02_Intercultural Management Implementation.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 19
 2. INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION
2. INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION
 MANAGEMENT FOCUS Skills and knowledge: Entrepreneur's knowledge Company’s Knowledge Environment Internal environment External environment
MANAGEMENT FOCUS Skills and knowledge: Entrepreneur's knowledge Company’s Knowledge Environment Internal environment External environment
 Differences goes from… • • Economical factors Political factors Legal factors (property defense) Social factors Infrastructure Labor market and quality of education Transparency
Differences goes from… • • Economical factors Political factors Legal factors (property defense) Social factors Infrastructure Labor market and quality of education Transparency
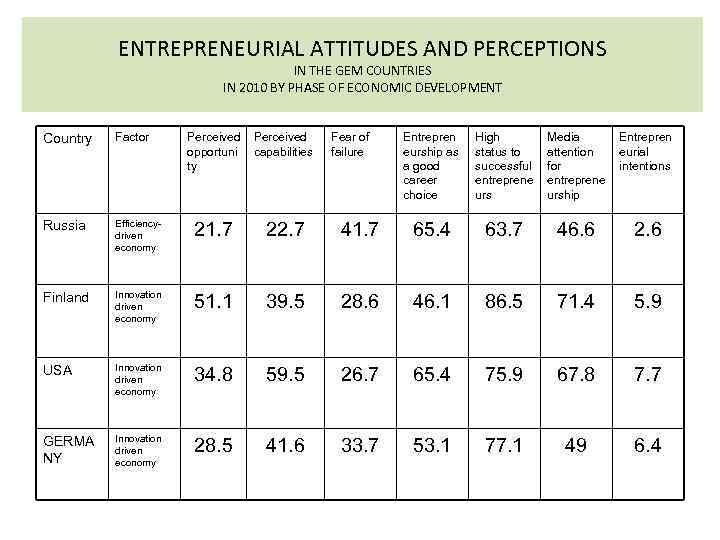 ENTREPRENEURIAL ATTITUDES AND PERCEPTIONS IN THE GEM COUNTRIES IN 2010 BY PHASE OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Country Factor Perceived opportuni capabilities ty Russia Efficiencydriven economy 21. 7 22. 7 Finland Innovation driven economy 51. 1 USA Innovation driven economy GERMA NY Innovation driven economy Fear of failure Entrepren eurship as a good career choice High status to successful entreprene urs Media attention for entreprene urship Entrepren eurial intentions 41. 7 65. 4 63. 7 46. 6 2. 6 39. 5 28. 6 46. 1 86. 5 71. 4 5. 9 34. 8 59. 5 26. 7 65. 4 75. 9 67. 8 7. 7 28. 5 41. 6 33. 7 53. 1 77. 1 49 6. 4
ENTREPRENEURIAL ATTITUDES AND PERCEPTIONS IN THE GEM COUNTRIES IN 2010 BY PHASE OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Country Factor Perceived opportuni capabilities ty Russia Efficiencydriven economy 21. 7 22. 7 Finland Innovation driven economy 51. 1 USA Innovation driven economy GERMA NY Innovation driven economy Fear of failure Entrepren eurship as a good career choice High status to successful entreprene urs Media attention for entreprene urship Entrepren eurial intentions 41. 7 65. 4 63. 7 46. 6 2. 6 39. 5 28. 6 46. 1 86. 5 71. 4 5. 9 34. 8 59. 5 26. 7 65. 4 75. 9 67. 8 7. 7 28. 5 41. 6 33. 7 53. 1 77. 1 49 6. 4
 INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT Business culture Organizational culture Management culture
INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT Business culture Organizational culture Management culture
 MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION: Intercultural teamwork Motivation Leadership Decision making Conflicts resolution Knowledge Transfer
MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION: Intercultural teamwork Motivation Leadership Decision making Conflicts resolution Knowledge Transfer
 INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION: • • • Intercultural teamwork Motivation Leadership Decision making Conflicts resolution Knowledge Transfer
INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION: • • • Intercultural teamwork Motivation Leadership Decision making Conflicts resolution Knowledge Transfer
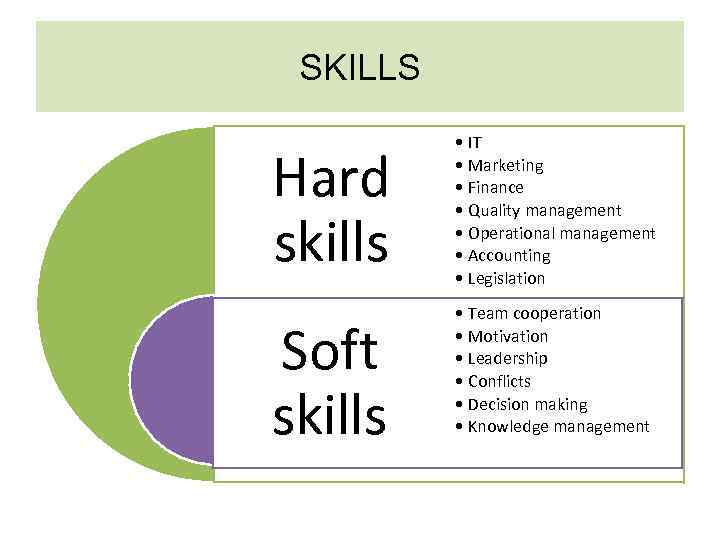 SKILLS Hard skills Soft skills • IT • Marketing • Finance • Quality management • Operational management • Accounting • Legislation • Team cooperation • Motivation • Leadership • Conflicts • Decision making • Knowledge management
SKILLS Hard skills Soft skills • IT • Marketing • Finance • Quality management • Operational management • Accounting • Legislation • Team cooperation • Motivation • Leadership • Conflicts • Decision making • Knowledge management
 POLICIES: • • Safety Policy Human Resources policy Trade Unions’ (Corporate) Social Responsibility Ecology Responsibility Property defense Ethics Intellectual property
POLICIES: • • Safety Policy Human Resources policy Trade Unions’ (Corporate) Social Responsibility Ecology Responsibility Property defense Ethics Intellectual property
 THE MOST POPULAR EMPLOYERS IN RUSSIA* • Gazprom – 33% • Rosneft – 23% • Sberbank – 19% http: //wciom. ru/
THE MOST POPULAR EMPLOYERS IN RUSSIA* • Gazprom – 33% • Rosneft – 23% • Sberbank – 19% http: //wciom. ru/
 TEAMWORK CHALLENGIES • Direct versus indirect communication • Trouble with accents and fluency • Differing attitudes toward hierarchy and authority • Conflicting norms for decision making
TEAMWORK CHALLENGIES • Direct versus indirect communication • Trouble with accents and fluency • Differing attitudes toward hierarchy and authority • Conflicting norms for decision making
 FOUR STRATEGIES • ADAPTATION (acknowledge in cultural gaps openly and working around them) • STRUCTURAL INTERVENTION (changing the shape of the team) • MANAGERIAL INTERVENTION (setting norms early or bringing in a higher-level manager) • EXIT (removing a team member when other options have failed)
FOUR STRATEGIES • ADAPTATION (acknowledge in cultural gaps openly and working around them) • STRUCTURAL INTERVENTION (changing the shape of the team) • MANAGERIAL INTERVENTION (setting norms early or bringing in a higher-level manager) • EXIT (removing a team member when other options have failed)
 СASE Tension in the team was growing. Things were going well at the company. Its management was examining the possibilities of new development aims and had invited in a group of consultants, who recommended introducing a new system of motivation into the organisation. One of the elements of this system was making annual bonuses dependent on the ratio between income and administrative expenses within each department. “Why do we have to bear this cross? ” asked Ksenia, after a moment’s silence. “We all work, like idiots, and he doesn’t even realise that we earn him his bread and butter. Then he even has the cheek to shout at us and boss us around!” Everyone sat there looking dejected; it was obvious that this was not the first time this had happened. They were talking about Nikolai, the deputy manager of the department, who was the relative of one of a high-ranking bureaucrat in the industry. His presence in the organisation was taboo, but he cost the company a considerable amount in expenses. Besides his salary, Nikolai had a company car with a driver, and both entertainment expenses and travel expenses. “What travel and entertainment expenses? ” the employees would whisper. “He’s not even capable of making a single deal!” The main task was trying to make sure he didn’t stop them from working properly. Those endless empty speeches and meaningless babblings took up a lot of valuable working time. And now innovations were being introduced in the form of bonuses that depended on administrative expenses. The department manager entered the room, and Vyacheslav, the quietist and calmest of all the employees, who had brought the company 12 percent of all its new clients the year before, said, “Alexei Semyonovich, our patience has run out: It’s either us or him!” What would you advise the department head to do in this situation?
СASE Tension in the team was growing. Things were going well at the company. Its management was examining the possibilities of new development aims and had invited in a group of consultants, who recommended introducing a new system of motivation into the organisation. One of the elements of this system was making annual bonuses dependent on the ratio between income and administrative expenses within each department. “Why do we have to bear this cross? ” asked Ksenia, after a moment’s silence. “We all work, like idiots, and he doesn’t even realise that we earn him his bread and butter. Then he even has the cheek to shout at us and boss us around!” Everyone sat there looking dejected; it was obvious that this was not the first time this had happened. They were talking about Nikolai, the deputy manager of the department, who was the relative of one of a high-ranking bureaucrat in the industry. His presence in the organisation was taboo, but he cost the company a considerable amount in expenses. Besides his salary, Nikolai had a company car with a driver, and both entertainment expenses and travel expenses. “What travel and entertainment expenses? ” the employees would whisper. “He’s not even capable of making a single deal!” The main task was trying to make sure he didn’t stop them from working properly. Those endless empty speeches and meaningless babblings took up a lot of valuable working time. And now innovations were being introduced in the form of bonuses that depended on administrative expenses. The department manager entered the room, and Vyacheslav, the quietist and calmest of all the employees, who had brought the company 12 percent of all its new clients the year before, said, “Alexei Semyonovich, our patience has run out: It’s either us or him!” What would you advise the department head to do in this situation?
 LEADERSHIP The ability to influence, motivate, and enable others to contribute to the effectiveness and success of the organizations of which they are members The process of influencing individuals or groups to accomplish an organizational goal or mission
LEADERSHIP The ability to influence, motivate, and enable others to contribute to the effectiveness and success of the organizations of which they are members The process of influencing individuals or groups to accomplish an organizational goal or mission
 OBJECTIVES OF A LEADER: • To gain the commitment and cooperation of his team. • To get the group into action to achieve agreed objectives. • To make the best use of the skills, energies and talents of team.
OBJECTIVES OF A LEADER: • To gain the commitment and cooperation of his team. • To get the group into action to achieve agreed objectives. • To make the best use of the skills, energies and talents of team.
 THE NEEDS WHICH THE LEADER IS THERE TO SATISFY: Task need Group need Individual need
THE NEEDS WHICH THE LEADER IS THERE TO SATISFY: Task need Group need Individual need
 CASE Irina had always been an optimist. She was born and grew up in a small town in the Arkhangelsk region, but dreamed of moving to a big city like St. Petersburg. She gained a place at St. Petersburg University, completed her degree, got a good job, got married and had two daughters. However, tragedy struck on a family holiday. Following a car accident, Irina became paralysed. Her chances of recovering her mobility were slim. But Irina was determined, and worked on regaining her strength. She was an active person before the accident, and staying at home all day while her husband was at work and daughters at school was very hard for her to get used to. Irina had a successful career in the field of client service, and decided to return to work. The first unpleasant moment was when her company failed to support her, saying that there were no vacancies at that time. Irina began to look for a new job. She found that when she sent out her CV and included information about her disability, she received no phone calls. But when she did not mention it on her CV, she was immediately invited to attend an interview, since her experience and references were impressive. Once she saw a TV advert for a company that marketed itself as a socially responsible firm that worked with many different clients, including those with physical disabilities. Irina wanted to work for this company. She quickly searched for vacancies on the company’s website, and was delighted when she saw a vacancy that corresponded to her skills. She sent off her CV and was invited to go to the company’s office for an interview. However, upon arriving in a wheelchair, she realised that the company’s advertising slogans did not correspond to reality. In front of her were five steps, and there were no special rails to help her ascend them. It turned out that the steps were symbolic of the company’s attitude to people with physical disabilities. When the line manager saw her, he looked uncomfortable, and tactlessly said that no one had warned him that a disabled person was coming. Within a week, the company had rejected Irina’s application. After consulting a lawyer, Irina decided to take the company to court… How important do you consider a company’s social policy principles to be?
CASE Irina had always been an optimist. She was born and grew up in a small town in the Arkhangelsk region, but dreamed of moving to a big city like St. Petersburg. She gained a place at St. Petersburg University, completed her degree, got a good job, got married and had two daughters. However, tragedy struck on a family holiday. Following a car accident, Irina became paralysed. Her chances of recovering her mobility were slim. But Irina was determined, and worked on regaining her strength. She was an active person before the accident, and staying at home all day while her husband was at work and daughters at school was very hard for her to get used to. Irina had a successful career in the field of client service, and decided to return to work. The first unpleasant moment was when her company failed to support her, saying that there were no vacancies at that time. Irina began to look for a new job. She found that when she sent out her CV and included information about her disability, she received no phone calls. But when she did not mention it on her CV, she was immediately invited to attend an interview, since her experience and references were impressive. Once she saw a TV advert for a company that marketed itself as a socially responsible firm that worked with many different clients, including those with physical disabilities. Irina wanted to work for this company. She quickly searched for vacancies on the company’s website, and was delighted when she saw a vacancy that corresponded to her skills. She sent off her CV and was invited to go to the company’s office for an interview. However, upon arriving in a wheelchair, she realised that the company’s advertising slogans did not correspond to reality. In front of her were five steps, and there were no special rails to help her ascend them. It turned out that the steps were symbolic of the company’s attitude to people with physical disabilities. When the line manager saw her, he looked uncomfortable, and tactlessly said that no one had warned him that a disabled person was coming. Within a week, the company had rejected Irina’s application. After consulting a lawyer, Irina decided to take the company to court… How important do you consider a company’s social policy principles to be?
 CULTURAL VARIABLES AFFECTING DECISION MAKING • OBJECTIVE (basing decisions on rationality) versus SUBJECTIVE (basing decisions on emotions) approach • RISK TOLERANCE • LOCUS OF CONTROL – INTERNAL (managers in control of events), or EXTERNAL (managers have little control over events) © 2006 Prentice Hall
CULTURAL VARIABLES AFFECTING DECISION MAKING • OBJECTIVE (basing decisions on rationality) versus SUBJECTIVE (basing decisions on emotions) approach • RISK TOLERANCE • LOCUS OF CONTROL – INTERNAL (managers in control of events), or EXTERNAL (managers have little control over events) © 2006 Prentice Hall
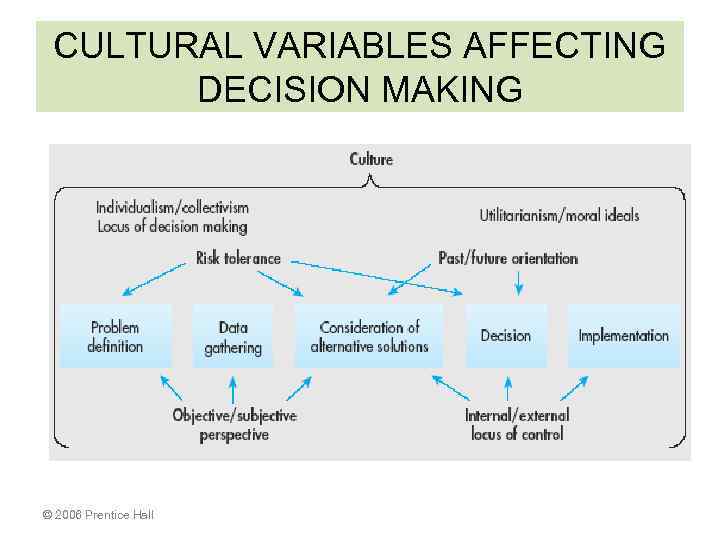 CULTURAL VARIABLES AFFECTING DECISION MAKING © 2006 Prentice Hall
CULTURAL VARIABLES AFFECTING DECISION MAKING © 2006 Prentice Hall


