4c6d61c2128127e95e56d4b12608a7e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 2 -1
2 -1
 Summary of Previous Presentation u A Global View of Operations u Developing Missions And Strategies u Mission u Strategy u Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Operations u Competing On Differentiation u Competing On Cost u Competing On Response u Ten Strategic OM Decisions u Process Design 2 -2
Summary of Previous Presentation u A Global View of Operations u Developing Missions And Strategies u Mission u Strategy u Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Operations u Competing On Differentiation u Competing On Cost u Competing On Response u Ten Strategic OM Decisions u Process Design 2 -2
 Outline u Strategy development and implementation u Global Operations Strategy Options u International Strategy u Multi domestic Strategy u Global Strategy u Transnational Strategy 2 -3
Outline u Strategy development and implementation u Global Operations Strategy Options u International Strategy u Multi domestic Strategy u Global Strategy u Transnational Strategy 2 -3
 Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (1/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Product Selection and Design Heavy R&D investment; extensive labs; focus on development in a broad range of drug categories Low R&D investment; focus on development of generic drugs Quality Major priority, exceed regulatory requirements Meets regulatory requirements on a country by country basis Table 2. 2 2 -4
Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (1/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Product Selection and Design Heavy R&D investment; extensive labs; focus on development in a broad range of drug categories Low R&D investment; focus on development of generic drugs Quality Major priority, exceed regulatory requirements Meets regulatory requirements on a country by country basis Table 2. 2 2 -4
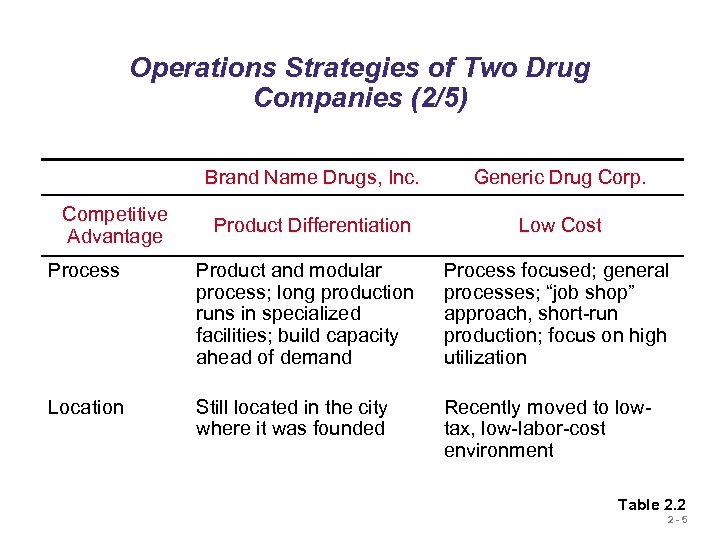 Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (2/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Process Product and modular process; long production runs in specialized facilities; build capacity ahead of demand Process focused; general processes; “job shop” approach, short-run production; focus on high utilization Location Still located in the city where it was founded Recently moved to lowtax, low-labor-cost environment Table 2. 2 2 -5
Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (2/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Process Product and modular process; long production runs in specialized facilities; build capacity ahead of demand Process focused; general processes; “job shop” approach, short-run production; focus on high utilization Location Still located in the city where it was founded Recently moved to lowtax, low-labor-cost environment Table 2. 2 2 -5
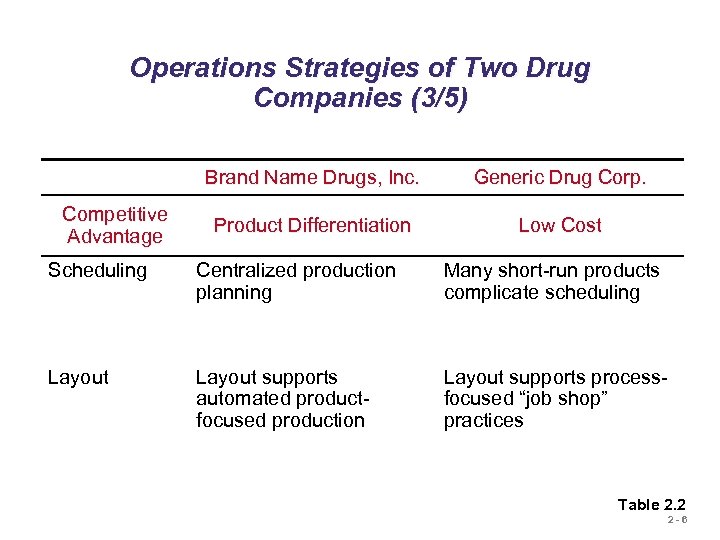 Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (3/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Scheduling Centralized production planning Many short-run products complicate scheduling Layout supports automated productfocused production Layout supports processfocused “job shop” practices Table 2. 2 2 -6
Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (3/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Scheduling Centralized production planning Many short-run products complicate scheduling Layout supports automated productfocused production Layout supports processfocused “job shop” practices Table 2. 2 2 -6
 Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (4/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Human Resources Hire the best; nationwide searches Very experienced top executives; other personnel paid below industry average Supply Chain Long-term supplier relationships Tends to purchase competitively to find bargains Table 2. 2 2 -7
Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (4/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Human Resources Hire the best; nationwide searches Very experienced top executives; other personnel paid below industry average Supply Chain Long-term supplier relationships Tends to purchase competitively to find bargains Table 2. 2 2 -7
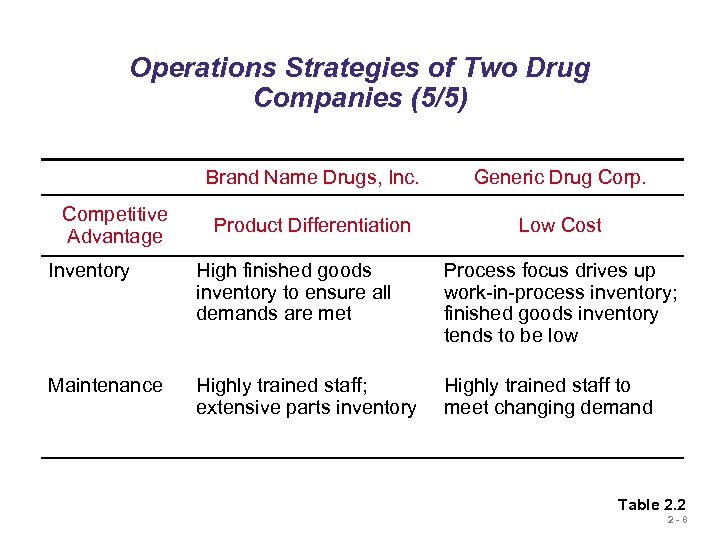 Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (5/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Inventory High finished goods inventory to ensure all demands are met Process focus drives up work-in-process inventory; finished goods inventory tends to be low Maintenance Highly trained staff; extensive parts inventory Highly trained staff to meet changing demand Table 2. 2 2 -8
Operations Strategies of Two Drug Companies (5/5) Brand Name Drugs, Inc. Competitive Advantage Generic Drug Corp. Product Differentiation Low Cost Inventory High finished goods inventory to ensure all demands are met Process focus drives up work-in-process inventory; finished goods inventory tends to be low Maintenance Highly trained staff; extensive parts inventory Highly trained staff to meet changing demand Table 2. 2 2 -8
 Issues In Operations Strategy u Resources view u Value Chain analysis u Porter’s Five Forces model u Also taking in consideration in the constant change 2 -9
Issues In Operations Strategy u Resources view u Value Chain analysis u Porter’s Five Forces model u Also taking in consideration in the constant change 2 -9
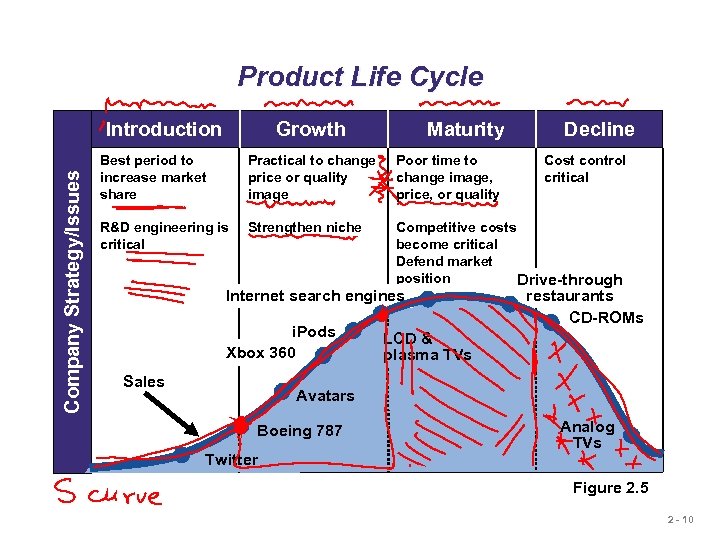 Product Life Cycle Company Strategy/Issues Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Best period to increase market share Practical to change price or quality image Poor time to change image, price, or quality R&D engineering is critical Strengthen niche Competitive costs become critical Defend market position Drive-through Internet search engines i. Pods Xbox 360 Sales Cost control critical restaurants CD-ROMs LCD & plasma TVs Avatars Boeing 787 Twitter Analog TVs Figure 2. 5 2 - 10
Product Life Cycle Company Strategy/Issues Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Best period to increase market share Practical to change price or quality image Poor time to change image, price, or quality R&D engineering is critical Strengthen niche Competitive costs become critical Defend market position Drive-through Internet search engines i. Pods Xbox 360 Sales Cost control critical restaurants CD-ROMs LCD & plasma TVs Avatars Boeing 787 Twitter Analog TVs Figure 2. 5 2 - 10
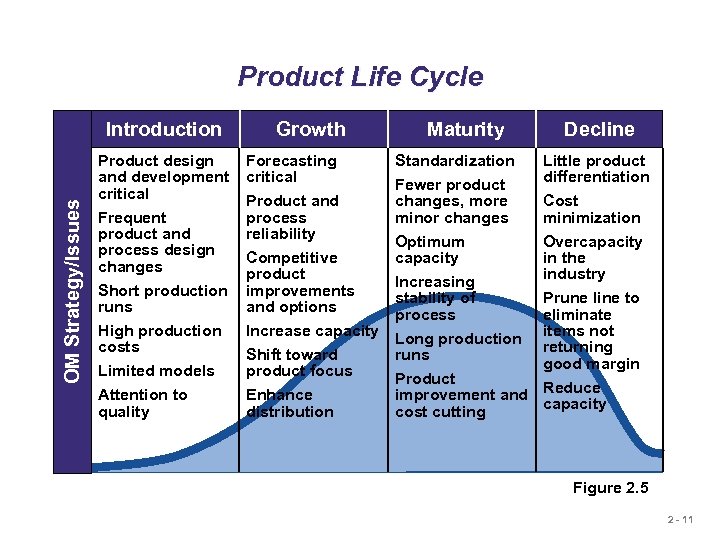 Product Life Cycle OM Strategy/Issues Introduction Product design and development critical Frequent product and process design changes Short production runs High production costs Limited models Attention to quality Growth Forecasting critical Maturity Standardization Fewer product Product and changes, more process minor changes reliability Optimum Competitive capacity product Increasing improvements stability of and options process Increase capacity Long production runs Shift toward product focus Product improvement and Enhance cost cutting distribution Decline Little product differentiation Cost minimization Overcapacity in the industry Prune line to eliminate items not returning good margin Reduce capacity Figure 2. 5 2 - 11
Product Life Cycle OM Strategy/Issues Introduction Product design and development critical Frequent product and process design changes Short production runs High production costs Limited models Attention to quality Growth Forecasting critical Maturity Standardization Fewer product Product and changes, more process minor changes reliability Optimum Competitive capacity product Increasing improvements stability of and options process Increase capacity Long production runs Shift toward product focus Product improvement and Enhance cost cutting distribution Decline Little product differentiation Cost minimization Overcapacity in the industry Prune line to eliminate items not returning good margin Reduce capacity Figure 2. 5 2 - 11
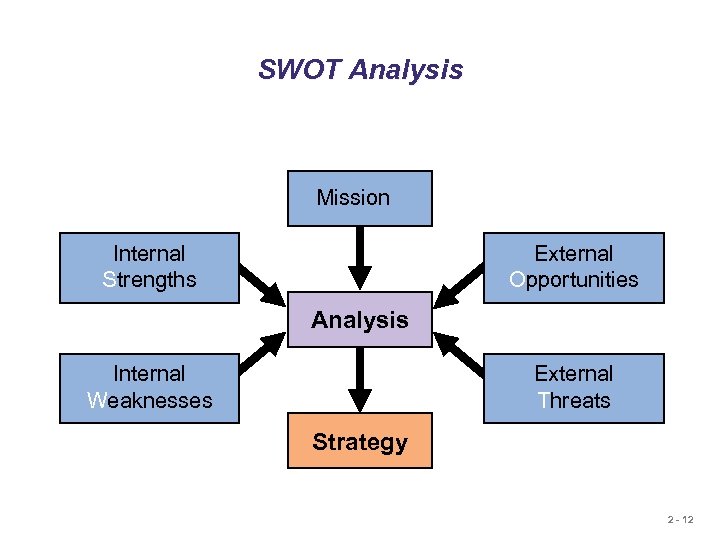 SWOT Analysis Mission Internal Strengths External Opportunities Analysis Internal Weaknesses External Threats Strategy 2 - 12
SWOT Analysis Mission Internal Strengths External Opportunities Analysis Internal Weaknesses External Threats Strategy 2 - 12
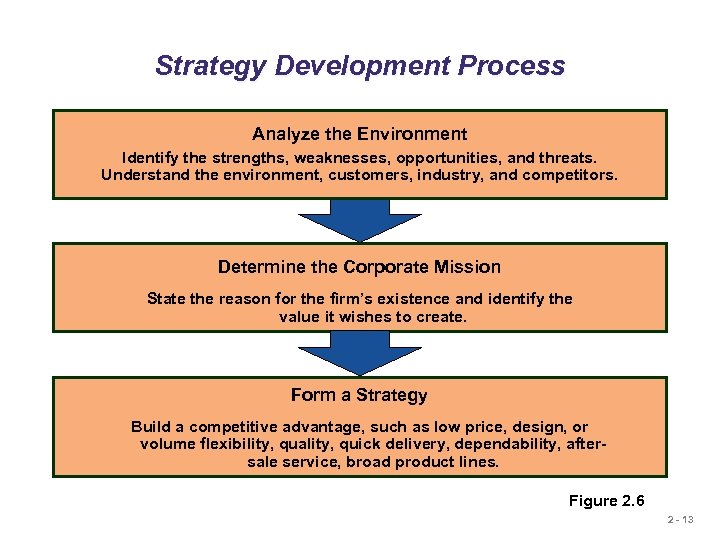 Strategy Development Process Analyze the Environment Identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understand the environment, customers, industry, and competitors. Determine the Corporate Mission State the reason for the firm’s existence and identify the value it wishes to create. Form a Strategy Build a competitive advantage, such as low price, design, or volume flexibility, quality, quick delivery, dependability, aftersale service, broad product lines. Figure 2. 6 2 - 13
Strategy Development Process Analyze the Environment Identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understand the environment, customers, industry, and competitors. Determine the Corporate Mission State the reason for the firm’s existence and identify the value it wishes to create. Form a Strategy Build a competitive advantage, such as low price, design, or volume flexibility, quality, quick delivery, dependability, aftersale service, broad product lines. Figure 2. 6 2 - 13
 Strategy Development and Implementation u Identify key success factors u Build and staff the organization u Integrate OM with other activities The operations manager’s job is to implement an OM strategy, provide competitive advantage, and increase productivity 2 - 14
Strategy Development and Implementation u Identify key success factors u Build and staff the organization u Integrate OM with other activities The operations manager’s job is to implement an OM strategy, provide competitive advantage, and increase productivity 2 - 14
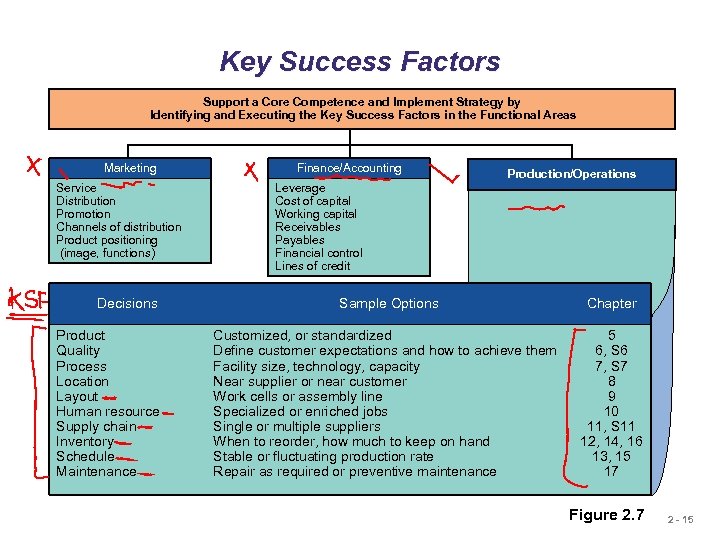 Key Success Factors Support a Core Competence and Implement Strategy by Identifying and Executing the Key Success Factors in the Functional Areas Marketing Service Distribution Promotion Channels of distribution Product positioning (image, functions) Decisions Product Quality Process Location Layout Human resource Supply chain Inventory Schedule Maintenance Finance/Accounting Production/Operations Leverage Cost of capital Working capital Receivables Payables Financial control Lines of credit Sample Options Chapter Customized, or standardized Define customer expectations and how to achieve them Facility size, technology, capacity Near supplier or near customer Work cells or assembly line Specialized or enriched jobs Single or multiple suppliers When to reorder, how much to keep on hand Stable or fluctuating production rate Repair as required or preventive maintenance 5 6, S 6 7, S 7 8 9 10 11, S 11 12, 14, 16 13, 15 17 Figure 2. 7 2 - 15
Key Success Factors Support a Core Competence and Implement Strategy by Identifying and Executing the Key Success Factors in the Functional Areas Marketing Service Distribution Promotion Channels of distribution Product positioning (image, functions) Decisions Product Quality Process Location Layout Human resource Supply chain Inventory Schedule Maintenance Finance/Accounting Production/Operations Leverage Cost of capital Working capital Receivables Payables Financial control Lines of credit Sample Options Chapter Customized, or standardized Define customer expectations and how to achieve them Facility size, technology, capacity Near supplier or near customer Work cells or assembly line Specialized or enriched jobs Single or multiple suppliers When to reorder, how much to keep on hand Stable or fluctuating production rate Repair as required or preventive maintenance 5 6, S 6 7, S 7 8 9 10 11, S 11 12, 14, 16 13, 15 17 Figure 2. 7 2 - 15
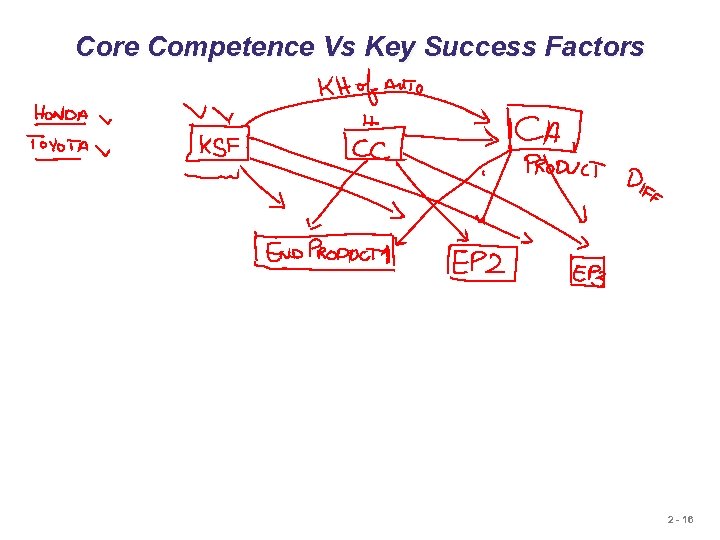 Core Competence Vs Key Success Factors 2 - 16
Core Competence Vs Key Success Factors 2 - 16
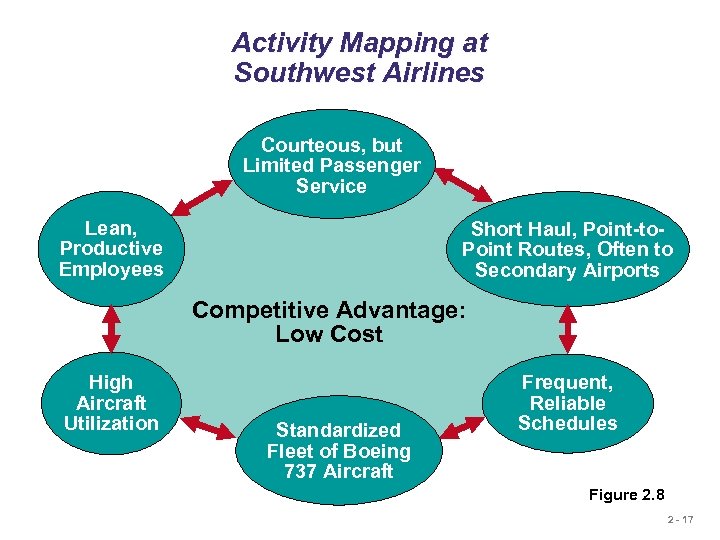 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Competitive Advantage: Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 17
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Competitive Advantage: Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 17
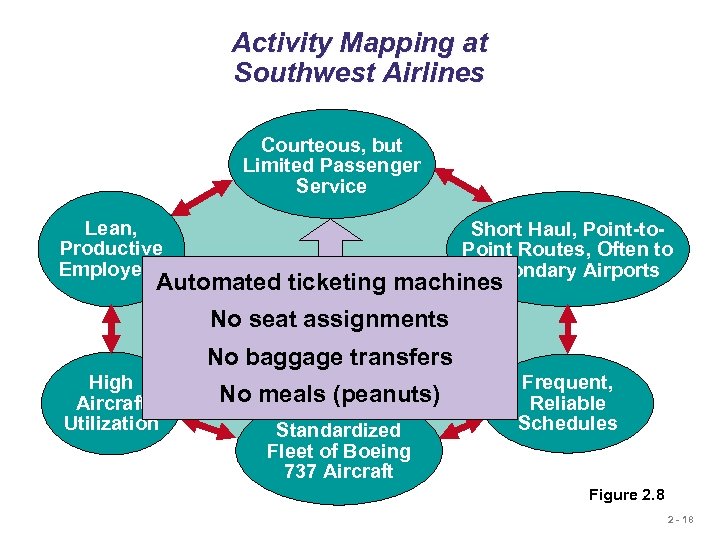 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Automated ticketing machines Competitive Advantage: No seat assignments Low Cost No baggage transfers High Aircraft Utilization No meals (peanuts) Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 18
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service Lean, Productive Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Automated ticketing machines Competitive Advantage: No seat assignments Low Cost No baggage transfers High Aircraft Utilization No meals (peanuts) Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 18
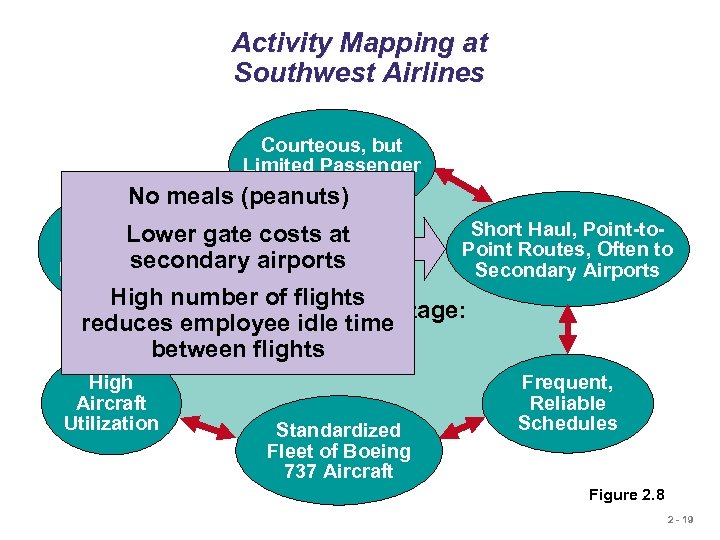 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service No meals (peanuts) Lean, Lower gate costs at Productive secondary airports Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports High number of flights Competitive Advantage: reduces employee idle time Low Cost between flights High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 19
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Service No meals (peanuts) Lean, Lower gate costs at Productive secondary airports Employees Short Haul, Point-to. Point Routes, Often to Secondary Airports High number of flights Competitive Advantage: reduces employee idle time Low Cost between flights High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 19
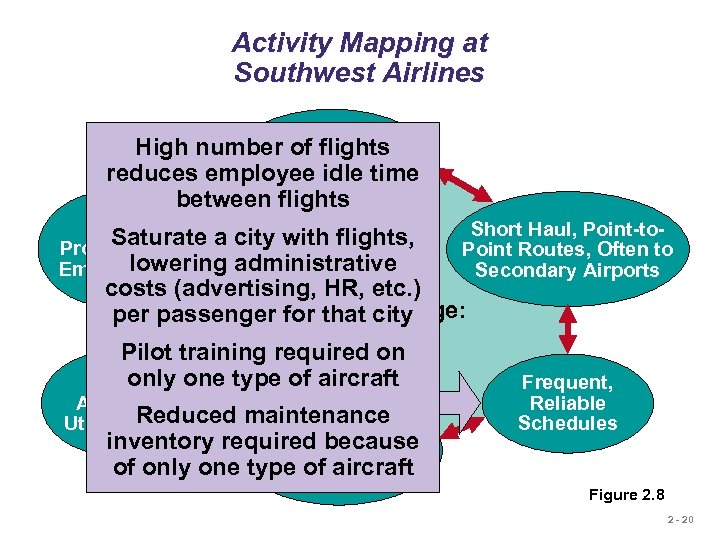 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but High number of flights Limited idle time reduces employee Passenger Service between flights Lean, Saturate a Productive lowering Employees Short Haul, Point-tocity with flights, Point Routes, Often to administrative Secondary Airports costs (advertising, HR, etc. ) Competitive Advantage: per passenger for that city Low Cost Pilot training required on only one type of aircraft High Frequent, Aircraft Reduced Utilization maintenance Standardized inventory required of Boeing Fleet because of only one type of. Aircraft 737 aircraft Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 20
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but High number of flights Limited idle time reduces employee Passenger Service between flights Lean, Saturate a Productive lowering Employees Short Haul, Point-tocity with flights, Point Routes, Often to administrative Secondary Airports costs (advertising, HR, etc. ) Competitive Advantage: per passenger for that city Low Cost Pilot training required on only one type of aircraft High Frequent, Aircraft Reduced Utilization maintenance Standardized inventory required of Boeing Fleet because of only one type of. Aircraft 737 aircraft Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 20
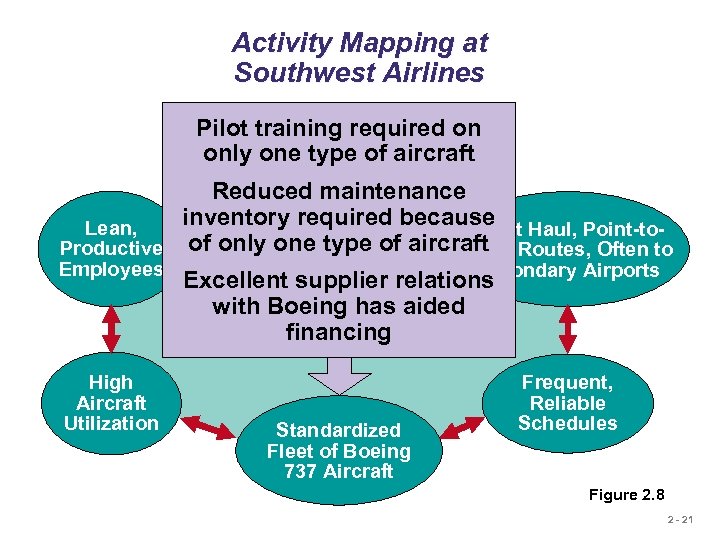 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Pilot training required on Courteous, but only one type of aircraft Limited Passenger Service Reduced maintenance inventory required because Haul, Point-to. Lean, Short of only one type of aircraft Routes, Often to Productive Point Employees Secondary Airports Excellent supplier relations with Boeing has aided Competitive Advantage: financing Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 21
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Pilot training required on Courteous, but only one type of aircraft Limited Passenger Service Reduced maintenance inventory required because Haul, Point-to. Lean, Short of only one type of aircraft Routes, Often to Productive Point Employees Secondary Airports Excellent supplier relations with Boeing has aided Competitive Advantage: financing Low Cost High Aircraft Utilization Standardized Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Frequent, Reliable Schedules Figure 2. 8 2 - 21
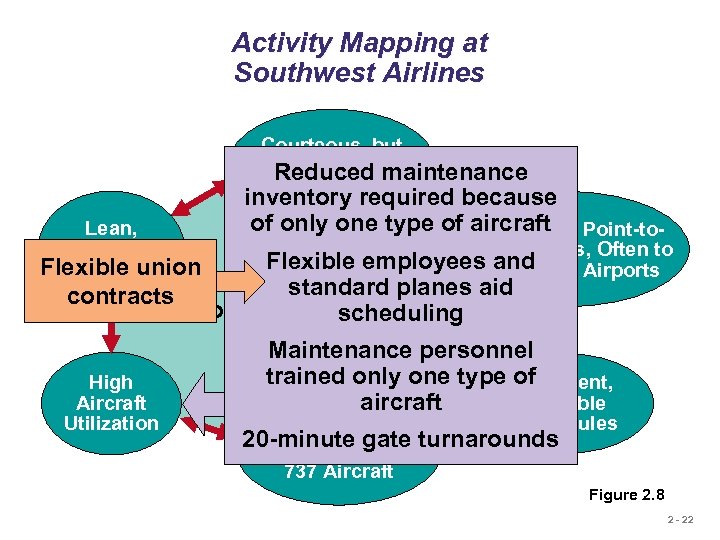 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Reduced maintenance Service Lean, Productive Flexible union Employees inventory required because of only one type of aircraft Point-to. Short Haul, Point Routes, Often to Flexible employees and Secondary Airports standard planes aid contracts Competitive Advantage: scheduling Low Cost Maintenance personnel trained only one type of High Frequent, Aircraft Reliable aircraft Utilization Standardized 20 -minute gate Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Schedules turnarounds Figure 2. 8 2 - 22
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Courteous, but Limited Passenger Reduced maintenance Service Lean, Productive Flexible union Employees inventory required because of only one type of aircraft Point-to. Short Haul, Point Routes, Often to Flexible employees and Secondary Airports standard planes aid contracts Competitive Advantage: scheduling Low Cost Maintenance personnel trained only one type of High Frequent, Aircraft Reliable aircraft Utilization Standardized 20 -minute gate Fleet of Boeing 737 Aircraft Schedules turnarounds Figure 2. 8 2 - 22
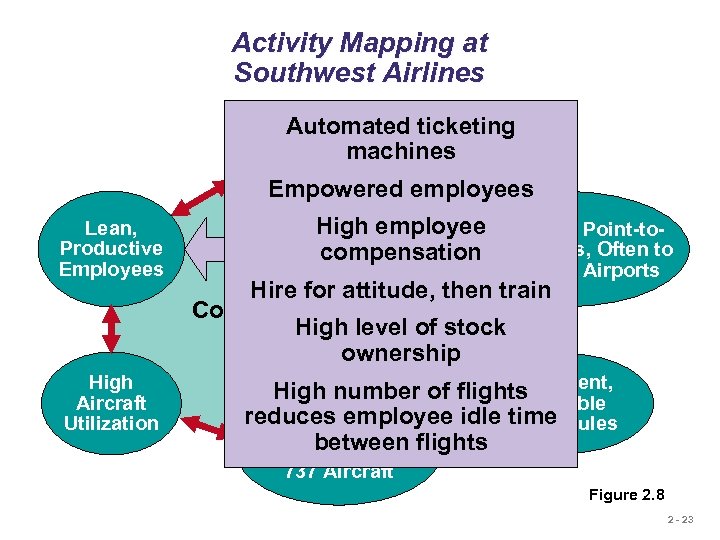 Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Automated ticketing Courteous, but machines Limited Passenger Service Empowered employees Lean, Productive Employees High Aircraft Utilization High employee Short Haul, Point-to. Point compensation Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Hire for attitude, then train Competitive Advantage: High level Low Cost of stock ownership Frequent, High number of flights Reliable reduces employee idle time Schedules Standardized Fleetbetween flights of Boeing 737 Aircraft Figure 2. 8 2 - 23
Activity Mapping at Southwest Airlines Automated ticketing Courteous, but machines Limited Passenger Service Empowered employees Lean, Productive Employees High Aircraft Utilization High employee Short Haul, Point-to. Point compensation Routes, Often to Secondary Airports Hire for attitude, then train Competitive Advantage: High level Low Cost of stock ownership Frequent, High number of flights Reliable reduces employee idle time Schedules Standardized Fleetbetween flights of Boeing 737 Aircraft Figure 2. 8 2 - 23
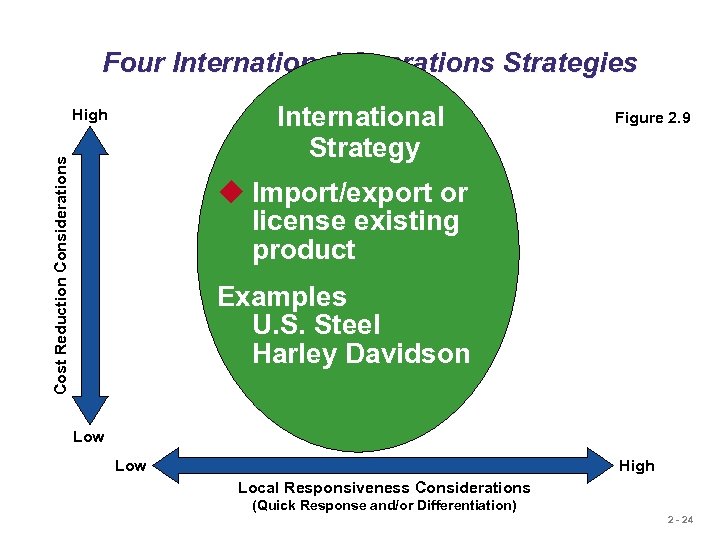 Four International Operations Strategies International Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations High Figure 2. 9 u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 24
Four International Operations Strategies International Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations High Figure 2. 9 u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 24
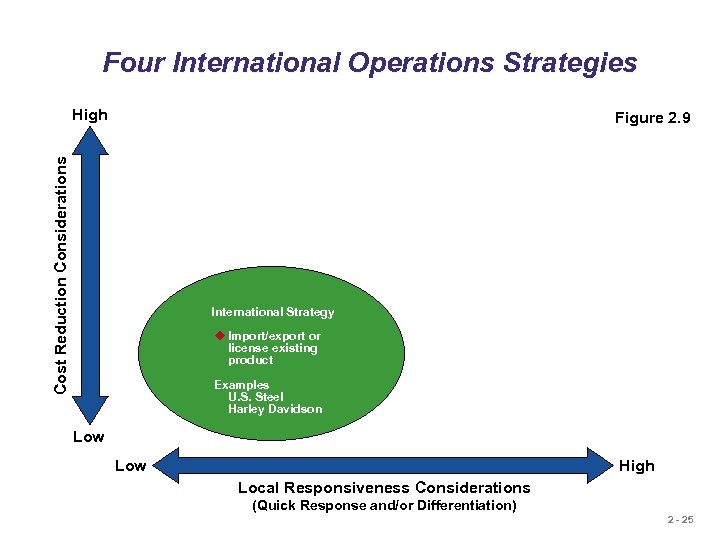 Four International Operations Strategies High Cost Reduction Considerations Figure 2. 9 International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 25
Four International Operations Strategies High Cost Reduction Considerations Figure 2. 9 International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 25
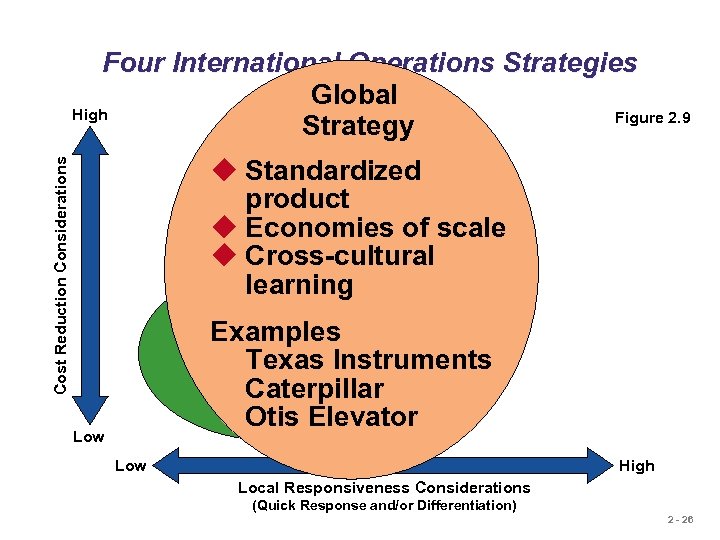 Four International Operations Strategies Global High Figure 2. 9 Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning International Strategy u Import/export or Examples license existing product Texas Instruments Examples Caterpillar U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Otis Elevator Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 26
Four International Operations Strategies Global High Figure 2. 9 Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning International Strategy u Import/export or Examples license existing product Texas Instruments Examples Caterpillar U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Otis Elevator Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 26
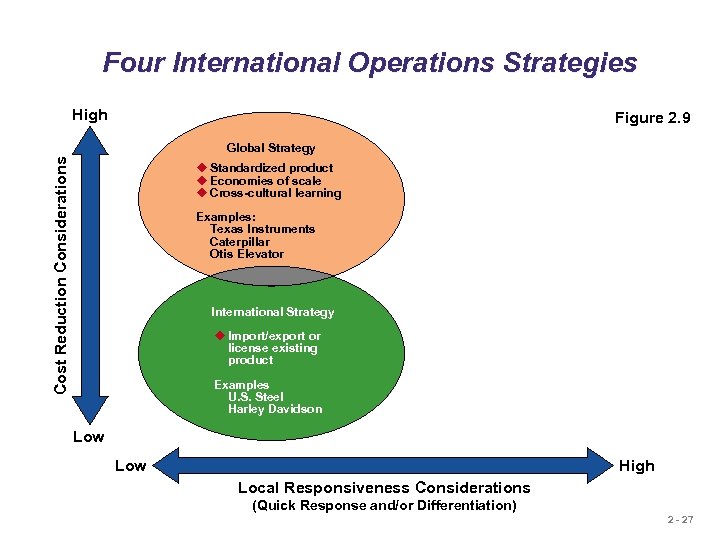 Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 27
Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator International Strategy u Import/export or license existing product Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 27
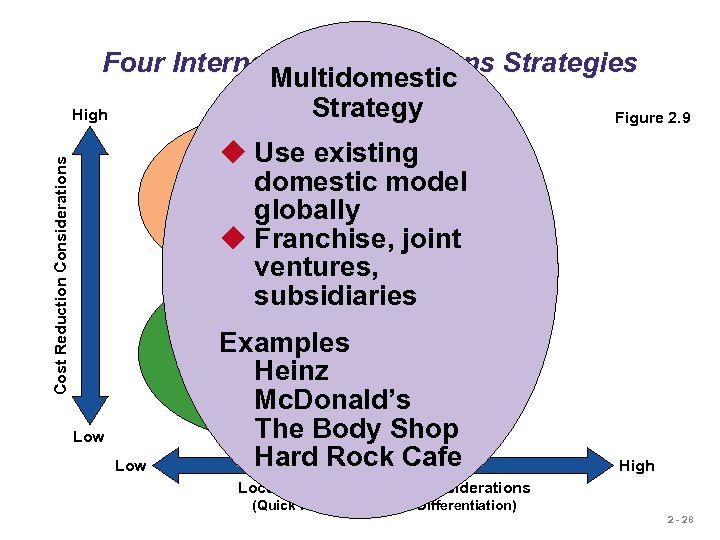 Four International Operations Strategies Multidomestic Strategy High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Use existing u Standardized product u Economies of scale domestic model u Cross-cultural learning Examples: globally Texas Instruments Caterpillar u Franchise, joint Otis Elevator ventures, subsidiaries International Strategy Examples Heinz Examples U. S. Steel Mc. Donald’s Harley Davidson The Body Shop Hard Rock Cafe u Import/export or license existing product Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 28
Four International Operations Strategies Multidomestic Strategy High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Use existing u Standardized product u Economies of scale domestic model u Cross-cultural learning Examples: globally Texas Instruments Caterpillar u Franchise, joint Otis Elevator ventures, subsidiaries International Strategy Examples Heinz Examples U. S. Steel Mc. Donald’s Harley Davidson The Body Shop Hard Rock Cafe u Import/export or license existing product Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 28
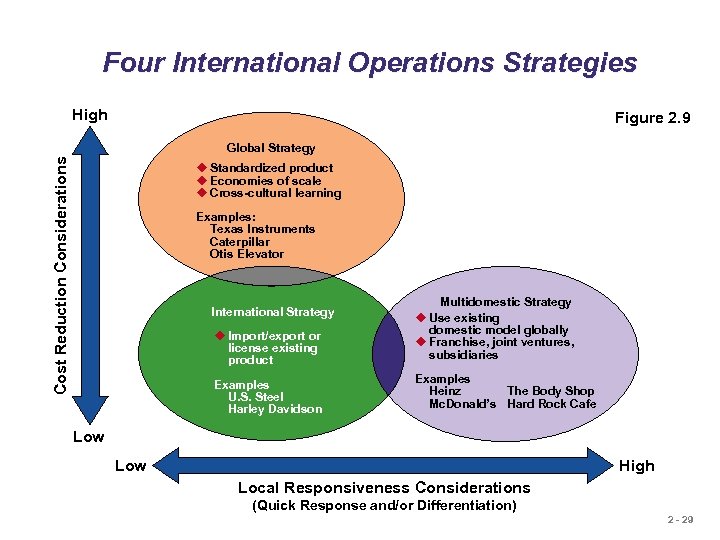 Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 29
Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 29
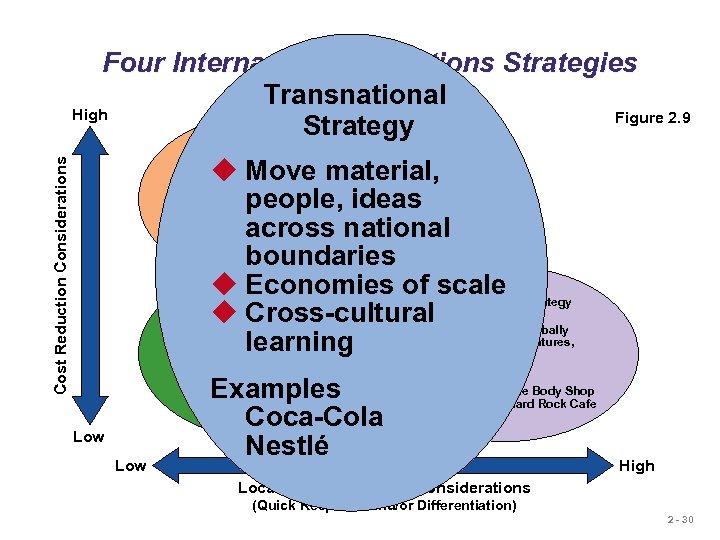 Four International Operations Strategies Transnational High Figure 2. 9 Strategy Global Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations u Move material, people, ideas Examples: Texas across national Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator boundaries u Economies of scale Strategy Multidomestic International Strategy u Use u Cross-cultural existing globally domestic model u Import/export or u Franchise, joint ventures, learning license existing subsidiaries product u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 30
Four International Operations Strategies Transnational High Figure 2. 9 Strategy Global Strategy Cost Reduction Considerations u Move material, people, ideas Examples: Texas across national Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator boundaries u Economies of scale Strategy Multidomestic International Strategy u Use u Cross-cultural existing globally domestic model u Import/export or u Franchise, joint ventures, learning license existing subsidiaries product u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Low Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 30
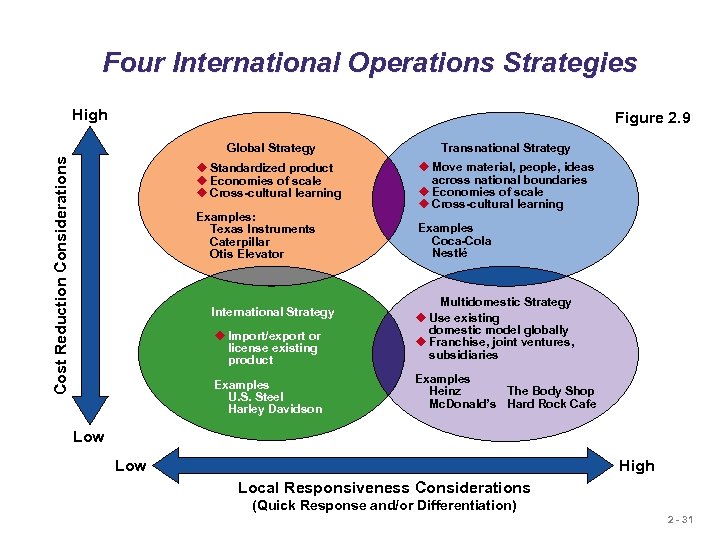 Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Transnational Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Move material, people, ideas across national boundaries u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 31
Four International Operations Strategies High Figure 2. 9 Transnational Strategy u Standardized product u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Cost Reduction Considerations Global Strategy u Move material, people, ideas across national boundaries u Economies of scale u Cross-cultural learning Examples: Texas Instruments Caterpillar Otis Elevator Examples Coca-Cola Nestlé u Import/export or license existing product Multidomestic Strategy u Use existing domestic model globally u Franchise, joint ventures, subsidiaries Examples U. S. Steel Harley Davidson Examples Heinz The Body Shop Mc. Donald’s Hard Rock Cafe International Strategy Low High Local Responsiveness Considerations (Quick Response and/or Differentiation) 2 - 31
 Summary of Chapter 2 u A Global View of Operations u Developing Missions And Strategies u Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Operations u Ten Strategic OM Decisions u Strategy Development and Implementation 2 - 32
Summary of Chapter 2 u A Global View of Operations u Developing Missions And Strategies u Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Operations u Ten Strategic OM Decisions u Strategy Development and Implementation 2 - 32


