cc05d443e4db85c74e5311bf0d488c22.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 2 II 60 Technology of Information Systems Course 2008 Architecture of Information Systems Group Department of Computer Science K. M. van Hee Technology of information systems
2 II 60 Technology of Information Systems Course 2008 Architecture of Information Systems Group Department of Computer Science K. M. van Hee Technology of information systems
 Goals of the course • Learn how modern information systems are built out of components. • Learn what type of components there are. • Learn what techniques there are to select, configure and integrate these components. • Build up some experience with these techniques • Learn how industrial / commercial components work Technology of information systems
Goals of the course • Learn how modern information systems are built out of components. • Learn what type of components there are. • Learn what techniques there are to select, configure and integrate these components. • Build up some experience with these techniques • Learn how industrial / commercial components work Technology of information systems
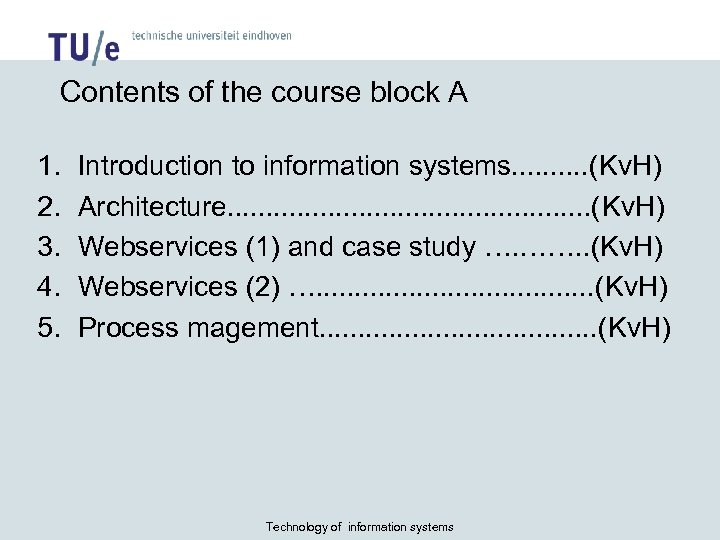 Contents of the course block A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction to information systems. . (Kv. H) Architecture. . . (Kv. H) Webservices (1) and case study …. ……. . (Kv. H) Webservices (2) …. . . . . (Kv. H) Process magement. . . . . (Kv. H) Technology of information systems
Contents of the course block A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction to information systems. . (Kv. H) Architecture. . . (Kv. H) Webservices (1) and case study …. ……. . (Kv. H) Webservices (2) …. . . . . (Kv. H) Process magement. . . . . (Kv. H) Technology of information systems
 Contents of the course block B 6. Business Process Execution Language…. (EV) 7. IBM Websphere. . . (F. Nieuwerth) 8. Cordys. . . . (Gerwin Ligtenberg) 9. MS Biz. Talk. . . . . (Lex Oskam) 10. ERP-packages. . . . (A. Klappe, Deloitte) Technology of information systems
Contents of the course block B 6. Business Process Execution Language…. (EV) 7. IBM Websphere. . . (F. Nieuwerth) 8. Cordys. . . . (Gerwin Ligtenberg) 9. MS Biz. Talk. . . . . (Lex Oskam) 10. ERP-packages. . . . (A. Klappe, Deloitte) Technology of information systems
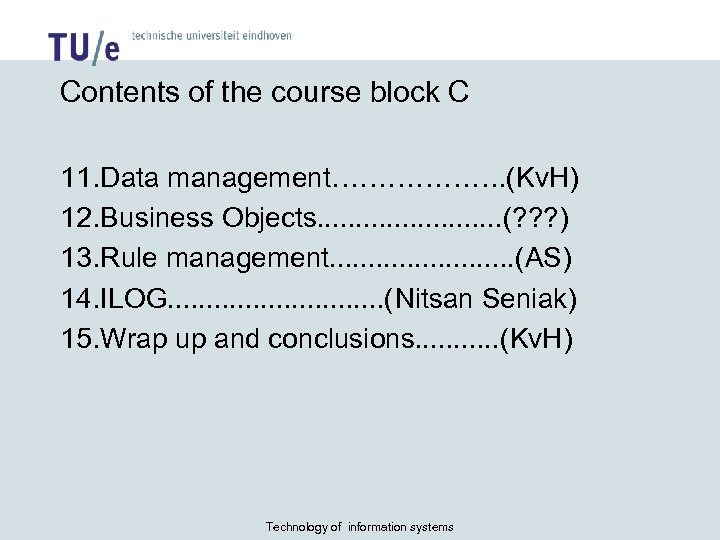 Contents of the course block C 11. Data management………………. (Kv. H) 12. Business Objects. . . (? ? ? ) 13. Rule management. . . (AS) 14. ILOG. . . . (Nitsan Seniak) 15. Wrap up and conclusions. . . (Kv. H) Technology of information systems
Contents of the course block C 11. Data management………………. (Kv. H) 12. Business Objects. . . (? ? ? ) 13. Rule management. . . (AS) 14. ILOG. . . . (Nitsan Seniak) 15. Wrap up and conclusions. . . (Kv. H) Technology of information systems
 Examination • Students do a multiple choice test that covers the concepts treated in the course. • Students (in groups) do a project in which they build an information system with components. They produce a concise report and they give a demonstration. Technology of information systems
Examination • Students do a multiple choice test that covers the concepts treated in the course. • Students (in groups) do a project in which they build an information system with components. They produce a concise report and they give a demonstration. Technology of information systems
 Lecture 1 Component-based Information Systems Technology of information systems
Lecture 1 Component-based Information Systems Technology of information systems
 Contents • • Enterprises Functions of information systems The component-based world Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems Technology of information systems
Contents • • Enterprises Functions of information systems The component-based world Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems Technology of information systems
 Enterprises (1) An enterprise is a system or organization that is producing (physical) products or services for clients by executing business process and using resources. Technology of information systems
Enterprises (1) An enterprise is a system or organization that is producing (physical) products or services for clients by executing business process and using resources. Technology of information systems
 Enterprises (2) • Typical types of resources are: – – – – Buildings Money Energy Equipment (vehicles, machines) People Knowledge (e. g. recipes, market information) Information systems Supplies (e. g. raw materials or components) • Resources are durable or consumable (classify them yourself) Technology of information systems
Enterprises (2) • Typical types of resources are: – – – – Buildings Money Energy Equipment (vehicles, machines) People Knowledge (e. g. recipes, market information) Information systems Supplies (e. g. raw materials or components) • Resources are durable or consumable (classify them yourself) Technology of information systems
 Enterprises (3) Classification of business processes • The business processes (BP) are essential: they are needed to make the products or services. We distinguish three types of BP’s: • Primary BP’s: they produce the products and services using the resources: they are directly related to the production orders. • Secondary BP’s: they enable the primary BP’s by providing and maintaining the resources and by controlling relationships with customers and suppliers. • Tertiary BP’s: they take care of the control of the enterprise as a whole and of the coordination of the primary and secondary BP’s Technology of information systems
Enterprises (3) Classification of business processes • The business processes (BP) are essential: they are needed to make the products or services. We distinguish three types of BP’s: • Primary BP’s: they produce the products and services using the resources: they are directly related to the production orders. • Secondary BP’s: they enable the primary BP’s by providing and maintaining the resources and by controlling relationships with customers and suppliers. • Tertiary BP’s: they take care of the control of the enterprise as a whole and of the coordination of the primary and secondary BP’s Technology of information systems
 Enterprises (4) • An enterprise obtains (buys, rents) the resources from suppliers. Suppliers are enterprises themselves. • The stakeholders of an enterprise are people or organizations that have some interest (stake) in the enterprise. • Main stakeholders are: – – – Shareholders who own the enterprise Employees who work as human resources for the enterprise Clients who buy products or services Suppliers who sell raw materials or components Government (departments for tax, environment, economical affairs etc) Technology of information systems
Enterprises (4) • An enterprise obtains (buys, rents) the resources from suppliers. Suppliers are enterprises themselves. • The stakeholders of an enterprise are people or organizations that have some interest (stake) in the enterprise. • Main stakeholders are: – – – Shareholders who own the enterprise Employees who work as human resources for the enterprise Clients who buy products or services Suppliers who sell raw materials or components Government (departments for tax, environment, economical affairs etc) Technology of information systems
 Functions of information systems(1) Information Systems (IS) support an enterprise by • Monitoring of business processes: • Planning of business processes: – Decisions are made about resource assignment and scheduling of activities • Execution of business processes: – Is in fact a business transaction • Support of employees: – With cooperation – With knowledge sharing Technology of information systems
Functions of information systems(1) Information Systems (IS) support an enterprise by • Monitoring of business processes: • Planning of business processes: – Decisions are made about resource assignment and scheduling of activities • Execution of business processes: – Is in fact a business transaction • Support of employees: – With cooperation – With knowledge sharing Technology of information systems
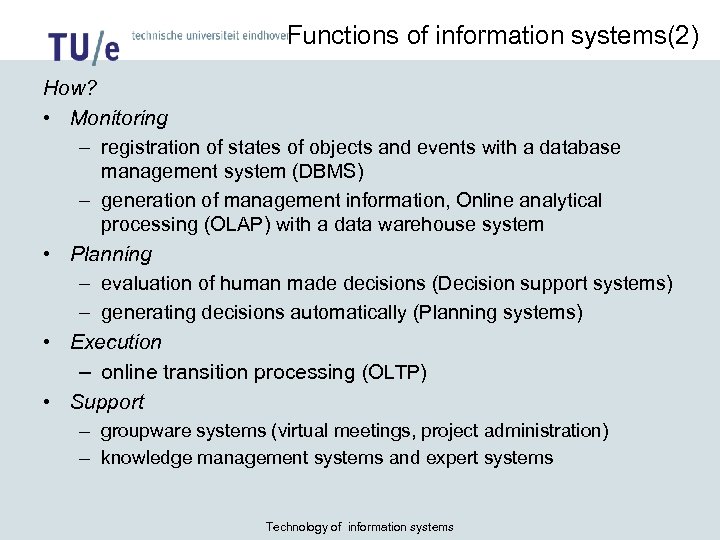 Functions of information systems(2) How? • Monitoring – registration of states of objects and events with a database management system (DBMS) – generation of management information, Online analytical processing (OLAP) with a data warehouse system • Planning – evaluation of human made decisions (Decision support systems) – generating decisions automatically (Planning systems) • Execution – online transition processing (OLTP) • Support – groupware systems (virtual meetings, project administration) – knowledge management systems and expert systems Technology of information systems
Functions of information systems(2) How? • Monitoring – registration of states of objects and events with a database management system (DBMS) – generation of management information, Online analytical processing (OLAP) with a data warehouse system • Planning – evaluation of human made decisions (Decision support systems) – generating decisions automatically (Planning systems) • Execution – online transition processing (OLTP) • Support – groupware systems (virtual meetings, project administration) – knowledge management systems and expert systems Technology of information systems
 IS vs ES • IS support business processes inside an enterprise. • They are also called: Enterprise Information Systems • Between two or more enterprises (also called: e-Business Systems or Interorganizational Information Systems) • Embedded systems (ES) support a physical device • ES have more simple data structures • ES have stronger time and resource constraints despite the differences, most methods apply to both type of systems Technology of information systems
IS vs ES • IS support business processes inside an enterprise. • They are also called: Enterprise Information Systems • Between two or more enterprises (also called: e-Business Systems or Interorganizational Information Systems) • Embedded systems (ES) support a physical device • ES have more simple data structures • ES have stronger time and resource constraints despite the differences, most methods apply to both type of systems Technology of information systems
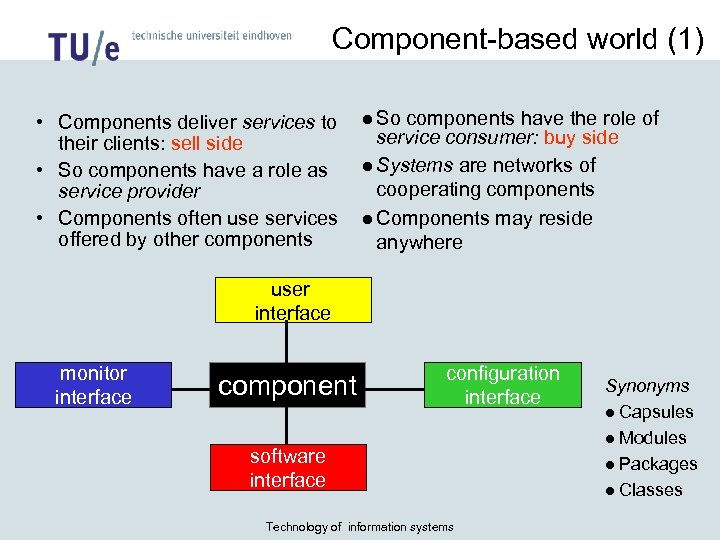 Component-based world (1) • Components deliver services to their clients: sell side • So components have a role as service provider • Components often use services offered by other components l So components have the role of service consumer: buy side l Systems are networks of cooperating components l Components may reside anywhere user interface monitor interface component configuration interface software interface Technology of information systems Synonyms l Capsules l Modules l Packages l Classes
Component-based world (1) • Components deliver services to their clients: sell side • So components have a role as service provider • Components often use services offered by other components l So components have the role of service consumer: buy side l Systems are networks of cooperating components l Components may reside anywhere user interface monitor interface component configuration interface software interface Technology of information systems Synonyms l Capsules l Modules l Packages l Classes
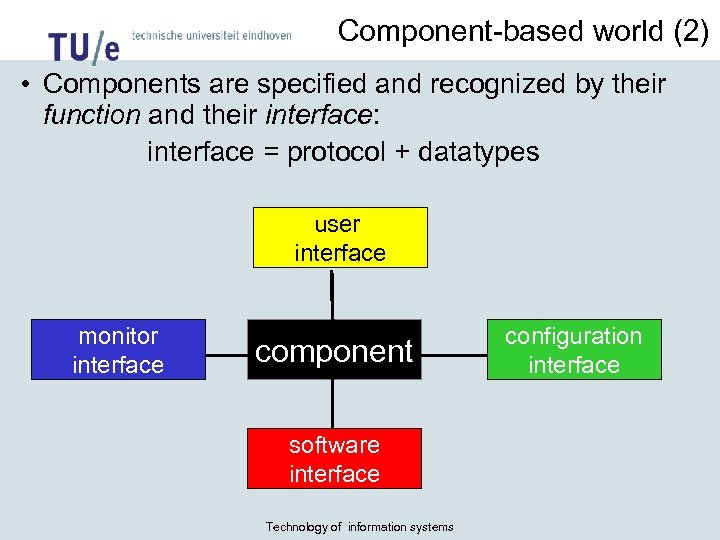 Component-based world (2) • Components are specified and recognized by their function and their interface: interface = protocol + datatypes user interface monitor interface component software interface Technology of information systems configuration interface
Component-based world (2) • Components are specified and recognized by their function and their interface: interface = protocol + datatypes user interface monitor interface component software interface Technology of information systems configuration interface
 Component based world (3) Commercial Of The Shelf (COTS) components Numetrix e. g. : a telco operator is built of about 20 COTS components Technology of information systems
Component based world (3) Commercial Of The Shelf (COTS) components Numetrix e. g. : a telco operator is built of about 20 COTS components Technology of information systems
 Component-based world(4) • Distinguish two kinds of components: small and large ones • Small ones are found in public libraries, often freeware. They fulfill some specific, small task, like sorting a file. • Large components have a vendor and they support a complex business process, like bookkeeping • Webservices is focusing on small components • Software packages and ASP services can be considered as large components Technology of information systems
Component-based world(4) • Distinguish two kinds of components: small and large ones • Small ones are found in public libraries, often freeware. They fulfill some specific, small task, like sorting a file. • Large components have a vendor and they support a complex business process, like bookkeeping • Webservices is focusing on small components • Software packages and ASP services can be considered as large components Technology of information systems
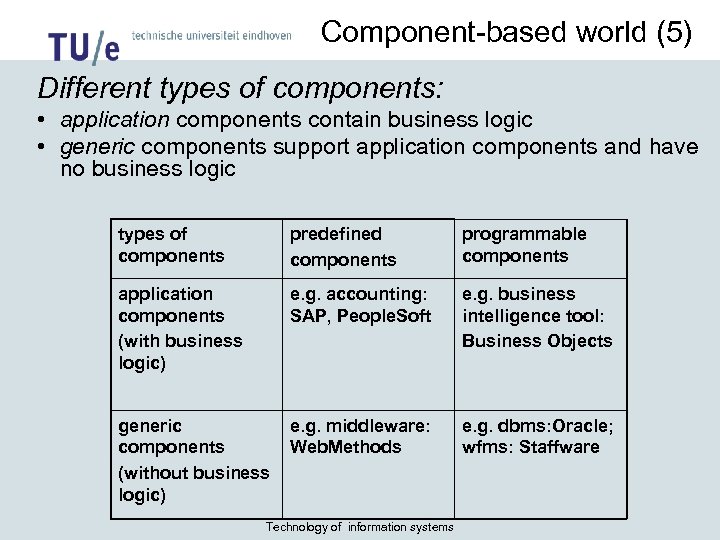 Component-based world (5) Different types of components: • application components contain business logic • generic components support application components and have no business logic types of components predefined components programmable components application components (with business logic) e. g. accounting: SAP, People. Soft e. g. business intelligence tool: Business Objects generic components (without business logic) e. g. middleware: Web. Methods e. g. dbms: Oracle; wfms: Staffware Technology of information systems
Component-based world (5) Different types of components: • application components contain business logic • generic components support application components and have no business logic types of components predefined components programmable components application components (with business logic) e. g. accounting: SAP, People. Soft e. g. business intelligence tool: Business Objects generic components (without business logic) e. g. middleware: Web. Methods e. g. dbms: Oracle; wfms: Staffware Technology of information systems
 Component-based world (6) Parameters of predefined components: • parameters are options, selected from a list or input as simple data (often a tree of option lists) • limited flexibility, but easy to use • little ICT knowledge but much application knowledge required Technology of information systems
Component-based world (6) Parameters of predefined components: • parameters are options, selected from a list or input as simple data (often a tree of option lists) • limited flexibility, but easy to use • little ICT knowledge but much application knowledge required Technology of information systems
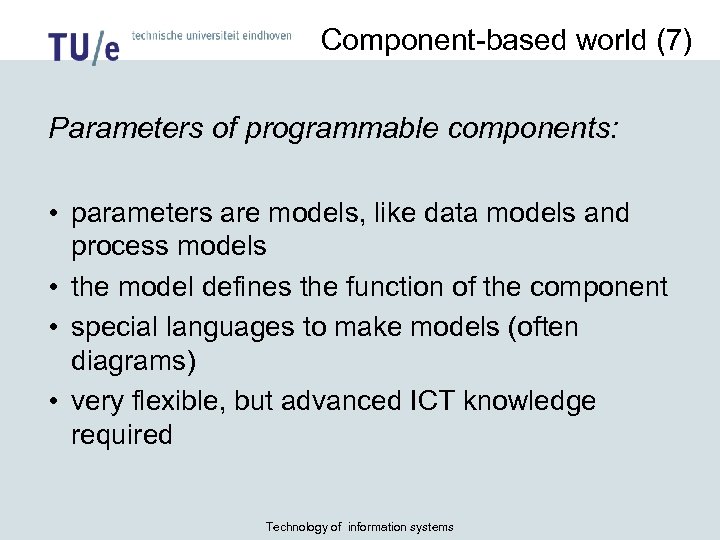 Component-based world (7) Parameters of programmable components: • parameters are models, like data models and process models • the model defines the function of the component • special languages to make models (often diagrams) • very flexible, but advanced ICT knowledge required Technology of information systems
Component-based world (7) Parameters of programmable components: • parameters are models, like data models and process models • the model defines the function of the component • special languages to make models (often diagrams) • very flexible, but advanced ICT knowledge required Technology of information systems
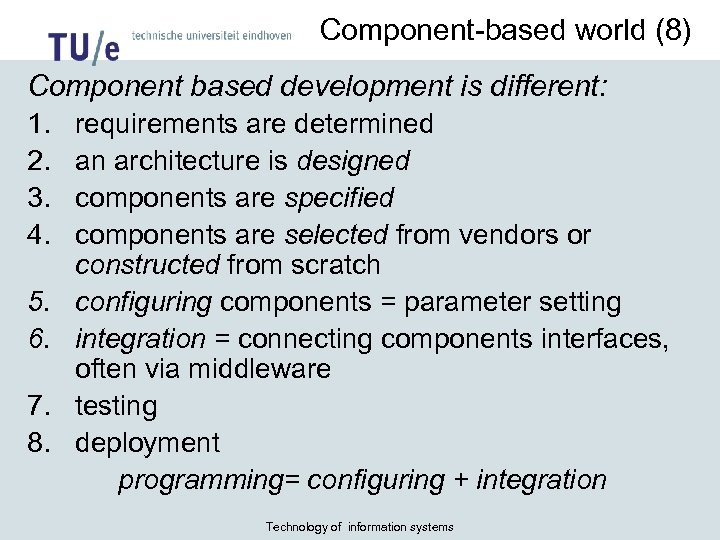 Component-based world (8) Component based development is different: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. requirements are determined an architecture is designed components are specified components are selected from vendors or constructed from scratch configuring components = parameter setting integration = connecting components interfaces, often via middleware testing deployment programming= configuring + integration Technology of information systems
Component-based world (8) Component based development is different: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. requirements are determined an architecture is designed components are specified components are selected from vendors or constructed from scratch configuring components = parameter setting integration = connecting components interfaces, often via middleware testing deployment programming= configuring + integration Technology of information systems
 Component-based world (9) • Component-based systems will behave in an ‘organic way’: – periodically components will be replaced by better ones – new functionality will be realised by new components • Vendors will compete with the best functionality of their individual components Technology of information systems
Component-based world (9) • Component-based systems will behave in an ‘organic way’: – periodically components will be replaced by better ones – new functionality will be realised by new components • Vendors will compete with the best functionality of their individual components Technology of information systems
 Component-based world (10) • Prepacked solutions will be offered by third parties: – combinations of components with parameters that can be used as a new predefined component – prepacked solutions can be made by ‘third parties’ • ‘Prepackers’ will compete with vendors of packages • Components may be outsourced to an ASP: Software As A Service (SAAS) Technology of information systems
Component-based world (10) • Prepacked solutions will be offered by third parties: – combinations of components with parameters that can be used as a new predefined component – prepacked solutions can be made by ‘third parties’ • ‘Prepackers’ will compete with vendors of packages • Components may be outsourced to an ASP: Software As A Service (SAAS) Technology of information systems
 Component-based world (11) Features of IS to be componentized – Data management – User interaction – Business process (workflow) – Business logic – Coordination (orchestration, choreography) – Security control – …. ? ? ? Technology of information systems
Component-based world (11) Features of IS to be componentized – Data management – User interaction – Business process (workflow) – Business logic – Coordination (orchestration, choreography) – Security control – …. ? ? ? Technology of information systems
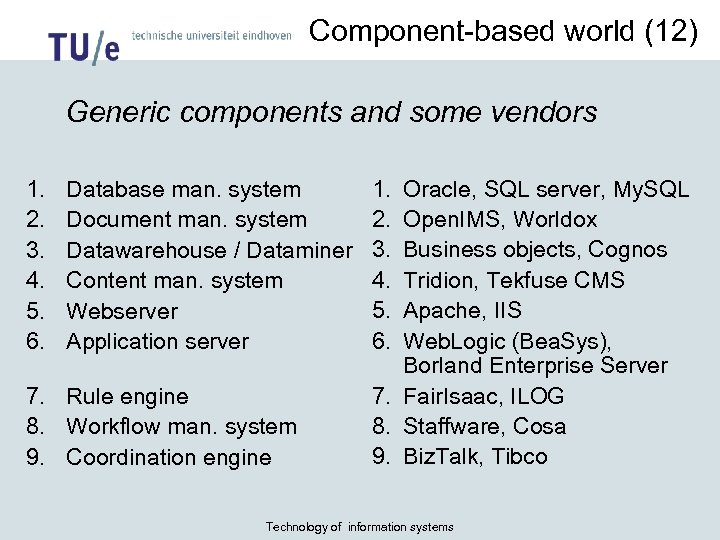 Component-based world (12) Generic components and some vendors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Database man. system Document man. system Datawarehouse / Dataminer Content man. system Webserver Application server 7. Rule engine 8. Workflow man. system 9. Coordination engine 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Oracle, SQL server, My. SQL Open. IMS, Worldox Business objects, Cognos Tridion, Tekfuse CMS Apache, IIS Web. Logic (Bea. Sys), Borland Enterprise Server 7. Fair. Isaac, ILOG 8. Staffware, Cosa 9. Biz. Talk, Tibco Technology of information systems
Component-based world (12) Generic components and some vendors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Database man. system Document man. system Datawarehouse / Dataminer Content man. system Webserver Application server 7. Rule engine 8. Workflow man. system 9. Coordination engine 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Oracle, SQL server, My. SQL Open. IMS, Worldox Business objects, Cognos Tridion, Tekfuse CMS Apache, IIS Web. Logic (Bea. Sys), Borland Enterprise Server 7. Fair. Isaac, ILOG 8. Staffware, Cosa 9. Biz. Talk, Tibco Technology of information systems
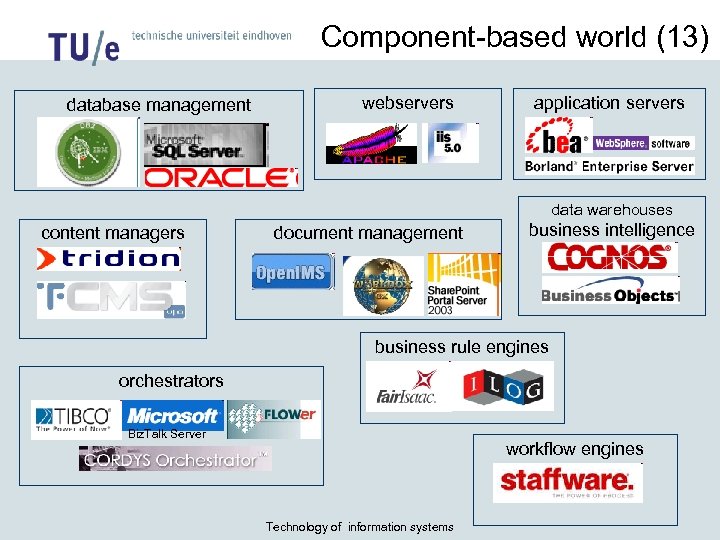 Component-based world (13) database management webservers application servers data warehouses content managers document management business intelligence business rule engines orchestrators Biz. Talk Server workflow engines Technology of information systems
Component-based world (13) database management webservers application servers data warehouses content managers document management business intelligence business rule engines orchestrators Biz. Talk Server workflow engines Technology of information systems
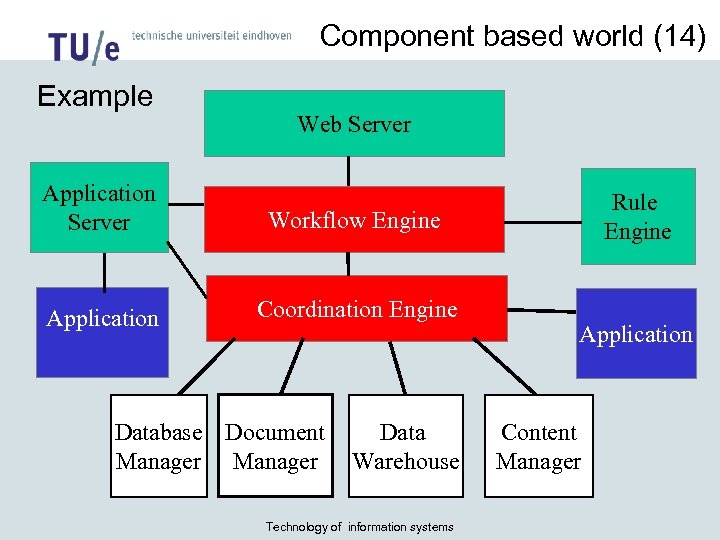 Component based world (14) Example Web Server Application Server Workflow Engine Application Coordination Engine Database Document Manager Data Warehouse Technology of information systems Rule Engine Application Content Manager
Component based world (14) Example Web Server Application Server Workflow Engine Application Coordination Engine Database Document Manager Data Warehouse Technology of information systems Rule Engine Application Content Manager
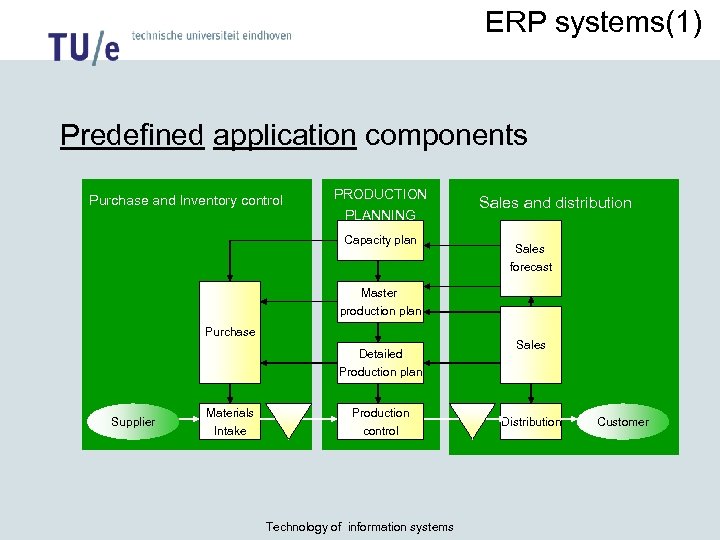 ERP systems(1) Predefined application components Purchase and Inventory control PRODUCTION PLANNING Capacity plan Sales and distribution Sales forecast Master production plan Purchase Detailed Production plan Supplier Materials Intake Production control Technology of information systems Sales Distribution Customer
ERP systems(1) Predefined application components Purchase and Inventory control PRODUCTION PLANNING Capacity plan Sales and distribution Sales forecast Master production plan Purchase Detailed Production plan Supplier Materials Intake Production control Technology of information systems Sales Distribution Customer
 ERP systems(2) ERP functions • • • Purchase and supplier management Sales and distribution planning (invoicing, transport planning) Inventory control Quality control Production planning (material planning, capacity planning) Means of production planning (equipment, maintenance) Human resource planning (payroll, timesheets, personnel and organization chart) Financial management (general ledger, debtors, creditors, asset management, treasury management) Supporting functions: – Workflow management – Data warehousing • Industry specific functions (telco, health care etc) Technology of information systems
ERP systems(2) ERP functions • • • Purchase and supplier management Sales and distribution planning (invoicing, transport planning) Inventory control Quality control Production planning (material planning, capacity planning) Means of production planning (equipment, maintenance) Human resource planning (payroll, timesheets, personnel and organization chart) Financial management (general ledger, debtors, creditors, asset management, treasury management) Supporting functions: – Workflow management – Data warehousing • Industry specific functions (telco, health care etc) Technology of information systems
 ERP systems(3) Evolution of functions It started with the financial administration Then inventory control appeared Three phases: 1. Islands of automation 2. Internally integrated 3. Externally integrated: • Supply chain management • E-Procurement • Customer relationship management • E-commerce/ E-business Technology of information systems
ERP systems(3) Evolution of functions It started with the financial administration Then inventory control appeared Three phases: 1. Islands of automation 2. Internally integrated 3. Externally integrated: • Supply chain management • E-Procurement • Customer relationship management • E-commerce/ E-business Technology of information systems
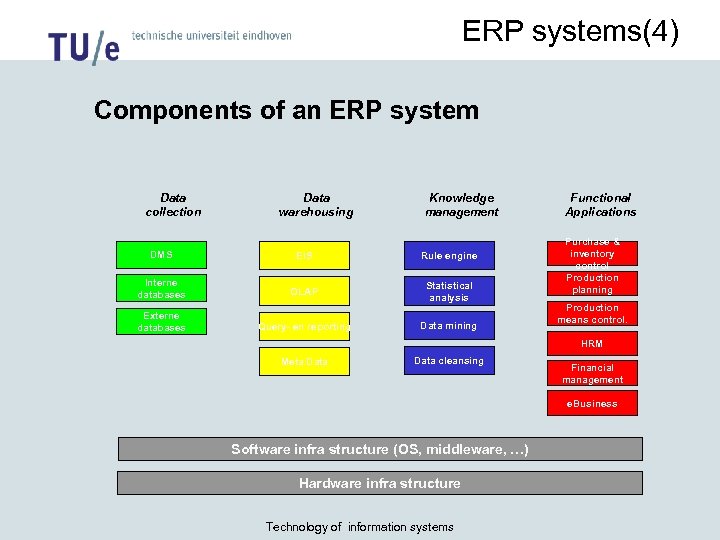 ERP systems(4) Components of an ERP system Data collection Data warehousing Knowledge management DMS EIS Rule engine Interne databases OLAP Statistical analysis Externe databases Query- en reporting Data mining Functional Applications Purchase & inventory control Production planning Production means control. HRM Meta Data cleansing Financial management e. Business Software infra structure (OS, middleware, …) Hardware infra structure Technology of information systems
ERP systems(4) Components of an ERP system Data collection Data warehousing Knowledge management DMS EIS Rule engine Interne databases OLAP Statistical analysis Externe databases Query- en reporting Data mining Functional Applications Purchase & inventory control Production planning Production means control. HRM Meta Data cleansing Financial management e. Business Software infra structure (OS, middleware, …) Hardware infra structure Technology of information systems
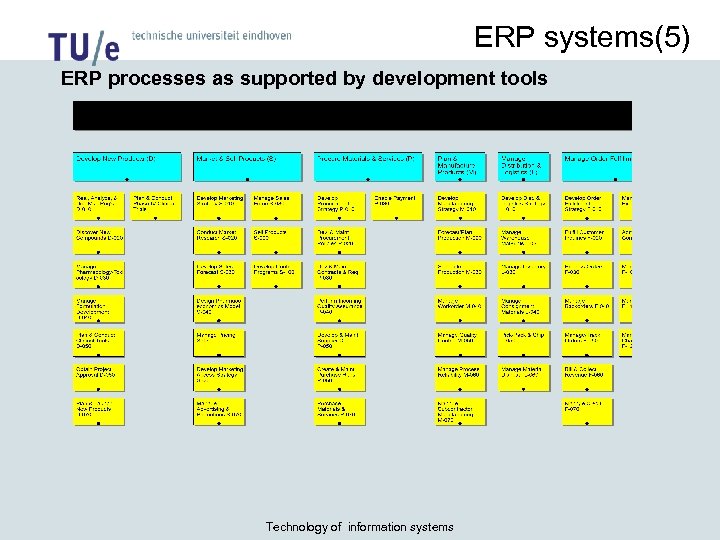 ERP systems(5) ERP processes as supported by development tools Technology of information systems
ERP systems(5) ERP processes as supported by development tools Technology of information systems
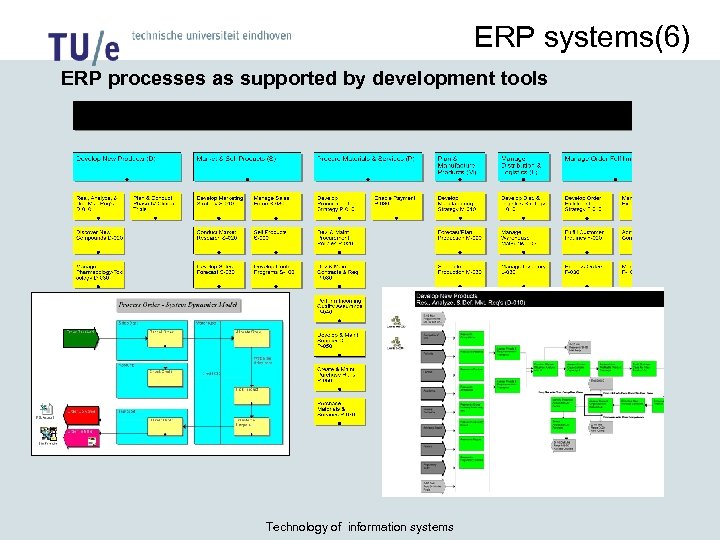 ERP systems(6) ERP processes as supported by development tools Technology of information systems
ERP systems(6) ERP processes as supported by development tools Technology of information systems


