25fe4e0f51dffd42caec292189512def.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 100
 2 A generic and modular platform for automated sequence processing and annotation Arthur Gruber Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Universidade de São Paulo AG-ICB-USP
2 A generic and modular platform for automated sequence processing and annotation Arthur Gruber Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Universidade de São Paulo AG-ICB-USP
 2 Sequence processing and annotation • Analyzing and processing sequencing reads is a tedious and error-prone job • Multistep process • All sequences are submitted to the same processing steps • Sequences processed by a given step are the input for the next one • Require different programs • Integrated system – PIPELINE AG-ICB-USP
2 Sequence processing and annotation • Analyzing and processing sequencing reads is a tedious and error-prone job • Multistep process • All sequences are submitted to the same processing steps • Sequences processed by a given step are the input for the next one • Require different programs • Integrated system – PIPELINE AG-ICB-USP
 2 Problem: how to build pipelines • Creating scripts for new pipelines involves good programming knowledge • Once created, most pipelines are difficult to change and customize • Many programs must be used • Phred, Cross_match, Phrap, CAP 3, Blast, HMMer, Interpro. Scan, TMHMM, etc. AG-ICB-USP
2 Problem: how to build pipelines • Creating scripts for new pipelines involves good programming knowledge • Once created, most pipelines are difficult to change and customize • Many programs must be used • Phred, Cross_match, Phrap, CAP 3, Blast, HMMer, Interpro. Scan, TMHMM, etc. AG-ICB-USP
 2 Problem: how to build pipelines • Each program needs a specific environment to work (e. g. directories with specific names) • Each program produces output in different ways and formats • Integrating programs is a hard task AG-ICB-USP
2 Problem: how to build pipelines • Each program needs a specific environment to work (e. g. directories with specific names) • Each program produces output in different ways and formats • Integrating programs is a hard task AG-ICB-USP
 Solution: creating an environment to build pipelines 2 Requirements: • Abstract the environment of each program • Abstract output format • Easily specify “coupling” of different programs • Document how the pipe was built • • Easy to inspect and monitor Easy to store (e. g. in a database) AG-ICB-USP
Solution: creating an environment to build pipelines 2 Requirements: • Abstract the environment of each program • Abstract output format • Easily specify “coupling” of different programs • Document how the pipe was built • • Easy to inspect and monitor Easy to store (e. g. in a database) AG-ICB-USP
 2 EGene Aims and characteristics: • To develop a simple to use and configure platform for pipeline construction • Big sequencing centers already have sophisticated pipelines, but many are not published and/or publicly available • They are too complex for the small-/mid-sized labs • Platform should be generic • Useful for any sequencing project • Platform should provide components for the most common tasks • New components should be easy to develop AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene Aims and characteristics: • To develop a simple to use and configure platform for pipeline construction • Big sequencing centers already have sophisticated pipelines, but many are not published and/or publicly available • They are too complex for the small-/mid-sized labs • Platform should be generic • Useful for any sequencing project • Platform should provide components for the most common tasks • New components should be easy to develop AG-ICB-USP
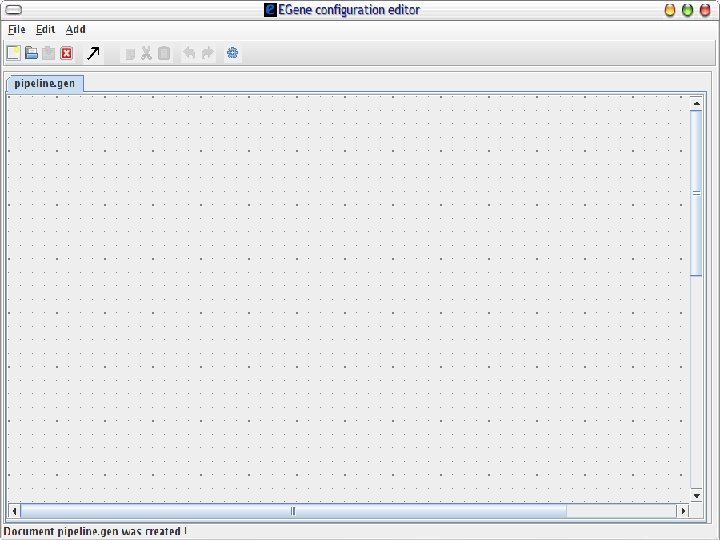
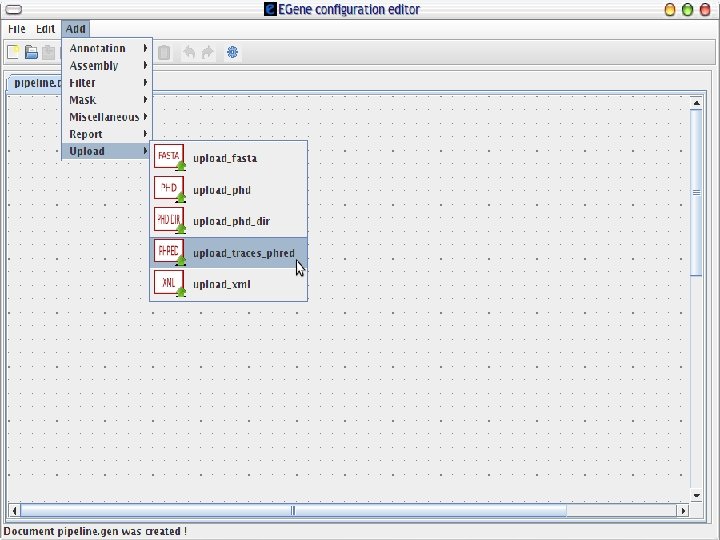
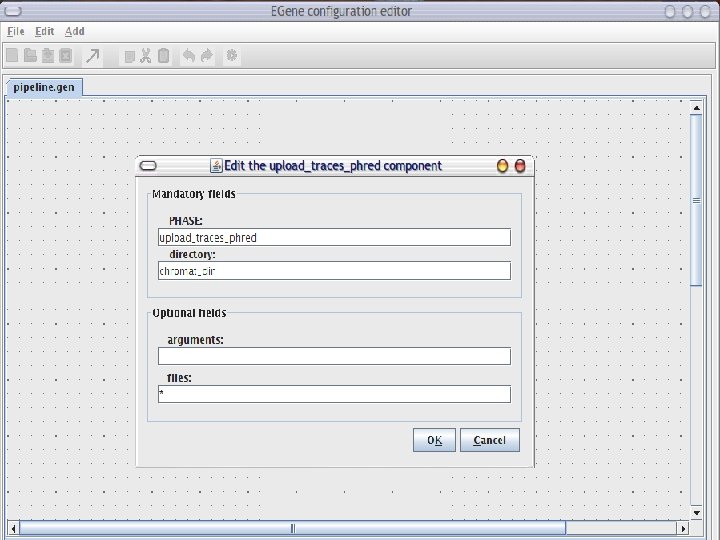
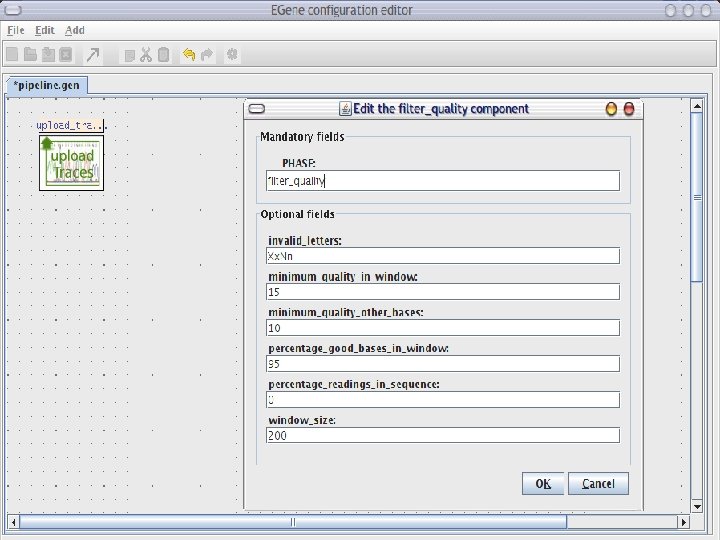
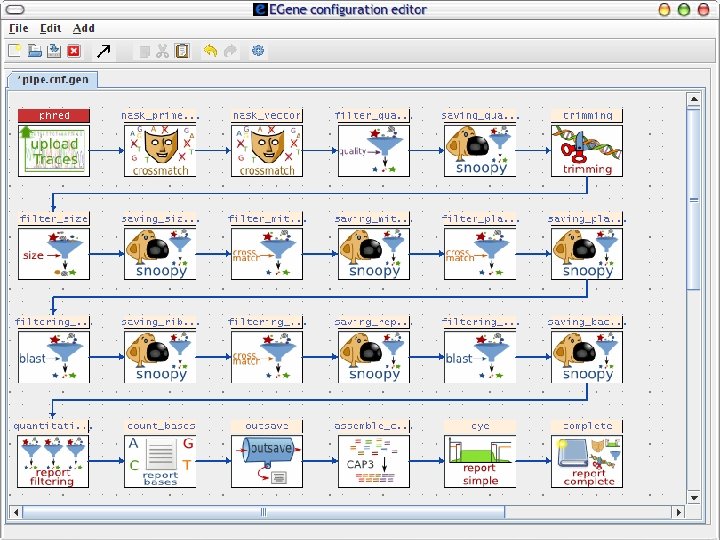
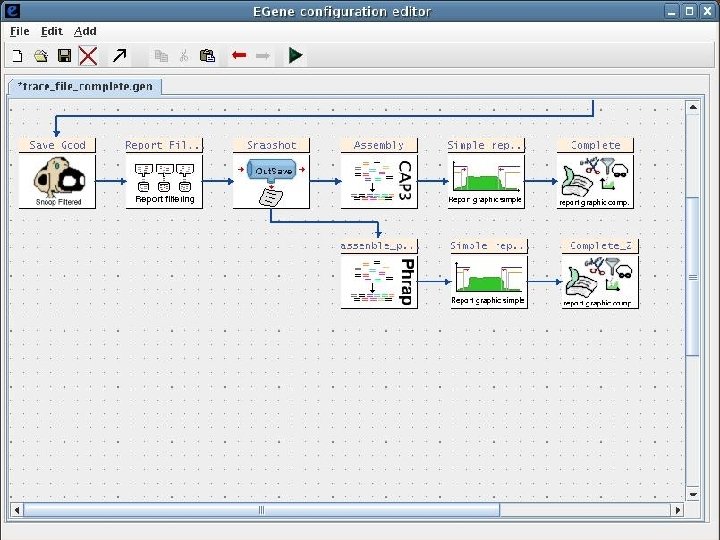
 2 EGene: a generic platform for pipeline construction Characteristics: • Written in Perl language • Modular • Easy to build specific components to interact with third-party programs • EGene components can be integrated to fulfill user-specific needs • Co. Ed – a graphical configuration editor written in Java – user-friendly interface AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene: a generic platform for pipeline construction Characteristics: • Written in Perl language • Modular • Easy to build specific components to interact with third-party programs • EGene components can be integrated to fulfill user-specific needs • Co. Ed – a graphical configuration editor written in Java – user-friendly interface AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
 AG-ICB-USP
AG-ICB-USP
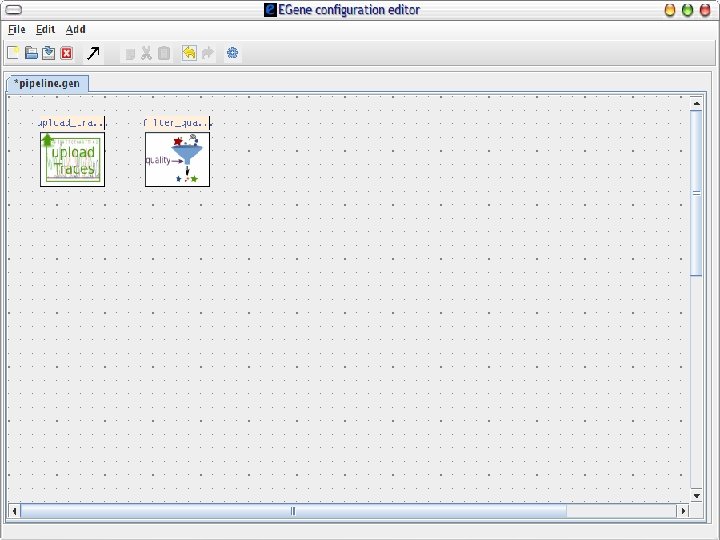
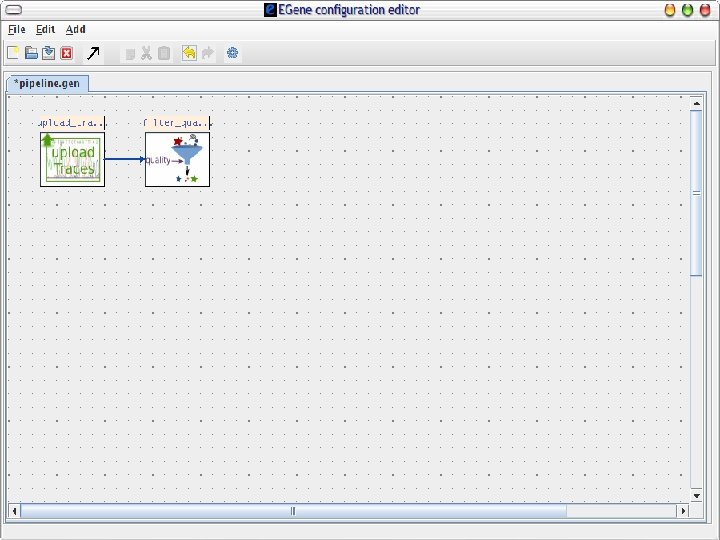
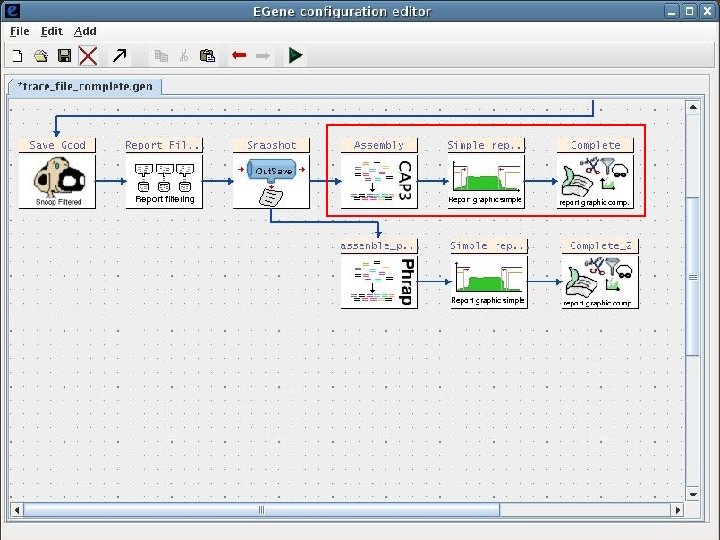
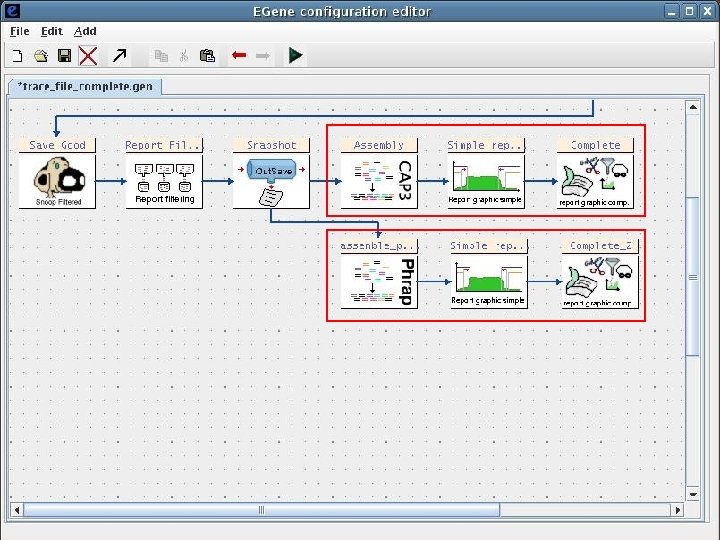
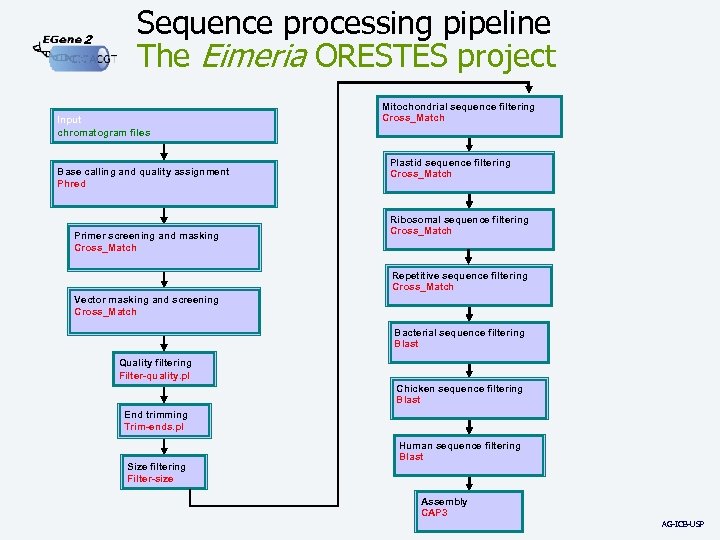 2 Sequence processing pipeline The Eimeria ORESTES project Input chromatogram files Base calling and quality assignment Phred Primer screening and masking Cross_Match Mitochondrial sequence filtering Cross_Match Plastid sequence filtering Cross_Match Ribosomal sequence filtering Cross_Match Repetitive sequence filtering Cross_Match Vector masking and screening Cross_Match Bacterial sequence filtering Blast Quality filtering Filter-quality. pl Chicken sequence filtering Blast End trimming Trim-ends. pl Size filtering Filter-size Human sequence filtering Blast Assembly CAP 3 AG-ICB-USP
2 Sequence processing pipeline The Eimeria ORESTES project Input chromatogram files Base calling and quality assignment Phred Primer screening and masking Cross_Match Mitochondrial sequence filtering Cross_Match Plastid sequence filtering Cross_Match Ribosomal sequence filtering Cross_Match Repetitive sequence filtering Cross_Match Vector masking and screening Cross_Match Bacterial sequence filtering Blast Quality filtering Filter-quality. pl Chicken sequence filtering Blast End trimming Trim-ends. pl Size filtering Filter-size Human sequence filtering Blast Assembly CAP 3 AG-ICB-USP
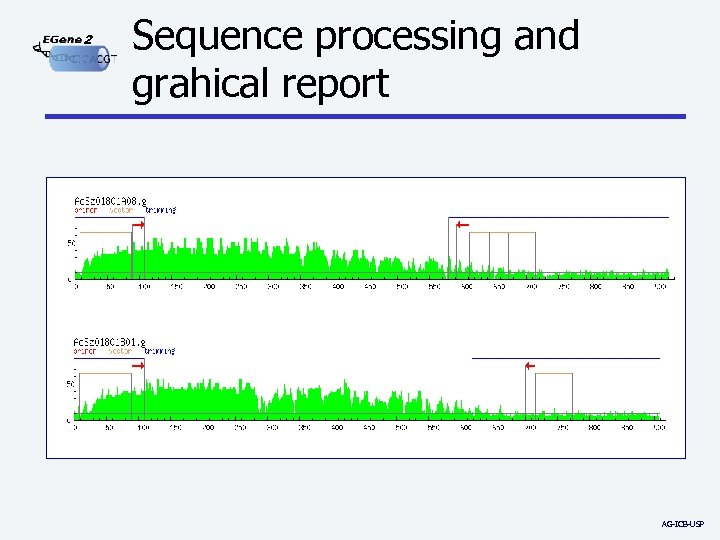 2 Sequence processing and grahical report AG-ICB-USP
2 Sequence processing and grahical report AG-ICB-USP
 2 How to get EGene Internet site: http: //www. coccidia. icb. usp. br/egene - EGene is distributed under the GNU General Public License - EGene is Open Source AG-ICB-USP
2 How to get EGene Internet site: http: //www. coccidia. icb. usp. br/egene - EGene is distributed under the GNU General Public License - EGene is Open Source AG-ICB-USP
 2 How to get EGene Internet site: http: //www. coccidia. icb. usp. br/egene - EGene is distributed under the GNU General Public License - EGene is Open Source AG-ICB-USP
2 How to get EGene Internet site: http: //www. coccidia. icb. usp. br/egene - EGene is distributed under the GNU General Public License - EGene is Open Source AG-ICB-USP
 2 • • Recent developments Incorporation of forks Enhancement of the data model – incorporation of annotation evidences Development of annotation components Evidence-based annotation AG-ICB-USP
2 • • Recent developments Incorporation of forks Enhancement of the data model – incorporation of annotation evidences Development of annotation components Evidence-based annotation AG-ICB-USP
 2 • • Genome annotation Annotation is the process of adding information to DNA sequence. The information usually has a DNA coordinate. Features could be repeats, genes, promoters, protein domains, etc. Features can be cross-referenced to other databases (e. g. Pfam/Pubmed) AG-ICB-USP
2 • • Genome annotation Annotation is the process of adding information to DNA sequence. The information usually has a DNA coordinate. Features could be repeats, genes, promoters, protein domains, etc. Features can be cross-referenced to other databases (e. g. Pfam/Pubmed) AG-ICB-USP
 2 • • Genome annotation Annotation is the process of adding information to DNA sequence. The information usually has a DNA coordinate. Features could be repeats, genes, promoters, protein domains, etc. Features can be cross-referenced to other databases (e. g. Pfam/Pubmed) AG-ICB-USP
2 • • Genome annotation Annotation is the process of adding information to DNA sequence. The information usually has a DNA coordinate. Features could be repeats, genes, promoters, protein domains, etc. Features can be cross-referenced to other databases (e. g. Pfam/Pubmed) AG-ICB-USP
 2 Annotation file A typical annotation file contains: A header with: • • • Information about the sequence Organism Authors References Comments A feature table containing • Sequence features and co-ordinates AG-ICB-USP
2 Annotation file A typical annotation file contains: A header with: • • • Information about the sequence Organism Authors References Comments A feature table containing • Sequence features and co-ordinates AG-ICB-USP
 2 • • Feature table format Flatfile format Format definition available at http: //www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/projects/collab/FT/ • Covers DDBJ/EMBL/Gen. Bank • Defines all accepted annotation terms and hierarchy AG-ICB-USP
2 • • Feature table format Flatfile format Format definition available at http: //www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/projects/collab/FT/ • Covers DDBJ/EMBL/Gen. Bank • Defines all accepted annotation terms and hierarchy AG-ICB-USP
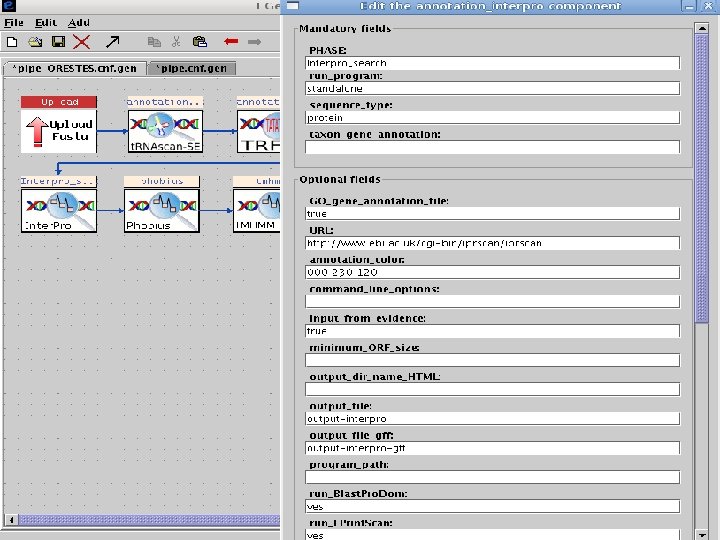
 2 Incorporating annotation • EGene’s data model was enriched to incorporate annotation information into the representation of the sequences • All collected data is converted into a proprietary XML format • The XML can be easily converted into different annotation formats: Feature Table, GFF 3, etc. • We provide some converters and new ones can be easily implemented AG-ICB-USP
2 Incorporating annotation • EGene’s data model was enriched to incorporate annotation information into the representation of the sequences • All collected data is converted into a proprietary XML format • The XML can be easily converted into different annotation formats: Feature Table, GFF 3, etc. • We provide some converters and new ones can be easily implemented AG-ICB-USP
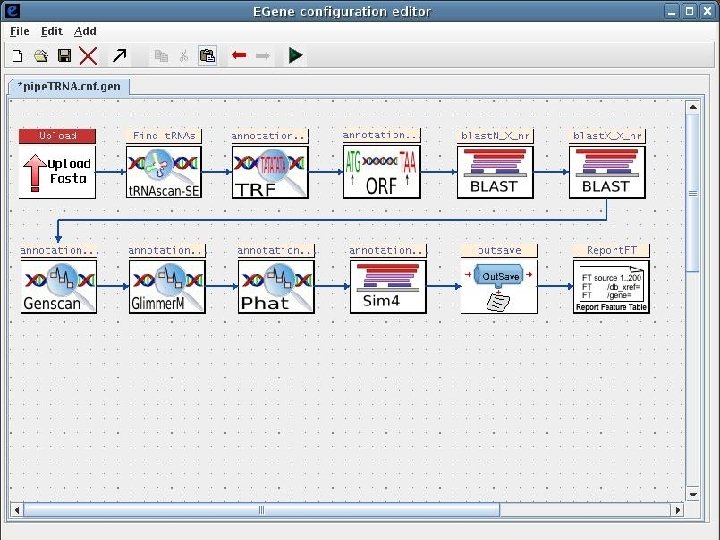
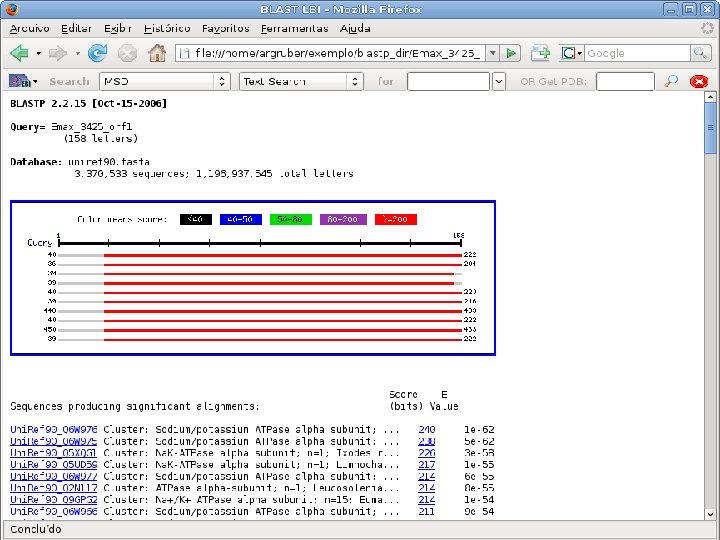
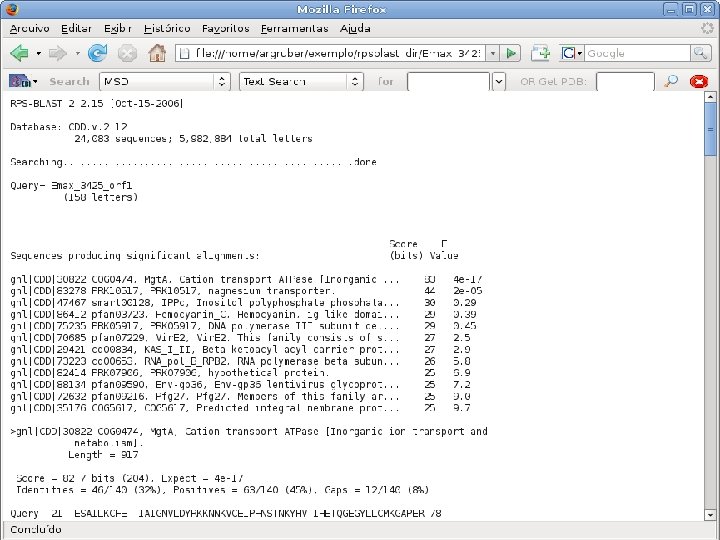
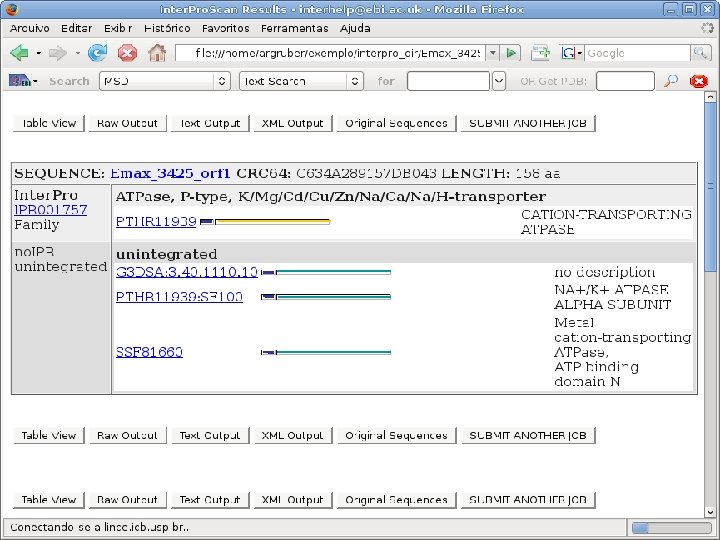
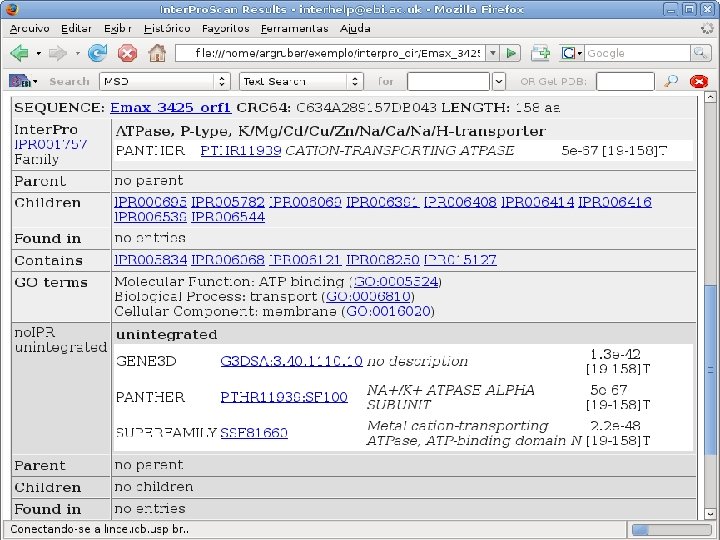
 2 Annotation components • A comprehensive set of annotation components has been implemented: • • ORF finding and translation Tandem repeats finding: TRF, String, m. REPS t. RNA finding: t. RNAscan-SE Gene Prediction: Genscan, Glimmer. M, Glimmer. HMM, Twinscan, Phat, ESTscan, SNAP Motif finding: HMMer x Pfam, RPS-BLAST, Interpro. Scan Similarity search: BLAST EST mapping: Sim 4, Exonerate AG-ICB-USP
2 Annotation components • A comprehensive set of annotation components has been implemented: • • ORF finding and translation Tandem repeats finding: TRF, String, m. REPS t. RNA finding: t. RNAscan-SE Gene Prediction: Genscan, Glimmer. M, Glimmer. HMM, Twinscan, Phat, ESTscan, SNAP Motif finding: HMMer x Pfam, RPS-BLAST, Interpro. Scan Similarity search: BLAST EST mapping: Sim 4, Exonerate AG-ICB-USP
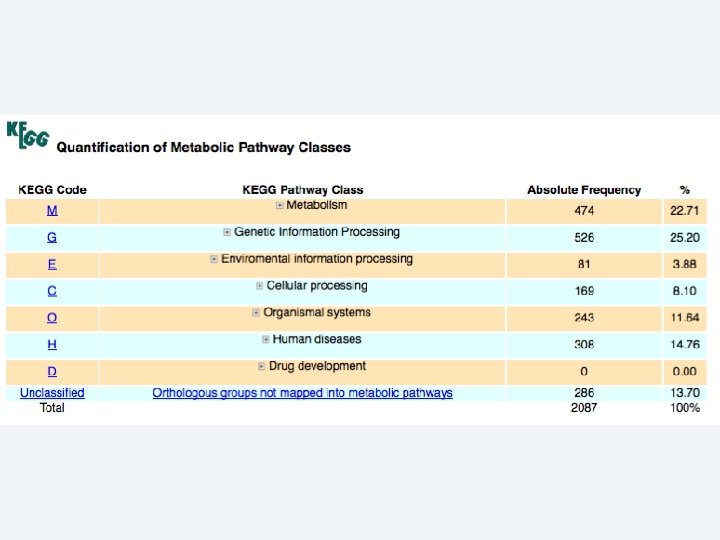
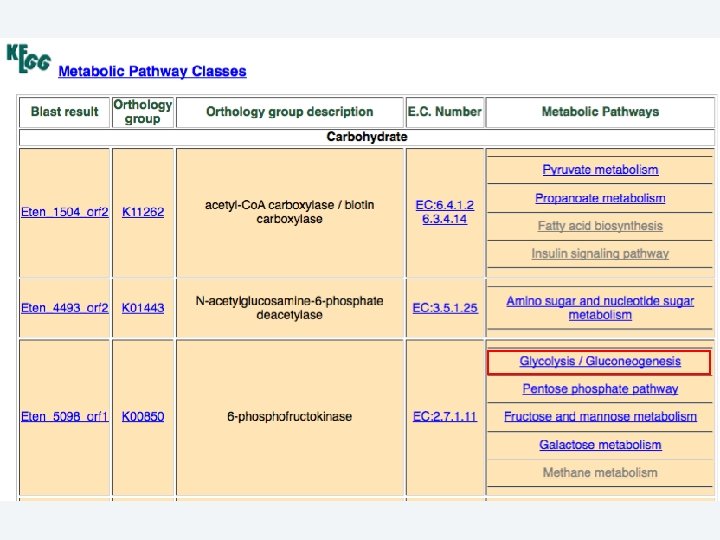
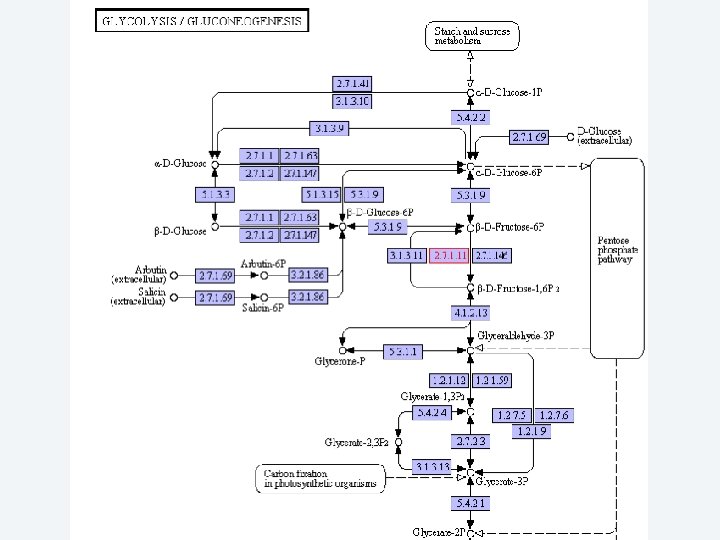
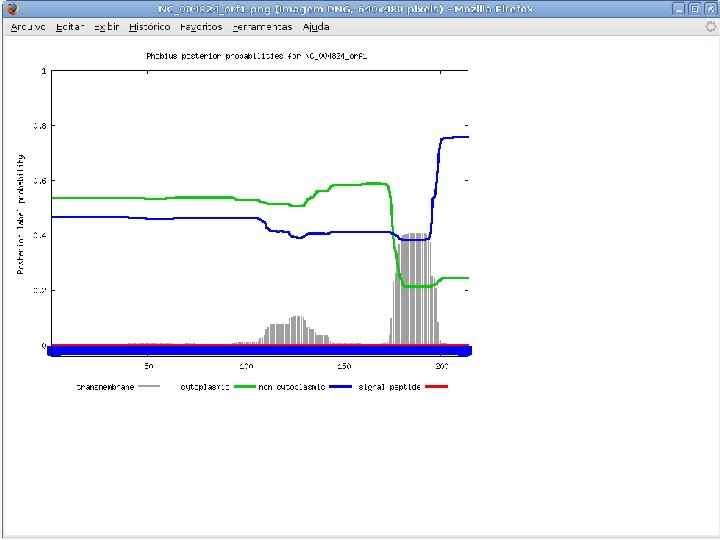
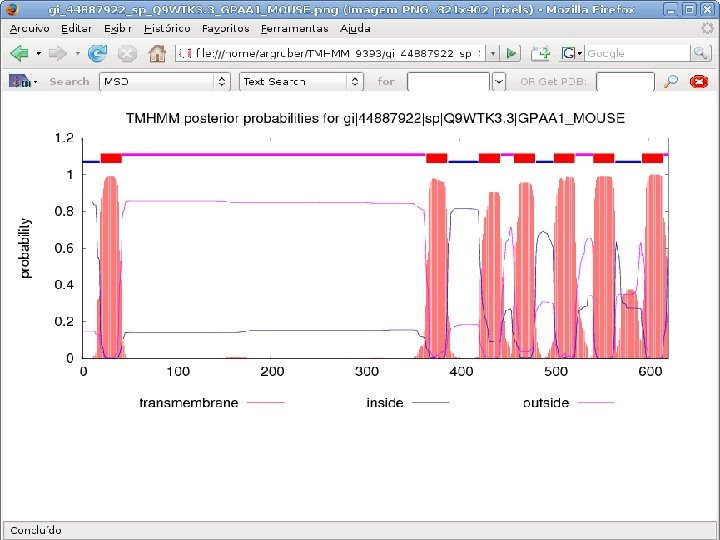
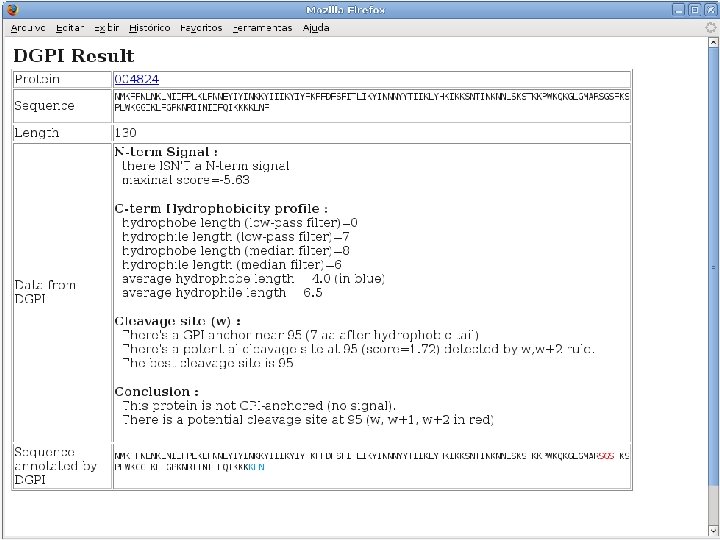
 2 Annotation components • A comprehensive set of annotation components has been implemented: • • • Transmembrane domain finding: TMHMM, Phobius Signal peptide: Signal. P, Phobius GPI anchor: DGPI GO mapping and quantification Orthology assignment and quantification: COG/KOG Pathway mapping: KEGG Annotation visualization with GBrowse: web inspection Annotation report generation: feature table, GFF 3 Web site generation: HTML/PHP AG-ICB-USP
2 Annotation components • A comprehensive set of annotation components has been implemented: • • • Transmembrane domain finding: TMHMM, Phobius Signal peptide: Signal. P, Phobius GPI anchor: DGPI GO mapping and quantification Orthology assignment and quantification: COG/KOG Pathway mapping: KEGG Annotation visualization with GBrowse: web inspection Annotation report generation: feature table, GFF 3 Web site generation: HTML/PHP AG-ICB-USP
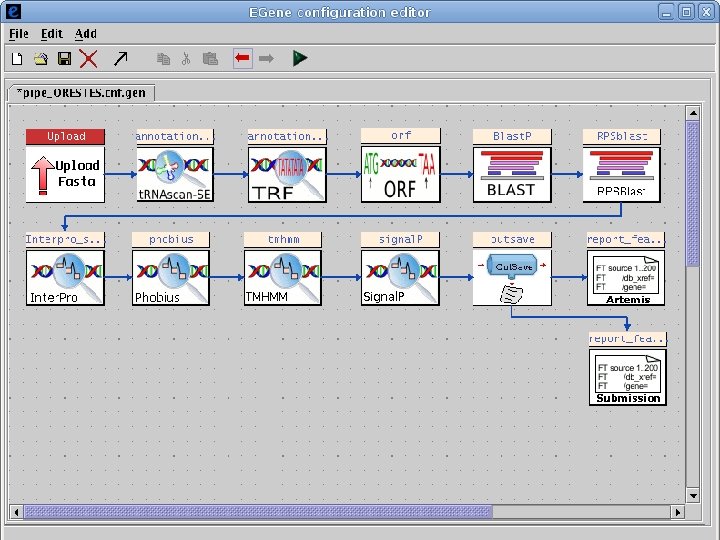
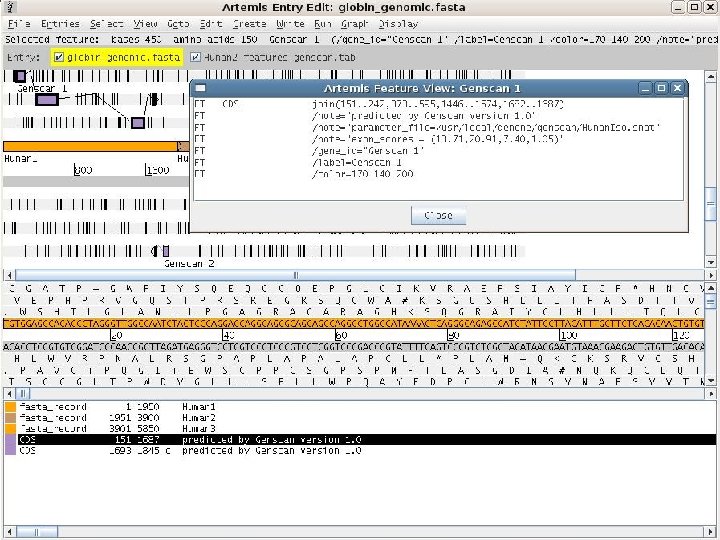
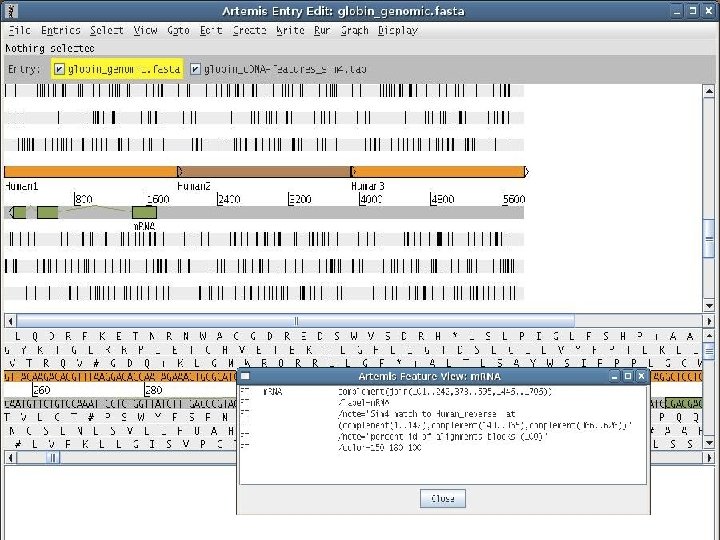
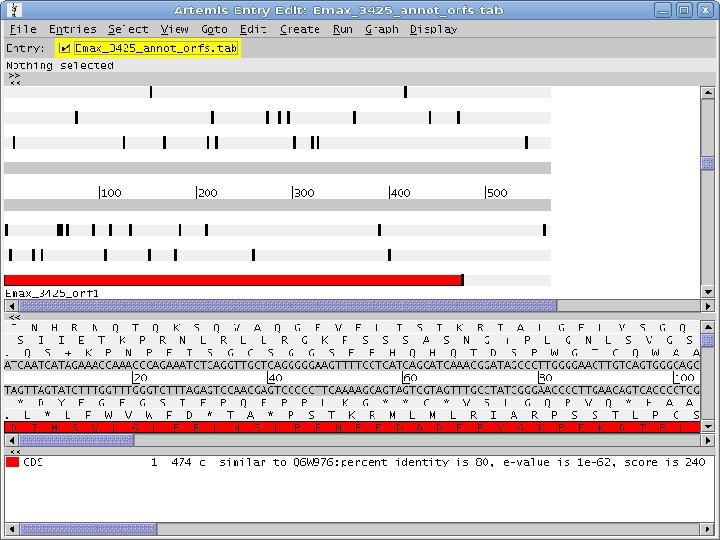
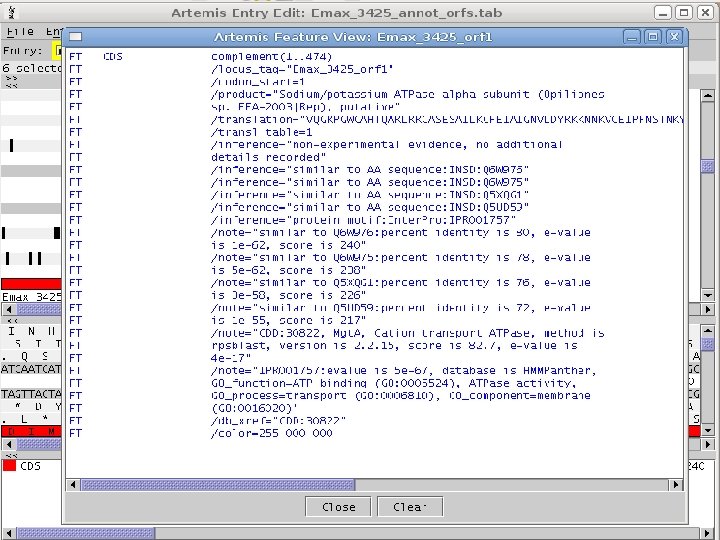
 2 EGene generates annotation files that can be inspected using regular editors (Artemis, Apollo, etc. ) AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene generates annotation files that can be inspected using regular editors (Artemis, Apollo, etc. ) AG-ICB-USP
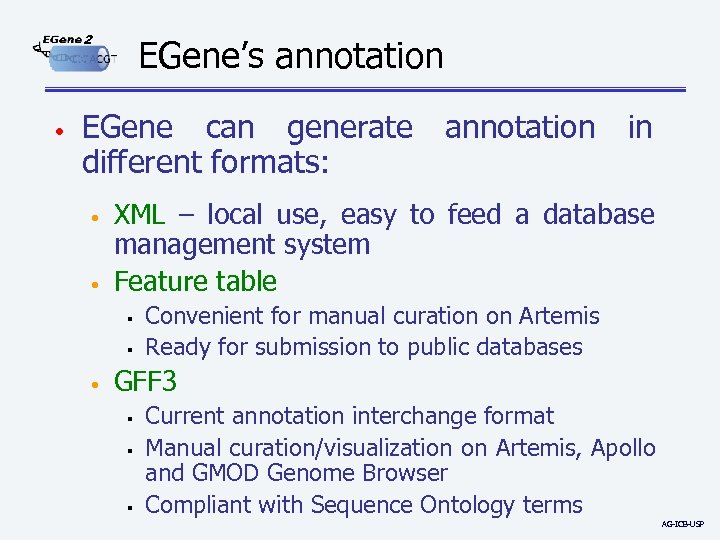 2 • EGene’s annotation EGene can generate different formats: • • in XML – local use, easy to feed a database management system Feature table § § • annotation Convenient for manual curation on Artemis Ready for submission to public databases GFF 3 § § § Current annotation interchange format Manual curation/visualization on Artemis, Apollo and GMOD Genome Browser Compliant with Sequence Ontology terms AG-ICB-USP
2 • EGene’s annotation EGene can generate different formats: • • in XML – local use, easy to feed a database management system Feature table § § • annotation Convenient for manual curation on Artemis Ready for submission to public databases GFF 3 § § § Current annotation interchange format Manual curation/visualization on Artemis, Apollo and GMOD Genome Browser Compliant with Sequence Ontology terms AG-ICB-USP
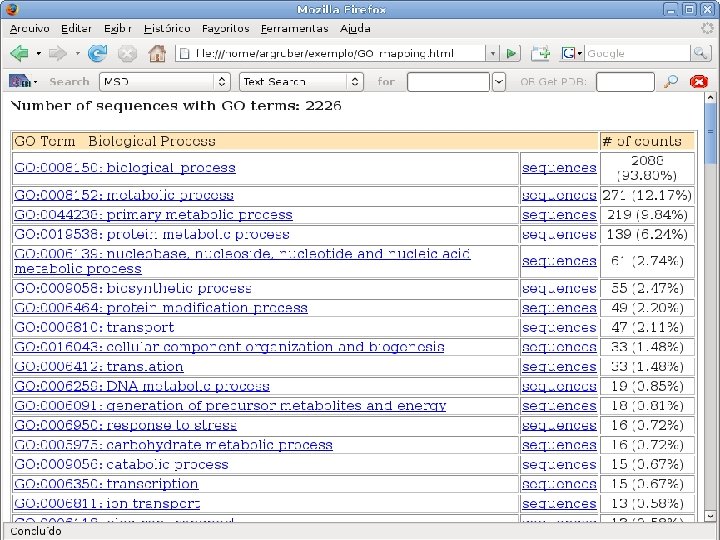
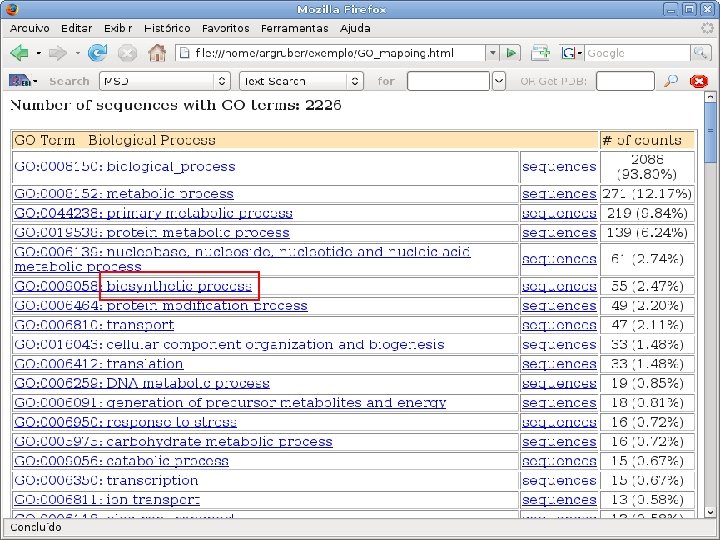
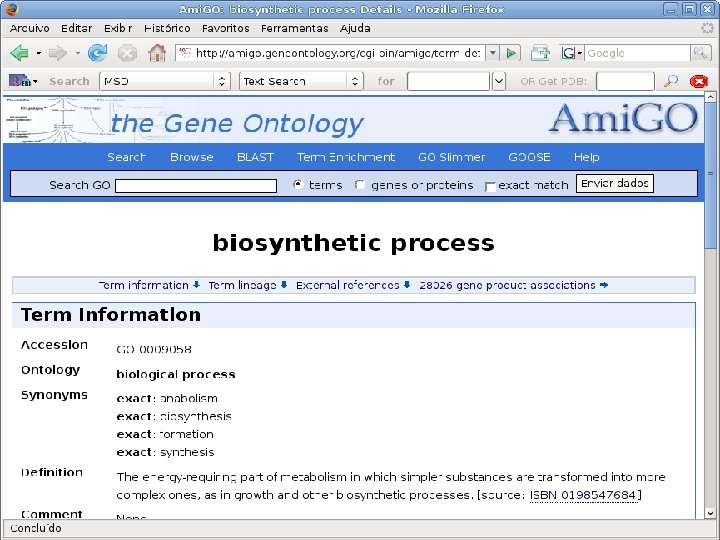
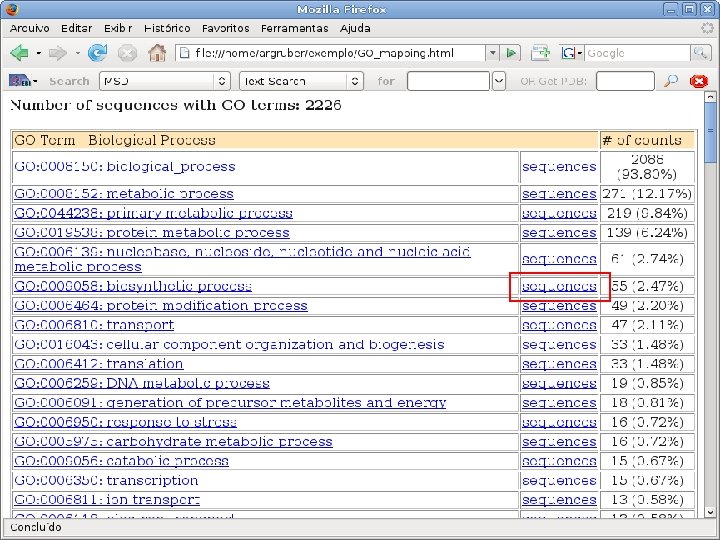
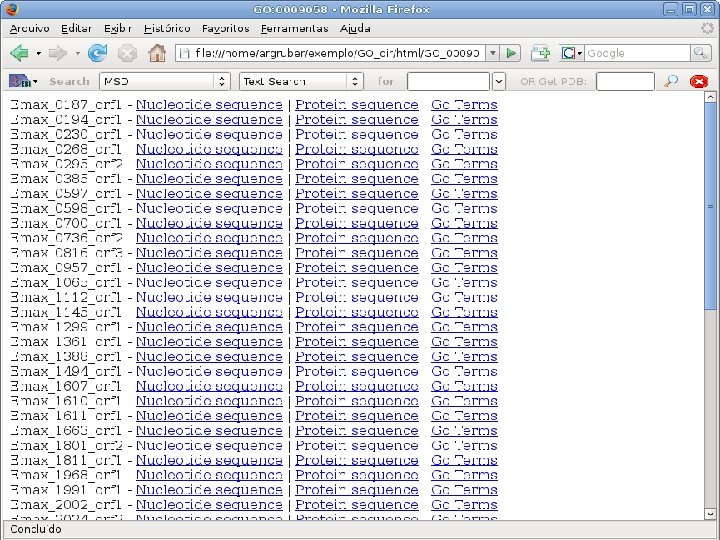
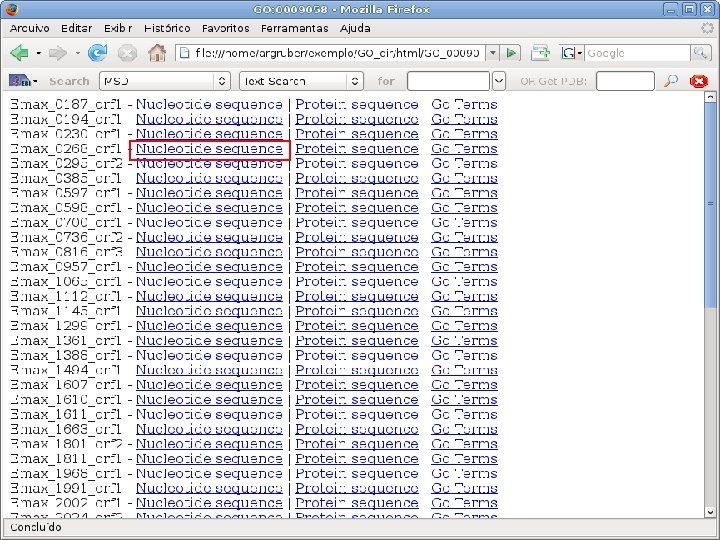
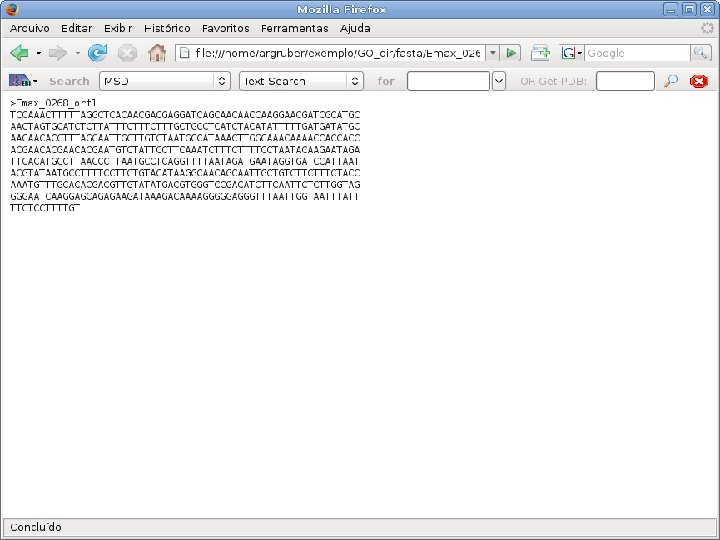
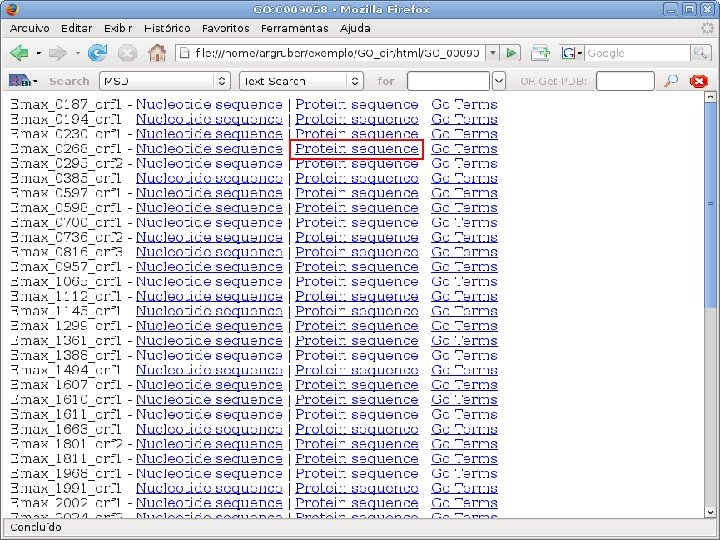
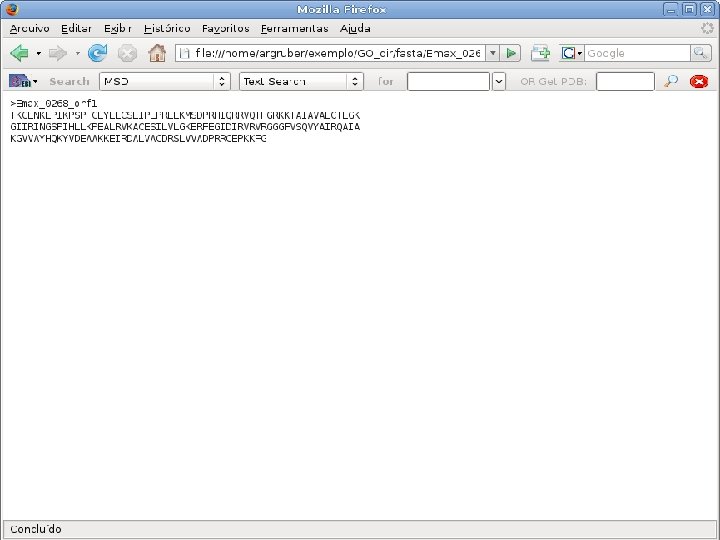
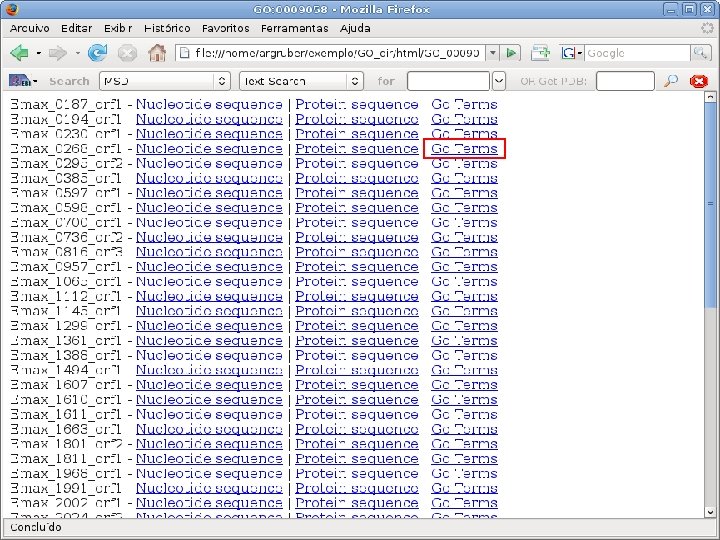
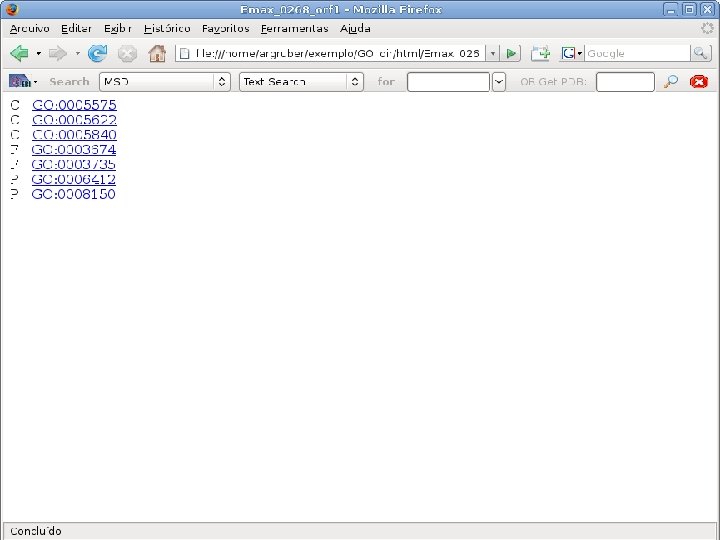
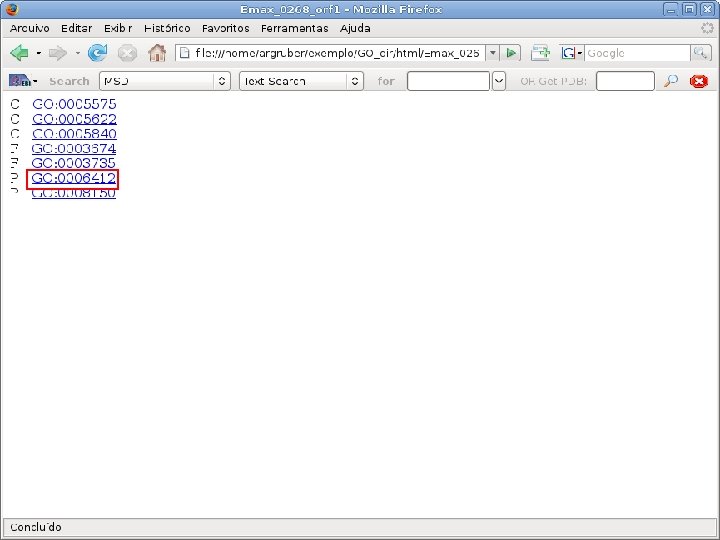
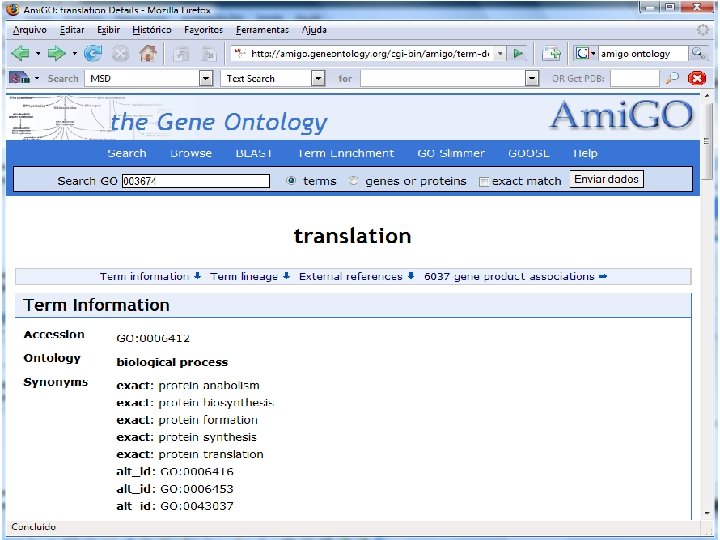
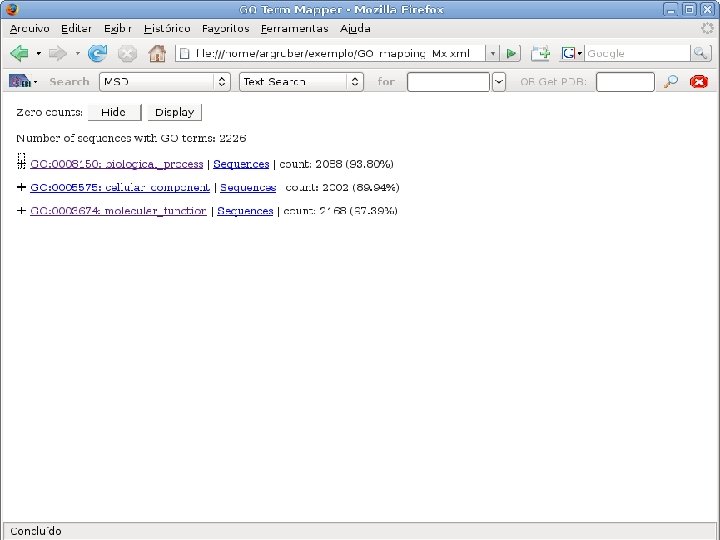
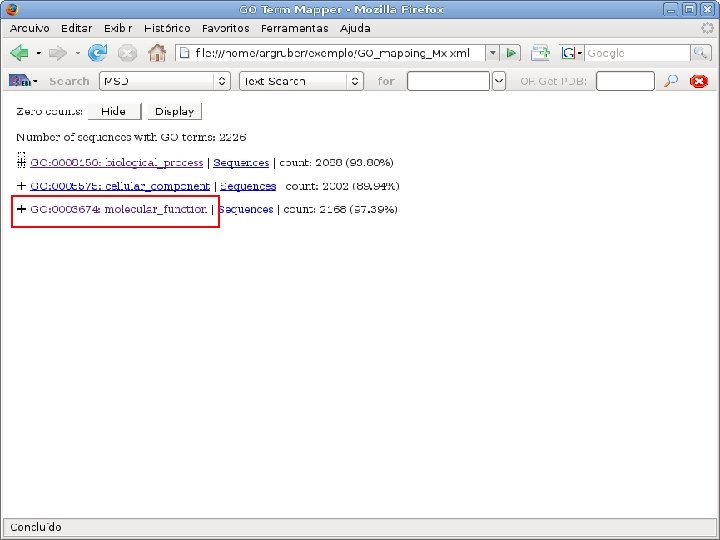
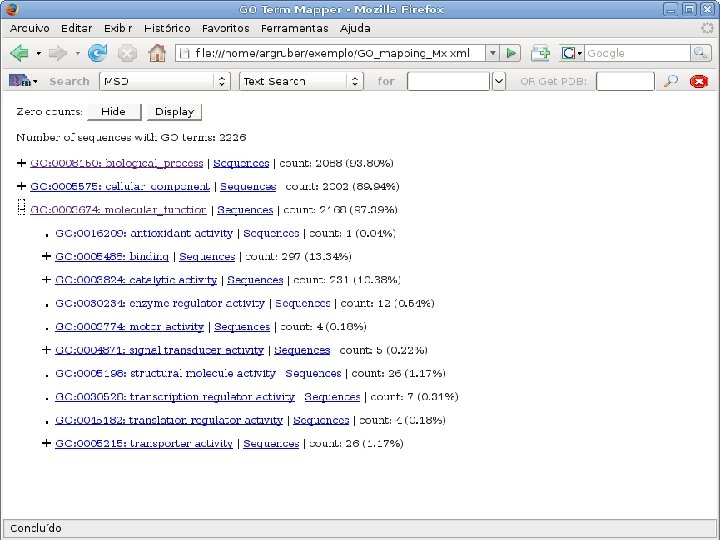
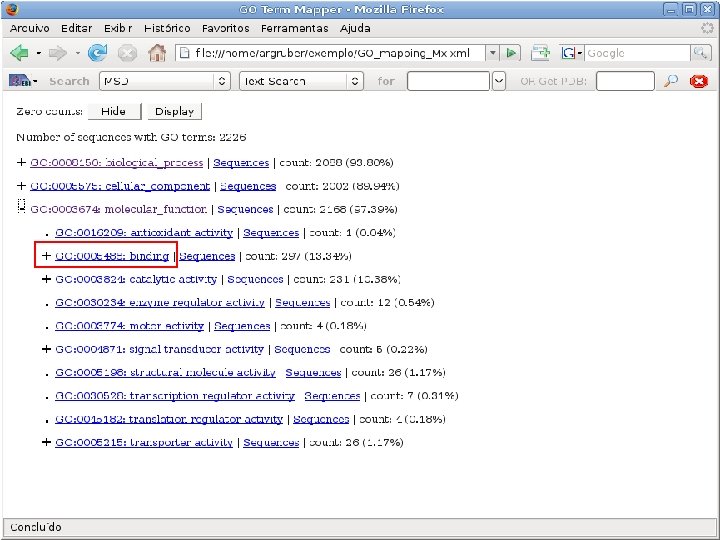
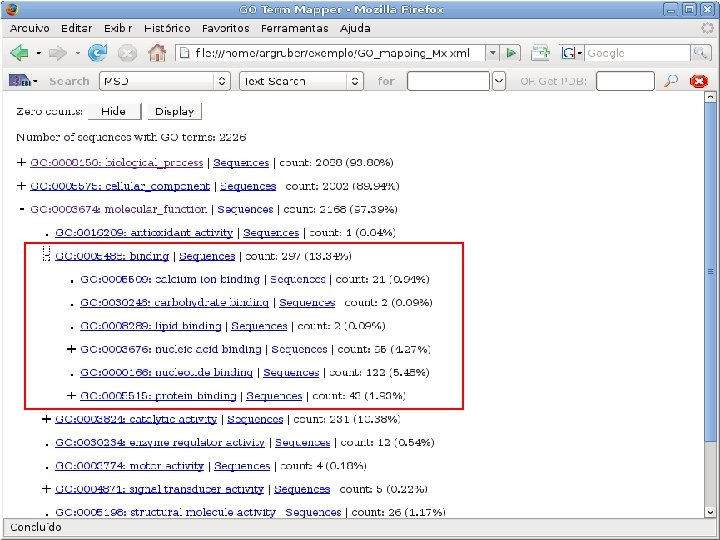
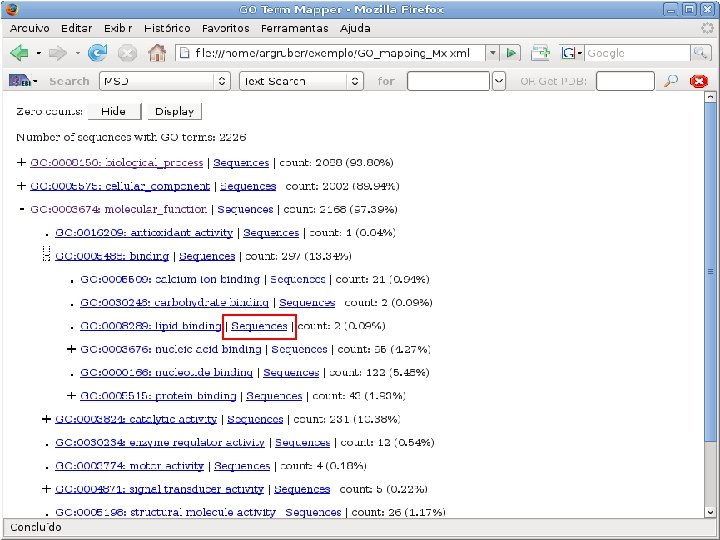
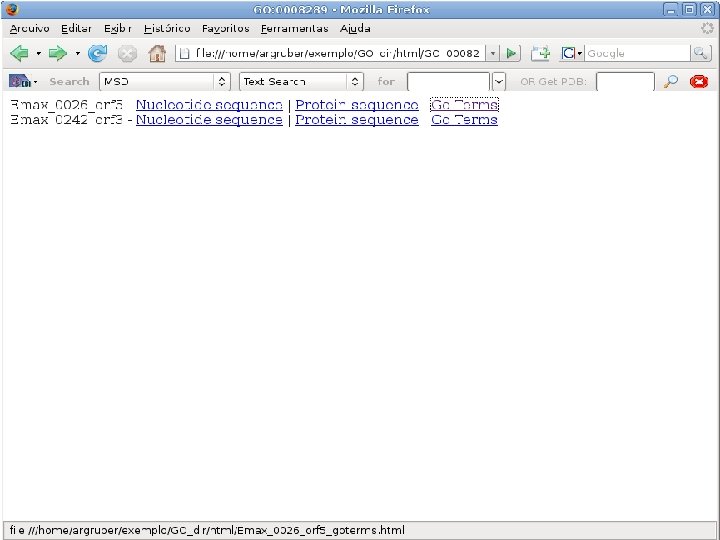
 2 EGene performs GO term mapping and constructs web pages for inspection AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene performs GO term mapping and constructs web pages for inspection AG-ICB-USP
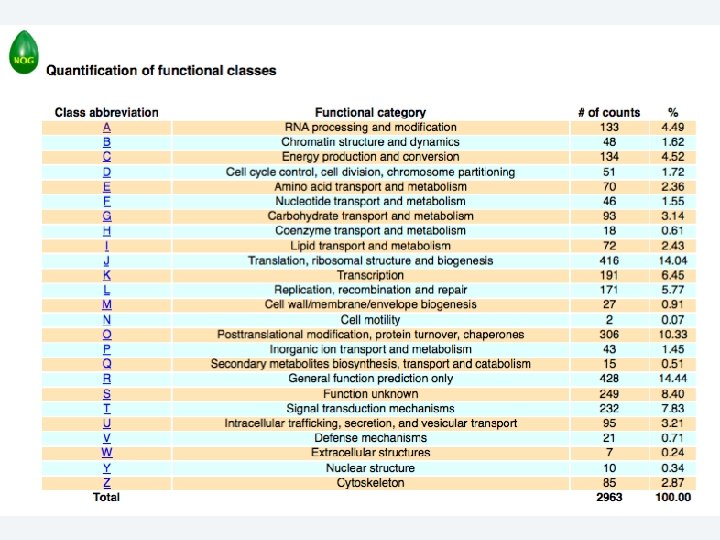
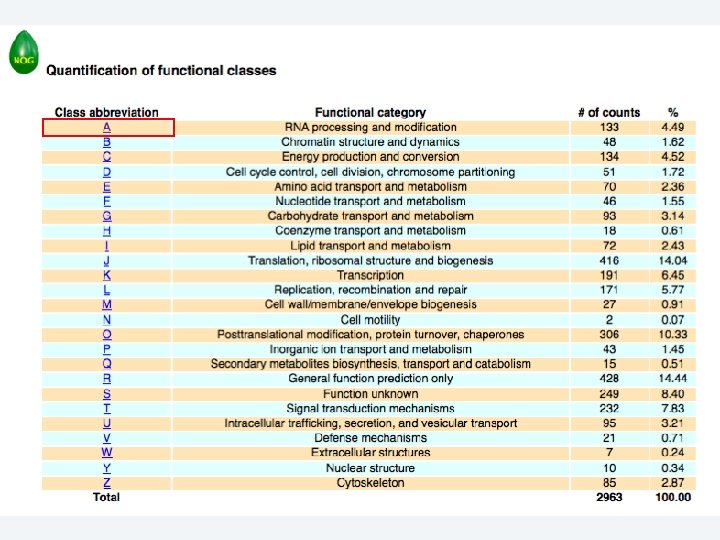
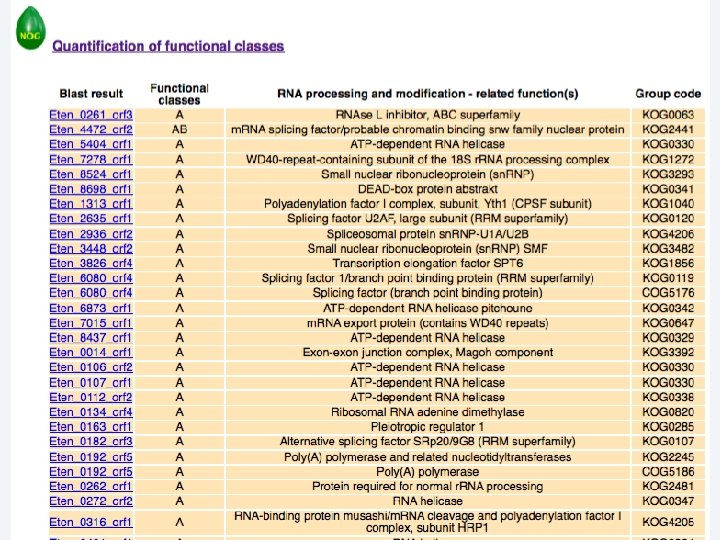
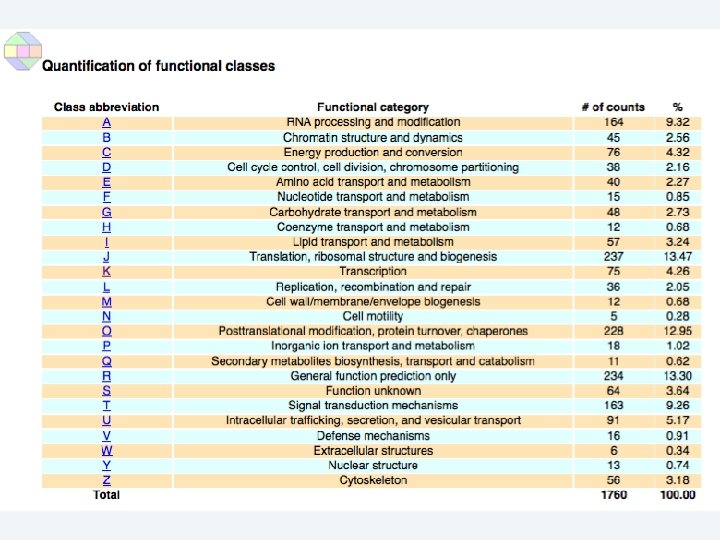
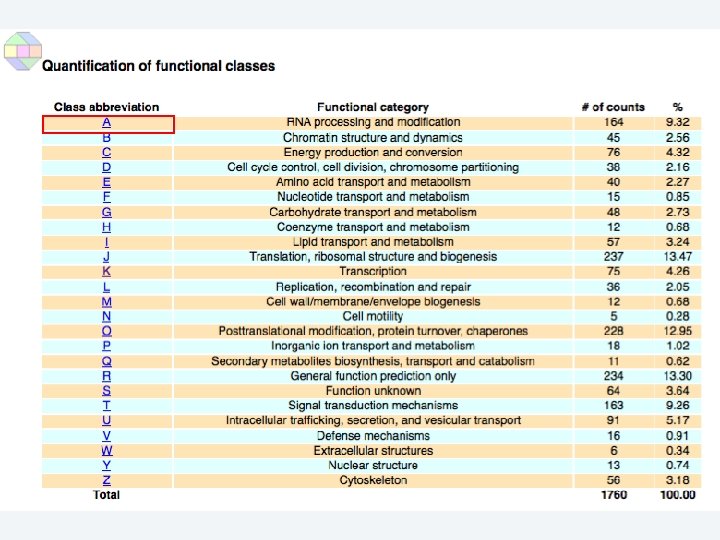
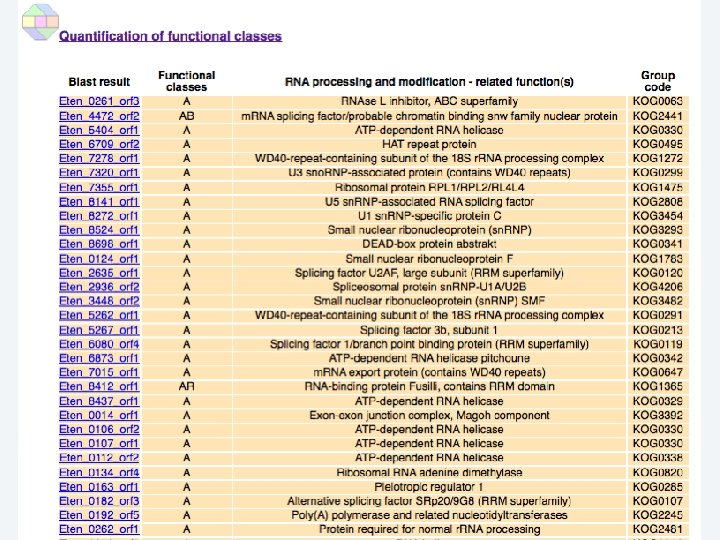
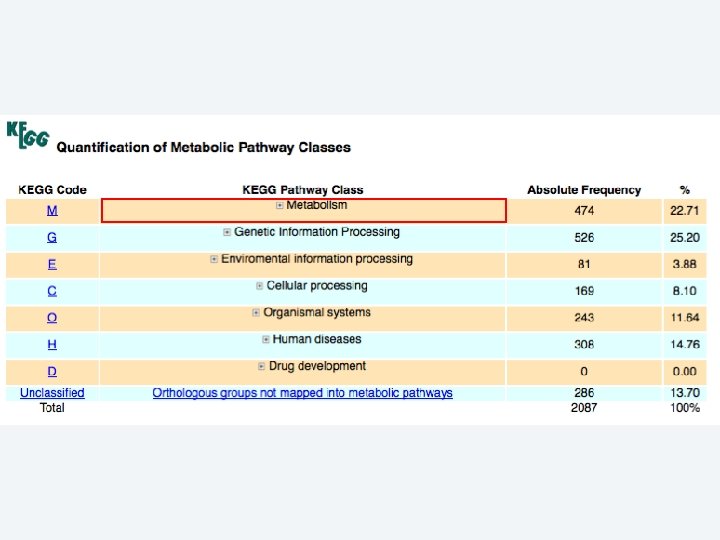
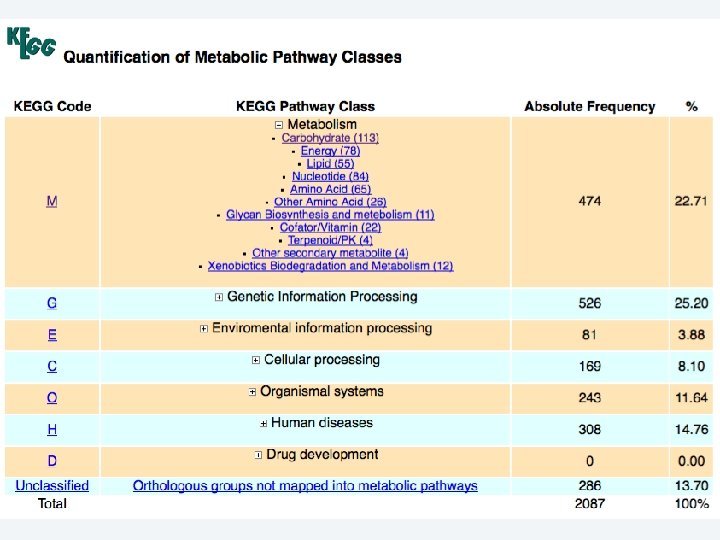
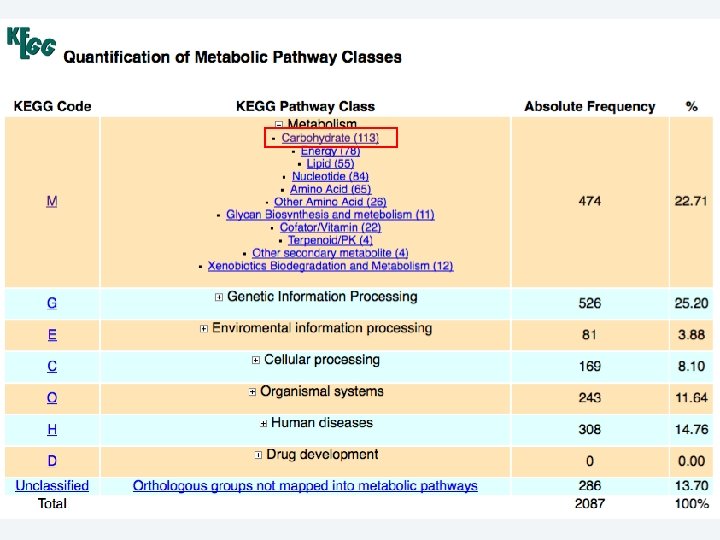
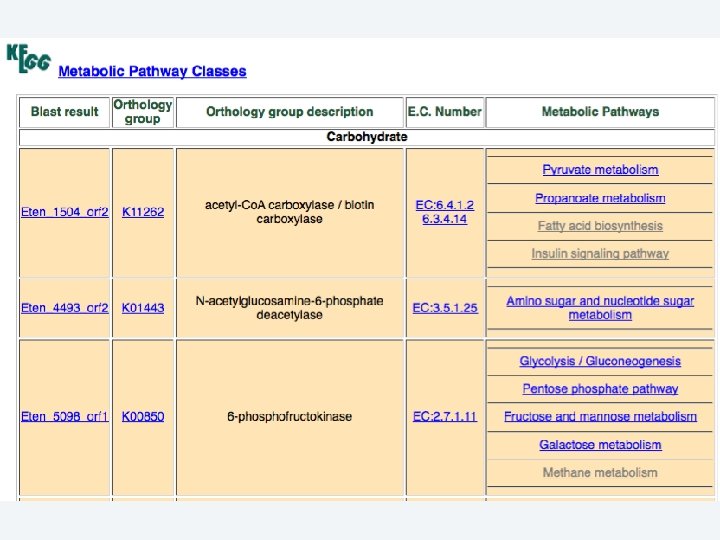
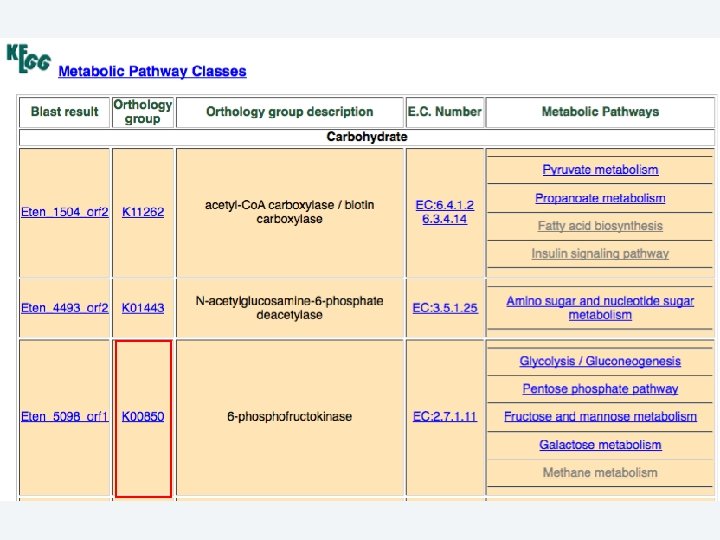
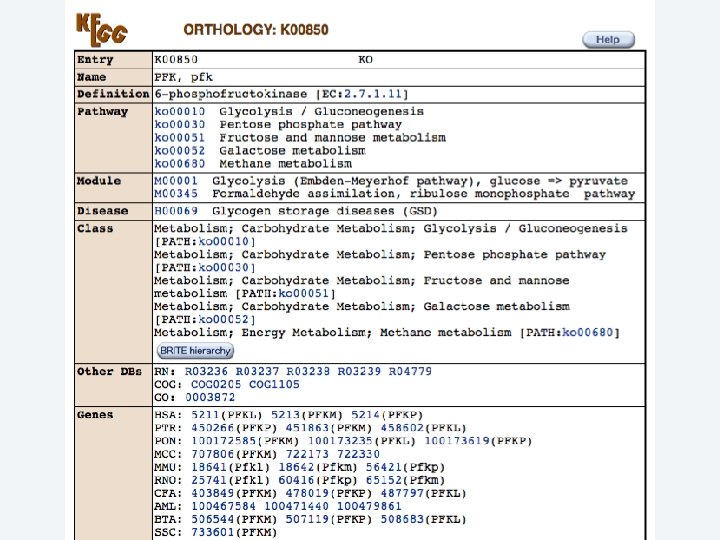
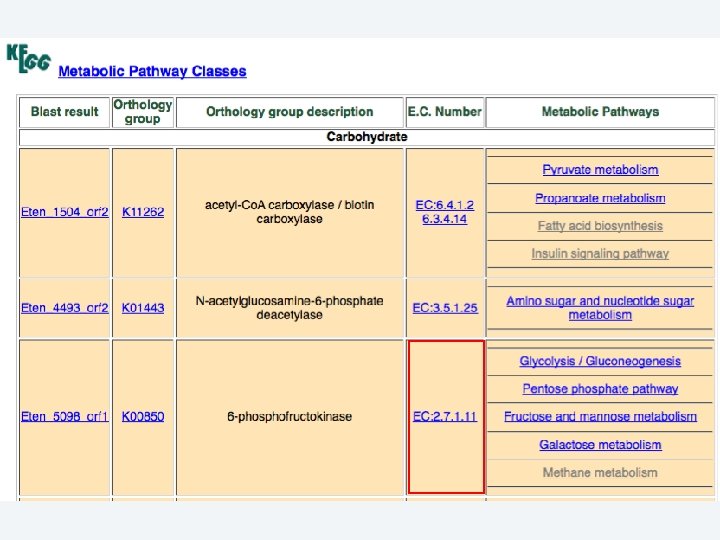
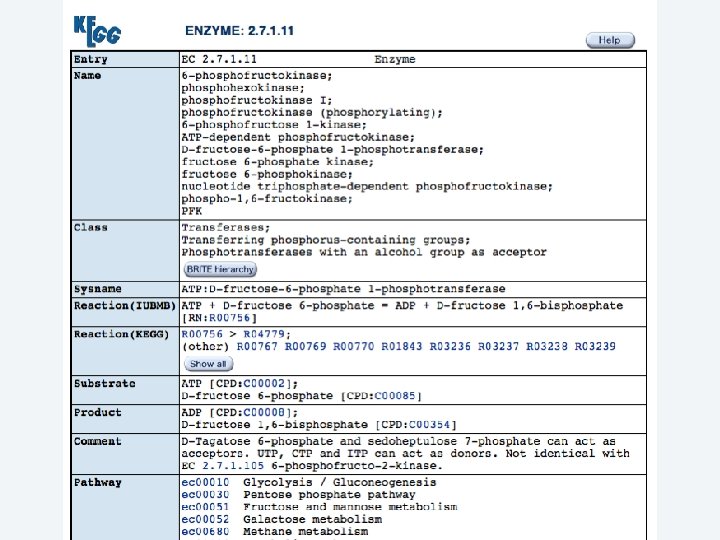
 2 EGene performs an integrated and quantitative orthology analysis (COG/KOG) and constructs web pages AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene performs an integrated and quantitative orthology analysis (COG/KOG) and constructs web pages AG-ICB-USP
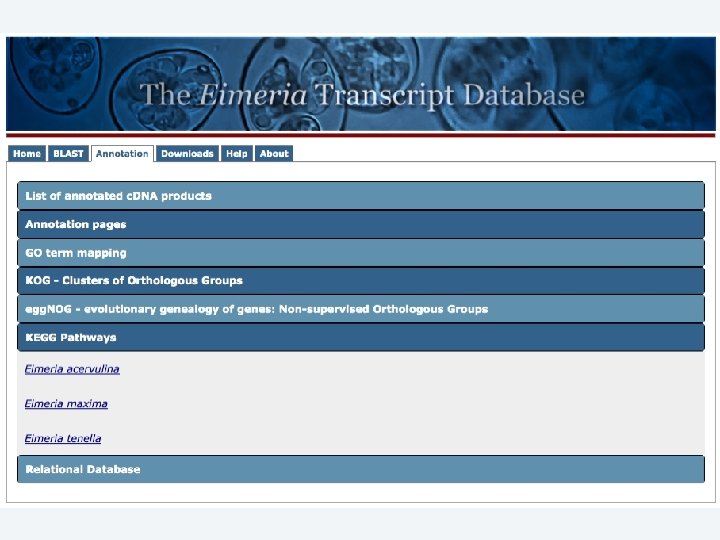
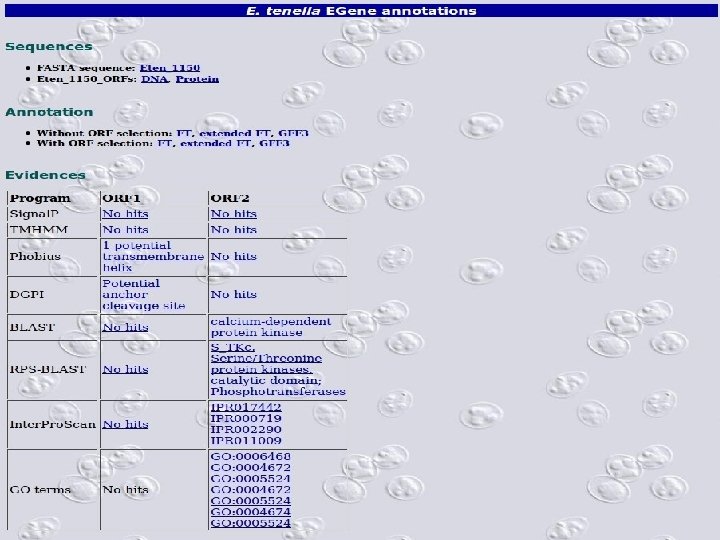
 2 EGene automatically constructs a full web site for evidence inspection AG-ICB-USP
2 EGene automatically constructs a full web site for evidence inspection AG-ICB-USP
 2 • • Current developments Full integration with a database management system Automated task distribution management across multiple processing nodes Development of a graphical interface for evidence inspection and manual curation “Intelligent” annotation – use of probalistic methods to evaluate evidence and designate protein functions AG-ICB-USP
2 • • Current developments Full integration with a database management system Automated task distribution management across multiple processing nodes Development of a graphical interface for evidence inspection and manual curation “Intelligent” annotation – use of probalistic methods to evaluate evidence and designate protein functions AG-ICB-USP
 2 • Ideal for small- and mid-sized laboratories • • • Genome and EST sequencing projects Conceived for Biologists • • Why use EGene 2 ? Does not require programming skills Generic tool for any sequencing/annotation project – customized for specific user’s requirements Very easy to implement new components Multiplatform - Mac. OS, UNIX, Linux, etc. Well documented – HOWTOs, tutorials, example datasets available Easy configuration • • Co. Ed - Application with a GUI for pipeline construction Generic pipeline templates provided AG-ICB-USP
2 • Ideal for small- and mid-sized laboratories • • • Genome and EST sequencing projects Conceived for Biologists • • Why use EGene 2 ? Does not require programming skills Generic tool for any sequencing/annotation project – customized for specific user’s requirements Very easy to implement new components Multiplatform - Mac. OS, UNIX, Linux, etc. Well documented – HOWTOs, tutorials, example datasets available Easy configuration • • Co. Ed - Application with a GUI for pipeline construction Generic pipeline templates provided AG-ICB-USP
 2 Research team Prof. Alan M. Durham – IME-USP Annotation Milene Ferro – ICB-USP Ricardo Yamamoto Abe – IME-USP Luiz Thiberio Rangel – ICB-USP Sequence pre-processing André Yoshiaki Kashiwabara - IME-USP Fernando Tadashi G. Matsunaga - ICB-USP Paulo Henrique Ahagon - ICB-USP Leonardo Varuzza - ICB-USP AG-ICB-USP
2 Research team Prof. Alan M. Durham – IME-USP Annotation Milene Ferro – ICB-USP Ricardo Yamamoto Abe – IME-USP Luiz Thiberio Rangel – ICB-USP Sequence pre-processing André Yoshiaki Kashiwabara - IME-USP Fernando Tadashi G. Matsunaga - ICB-USP Paulo Henrique Ahagon - ICB-USP Leonardo Varuzza - ICB-USP AG-ICB-USP
 2 Financial Support • FAPESP - São Paulo State Science Foundation • CNPq - National Research Council AG-ICB-USP
2 Financial Support • FAPESP - São Paulo State Science Foundation • CNPq - National Research Council AG-ICB-USP
 Thanks for your attention AG-ICB-USP
Thanks for your attention AG-ICB-USP


