LlectureNo4_on_Physics_1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 24
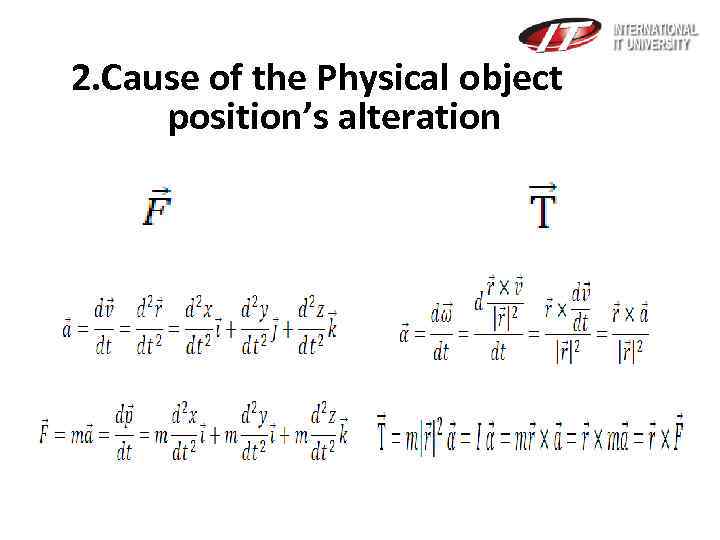
2. Cause of the Physical object position’s alteration
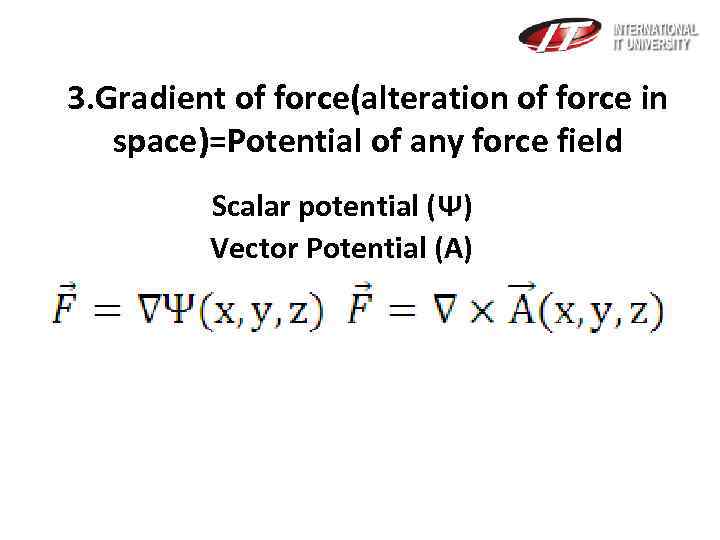
3. Gradient of force(alteration of force in space)=Potential of any force field Scalar potential (Ψ) Vector Potential (A)
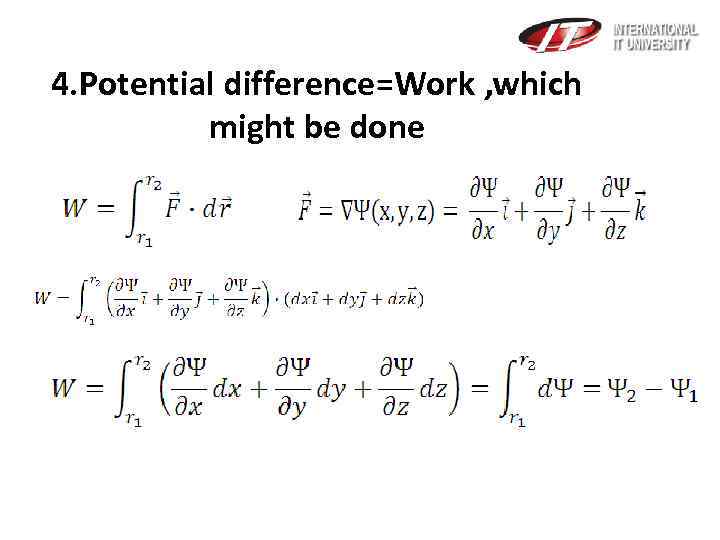
4. Potential difference=Work , which might be done
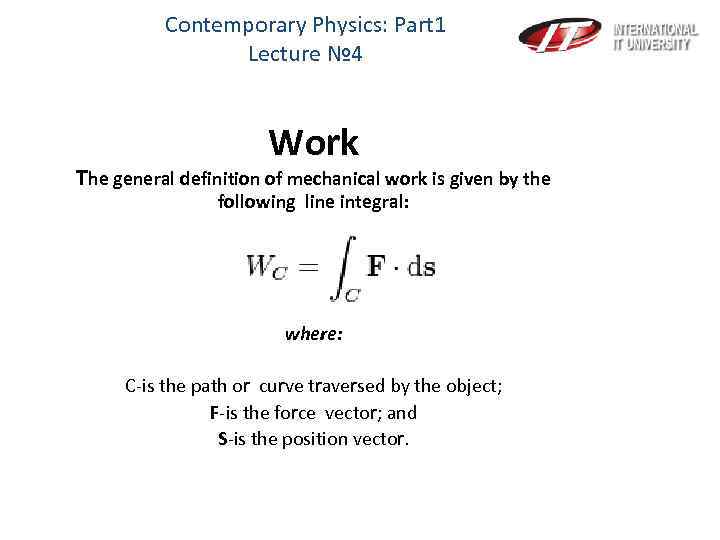
Contemporary Physics: Part 1 Lecture № 4 Work The general definition of mechanical work is given by the following line integral: where: C-is the path or curve traversed by the object; F-is the force vector; and S-is the position vector.

Energy conservation law Energy is subject to the law of conservation of energy. According to this law, energy can neither be created (produced) nor destroyed by itself. It can only be transformed. According to energy conservation law the total inflow of energy into a system must equal the total outflow of energy from the system, plus the change in the energy contained within the system.

1. Energy and Work In physics, mechanical work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Like energy, it is a scalar quantity, with SI units of joules. The term work was first coined in 1826 by the French mathematician Gaspard Gustave Coriolis

Kinetic energy -Work Kinetic energy, symbols Ek, T or K, is the work required to accelerate an object to a given speed. Indeed, calculating this work one easily obtains the following:

Elastic potential energy-Work Hook’s law The elastic potential energy stored in a stretched spring can be calculated by finding the work necessary to stretch the spring a distance x from its un-stretched length: F = − kx
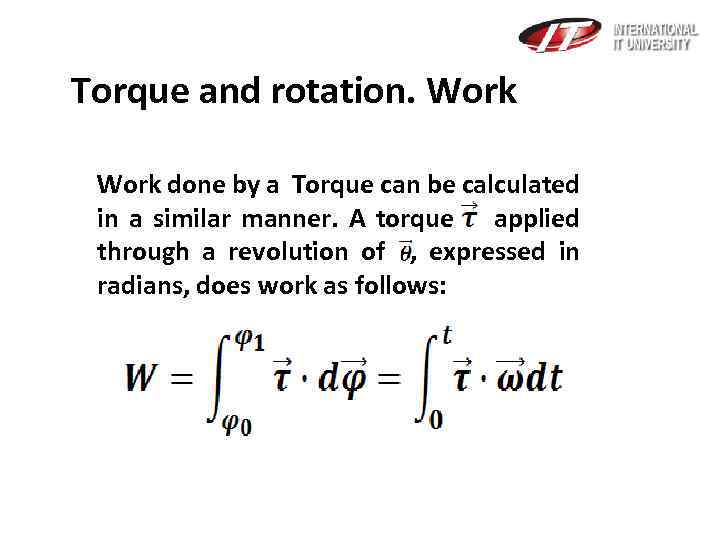
Torque and rotation. Work done by a Torque can be calculated in a similar manner. A torque applied through a revolution of , expressed in radians, does work as follows:
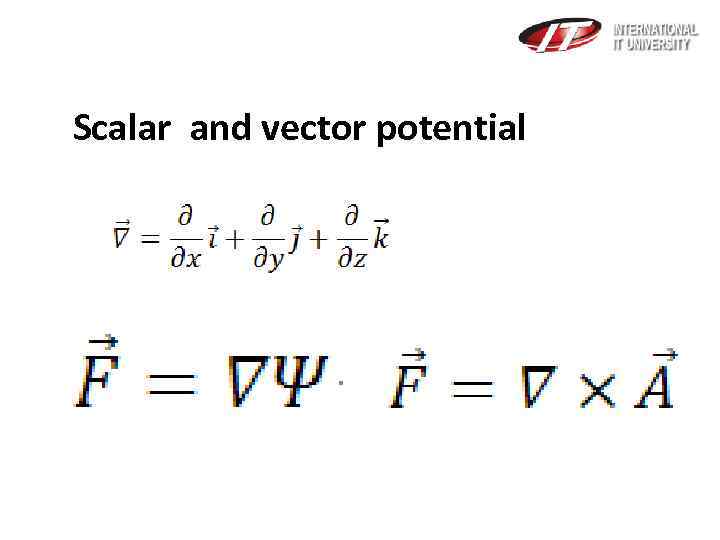
Scalar and vector potential .
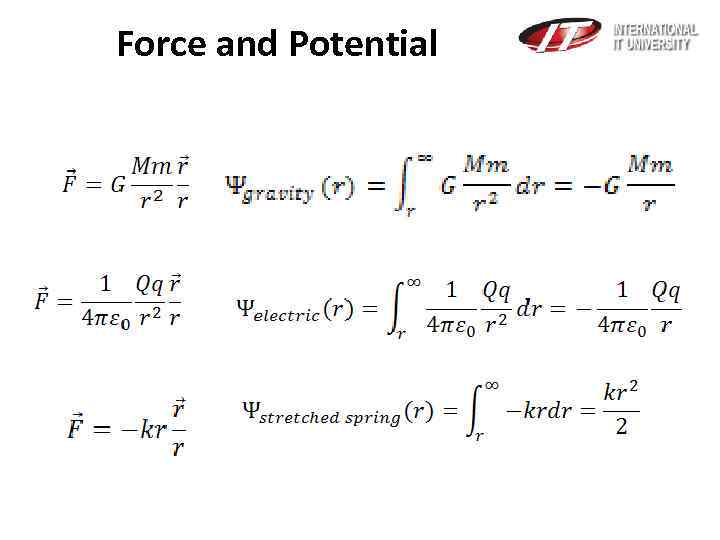
Force and Potential
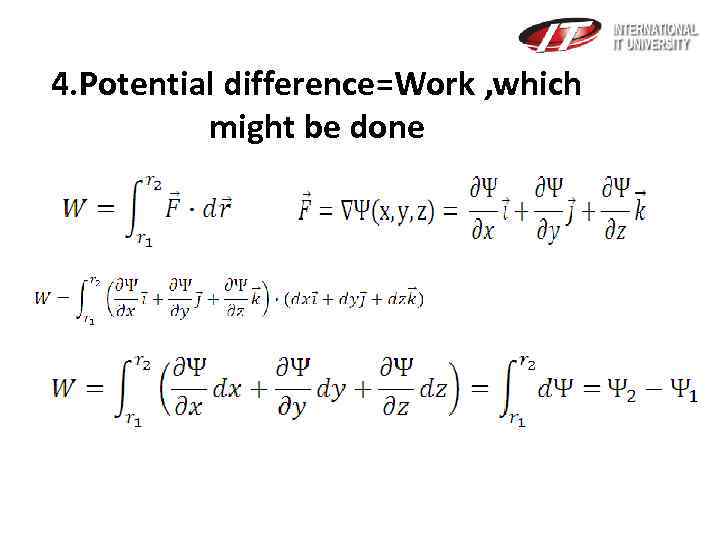
4. Potential difference=Work , which might be done
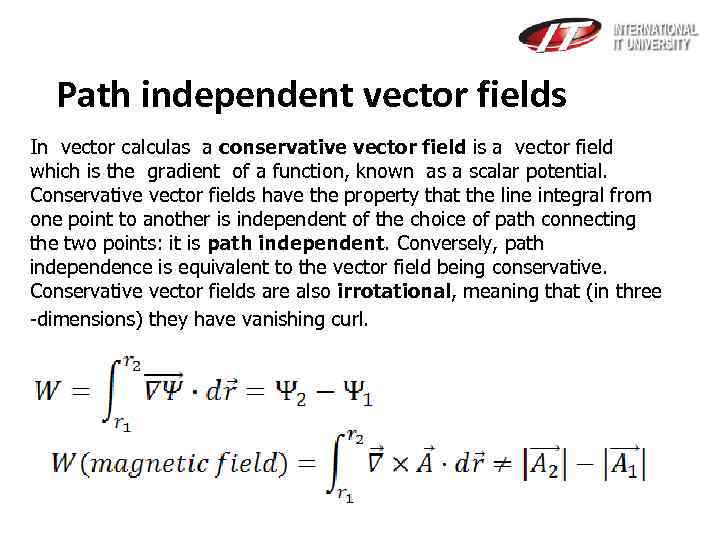
Path independent vector fields In vector calculas a conservative vector field is a vector field which is the gradient of a function, known as a scalar potential. Conservative vector fields have the property that the line integral from one point to another is independent of the choice of path connecting the two points: it is path independent. Conversely, path independence is equivalent to the vector field being conservative. Conservative vector fields are also irrotational, meaning that (in three -dimensions) they have vanishing curl.

Gravitational Force Assuming SI units , F is measured in newtons (N), m 1 and m 2 in kilograms (kg), r in meters (m), and the constant G is approximately equal to 6. 674× 10− 11 N m 2 kg− 2
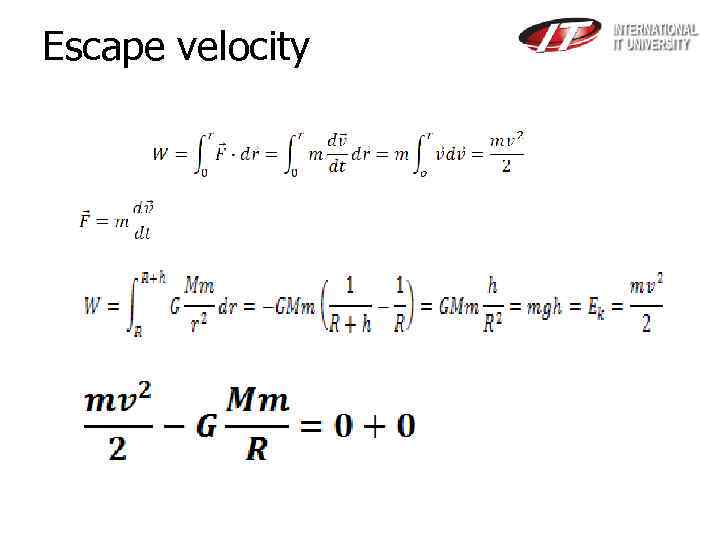
Escape velocity
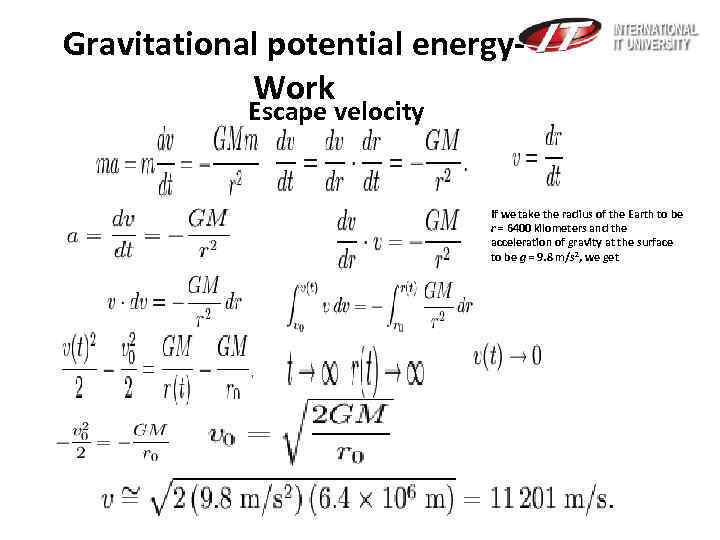
Gravitational potential energy. Work Escape velocity If we take the radius of the Earth to be r = 6400 kilometers and the acceleration of gravity at the surface to be g = 9. 8 m/s 2, we get
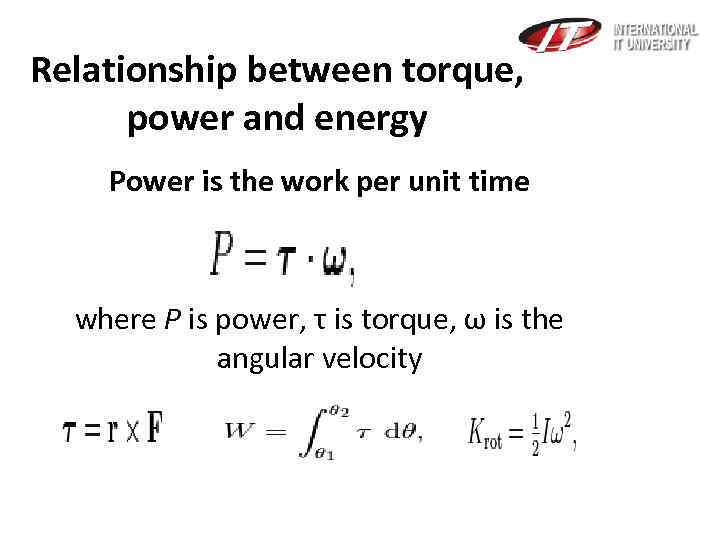
Relationship between torque, power and energy Power is the work per unit time where P is power, τ is torque, ω is the angular velocity

Quiz If A is vector then equals 1. 2. 3. 4. 0 1 -1 uncertain

Quiz If A is vector then equals 1. 2. 3. 4. 0 1 -1 uncertain

Quiz The point mass is: 1. The size of the physical object might be neglected with the size of the interacting distance 2. The size of the physical object might not be neglected with the size of the interacting distance 3. The size of the physical object might be of the same order compared with the size of the interacting distance

Quiz Gravitational and electric forces are : 1. Of the same order 2. Differ in 100 times 3. times greater 4. times less 5. Absolutely equal

Quiz Elementary Charge e : 1. Depends on system of reference 2. Does not depend on system of reference

Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. Electron mass : Depends on the system of reference Does not depend on the system of reference Inversely proportional to its speed Proportional to its speed

Quiz The angular and tangential velocity: 1. Equal 2. Different
LlectureNo4_on_Physics_1.pptx