusters being delivered to the market and the number of blockbusters with expiring patents Number of blockbusters launched, 25 120 Result 20 Number of blockbusters with expiring patents Total number of blockbusters sold on the market 15 Number of blockbusters Forecast Number of blockbusters delivered to the market annually (average over 3 years*) 100 80 60 10 40 5 Number of blockbusters expiring annually after average patent term (average over 3 years) 0 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 20 0 2010 (Launch Year ) Stagnation of new deliveries and the expiration of patents will simultaneously brake market growth. * The number of products delivered to the market for 2001 -2010 is based on risk-adjusted estimates Note: Blockbusters are those drug products with peak sales of US$500 million or more based on 2001 prices. The ranking of the top 10 drug companies was based on the 2001 market; since that time some of those companies have been amalgamated through the M&A process. Source: FDA, Lehman Brothers, Paine Webber, Scrip, BCG analysis
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The total number of blockbusters produced by the top 10 drug companies, the number of blockbusters being delivered to the market and the number of blockbusters with expiring patents Number of blockbusters launched, 25 120 Result 20 Number of blockbusters with expiring patents Total number of blockbusters sold on the market 15 Number of blockbusters Forecast Number of blockbusters delivered to the market annually (average over 3 years*) 100 80 60 10 40 5 Number of blockbusters expiring annually after average patent term (average over 3 years) 0 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 20 0 2010 (Launch Year ) Stagnation of new deliveries and the expiration of patents will simultaneously brake market growth. * The number of products delivered to the market for 2001 -2010 is based on risk-adjusted estimates Note: Blockbusters are those drug products with peak sales of US$500 million or more based on 2001 prices. The ranking of the top 10 drug companies was based on the 2001 market; since that time some of those companies have been amalgamated through the M&A process. Source: FDA, Lehman Brothers, Paine Webber, Scrip, BCG analysis
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China ■ There will be four basic types of players in the future market a. Super-scale players: 2 -3 companies – Focusing on the conventional market, they compete with size as their advantage. – In order to resist the pressure of falling earnings brought about by decreasing market growth rates, they buy out their competitors (achieving cost synergies) and advance the process of consolidation between superior companies. – Global market share of the top player is 20 -30%. b. Specialized players: many – As the market becomes increasingly complex, they capitalize on a single strength unrivaled by others. – A diverse range of specialized players exists and new players will continue to enter the market. c. Global category players: 5 -10 companies – They have global reach, and construct top-level franchises in multiple highly specialized therapeutic areas/diseases. – While not greatly affected by the declining growth of conventional markets, they can sustain their level of growth by taking advantage of the increasing market complexity. d. Local players – Develop business in local markets by focusing on generics.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China ■ There will be four basic types of players in the future market a. Super-scale players: 2 -3 companies – Focusing on the conventional market, they compete with size as their advantage. – In order to resist the pressure of falling earnings brought about by decreasing market growth rates, they buy out their competitors (achieving cost synergies) and advance the process of consolidation between superior companies. – Global market share of the top player is 20 -30%. b. Specialized players: many – As the market becomes increasingly complex, they capitalize on a single strength unrivaled by others. – A diverse range of specialized players exists and new players will continue to enter the market. c. Global category players: 5 -10 companies – They have global reach, and construct top-level franchises in multiple highly specialized therapeutic areas/diseases. – While not greatly affected by the declining growth of conventional markets, they can sustain their level of growth by taking advantage of the increasing market complexity. d. Local players – Develop business in local markets by focusing on generics.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Brief on China Pharma market • About 400 M covered by urban worker’s and resident insurance. • About 800 M covered by New Rural Cooperative health program for primary care • Market size reached RMB 210 Billion with growth of 27% in 2009. • Progress of new healthcare reform has profound impact on the industry. • Healthcare technology assessment to be used for price negotiation for expensive drugs
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Brief on China Pharma market • About 400 M covered by urban worker’s and resident insurance. • About 800 M covered by New Rural Cooperative health program for primary care • Market size reached RMB 210 Billion with growth of 27% in 2009. • Progress of new healthcare reform has profound impact on the industry. • Healthcare technology assessment to be used for price negotiation for expensive drugs
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Total China hospital market Reached 243. 9 billion RMB in 2009 % 8 22. = R r 5 y G CA Local companies were driving the increase of china pharma MKT. Source: IMS 4 Q 09
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Total China hospital market Reached 243. 9 billion RMB in 2009 % 8 22. = R r 5 y G CA Local companies were driving the increase of china pharma MKT. Source: IMS 4 Q 09
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading MNCs Ranking in past decade Besides company merging, new product launching is another engine for MNCs to improve ranking in China market.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading MNCs Ranking in past decade Besides company merging, new product launching is another engine for MNCs to improve ranking in China market.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China New products play an important role to China business New product= launched within 5 years
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China New products play an important role to China business New product= launched within 5 years
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading therapy class by Country in past years
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Leading therapy class by Country in past years
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Affluence is changing lifestyle and prevalence of chronic condition such as diabetes, hypertension and cerebro-vascular is rising rapidly. CAGR 93 -03 12. 5% Hypertension 4. 8% Heart Diseases 16. 7% Diabetes 8. 6% Cerebrovascular Diseases 2. 4% Genitourinary Diseases -0. 5% Acute Gastritis 0. 9% 1998 Gallbladder Disorders 1993 Arthritis -1. 0% -2. 2% 2003 Geriatric Chronic Bronchitis Eye Diseases 1. 4% Neurological Diseases 7. 0% Malignant tumors -3. 3% Infectious Diseases 6. 9% Psychotic disorders 7. 4% Injury and poisoning 0 5 10 15 Urban Patient Number (Mil) Source: MOH statistics yearbook 2008 20 25 30
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Affluence is changing lifestyle and prevalence of chronic condition such as diabetes, hypertension and cerebro-vascular is rising rapidly. CAGR 93 -03 12. 5% Hypertension 4. 8% Heart Diseases 16. 7% Diabetes 8. 6% Cerebrovascular Diseases 2. 4% Genitourinary Diseases -0. 5% Acute Gastritis 0. 9% 1998 Gallbladder Disorders 1993 Arthritis -1. 0% -2. 2% 2003 Geriatric Chronic Bronchitis Eye Diseases 1. 4% Neurological Diseases 7. 0% Malignant tumors -3. 3% Infectious Diseases 6. 9% Psychotic disorders 7. 4% Injury and poisoning 0 5 10 15 Urban Patient Number (Mil) Source: MOH statistics yearbook 2008 20 25 30
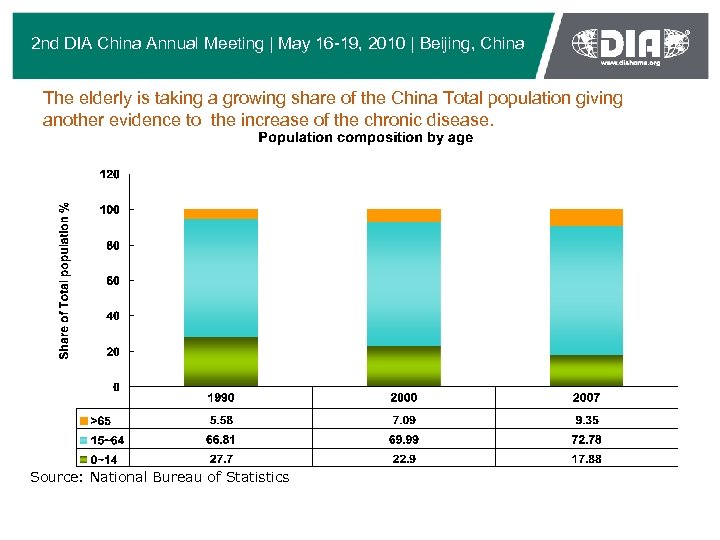 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The elderly is taking a growing share of the China Total population giving another evidence to the increase of the chronic disease. Source: National Bureau of Statistics
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The elderly is taking a growing share of the China Total population giving another evidence to the increase of the chronic disease. Source: National Bureau of Statistics
 Chronic diseaes 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Antibiotics lost its share in the last decade while share of TCM and Oncology's are increasing drastically Source: IMS 4 Q 08
Chronic diseaes 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Antibiotics lost its share in the last decade while share of TCM and Oncology's are increasing drastically Source: IMS 4 Q 08
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China In 6 of top 10 TCIII in China market, the sales of generic product is even bigger than the origin product (red line) Source: IMS
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China In 6 of top 10 TCIII in China market, the sales of generic product is even bigger than the origin product (red line) Source: IMS
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Comparison of Pharma Industry of China and India • Similarity – Production of low cost, low concentration of industry – Mainly produce Generics – Small share of independent innovation research and the proportion of drugs • Difference – The manufactures in china always copy low-tech product and compete in the market with low price but seldom choose hightech product – The India manufactures choose a better way– innovative copy and get their own patent so that get more profit.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Comparison of Pharma Industry of China and India • Similarity – Production of low cost, low concentration of industry – Mainly produce Generics – Small share of independent innovation research and the proportion of drugs • Difference – The manufactures in china always copy low-tech product and compete in the market with low price but seldom choose hightech product – The India manufactures choose a better way– innovative copy and get their own patent so that get more profit.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Pharma R&D in China • Majority of pharma industry have been focusing on copying in past few decades. • China has decided to become an innovative state in 2007. • Many budget allocated for life science, RMB 6. 6 Billion allocated to various projects since late 2008. – Projects included all types of collaboration of industry and research institutions and healthcare institutions. – Grant amount usually less than 200 M per institute. • R&D is encouraged by the government but not sufficient for return to investment for pharma R&D due to regulatory and risk sharing system in China.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Pharma R&D in China • Majority of pharma industry have been focusing on copying in past few decades. • China has decided to become an innovative state in 2007. • Many budget allocated for life science, RMB 6. 6 Billion allocated to various projects since late 2008. – Projects included all types of collaboration of industry and research institutions and healthcare institutions. – Grant amount usually less than 200 M per institute. • R&D is encouraged by the government but not sufficient for return to investment for pharma R&D due to regulatory and risk sharing system in China.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Marketing Authorization System Key barriers for Pharma R&D in China under current registration system • Requesting Pharma R&D may not be equipped with the production facilities • Pharma R&D have to transfer the technology to drug manufacturer, the right and benefits are not well protected Key benefits of market authorization system for Pharma R&D in China • Pharma R&D can be the Marketing Authorization Holder without production facilities • Pharma R&D can collaborate with drug manufacturer for toll manufacturing with/without mandatory technology transfer • Reasonable amount of return back to R&D as incentive for stimulating sustainable R&D • Pharma R&D can focus on R&D with their key competence 38
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Marketing Authorization System Key barriers for Pharma R&D in China under current registration system • Requesting Pharma R&D may not be equipped with the production facilities • Pharma R&D have to transfer the technology to drug manufacturer, the right and benefits are not well protected Key benefits of market authorization system for Pharma R&D in China • Pharma R&D can be the Marketing Authorization Holder without production facilities • Pharma R&D can collaborate with drug manufacturer for toll manufacturing with/without mandatory technology transfer • Reasonable amount of return back to R&D as incentive for stimulating sustainable R&D • Pharma R&D can focus on R&D with their key competence 38
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China About clinical trial in China
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China About clinical trial in China
 China Is China Annual Meeting | Relative To Other Countries 2 nd DIA Underrepresented May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Based On Its Population And Market Size Phase III trials sponsored by industry Number of trials (2007) Number of trials per 100 million population (2007) Number of trials per $1 bn drug sales (2007) CAGR* of trials (2003 -2007) China India Czech Poland Russia 32 106 11 100 54 963 144 128 44 378 90 Argentina 48 Mexico 85 Source: Clinicaltrials. gov; Global Insight; IMS; team analysis *CAGR Cumulative Annual Growth Rate 26 17 250 Brazil 23 25 26 34 36 28 25
China Is China Annual Meeting | Relative To Other Countries 2 nd DIA Underrepresented May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Based On Its Population And Market Size Phase III trials sponsored by industry Number of trials (2007) Number of trials per 100 million population (2007) Number of trials per $1 bn drug sales (2007) CAGR* of trials (2003 -2007) China India Czech Poland Russia 32 106 11 100 54 963 144 128 44 378 90 Argentina 48 Mexico 85 Source: Clinicaltrials. gov; Global Insight; IMS; team analysis *CAGR Cumulative Annual Growth Rate 26 17 250 Brazil 23 25 26 34 36 28 25
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Global Clinical Trial in China • According to SFDA record during Jan 2004 and Apr 2008, the average evaluate time of global clinical trial is 7 month.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Global Clinical Trial in China • According to SFDA record during Jan 2004 and Apr 2008, the average evaluate time of global clinical trial is 7 month.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Simultaneous Global Development Benefits • Submission to and review by relevant regulatory authorities at the same time • Broader regulatory oversight and experiences • Earlier availability of innovative drug therapy to emerging market population; ultimately leads to reduction in “drug lag” • Enables science-based approach to better define intrinsic and extrinsic factors (risk-based) • Identify clinically meaningful ethnic differences & discuss next steps • Registration dossiers to include higher percentage of Asian data • Advance knowledge, experience and competence of drug clinical development of investigators / medical community 42
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Simultaneous Global Development Benefits • Submission to and review by relevant regulatory authorities at the same time • Broader regulatory oversight and experiences • Earlier availability of innovative drug therapy to emerging market population; ultimately leads to reduction in “drug lag” • Enables science-based approach to better define intrinsic and extrinsic factors (risk-based) • Identify clinically meaningful ethnic differences & discuss next steps • Registration dossiers to include higher percentage of Asian data • Advance knowledge, experience and competence of drug clinical development of investigators / medical community 42
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Simultaneous Global Development-2 Challenges • Longer CTA approval times (agency & ethics committee) & start-up times • Other general barriers (not inclusive of all countries) • Lack of harmonization – requirements, processes • Unique requirements, outside international standards (e. g. , country-specific Quality data) • Lack of formal mechanism for agency consultation • Inflexibility to CTA amendments (protocol & quality changes) • Uncertainty of ICH/WHO GCP enforcement • Inefficient/outdated review processes, lack of transparency • Unpredictable requests • Intellectual property concerns • Insufficient resources within regulatory agencies
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Simultaneous Global Development-2 Challenges • Longer CTA approval times (agency & ethics committee) & start-up times • Other general barriers (not inclusive of all countries) • Lack of harmonization – requirements, processes • Unique requirements, outside international standards (e. g. , country-specific Quality data) • Lack of formal mechanism for agency consultation • Inflexibility to CTA amendments (protocol & quality changes) • Uncertainty of ICH/WHO GCP enforcement • Inefficient/outdated review processes, lack of transparency • Unpredictable requests • Intellectual property concerns • Insufficient resources within regulatory agencies
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Global development could speed up product launch in China.
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Global development could speed up product launch in China.
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China RDPAC’s suggestion on SGD • • Separation administration of CTA and NDA Implementation of Special Review Procedures Speed up the approval process for clinical trial of innovative products Enhancement of clinical trial administration by allocating the responsibilities to all stakeholders • Introduction of Marketing Authorization System • Communication and interaction among stakeholders • Harmonization, the principle of “ sameness” will direct the development path For SGD, it is a race to change! Who will be left behind ? 45
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China RDPAC’s suggestion on SGD • • Separation administration of CTA and NDA Implementation of Special Review Procedures Speed up the approval process for clinical trial of innovative products Enhancement of clinical trial administration by allocating the responsibilities to all stakeholders • Introduction of Marketing Authorization System • Communication and interaction among stakeholders • Harmonization, the principle of “ sameness” will direct the development path For SGD, it is a race to change! Who will be left behind ? 45
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Trend – Increasing IMCT in China Source: RDPAC Drug Registration Timeline Survey
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Trend – Increasing IMCT in China Source: RDPAC Drug Registration Timeline Survey
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Drug Development Model in China Yesterday A Linear Development Model Following International Approval ≥ 4 years drug lag Global Development CPP R-CTA Review Clinical Trial Approval Outside China IDL Review 4 Years Approval In China A Parallel Development Model ≥ 2 years drug lag Today Global Development GCTA Review CPP R-CTA Review Clinical Trial CPP IDL Review 2 Years CPP = Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product R-CTA = Regional Clinical Trial Application IDL = Import Drug License GCTA = Global Clinical Trial Application - 47 -
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Drug Development Model in China Yesterday A Linear Development Model Following International Approval ≥ 4 years drug lag Global Development CPP R-CTA Review Clinical Trial Approval Outside China IDL Review 4 Years Approval In China A Parallel Development Model ≥ 2 years drug lag Today Global Development GCTA Review CPP R-CTA Review Clinical Trial CPP IDL Review 2 Years CPP = Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product R-CTA = Regional Clinical Trial Application IDL = Import Drug License GCTA = Global Clinical Trial Application - 47 -
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The Road To Enlightenment…Follow The Lights - 48 -
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China The Road To Enlightenment…Follow The Lights - 48 -
 2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Many thanks for your kind attention! Joseph. cho@cn. astellas. com www. astellas. com. cn www. rdpac. org 49
2 nd DIA China Annual Meeting | May 16 -19, 2010 | Beijing, China Many thanks for your kind attention! Joseph. cho@cn. astellas. com www. astellas. com. cn www. rdpac. org 49


