81330b6a6fccc4a730183624ab155415.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 2 Chapter 2: Approaches to System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition
2 Chapter 2: Approaches to System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition
 2 Learning Objectives u Explain the purpose and various phases of the systems development life cycle (SDLC) u Explain the differences between a model, a tool, a technique, and a methodology u Describe the two overall approaches used to develop information systems: the traditional method and the object-oriented method Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
2 Learning Objectives u Explain the purpose and various phases of the systems development life cycle (SDLC) u Explain the differences between a model, a tool, a technique, and a methodology u Describe the two overall approaches used to develop information systems: the traditional method and the object-oriented method Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
 2 Learning Objectives (continued) u Describe some of the variations of the system development life cycle (SDLC) u Describe the key features of current trends in system development: the spiral model, e. Xtreme Programming (XP), the Unified Process (UP), and Agile Modeling u Explain how automated tools are used in system development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
2 Learning Objectives (continued) u Describe some of the variations of the system development life cycle (SDLC) u Describe the key features of current trends in system development: the spiral model, e. Xtreme Programming (XP), the Unified Process (UP), and Agile Modeling u Explain how automated tools are used in system development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
 2 Overview u Systems l development life cycle (SDLC) Provides overall framework for managing system development process u Two main approaches to SDLC l Traditional approach: structured systems development and information engineering l Object-oriented approach: object technologies requires different approach to analysis, design, and programming u All projects use some variation of SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
2 Overview u Systems l development life cycle (SDLC) Provides overall framework for managing system development process u Two main approaches to SDLC l Traditional approach: structured systems development and information engineering l Object-oriented approach: object technologies requires different approach to analysis, design, and programming u All projects use some variation of SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
 2 Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) u Systems development project l Planned undertaking with fixed beginning and end l Produces desired result or product l Can be a large job of thousands of hours of effort or a small one month project u Successful development project: l Provides a detailed plan to follow l Organized, methodical sequence of tasks and activities l Produces reliable, robust, and efficient system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
2 Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) u Systems development project l Planned undertaking with fixed beginning and end l Produces desired result or product l Can be a large job of thousands of hours of effort or a small one month project u Successful development project: l Provides a detailed plan to follow l Organized, methodical sequence of tasks and activities l Produces reliable, robust, and efficient system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
 Phases of the Systems Development Lifecycle (SDLC) 2 u Project planning: initiate, ensure feasibility, plan schedule, obtain approval for project u Analysis: understand business needs and processing requirements u Design: define solution system based on requirements and analysis decisions u Implementation: construction, testing, user training, and installation of new system u Support: keep system running and improve Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 6
Phases of the Systems Development Lifecycle (SDLC) 2 u Project planning: initiate, ensure feasibility, plan schedule, obtain approval for project u Analysis: understand business needs and processing requirements u Design: define solution system based on requirements and analysis decisions u Implementation: construction, testing, user training, and installation of new system u Support: keep system running and improve Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 6
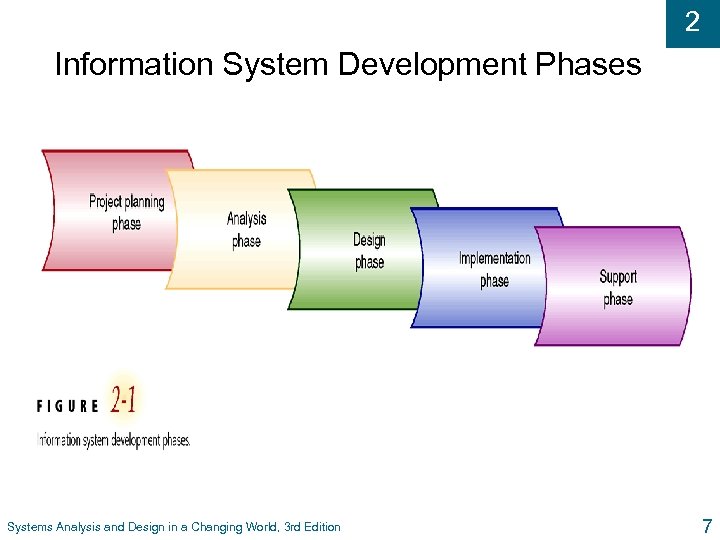 2 Information System Development Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 7
2 Information System Development Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 7
 2 SDLC and problem-solving u Similar to problem-solving approach l Organization recognizes problem (Project Planning) l Project team investigates, understands problem and solution requirements (Analysis) l Solution is specified in detail (Design) l System that solves problem built and installed (Implementation) l System used, maintained, and enhanced to continue to provide intended benefits (Support) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
2 SDLC and problem-solving u Similar to problem-solving approach l Organization recognizes problem (Project Planning) l Project team investigates, understands problem and solution requirements (Analysis) l Solution is specified in detail (Design) l System that solves problem built and installed (Implementation) l System used, maintained, and enhanced to continue to provide intended benefits (Support) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
 2 Planning Phase of SDLC u Define business problem and scope u Produce detailed project schedule u Confirm project feasibility l Economic, organizational, technical, resource, and schedule u Staff the project (resource management) u Launch project official announcement Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
2 Planning Phase of SDLC u Define business problem and scope u Produce detailed project schedule u Confirm project feasibility l Economic, organizational, technical, resource, and schedule u Staff the project (resource management) u Launch project official announcement Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
 2 Analysis Phase of SDLC u Gather information to learn problem domain u Define system requirements u Build prototypes for discovery of requirements u Prioritize requirements u Generate u Review and evaluate alternatives recommendations with management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10
2 Analysis Phase of SDLC u Gather information to learn problem domain u Define system requirements u Build prototypes for discovery of requirements u Prioritize requirements u Generate u Review and evaluate alternatives recommendations with management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10
 2 Design Phase of SDLC u Design and integrate the network u Design the application architecture u Design the user interfaces u Design the system interfaces u Design and integrate the database u Prototype u Design for design details and integrate system controls Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
2 Design Phase of SDLC u Design and integrate the network u Design the application architecture u Design the user interfaces u Design the system interfaces u Design and integrate the database u Prototype u Design for design details and integrate system controls Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
 2 Implementation Phase of SDLC u Construct u Verify and test u Convert u Train software components data users and document the system u Install the system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
2 Implementation Phase of SDLC u Construct u Verify and test u Convert u Train software components data users and document the system u Install the system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
 2 Support Phase of SDLC u Maintain l system Small patches, repairs, and updates u Enhance system l Small upgrades or enhancements to expand system capabilities l Larger enhancements may require separate development project u Support l users Help desk and/or support team Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 13
2 Support Phase of SDLC u Maintain l system Small patches, repairs, and updates u Enhance system l Small upgrades or enhancements to expand system capabilities l Larger enhancements may require separate development project u Support l users Help desk and/or support team Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 13
 2 Scheduling Project Phases u Waterfall approach – each phase falls into next phase l Freeze planning specifications before analysis l Freeze analysis specifications before design l Once go over the waterfall for each phase, do not go back u Overlapping (or concurrent) phases l Waterfall is not realistic, we are not perfect l Overlaps can be more efficient than waterfall Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
2 Scheduling Project Phases u Waterfall approach – each phase falls into next phase l Freeze planning specifications before analysis l Freeze analysis specifications before design l Once go over the waterfall for each phase, do not go back u Overlapping (or concurrent) phases l Waterfall is not realistic, we are not perfect l Overlaps can be more efficient than waterfall Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
 2 Scheduling Project Phases (continued) u Iteration - Work activities are repeated l Each iteration refines previous result l Approach assumes no one gets it right the first time l There a series of mini projects for each iteration u Example: Outline, rough draft, edited result u Example: Blueprint, frame, completed house Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
2 Scheduling Project Phases (continued) u Iteration - Work activities are repeated l Each iteration refines previous result l Approach assumes no one gets it right the first time l There a series of mini projects for each iteration u Example: Outline, rough draft, edited result u Example: Blueprint, frame, completed house Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
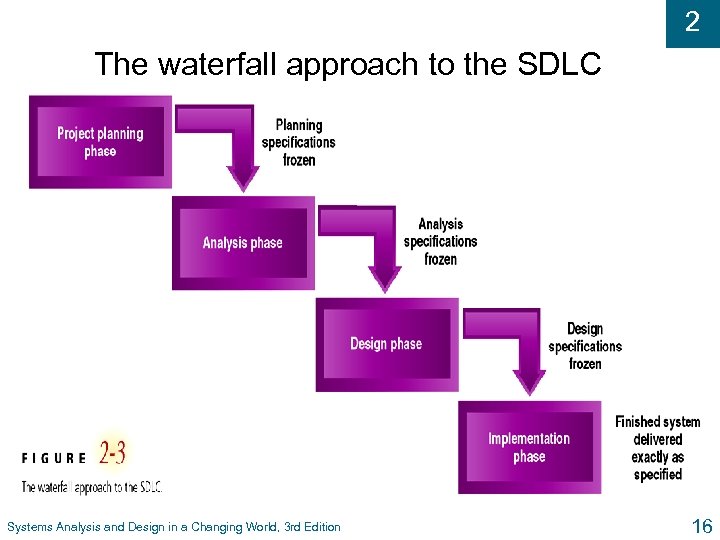 2 The waterfall approach to the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
2 The waterfall approach to the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
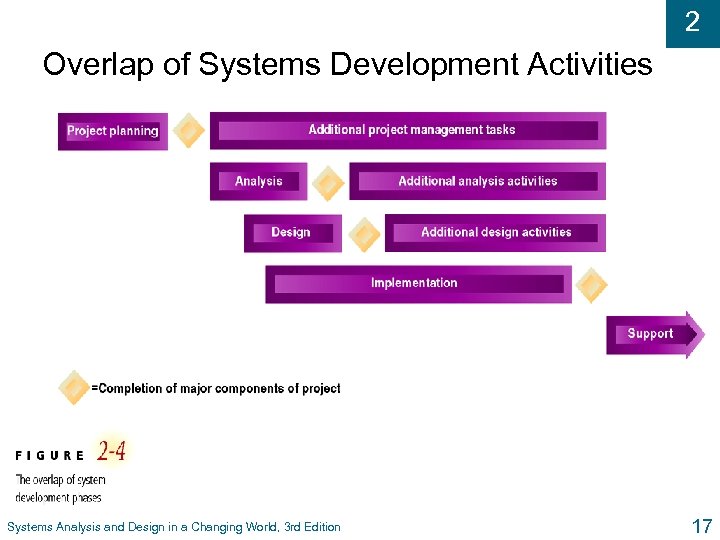 2 Overlap of Systems Development Activities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17
2 Overlap of Systems Development Activities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17
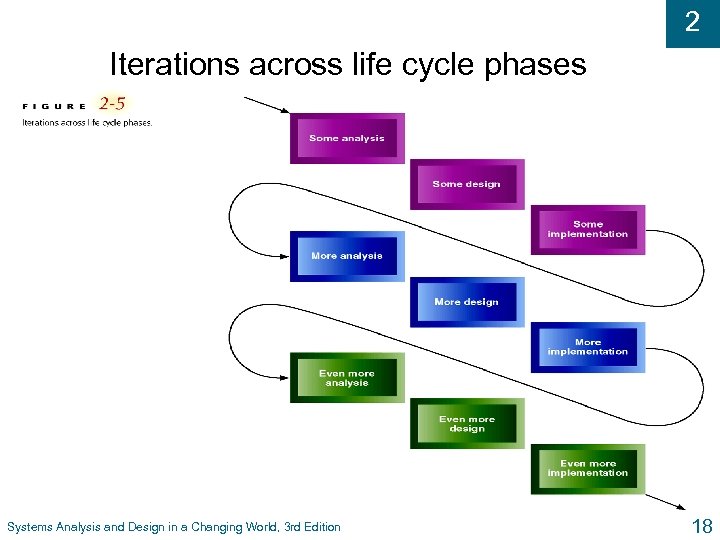 2 Iterations across life cycle phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 18
2 Iterations across life cycle phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 18
 2 Methodologies and Models u Methodologies l Comprehensive guidelines to follow for completing every SDLC activity l Collection of models, tools, and techniques u Models l Representation of an important aspect of real world, but not same as real thing l Abstraction used to separate out aspect l Diagrams and charts l Project planning and budgeting aids Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 19
2 Methodologies and Models u Methodologies l Comprehensive guidelines to follow for completing every SDLC activity l Collection of models, tools, and techniques u Models l Representation of an important aspect of real world, but not same as real thing l Abstraction used to separate out aspect l Diagrams and charts l Project planning and budgeting aids Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 19
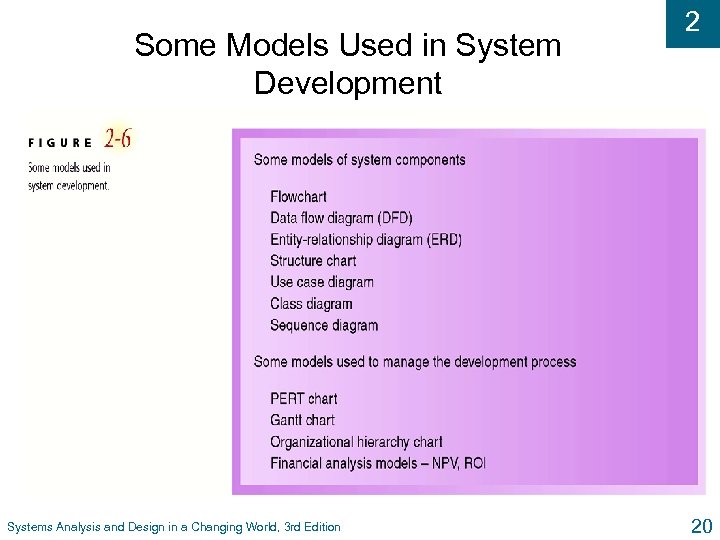 Some Models Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 20
Some Models Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 20
 2 Tools and Techniques u Tools l Software support that helps create models or other required project components l Range from simple drawing programs to complex CASE tools u Techniques l Collection of guidelines that help analyst complete system development activity or task l Can be step-by-step instructions or just general advice Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 21
2 Tools and Techniques u Tools l Software support that helps create models or other required project components l Range from simple drawing programs to complex CASE tools u Techniques l Collection of guidelines that help analyst complete system development activity or task l Can be step-by-step instructions or just general advice Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 21
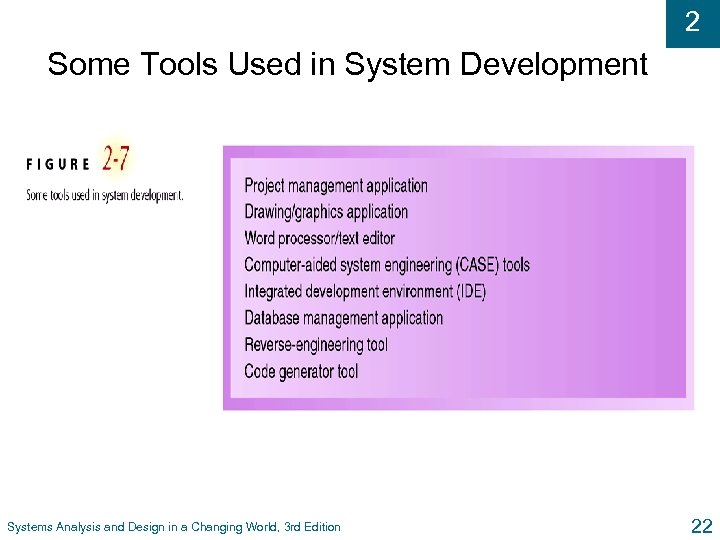 2 Some Tools Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 22
2 Some Tools Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 22
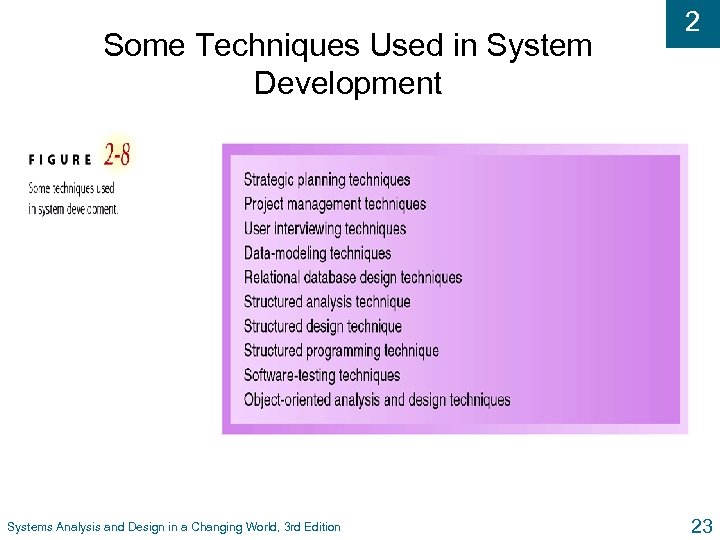 Some Techniques Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 23
Some Techniques Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 23
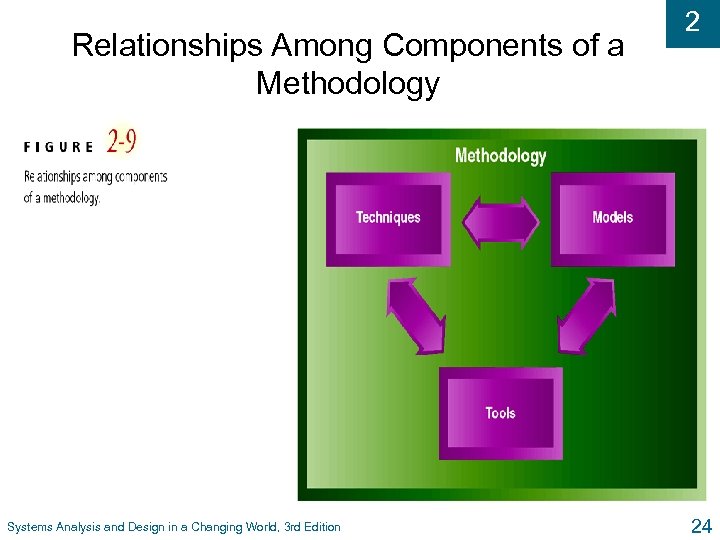 Relationships Among Components of a Methodology Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 24
Relationships Among Components of a Methodology Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 24
 2 Two Approaches to System Development u Traditional Approach l Also called structured system development l Structured analysis and design technique (SADT) u Structured programming l Improves computer program quality l Allows other programmers to easily read and modify code l Each program module has one beginning and one ending l Three programming constructs (sequence, decision, repetition) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 25
2 Two Approaches to System Development u Traditional Approach l Also called structured system development l Structured analysis and design technique (SADT) u Structured programming l Improves computer program quality l Allows other programmers to easily read and modify code l Each program module has one beginning and one ending l Three programming constructs (sequence, decision, repetition) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 25
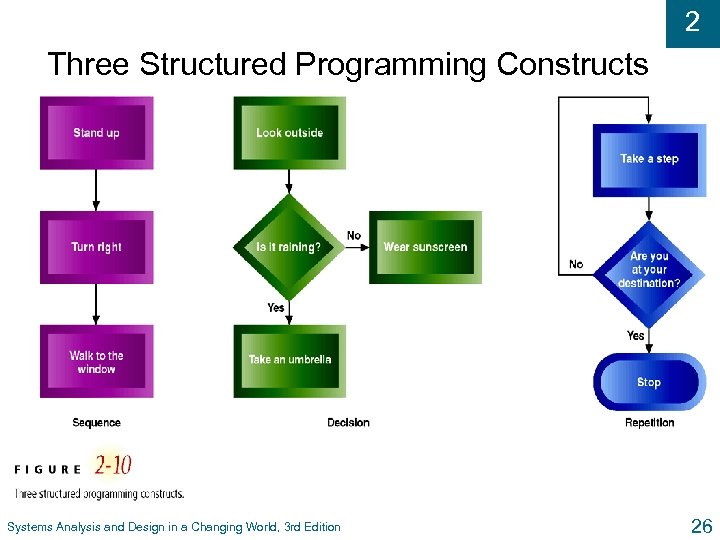 2 Three Structured Programming Constructs Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 26
2 Three Structured Programming Constructs Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 26
 2 Top-Down Programming u Divides complex programs into hierarchy of modules u The module at top controls execution by “calling” lower level modules u Modular l programming Similar to top-down programming u One program calls other programs to work together as single system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 27
2 Top-Down Programming u Divides complex programs into hierarchy of modules u The module at top controls execution by “calling” lower level modules u Modular l programming Similar to top-down programming u One program calls other programs to work together as single system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 27
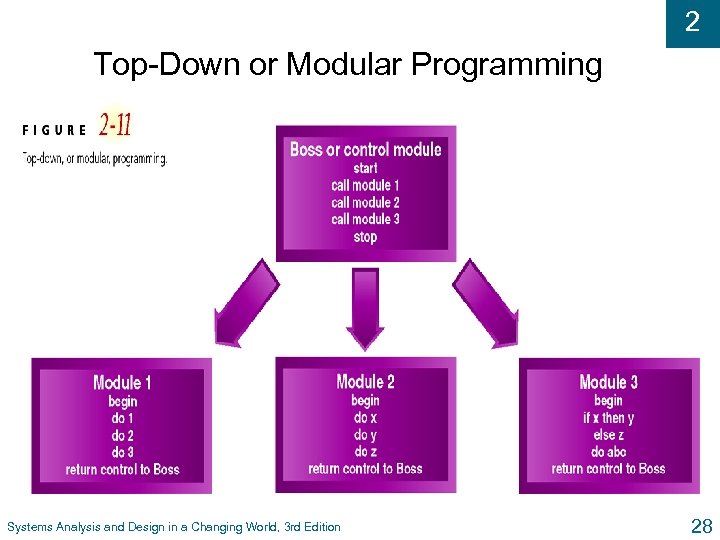 2 Top-Down or Modular Programming Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 28
2 Top-Down or Modular Programming Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 28
 2 Structured Design u Technique guidelines developed to provide design l What set of programs should be l What program should accomplish l How programs should be organized into a hierarchy u Modules u Main are shown with structure chart principle of program modules l Loosely coupled – module is independent of other modules l Highly cohesive – module has one clear task Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
2 Structured Design u Technique guidelines developed to provide design l What set of programs should be l What program should accomplish l How programs should be organized into a hierarchy u Modules u Main are shown with structure chart principle of program modules l Loosely coupled – module is independent of other modules l Highly cohesive – module has one clear task Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
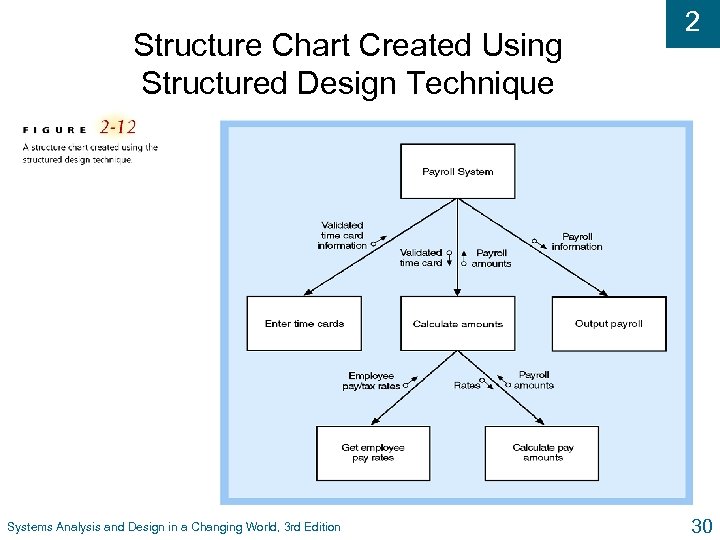 Structure Chart Created Using Structured Design Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 30
Structure Chart Created Using Structured Design Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 30
 2 Structured Analysis u Define what system needs to do (processing requirements) u Define data system needs to store and use (data requirements) u Define inputs and outputs u Define how functions work together to accomplish tasks u Data flow diagrams and entity relationship diagrams show results of structured analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 31
2 Structured Analysis u Define what system needs to do (processing requirements) u Define data system needs to store and use (data requirements) u Define inputs and outputs u Define how functions work together to accomplish tasks u Data flow diagrams and entity relationship diagrams show results of structured analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 31
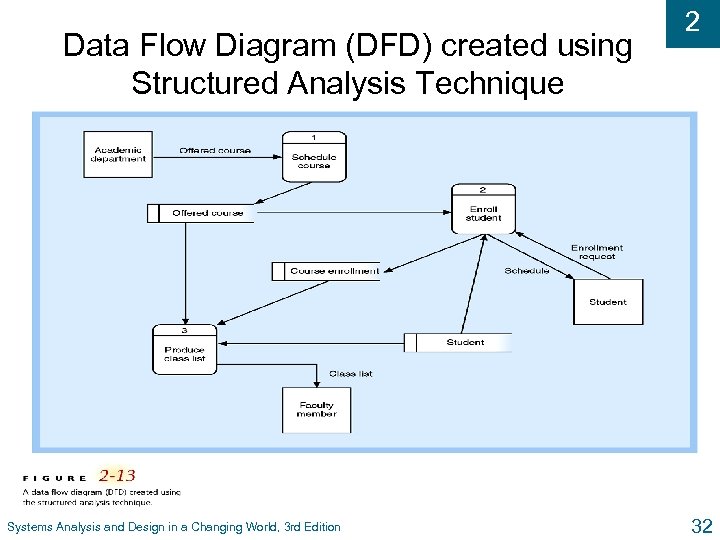 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) created using Structured Analysis Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 32
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) created using Structured Analysis Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 32
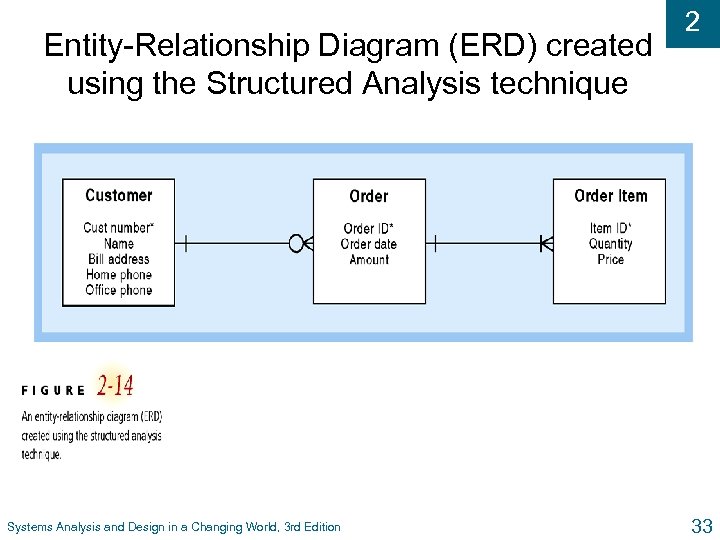 Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) created using the Structured Analysis technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 33
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) created using the Structured Analysis technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 33
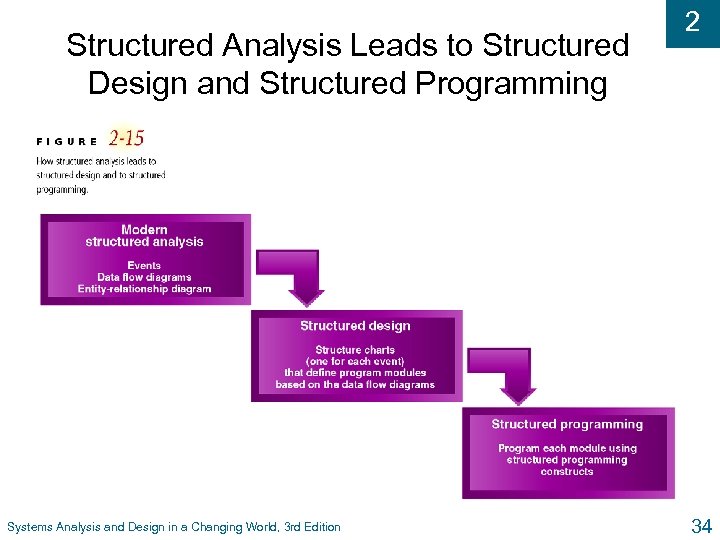 Structured Analysis Leads to Structured Design and Structured Programming Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 34
Structured Analysis Leads to Structured Design and Structured Programming Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 34
 2 Information Engineering (IE) u Refinement to structured development u Methodology with strategic planning, data modeling, automated tools focus u More rigorous and complete than SADT u Uses process dependency diagram u Industry merged key concepts from structured development and information engineering approaches into traditional approach Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 35
2 Information Engineering (IE) u Refinement to structured development u Methodology with strategic planning, data modeling, automated tools focus u More rigorous and complete than SADT u Uses process dependency diagram u Industry merged key concepts from structured development and information engineering approaches into traditional approach Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 35
 2 Object-Oriented Approach u Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks l Objects - things in computer system that can respond to messages l No processes, programs, data entities, or files are defined – just objects u Object-oriented analysis (OOA) l Defines types of objects that do work of system l Shows how objects interact with users to complete tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 36
2 Object-Oriented Approach u Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks l Objects - things in computer system that can respond to messages l No processes, programs, data entities, or files are defined – just objects u Object-oriented analysis (OOA) l Defines types of objects that do work of system l Shows how objects interact with users to complete tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 36
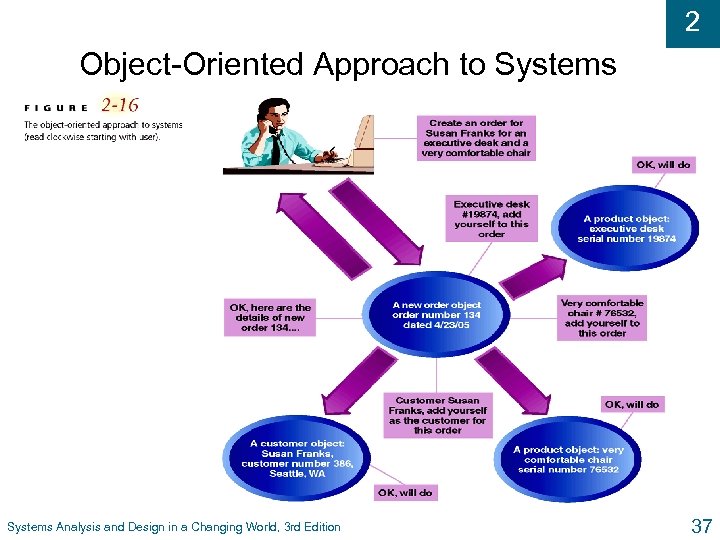 2 Object-Oriented Approach to Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 37
2 Object-Oriented Approach to Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 37
 2 Object-Oriented Approach (continued) u Object-oriented design (OOD) l Defines object types needed to communicate with people and devices in system l Shows how objects interact to complete tasks l Refines each type of object for implementation with specific language of environment u Object-oriented l programming (OOP) Writing statements in programming language to define what each type of object does u Benefits of OOA include naturalness and reuse Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 38
2 Object-Oriented Approach (continued) u Object-oriented design (OOD) l Defines object types needed to communicate with people and devices in system l Shows how objects interact to complete tasks l Refines each type of object for implementation with specific language of environment u Object-oriented l programming (OOP) Writing statements in programming language to define what each type of object does u Benefits of OOA include naturalness and reuse Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 38
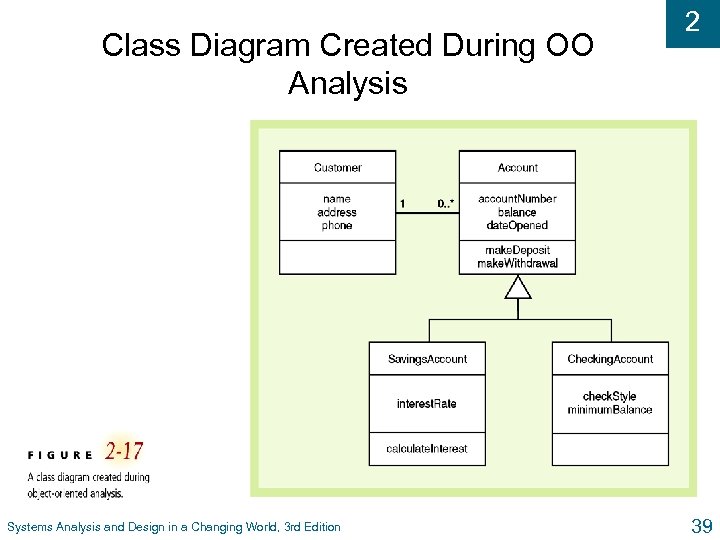 Class Diagram Created During OO Analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 39
Class Diagram Created During OO Analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 39
 2 SDLC Variations u Many l variations of SDLC in practice No matter which one, tasks are similar u Based l SDLC compared to IE compared to UP u Based l on variation of names for phases on emphasis on people User-centered design, participatory design u Based on speed of development l Rapid application development (RAD) l Prototyping Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 40
2 SDLC Variations u Many l variations of SDLC in practice No matter which one, tasks are similar u Based l SDLC compared to IE compared to UP u Based l on variation of names for phases on emphasis on people User-centered design, participatory design u Based on speed of development l Rapid application development (RAD) l Prototyping Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 40
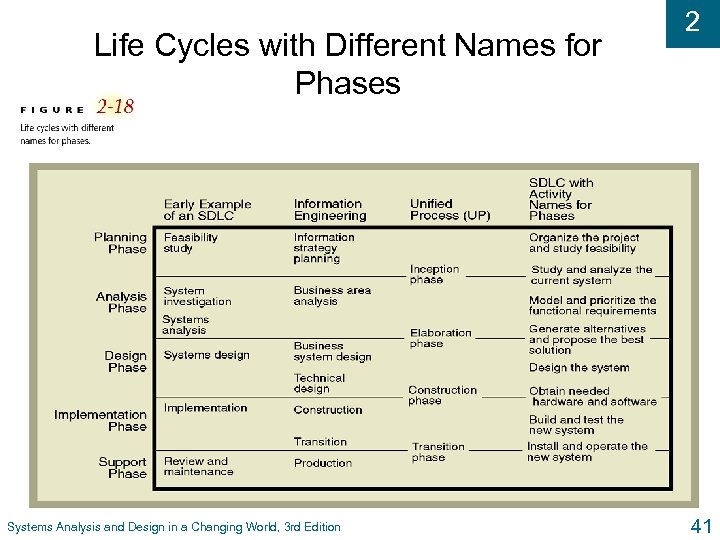 Life Cycles with Different Names for Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 41
Life Cycles with Different Names for Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 41
 2 Current Trends in Development u Spiral Model l Highly iterative approach l Works around the phases (analysis, design, construction, testing, integration with previous prototype component) in a spiral until project is complete l Initial planning is to do just enough analysis to build initial prototype l Each iteration in the spiral addresses greatest risk Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 42
2 Current Trends in Development u Spiral Model l Highly iterative approach l Works around the phases (analysis, design, construction, testing, integration with previous prototype component) in a spiral until project is complete l Initial planning is to do just enough analysis to build initial prototype l Each iteration in the spiral addresses greatest risk Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 42
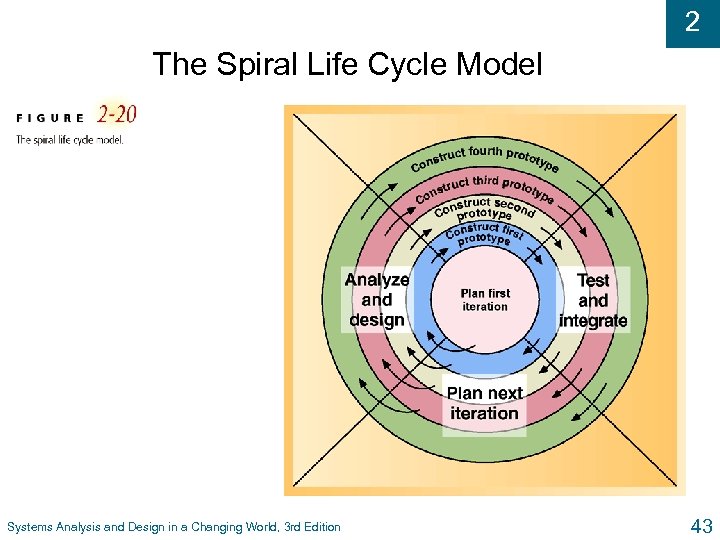 2 The Spiral Life Cycle Model Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 43
2 The Spiral Life Cycle Model Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 43
 2 Extreme Programming (XP) u Recent, lightweight, development approach to keep process simple and efficient u Describes system support needed and required system functionality through informal user stories u Has users describe acceptance tests to demonstrate defined outcomes u Relies on continuous testing and integration, heavy user involvement, programming done by small teams Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 44
2 Extreme Programming (XP) u Recent, lightweight, development approach to keep process simple and efficient u Describes system support needed and required system functionality through informal user stories u Has users describe acceptance tests to demonstrate defined outcomes u Relies on continuous testing and integration, heavy user involvement, programming done by small teams Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 44
 2 The Unified Process (UP) u Object-oriented u Offered l development approach by IBM / Rational Booch, Rumbaugh, Jacobson u Unified Modeling Language (UML) used primarily for modeling u UML u UP l can be used with any OO methodology defines 4 life cycle phases Inception, elaboration, construction, transition Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 45
2 The Unified Process (UP) u Object-oriented u Offered l development approach by IBM / Rational Booch, Rumbaugh, Jacobson u Unified Modeling Language (UML) used primarily for modeling u UML u UP l can be used with any OO methodology defines 4 life cycle phases Inception, elaboration, construction, transition Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 45
 2 The Unified Process (UP) (continued) u Reinforces six best practices l Develop iteratively l Define and manage system requirements l Use component architectures l Create visual models l Verify quality l Control changes Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 46
2 The Unified Process (UP) (continued) u Reinforces six best practices l Develop iteratively l Define and manage system requirements l Use component architectures l Create visual models l Verify quality l Control changes Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 46
 2 Agile Modeling u Hybrid of XP and UP (Scott Ambler) has more models than XP, less documents than UP u Interactive and Incremental Modeling: l Apply right models l Create several models in parallel l Model in small increments u Teamwork: l Get active stakeholder participation l Encourage collective ownership l Model with others and display models publicly Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 47
2 Agile Modeling u Hybrid of XP and UP (Scott Ambler) has more models than XP, less documents than UP u Interactive and Incremental Modeling: l Apply right models l Create several models in parallel l Model in small increments u Teamwork: l Get active stakeholder participation l Encourage collective ownership l Model with others and display models publicly Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 47
 2 Agile Modeling (continued) u Simplicity: l Use simple content l Depict models simply l Use simplest modeling tools u Validation l Consider testability l Prove model is right with code Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 48
2 Agile Modeling (continued) u Simplicity: l Use simple content l Depict models simply l Use simplest modeling tools u Validation l Consider testability l Prove model is right with code Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 48
 2 Tools to Support System Development u Computer-Aided System Engineering (CASE) l Automated tools to improve the speed and quality of system development work l Contains database of information about system called repository u Upper CASE - support for analysis and design u Lower CASE - support for implementation u ICASE - integrated CASE tools Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 49
2 Tools to Support System Development u Computer-Aided System Engineering (CASE) l Automated tools to improve the speed and quality of system development work l Contains database of information about system called repository u Upper CASE - support for analysis and design u Lower CASE - support for implementation u ICASE - integrated CASE tools Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 49
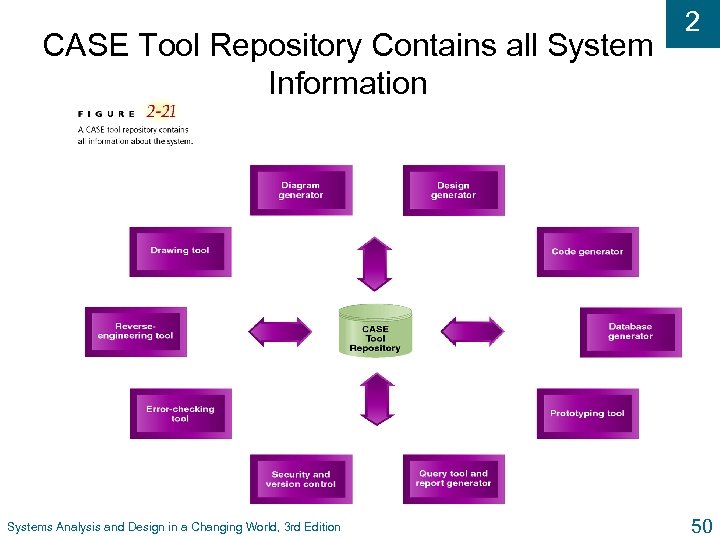 CASE Tool Repository Contains all System Information Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 50
CASE Tool Repository Contains all System Information Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2 50
 2 Summary u Systems development projects are organized around the SDLC u SDLC Phases include project planning, analysis, design, implementation, and support to be completed for each project u Systems developers learn SDLC based on the sequential waterfall approach u In practice, phases overlap and projects contain many iterations of analysis, design, and implementation activities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 51
2 Summary u Systems development projects are organized around the SDLC u SDLC Phases include project planning, analysis, design, implementation, and support to be completed for each project u Systems developers learn SDLC based on the sequential waterfall approach u In practice, phases overlap and projects contain many iterations of analysis, design, and implementation activities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 51
 2 Summary (continued) u All development approaches use a SDLC to manage the project. u Models, techniques, and tools make up a systems development methodology u System development methodologies are based on traditional approach or object-oriented approach u System development methodology provides guidelines to complete every activity in the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 52
2 Summary (continued) u All development approaches use a SDLC to manage the project. u Models, techniques, and tools make up a systems development methodology u System development methodologies are based on traditional approach or object-oriented approach u System development methodology provides guidelines to complete every activity in the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 52
 2 Summary (continued) u Original u Most SDLC was waterfall approach SDLC use iteration across phases u Rapid application development (RAD) goal is to speed up development u Current trends include: spiral model, e. Xtreme Programming (XP), Unified Process (UP) and Agile Modeling u CASE tools are designed to help analysts complete tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 53
2 Summary (continued) u Original u Most SDLC was waterfall approach SDLC use iteration across phases u Rapid application development (RAD) goal is to speed up development u Current trends include: spiral model, e. Xtreme Programming (XP), Unified Process (UP) and Agile Modeling u CASE tools are designed to help analysts complete tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 53


