5025a511d5eabc1bd1bf529352cfe4d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 2 Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2007 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
2 Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2007 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Learning Objectives § § List and briefly discuss the primary ways that business organizations compete. List five reasons for the poor competitiveness of some companies. Define the term strategy and explain why strategy is important for competitiveness. Contrast strategy and tactics. 2
Learning Objectives § § List and briefly discuss the primary ways that business organizations compete. List five reasons for the poor competitiveness of some companies. Define the term strategy and explain why strategy is important for competitiveness. Contrast strategy and tactics. 2
 Learning Objectives § Discuss and compare organization strategy and operations strategy, and explain why it is important to link the two. § Describe and give examples of time-based strategies. § Define the term productivity and explain why it is important to organizations and to countries. § List some of the reasons for poor productivity and some ways of improving it. 3
Learning Objectives § Discuss and compare organization strategy and operations strategy, and explain why it is important to link the two. § Describe and give examples of time-based strategies. § Define the term productivity and explain why it is important to organizations and to countries. § List some of the reasons for poor productivity and some ways of improving it. 3
 Competitiveness: How effectively an organization meets the wants and needs of customers relative to others that offer similar goods or services 4
Competitiveness: How effectively an organization meets the wants and needs of customers relative to others that offer similar goods or services 4
 Businesses Compete Using Marketing § Identifying consumer wants and needs § Pricing § Advertising and promotion 5
Businesses Compete Using Marketing § Identifying consumer wants and needs § Pricing § Advertising and promotion 5
 Businesses Compete Using Operations § Product and service design § Cost § Location § Quality § Quick response 6
Businesses Compete Using Operations § Product and service design § Cost § Location § Quality § Quick response 6
 Businesses Compete Using Operations § § § Flexibility Inventory management Supply chain management Service and service quality Managers and workers 7
Businesses Compete Using Operations § § § Flexibility Inventory management Supply chain management Service and service quality Managers and workers 7
 Why Some Organizations Fail § Too much emphasis on short-term financial performance § Failing to take advantage of strengths and opportunities § Neglecting operations strategy § Failing to recognize competitive threats 8
Why Some Organizations Fail § Too much emphasis on short-term financial performance § Failing to take advantage of strengths and opportunities § Neglecting operations strategy § Failing to recognize competitive threats 8
 Why Some Organizations Fail § Too much emphasis in product and service design and not enough on improvement § Neglecting investments in capital and human resources § Failing to establish good internal communications § Failing to consider customer wants and needs 9
Why Some Organizations Fail § Too much emphasis in product and service design and not enough on improvement § Neglecting investments in capital and human resources § Failing to establish good internal communications § Failing to consider customer wants and needs 9
 Mission/Strategy/Tactics Mission Strategy Tactics How does mission, strategies and tactics relate to decision making and distinctive competencies? 10
Mission/Strategy/Tactics Mission Strategy Tactics How does mission, strategies and tactics relate to decision making and distinctive competencies? 10
 Strategy § Mission § The reason for existence for an organization § Mission Statement § States the purpose of an organization § Goals § § Provide detail and scope of mission Strategies § Plans for achieving organizational goals § Tactics § The methods and actions taken to accomplish strategies 11
Strategy § Mission § The reason for existence for an organization § Mission Statement § States the purpose of an organization § Goals § § Provide detail and scope of mission Strategies § Plans for achieving organizational goals § Tactics § The methods and actions taken to accomplish strategies 11
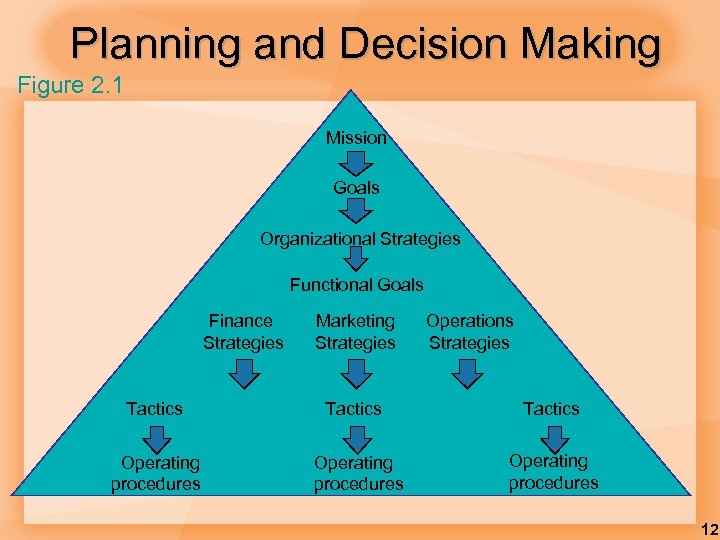 Planning and Decision Making Figure 2. 1 Mission Goals Organizational Strategies Functional Goals Finance Strategies Tactics Operating procedures Marketing Strategies Tactics Operating procedures Operations Strategies Tactics Operating procedures 12
Planning and Decision Making Figure 2. 1 Mission Goals Organizational Strategies Functional Goals Finance Strategies Tactics Operating procedures Marketing Strategies Tactics Operating procedures Operations Strategies Tactics Operating procedures 12
 Strategy Example 1 Rita is a high school student. She would like to have a career in business, have a good job, and earn enough income to live comfortably Mission: § Goal: § Strategy: § Tactics: § Operations: job Live a good life Successful career, good income Obtain a college education Select a college and a major Register, buy books, take courses, study, graduate, get 13
Strategy Example 1 Rita is a high school student. She would like to have a career in business, have a good job, and earn enough income to live comfortably Mission: § Goal: § Strategy: § Tactics: § Operations: job Live a good life Successful career, good income Obtain a college education Select a college and a major Register, buy books, take courses, study, graduate, get 13
 Examples of Strategies § § § Low cost Scale-based strategies Specialization Flexible operations High quality Service 14
Examples of Strategies § § § Low cost Scale-based strategies Specialization Flexible operations High quality Service 14
 Strategy and Tactics § Distinctive Competencies The special attributes or abilities that give an organization a competitive edge. § Strategy Factors § § § Price Quality Time Flexibility Service Location 15
Strategy and Tactics § Distinctive Competencies The special attributes or abilities that give an organization a competitive edge. § Strategy Factors § § § Price Quality Time Flexibility Service Location 15
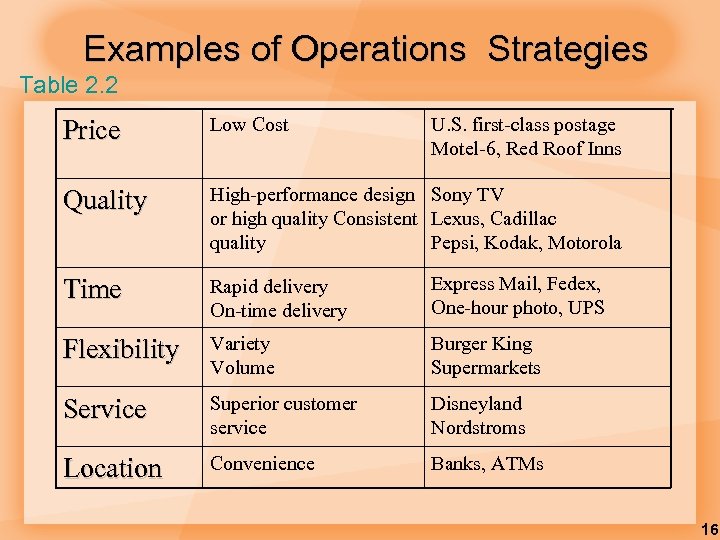 Examples of Operations Strategies Table 2. 2 Price Low Cost U. S. first-class postage Motel-6, Red Roof Inns Quality High-performance design Sony TV or high quality Consistent Lexus, Cadillac quality Pepsi, Kodak, Motorola Time Rapid delivery On-time delivery Express Mail, Fedex, One-hour photo, UPS Flexibility Variety Volume Burger King Supermarkets Service Superior customer service Disneyland Nordstroms Location Convenience Banks, ATMs 16
Examples of Operations Strategies Table 2. 2 Price Low Cost U. S. first-class postage Motel-6, Red Roof Inns Quality High-performance design Sony TV or high quality Consistent Lexus, Cadillac quality Pepsi, Kodak, Motorola Time Rapid delivery On-time delivery Express Mail, Fedex, One-hour photo, UPS Flexibility Variety Volume Burger King Supermarkets Service Superior customer service Disneyland Nordstroms Location Convenience Banks, ATMs 16
 Global Strategy § Strategic decisions must be made with respect to globalization § What works in one country may not work in another § Strategies must be changed to account for these differences § Other issues § Political, social, cultural, and economic differences 17
Global Strategy § Strategic decisions must be made with respect to globalization § What works in one country may not work in another § Strategies must be changed to account for these differences § Other issues § Political, social, cultural, and economic differences 17
 Strategy Formulation § § § Distinctive competencies Environmental scanning SWOT Order qualifiers Order winners 18
Strategy Formulation § § § Distinctive competencies Environmental scanning SWOT Order qualifiers Order winners 18
 Strategy Formulation § Order qualifiers § Characteristics that customers perceive as minimum standards of acceptability to be considered as a potential purchase § Order winners § Characteristics of an organization’s goods or services that cause it to be perceived as better than the competition 19
Strategy Formulation § Order qualifiers § Characteristics that customers perceive as minimum standards of acceptability to be considered as a potential purchase § Order winners § Characteristics of an organization’s goods or services that cause it to be perceived as better than the competition 19
 Key External Factors § § § Economic conditions Political conditions Legal environment Technology Competition Markets 20
Key External Factors § § § Economic conditions Political conditions Legal environment Technology Competition Markets 20
 Key Internal Factors § § § § Human Resources Facilities and equipment Financial resources Customers Products and services Technology Suppliers 21
Key Internal Factors § § § § Human Resources Facilities and equipment Financial resources Customers Products and services Technology Suppliers 21
 Operations Strategy § Operations strategy – The approach, consistent with organization strategy, that is used to guide the operations function. 22
Operations Strategy § Operations strategy – The approach, consistent with organization strategy, that is used to guide the operations function. 22
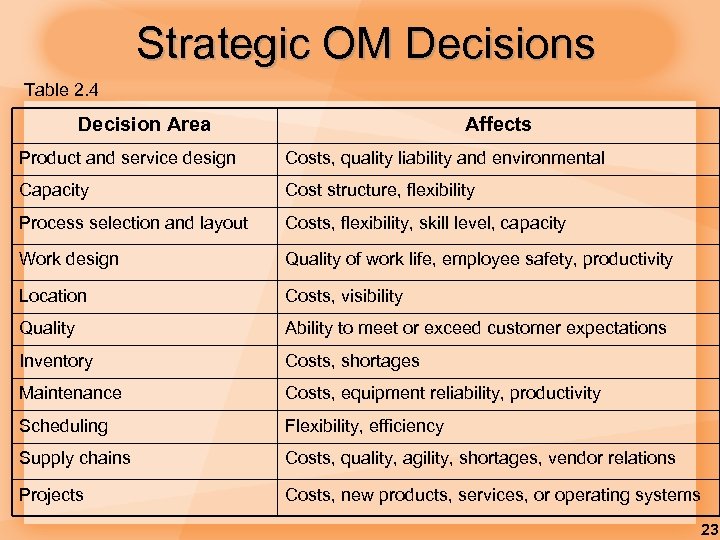 Strategic OM Decisions Table 2. 4 Decision Area Affects Product and service design Costs, quality liability and environmental Capacity Cost structure, flexibility Process selection and layout Costs, flexibility, skill level, capacity Work design Quality of work life, employee safety, productivity Location Costs, visibility Quality Ability to meet or exceed customer expectations Inventory Costs, shortages Maintenance Costs, equipment reliability, productivity Scheduling Flexibility, efficiency Supply chains Costs, quality, agility, shortages, vendor relations Projects Costs, new products, services, or operating systems 23
Strategic OM Decisions Table 2. 4 Decision Area Affects Product and service design Costs, quality liability and environmental Capacity Cost structure, flexibility Process selection and layout Costs, flexibility, skill level, capacity Work design Quality of work life, employee safety, productivity Location Costs, visibility Quality Ability to meet or exceed customer expectations Inventory Costs, shortages Maintenance Costs, equipment reliability, productivity Scheduling Flexibility, efficiency Supply chains Costs, quality, agility, shortages, vendor relations Projects Costs, new products, services, or operating systems 23
 Quality and Time Strategies § Quality-based strategies § § Focuses on maintaining or improving the quality of an organization’s products or services Quality at the source § Time-based strategies § Focuses on reduction of time needed to accomplish tasks 24
Quality and Time Strategies § Quality-based strategies § § Focuses on maintaining or improving the quality of an organization’s products or services Quality at the source § Time-based strategies § Focuses on reduction of time needed to accomplish tasks 24
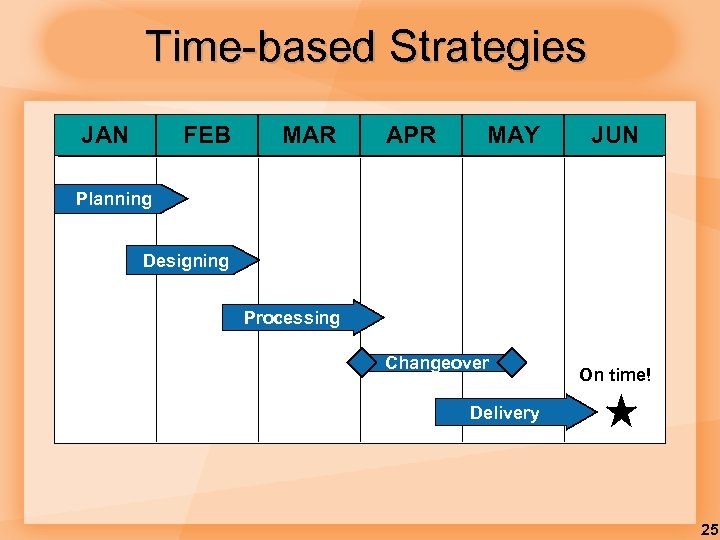 Time-based Strategies JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN Planning Designing Processing Changeover On time! Delivery 25
Time-based Strategies JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN Planning Designing Processing Changeover On time! Delivery 25
 Productivity § A measure of the effective use of resources, usually expressed as the ratio of output to input § Productivity ratios are used for § Planning workforce requirements § Scheduling equipment § Financial analysis 26
Productivity § A measure of the effective use of resources, usually expressed as the ratio of output to input § Productivity ratios are used for § Planning workforce requirements § Scheduling equipment § Financial analysis 26
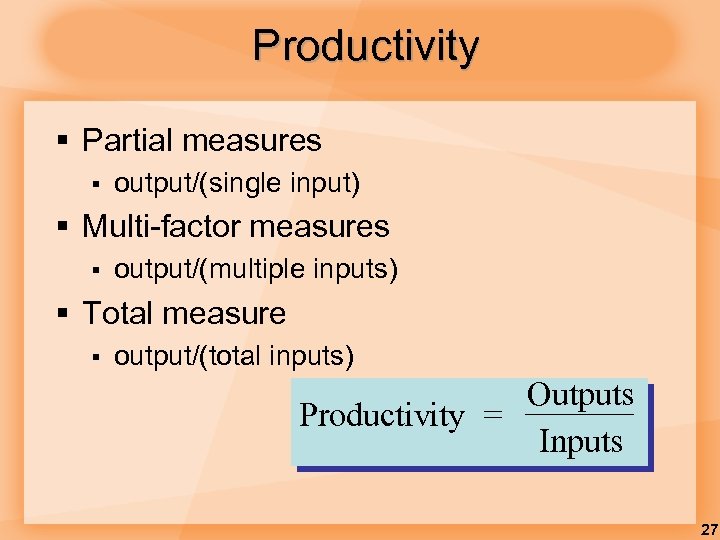 Productivity § Partial measures § output/(single input) § Multi-factor measures § output/(multiple inputs) § Total measure § output/(total inputs) Outputs Productivity = Inputs 27
Productivity § Partial measures § output/(single input) § Multi-factor measures § output/(multiple inputs) § Total measure § output/(total inputs) Outputs Productivity = Inputs 27
 Productivity Growth = Current Period Productivity – Previous Period Productivity 28
Productivity Growth = Current Period Productivity – Previous Period Productivity 28
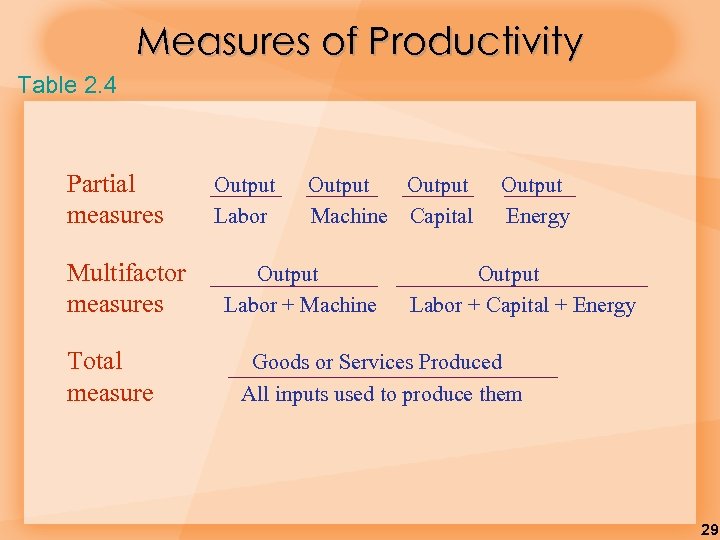 Measures of Productivity Table 2. 4 Partial measures Multifactor measures Total measure Output Labor Output Machine Capital Output Labor + Machine Output Energy Output Labor + Capital + Energy Goods or Services Produced All inputs used to produce them 29
Measures of Productivity Table 2. 4 Partial measures Multifactor measures Total measure Output Labor Output Machine Capital Output Labor + Machine Output Energy Output Labor + Capital + Energy Goods or Services Produced All inputs used to produce them 29
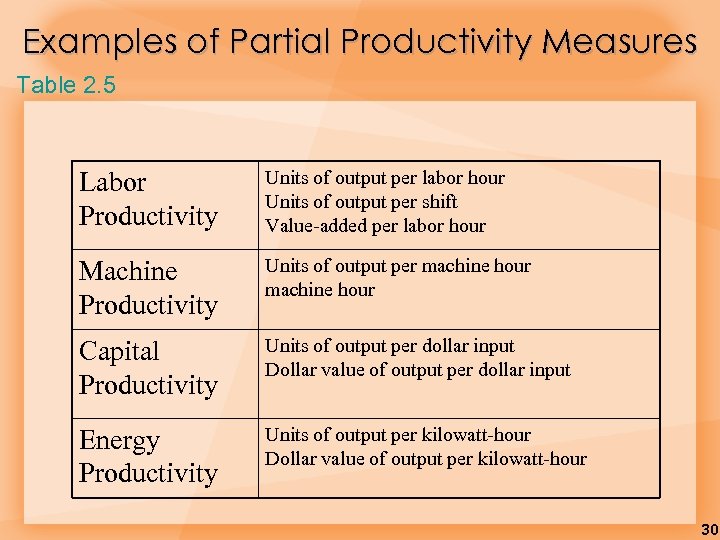 Examples of Partial Productivity Measures Table 2. 5 Labor Productivity Units of output per labor hour Units of output per shift Value-added per labor hour Machine Productivity Units of output per machine hour Capital Productivity Units of output per dollar input Dollar value of output per dollar input Energy Productivity Units of output per kilowatt-hour Dollar value of output per kilowatt-hour 30
Examples of Partial Productivity Measures Table 2. 5 Labor Productivity Units of output per labor hour Units of output per shift Value-added per labor hour Machine Productivity Units of output per machine hour Capital Productivity Units of output per dollar input Dollar value of output per dollar input Energy Productivity Units of output per kilowatt-hour Dollar value of output per kilowatt-hour 30
 Example 3 7040 Units Produced Cost of labor of $1, 000 Cost of materials: $520 Cost of overhead: $2000 What is the multifactor productivity? Ans. 2. 0 units per dollar of input 31
Example 3 7040 Units Produced Cost of labor of $1, 000 Cost of materials: $520 Cost of overhead: $2000 What is the multifactor productivity? Ans. 2. 0 units per dollar of input 31
 Example 3 Solution MFP = Output Labor + Materials + Overhead MFP = (7040 units) $1000 + $520 + $2000 MFP = 2. 0 units per dollar of input 32
Example 3 Solution MFP = Output Labor + Materials + Overhead MFP = (7040 units) $1000 + $520 + $2000 MFP = 2. 0 units per dollar of input 32
 Process Yield § Process yield is the ratio of output of good product to input § Defective product is not included in the output § Service example: § Ratio of cars rented to cars available to rent 33
Process Yield § Process yield is the ratio of output of good product to input § Defective product is not included in the output § Service example: § Ratio of cars rented to cars available to rent 33
 Factors Affecting Productivity Capital Quality Technology Management 34
Factors Affecting Productivity Capital Quality Technology Management 34
 Other Factors Affecting Productivity § § § § Standardization Quality Use of Internet Computer viruses Searching for lost or misplaced items Scrap rates New workers 35
Other Factors Affecting Productivity § § § § Standardization Quality Use of Internet Computer viruses Searching for lost or misplaced items Scrap rates New workers 35
 Other Factors Affecting Productivity § § § Safety Shortage of IT workers Layoffs Labor turnover Design of the workspace Incentive plans that reward productivity 36
Other Factors Affecting Productivity § § § Safety Shortage of IT workers Layoffs Labor turnover Design of the workspace Incentive plans that reward productivity 36
 Outsourcing § Higher productivity in another company is a key reason organizations outsource work § Improving productivity may reduce the need for outsourcing 37
Outsourcing § Higher productivity in another company is a key reason organizations outsource work § Improving productivity may reduce the need for outsourcing 37
 Improving Productivity § Develop productivity measures § Determine critical (bottleneck) operations § Develop methods for productivity improvements § Establish reasonable goals § Get management support § Measure and publicize improvements § Don’t confuse productivity with efficiency 38
Improving Productivity § Develop productivity measures § Determine critical (bottleneck) operations § Develop methods for productivity improvements § Establish reasonable goals § Get management support § Measure and publicize improvements § Don’t confuse productivity with efficiency 38


