918441cccc92be15b42e041504be0f9a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99
 2 July 2010 1 st Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group (DMWG) Agenda • Announcements: – New Members: – This week: • IDEAS, OMG email trails on Milestones, Projects, PES, XMI, … – Levine to contact Bailey re XSD generator and IDEAS plugin – Upcoming: • 12 August 2010 Do. DAF Plenary • DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June – Services to meet re DARS rqmts, DARS “compliant”, put what in DARS, R = repository, registry, or both – AV-1 XML X DM 2 • MDR WG and COI Forum • New References: – none • New submissions by members: – N/A • Do. D EA COI Charter – Step through 8320. 02 G and relate to Do. D EA COI – Action Items for next quarter’s meeting • Others: – TBS PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
2 July 2010 1 st Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group (DMWG) Agenda • Announcements: – New Members: – This week: • IDEAS, OMG email trails on Milestones, Projects, PES, XMI, … – Levine to contact Bailey re XSD generator and IDEAS plugin – Upcoming: • 12 August 2010 Do. DAF Plenary • DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June – Services to meet re DARS rqmts, DARS “compliant”, put what in DARS, R = repository, registry, or both – AV-1 XML X DM 2 • MDR WG and COI Forum • New References: – none • New submissions by members: – N/A • Do. D EA COI Charter – Step through 8320. 02 G and relate to Do. D EA COI – Action Items for next quarter’s meeting • Others: – TBS PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
 Table C 2. T 1. Key COI Attributes • Formed to meet a specific data sharing mission or fulfill a task • Composed of stakeholders cooperating on behalf of various organizations, with emphasis on cross-Component activities • Members committed to actively sharing information in relation to their mission and/or task objectives • Recognize potential for authorized but unanticipated users and therefore, strive to make their data visible, accessible, and understandable to those inside and outside their community. • • • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI Reuse, compliance (solutions, C&A), interoperabilty, net-centricity, data sharing, federation, solutions arch standization, … in support of the 6 core processes (JCIDS, DAS, PPBE, CPM, SE, Ops Plng) CSA’s, CIOs, Acq’s, inter-agency (at specific reification / meta levels), PM’s, Governance, e. g. , DTM-93, CJCSI’s 6212. 01 F & 3170, NCSS, NCDS, DODD/I 4630, Arch Do. DI, DISA cross -agency (DHS, NGO’s) Visible -- DARS, NCES Enterprise Search, MDR, DISR, Understandable -- DM 2, UCORE, IDEAS Accessible – SSO, Intelipedia (U), … distribution restrictions, aggregation problem, pedigree
Table C 2. T 1. Key COI Attributes • Formed to meet a specific data sharing mission or fulfill a task • Composed of stakeholders cooperating on behalf of various organizations, with emphasis on cross-Component activities • Members committed to actively sharing information in relation to their mission and/or task objectives • Recognize potential for authorized but unanticipated users and therefore, strive to make their data visible, accessible, and understandable to those inside and outside their community. • • • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI Reuse, compliance (solutions, C&A), interoperabilty, net-centricity, data sharing, federation, solutions arch standization, … in support of the 6 core processes (JCIDS, DAS, PPBE, CPM, SE, Ops Plng) CSA’s, CIOs, Acq’s, inter-agency (at specific reification / meta levels), PM’s, Governance, e. g. , DTM-93, CJCSI’s 6212. 01 F & 3170, NCSS, NCDS, DODD/I 4630, Arch Do. DI, DISA cross -agency (DHS, NGO’s) Visible -- DARS, NCES Enterprise Search, MDR, DISR, Understandable -- DM 2, UCORE, IDEAS Accessible – SSO, Intelipedia (U), … distribution restrictions, aggregation problem, pedigree
 Table C 2. T 2. Primary Responsibilities of COIs • Identify data assets and information sharing capabilities, both operational and developmental, that should conform to the data strategy goals of NCDS. • Identify approaches to enable those data assets and information sharing capabilities to satisfy data strategy goals and to measure the value to consumers of shared data. • Develop and maintain semantic and structural agreements to ensure that data assets can be understood and used effectively by COI members and unanticipated users. • Register appropriate metadata artifacts for use by the COI members and others. • Extend the Do. D Discovery Metadata Specification (DDMS) (Reference (c)) as required to ensure that COI-specific discovery metadata is understandable for enterprise searches. • Partner with a governing authority, as appropriate, to ensure that COI recommendations are adopted and implemented through programs, processes, systems and organizations • • • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI Naval Architecture Repository System (NARS), MCAE, CADIE, SADIE? , JACAE, AF? , DLA? , AMC? , EISP DB? BEA encyclopedia, TV repository in DISR? …all sorts of other locations, e. g. , sharepoints, legacy fileservers – in future DM 2 PES XML files % completeness, # registered users & level of activity in COI, DM 2, IDEAS, Do. DAF, UCORE-relationship, DDMS-relationship DM 2 CDM, LDM, PES XSD, and documentation registered in MDR in Arch namespace Need to develop discovery use cases, DARS rqmt? , register extensions in MDR, IC? 500 -21 IRM 1. 0 maps to DDMS 2. 0, cross-domain discovery and retrieval FAC, Army NCDS ideas (ADTP, Army Data Transformation Plan)
Table C 2. T 2. Primary Responsibilities of COIs • Identify data assets and information sharing capabilities, both operational and developmental, that should conform to the data strategy goals of NCDS. • Identify approaches to enable those data assets and information sharing capabilities to satisfy data strategy goals and to measure the value to consumers of shared data. • Develop and maintain semantic and structural agreements to ensure that data assets can be understood and used effectively by COI members and unanticipated users. • Register appropriate metadata artifacts for use by the COI members and others. • Extend the Do. D Discovery Metadata Specification (DDMS) (Reference (c)) as required to ensure that COI-specific discovery metadata is understandable for enterprise searches. • Partner with a governing authority, as appropriate, to ensure that COI recommendations are adopted and implemented through programs, processes, systems and organizations • • • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI Naval Architecture Repository System (NARS), MCAE, CADIE, SADIE? , JACAE, AF? , DLA? , AMC? , EISP DB? BEA encyclopedia, TV repository in DISR? …all sorts of other locations, e. g. , sharepoints, legacy fileservers – in future DM 2 PES XML files % completeness, # registered users & level of activity in COI, DM 2, IDEAS, Do. DAF, UCORE-relationship, DDMS-relationship DM 2 CDM, LDM, PES XSD, and documentation registered in MDR in Arch namespace Need to develop discovery use cases, DARS rqmt? , register extensions in MDR, IC? 500 -21 IRM 1. 0 maps to DDMS 2. 0, cross-domain discovery and retrieval FAC, Army NCDS ideas (ADTP, Army Data Transformation Plan)
 Table C 2. T 3. Summary Descriptions of COI Roles ROLE DESCRIPTION COI Governing Authority Individual or organization that will review and adjudicate COI conflicts and push for Do. D Component implementation and support of COI data sharing agreements. The appropriate governance forums and authorities may already exist and should be leveraged where possible. This role is typically filled by the Mission Area lead, but in the initial stages of operationalizing portfolio management, may also be a Combatant Command or Functional Support Agency (e. g. , DLA). The COI governing authority acts as an external champion with authority and cross-COI visibility to affect change. Responsibilities: Identify information sharing problems and COI missions Review and adjudicate resolution of discrepancies across COIs Promote and endorse COI activities and implement agreements through the Joint Capabilities Integration and Development System, Acquisition, and Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution process Promote COI support to Do. D Components Review COI plan of action and milestones (POAM) status and success measures COI Lead An individual from a specific Do. D Component who has been tasked with managing the COI. Generally, the organization leading the COI activity has committed to driving the COI to a data sharing solution and will advocate that data sharing agreements be implemented within Do. D Component plans, programs, and budgets. The COI lead helps address internal COI conflicts and issues, keeping the COI on track. The COI lead role may be established on a shared or rotating basis, and should be filled by a functional expert, rather than an IT specialist. Responsibilities: Ensure that appropriate stakeholders participate in COIs via COI working groups, and appropriate representatives participate via the governing authority Lead the COI, including developing and tracking POAMs Act as a primary point of contact (POC) for the COI Promote policies and practices for data sharing and participating in cross-Component COIs Identify mission-specific success criteria for the COI Stakeholder s Organizations or personnel who have an interest in the outcome of the COI effort. These may not be active participants in the COI, but will likely use and/or benefit from the capability, such as data consumers. COI stakeholders are those who stand to benefit, and those whose processes and/or systems will change, as a result of COI activity. Responsibilities: Promote policies across Do. D Components in terms of practices and standards in the implementation areas, including those for data tagging, data access services, and registration of metadata artifacts Promote the reuse of data access services within programs and systems Track Do. D Component implementation of Reference (a) through COI activities Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements, contribute to COI requirements gathering processes, and provide feedback on COI-defined information sharing capabilities Who / How in Do. D EA COI?
Table C 2. T 3. Summary Descriptions of COI Roles ROLE DESCRIPTION COI Governing Authority Individual or organization that will review and adjudicate COI conflicts and push for Do. D Component implementation and support of COI data sharing agreements. The appropriate governance forums and authorities may already exist and should be leveraged where possible. This role is typically filled by the Mission Area lead, but in the initial stages of operationalizing portfolio management, may also be a Combatant Command or Functional Support Agency (e. g. , DLA). The COI governing authority acts as an external champion with authority and cross-COI visibility to affect change. Responsibilities: Identify information sharing problems and COI missions Review and adjudicate resolution of discrepancies across COIs Promote and endorse COI activities and implement agreements through the Joint Capabilities Integration and Development System, Acquisition, and Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution process Promote COI support to Do. D Components Review COI plan of action and milestones (POAM) status and success measures COI Lead An individual from a specific Do. D Component who has been tasked with managing the COI. Generally, the organization leading the COI activity has committed to driving the COI to a data sharing solution and will advocate that data sharing agreements be implemented within Do. D Component plans, programs, and budgets. The COI lead helps address internal COI conflicts and issues, keeping the COI on track. The COI lead role may be established on a shared or rotating basis, and should be filled by a functional expert, rather than an IT specialist. Responsibilities: Ensure that appropriate stakeholders participate in COIs via COI working groups, and appropriate representatives participate via the governing authority Lead the COI, including developing and tracking POAMs Act as a primary point of contact (POC) for the COI Promote policies and practices for data sharing and participating in cross-Component COIs Identify mission-specific success criteria for the COI Stakeholder s Organizations or personnel who have an interest in the outcome of the COI effort. These may not be active participants in the COI, but will likely use and/or benefit from the capability, such as data consumers. COI stakeholders are those who stand to benefit, and those whose processes and/or systems will change, as a result of COI activity. Responsibilities: Promote policies across Do. D Components in terms of practices and standards in the implementation areas, including those for data tagging, data access services, and registration of metadata artifacts Promote the reuse of data access services within programs and systems Track Do. D Component implementation of Reference (a) through COI activities Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements, contribute to COI requirements gathering processes, and provide feedback on COI-defined information sharing capabilities Who / How in Do. D EA COI?
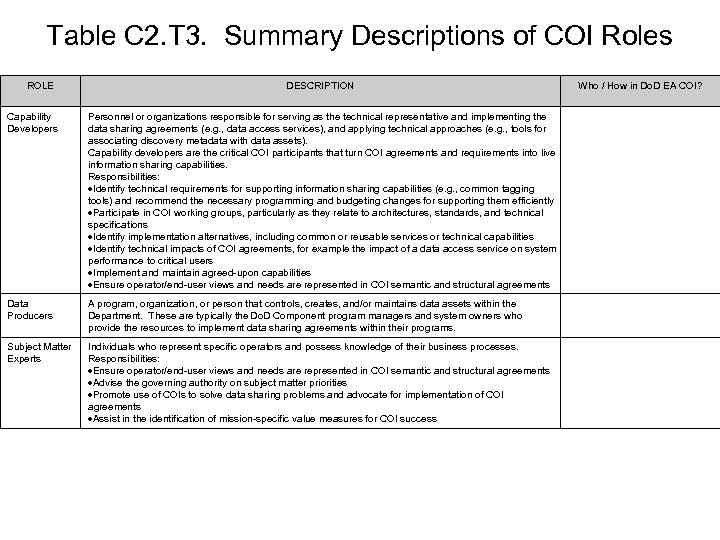 Table C 2. T 3. Summary Descriptions of COI Roles ROLE DESCRIPTION Capability Developers Personnel or organizations responsible for serving as the technical representative and implementing the data sharing agreements (e. g. , data access services), and applying technical approaches (e. g. , tools for associating discovery metadata with data assets). Capability developers are the critical COI participants that turn COI agreements and requirements into live information sharing capabilities. Responsibilities: Identify technical requirements for supporting information sharing capabilities (e. g. , common tagging tools) and recommend the necessary programming and budgeting changes for supporting them efficiently Participate in COI working groups, particularly as they relate to architectures, standards, and technical specifications Identify implementation alternatives, including common or reusable services or technical capabilities Identify technical impacts of COI agreements, for example the impact of a data access service on system performance to critical users Implement and maintain agreed-upon capabilities Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements Data Producers A program, organization, or person that controls, creates, and/or maintains data assets within the Department. These are typically the Do. D Component program managers and system owners who provide the resources to implement data sharing agreements within their programs. Subject Matter Experts Individuals who represent specific operators and possess knowledge of their business processes. Responsibilities: Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements Advise the governing authority on subject matter priorities Promote use of COIs to solve data sharing problems and advocate for implementation of COI agreements Assist in the identification of mission-specific value measures for COI success Who / How in Do. D EA COI?
Table C 2. T 3. Summary Descriptions of COI Roles ROLE DESCRIPTION Capability Developers Personnel or organizations responsible for serving as the technical representative and implementing the data sharing agreements (e. g. , data access services), and applying technical approaches (e. g. , tools for associating discovery metadata with data assets). Capability developers are the critical COI participants that turn COI agreements and requirements into live information sharing capabilities. Responsibilities: Identify technical requirements for supporting information sharing capabilities (e. g. , common tagging tools) and recommend the necessary programming and budgeting changes for supporting them efficiently Participate in COI working groups, particularly as they relate to architectures, standards, and technical specifications Identify implementation alternatives, including common or reusable services or technical capabilities Identify technical impacts of COI agreements, for example the impact of a data access service on system performance to critical users Implement and maintain agreed-upon capabilities Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements Data Producers A program, organization, or person that controls, creates, and/or maintains data assets within the Department. These are typically the Do. D Component program managers and system owners who provide the resources to implement data sharing agreements within their programs. Subject Matter Experts Individuals who represent specific operators and possess knowledge of their business processes. Responsibilities: Ensure operator/end-user views and needs are represented in COI semantic and structural agreements Advise the governing authority on subject matter priorities Promote use of COIs to solve data sharing problems and advocate for implementation of COI agreements Assist in the identification of mission-specific value measures for COI success Who / How in Do. D EA COI?
 Duties • COI FORMATION AND EXECUTION – ESTABLISH AND EVOLVE A COI – COI MANAGEMENT AND GOVERNANCE – CAPABILITY PLANNING AND USER EVALUATION • DATA SHARING IMPLEMENTATION – MAKING DATA VISIBLE – MAKING DATA ACCESSIBLE – MAKING DATA UNDERSTANDABLE – PROMOTING TRUST • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI
Duties • COI FORMATION AND EXECUTION – ESTABLISH AND EVOLVE A COI – COI MANAGEMENT AND GOVERNANCE – CAPABILITY PLANNING AND USER EVALUATION • DATA SHARING IMPLEMENTATION – MAKING DATA VISIBLE – MAKING DATA ACCESSIBLE – MAKING DATA UNDERSTANDABLE – PROMOTING TRUST • Relevance / meaning to Do. D EA COI
 25 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – – New Members: This week: • • – JMT Use Case (Vicense) Capability model (Terebesi) SV-1 QA Problem Status Update (Lee) So. A High-Pri issues (Ellis) – inc. So. AML terms submitted by Dandashi 2. 02 Plan: – – – • Services / So. AML / Service oriented architecture Modeling Language (Soa. ML) - Specification for the UML Profile and Metamodel for Services (UPMS) New submissions by members: – – • INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 agenda out DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June MDR WG and COI Forum New References: – • OMG Technical Meeting Semantic Technology Conference NCOIC June Plenary in Brussels – NATO and NAF Military Operations Research Society Upcoming: • • • PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING Review new Action Items, 66 of them – 7 teed up in read-ahead Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 90 of them: start with ones to right: Progress update on 2. 02 AI’s Others: – – Naming pattern, System meaning inputs – Alex TBS
25 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – – New Members: This week: • • – JMT Use Case (Vicense) Capability model (Terebesi) SV-1 QA Problem Status Update (Lee) So. A High-Pri issues (Ellis) – inc. So. AML terms submitted by Dandashi 2. 02 Plan: – – – • Services / So. AML / Service oriented architecture Modeling Language (Soa. ML) - Specification for the UML Profile and Metamodel for Services (UPMS) New submissions by members: – – • INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 agenda out DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June MDR WG and COI Forum New References: – • OMG Technical Meeting Semantic Technology Conference NCOIC June Plenary in Brussels – NATO and NAF Military Operations Research Society Upcoming: • • • PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING Review new Action Items, 66 of them – 7 teed up in read-ahead Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 90 of them: start with ones to right: Progress update on 2. 02 AI’s Others: – – Naming pattern, System meaning inputs – Alex TBS
 IST NR KPP WG • Day 1 28 June 2010 -NII 1/2 DAY • **Interoperability and Supportability Policy Discussion **Architecture • **Policy Discussion -DOTE IA Crosswalk Test WG • Briefing Day 2 29 June 2010 • -NSA • -JFCOM • -CJCSI 6212. 01 F Review/Discussion
IST NR KPP WG • Day 1 28 June 2010 -NII 1/2 DAY • **Interoperability and Supportability Policy Discussion **Architecture • **Policy Discussion -DOTE IA Crosswalk Test WG • Briefing Day 2 29 June 2010 • -NSA • -JFCOM • -CJCSI 6212. 01 F Review/Discussion
 Enterprise Architect to DM 2 Mapping and Measures Use Case Dr. David Dryer Mr. Johnny Yohman Mr. Walter Pierce Visense dryerd@visense. net 757 -966 -5780
Enterprise Architect to DM 2 Mapping and Measures Use Case Dr. David Dryer Mr. Johnny Yohman Mr. Walter Pierce Visense dryerd@visense. net 757 -966 -5780
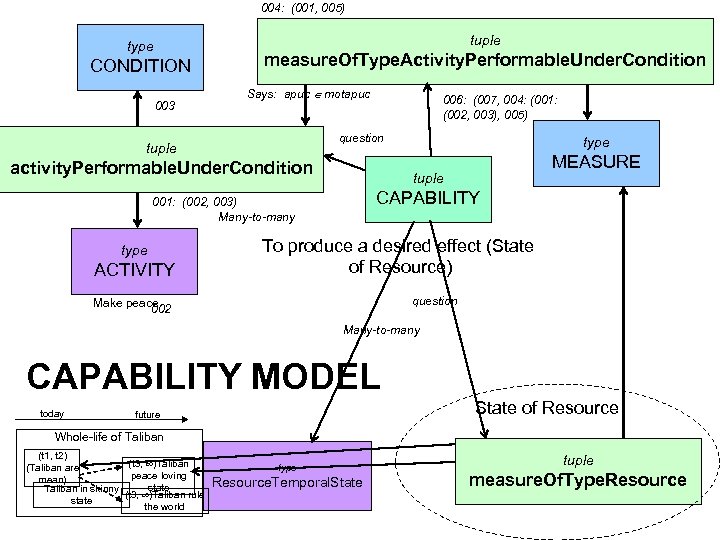 004: (001, 005) tuple type CONDITION 003 measure. Of. Type. Activity. Performable. Under. Condition Says: apuc Î motapuc 006: (007, 004: (001: (002, 003), 005) question tuple activity. Performable. Under. Condition ACTIVITY MEASURE tuple CAPABILITY 001: (002, 003) Many-to-many type To produce a desired effect (State of Resource) question Make peace 002 Many-to-many CAPABILITY MODEL today State of Resource future Whole-life of Taliban (t 1, t 2) (t 3, ¥)Taliban (Taliban are peace loving mean) state Taliban in skinny (t 3, ¥)Taliban rule state the world type Resource. Temporal. State tuple measure. Of. Type. Resource
004: (001, 005) tuple type CONDITION 003 measure. Of. Type. Activity. Performable. Under. Condition Says: apuc Î motapuc 006: (007, 004: (001: (002, 003), 005) question tuple activity. Performable. Under. Condition ACTIVITY MEASURE tuple CAPABILITY 001: (002, 003) Many-to-many type To produce a desired effect (State of Resource) question Make peace 002 Many-to-many CAPABILITY MODEL today State of Resource future Whole-life of Taliban (t 1, t 2) (t 3, ¥)Taliban (Taliban are peace loving mean) state Taliban in skinny (t 3, ¥)Taliban rule state the world type Resource. Temporal. State tuple measure. Of. Type. Resource
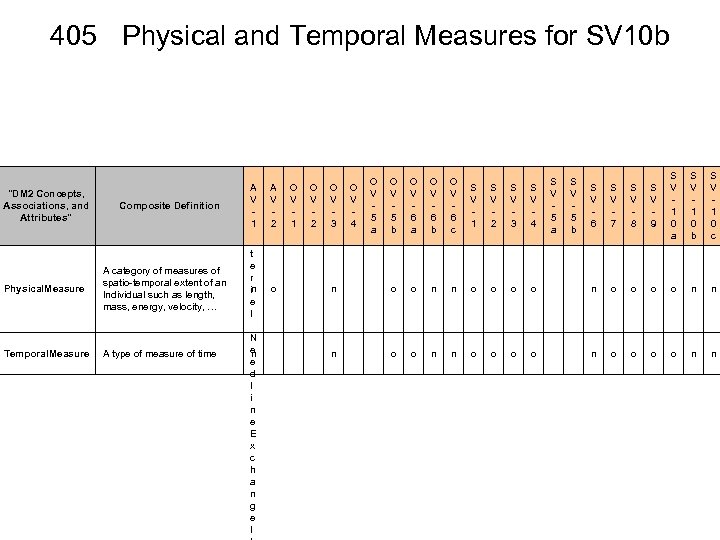 405 Physical and Temporal Measures for SV 10 b "DM 2 Concepts, Associations, and Attributes" Composite Definition Physical. Measure A category of measures of spatio-temporal extent of an Individual such as length, mass, energy, velocity, … Temporal. Measure A type of measure of time A V 1 M a t e r in e l N e n e d l i n e E x c h a n g e I A V 2 O V 1 O V 2 O V 3 O V 4 O V 5 a O V 5 b O V 6 a O V 6 b O V 6 c S V 1 S V 2 S V 3 S V 4 S V 5 a S V 5 b S V 6 S V 7 S V 8 S V 9 S V 1 0 a S V 1 0 b S V 1 0 c o n o o n n o o o o n n
405 Physical and Temporal Measures for SV 10 b "DM 2 Concepts, Associations, and Attributes" Composite Definition Physical. Measure A category of measures of spatio-temporal extent of an Individual such as length, mass, energy, velocity, … Temporal. Measure A type of measure of time A V 1 M a t e r in e l N e n e d l i n e E x c h a n g e I A V 2 O V 1 O V 2 O V 3 O V 4 O V 5 a O V 5 b O V 6 a O V 6 b O V 6 c S V 1 S V 2 S V 3 S V 4 S V 5 a S V 5 b S V 6 S V 7 S V 8 S V 9 S V 1 0 a S V 1 0 b S V 1 0 c o n o o n n o o o o n n
 405 Physical and Temporal Measures for SV 10 b M a t e r i e l N e e d l i n e E x c h a n g e I
405 Physical and Temporal Measures for SV 10 b M a t e r i e l N e e d l i n e E x c h a n g e I
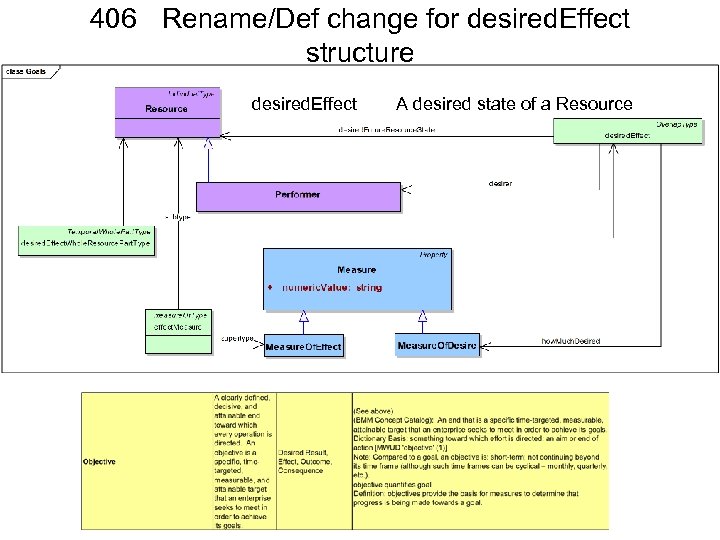 406 Rename/Def change for desired. Effect structure desired. Effect A desired state of a Resource
406 Rename/Def change for desired. Effect structure desired. Effect A desired state of a Resource
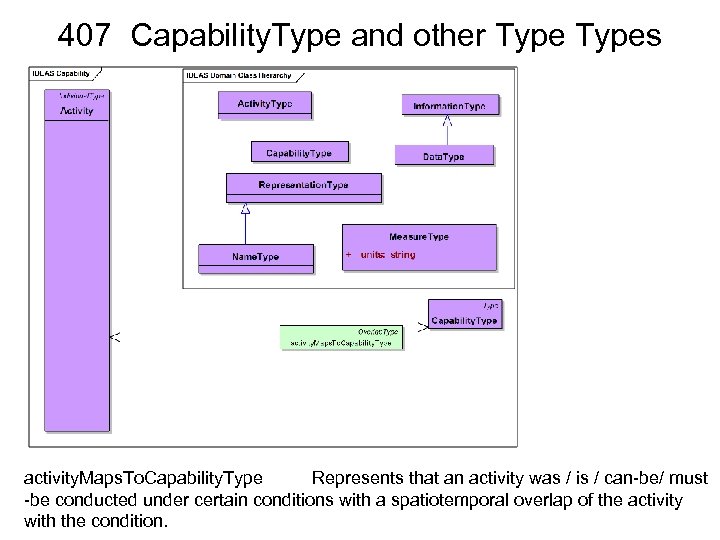 407 Capability. Type and other Types activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type Represents that an activity was / is / can-be/ must -be conducted under certain conditions with a spatiotemporal overlap of the activity with the condition.
407 Capability. Type and other Types activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type Represents that an activity was / is / can-be/ must -be conducted under certain conditions with a spatiotemporal overlap of the activity with the condition.
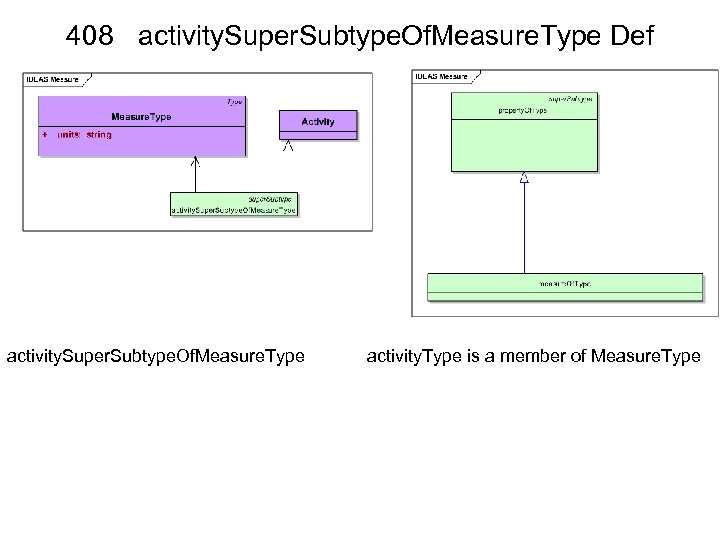 408 activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type Def activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type activity. Type is a member of Measure. Type
408 activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type Def activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type activity. Type is a member of Measure. Type
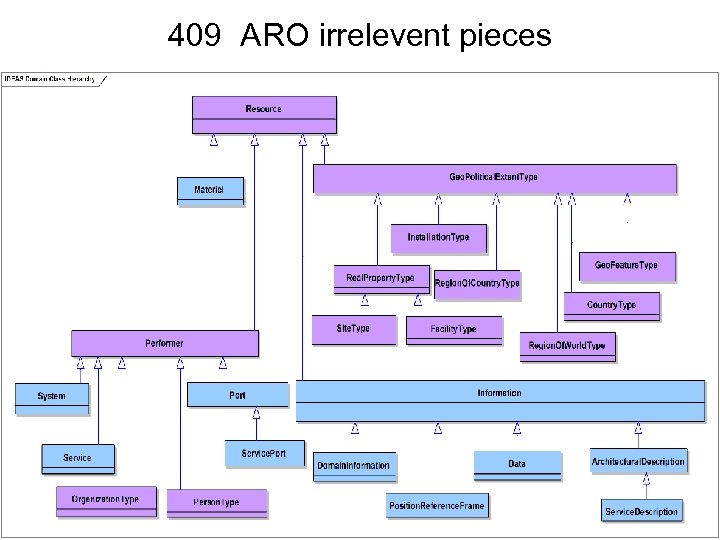 409 ARO irrelevent pieces
409 ARO irrelevent pieces
 410 Missing relationships
410 Missing relationships
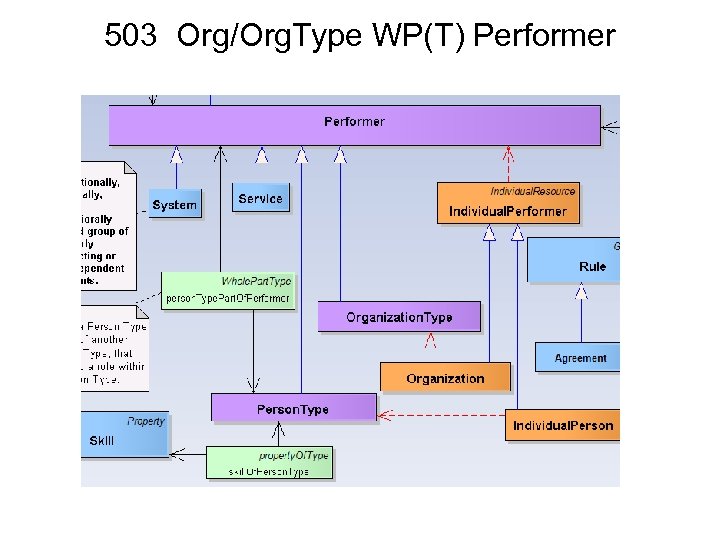 503 Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer
503 Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer
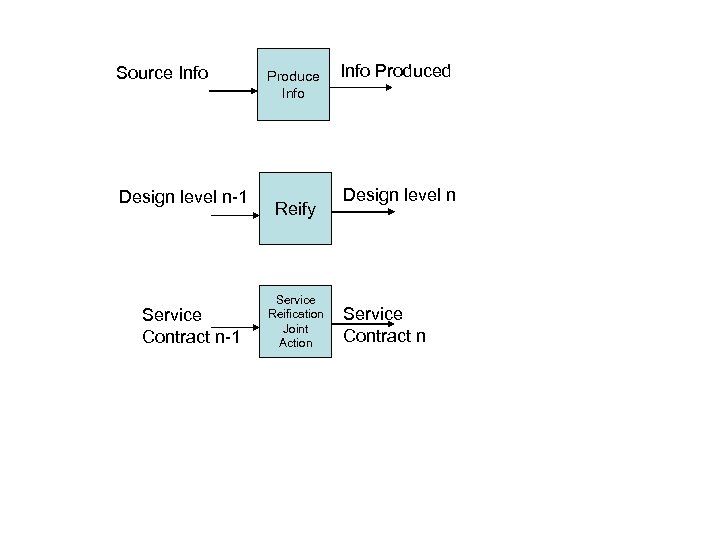 Source Info Design level n-1 Service Contract n-1 Produce Info Reify Service Reification Joint Action Info Produced Design level n Service Contract n
Source Info Design level n-1 Service Contract n-1 Produce Info Reify Service Reification Joint Action Info Produced Design level n Service Contract n
 18 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: – Upcoming: • • • OMG Technical Meeting Minneapolis next week INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June IDEAS Linked-in: http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? view. Members=&gid=3122051 DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June Semantic Technology Conference next week – San Francisco NCOIC June Plenary in Brussels – NATO and NAF MDR WG and COI Forum New References: – none • New submissions by members: – SV- 1 QA Problems (Lee) – BPMN or business processes tied to EA potential benefits in a IT (SOA) services construct. (Stenerson) – Capability model (Terebesi) – JMT Use Case (Vicense) • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 66 of them – 7 teed up in read-ahead – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 90 of them • Others: – Naming pattern inputs – Alex – TBS PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
18 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: – Upcoming: • • • OMG Technical Meeting Minneapolis next week INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June IDEAS Linked-in: http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? view. Members=&gid=3122051 DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June Semantic Technology Conference next week – San Francisco NCOIC June Plenary in Brussels – NATO and NAF MDR WG and COI Forum New References: – none • New submissions by members: – SV- 1 QA Problems (Lee) – BPMN or business processes tied to EA potential benefits in a IT (SOA) services construct. (Stenerson) – Capability model (Terebesi) – JMT Use Case (Vicense) • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 66 of them – 7 teed up in read-ahead – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 90 of them • Others: – Naming pattern inputs – Alex – TBS PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
 • • Name: Systems Interface Description One liner: The identification of systems, system items, and their interconnections. Description: – composition and interaction of Systems – links together the operational and systems architecture models -- a SV-1 may represent the realization of a requirement specified in an OV-2 – there may be many alternative SV models that could realize the operational requirement. – in an “As-Is” architecture, the OV-2 may simply be a simplified, logical representation of the SV-1 to allow communication of key Resource Flows to non-technical stakeholders. – A System Resource Flow is a simplified representation of a pathway or network pattern , – Note that Resource Flows between Systems may be further specified in detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description and SV-6 Systems Resource Flow Matrix. – Sub-System assemblies – SV-1 may also identify the Physical Assets (e. g. , Platforms) at which Resources are deployed – optionally overlay Operational Activities and Locations – In many cases, an operational activity and locations depicted in an OV-2 may well be the logical representation of the resource that is shown in SV-1. – The SV-1 is used in two complementary ways: • Describe the Resource Flows exchanged between resources in the architecture. • Describe a solution, or solution option, in terms of the components of capability and their physical integration on platforms and other facilities. Detailed Description: – Systems and sub-systems – The real benefit of a SV-1 is its ability to show the human aspects of an architecture, and how these interact with Systems. – Capability and Performers which is used to gather together systems, assets and people into a configuration, which can meet a specific capability. – A primary purpose of a SV-1 Do. DAF-described Model is to show resource structure, i. e. , identify the primary sub-systems, performer and activities (functions) and their interactions. – SV-1 contributes to user understanding of the structural characteristics of the capability. – The physical resources contributing to a capability are either an organizational resource or a physical asset, i. e. , a system cannot contribute alone (it must be hosted on a physical asset used by an organizational resource of both). – Organizational aspects can now be shown on SV-1 (e. g. , who uses System). – Resource structures may be identified in SV-1 – Do. DAF does not specifically use terms such as, sub-System and component as these terms often denote a position relative to a structural hierarchy. – Any System may combine hardware and software or these can be treated as separate (sub) Systems. Do. DAF V 2. 0 includes human factors (as Personnel Types and a type of Performer). Should an architect wish to describe a System which has human elements, then Systems, Personnel Types and Performers should be used to wrap the human and system elements together. – optionally be annotated with Operational Activities, Capabilities, and/or Locations originally specified in OV-2 – shows Systems, Physical Assets and System interfaces for the entire Architectural Description on the same diagram. – Some Resources can carry out System Functions (Activities) as described in SV-4 – these functions can optionally be overlaid on a SV-1. – the SV-1 and the SV-4 model provide complementary representations (structure and function). – Either could be modeled first, but usually an iterative approach is used to model these together gradually building up the level of detail in the System description. – Note that the same type (class) of resource may be used in different contexts in a given SV-1. For this reason, the tracing of functions to resources is specified in context of their usage (see DM 2 for details). – addresses Resource Flows. A Resource Flow, as depicted in SV-1, is an indicator that resources pass between one System and the other. – In the case of Systems, this can be expanded into further detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description. – Interactions are only possible between Systems and Services. – System Resource Flows provide a specification for how the operational Resource Flows Exchanges specified in Needlines are realized with Systems. – A single Needline shown in the OV-2 Operational Resource Flow Description model may translate into multiple System Resource Flows. – The actual implementation of a System Resource Flow may take more than one form (e. g. , multiple physical links). – Details of the physical pathways or network patterns that implement the interfaces are documented in SV-2. – System Resource Flows are summarized in a SV-3 b. – The functions performed by the resources are specified in a SV-4, but may optionally be overlaid on the Resources in a SV-1. – An Operational Viewpoint (OV) suite may specify a set of requirements – either as a specific operational plan, or a scenario for procurement. – As OV-2 and OV-5 specify the logical structure and behavior, SV-1 and SV-4 specify the physical structure and behavior – separation of logical and physical presents – The structural and behavioral models in the OVs and SVs allow architects and stakeholders to quickly ascertain which functions are carried out by humans and which by Systems for each alternative specification and so carry out trade analysis based on risk, cost, reliability, etc. SV-1 Issues
• • Name: Systems Interface Description One liner: The identification of systems, system items, and their interconnections. Description: – composition and interaction of Systems – links together the operational and systems architecture models -- a SV-1 may represent the realization of a requirement specified in an OV-2 – there may be many alternative SV models that could realize the operational requirement. – in an “As-Is” architecture, the OV-2 may simply be a simplified, logical representation of the SV-1 to allow communication of key Resource Flows to non-technical stakeholders. – A System Resource Flow is a simplified representation of a pathway or network pattern , – Note that Resource Flows between Systems may be further specified in detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description and SV-6 Systems Resource Flow Matrix. – Sub-System assemblies – SV-1 may also identify the Physical Assets (e. g. , Platforms) at which Resources are deployed – optionally overlay Operational Activities and Locations – In many cases, an operational activity and locations depicted in an OV-2 may well be the logical representation of the resource that is shown in SV-1. – The SV-1 is used in two complementary ways: • Describe the Resource Flows exchanged between resources in the architecture. • Describe a solution, or solution option, in terms of the components of capability and their physical integration on platforms and other facilities. Detailed Description: – Systems and sub-systems – The real benefit of a SV-1 is its ability to show the human aspects of an architecture, and how these interact with Systems. – Capability and Performers which is used to gather together systems, assets and people into a configuration, which can meet a specific capability. – A primary purpose of a SV-1 Do. DAF-described Model is to show resource structure, i. e. , identify the primary sub-systems, performer and activities (functions) and their interactions. – SV-1 contributes to user understanding of the structural characteristics of the capability. – The physical resources contributing to a capability are either an organizational resource or a physical asset, i. e. , a system cannot contribute alone (it must be hosted on a physical asset used by an organizational resource of both). – Organizational aspects can now be shown on SV-1 (e. g. , who uses System). – Resource structures may be identified in SV-1 – Do. DAF does not specifically use terms such as, sub-System and component as these terms often denote a position relative to a structural hierarchy. – Any System may combine hardware and software or these can be treated as separate (sub) Systems. Do. DAF V 2. 0 includes human factors (as Personnel Types and a type of Performer). Should an architect wish to describe a System which has human elements, then Systems, Personnel Types and Performers should be used to wrap the human and system elements together. – optionally be annotated with Operational Activities, Capabilities, and/or Locations originally specified in OV-2 – shows Systems, Physical Assets and System interfaces for the entire Architectural Description on the same diagram. – Some Resources can carry out System Functions (Activities) as described in SV-4 – these functions can optionally be overlaid on a SV-1. – the SV-1 and the SV-4 model provide complementary representations (structure and function). – Either could be modeled first, but usually an iterative approach is used to model these together gradually building up the level of detail in the System description. – Note that the same type (class) of resource may be used in different contexts in a given SV-1. For this reason, the tracing of functions to resources is specified in context of their usage (see DM 2 for details). – addresses Resource Flows. A Resource Flow, as depicted in SV-1, is an indicator that resources pass between one System and the other. – In the case of Systems, this can be expanded into further detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description. – Interactions are only possible between Systems and Services. – System Resource Flows provide a specification for how the operational Resource Flows Exchanges specified in Needlines are realized with Systems. – A single Needline shown in the OV-2 Operational Resource Flow Description model may translate into multiple System Resource Flows. – The actual implementation of a System Resource Flow may take more than one form (e. g. , multiple physical links). – Details of the physical pathways or network patterns that implement the interfaces are documented in SV-2. – System Resource Flows are summarized in a SV-3 b. – The functions performed by the resources are specified in a SV-4, but may optionally be overlaid on the Resources in a SV-1. – An Operational Viewpoint (OV) suite may specify a set of requirements – either as a specific operational plan, or a scenario for procurement. – As OV-2 and OV-5 specify the logical structure and behavior, SV-1 and SV-4 specify the physical structure and behavior – separation of logical and physical presents – The structural and behavioral models in the OVs and SVs allow architects and stakeholders to quickly ascertain which functions are carried out by humans and which by Systems for each alternative specification and so carry out trade analysis based on risk, cost, reliability, etc. SV-1 Issues
 SV-1 Content Guidance for Template and Description Streamlining: AI#535 • Severn distinct pieces are currently described. They should be broken out as follows: : 1. SV-1 a Interface Description. The SV-1 a shows interfaces (Resource Flows) between Systems, Services, and/or Person Types 2. SV-1 b Perfomer Configuration Diagram. Interface Description plus composition (whole-parts) of Resources involved. If Locations are involved in the configuration, relationships to Resources. 3. SV-1 c Functional Allocation. Activities (System Functions) performed by Systems, Services, and Person Types 4. SV-1 d Organizational Resources. Shows Resources that are part of (whole-part) Organizations. 5. SV-1 e Organizational Dependencies. Shows Organizations whose Activities are reified by System Functions (Activities) performed by Performer Configurations. 6. All views should show traceability to higher-order reifications, other views that constitute requirements, and/or other non-view requirements. This should be restated for just about every model. 7. Relationship to Capabilities – already in SV-5
SV-1 Content Guidance for Template and Description Streamlining: AI#535 • Severn distinct pieces are currently described. They should be broken out as follows: : 1. SV-1 a Interface Description. The SV-1 a shows interfaces (Resource Flows) between Systems, Services, and/or Person Types 2. SV-1 b Perfomer Configuration Diagram. Interface Description plus composition (whole-parts) of Resources involved. If Locations are involved in the configuration, relationships to Resources. 3. SV-1 c Functional Allocation. Activities (System Functions) performed by Systems, Services, and Person Types 4. SV-1 d Organizational Resources. Shows Resources that are part of (whole-part) Organizations. 5. SV-1 e Organizational Dependencies. Shows Organizations whose Activities are reified by System Functions (Activities) performed by Performer Configurations. 6. All views should show traceability to higher-order reifications, other views that constitute requirements, and/or other non-view requirements. This should be restated for just about every model. 7. Relationship to Capabilities – already in SV-5
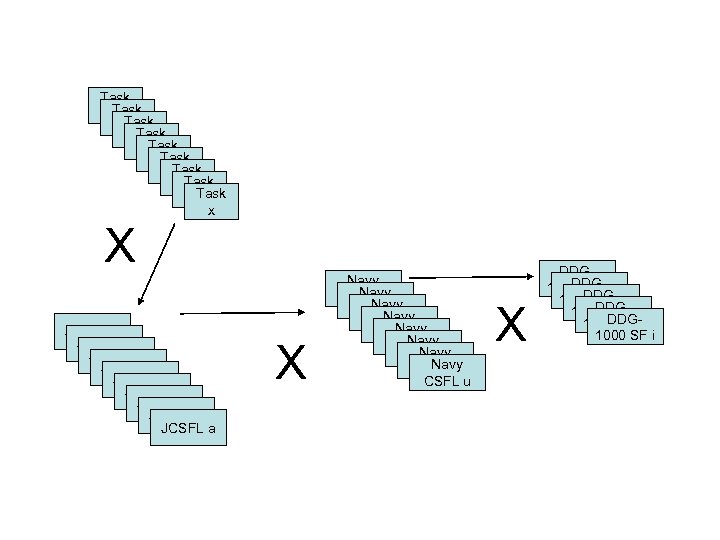 Task x Task x Task x x X JCSFL a JCSFL a JCSFL a X Navy CSFL u Navy CSFL u X DDGDDG 1000 SF i 1000 SF i
Task x Task x Task x x X JCSFL a JCSFL a JCSFL a X Navy CSFL u Navy CSFL u X DDGDDG 1000 SF i 1000 SF i
 11 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: • • FAC Tuesday – AI #418 DHS Emergency X DM 2 – NIEM, UCORE, C 2 Core Information / Data names – Upcoming: • • • Do. DAF Plenary 12 Aug -- topic inputs OMG Technical Meeting Minneapolis 21 -25 June INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group startup discussion -- quarterly, 1 st mtg in July IDEAS Linked-in: http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? view. Members=&gid=3122051 DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June New References: – Do. DAF - DM 2 CSAR June 2010 rev 1. doc • New submissions by members: – Capability model (Terebesi) – JMT Use Case • 2. 02 Plan: – Structural issues with triples vs two or three couples – Review new Action Items, 73 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Naming pattern inputs – Alex – TBS – PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO USE MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
11 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: • • FAC Tuesday – AI #418 DHS Emergency X DM 2 – NIEM, UCORE, C 2 Core Information / Data names – Upcoming: • • • Do. DAF Plenary 12 Aug -- topic inputs OMG Technical Meeting Minneapolis 21 -25 June INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group startup discussion -- quarterly, 1 st mtg in July IDEAS Linked-in: http: //www. linkedin. com/groups? view. Members=&gid=3122051 DARS Users and Vendors Day 28 -29 June New References: – Do. DAF - DM 2 CSAR June 2010 rev 1. doc • New submissions by members: – Capability model (Terebesi) – JMT Use Case • 2. 02 Plan: – Structural issues with triples vs two or three couples – Review new Action Items, 73 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Naming pattern inputs – Alex – TBS – PLEASE BE ATTENTIVE TO USE MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
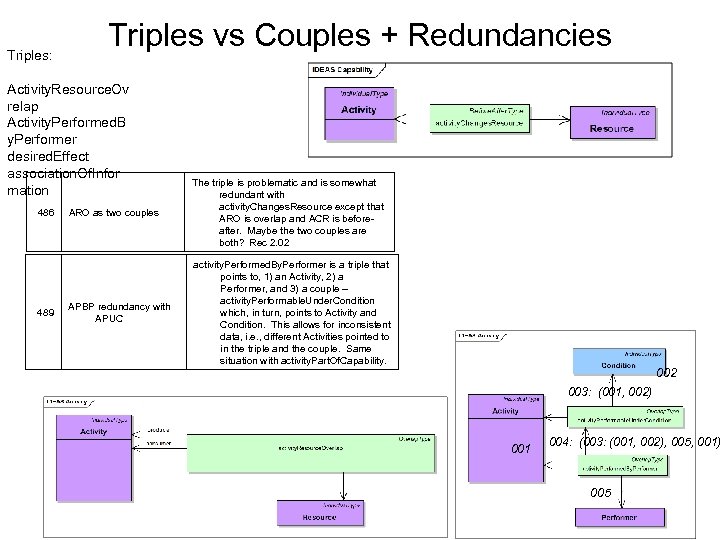 Triples: Triples vs Couples + Redundancies Activity. Resource. Ov relap Activity. Performed. B y. Performer desired. Effect association. Of. Infor mation 486 489 ARO as two couples The triple is problematic and is somewhat redundant with activity. Changes. Resource except that ARO is overlap and ACR is beforeafter. Maybe the two couples are both? Rec 2. 02 APBP redundancy with APUC activity. Performed. By. Performer is a triple that points to, 1) an Activity, 2) a Performer, and 3) a couple -- activity. Performable. Under. Condition which, in turn, points to Activity and Condition. This allows for inconsistent data, i. e. , different Activities pointed to in the triple and the couple. Same situation with activity. Part. Of. Capability. 002 003: (001, 002) 001 004: (003: (001, 002), 005, 001) 005
Triples: Triples vs Couples + Redundancies Activity. Resource. Ov relap Activity. Performed. B y. Performer desired. Effect association. Of. Infor mation 486 489 ARO as two couples The triple is problematic and is somewhat redundant with activity. Changes. Resource except that ARO is overlap and ACR is beforeafter. Maybe the two couples are both? Rec 2. 02 APBP redundancy with APUC activity. Performed. By. Performer is a triple that points to, 1) an Activity, 2) a Performer, and 3) a couple -- activity. Performable. Under. Condition which, in turn, points to Activity and Condition. This allows for inconsistent data, i. e. , different Activities pointed to in the triple and the couple. Same situation with activity. Part. Of. Capability. 002 003: (001, 002) 001 004: (003: (001, 002), 005, 001) 005
 04 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – – New Members: This week: • – Upcoming: • • Enterprise Phase email discussion JMT Use Case http: //www. dtic. mil/futurejointwarfare/cap_areas. htm 2. 02 Plan: – – • CJCSIs/Capability Based Assessment - cba_guidev 3. pdf JMT/JMTUse. Case. pptx (Yohman) JMT/SOP v 1. 0 dtd 2010 May 03. pdf Walkthru using IDEAS Profile in EA New submissions by members: – – – • FAC Tuesday OMG Technical Meeting Minnepolis 21 -25 June INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Do. DAF Plenary inputs 12 Aug Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June New References: – – – • • IST NR KPP – 6212 F updates in June being staffed. EISP being tested now. OV-5 process for 6212. DISA/DARS Do. DAF patterns – Jackie Knudson. TV-1 & DISR, tool not working well – new system GTG Dave Brown new web interface for TV 1 and stds profiling. Templates for Do. DAF 2 -- start working in June. Review new Action Items, 73 of them Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them Others: – – Naming pattern inputs – Alex USE MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
04 June 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – – New Members: This week: • – Upcoming: • • Enterprise Phase email discussion JMT Use Case http: //www. dtic. mil/futurejointwarfare/cap_areas. htm 2. 02 Plan: – – • CJCSIs/Capability Based Assessment - cba_guidev 3. pdf JMT/JMTUse. Case. pptx (Yohman) JMT/SOP v 1. 0 dtd 2010 May 03. pdf Walkthru using IDEAS Profile in EA New submissions by members: – – – • FAC Tuesday OMG Technical Meeting Minnepolis 21 -25 June INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. IST NR KPP WG 28 Jun 10 - 29 Jun 10 Do. DAF Plenary inputs 12 Aug Military Operations Research Society 22 -24 June New References: – – – • • IST NR KPP – 6212 F updates in June being staffed. EISP being tested now. OV-5 process for 6212. DISA/DARS Do. DAF patterns – Jackie Knudson. TV-1 & DISR, tool not working well – new system GTG Dave Brown new web interface for TV 1 and stds profiling. Templates for Do. DAF 2 -- start working in June. Review new Action Items, 73 of them Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them Others: – – Naming pattern inputs – Alex USE MUTE WHEN NOT SPEAKING
 Chat Logs • • • • • • Dave Putman (to All - Entire Audience): DM 2 LDM = Enterprise: An umbrella term for the management systems, information systems and computer systems within an organization. [potentially related: System] DM 2 LDM Description 100228. doc, Table 6. Aliases and Composite Terms Related to Performers Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Heard everything fine, but couldn't break in on audio. Will have some comments in an email. We've been all over this before. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Sounds like Capability Phase has to do with representing WHEN a certain set of PERFORMERS doing certain ACTIVITIES can provide a certain EFFECT to a certain STANDARD as quantified by one or more MEASURES. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): and with representing such transitions of something like a GANNT Chart. Graham (to Organizer(s) Only): In MODAF, UDM this is an enterprise pahse Graham (to All - Entire Audience): In MODAF, UDM this is an enterprise phase Graham (to All - Entire Audience): but the problem is the concept of a capability phase Graham (to All - Entire Audience): Capabilities are timeless therefore there fore they have no start or stop date Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): But ACTIVITIES and PERFORMERS do have time lines and changing either affects the ability to achieve the desired EFFECT. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Forrest is out of here. CU all next week!
Chat Logs • • • • • • Dave Putman (to All - Entire Audience): DM 2 LDM = Enterprise: An umbrella term for the management systems, information systems and computer systems within an organization. [potentially related: System] DM 2 LDM Description 100228. doc, Table 6. Aliases and Composite Terms Related to Performers Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Heard everything fine, but couldn't break in on audio. Will have some comments in an email. We've been all over this before. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Sounds like Capability Phase has to do with representing WHEN a certain set of PERFORMERS doing certain ACTIVITIES can provide a certain EFFECT to a certain STANDARD as quantified by one or more MEASURES. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): and with representing such transitions of something like a GANNT Chart. Graham (to Organizer(s) Only): In MODAF, UDM this is an enterprise pahse Graham (to All - Entire Audience): In MODAF, UDM this is an enterprise phase Graham (to All - Entire Audience): but the problem is the concept of a capability phase Graham (to All - Entire Audience): Capabilities are timeless therefore there fore they have no start or stop date Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): But ACTIVITIES and PERFORMERS do have time lines and changing either affects the ability to achieve the desired EFFECT. Forrest Snyder (to All - Entire Audience): Forrest is out of here. CU all next week!
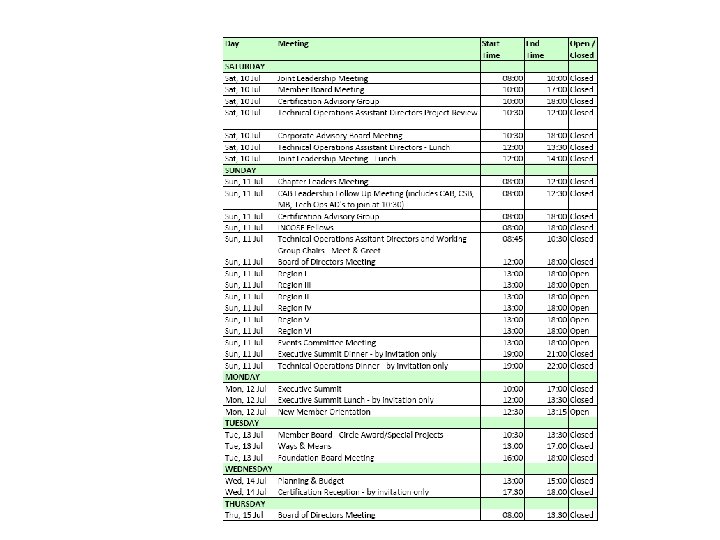
 June & July IST NR KPP WG • Dates for June and July. – Mon. , 28 Jun 10 - Tues. , 29 Jun 10 – Wed. , 21 Jul 10 - Thurs. , 22 Jul 10 • Tentative Agenda for June: – 28 June 2010 - NII DAY (Suggested topics) ** I • Interoperability and Supportability Discussion ** Architecture Policy – 29 June - NSA - JFCOM - CJCSI 6212. 01 F
June & July IST NR KPP WG • Dates for June and July. – Mon. , 28 Jun 10 - Tues. , 29 Jun 10 – Wed. , 21 Jul 10 - Thurs. , 22 Jul 10 • Tentative Agenda for June: – 28 June 2010 - NII DAY (Suggested topics) ** I • Interoperability and Supportability Discussion ** Architecture Policy – 29 June - NSA - JFCOM - CJCSI 6212. 01 F
 1 2 3
1 2 3
 MODAF Enterprise Phase • Ian Bailey courtesy Graham Bleakley: – – • An EP is just a phase of the enterprise you’re modelling – in IDEAS/DM 2 terms that would be an individual with the spatial extent of the enterprise, and a finite temporal extent defined by the start and the end of the phase. It’s pretty much the only bit of 4 D in M 3, so should drop straight into DM 2 without translation. The WLEP is also a phase, it’s just that it lasts the whole life of the enterprise (hence it is a special case of an enterprise phase, and therefore a subtype). That’s not circular, it’s just simple plain old logic. Projects deliver capability, and they also have phases, the starts/ends of which are shown as project milestones in MODAF. It’s imperative to keep this separate from the enterprise phase, because project are about delivery and enterprise phases are about strategic intent. If someone states a capability for a future enterprise phase, that is a statement of requirement – e. g. “we need bad weather ISTAR by 2015”. The project that delivers that capability may well intend to deliver on time, but may slip. By keeping these two aspects separate, we can see how reality matches the requirement. Antoine (Mega) on behalf of UPDM Team: – – During our email discussions all members of the UPDM group have converged on the same position regarding enterprise phase and project. There is a large unanimity on this topic from people coming from different viewpoints. I have looked at documents from the Do. D* that reinforce the position that “capability planning” is linked to strategy. The debate is about the clarification of “desired effect” the conclusion being that “objectives are truly the basis of military planning” (see attached document). Consequently, when we say “capability” in this paper, we mean: the ability to achieve an objective in a military operation. We do not reject the notion of an effect. Physical and behavioral conditions matter, and the definition above does not preclude you from considering effects as defined by Joint Publication 3. 0. However, objectives are truly the basis of military planning, and defining capabilities in that way is more straightforward. The UPDM/MOD approach provides a formal solution for this (capabilities, enterprise phases, and capability requirements for each phase). The traditional “requirement/acquisition management” has to be reconsidered because of the introduction of a new time dimension. Therefore, the time for the enterprise/strategy planning has to be assessed and aligned with the time for capability configuration availability. Mixing these two dimensions may prevent from achieving effective EA governance processes. * e. g. , Capabilities-Based Assessment (CBA) User’s Guide
MODAF Enterprise Phase • Ian Bailey courtesy Graham Bleakley: – – • An EP is just a phase of the enterprise you’re modelling – in IDEAS/DM 2 terms that would be an individual with the spatial extent of the enterprise, and a finite temporal extent defined by the start and the end of the phase. It’s pretty much the only bit of 4 D in M 3, so should drop straight into DM 2 without translation. The WLEP is also a phase, it’s just that it lasts the whole life of the enterprise (hence it is a special case of an enterprise phase, and therefore a subtype). That’s not circular, it’s just simple plain old logic. Projects deliver capability, and they also have phases, the starts/ends of which are shown as project milestones in MODAF. It’s imperative to keep this separate from the enterprise phase, because project are about delivery and enterprise phases are about strategic intent. If someone states a capability for a future enterprise phase, that is a statement of requirement – e. g. “we need bad weather ISTAR by 2015”. The project that delivers that capability may well intend to deliver on time, but may slip. By keeping these two aspects separate, we can see how reality matches the requirement. Antoine (Mega) on behalf of UPDM Team: – – During our email discussions all members of the UPDM group have converged on the same position regarding enterprise phase and project. There is a large unanimity on this topic from people coming from different viewpoints. I have looked at documents from the Do. D* that reinforce the position that “capability planning” is linked to strategy. The debate is about the clarification of “desired effect” the conclusion being that “objectives are truly the basis of military planning” (see attached document). Consequently, when we say “capability” in this paper, we mean: the ability to achieve an objective in a military operation. We do not reject the notion of an effect. Physical and behavioral conditions matter, and the definition above does not preclude you from considering effects as defined by Joint Publication 3. 0. However, objectives are truly the basis of military planning, and defining capabilities in that way is more straightforward. The UPDM/MOD approach provides a formal solution for this (capabilities, enterprise phases, and capability requirements for each phase). The traditional “requirement/acquisition management” has to be reconsidered because of the introduction of a new time dimension. Therefore, the time for the enterprise/strategy planning has to be assessed and aligned with the time for capability configuration availability. Mixing these two dimensions may prevent from achieving effective EA governance processes. * e. g. , Capabilities-Based Assessment (CBA) User’s Guide
 28 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: • NAF issues • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting • Do. DAF – TOGAF paper – Reminders: • OMG Technical Meeting Minnepolis • INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. Early bird registration by 31 May • New References: – State Machines (Kihlstrom) – Services/OASIS SOA/Do. DAF 2. 0_Joint_Action-0. 2. pptx (Ellis) – UCORE/Comments on UCore SL 00 -20. ppt (Bocast) • WG Member submissions – Capability and Enterprise Phase – Bleakley – Definitions guidance -- Bocast • • Walkthru using IDEAS Profile in EA 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 61 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Measures mapping use case – Dave Dryer to send – Naming pattern inputs -- Alex
28 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: – This week: • NAF issues • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting • Do. DAF – TOGAF paper – Reminders: • OMG Technical Meeting Minnepolis • INCOSE International Symposium, to be held 12 - 15 July Chicago. Early bird registration by 31 May • New References: – State Machines (Kihlstrom) – Services/OASIS SOA/Do. DAF 2. 0_Joint_Action-0. 2. pptx (Ellis) – UCORE/Comments on UCore SL 00 -20. ppt (Bocast) • WG Member submissions – Capability and Enterprise Phase – Bleakley – Definitions guidance -- Bocast • • Walkthru using IDEAS Profile in EA 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 61 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Measures mapping use case – Dave Dryer to send – Naming pattern inputs -- Alex
 Alex’s Thoughts on Definitions • • • (1) We should establish a demotic authority for all those terms not entailed within the model. I suggest Word. Net. And then I suggest that current definitions should be revisited to ensure that they still make sense using Word. Net as the authoritative source of conversational usage. (2) Within the model, definitions of classes that are specializations (subclasses) should properly begin by stating the genus (the parent or immediate superclass) of the thing defined. For example, the definition for "system" might begin "a Performer that. . . ", thus entailing the definition of "Performer". (3) We should establish a vocabulary distinct from the model for such things that we do not grant ontic significance. (You mentioned the use of aliases for such useful terms, but I have not yet found these aliases. . . ) (4) We should establish a definitional metalanguage for Do. DAF. How should Do. DAF definitions be constructed? What should be the grammar of a Do. DAF definition? What terms should be used to construct definitional statements? How should time to be treated grammatically and semantically? And so on. . . (4) I matured the style of analysis I used to deconstruct the definitional statement for "system" while examining the UCore SL ontology for Barry Smith. I've attached that commentary. My analysis may not be terribly sophisticated but I am at least persistent. I would rather like an invitation to similarly analyze the Do. DAF DM 2 definitions.
Alex’s Thoughts on Definitions • • • (1) We should establish a demotic authority for all those terms not entailed within the model. I suggest Word. Net. And then I suggest that current definitions should be revisited to ensure that they still make sense using Word. Net as the authoritative source of conversational usage. (2) Within the model, definitions of classes that are specializations (subclasses) should properly begin by stating the genus (the parent or immediate superclass) of the thing defined. For example, the definition for "system" might begin "a Performer that. . . ", thus entailing the definition of "Performer". (3) We should establish a vocabulary distinct from the model for such things that we do not grant ontic significance. (You mentioned the use of aliases for such useful terms, but I have not yet found these aliases. . . ) (4) We should establish a definitional metalanguage for Do. DAF. How should Do. DAF definitions be constructed? What should be the grammar of a Do. DAF definition? What terms should be used to construct definitional statements? How should time to be treated grammatically and semantically? And so on. . . (4) I matured the style of analysis I used to deconstruct the definitional statement for "system" while examining the UCore SL ontology for Barry Smith. I've attached that commentary. My analysis may not be terribly sophisticated but I am at least persistent. I would rather like an invitation to similarly analyze the Do. DAF DM 2 definitions.
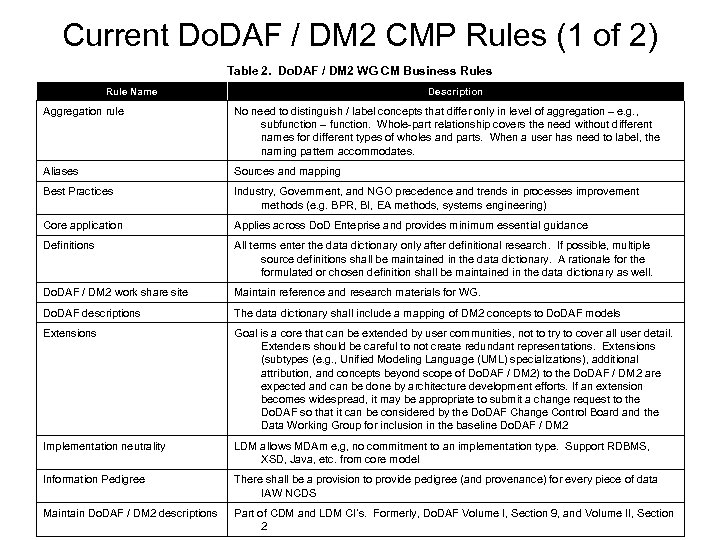 Current Do. DAF / DM 2 CMP Rules (1 of 2) Table 2. Do. DAF / DM 2 WG CM Business Rule Name Description Aggregation rule No need to distinguish / label concepts that differ only in level of aggregation – e. g. , subfunction – function. Whole-part relationship covers the need without different names for different types of wholes and parts. When a user has need to label, the naming pattern accommodates. Aliases Sources and mapping Best Practices Industry, Government, and NGO precedence and trends in processes improvement methods (e. g. BPR, BI, EA methods, systems engineering) Core application Applies across Do. D Enteprise and provides minimum essential guidance Definitions All terms enter the data dictionary only after definitional research. If possible, multiple source definitions shall be maintained in the data dictionary. A rationale for the formulated or chosen definition shall be maintained in the data dictionary as well. Do. DAF / DM 2 work share site Maintain reference and research materials for WG. Do. DAF descriptions The data dictionary shall include a mapping of DM 2 concepts to Do. DAF models Extensions Goal is a core that can be extended by user communities, not to try to cover all user detail. Extenders should be careful to not create redundant representations. Extensions (subtypes (e. g. , Unified Modeling Language (UML) specializations), additional attribution, and concepts beyond scope of Do. DAF / DM 2) to the Do. DAF / DM 2 are expected and can be done by architecture development efforts. If an extension becomes widespread, it may be appropriate to submit a change request to the Do. DAF so that it can be considered by the Do. DAF Change Control Board and the Data Working Group for inclusion in the baseline Do. DAF / DM 2 Implementation neutrality LDM allows MDAm e, g, no commitment to an implementation type. Support RDBMS, XSD, Java, etc. from core model Information Pedigree There shall be a provision to provide pedigree (and provenance) for every piece of data IAW NCDS Maintain Do. DAF / DM 2 descriptions Part of CDM and LDM CI’s. Formerly, Do. DAF Volume I, Section 9, and Volume II, Section 2
Current Do. DAF / DM 2 CMP Rules (1 of 2) Table 2. Do. DAF / DM 2 WG CM Business Rule Name Description Aggregation rule No need to distinguish / label concepts that differ only in level of aggregation – e. g. , subfunction – function. Whole-part relationship covers the need without different names for different types of wholes and parts. When a user has need to label, the naming pattern accommodates. Aliases Sources and mapping Best Practices Industry, Government, and NGO precedence and trends in processes improvement methods (e. g. BPR, BI, EA methods, systems engineering) Core application Applies across Do. D Enteprise and provides minimum essential guidance Definitions All terms enter the data dictionary only after definitional research. If possible, multiple source definitions shall be maintained in the data dictionary. A rationale for the formulated or chosen definition shall be maintained in the data dictionary as well. Do. DAF / DM 2 work share site Maintain reference and research materials for WG. Do. DAF descriptions The data dictionary shall include a mapping of DM 2 concepts to Do. DAF models Extensions Goal is a core that can be extended by user communities, not to try to cover all user detail. Extenders should be careful to not create redundant representations. Extensions (subtypes (e. g. , Unified Modeling Language (UML) specializations), additional attribution, and concepts beyond scope of Do. DAF / DM 2) to the Do. DAF / DM 2 are expected and can be done by architecture development efforts. If an extension becomes widespread, it may be appropriate to submit a change request to the Do. DAF so that it can be considered by the Do. DAF Change Control Board and the Data Working Group for inclusion in the baseline Do. DAF / DM 2 Implementation neutrality LDM allows MDAm e, g, no commitment to an implementation type. Support RDBMS, XSD, Java, etc. from core model Information Pedigree There shall be a provision to provide pedigree (and provenance) for every piece of data IAW NCDS Maintain Do. DAF / DM 2 descriptions Part of CDM and LDM CI’s. Formerly, Do. DAF Volume I, Section 9, and Volume II, Section 2
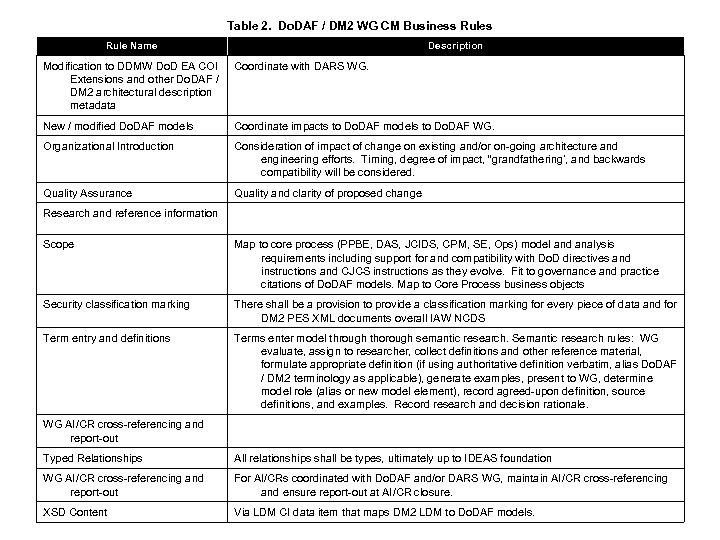 Table 2. Do. DAF / DM 2 WG CM Business Rule Name Description Modification to DDMW Do. D EA COI Extensions and other Do. DAF / DM 2 architectural description metadata Coordinate with DARS WG. New / modified Do. DAF models Coordinate impacts to Do. DAF models to Do. DAF WG. Organizational Introduction Consideration of impact of change on existing and/or on-going architecture and engineering efforts. Timing, degree of impact, “grandfathering’, and backwards compatibility will be considered. Quality Assurance Quality and clarity of proposed change Research and reference information Scope Map to core process (PPBE, DAS, JCIDS, CPM, SE, Ops) model and analysis requirements including support for and compatibility with Do. D directives and instructions and CJCS instructions as they evolve. Fit to governance and practice citations of Do. DAF models. Map to Core Process business objects Security classification marking There shall be a provision to provide a classification marking for every piece of data and for DM 2 PES XML documents overall IAW NCDS Term entry and definitions Terms enter model through thorough semantic research. Semantic research rules: WG evaluate, assign to researcher, collect definitions and other reference material, formulate appropriate definition (if using authoritative definition verbatim, alias Do. DAF / DM 2 terminology as applicable), generate examples, present to WG, determine model role (alias or new model element), record agreed-upon definition, source definitions, and examples. Record research and decision rationale. WG AI/CR cross-referencing and report-out Typed Relationships All relationships shall be types, ultimately up to IDEAS foundation WG AI/CR cross-referencing and report-out For AI/CRs coordinated with Do. DAF and/or DARS WG, maintain AI/CR cross-referencing and ensure report-out at AI/CR closure. XSD Content Via LDM CI data item that maps DM 2 LDM to Do. DAF models.
Table 2. Do. DAF / DM 2 WG CM Business Rule Name Description Modification to DDMW Do. D EA COI Extensions and other Do. DAF / DM 2 architectural description metadata Coordinate with DARS WG. New / modified Do. DAF models Coordinate impacts to Do. DAF models to Do. DAF WG. Organizational Introduction Consideration of impact of change on existing and/or on-going architecture and engineering efforts. Timing, degree of impact, “grandfathering’, and backwards compatibility will be considered. Quality Assurance Quality and clarity of proposed change Research and reference information Scope Map to core process (PPBE, DAS, JCIDS, CPM, SE, Ops) model and analysis requirements including support for and compatibility with Do. D directives and instructions and CJCS instructions as they evolve. Fit to governance and practice citations of Do. DAF models. Map to Core Process business objects Security classification marking There shall be a provision to provide a classification marking for every piece of data and for DM 2 PES XML documents overall IAW NCDS Term entry and definitions Terms enter model through thorough semantic research. Semantic research rules: WG evaluate, assign to researcher, collect definitions and other reference material, formulate appropriate definition (if using authoritative definition verbatim, alias Do. DAF / DM 2 terminology as applicable), generate examples, present to WG, determine model role (alias or new model element), record agreed-upon definition, source definitions, and examples. Record research and decision rationale. WG AI/CR cross-referencing and report-out Typed Relationships All relationships shall be types, ultimately up to IDEAS foundation WG AI/CR cross-referencing and report-out For AI/CRs coordinated with Do. DAF and/or DARS WG, maintain AI/CR cross-referencing and ensure report-out at AI/CR closure. XSD Content Via LDM CI data item that maps DM 2 LDM to Do. DAF models.
 21 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: • • • Herr, Julie Fink, Mark Fiebrandt, Mark Communications Strategy & Architecture Branch, USPACOM J 62 PACOM Chief Architect JT&E – This week: • • EA Conference last week JMT Measures Development SOP comments went in Monday – – JFCOM Measures Reference Model – Reminders: • • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) registration due New References: – none • WG Member submissions – UPDM mappings progress – System – Joint Action • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 69 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Measures mapping use case – Dave Dryer to send – Capabiilty and Enterprise Phase – Graham – Naming pattern inputs -- Alex
21 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: • • • Herr, Julie Fink, Mark Fiebrandt, Mark Communications Strategy & Architecture Branch, USPACOM J 62 PACOM Chief Architect JT&E – This week: • • EA Conference last week JMT Measures Development SOP comments went in Monday – – JFCOM Measures Reference Model – Reminders: • • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) registration due New References: – none • WG Member submissions – UPDM mappings progress – System – Joint Action • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 69 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – Measures mapping use case – Dave Dryer to send – Capabiilty and Enterprise Phase – Graham – Naming pattern inputs -- Alex

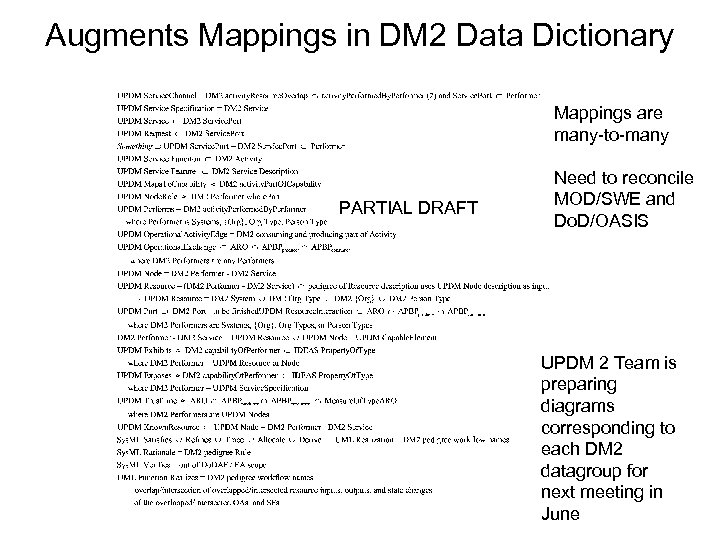 Augments Mappings in DM 2 Data Dictionary Mappings are many-to-many PARTIAL DRAFT Need to reconcile MOD/SWE and Do. D/OASIS UPDM 2 Team is preparing diagrams corresponding to each DM 2 datagroup for next meeting in June
Augments Mappings in DM 2 Data Dictionary Mappings are many-to-many PARTIAL DRAFT Need to reconcile MOD/SWE and Do. D/OASIS UPDM 2 Team is preparing diagrams corresponding to each DM 2 datagroup for next meeting in June
 Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2 comments on definitions v 00. 02
Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2 comments on definitions v 00. 02
 IN PROGRESS Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 1 • • thing : system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. no citation no annotation or comment 9 i 9 6 9 2 1 6 5 8 system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. 4 7 10 10 1. Semantic insufficiency. The word “group” signifies an observational construct. A group is a concept that an observer imposes upon the world to make sense of what is observed. A group does not have its own ontic significance: a group is merely an abbreviated way to refer to some set of things without enumerating and naming those things. In other words, groupness is in the eyes of the beholder; epistemologically, we can never be certain that what is counted in my group is counted in your group. 2. Grammar. Missing hyphen. 3. Semantics: pesky disjunction. Read as combinatorial conjunction: the ways in which things may be related includes functional, physical, and behavioral ways. 4. Grammar. The phrase “functionally, … related” modifies the word “group”, but “group” is given in the singular. The adjective “related” asserts a relationship between this group and something else, but that something else is here unspecified. If the asserted relationship is to be with another group, then “group” must be given in the plural. However, the authors may have intended the phrase “functionally, … related” to characterize “elements”; if so, the phrase is on the wrong side of “group”. 5. Semantics: pesky disjunction. Read as nonexclusive conjunction of permitted possibilities: these elements may be interacting and they may be interdependent. Definitionally, this leaves us at a loss because definition requires certainty. If these elements may be not-interacting and may also be notinterdependent, then these elements may be neither. What is wanted here is a higher-level abstraction to absorb this indeterminacy. 6. Definitional epistemology. How are we to determine the dividing line between regularly and not-regularly? What yardstick are we to use to measure regularness? 7. Grammar: unexpected distribution. Grammatically, the word “regularly” distributes across the disjunction: of regularly interacting or regularly interdependent elements. The resulting phrase—regularly interdependent—is problematic. 8. Semantic insufficiency. An element is generally taken to be something tangible and observable. The use of this term implies that system is here intended to be something that may be observed only as a static snapshot of physical things. In some communities, the notion of system may encompass processes that play out dynamically, that is, a system is something that does rather than something that is. What is needed is definition of “element” in this context: should this term signify physical entity or should this term signify process as well as artifact? element — an artifact that is one of the individual parts of which a composite entity is made up; especially a part that can be separated from or attached to a system [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23]; a fundamental, essential, or irreducible constituent of a composite entity [AHD; 2010 -04 -23]; a separate identifiable part of something, or a distinct group within a larger group [Encarta; 2010 -04 -23]; a constituent part [M-W; 2010 -04 -23] group — any number of entities (members) considered as a unit [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23]
IN PROGRESS Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 1 • • thing : system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. no citation no annotation or comment 9 i 9 6 9 2 1 6 5 8 system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. 4 7 10 10 1. Semantic insufficiency. The word “group” signifies an observational construct. A group is a concept that an observer imposes upon the world to make sense of what is observed. A group does not have its own ontic significance: a group is merely an abbreviated way to refer to some set of things without enumerating and naming those things. In other words, groupness is in the eyes of the beholder; epistemologically, we can never be certain that what is counted in my group is counted in your group. 2. Grammar. Missing hyphen. 3. Semantics: pesky disjunction. Read as combinatorial conjunction: the ways in which things may be related includes functional, physical, and behavioral ways. 4. Grammar. The phrase “functionally, … related” modifies the word “group”, but “group” is given in the singular. The adjective “related” asserts a relationship between this group and something else, but that something else is here unspecified. If the asserted relationship is to be with another group, then “group” must be given in the plural. However, the authors may have intended the phrase “functionally, … related” to characterize “elements”; if so, the phrase is on the wrong side of “group”. 5. Semantics: pesky disjunction. Read as nonexclusive conjunction of permitted possibilities: these elements may be interacting and they may be interdependent. Definitionally, this leaves us at a loss because definition requires certainty. If these elements may be not-interacting and may also be notinterdependent, then these elements may be neither. What is wanted here is a higher-level abstraction to absorb this indeterminacy. 6. Definitional epistemology. How are we to determine the dividing line between regularly and not-regularly? What yardstick are we to use to measure regularness? 7. Grammar: unexpected distribution. Grammatically, the word “regularly” distributes across the disjunction: of regularly interacting or regularly interdependent elements. The resulting phrase—regularly interdependent—is problematic. 8. Semantic insufficiency. An element is generally taken to be something tangible and observable. The use of this term implies that system is here intended to be something that may be observed only as a static snapshot of physical things. In some communities, the notion of system may encompass processes that play out dynamically, that is, a system is something that does rather than something that is. What is needed is definition of “element” in this context: should this term signify physical entity or should this term signify process as well as artifact? element — an artifact that is one of the individual parts of which a composite entity is made up; especially a part that can be separated from or attached to a system [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23]; a fundamental, essential, or irreducible constituent of a composite entity [AHD; 2010 -04 -23]; a separate identifiable part of something, or a distinct group within a larger group [Encarta; 2010 -04 -23]; a constituent part [M-W; 2010 -04 -23] group — any number of entities (members) considered as a unit [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23]
 IN PROGRESS 9 i 9 Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 2 6 9 2 1 6 5 8 system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. 4 9. 7 10 10 Domain knowledge. On what grounds are these sorts of relations—functional, physical, behavioral—asserted as the defining relations among groups or among elements of a system? Lacking entailed definitions for these terms, we can only kinda sorta guess at the authors’ intent. 10. Otiose. Things that interact or are interdependent necessarily are related in functional, physical, and behavioral ways. See also comment 4. by deconstruction & reconstruction 2 ii system ≈ a group of things related in functional, physical, and behavioral ways. 1 1. Semantics: Diogenistic poultry. By this statement, a gaggle of geese is a system, a brick retaining wall is a system, and a stage production of Our Town is a system. 2. Semantics: conceptual asymmetry. The problem becomes apparent when we try to avoid the vagueness of the word “ways”. We want to say something like: related by function, behavior, and … What are we now to do with “physical ways”? The wording “related by function, behavior, and physics” would be quite odd. behavior — the action or reaction of something (as a machine or substance) under specified circumstances [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] behaviorally — the way in which something functions or operates [M-W; 2010 -04 -23] behavioral — of or relating to behavior [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] function — what something is used for [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] functionally — with respect to function [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] physically — in accord with physical laws [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] system — see following slide…
IN PROGRESS 9 i 9 Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 2 6 9 2 1 6 5 8 system — A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. 4 9. 7 10 10 Domain knowledge. On what grounds are these sorts of relations—functional, physical, behavioral—asserted as the defining relations among groups or among elements of a system? Lacking entailed definitions for these terms, we can only kinda sorta guess at the authors’ intent. 10. Otiose. Things that interact or are interdependent necessarily are related in functional, physical, and behavioral ways. See also comment 4. by deconstruction & reconstruction 2 ii system ≈ a group of things related in functional, physical, and behavioral ways. 1 1. Semantics: Diogenistic poultry. By this statement, a gaggle of geese is a system, a brick retaining wall is a system, and a stage production of Our Town is a system. 2. Semantics: conceptual asymmetry. The problem becomes apparent when we try to avoid the vagueness of the word “ways”. We want to say something like: related by function, behavior, and … What are we now to do with “physical ways”? The wording “related by function, behavior, and physics” would be quite odd. behavior — the action or reaction of something (as a machine or substance) under specified circumstances [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] behaviorally — the way in which something functions or operates [M-W; 2010 -04 -23] behavioral — of or relating to behavior [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] function — what something is used for [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] functionally — with respect to function [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] physically — in accord with physical laws [Word. Net; 2010 -04 -23] system — see following slide…
 • • • (Do. DAF): Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (Do. DAF/CADM): An organized assembly of interactive components and procedures forming a unit. (DDDS Counter (19607/1)(A)) (MODAF): Any organised assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (IEEE): A collection of components organized to accomplish a specific function or set of functions. (BEA): Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (NAF): A collection of components organized to accomplish a specific function or set of functions. (GEN TERM) (NAF): A coherent combination of physical artifacts, energy and information, assembled for a purpose. (MM) (JCS 1 -02): A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements; that group of elements forming a unified whole. (JP 3 -0) (Zachman): A MECHANISM TYPE that consists of one of more linked computers, along with associated software. (Webster's): 1. An assemblage or combination of things or parts forming a complex or unitary whole. 2. Any assemblage or set of correlated members. 3. An ordered and comprehensive assemblage of facts, principles, doctrines, or the like in a particular field of knowledge or thought. 4. A coordinated body of methods or a scheme or plan of procedure; organizational scheme. 5. Any formulated, regular, or special method or plan of procedure (INCOSE) A system is a construct or collection of different elements that together produce results not obtainable by the elements alone. The elements, or parts, can include people, hardware, software, facilities, policies, and documents; that is, all things required to produce systems-level results. The results include system level qualities, properties, characteristics, functions, behavior and performance. The value added by the system as a whole, beyond that contributed independently by the parts, is primarily created by the relationship among the parts; that is, how they are interconnected (Rechtin, 2000). (Word. Net)
• • • (Do. DAF): Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (Do. DAF/CADM): An organized assembly of interactive components and procedures forming a unit. (DDDS Counter (19607/1)(A)) (MODAF): Any organised assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (IEEE): A collection of components organized to accomplish a specific function or set of functions. (BEA): Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. (NAF): A collection of components organized to accomplish a specific function or set of functions. (GEN TERM) (NAF): A coherent combination of physical artifacts, energy and information, assembled for a purpose. (MM) (JCS 1 -02): A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements; that group of elements forming a unified whole. (JP 3 -0) (Zachman): A MECHANISM TYPE that consists of one of more linked computers, along with associated software. (Webster's): 1. An assemblage or combination of things or parts forming a complex or unitary whole. 2. Any assemblage or set of correlated members. 3. An ordered and comprehensive assemblage of facts, principles, doctrines, or the like in a particular field of knowledge or thought. 4. A coordinated body of methods or a scheme or plan of procedure; organizational scheme. 5. Any formulated, regular, or special method or plan of procedure (INCOSE) A system is a construct or collection of different elements that together produce results not obtainable by the elements alone. The elements, or parts, can include people, hardware, software, facilities, policies, and documents; that is, all things required to produce systems-level results. The results include system level qualities, properties, characteristics, functions, behavior and performance. The value added by the system as a whole, beyond that contributed independently by the parts, is primarily created by the relationship among the parts; that is, how they are interconnected (Rechtin, 2000). (Word. Net)
 IN PROGRESS Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 3 From Word. Net [2010 -04 -24]: (n) system (instrumentality that combines interrelated interacting artifacts designed to work as a coherent entity) "he bought a new stereo system"; "the system consists of a motor and a small computer" (n) system, scheme (a group of independent but interrelated elements comprising a unified whole) "a vast system of production and distribution and consumption keep the country going" (n) system ((physical chemistry) a sample of matter in which substances in different phases are in equilibrium) "in a static system oil cannot be replaced by water on a surface"; "a system generating hydrogen peroxide" (n) system, system of rules (a complex of methods or rules governing behavior) "they have to operate under a system they oppose"; "that language has a complex system for indicating gender" (n) arrangement, organization, organisation, system (an organized structure for arranging or classifying) "he changed the arrangement of the topics"; "the facts were familiar but it was in the organization of them that he was original"; "he tried to understand their system of classification" (n) system (a group of physiologically or anatomically related organs or parts) "the body has a system of organs for digestion" (n) system (a procedure or process for obtaining an objective) "they had to devise a system that did not depend on cooperation" (n) system (the living body considered as made up of interdependent components forming a unified whole) "exercise helped him get the alcohol out of his system" (n) organization, organisation, system (an ordered manner; orderliness by virtue of being methodical and well organized) "his compulsive organization was not an endearing quality"; "we can't do it unless we establish some system around here"
IN PROGRESS Do. DAF 2. 0 DM 2: system 3 From Word. Net [2010 -04 -24]: (n) system (instrumentality that combines interrelated interacting artifacts designed to work as a coherent entity) "he bought a new stereo system"; "the system consists of a motor and a small computer" (n) system, scheme (a group of independent but interrelated elements comprising a unified whole) "a vast system of production and distribution and consumption keep the country going" (n) system ((physical chemistry) a sample of matter in which substances in different phases are in equilibrium) "in a static system oil cannot be replaced by water on a surface"; "a system generating hydrogen peroxide" (n) system, system of rules (a complex of methods or rules governing behavior) "they have to operate under a system they oppose"; "that language has a complex system for indicating gender" (n) arrangement, organization, organisation, system (an organized structure for arranging or classifying) "he changed the arrangement of the topics"; "the facts were familiar but it was in the organization of them that he was original"; "he tried to understand their system of classification" (n) system (a group of physiologically or anatomically related organs or parts) "the body has a system of organs for digestion" (n) system (a procedure or process for obtaining an objective) "they had to devise a system that did not depend on cooperation" (n) system (the living body considered as made up of interdependent components forming a unified whole) "exercise helped him get the alcohol out of his system" (n) organization, organisation, system (an ordered manner; orderliness by virtue of being methodical and well organized) "his compulsive organization was not an endearing quality"; "we can't do it unless we establish some system around here"
 Do. DAF 2. 0/OASIS SOA-RAF Joint Action & Willingness David E. Ellis May 17 th, 2010
Do. DAF 2. 0/OASIS SOA-RAF Joint Action & Willingness David E. Ellis May 17 th, 2010
 Joint Action Use Case
Joint Action Use Case
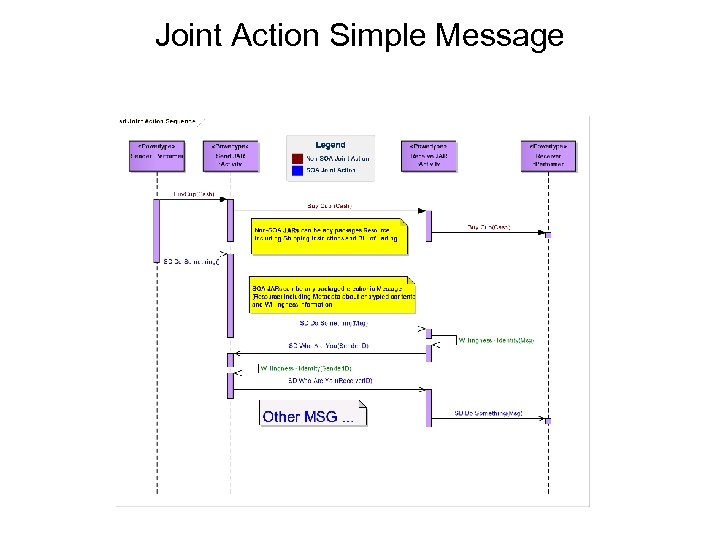 Joint Action Simple Message
Joint Action Simple Message
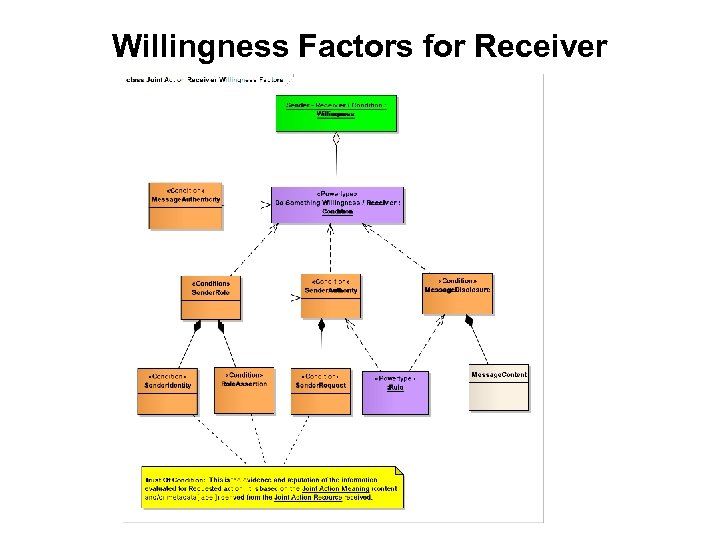 Willingness Factors for Receiver
Willingness Factors for Receiver
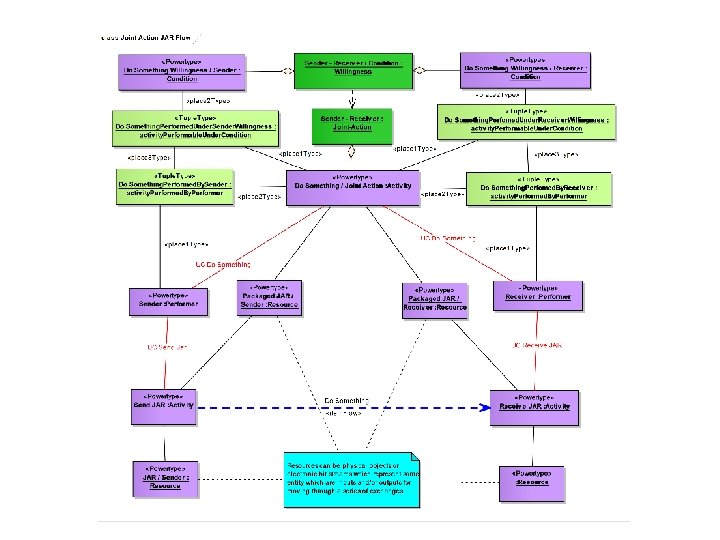
 7 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • FAC – Reminders: • • • Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX next week! IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 72 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – – – Measures use case from JFCOM using JMT – Dave Dryer to send read-ahead Intertech consumes JMTs in EA. SADIE DM 2 DB JPRS – Silverlight client GFM and JIAMDO OPTEVFOR use JMT Normalize through DM 2 – advocates and some maturity
7 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • FAC – Reminders: • • • Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX next week! IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 72 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – – – Measures use case from JFCOM using JMT – Dave Dryer to send read-ahead Intertech consumes JMTs in EA. SADIE DM 2 DB JPRS – Silverlight client GFM and JIAMDO OPTEVFOR use JMT Normalize through DM 2 – advocates and some maturity
 • UPDM Port = socket and jack • UPDM Post = MODAF Post Type = Financial Manager = DM 2 Person Type • UPDM Actual Post = MODAF Post (Financial Manager of BAE) = DM 2 • UPDM Post Description = not filled post • MODAF Role Type = UPDM Responsibility = DM 2 APBP • DM 2 Person Type (Dentist) • Enortu has-parts Dentists, in DM 2/IDEAS is {Enortu} WPT Dentists • UPDM Competence = DM 2 Skill (Active Listening) • UPDM Actual Person out of scope of Do. DAF
• UPDM Port = socket and jack • UPDM Post = MODAF Post Type = Financial Manager = DM 2 Person Type • UPDM Actual Post = MODAF Post (Financial Manager of BAE) = DM 2 • UPDM Post Description = not filled post • MODAF Role Type = UPDM Responsibility = DM 2 APBP • DM 2 Person Type (Dentist) • Enortu has-parts Dentists, in DM 2/IDEAS is {Enortu} WPT Dentists • UPDM Competence = DM 2 Skill (Active Listening) • UPDM Actual Person out of scope of Do. DAF
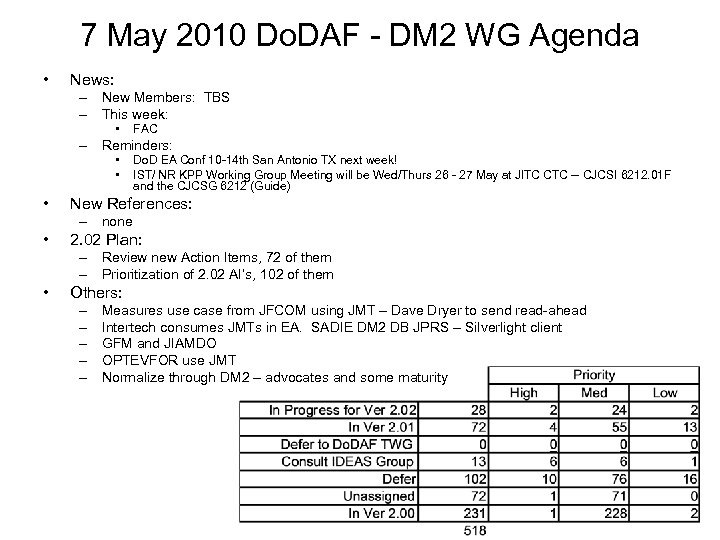 7 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • FAC – Reminders: • • • Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX next week! IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 72 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – – – Measures use case from JFCOM using JMT – Dave Dryer to send read-ahead Intertech consumes JMTs in EA. SADIE DM 2 DB JPRS – Silverlight client GFM and JIAMDO OPTEVFOR use JMT Normalize through DM 2 – advocates and some maturity
7 May 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • FAC – Reminders: • • • Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX next week! IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 72 of them – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – – – Measures use case from JFCOM using JMT – Dave Dryer to send read-ahead Intertech consumes JMTs in EA. SADIE DM 2 DB JPRS – Silverlight client GFM and JIAMDO OPTEVFOR use JMT Normalize through DM 2 – advocates and some maturity
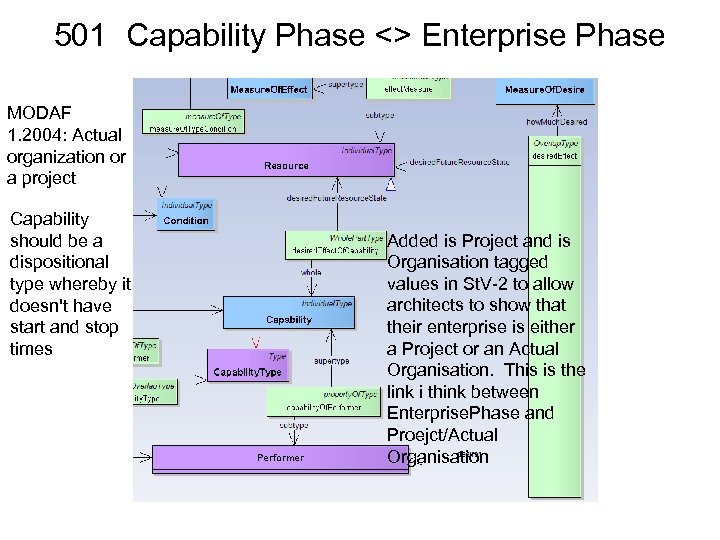 501 Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase MODAF 1. 2004: Actual organization or a project Capability should be a dispositional type whereby it doesn't have start and stop times Added is Project and is Organisation tagged values in St. V-2 to allow architects to show that their enterprise is either a Project or an Actual Organisation. This is the link i think between Enterprise. Phase and Proejct/Actual Organisation
501 Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase MODAF 1. 2004: Actual organization or a project Capability should be a dispositional type whereby it doesn't have start and stop times Added is Project and is Organisation tagged values in St. V-2 to allow architects to show that their enterprise is either a Project or an Actual Organisation. This is the link i think between Enterprise. Phase and Proejct/Actual Organisation
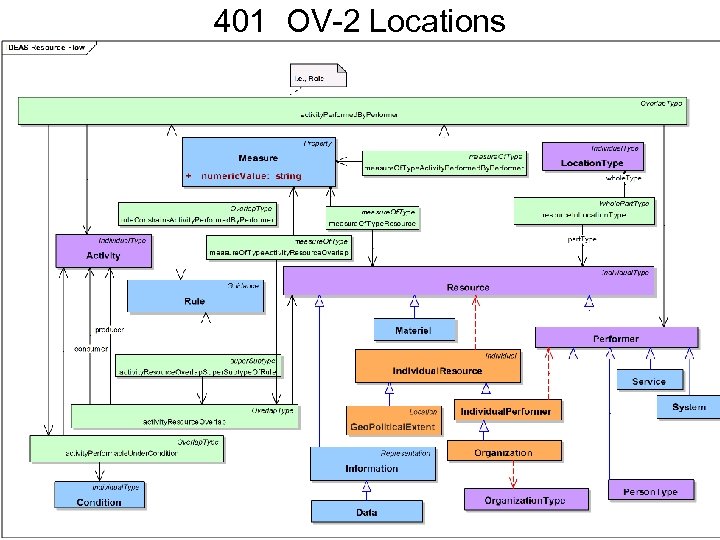 401 OV-2 Locations
401 OV-2 Locations
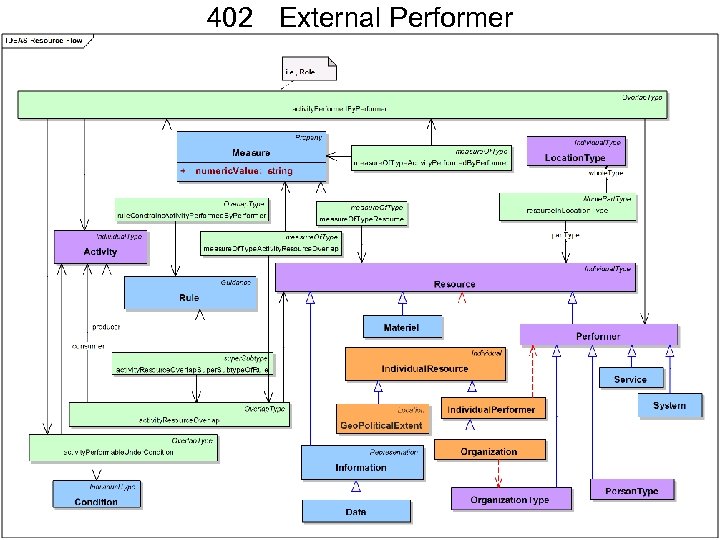 402 External Performer
402 External Performer
 403 Do. DAF CMP Industry Ref • CMP is using a 9 year-old ANSI Draft for a reference. ISO 11179 volumes 1 -6 may be a better reference with more definitions. For continuity, it also includes definitions from older, related ISO/IEC documents (e. g. ISO 2382). These are all available free on the Internet (not all ISO pubs are).
403 Do. DAF CMP Industry Ref • CMP is using a 9 year-old ANSI Draft for a reference. ISO 11179 volumes 1 -6 may be a better reference with more definitions. For continuity, it also includes definitions from older, related ISO/IEC documents (e. g. ISO 2382). These are all available free on the Internet (not all ISO pubs are).
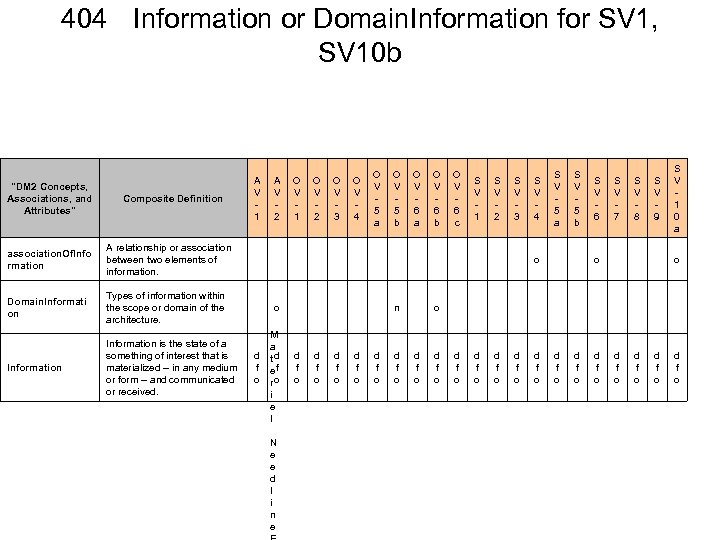 404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b A V 2 O V 1 O V 2 O V 3 O V 4 O V 5 a O V 5 b O V 6 a O V 6 b O V 6 c S V 1 S V 2 S V 3 S V 4 S V 5 a S V 5 b S V 6 S V 7 S V 8 S V 9 S V 1 0 a "DM 2 Concepts, Associations, and Attributes" Composite Definition A V 1 association. Of. Info rmation A relationship or association between two elements of information. o o o Domain. Informati on Types of information within the scope or domain of the architecture. o n o Information is the state of a something of interest that is materialized -- in any medium or form -- and communicated or received. d f o d f o d f o d f o d f o d f o M a td ef ro i e l N e e d l i n e
404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b A V 2 O V 1 O V 2 O V 3 O V 4 O V 5 a O V 5 b O V 6 a O V 6 b O V 6 c S V 1 S V 2 S V 3 S V 4 S V 5 a S V 5 b S V 6 S V 7 S V 8 S V 9 S V 1 0 a "DM 2 Concepts, Associations, and Attributes" Composite Definition A V 1 association. Of. Info rmation A relationship or association between two elements of information. o o o Domain. Informati on Types of information within the scope or domain of the architecture. o n o Information is the state of a something of interest that is materialized -- in any medium or form -- and communicated or received. d f o d f o d f o d f o d f o d f o M a td ef ro i e l N e e d l i n e
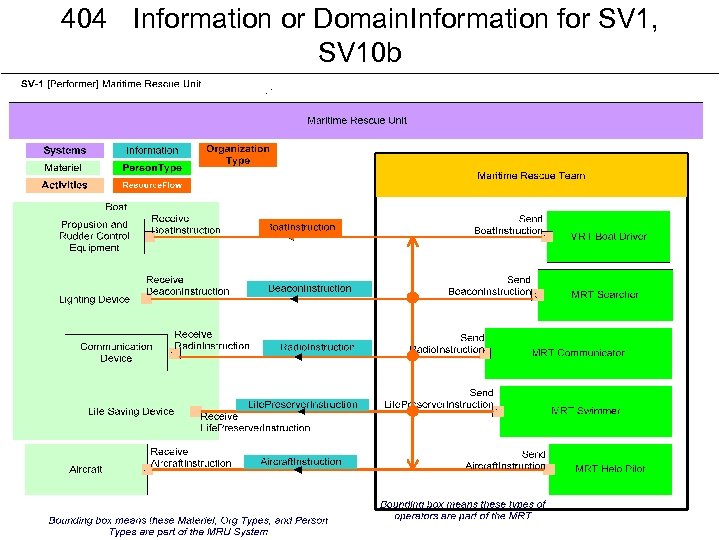 404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b
404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b
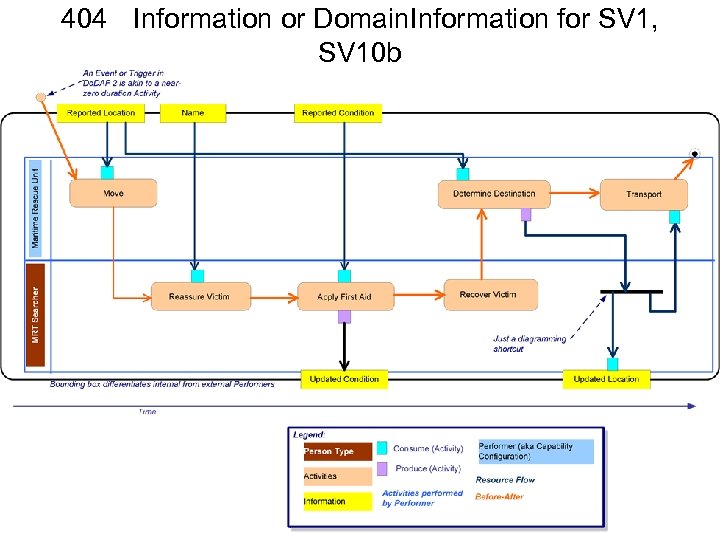 404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b
404 Information or Domain. Information for SV 1, SV 10 b
 30 Apr 2010 Do. DAF – Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: Holliday, Jim; Walton, Tony L; Dougherty, Mike; Link, William – This week: • • NR-KPP / DODI 4630 / CJCSI 6212 SSTC – good turnout at Do. DAF brief; MCTSSA followup; INCOSE – system spec; CV-6 – Reminders: • • FAC IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) – can Dave post on R&R site? Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX. UPDM meetings New References: – none • • Update on on-going AI’s. 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 39 of them) – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary
30 Apr 2010 Do. DAF – Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: Holliday, Jim; Walton, Tony L; Dougherty, Mike; Link, William – This week: • • NR-KPP / DODI 4630 / CJCSI 6212 SSTC – good turnout at Do. DAF brief; MCTSSA followup; INCOSE – system spec; CV-6 – Reminders: • • FAC IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) – can Dave post on R&R site? Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX. UPDM meetings New References: – none • • Update on on-going AI’s. 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items, 39 of them) – Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s, 102 of them • Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary
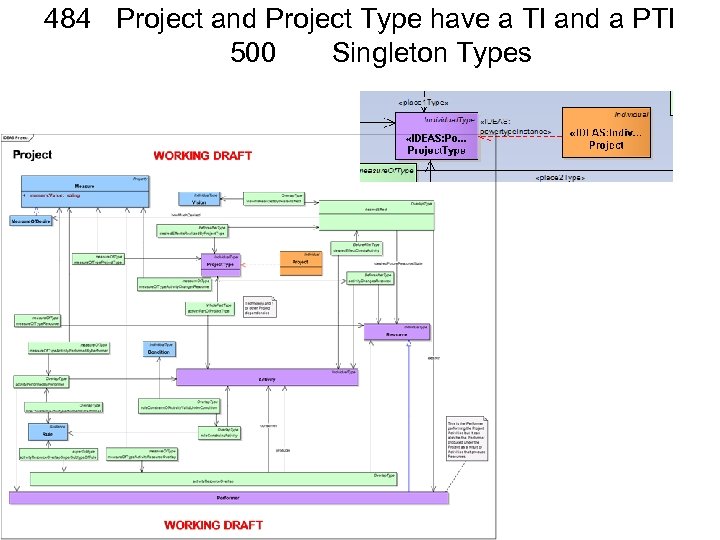 484 Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI 500 Singleton Types
484 Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI 500 Singleton Types
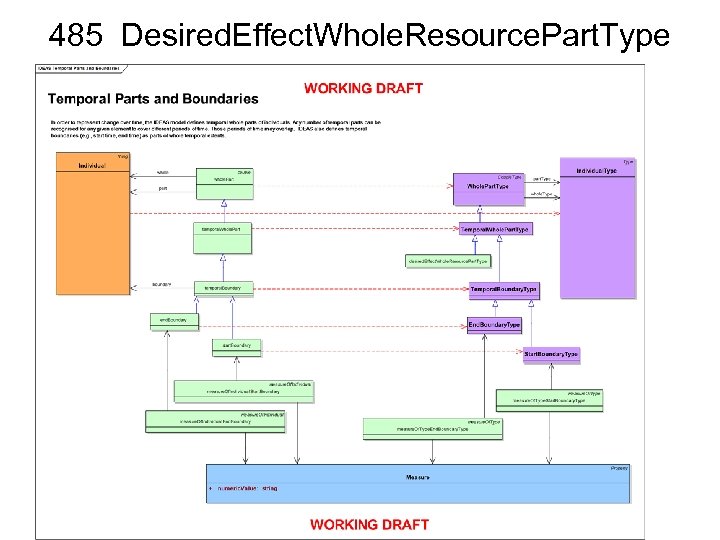 485 Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type
485 Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type
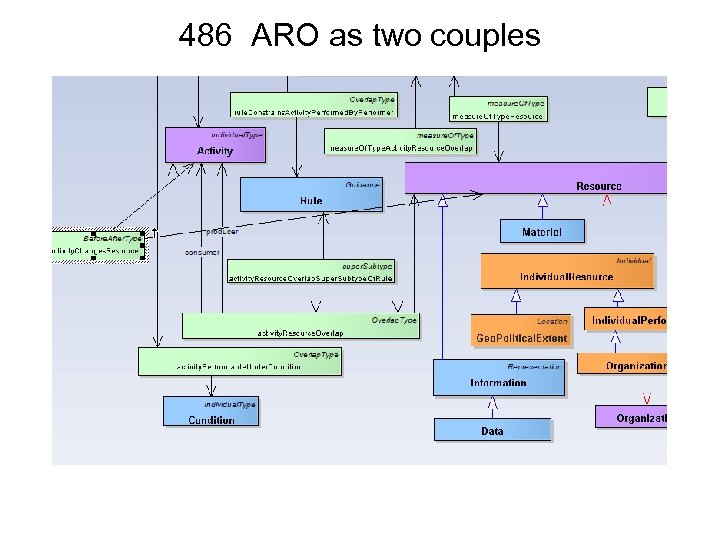 486 ARO as two couples
486 ARO as two couples
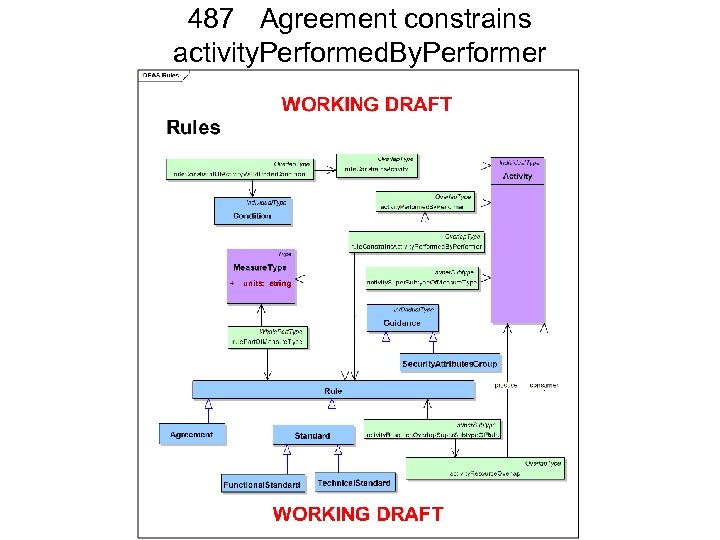 487 Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer
487 Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer
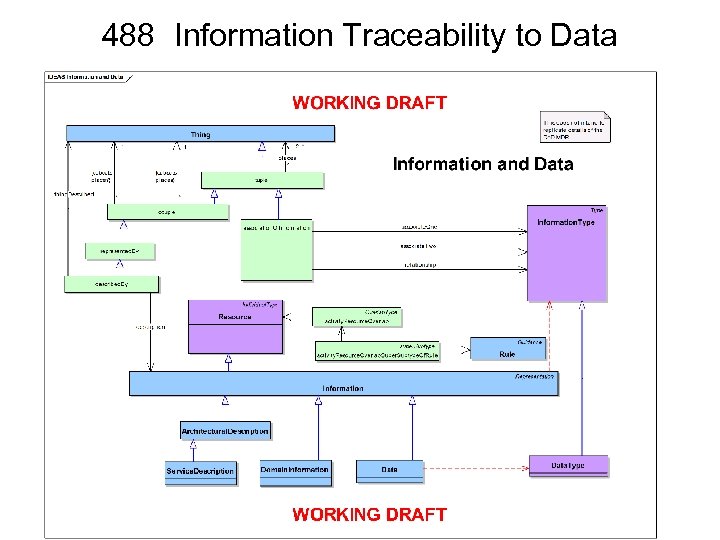 488 Information Traceability to Data
488 Information Traceability to Data
 23 Apr 2010 Do. DAF – Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • • JAIWG Architecture Federation SWG Meeting Tuesday – Suma JCSFL, Dryer JMT’s near to hook up to portal. CADIE (TRADOC) web service I/F’s. DM 2 X CADM mapping. Performer Type. Relook at Event. AI # 330. Do. D Services Conference Wed and Thurs – Semantic Web by Top Quadrant “Top Braid” FEAC IDGA EA Conference – FEAF is higher-level but we hook into it. Dave post briefs from Paul. DON Do. DAF 2 memo – post on R&R site Army G 6/CIO --DM 2 tools – Casewise, DM 2 DB OASIS RAF more clarification and maybe white paper. Unified defs of Service; So. A Service extrapolated. Performer – Capability relationship. Precondition and postcondition definitions. – Reminders: • • • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) – can Dave post on R&R site? Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX. UPDM meetings. New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) • Others: – MCCDC question – routes on CM plan for entry of CR’s, not always via ASRG – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • • • Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary Putman -- sounds like you want a state-transition for the object called Service. Contract
23 Apr 2010 Do. DAF – Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda • News: – New Members: TBS – This week: • • JAIWG Architecture Federation SWG Meeting Tuesday – Suma JCSFL, Dryer JMT’s near to hook up to portal. CADIE (TRADOC) web service I/F’s. DM 2 X CADM mapping. Performer Type. Relook at Event. AI # 330. Do. D Services Conference Wed and Thurs – Semantic Web by Top Quadrant “Top Braid” FEAC IDGA EA Conference – FEAF is higher-level but we hook into it. Dave post briefs from Paul. DON Do. DAF 2 memo – post on R&R site Army G 6/CIO --DM 2 tools – Casewise, DM 2 DB OASIS RAF more clarification and maybe white paper. Unified defs of Service; So. A Service extrapolated. Performer – Capability relationship. Precondition and postcondition definitions. – Reminders: • • • IST/ NR KPP Working Group Meeting will be Wed/Thurs 26 - 27 May at JITC CTC -- CJCSI 6212. 01 F and the CJCSG 6212 (Guide) – can Dave post on R&R site? Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX. UPDM meetings. New References: – none • 2. 02 Plan: – Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) • Others: – MCCDC question – routes on CM plan for entry of CR’s, not always via ASRG – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • • • Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary Putman -- sounds like you want a state-transition for the object called Service. Contract
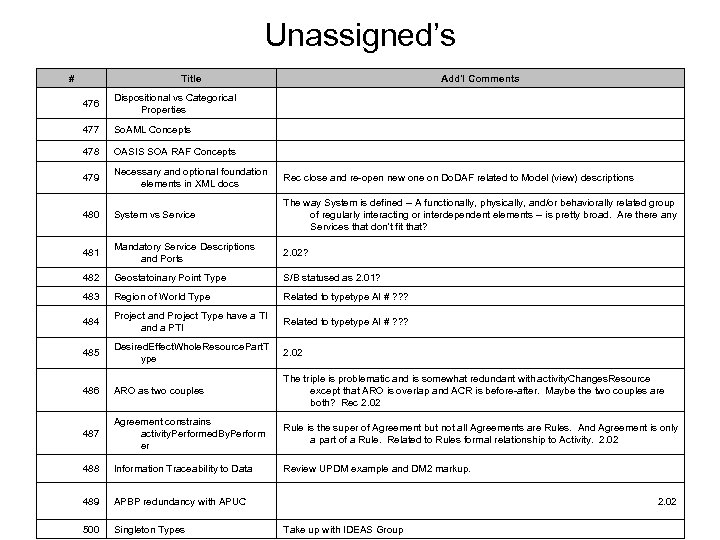 Unassigned’s # Title Add'l Comments 476 Dispositional vs Categorical Properties 477 So. AML Concepts 478 OASIS SOA RAF Concepts 479 Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs Rec close and re-open new one on Do. DAF related to Model (view) descriptions 480 System vs Service The way System is defined -- A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements -- is pretty broad. Are there any Services that don't fit that? 481 Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports 2. 02? 482 Geostatoinary Point Type S/B statused as 2. 01? 483 Region of World Type Related to type AI # ? ? ? 484 Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Related to type AI # ? ? ? 485 Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. T ype 2. 02 486 ARO as two couples The triple is problematic and is somewhat redundant with activity. Changes. Resource except that ARO is overlap and ACR is before-after. Maybe the two couples are both? Rec 2. 02 487 Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Perform er Rule is the super of Agreement but not all Agreements are Rules. And Agreement is only a part of a Rule. Related to Rules formal relationship to Activity. 2. 02 488 Information Traceability to Data Review UPDM example and DM 2 markup. 489 APBP redundancy with APUC 500 Singleton Types 2. 02 Take up with IDEAS Group
Unassigned’s # Title Add'l Comments 476 Dispositional vs Categorical Properties 477 So. AML Concepts 478 OASIS SOA RAF Concepts 479 Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs Rec close and re-open new one on Do. DAF related to Model (view) descriptions 480 System vs Service The way System is defined -- A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements -- is pretty broad. Are there any Services that don't fit that? 481 Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports 2. 02? 482 Geostatoinary Point Type S/B statused as 2. 01? 483 Region of World Type Related to type AI # ? ? ? 484 Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Related to type AI # ? ? ? 485 Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. T ype 2. 02 486 ARO as two couples The triple is problematic and is somewhat redundant with activity. Changes. Resource except that ARO is overlap and ACR is before-after. Maybe the two couples are both? Rec 2. 02 487 Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Perform er Rule is the super of Agreement but not all Agreements are Rules. And Agreement is only a part of a Rule. Related to Rules formal relationship to Activity. 2. 02 488 Information Traceability to Data Review UPDM example and DM 2 markup. 489 APBP redundancy with APUC 500 Singleton Types 2. 02 Take up with IDEAS Group
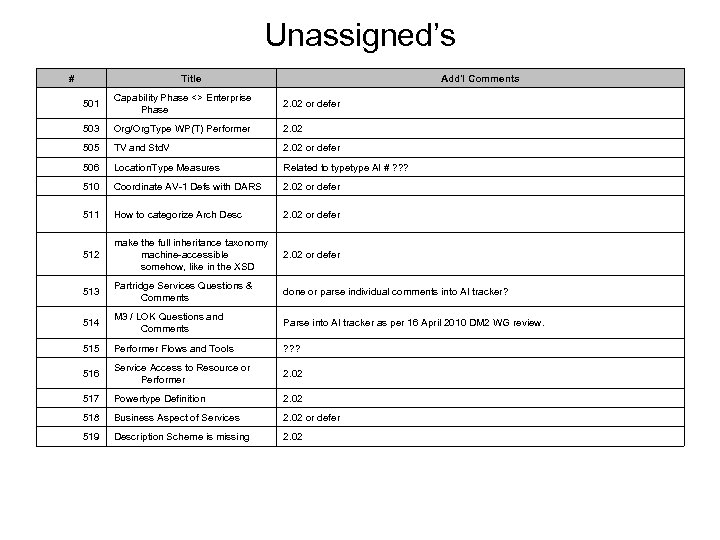 Unassigned’s # Title Add'l Comments 501 Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase 2. 02 or defer 503 Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer 2. 02 505 TV and Std. V 2. 02 or defer 506 Location. Type Measures Related to type AI # ? ? ? 510 Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS 2. 02 or defer 511 How to categorize Arch Desc 2. 02 or defer 512 make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD 2. 02 or defer 513 Partridge Services Questions & Comments done or parse individual comments into AI tracker? 514 M 3 / LOK Questions and Comments Parse into AI tracker as per 16 April 2010 DM 2 WG review. 515 Performer Flows and Tools ? ? ? 516 Service Access to Resource or Performer 2. 02 517 Powertype Definition 2. 02 518 Business Aspect of Services 2. 02 or defer 519 Description Scheme is missing 2. 02
Unassigned’s # Title Add'l Comments 501 Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase 2. 02 or defer 503 Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer 2. 02 505 TV and Std. V 2. 02 or defer 506 Location. Type Measures Related to type AI # ? ? ? 510 Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS 2. 02 or defer 511 How to categorize Arch Desc 2. 02 or defer 512 make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD 2. 02 or defer 513 Partridge Services Questions & Comments done or parse individual comments into AI tracker? 514 M 3 / LOK Questions and Comments Parse into AI tracker as per 16 April 2010 DM 2 WG review. 515 Performer Flows and Tools ? ? ? 516 Service Access to Resource or Performer 2. 02 517 Powertype Definition 2. 02 518 Business Aspect of Services 2. 02 or defer 519 Description Scheme is missing 2. 02
 16 Apr 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda 1. News: – New Members: • • – – – – M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS Meetings this week Others this week: JAIWG – Dave check JKO for briefs Do. D MDRWG – new portal I/F, DDMS 3. 0 + new IC-ISM = 3. 1 – remove html from Namespace or single mht Do. D COI Forum NR-KPP WG – DISA-J 6 -NII triad interop issues – AS&I role? CDR Mike Moore J 8 & Tom J 6 re ICD & Do. DAF; TRADOC – 6 core processes what’s important in each – check against DM 2, IDEAS, UPDM, -- intersections. Start with JCIDS. Use of Do. DAF. ISP & ICD appendix. CSA process issues. JFIP Tech Team. Good progress on DM 2. Brief / demo at Do. D EA conf. Reminder: • • 2. Do. D Services Conference w/o 19 April, Do. D EA Conference coming up soon Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX New References: • • 3. 4. 5. 6. Walter Wilson – LMCO Santa Maria, CA. AFSC AEHF mission planning. CA Assoc EA’s. Privacy Assurance. FEAC inst EE. Execution level use of F/W. Certified for use in simulations. Wally Chang – MITRE PEO-Integration. Boeing map Views X RR. SV-4, 5 a, 6. UCORE Folder updated NIEM Parse of M 3/IDEAS Group comments into DM 2 AI list Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary TBS from WG tomorrow
16 Apr 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda 1. News: – New Members: • • – – – – M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS Meetings this week Others this week: JAIWG – Dave check JKO for briefs Do. D MDRWG – new portal I/F, DDMS 3. 0 + new IC-ISM = 3. 1 – remove html from Namespace or single mht Do. D COI Forum NR-KPP WG – DISA-J 6 -NII triad interop issues – AS&I role? CDR Mike Moore J 8 & Tom J 6 re ICD & Do. DAF; TRADOC – 6 core processes what’s important in each – check against DM 2, IDEAS, UPDM, -- intersections. Start with JCIDS. Use of Do. DAF. ISP & ICD appendix. CSA process issues. JFIP Tech Team. Good progress on DM 2. Brief / demo at Do. D EA conf. Reminder: • • 2. Do. D Services Conference w/o 19 April, Do. D EA Conference coming up soon Do. D EA Conf 10 -14 th San Antonio TX New References: • • 3. 4. 5. 6. Walter Wilson – LMCO Santa Maria, CA. AFSC AEHF mission planning. CA Assoc EA’s. Privacy Assurance. FEAC inst EE. Execution level use of F/W. Certified for use in simulations. Wally Chang – MITRE PEO-Integration. Boeing map Views X RR. SV-4, 5 a, 6. UCORE Folder updated NIEM Parse of M 3/IDEAS Group comments into DM 2 AI list Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary TBS from WG tomorrow
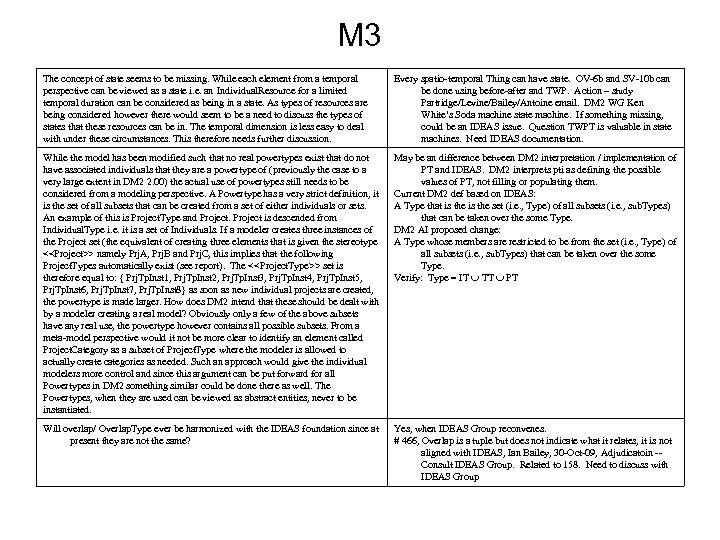 M 3 The concept of state seems to be missing. While each element from a temporal perspective can be viewed as a state i. e. an Individual. Resource for a limited temporal duration can be considered as being in a state. As types of resources are being considered however there would seem to be a need to discuss the types of states that these resources can be in. The temporal dimension is less easy to deal with under these circumstances. This therefore needs further discussion. Every spatio-temporal Thing can have state. OV-6 b and SV-10 b can be done using before-after and TWP. Action – study Partridge/Levine/Bailey/Antoine email. DM 2 WG Ken White’s Soda machine state machine. If something missing, could be an IDEAS issue. Question TWPT is valuable in state machines. Need IDEAS documentation. While the model has been modified such that no real powertypes exist that do not have associated individuals that they are a powertype of (previously the case to a very large extent in DM 2 2. 00) the actual use of powertypes still needs to be considered from a modeling perspective. A Powertype has a very strict definition, it is the set of all subsets that can be created from a set of either individuals or sets. An example of this is Project. Type and Project is descended from Individual. Type i. e. it is a set of Individuals. If a modeler creates three instances of the Project set (the equivalent of creating three elements that is given the stereotype <
M 3 The concept of state seems to be missing. While each element from a temporal perspective can be viewed as a state i. e. an Individual. Resource for a limited temporal duration can be considered as being in a state. As types of resources are being considered however there would seem to be a need to discuss the types of states that these resources can be in. The temporal dimension is less easy to deal with under these circumstances. This therefore needs further discussion. Every spatio-temporal Thing can have state. OV-6 b and SV-10 b can be done using before-after and TWP. Action – study Partridge/Levine/Bailey/Antoine email. DM 2 WG Ken White’s Soda machine state machine. If something missing, could be an IDEAS issue. Question TWPT is valuable in state machines. Need IDEAS documentation. While the model has been modified such that no real powertypes exist that do not have associated individuals that they are a powertype of (previously the case to a very large extent in DM 2 2. 00) the actual use of powertypes still needs to be considered from a modeling perspective. A Powertype has a very strict definition, it is the set of all subsets that can be created from a set of either individuals or sets. An example of this is Project. Type and Project is descended from Individual. Type i. e. it is a set of Individuals. If a modeler creates three instances of the Project set (the equivalent of creating three elements that is given the stereotype <
 M 3 The use of named. By, described. By and represented. By needs to be discussed (see 2. 4 as well as 2. 7). OK Information is indicated as a Type, i. e. it is a set of sets. Information. Type is its Powertype, i. e. it is the set of all subsets of a set of sets. Why is association. Of. Information attached to it, would it not be better to make use of Information instead if the intent of the element is to describe the structure of a particular kind of information type (an instance of the Information set). Information. Type is not connected anywhere with the exception of the tuple and the powertype association. The same could be stated for Data. Type. Record DM 2 AI for what are currently are called Info Type and Data Type to be the resource types that flow in the resource flow model. This is because it is not the actual Individual Type Information that is modeled in the flow, but the Type. This requires a person to understand that the Individual information or data is at the utterance or copy level. In the latest version of the model desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type has been moved to the side, i. e. it is no longer situated within an inheritance hierarchy. What purpose does this element have? It seems consistently to be in the wrong color in the model. Looks like leftover from Desired. Effect structuring. Subtyped wrong, place positions wrong, unnecessary. Record DM 2 AI. Why have Measure. Range and Measure. Point (integrated from IDEAS foundation up until the latest version), been deleted? (see also 2. 6 in the report) DM 2 WG did not want to emphasize just two value ranges and went with more general setup. Need to record AI to discuss with IDEAS Group. Why have measure. Of. Individual been treated differently from Measure. Of. Type (see 2. 6 in the report). Put all subtypes of mo. I and mo. T on Measure diagram and do all associations to Measure via supertype, excepting those that go to a subtype of Measure. DM 2 AI. There is a need to get final confirmation regarding the rules described in paragraph 2. 7 of the big report. DM 2 AI to add to PES/IDEAS description document and enforce in LDM or PES as possible. Will the DM 2 Naming and description pattern be brought in line with the IDEAS foundation? DM 2 AI to verify that it’s subclasses and add the omitted subclasses to the PES/IDEAS description document. It has been stated previously that Individual. Person is to be considered as meta-data. It is however still shown as part of the Performer data group. Does this mean that the use of Individual. Person has changed? No, Individual. Person is not a Do. DAF requirement except for AV-1. DM 2 AI to remove from diagram; consider a metadata or AV-1 -ish diagram in the metadata package. (Also note, Info Pedigree is actually part of design reification, not just metadata. Consider a design reification diagram. Also, note that info. Pedigree may need to be resource. Pedigree. An example of how this works would be good. )
M 3 The use of named. By, described. By and represented. By needs to be discussed (see 2. 4 as well as 2. 7). OK Information is indicated as a Type, i. e. it is a set of sets. Information. Type is its Powertype, i. e. it is the set of all subsets of a set of sets. Why is association. Of. Information attached to it, would it not be better to make use of Information instead if the intent of the element is to describe the structure of a particular kind of information type (an instance of the Information set). Information. Type is not connected anywhere with the exception of the tuple and the powertype association. The same could be stated for Data. Type. Record DM 2 AI for what are currently are called Info Type and Data Type to be the resource types that flow in the resource flow model. This is because it is not the actual Individual Type Information that is modeled in the flow, but the Type. This requires a person to understand that the Individual information or data is at the utterance or copy level. In the latest version of the model desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type has been moved to the side, i. e. it is no longer situated within an inheritance hierarchy. What purpose does this element have? It seems consistently to be in the wrong color in the model. Looks like leftover from Desired. Effect structuring. Subtyped wrong, place positions wrong, unnecessary. Record DM 2 AI. Why have Measure. Range and Measure. Point (integrated from IDEAS foundation up until the latest version), been deleted? (see also 2. 6 in the report) DM 2 WG did not want to emphasize just two value ranges and went with more general setup. Need to record AI to discuss with IDEAS Group. Why have measure. Of. Individual been treated differently from Measure. Of. Type (see 2. 6 in the report). Put all subtypes of mo. I and mo. T on Measure diagram and do all associations to Measure via supertype, excepting those that go to a subtype of Measure. DM 2 AI. There is a need to get final confirmation regarding the rules described in paragraph 2. 7 of the big report. DM 2 AI to add to PES/IDEAS description document and enforce in LDM or PES as possible. Will the DM 2 Naming and description pattern be brought in line with the IDEAS foundation? DM 2 AI to verify that it’s subclasses and add the omitted subclasses to the PES/IDEAS description document. It has been stated previously that Individual. Person is to be considered as meta-data. It is however still shown as part of the Performer data group. Does this mean that the use of Individual. Person has changed? No, Individual. Person is not a Do. DAF requirement except for AV-1. DM 2 AI to remove from diagram; consider a metadata or AV-1 -ish diagram in the metadata package. (Also note, Info Pedigree is actually part of design reification, not just metadata. Consider a design reification diagram. Also, note that info. Pedigree may need to be resource. Pedigree. An example of how this works would be good. )
 M 3 The element rule. Part. Of. Measure. Type is defined as: "A couple that represents the whole part relationship between types of measures and rules. " This is strange since it descends from Whole. Part. Type which in turn descends from Couple. Type. Furthermore Measure. Type is a Powertype (of Measure). Measure is a set of sets, i. e. Measure. Type is the set of all subsets of a set of sets. Rule is also a set of sets. Is an instance of the Rule set, i. e. for example set rule. A, really a part of the a set that is a subset of the set of sets that is Measure? Rule should be constraining the Activity of Measure. Type. Something that connects the Measure. Type with the Activity of measuring, e. g. , “measure mass”. DM 2 AI and the recommend to consult with IDEAS Group. Look for UOM vs Measure. Type. The element measure. Of. Type. Whole. Part. Type appears in a number of places. Is the intent here to apply a measure onto a rules based approach of the Whole. Part. Type concept? Ians comment regarding the inability in general to apply measures to relationships needs to be noted here. Is anything intended to be done as regards this in the future? DM 2 AI system with Consult IDEAS Group status. Issue of counting and cardinality which seems to apply to the WP relationship, not to individual place positions. See Brian Ellis. Ordinal and cardinal measures. In earlier versions of DM 2, notably from October 2009 a significant amount of additional elements were included under the foundation folder in DM 2. All of this has since been removed. What was the reason for this? It is the understanding of the author that the items contained acted as grounding for significant portions of the model, needed in order to handle things at Type level. Yes, IDEAS specializes associations whereas DM 2 uses inheritance. Related to association superclass rules. Might be some issues, none known at this time other than perhaps Person. Type WPT [OT] Person. Type. Related to DM 2 AI’s # 373 and 470. Capability is related to Performer via capability. Of. Performer. This in turn is descended from property. Of. Type which is defined as " A super. Subtype that asserts an Individual. Type is a subtype of a Property - i. e. it asserts all members of the Individual type "have" a property. Examples: All London Buses are red, All Porsche 911 2. 2 S have a mass between 900 and 960 kg. ". In Property. Of. Type <
M 3 The element rule. Part. Of. Measure. Type is defined as: "A couple that represents the whole part relationship between types of measures and rules. " This is strange since it descends from Whole. Part. Type which in turn descends from Couple. Type. Furthermore Measure. Type is a Powertype (of Measure). Measure is a set of sets, i. e. Measure. Type is the set of all subsets of a set of sets. Rule is also a set of sets. Is an instance of the Rule set, i. e. for example set rule. A, really a part of the a set that is a subset of the set of sets that is Measure? Rule should be constraining the Activity of Measure. Type. Something that connects the Measure. Type with the Activity of measuring, e. g. , “measure mass”. DM 2 AI and the recommend to consult with IDEAS Group. Look for UOM vs Measure. Type. The element measure. Of. Type. Whole. Part. Type appears in a number of places. Is the intent here to apply a measure onto a rules based approach of the Whole. Part. Type concept? Ians comment regarding the inability in general to apply measures to relationships needs to be noted here. Is anything intended to be done as regards this in the future? DM 2 AI system with Consult IDEAS Group status. Issue of counting and cardinality which seems to apply to the WP relationship, not to individual place positions. See Brian Ellis. Ordinal and cardinal measures. In earlier versions of DM 2, notably from October 2009 a significant amount of additional elements were included under the foundation folder in DM 2. All of this has since been removed. What was the reason for this? It is the understanding of the author that the items contained acted as grounding for significant portions of the model, needed in order to handle things at Type level. Yes, IDEAS specializes associations whereas DM 2 uses inheritance. Related to association superclass rules. Might be some issues, none known at this time other than perhaps Person. Type WPT [OT] Person. Type. Related to DM 2 AI’s # 373 and 470. Capability is related to Performer via capability. Of. Performer. This in turn is descended from property. Of. Type which is defined as " A super. Subtype that asserts an Individual. Type is a subtype of a Property - i. e. it asserts all members of the Individual type "have" a property. Examples: All London Buses are red, All Porsche 911 2. 2 S have a mass between 900 and 960 kg. ". In Property. Of. Type <
 M 3 Capability connects to Resource via desired. Effect. Of. Capability which is descended from Whole. Part. Type. Capability is descended from Individual. Type, i. e. it is the set of sets where the instances of each of the sets it contains are entities that have a capability, i. e. some of these can easily contain individuals that are kinds of performers. There is no argument however concerning the need to have something that connects a capability to a desired outcome in the form of a state of a given resource. As an example taken from the SAR it would seem likely that the end desired effect of a Maritime search and rescue would be that the state of the resources that are in need of rescue is changed from "in need of rescue" to "rescued and safe" and that the state of the resource "a place of safety" is changed from having "no rescued" to "all in need rescued". This would however seem to imply a certain multiplicity as regards the resource. Is this assumption relating to multiplicity correct? The naming of the element gives the impression that it has something to do with desired. Effect which however is not the case. This would seem to require some handling to avoid misunderstandings. An associated element is effect. Measure and Measure. Of. Effect. The definition of effect. Measure talks about desired. Effect in spite of the fact that there is no relationship to this element. A change of definition would seem to be in order here. DM 2 AI rec change desired. Effect. Of. Capability name to desired. Future. Resource. State. Of. Capability. Also, fix def of Meausre. Of. Effect to remove “desired. ” Link to desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type. DM 2 AI Capability must have at least one of these. May also for Performer to say it must perform at least one Activity. Etc. Two performers to exchange a Resource.
M 3 Capability connects to Resource via desired. Effect. Of. Capability which is descended from Whole. Part. Type. Capability is descended from Individual. Type, i. e. it is the set of sets where the instances of each of the sets it contains are entities that have a capability, i. e. some of these can easily contain individuals that are kinds of performers. There is no argument however concerning the need to have something that connects a capability to a desired outcome in the form of a state of a given resource. As an example taken from the SAR it would seem likely that the end desired effect of a Maritime search and rescue would be that the state of the resources that are in need of rescue is changed from "in need of rescue" to "rescued and safe" and that the state of the resource "a place of safety" is changed from having "no rescued" to "all in need rescued". This would however seem to imply a certain multiplicity as regards the resource. Is this assumption relating to multiplicity correct? The naming of the element gives the impression that it has something to do with desired. Effect which however is not the case. This would seem to require some handling to avoid misunderstandings. An associated element is effect. Measure and Measure. Of. Effect. The definition of effect. Measure talks about desired. Effect in spite of the fact that there is no relationship to this element. A change of definition would seem to be in order here. DM 2 AI rec change desired. Effect. Of. Capability name to desired. Future. Resource. State. Of. Capability. Also, fix def of Meausre. Of. Effect to remove “desired. ” Link to desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type. DM 2 AI Capability must have at least one of these. May also for Performer to say it must perform at least one Activity. Etc. Two performers to exchange a Resource.
 M 3 The use of the powertype Capability. Type requires some further discussion since its utility is less than clear. Based on the definition it is automatically populated by the subsets of a set of sets (capability). The Overlap. Type descendent activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type is also less obvious especially given its definition: "Represents that an activity was / is / can-be/ must-be conducted under certain conditions with a spatiotemporal overlap of the activity with the condition. " which seems to be talking about something different. The fact that the element maps instances of a set of subsets (Activity) to instances of a set of subsets of a set of sets (Capability. Type) also needs to be considered. Capabilty. Type done for JCA’s, which aren’t really defined as Capabilities. What about making a JCA = union of the desired. Effects, Tasks/Activities, Conditions, etc. of the subs. Add to DM 2 AI Type issue for Activity. Type. axiom of reducibility was introduced by Bertrand Russell as part of his ramified theory of types Either Types are removed along with activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type or activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type needs a new def. But Lion Î Species activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type is defined as: " activity. Type is a member of Measure. Type". There is no element named activity. Type and this implies that the definition needs to be changed. Since Activity is the set of all subsets of Individual. Activity and Measure. Type is the set of all subsets of a set of sets of Individual Measures, the connection is less than obvious and the author of this report would like to discuss this. DM 2 AI for Def is incorrect or remove Type.
M 3 The use of the powertype Capability. Type requires some further discussion since its utility is less than clear. Based on the definition it is automatically populated by the subsets of a set of sets (capability). The Overlap. Type descendent activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type is also less obvious especially given its definition: "Represents that an activity was / is / can-be/ must-be conducted under certain conditions with a spatiotemporal overlap of the activity with the condition. " which seems to be talking about something different. The fact that the element maps instances of a set of subsets (Activity) to instances of a set of subsets of a set of sets (Capability. Type) also needs to be considered. Capabilty. Type done for JCA’s, which aren’t really defined as Capabilities. What about making a JCA = union of the desired. Effects, Tasks/Activities, Conditions, etc. of the subs. Add to DM 2 AI Type issue for Activity. Type. axiom of reducibility was introduced by Bertrand Russell as part of his ramified theory of types Either Types are removed along with activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type or activity. Maps. To. Capability. Type needs a new def. But Lion Î Species activity. Super. Subtype. Of. Measure. Type is defined as: " activity. Type is a member of Measure. Type". There is no element named activity. Type and this implies that the definition needs to be changed. Since Activity is the set of all subsets of Individual. Activity and Measure. Type is the set of all subsets of a set of sets of Individual Measures, the connection is less than obvious and the author of this report would like to discuss this. DM 2 AI for Def is incorrect or remove Type.
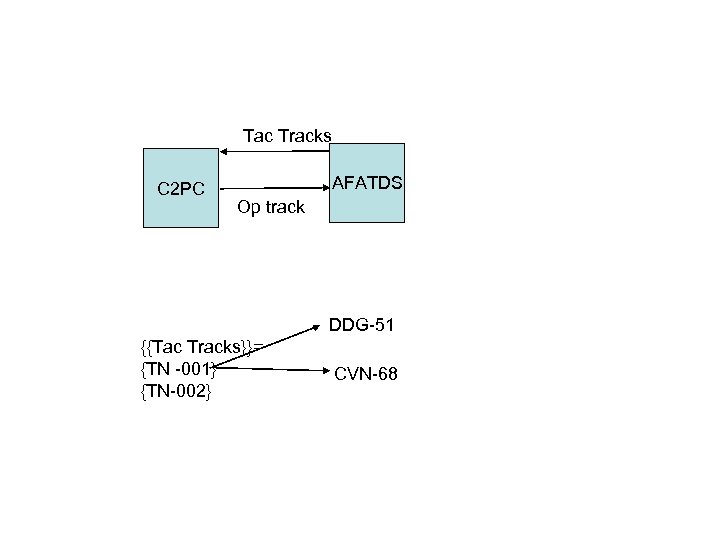 Tac Tracks C 2 PC AFATDS Op track DDG-51 {{Tac Tracks}}= {TN -001} {TN-002} CVN-68
Tac Tracks C 2 PC AFATDS Op track DDG-51 {{Tac Tracks}}= {TN -001} {TN-002} CVN-68
 M 3 activity. Resource. Overlap is used to indicate flow of resources from one activity to another. Since Resources are transferred this gives rise to some rather strange interactions given that Performer is a subset of Resource. As a result of this all elements that are subsets of Performer can flow between activities in addition to Materiel and Information (and all of its subsets), Geo. Political. Extent. Type (and all of its subsets), i. e. System, Service, Person. Type, Organisation. Type, Port, Service. Port, Geo. Political. Extent. Type (the subsets that are categorized properly). Is this really the intention? How to split out the relevant pieces or indicate impossible couplings? How does this work in the XML with DF? AI to DM 2 WG It is generally felt that the number of distinct elements that define how resources can be combined are few and far between and that unless foundational elements are made use of no really complex resource combinations can really be defined properly. The roles that the various entities play in different combinations are also not covered to any extent. DM 2 WG to flush out missing relationships if guidance that higher term relationships (before. After, whole. Part) are for like classes only.
M 3 activity. Resource. Overlap is used to indicate flow of resources from one activity to another. Since Resources are transferred this gives rise to some rather strange interactions given that Performer is a subset of Resource. As a result of this all elements that are subsets of Performer can flow between activities in addition to Materiel and Information (and all of its subsets), Geo. Political. Extent. Type (and all of its subsets), i. e. System, Service, Person. Type, Organisation. Type, Port, Service. Port, Geo. Political. Extent. Type (the subsets that are categorized properly). Is this really the intention? How to split out the relevant pieces or indicate impossible couplings? How does this work in the XML with DF? AI to DM 2 WG It is generally felt that the number of distinct elements that define how resources can be combined are few and far between and that unless foundational elements are made use of no really complex resource combinations can really be defined properly. The roles that the various entities play in different combinations are also not covered to any extent. DM 2 WG to flush out missing relationships if guidance that higher term relationships (before. After, whole. Part) are for like classes only.
 9 Apr 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda 1. Service Discussion with MOD 2. News: – – FAC meeting this week JAIWG Federated Data Exchange Pilots Progress “M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS” Meetings next week Do. D Services Conference w/o 19 April 3. New References: • • Baseline: DM 2 VDD v 2. 01. doc DM 2 WG Organizational and Meetings Information: FAC_meeeting__04_06_2010__Announcement_Agenda__V__2. 2. doc and FAC_meeting__04_06_2010_BL_V_1. 1 w. Do. DAF. ppt 4. Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) • Start with AIs 507 -509 needed for JFCOM Federated Data Exchange Pilots 5. Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 6. Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary • TBS from WG tomorrow
9 Apr 2010 Do. DAF - DM 2 WG Agenda 1. Service Discussion with MOD 2. News: – – FAC meeting this week JAIWG Federated Data Exchange Pilots Progress “M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS” Meetings next week Do. D Services Conference w/o 19 April 3. New References: • • Baseline: DM 2 VDD v 2. 01. doc DM 2 WG Organizational and Meetings Information: FAC_meeeting__04_06_2010__Announcement_Agenda__V__2. 2. doc and FAC_meeting__04_06_2010_BL_V_1. 1 w. Do. DAF. ppt 4. Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) • Start with AIs 507 -509 needed for JFCOM Federated Data Exchange Pilots 5. Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 6. Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary • TBS from WG tomorrow
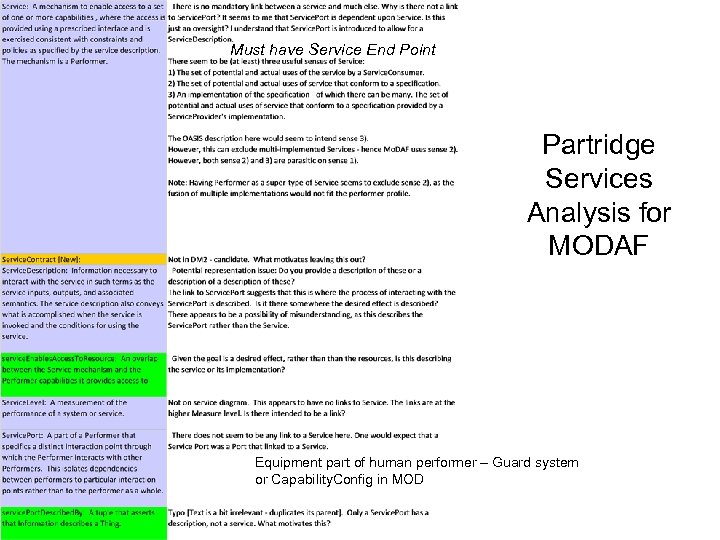 Must have Service End Point Partridge Services Analysis for MODAF Equipment part of human performer – Guard system or Capability. Config in MOD
Must have Service End Point Partridge Services Analysis for MODAF Equipment part of human performer – Guard system or Capability. Config in MOD
![MODAF Services Analysis OASIS-RM[1] TOG-SO Soa. ML a mechanism to enable access to one MODAF Services Analysis OASIS-RM[1] TOG-SO Soa. ML a mechanism to enable access to one](https://present5.com/presentation/918441cccc92be15b42e041504be0f9a/image-81.jpg) MODAF Services Analysis OASIS-RM[1] TOG-SO Soa. ML a mechanism to enable access to one or more capabilities, where the access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with constraints and policies as specified by the service description. A logical representation of a repeatable business activity that has a specified outcome (e. g. , check customer credit; provide weather data, consolidate drilling reports). It is self-contained, may be composed of other services, and is a “black box” to its consumers. (TOG-SSB also includes a second (different) definition: “A service is a repeatable activity that has a specified outcome”[2]. This effectively moves the definition down a level of representation. OASIS-RAF has no direct definition of a Service. ) Service is defined as a resource that enables access to one or more capabilities. Here, the access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with constraints and policies as specified by the service description. This access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with all constraints and policies as specified by the service description. A service is provided by an entity - called the provider - for use by others. The eventual consumers of the service may not be known to the service provider and may demonstrate uses of the service beyond the scope originally conceived by the provider. Identifies or specifies a cohesive set of functions or capabilities that a service provides. [1] The OASIS-RM definition is used in DM 2 and noted in M 3.
MODAF Services Analysis OASIS-RM[1] TOG-SO Soa. ML a mechanism to enable access to one or more capabilities, where the access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with constraints and policies as specified by the service description. A logical representation of a repeatable business activity that has a specified outcome (e. g. , check customer credit; provide weather data, consolidate drilling reports). It is self-contained, may be composed of other services, and is a “black box” to its consumers. (TOG-SSB also includes a second (different) definition: “A service is a repeatable activity that has a specified outcome”[2]. This effectively moves the definition down a level of representation. OASIS-RAF has no direct definition of a Service. ) Service is defined as a resource that enables access to one or more capabilities. Here, the access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with constraints and policies as specified by the service description. This access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with all constraints and policies as specified by the service description. A service is provided by an entity - called the provider - for use by others. The eventual consumers of the service may not be known to the service provider and may demonstrate uses of the service beyond the scope originally conceived by the provider. Identifies or specifies a cohesive set of functions or capabilities that a service provides. [1] The OASIS-RM definition is used in DM 2 and noted in M 3.
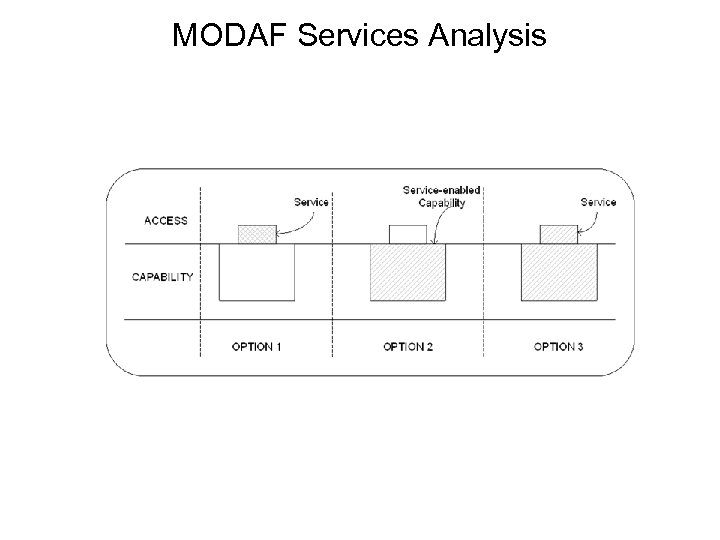 MODAF Services Analysis
MODAF Services Analysis
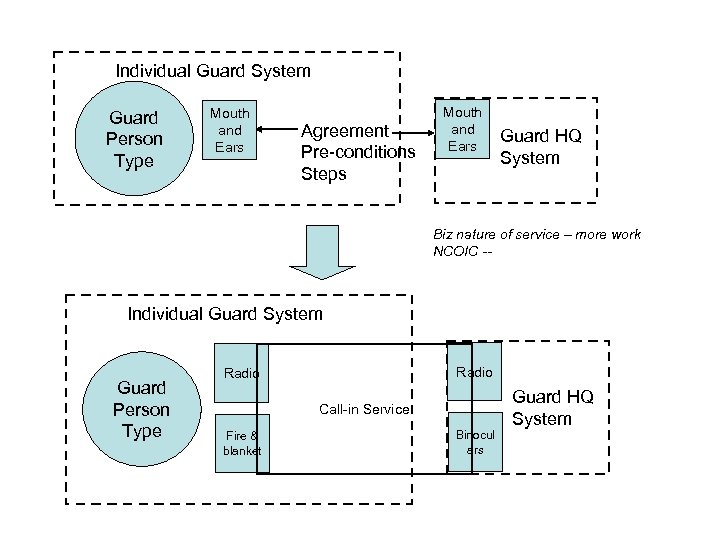 Individual Guard System Guard Person Type Mouth and Ears Agreement Pre-conditions Steps Mouth and Ears Guard HQ System Biz nature of service – more work NCOIC -- Individual Guard System Guard Person Type Radio Call-in Service Fire & blanket Binocul ars Guard HQ System
Individual Guard System Guard Person Type Mouth and Ears Agreement Pre-conditions Steps Mouth and Ears Guard HQ System Biz nature of service – more work NCOIC -- Individual Guard System Guard Person Type Radio Call-in Service Fire & blanket Binocul ars Guard HQ System
 NCOIC Anti-Piracy • Human parts – Do. DAF not Human Factors and Mo. DAF does • Competency and roles. Willingness and trust. • IDEAS – disposition and manifestation
NCOIC Anti-Piracy • Human parts – Do. DAF not Human Factors and Mo. DAF does • Competency and roles. Willingness and trust. • IDEAS – disposition and manifestation
 Ken’s Input to CP • • After SOA-RM was deep into the final approval process, it became obvious that one really needed to differentiate between the idea of “business service” and the “SOA service” that is all the rage as an IT artifact. It was too late to add it to the RM but there was a discussion thread on the OASIS email list on this distinction. I tend to emphasize it because I find it avoids conflating different definitions and keeps any discussion on track. I think the Service. Point entered because a big part of WSDL is where is the endpoint. In reality, the Service. Point/endpoint is one piece of description about a (SOA) service. I agree that some, and probably most, of the Service Provider should be outside the Service box. The TOG-SO definition of service seems to be more on the business side, being a “logical representation” rather than an access mechanism. However, the idea of a “specified outcome” aligns with the SOA-RM concept of real world effect. Chris captures this point in the text following the Soa. ML Service. Point definition box. Chris notes the “unorthodox” sense in which SOA-RM defines service. This was done on purpose per the caveat in the section 1. 4: Note that while the concepts and relationships described in this reference model may apply to other "service" environments, the definitions and descriptions contained herein focus on the field of software architecture and make no attempt to completely account for use outside of the software domain. Examples included in this document that are taken from other domains are used strictly for illustrative purposes. Preparing to contract – execution context Trust model – trust, risk, real-world effects In Chris’ final point about the taxi service, an imperfect analogy (refer again to the caveat about examples) is the taxi service is an example of a capability that provides the business function of hired transportation, i. e. its business service. The business service/capability can likely be accessed through several mechanisms: phone, maybe fax, possibly a Web form, or the traditional waving at a taxi driving by. These access mechanisms are akin to the SOA service. Note the power of this. I have a capability but I may get greater value from it by changing the mechanism through which it can be accessed. Maybe it will provide access through a Web service so a travel agent can automatically make a taxi reservation. However, while the access mechanisms can change, there still needs to be a well-defined business function that needs to be satisfied and a well-defined implementation that can provide that function and realize its real world effects. Without that, SOA or any other kind of access has nothing to access. This leads to the common problem of trying to identify SOA services before your identify your business and how you expect to do it.
Ken’s Input to CP • • After SOA-RM was deep into the final approval process, it became obvious that one really needed to differentiate between the idea of “business service” and the “SOA service” that is all the rage as an IT artifact. It was too late to add it to the RM but there was a discussion thread on the OASIS email list on this distinction. I tend to emphasize it because I find it avoids conflating different definitions and keeps any discussion on track. I think the Service. Point entered because a big part of WSDL is where is the endpoint. In reality, the Service. Point/endpoint is one piece of description about a (SOA) service. I agree that some, and probably most, of the Service Provider should be outside the Service box. The TOG-SO definition of service seems to be more on the business side, being a “logical representation” rather than an access mechanism. However, the idea of a “specified outcome” aligns with the SOA-RM concept of real world effect. Chris captures this point in the text following the Soa. ML Service. Point definition box. Chris notes the “unorthodox” sense in which SOA-RM defines service. This was done on purpose per the caveat in the section 1. 4: Note that while the concepts and relationships described in this reference model may apply to other "service" environments, the definitions and descriptions contained herein focus on the field of software architecture and make no attempt to completely account for use outside of the software domain. Examples included in this document that are taken from other domains are used strictly for illustrative purposes. Preparing to contract – execution context Trust model – trust, risk, real-world effects In Chris’ final point about the taxi service, an imperfect analogy (refer again to the caveat about examples) is the taxi service is an example of a capability that provides the business function of hired transportation, i. e. its business service. The business service/capability can likely be accessed through several mechanisms: phone, maybe fax, possibly a Web form, or the traditional waving at a taxi driving by. These access mechanisms are akin to the SOA service. Note the power of this. I have a capability but I may get greater value from it by changing the mechanism through which it can be accessed. Maybe it will provide access through a Web service so a travel agent can automatically make a taxi reservation. However, while the access mechanisms can change, there still needs to be a well-defined business function that needs to be satisfied and a well-defined implementation that can provide that function and realize its real world effects. Without that, SOA or any other kind of access has nothing to access. This leads to the common problem of trying to identify SOA services before your identify your business and how you expect to do it.
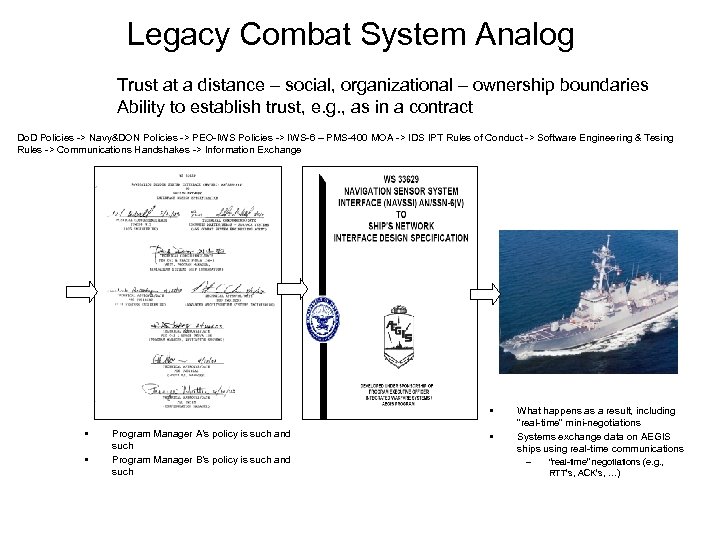 Legacy Combat System Analog Trust at a distance – social, organizational – ownership boundaries Ability to establish trust, e. g. , as in a contract Do. D Policies -> Navy&DON Policies -> PEO-IWS Policies -> IWS-6 – PMS-400 MOA -> IDS IPT Rules of Conduct -> Software Engineering & Tesing Rules -> Communications Handshakes -> Information Exchange • • • Program Manager A’s policy is such and such Program Manager B’s policy is such and such • What happens as a result, including “real-time” mini-negotiations Systems exchange data on AEGIS ships using real-time communications – “real-time” negotiations (e. g. , RTT’s, ACK’s, …)
Legacy Combat System Analog Trust at a distance – social, organizational – ownership boundaries Ability to establish trust, e. g. , as in a contract Do. D Policies -> Navy&DON Policies -> PEO-IWS Policies -> IWS-6 – PMS-400 MOA -> IDS IPT Rules of Conduct -> Software Engineering & Tesing Rules -> Communications Handshakes -> Information Exchange • • • Program Manager A’s policy is such and such Program Manager B’s policy is such and such • What happens as a result, including “real-time” mini-negotiations Systems exchange data on AEGIS ships using real-time communications – “real-time” negotiations (e. g. , RTT’s, ACK’s, …)
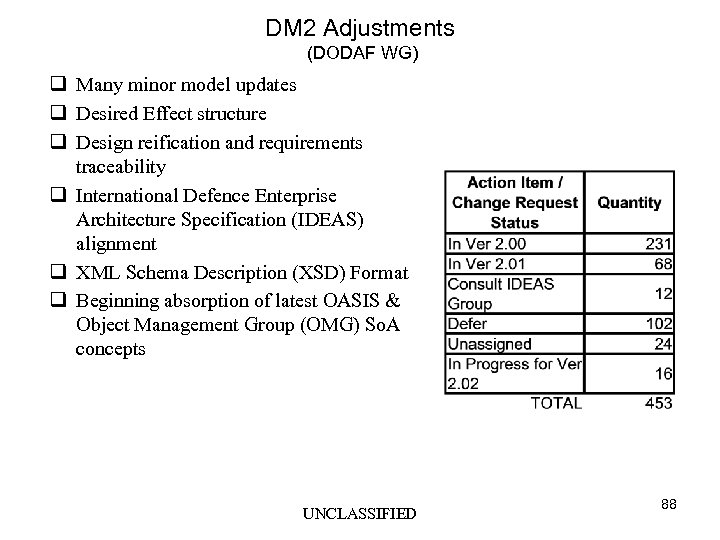 DM 2 Adjustments (DODAF WG) q Many minor model updates q Desired Effect structure q Design reification and requirements traceability q International Defence Enterprise Architecture Specification (IDEAS) alignment q XML Schema Description (XSD) Format q Beginning absorption of latest OASIS & Object Management Group (OMG) So. A concepts UNCLASSIFIED 88
DM 2 Adjustments (DODAF WG) q Many minor model updates q Desired Effect structure q Design reification and requirements traceability q International Defence Enterprise Architecture Specification (IDEAS) alignment q XML Schema Description (XSD) Format q Beginning absorption of latest OASIS & Object Management Group (OMG) So. A concepts UNCLASSIFIED 88
 DODAF CM Plan (DODAF WG) • Annex A: Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) Working Group (WG) • Annex B: Do. DAF Working Group (WG) UNCLASSIFIED 89
DODAF CM Plan (DODAF WG) • Annex A: Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) Working Group (WG) • Annex B: Do. DAF Working Group (WG) UNCLASSIFIED 89
 Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Plan • • Adopts terminology and process from EIA Standard 649, “National Consensus Standard for Configuration Management” Contents: – Configuration Identification – Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Interactions, e. g. , • Do. DAF / DM 2 Work Group – – The Do. DAF 2 Data TWG became the Do. DAF / DM 2 WG This group has been meeting every Friday since 2007 and has over 190 members and a very extensive collaboration and research site – Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Processes and Procedures, e. g. , • • Tracking of Change Requests Monthly submission to FAC of Configuration Status Accounting Report (CSAR) – Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Business Rules – Do. D EA COI, e. g. , • conduct of the Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group – Do. DAF / DM 2 Review of Federated Architectural Descriptions 90
Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Plan • • Adopts terminology and process from EIA Standard 649, “National Consensus Standard for Configuration Management” Contents: – Configuration Identification – Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Interactions, e. g. , • Do. DAF / DM 2 Work Group – – The Do. DAF 2 Data TWG became the Do. DAF / DM 2 WG This group has been meeting every Friday since 2007 and has over 190 members and a very extensive collaboration and research site – Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Processes and Procedures, e. g. , • • Tracking of Change Requests Monthly submission to FAC of Configuration Status Accounting Report (CSAR) – Do. DAF / DM 2 CM Business Rules – Do. D EA COI, e. g. , • conduct of the Do. D EA COI Data Management Working Group – Do. DAF / DM 2 Review of Federated Architectural Descriptions 90
 Unassigned (New) AI’s • • • • • • • • # 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 500 501 503 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 Title Dispositional vs Categorical Properties So. AML Concepts OASIS SOA RAF Concepts Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs System vs Service Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports Geostatoinary Point Type Region of World Type Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type ARO as two couples Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer Information Traceability to Data APBP redundancy with APUC Singleton Types Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer TV and Std. V Location. Type Measures Type… Forking under Conditions How to indicate methodology-dependent subclasses Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS How to categorize Arch Desc make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD Partridge Services Questions & Comments M 3 / LOK Questions and Comments Performer Flows and Tools Service Access to Resource or Performer Powertype Definition
Unassigned (New) AI’s • • • • • • • • # 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 500 501 503 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 Title Dispositional vs Categorical Properties So. AML Concepts OASIS SOA RAF Concepts Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs System vs Service Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports Geostatoinary Point Type Region of World Type Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type ARO as two couples Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer Information Traceability to Data APBP redundancy with APUC Singleton Types Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer TV and Std. V Location. Type Measures Type… Forking under Conditions How to indicate methodology-dependent subclasses Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS How to categorize Arch Desc make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD Partridge Services Questions & Comments M 3 / LOK Questions and Comments Performer Flows and Tools Service Access to Resource or Performer Powertype Definition
 2 Apr 2010 DM 2 WG Agenda 1. News: – – – FAC Do. DAF (inc. DM 2) CM Plan review JAIWG Federated Data Exchange Pilots Progress • • – – JCSFL in DM 2 DB and DM 2 PES XML – J 89 & APL, JACAE DM 2 JMTs in DM 2 DB, Services focus – J 89 in EA UPDM XMI DM 2 PES DM 2 SQL Server DB. OV-2 & SV-1 performer resource flows ARO M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS (LOK Questions) MODAF Services Analysis 2. New References: • • • References and ResearchState MachinesIDEAS-UPDM Email 2010 -03. eml References and ResearchServicesMODAF AnalysesDM 2 Benchmark. xls, Services - again. doc DM 2 WG Organizational and Meetings InformationQuestions and Issues summary. docx, DM 2_categorisation_rules. docx, ASRG_CONOPS__1 -04 -10__V_1 0 (2). pdf 3. Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) 4. Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 5. Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • – 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary AI 507 -509 – Greg and Dave to prep for Tuesday’s JAIWG
2 Apr 2010 DM 2 WG Agenda 1. News: – – – FAC Do. DAF (inc. DM 2) CM Plan review JAIWG Federated Data Exchange Pilots Progress • • – – JCSFL in DM 2 DB and DM 2 PES XML – J 89 & APL, JACAE DM 2 JMTs in DM 2 DB, Services focus – J 89 in EA UPDM XMI DM 2 PES DM 2 SQL Server DB. OV-2 & SV-1 performer resource flows ARO M 3 Incorporation of IDEAS (LOK Questions) MODAF Services Analysis 2. New References: • • • References and ResearchState MachinesIDEAS-UPDM Email 2010 -03. eml References and ResearchServicesMODAF AnalysesDM 2 Benchmark. xls, Services - again. doc DM 2 WG Organizational and Meetings InformationQuestions and Issues summary. docx, DM 2_categorisation_rules. docx, ASRG_CONOPS__1 -04 -10__V_1 0 (2). pdf 3. Review new Action Items (“unassigned”) 4. Prioritization of 2. 02 AI’s – in reverse order! 5. Others: – In queue but probably won’t have time to get to tomorrow: • – 20 So. AML terms to compare to DM 2 data dictionary AI 507 -509 – Greg and Dave to prep for Tuesday’s JAIWG
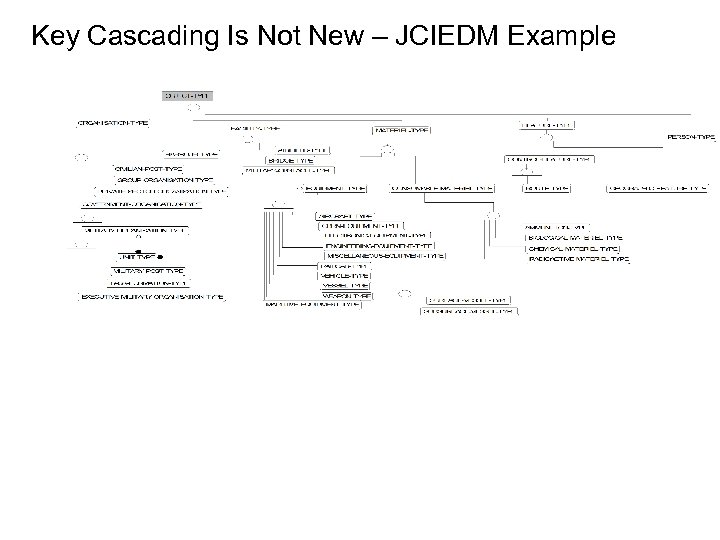 Key Cascading Is Not New – JCIEDM Example
Key Cascading Is Not New – JCIEDM Example
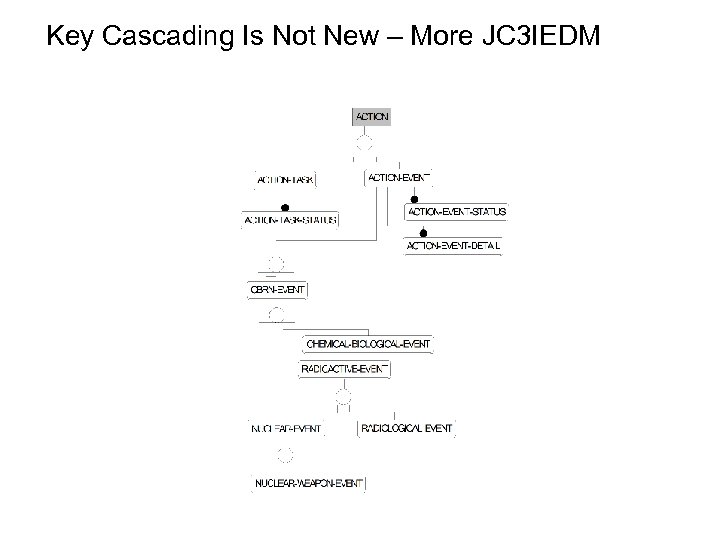 Key Cascading Is Not New – More JC 3 IEDM
Key Cascading Is Not New – More JC 3 IEDM
 DM 2 Superclass Association Rough Rules (LOK) • • • • • • • Rule: Elements categorized as "if" or "df" cannot be used in any view directly. The above elements are therefore excluded from direct use. Rule: Elements categorized as "ifo" or "dfo" can however be used directly within views: Rule: All elements that descend from Type can have subtypes of the same kind as the original element itself ( uper. Subtype principle). (It should s be noted that Individual. Type descends from Type, i. e. this principle also applies to all that descend from Individual. Type. ) Rule: All elements that descend from Individual. Type can have whole-parts of the same kind as the original element itself ( hole. Part. Type W principle). Rule: All elements that descend from Individual can have whole-parts of the same kind as the original element itself (whole. Part principle). Rule: All elements that descend from Type can have instances of themselves created based on instantiation provided that these instances have already bee recognised as distinct elements within DM 2. (This is a form of deviation from the general principle and would imply that there could never be an instance of Capability in a DM 2 compliant model unless an Individual. Capability element turned up in the DM 2 model. It could be argued that this principle would automatically be applicable if type. Instance was placed in the "if" category. This may have unfortunate consequences for PES however. ) Rule: A Name element can be attached to anything by means of named. By (named. By principle). Rule: An Information element can be attached to anything by means of described. By (described. By principle). Rule: A representation element can be attached to anything by means of epresented. By (represented. By principle). r Rule: A before. After relationship can be created between any elements that descend from Individual (before. After principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: A Before. After. Type relationship can be created between any element that descend from Individual. Type (Before. After. Type principle) ) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: An overlap n-ary relationship can be established between elements that descend from Individual (overlap principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: An Overlap. Type n-ary relationship can be established between any items that descend from Type (Overlap. Type principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. )
DM 2 Superclass Association Rough Rules (LOK) • • • • • • • Rule: Elements categorized as "if" or "df" cannot be used in any view directly. The above elements are therefore excluded from direct use. Rule: Elements categorized as "ifo" or "dfo" can however be used directly within views: Rule: All elements that descend from Type can have subtypes of the same kind as the original element itself ( uper. Subtype principle). (It should s be noted that Individual. Type descends from Type, i. e. this principle also applies to all that descend from Individual. Type. ) Rule: All elements that descend from Individual. Type can have whole-parts of the same kind as the original element itself ( hole. Part. Type W principle). Rule: All elements that descend from Individual can have whole-parts of the same kind as the original element itself (whole. Part principle). Rule: All elements that descend from Type can have instances of themselves created based on instantiation provided that these instances have already bee recognised as distinct elements within DM 2. (This is a form of deviation from the general principle and would imply that there could never be an instance of Capability in a DM 2 compliant model unless an Individual. Capability element turned up in the DM 2 model. It could be argued that this principle would automatically be applicable if type. Instance was placed in the "if" category. This may have unfortunate consequences for PES however. ) Rule: A Name element can be attached to anything by means of named. By (named. By principle). Rule: An Information element can be attached to anything by means of described. By (described. By principle). Rule: A representation element can be attached to anything by means of epresented. By (represented. By principle). r Rule: A before. After relationship can be created between any elements that descend from Individual (before. After principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: A Before. After. Type relationship can be created between any element that descend from Individual. Type (Before. After. Type principle) ) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: An overlap n-ary relationship can be established between elements that descend from Individual (overlap principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. ) Rule: An Overlap. Type n-ary relationship can be established between any items that descend from Type (Overlap. Type principle) that are of the same kind. (The same kind restriction does not follow explicitly but represents an imposed constraint. )
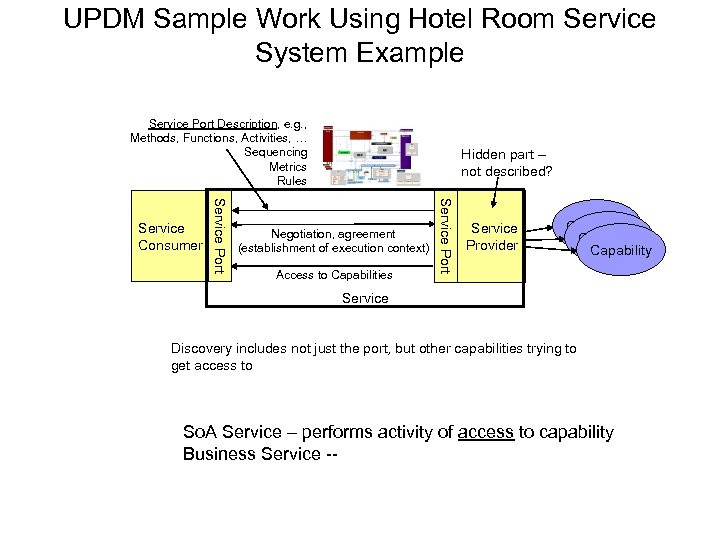 UPDM Sample Work Using Hotel Room Service System Example Service Port Description, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, … Sequencing Metrics Rules Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) Access to Capabilities Service Port Service Consumer Hidden part – not described? Service Provider Capability Service Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to So. A Service – performs activity of access to capability Business Service --
UPDM Sample Work Using Hotel Room Service System Example Service Port Description, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, … Sequencing Metrics Rules Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) Access to Capabilities Service Port Service Consumer Hidden part – not described? Service Provider Capability Service Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to So. A Service – performs activity of access to capability Business Service --
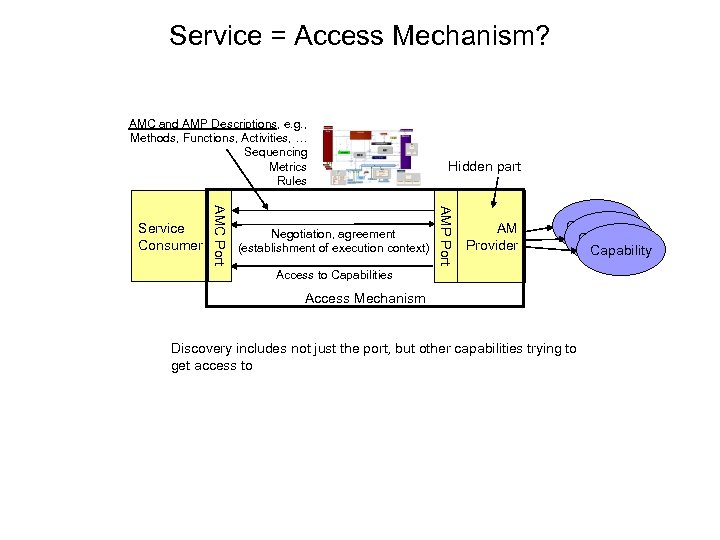 Service = Access Mechanism? AMC and AMP Descriptions, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, … Sequencing Metrics Rules Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) AMP Port AMC Port Service Consumer Hidden part AM Provider Capability Access to Capabilities Access Mechanism Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to
Service = Access Mechanism? AMC and AMP Descriptions, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, … Sequencing Metrics Rules Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) AMP Port AMC Port Service Consumer Hidden part AM Provider Capability Access to Capabilities Access Mechanism Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to
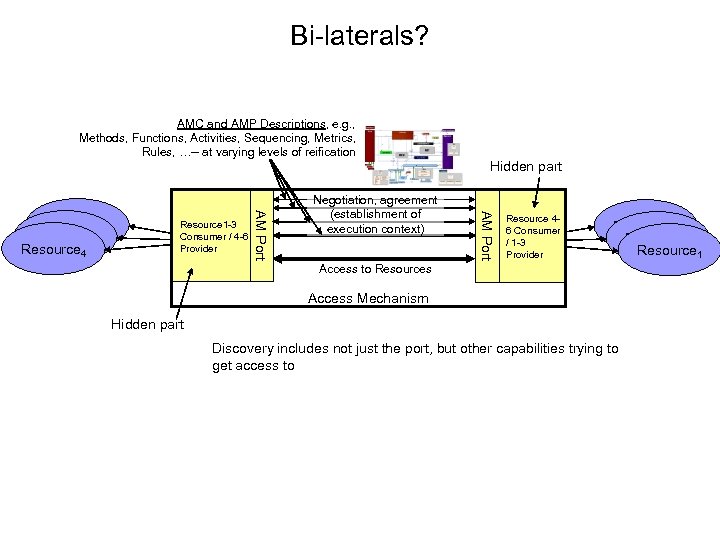 Bi-laterals? AMC and AMP Descriptions, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, Sequencing, Metrics, Rules, …-- at varying levels of reification AM Port Resource 1 -3 Consumer / 4 -6 Provider AM Port Resource 6 Resource 5 Resource 4 Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) Hidden part Resource 46 Consumer / 1 -3 Provider Resource 3 Resource 2 Resource 1 Access to Resources Access Mechanism Hidden part Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to
Bi-laterals? AMC and AMP Descriptions, e. g. , Methods, Functions, Activities, Sequencing, Metrics, Rules, …-- at varying levels of reification AM Port Resource 1 -3 Consumer / 4 -6 Provider AM Port Resource 6 Resource 5 Resource 4 Negotiation, agreement (establishment of execution context) Hidden part Resource 46 Consumer / 1 -3 Provider Resource 3 Resource 2 Resource 1 Access to Resources Access Mechanism Hidden part Discovery includes not just the port, but other capabilities trying to get access to
 New AIs • • • • • • • # 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 500 501 503 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 Title Dispositional vs Categorical Properties So. AML Concepts OASIS SOA RAF Concepts Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs System vs Service Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports Geostatoinary Point Type Region of World Type Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type ARO as two couples Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer Information Traceability to Data APBP redundancy with APUC Singleton Types Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer TV and Std. V Location. Type Measures Type… Forking under Conditions How to indicate methodology-dependent subclasses Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS How to categorize Arch Desc make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD
New AIs • • • • • • • # 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 500 501 503 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 Title Dispositional vs Categorical Properties So. AML Concepts OASIS SOA RAF Concepts Necessary and optional foundation elements in XML docs System vs Service Mandatory Service Descriptions and Ports Geostatoinary Point Type Region of World Type Project and Project Type have a TI and a PTI Desired. Effect. Whole. Resource. Part. Type ARO as two couples Agreement constrains activity. Performed. By. Performer Information Traceability to Data APBP redundancy with APUC Singleton Types Capability Phase <> Enterprise Phase Org/Org. Type WP(T) Performer TV and Std. V Location. Type Measures Type… Forking under Conditions How to indicate methodology-dependent subclasses Coordinate AV-1 Defs with DARS How to categorize Arch Desc make the full inheritance taxonomy machine-accessible somehow, like in the XSD


