b353da0a91f3a85fbbe189cf497f6c68.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 2 D & 3 D VIDEO PROCESSING FOR IMMERSIVE APPLICATIONS Emerging Convergence of Video, Vision & Graphics Harpreet S. Sawhney Rakesh Kumar
2 D & 3 D VIDEO PROCESSING FOR IMMERSIVE APPLICATIONS Emerging Convergence of Video, Vision & Graphics Harpreet S. Sawhney Rakesh Kumar
 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Collaborative Work with: Hai Tao Yanlin Guo Steve Hsu Supun Samarasekera Keith Hanna Aydin Arpa Rick Wildes
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Collaborative Work with: Hai Tao Yanlin Guo Steve Hsu Supun Samarasekera Keith Hanna Aydin Arpa Rick Wildes
 TECHNICAL SUCCESS OF CONVERGENCE TECHNOLOGIES PC based near real-time mosaicing Image based modeling for Entertainment Automated Video Enhancement: VHS-to-DVD Real-time Video Insertion Iris recognition, active vision
TECHNICAL SUCCESS OF CONVERGENCE TECHNOLOGIES PC based near real-time mosaicing Image based modeling for Entertainment Automated Video Enhancement: VHS-to-DVD Real-time Video Insertion Iris recognition, active vision
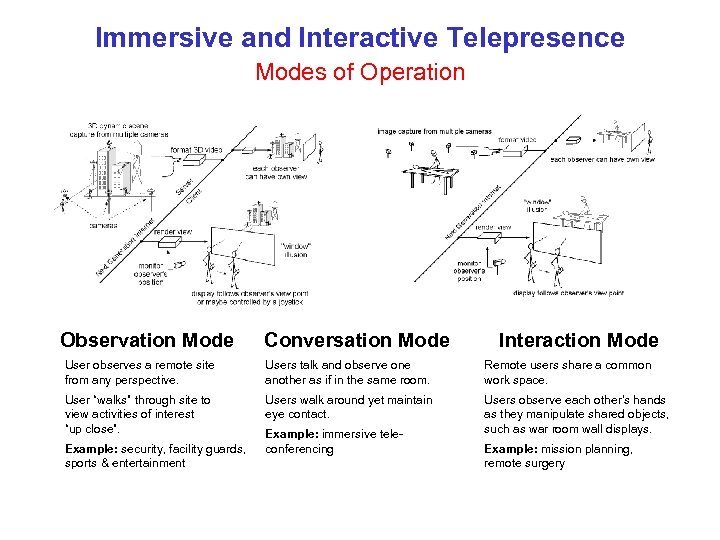 Immersive and Interactive Telepresence Modes of Operation Observation Mode Conversation Mode Interaction Mode User observes a remote site from any perspective. Users talk and observe one another as if in the same room. Remote users share a common work space. User “walks” through site to view activities of interest “up close”. Users walk around yet maintain eye contact. Users observe each other’s hands as they manipulate shared objects, such as war room wall displays. Example: security, facility guards, sports & entertainment Example: immersive teleconferencing Example: mission planning, remote surgery
Immersive and Interactive Telepresence Modes of Operation Observation Mode Conversation Mode Interaction Mode User observes a remote site from any perspective. Users talk and observe one another as if in the same room. Remote users share a common work space. User “walks” through site to view activities of interest “up close”. Users walk around yet maintain eye contact. Users observe each other’s hands as they manipulate shared objects, such as war room wall displays. Example: security, facility guards, sports & entertainment Example: immersive teleconferencing Example: mission planning, remote surgery
 Quality of Service for Tele-presence Critical Issues • High quality for immersive experience – – Artifact free recovery of 3 D shape from video streams Efficient 3 D video representation and compression High quality rendering of new views using 3 D shape and video streams Bandwidth available in the Next Generation Internet • Low latency for interactive applications – – Real time 3 D geometry recovery at the content server end Real time new view rendering at the browser client end Adaptive Stream management to handle user requests and network loads Error resilience and concealment to fill in missing packets
Quality of Service for Tele-presence Critical Issues • High quality for immersive experience – – Artifact free recovery of 3 D shape from video streams Efficient 3 D video representation and compression High quality rendering of new views using 3 D shape and video streams Bandwidth available in the Next Generation Internet • Low latency for interactive applications – – Real time 3 D geometry recovery at the content server end Real time new view rendering at the browser client end Adaptive Stream management to handle user requests and network loads Error resilience and concealment to fill in missing packets
 Convergence Technologies … for immersive & interactive visual applications. . . • Vision algorithms: High-quality 3 D shape recovery and dynamic scene analysis • ASICs, high performance hardware: Real-time video processing • Compact, low-cost cameras: CMOS cameras • Low latency and high quality compression: Error resilience • Real time view synthesis : Standard platforms, e. g. PCs • Immersive Displays
Convergence Technologies … for immersive & interactive visual applications. . . • Vision algorithms: High-quality 3 D shape recovery and dynamic scene analysis • ASICs, high performance hardware: Real-time video processing • Compact, low-cost cameras: CMOS cameras • Low latency and high quality compression: Error resilience • Real time view synthesis : Standard platforms, e. g. PCs • Immersive Displays
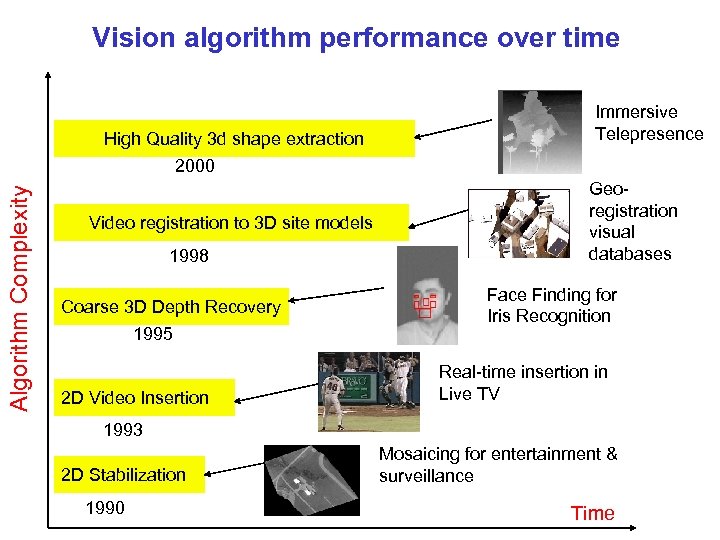 Vision algorithm performance over time High Quality 3 d shape extraction Immersive Telepresence Algorithm Complexity 2000 Video registration to 3 D site models 1998 Coarse 3 D Depth Recovery 1995 2 D Video Insertion Georegistration visual databases Face Finding for Iris Recognition Real-time insertion in Live TV 1993 2 D Stabilization 1990 Mosaicing for entertainment & surveillance Time
Vision algorithm performance over time High Quality 3 d shape extraction Immersive Telepresence Algorithm Complexity 2000 Video registration to 3 D site models 1998 Coarse 3 D Depth Recovery 1995 2 D Video Insertion Georegistration visual databases Face Finding for Iris Recognition Real-time insertion in Live TV 1993 2 D Stabilization 1990 Mosaicing for entertainment & surveillance Time
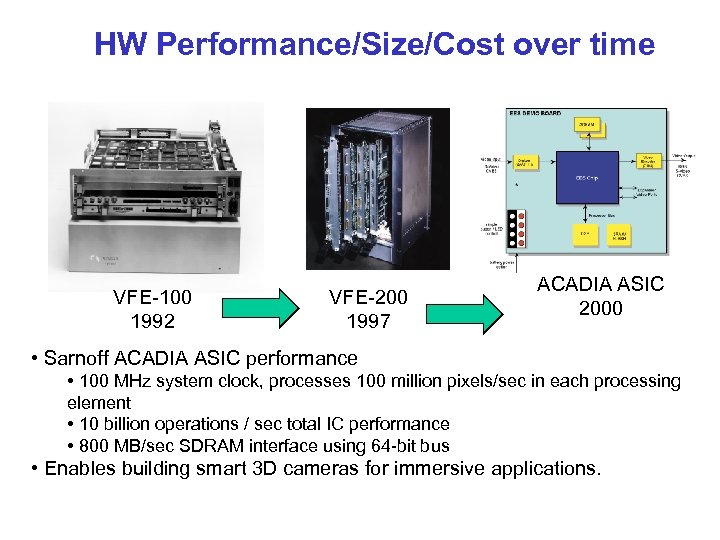 HW Performance/Size/Cost over time VFE-100 1992 VFE-200 1997 ACADIA ASIC 2000 • Sarnoff ACADIA ASIC performance • 100 MHz system clock, processes 100 million pixels/sec in each processing element • 10 billion operations / sec total IC performance • 800 MB/sec SDRAM interface using 64 -bit bus • Enables building smart 3 D cameras for immersive applications.
HW Performance/Size/Cost over time VFE-100 1992 VFE-200 1997 ACADIA ASIC 2000 • Sarnoff ACADIA ASIC performance • 100 MHz system clock, processes 100 million pixels/sec in each processing element • 10 billion operations / sec total IC performance • 800 MB/sec SDRAM interface using 64 -bit bus • Enables building smart 3 D cameras for immersive applications.
 Application Performance • Parametric Motion : Stabilization & Mosaicing – 720 x 240 fields @ 60 Hz OR 720 x 480 frames @ 30 Hz • Pyramid based Fusion : Dynamic Range, Focus Enhancement – 720 x 240 fields @ 60 Hz OR 720 x 480 frames @ 30 Hz • Stereo Depth Extraction – 720 x 240 field 32 disparity levels in 4 ms (250 Hz) – 720 x 240 field 60 disparity levels in 10 ms (100 Hz) – 60 disparities on 1 k x 1 k images at 55 ms (18 Hz)
Application Performance • Parametric Motion : Stabilization & Mosaicing – 720 x 240 fields @ 60 Hz OR 720 x 480 frames @ 30 Hz • Pyramid based Fusion : Dynamic Range, Focus Enhancement – 720 x 240 fields @ 60 Hz OR 720 x 480 frames @ 30 Hz • Stereo Depth Extraction – 720 x 240 field 32 disparity levels in 4 ms (250 Hz) – 720 x 240 field 60 disparity levels in 10 ms (100 Hz) – 60 disparities on 1 k x 1 k images at 55 ms (18 Hz)
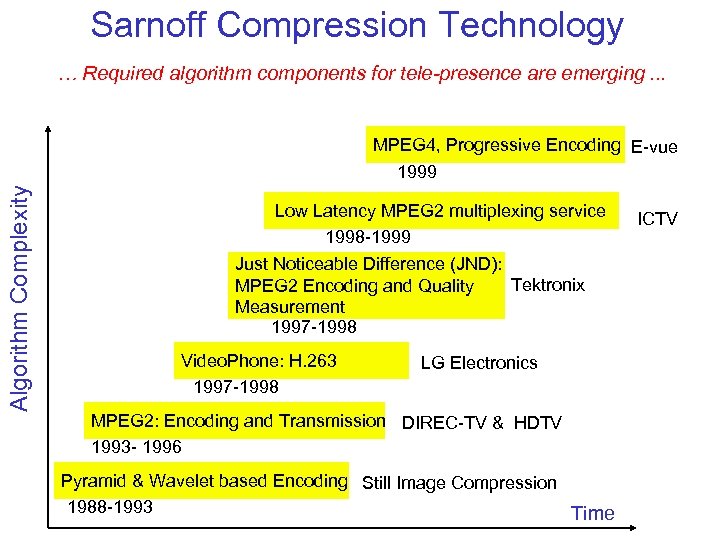 Sarnoff Compression Technology … Required algorithm components for tele-presence are emerging. . . Algorithm Complexity MPEG 4, Progressive Encoding E-vue 1999 Low Latency MPEG 2 multiplexing service 1998 -1999 Just Noticeable Difference (JND): Tektronix MPEG 2 Encoding and Quality Measurement 1997 -1998 Video. Phone: H. 263 1997 -1998 LG Electronics MPEG 2: Encoding and Transmission DIREC-TV & HDTV 1993 - 1996 Pyramid & Wavelet based Encoding Still Image Compression 1988 -1993 Time ICTV
Sarnoff Compression Technology … Required algorithm components for tele-presence are emerging. . . Algorithm Complexity MPEG 4, Progressive Encoding E-vue 1999 Low Latency MPEG 2 multiplexing service 1998 -1999 Just Noticeable Difference (JND): Tektronix MPEG 2 Encoding and Quality Measurement 1997 -1998 Video. Phone: H. 263 1997 -1998 LG Electronics MPEG 2: Encoding and Transmission DIREC-TV & HDTV 1993 - 1996 Pyramid & Wavelet based Encoding Still Image Compression 1988 -1993 Time ICTV
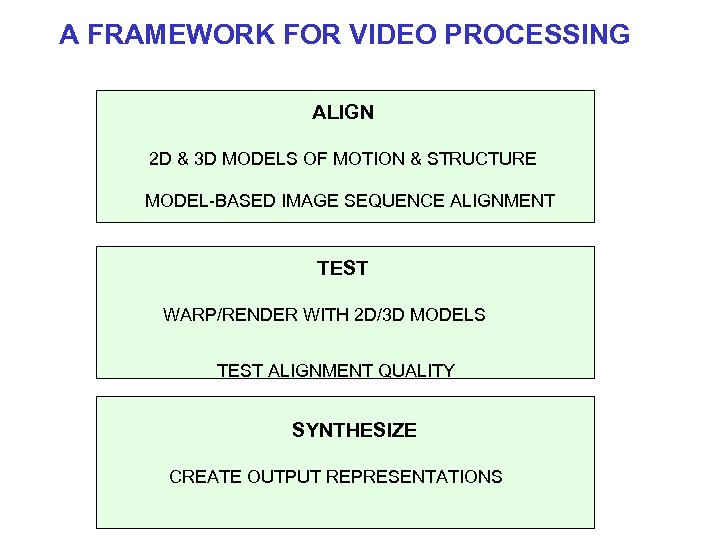 A FRAMEWORK FOR VIDEO PROCESSING ALIGN 2 D & 3 D MODELS OF MOTION & STRUCTURE MODEL-BASED IMAGE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT TEST WARP/RENDER WITH 2 D/3 D MODELS TEST ALIGNMENT QUALITY SYNTHESIZE CREATE OUTPUT REPRESENTATIONS
A FRAMEWORK FOR VIDEO PROCESSING ALIGN 2 D & 3 D MODELS OF MOTION & STRUCTURE MODEL-BASED IMAGE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT TEST WARP/RENDER WITH 2 D/3 D MODELS TEST ALIGNMENT QUALITY SYNTHESIZE CREATE OUTPUT REPRESENTATIONS
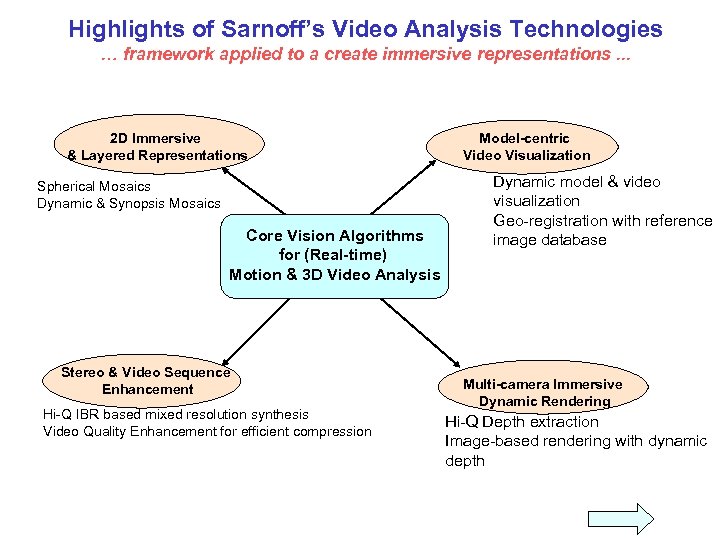 Highlights of Sarnoff’s Video Analysis Technologies … framework applied to a create immersive representations. . . 2 D Immersive & Layered Representations Spherical Mosaics Dynamic & Synopsis Mosaics Core Vision Algorithms for (Real-time) Motion & 3 D Video Analysis Stereo & Video Sequence Enhancement Hi-Q IBR based mixed resolution synthesis Video Quality Enhancement for efficient compression Model-centric Video Visualization Dynamic model & video visualization Geo-registration with reference image database Multi-camera Immersive Dynamic Rendering Hi-Q Depth extraction Image-based rendering with dynamic depth
Highlights of Sarnoff’s Video Analysis Technologies … framework applied to a create immersive representations. . . 2 D Immersive & Layered Representations Spherical Mosaics Dynamic & Synopsis Mosaics Core Vision Algorithms for (Real-time) Motion & 3 D Video Analysis Stereo & Video Sequence Enhancement Hi-Q IBR based mixed resolution synthesis Video Quality Enhancement for efficient compression Model-centric Video Visualization Dynamic model & video visualization Geo-registration with reference image database Multi-camera Immersive Dynamic Rendering Hi-Q Depth extraction Image-based rendering with dynamic depth
 TOPOLOGY INFERENCE & LOCAL-TO-GLOBAL ALIGNMENT SPHERICAL MOSAICS [Sawhney, Hsu, Kumar ECCV 98, Szeliski, Shum SIGGRAPH 98] Sarnoff Library Video Captures almost the complete sphere with 380 frames
TOPOLOGY INFERENCE & LOCAL-TO-GLOBAL ALIGNMENT SPHERICAL MOSAICS [Sawhney, Hsu, Kumar ECCV 98, Szeliski, Shum SIGGRAPH 98] Sarnoff Library Video Captures almost the complete sphere with 380 frames
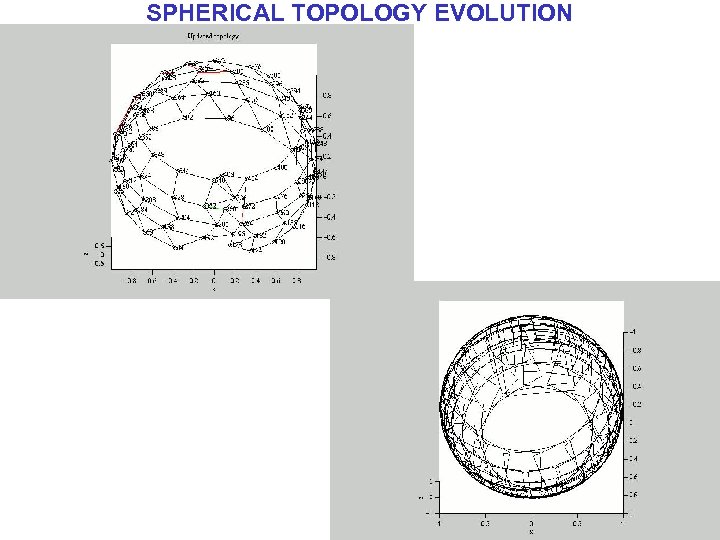 SPHERICAL TOPOLOGY EVOLUTION
SPHERICAL TOPOLOGY EVOLUTION
 SPHERICAL MOSAIC Sarnoff Library
SPHERICAL MOSAIC Sarnoff Library
 ACTIVE FOCUS OF ATTENTION WFOV/NFOV CONTROL
ACTIVE FOCUS OF ATTENTION WFOV/NFOV CONTROL
 DYNAMIC MOSAICS Original Video Stream with deleted moving object Dynamic Mosaic Video
DYNAMIC MOSAICS Original Video Stream with deleted moving object Dynamic Mosaic Video
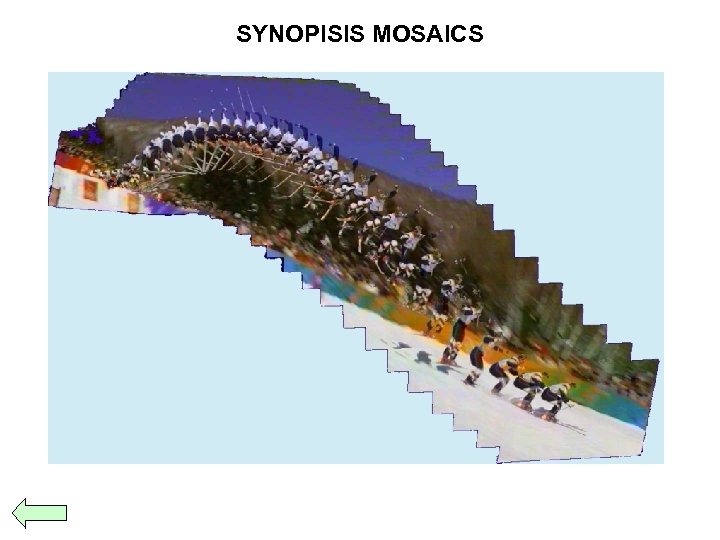 SYNOPISIS MOSAICS
SYNOPISIS MOSAICS
 ALIGNMENT & SYNTHESIS FOR HI-RES STEREO SYNTHESIS A HIGH END APPLICATION OF IBMR [Sawhney, Guo, Hanna, Kumar, Zhou, Adkins SIGGRAPH 2001] Low-Res Left Synthesized High-Res Left Original High-Res Right
ALIGNMENT & SYNTHESIS FOR HI-RES STEREO SYNTHESIS A HIGH END APPLICATION OF IBMR [Sawhney, Guo, Hanna, Kumar, Zhou, Adkins SIGGRAPH 2001] Low-Res Left Synthesized High-Res Left Original High-Res Right
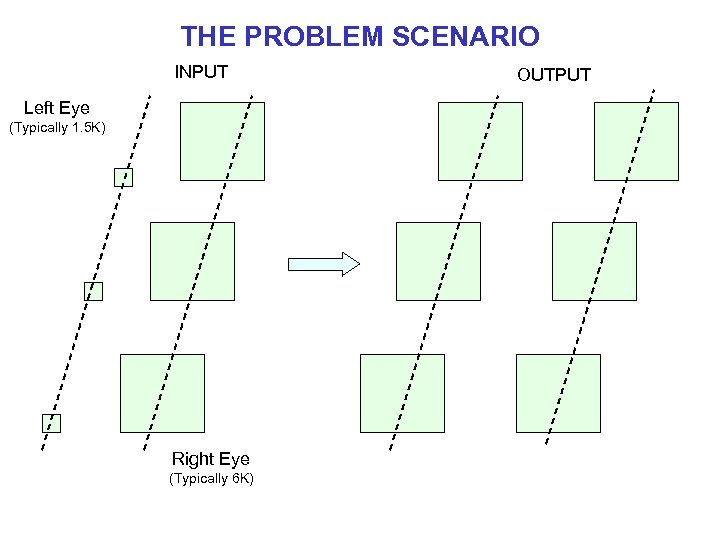 THE PROBLEM SCENARIO INPUT Left Eye (Typically 1. 5 K) Right Eye (Typically 6 K) OUTPUT
THE PROBLEM SCENARIO INPUT Left Eye (Typically 1. 5 K) Right Eye (Typically 6 K) OUTPUT
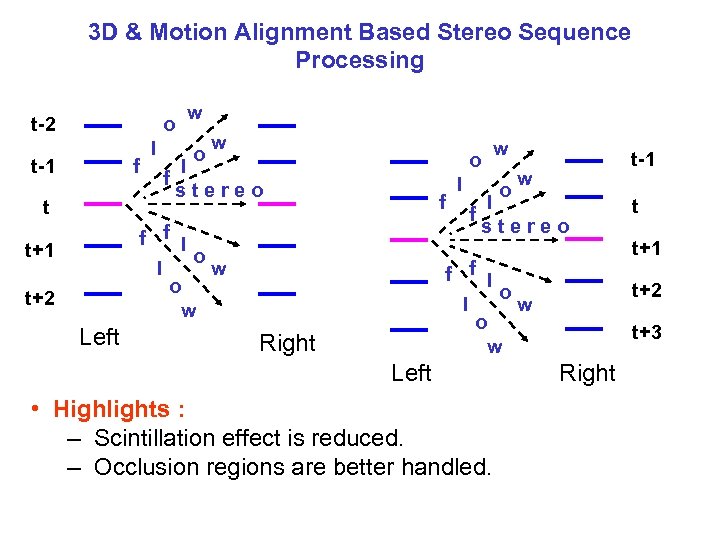 3 D & Motion Alignment Based Stereo Sequence Processing o t-2 f t-1 t l w o l f stereo f f f l o l w o w t+1 t+2 Left l w o f t-1 w l stereo f f l o l w o w Right Left • Highlights : – Scintillation effect is reduced. – Occlusion regions are better handled. t t+1 t+2 t+3 Right
3 D & Motion Alignment Based Stereo Sequence Processing o t-2 f t-1 t l w o l f stereo f f f l o l w o w t+1 t+2 Left l w o f t-1 w l stereo f f l o l w o w Right Left • Highlights : – Scintillation effect is reduced. – Occlusion regions are better handled. t t+1 t+2 t+3 Right
 SYNTHESIS RESULT ON REAL FOOTAGE
SYNTHESIS RESULT ON REAL FOOTAGE
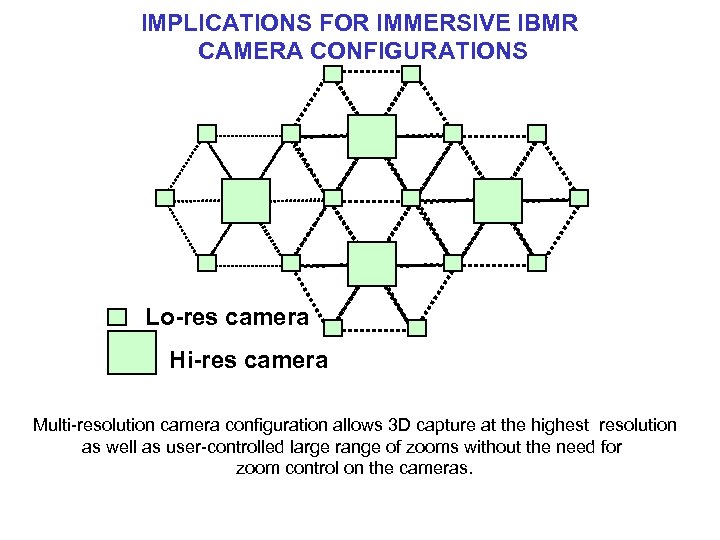 IMPLICATIONS FOR IMMERSIVE IBMR CAMERA CONFIGURATIONS Lo-res camera Hi-res camera Multi-resolution camera configuration allows 3 D capture at the highest resolution as well as user-controlled large range of zooms without the need for zoom control on the cameras.
IMPLICATIONS FOR IMMERSIVE IBMR CAMERA CONFIGURATIONS Lo-res camera Hi-res camera Multi-resolution camera configuration allows 3 D capture at the highest resolution as well as user-controlled large range of zooms without the need for zoom control on the cameras.
![Model-Centric Video Visualization OR Video-Centric Model Visualization [Hsu, Supun, Kumar, Sawhney CVPR 00] Original Model-Centric Video Visualization OR Video-Centric Model Visualization [Hsu, Supun, Kumar, Sawhney CVPR 00] Original](https://present5.com/presentation/b353da0a91f3a85fbbe189cf497f6c68/image-24.jpg) Model-Centric Video Visualization OR Video-Centric Model Visualization [Hsu, Supun, Kumar, Sawhney CVPR 00] Original Video Site model Georegistration of video to site model Re-projection of video after merging with model.
Model-Centric Video Visualization OR Video-Centric Model Visualization [Hsu, Supun, Kumar, Sawhney CVPR 00] Original Video Site model Georegistration of video to site model Re-projection of video after merging with model.
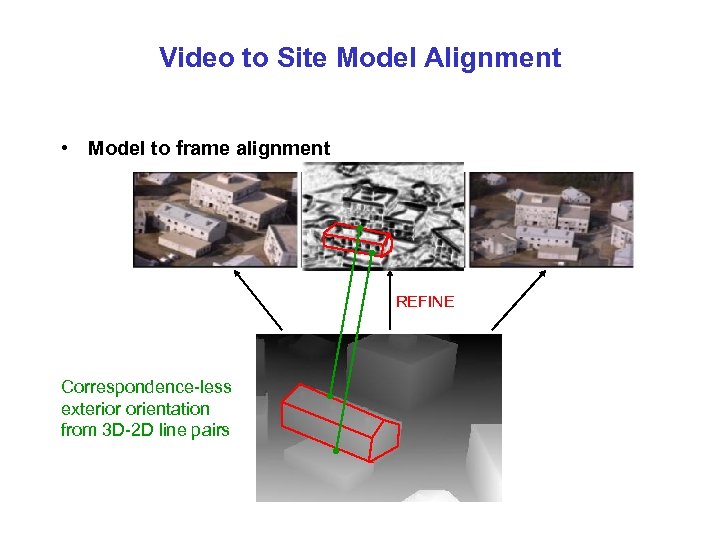 Video to Site Model Alignment • Model to frame alignment REFINE Correspondence-less exterior orientation from 3 D-2 D line pairs
Video to Site Model Alignment • Model to frame alignment REFINE Correspondence-less exterior orientation from 3 D-2 D line pairs
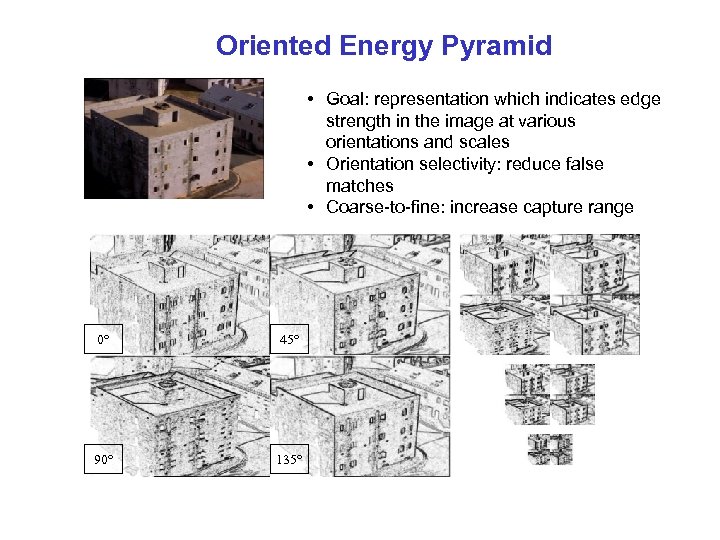 Oriented Energy Pyramid • Goal: representation which indicates edge strength in the image at various orientations and scales • Orientation selectivity: reduce false matches • Coarse-to-fine: increase capture range 0° 45° 90° 135°
Oriented Energy Pyramid • Goal: representation which indicates edge strength in the image at various orientations and scales • Orientation selectivity: reduce false matches • Coarse-to-fine: increase capture range 0° 45° 90° 135°
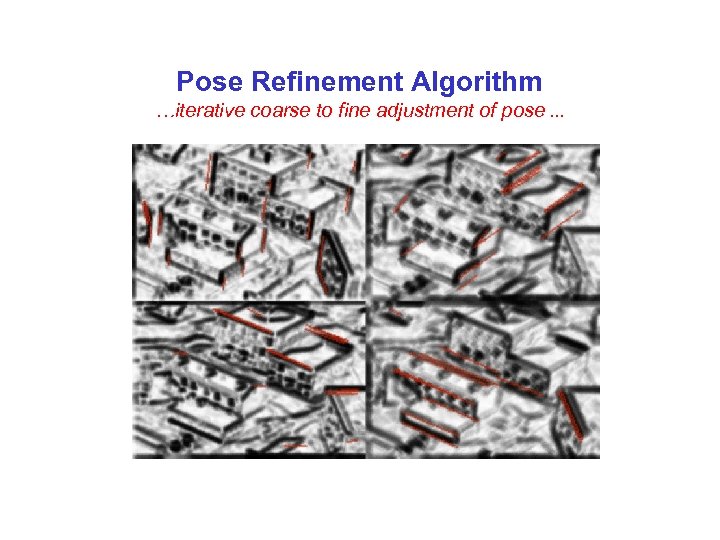 Pose Refinement Algorithm …iterative coarse to fine adjustment of pose. . . This will be an animation of the gradual improvement of alignment during the coarse to fine iterations regsite_animation. avi
Pose Refinement Algorithm …iterative coarse to fine adjustment of pose. . . This will be an animation of the gradual improvement of alignment during the coarse to fine iterations regsite_animation. avi
![Geo-Registration Video to Reference Database Alignment [Wildes et al. ICCV 01] Current Video 3 Geo-Registration Video to Reference Database Alignment [Wildes et al. ICCV 01] Current Video 3](https://present5.com/presentation/b353da0a91f3a85fbbe189cf497f6c68/image-28.jpg) Geo-Registration Video to Reference Database Alignment [Wildes et al. ICCV 01] Current Video 3 D Reference Imagery
Geo-Registration Video to Reference Database Alignment [Wildes et al. ICCV 01] Current Video 3 D Reference Imagery
 Registration : Radical Appearance Changes
Registration : Radical Appearance Changes
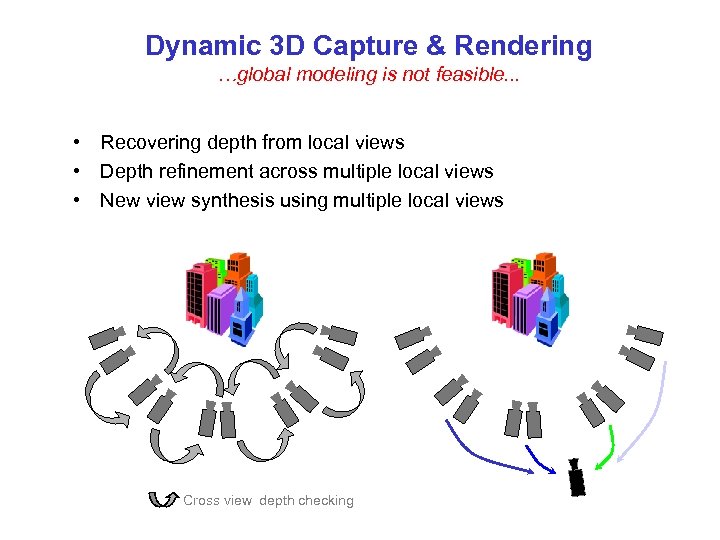 Dynamic 3 D Capture & Rendering …global modeling is not feasible. . . • Recovering depth from local views • Depth refinement across multiple local views • New view synthesis using multiple local views Cross view depth checking
Dynamic 3 D Capture & Rendering …global modeling is not feasible. . . • Recovering depth from local views • Depth refinement across multiple local views • New view synthesis using multiple local views Cross view depth checking
 3 D Shape/Depth Estimation from Multiple Views of a Scene Stereo Pair • Estimation of high quality, artifact free depth maps coregistered with video imagery for rendering new views. • Must work both outdoors and indoors
3 D Shape/Depth Estimation from Multiple Views of a Scene Stereo Pair • Estimation of high quality, artifact free depth maps coregistered with video imagery for rendering new views. • Must work both outdoors and indoors
![Multi-baseline depth estimation - requirements [Tao, Sawhney, Kumar WACV 00, ICCV 01] Accurate boundaries Multi-baseline depth estimation - requirements [Tao, Sawhney, Kumar WACV 00, ICCV 01] Accurate boundaries](https://present5.com/presentation/b353da0a91f3a85fbbe189cf497f6c68/image-32.jpg) Multi-baseline depth estimation - requirements [Tao, Sawhney, Kumar WACV 00, ICCV 01] Accurate boundaries Thin structures Depth maps New view rendering A traditional stereo algorithm Global matching method
Multi-baseline depth estimation - requirements [Tao, Sawhney, Kumar WACV 00, ICCV 01] Accurate boundaries Thin structures Depth maps New view rendering A traditional stereo algorithm Global matching method
 New view rendering using local depth estimation Local flow estimation (1992) Color segmentation based stereo algorithm (2000) Multiwindow plane+ parallax algorithm (1998) New view rendering
New view rendering using local depth estimation Local flow estimation (1992) Color segmentation based stereo algorithm (2000) Multiwindow plane+ parallax algorithm (1998) New view rendering
 Main ideas • Motivations – – be able to handle textureless regions handle object boundaries accurately global visibility constraints should be enforced Hypothesize reasonable depths for unmatched regions • Solutions – Global matching method - an analysis-by-synthesis approach – Representation - smooth depth representation in homogeneous region – Search method - neighborhood depth hypotheses generation – Efficient algorithm - incremental warping – Scene constraints - prior functions
Main ideas • Motivations – – be able to handle textureless regions handle object boundaries accurately global visibility constraints should be enforced Hypothesize reasonable depths for unmatched regions • Solutions – Global matching method - an analysis-by-synthesis approach – Representation - smooth depth representation in homogeneous region – Search method - neighborhood depth hypotheses generation – Efficient algorithm - incremental warping – Scene constraints - prior functions
![Color Segmentation Original image (frame 12) Original image (left) Color segmentation [Comanicius 97] Color Segmentation Original image (frame 12) Original image (left) Color segmentation [Comanicius 97]](https://present5.com/presentation/b353da0a91f3a85fbbe189cf497f6c68/image-35.jpg) Color Segmentation Original image (frame 12) Original image (left) Color segmentation [Comanicius 97]
Color Segmentation Original image (frame 12) Original image (left) Color segmentation [Comanicius 97]
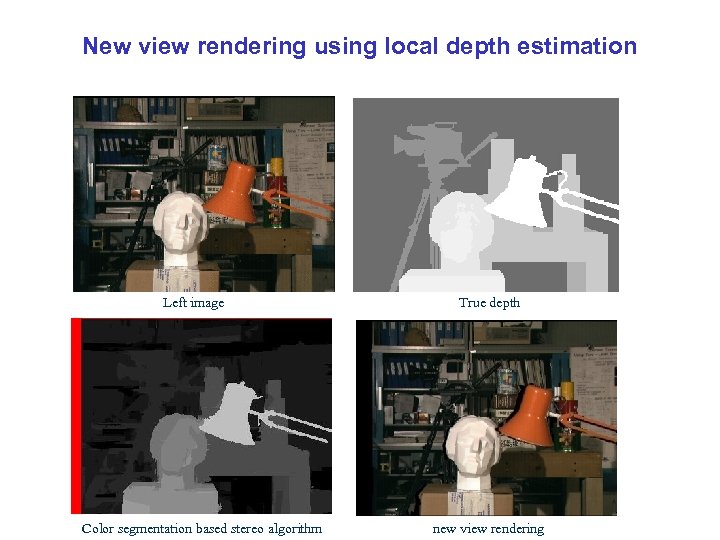 New view rendering using local depth estimation Left image Color segmentation based stereo algorithm True depth new view rendering
New view rendering using local depth estimation Left image Color segmentation based stereo algorithm True depth new view rendering
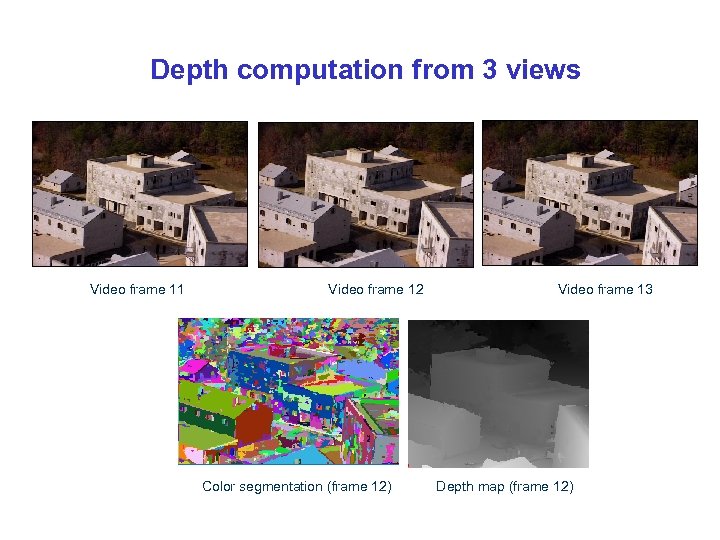 Depth computation from 3 views Video frame 11 Video frame 12 Color segmentation (frame 12) Video frame 13 Depth map (frame 12)
Depth computation from 3 views Video frame 11 Video frame 12 Color segmentation (frame 12) Video frame 13 Depth map (frame 12)
 Multiple View Depth Recovery and New View Rendering New view rendering from a single view. left: from frame 212, right: from frame 215 New view rendering from multiple views.
Multiple View Depth Recovery and New View Rendering New view rendering from a single view. left: from frame 212, right: from frame 215 New view rendering from multiple views.
 Multiple view depth recovery and new view rendering Original 14 video frames (frame 04 -17) New view rendering (71 frames) Depth map of frame 12 and 15
Multiple view depth recovery and new view rendering Original 14 video frames (frame 04 -17) New view rendering (71 frames) Depth map of frame 12 and 15
 Immersive Visualization of a Dynamic Event • Temporally consistent motion and 3 D shape extraction • Scintillation free dynamic high-quality rendering
Immersive Visualization of a Dynamic Event • Temporally consistent motion and 3 D shape extraction • Scintillation free dynamic high-quality rendering
 AN IMMERSIVE IBMR GRAND CHALLENGE
AN IMMERSIVE IBMR GRAND CHALLENGE
 AND IF WE DO IT RIGHT
AND IF WE DO IT RIGHT



