2fc7fc9757ee8c5b75e490e3f207f56a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Principles of Operations Management Total Quality Management Chapter 3 3 -1
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Principles of Operations Management Total Quality Management Chapter 3 3 -1
 Learning Objectives © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Define quality n State why quality is important n Explain total quality management (TQM) n Explain tools for total quality management n Describe inspection 3 -2
Learning Objectives © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Define quality n State why quality is important n Explain total quality management (TQM) n Explain tools for total quality management n Describe inspection 3 -2
 Definitions of Quality © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n ASQC: Product characteristics & features that affect customer satisfaction n User-Based: What consumer says it is n Mfg. -Based: Degree to which a product conforms to design specification n Product-Based: Level of measurable product characteristic 3 -3
Definitions of Quality © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n ASQC: Product characteristics & features that affect customer satisfaction n User-Based: What consumer says it is n Mfg. -Based: Degree to which a product conforms to design specification n Product-Based: Level of measurable product characteristic 3 -3
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Dimensions of Quality for Goods n Operation n Reliability & durability n Conformance n Serviceability n Appearance n Perceived quality 3 -4 Quality
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Dimensions of Quality for Goods n Operation n Reliability & durability n Conformance n Serviceability n Appearance n Perceived quality 3 -4 Quality
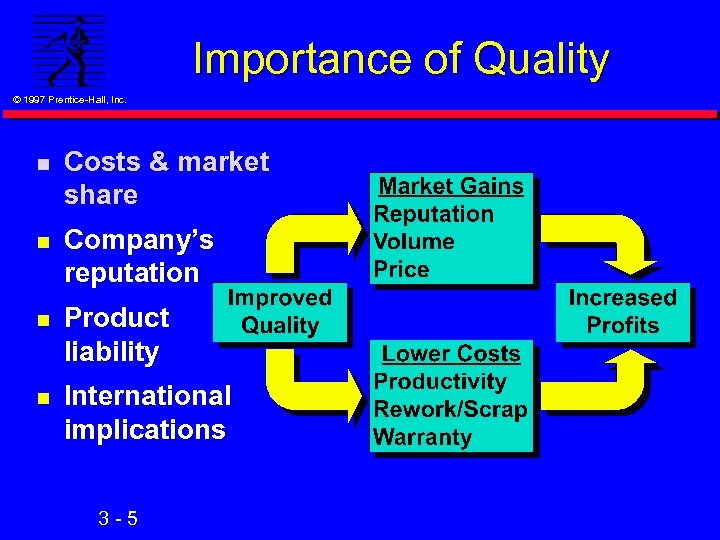 Importance of Quality © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Costs & market share n Company’s reputation n Product liability n International implications 3 -5
Importance of Quality © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Costs & market share n Company’s reputation n Product liability n International implications 3 -5
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Industrial Standard Z 8101 -1981 (Japan) l n Common quality standards for products sold in Europe (even if made in U. S. ) ISO 14000 series (Europe/EC) l n Specification for TQM ISO 9000 series (Europe/EC) l n International Quality Standards for recycling, labeling etc. ASQC Q 90 series; MILSTD (U. S. ) 3 -6
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Industrial Standard Z 8101 -1981 (Japan) l n Common quality standards for products sold in Europe (even if made in U. S. ) ISO 14000 series (Europe/EC) l n Specification for TQM ISO 9000 series (Europe/EC) l n International Quality Standards for recycling, labeling etc. ASQC Q 90 series; MILSTD (U. S. ) 3 -6
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award n Established in 1988 by the U. S. gov’t n Designed to promote TQM practices n Some criteria Senior executive leadership; strategic planning; mgt. of process quality l Quality results; customer satisfaction l n Recent winners l Corning Inc. ; GTE; AT&T; Eastman Chem. 3 -7
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award n Established in 1988 by the U. S. gov’t n Designed to promote TQM practices n Some criteria Senior executive leadership; strategic planning; mgt. of process quality l Quality results; customer satisfaction l n Recent winners l Corning Inc. ; GTE; AT&T; Eastman Chem. 3 -7
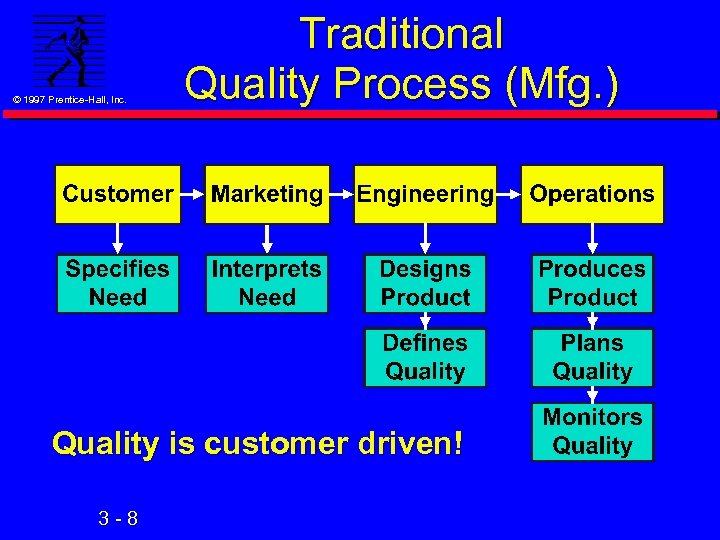 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Traditional Quality Process (Mfg. ) Quality is customer driven! 3 -8
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Traditional Quality Process (Mfg. ) Quality is customer driven! 3 -8
 Total Quality Management © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality system involving entire organization from supplier to customer n Objective: Meet or exceed customer needs through company-wide continuous improvement n Early proponents W. Edwards Deming l J. M. Juran l Philip B. Crosby l 3 -9
Total Quality Management © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality system involving entire organization from supplier to customer n Objective: Meet or exceed customer needs through company-wide continuous improvement n Early proponents W. Edwards Deming l J. M. Juran l Philip B. Crosby l 3 -9
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Total Quality Management Principles n Continuous improvement n Employee empowerment n Benchmarking n Just-in-time (JIT) n Knowledge of TQM tools © 1995 Corel Corp. 3 - 10
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Total Quality Management Principles n Continuous improvement n Employee empowerment n Benchmarking n Just-in-time (JIT) n Knowledge of TQM tools © 1995 Corel Corp. 3 - 10
 Continuous Improvement © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Represents continual improvement of process & customer satisfaction n Involves all operations & work units n Other names Kaizen (Japanese) l Zero-defects l Six sigma l 3 - 11 © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
Continuous Improvement © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Represents continual improvement of process & customer satisfaction n Involves all operations & work units n Other names Kaizen (Japanese) l Zero-defects l Six sigma l 3 - 11 © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
 Employee Empowerment © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Getting employees involved in product & process improvements l 85% of quality problems are due to process & material © 1995 Corel Corp. n Techniques Talk to workers l Support workers l Let workers make decisions l Build teams & quality circles l 3 - 12
Employee Empowerment © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Getting employees involved in product & process improvements l 85% of quality problems are due to process & material © 1995 Corel Corp. n Techniques Talk to workers l Support workers l Let workers make decisions l Build teams & quality circles l 3 - 12
 Quality Circles © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Group of 6 -12 employees from same work area n Meet regularly to solve work-related problems l 4 hours/month n Facilitator trains & helps with meetings 3 - 13 © 1995 Corel Corp.
Quality Circles © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Group of 6 -12 employees from same work area n Meet regularly to solve work-related problems l 4 hours/month n Facilitator trains & helps with meetings 3 - 13 © 1995 Corel Corp.
 Benchmarking © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Selecting best practices to use as a standard for performance n Steps Determine what to benchmark l Form benchmarking team l Identify benchmarking partners l Collect benchmarking information l Take action to meet or exceed benchmark l 3 - 14
Benchmarking © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Selecting best practices to use as a standard for performance n Steps Determine what to benchmark l Form benchmarking team l Identify benchmarking partners l Collect benchmarking information l Take action to meet or exceed benchmark l 3 - 14
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Benchmarking Thinking Challenge What specific & measurable variables would you benchmark in these areas? n Accounting n Hotel front desk n Data processing n Marketing 3 - 15 Alone Group Class
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Benchmarking Thinking Challenge What specific & measurable variables would you benchmark in these areas? n Accounting n Hotel front desk n Data processing n Marketing 3 - 15 Alone Group Class
 Just-In-Time (JIT) © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n ‘Pull’ system of production/purchasing l Customer starts production with an order n Involves ‘vendor partnership programs’ to improve quality of purchased items n Reduces all inventory levels l n Inventory hides process & material problems Improves process & product quality 3 - 16
Just-In-Time (JIT) © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n ‘Pull’ system of production/purchasing l Customer starts production with an order n Involves ‘vendor partnership programs’ to improve quality of purchased items n Reduces all inventory levels l n Inventory hides process & material problems Improves process & product quality 3 - 16
 TQM Tools © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality function deployment (QFD) n Pareto charts n Process charts n Cause & effect diagrams n Statistical process control (SPC) 3 - 17
TQM Tools © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality function deployment (QFD) n Pareto charts n Process charts n Cause & effect diagrams n Statistical process control (SPC) 3 - 17
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality Function Deployment (QFD) Product design process using cross-functional teams l Marketing, engineering, manufacturing n Translates customer preferences into specific product characteristics n Involves creating 4 tabular ‘Matrices’ or ‘Houses’ l Breakdown product design into increasing levels of detail 3 - 18
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Quality Function Deployment (QFD) Product design process using cross-functional teams l Marketing, engineering, manufacturing n Translates customer preferences into specific product characteristics n Involves creating 4 tabular ‘Matrices’ or ‘Houses’ l Breakdown product design into increasing levels of detail 3 - 18
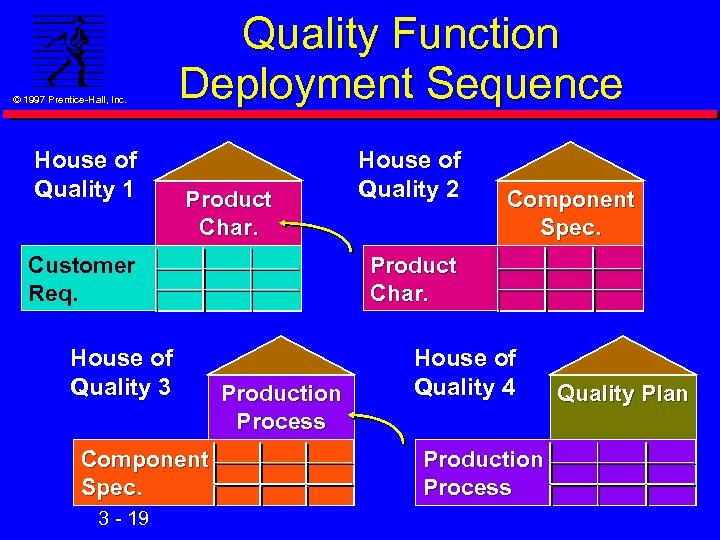 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. House of Quality 1 Quality Function Deployment Sequence Product Char. Customer Req. House of Quality 3 Component Spec. 3 - 19 House of Quality 2 Component Spec. Product Char. Production Process House of Quality 4 Production Process Quality Plan
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. House of Quality 1 Quality Function Deployment Sequence Product Char. Customer Req. House of Quality 3 Component Spec. 3 - 19 House of Quality 2 Component Spec. Product Char. Production Process House of Quality 4 Production Process Quality Plan
 House of Quality Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. You’ve been assigned temporarily to a QFD team. The goal of the team is to develop a new camera design. Build a House of Quality. © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co. 3 - 20
House of Quality Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. You’ve been assigned temporarily to a QFD team. The goal of the team is to develop a new camera design. Build a House of Quality. © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co. 3 - 20
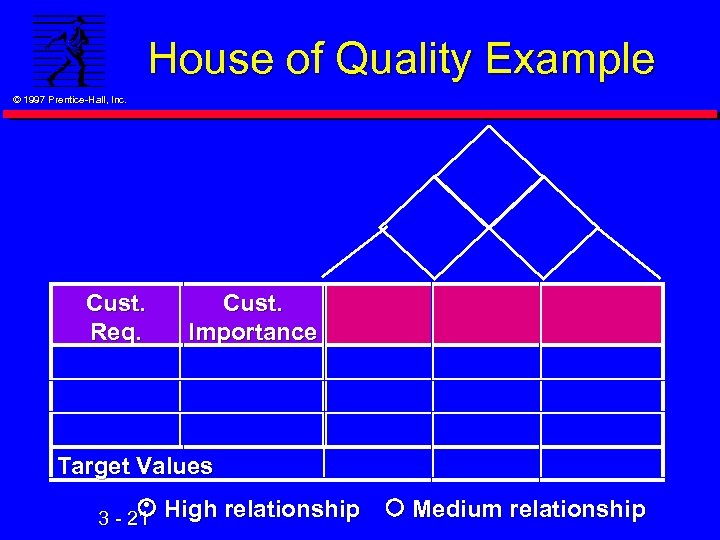 House of Quality Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Cust. Req. Cust. Importance Target Values High relationship Medium relationship 3 - 21
House of Quality Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Cust. Req. Cust. Importance Target Values High relationship Medium relationship 3 - 21
 Pareto Chart © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Vertical bar chart showing relative importance of problems or defects l n Makes identifying & solving them easier Based on Pareto Principle Most effects have relatively few causes l e. g. , 80% of quality problems come from 20% of machines, materials, or operators s Focus on ‘vital few’ 20% causes s Called 80 -20 rule l 3 - 22
Pareto Chart © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Vertical bar chart showing relative importance of problems or defects l n Makes identifying & solving them easier Based on Pareto Principle Most effects have relatively few causes l e. g. , 80% of quality problems come from 20% of machines, materials, or operators s Focus on ‘vital few’ 20% causes s Called 80 -20 rule l 3 - 22
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Pareto Chart Thinking Challenge You’re a quality analyst for Corning Glass. You’ve collected data on 100 rejected glasses: Nicks 80 Cuts 11 Scratches 3 Porosity 3 Misc. 3 Prepare a Pareto Chart. 3 - 23 Alone Group Class
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Pareto Chart Thinking Challenge You’re a quality analyst for Corning Glass. You’ve collected data on 100 rejected glasses: Nicks 80 Cuts 11 Scratches 3 Porosity 3 Misc. 3 Prepare a Pareto Chart. 3 - 23 Alone Group Class
 Process Chart © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Shows sequence of events in process n Depicts activity relationships n Has many uses Identify data collection points l Find problem sources l Identify places for improvement l Identify where travel distances can be reduced l 3 - 25
Process Chart © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Shows sequence of events in process n Depicts activity relationships n Has many uses Identify data collection points l Find problem sources l Identify places for improvement l Identify where travel distances can be reduced l 3 - 25
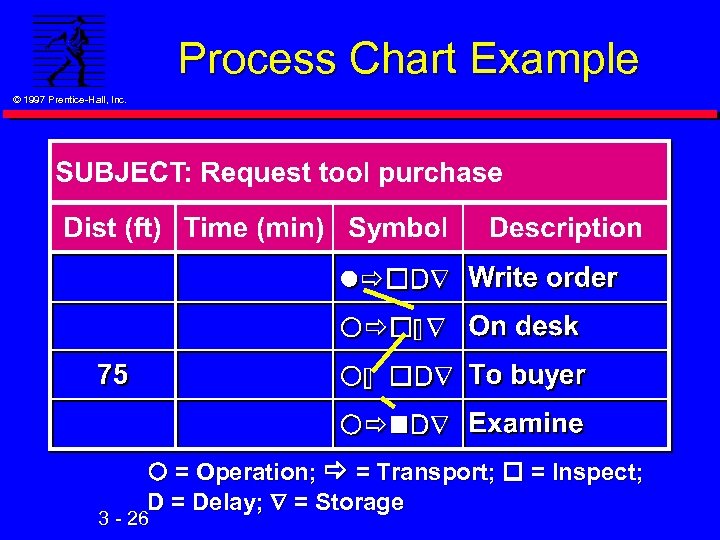 Process Chart Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. = Operation; = Transport; = Inspect; D = Delay; = Storage 3 - 26
Process Chart Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. = Operation; = Transport; = Inspect; D = Delay; = Storage 3 - 26
 Cause & Effect Diagram © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Used to find problem sources/solutions n Other names l n Fish-bone diagram, Ishikawa diagram Steps Identify problem to correct l Draw main causes for problem as ‘bones’ l Ask ‘What could have caused problems in these areas? ’ Repeat for each sub-area. l 3 - 27
Cause & Effect Diagram © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Used to find problem sources/solutions n Other names l n Fish-bone diagram, Ishikawa diagram Steps Identify problem to correct l Draw main causes for problem as ‘bones’ l Ask ‘What could have caused problems in these areas? ’ Repeat for each sub-area. l 3 - 27
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Statistical Process Control (SPC) n Uses statistics & control charts to tell when to adjust process n Developed by Shewhart in 1920’s n Involves Creating standards (upper & lower limits) l Measuring sample output (e. g. mean wgt. ) l Taking corrective action (if necessary) l n Done while product is being produced 3 - 29
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Statistical Process Control (SPC) n Uses statistics & control charts to tell when to adjust process n Developed by Shewhart in 1920’s n Involves Creating standards (upper & lower limits) l Measuring sample output (e. g. mean wgt. ) l Taking corrective action (if necessary) l n Done while product is being produced 3 - 29
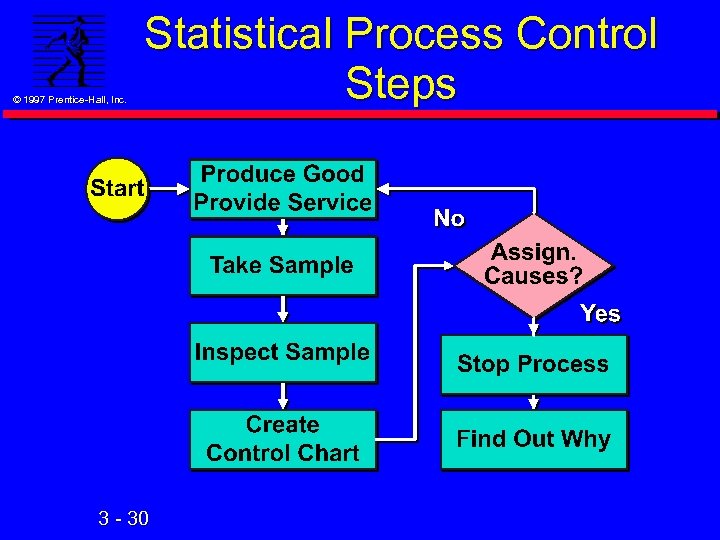 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Statistical Process Control Steps 3 - 30
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Statistical Process Control Steps 3 - 30
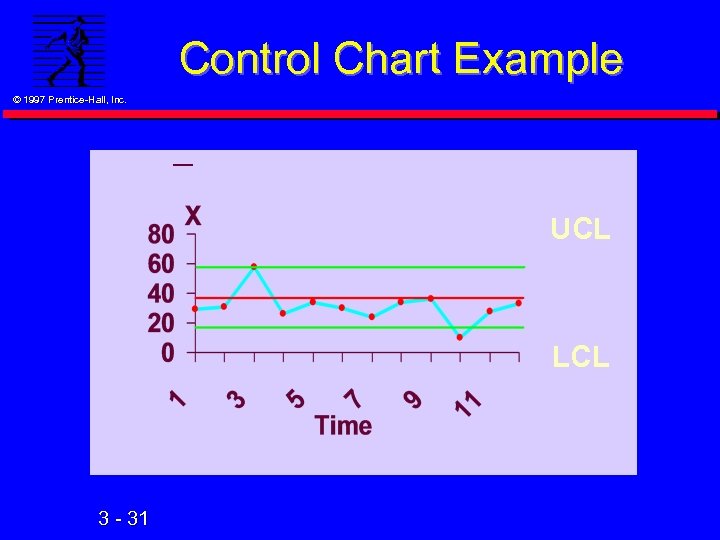 Control Chart Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. UCL LCL 3 - 31
Control Chart Example © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. UCL LCL 3 - 31
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3 - 32 Thinking Challenge: Compare & Contrast Alone Group Class
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3 - 32 Thinking Challenge: Compare & Contrast Alone Group Class
 Inspection © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Involves examining items to see if an item is good or defective n Objective: Detect a defective product l n Does not correct deficiencies in process or product Issues When to inspect l Where in process to inspect l 3 - 33
Inspection © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Involves examining items to see if an item is good or defective n Objective: Detect a defective product l n Does not correct deficiencies in process or product Issues When to inspect l Where in process to inspect l 3 - 33
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. When & Where to Inspect in Mfg. n At supplier’s plant while producing n Upon receipt of goods from supplier n Before costly or irreversible processes n During production process n When production is complete n Before shipment 3 - 34 © 1995 Corel Corp.
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. When & Where to Inspect in Mfg. n At supplier’s plant while producing n Upon receipt of goods from supplier n Before costly or irreversible processes n During production process n When production is complete n Before shipment 3 - 34 © 1995 Corel Corp.
 © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Business When & Where to Inspect in Services Where Variable Bank Teller station Speed, courtesy Checking Accuracy Store Stockrooms Stock rotation Display areas Attractiveness Counters Courtesy, knowledge 3 - 35
© 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Business When & Where to Inspect in Services Where Variable Bank Teller station Speed, courtesy Checking Accuracy Store Stockrooms Stock rotation Display areas Attractiveness Counters Courtesy, knowledge 3 - 35
 TQM in Services © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Service quality is more difficult to measure than for goods n Service quality perceptions depend on Expectations vs. reality l Process & outcome l n Types of service quality Normal: Routine service delivery l Exceptional: How problems are handled l 3 - 36
TQM in Services © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Service quality is more difficult to measure than for goods n Service quality perceptions depend on Expectations vs. reality l Process & outcome l n Types of service quality Normal: Routine service delivery l Exceptional: How problems are handled l 3 - 36
 Service Quality Attributes © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Reliability Responsiveness Tangibles Competence Understanding Access Security Courtesy © 1995 Corel Corp. Credibility 3 - 37 Communication
Service Quality Attributes © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Reliability Responsiveness Tangibles Competence Understanding Access Security Courtesy © 1995 Corel Corp. Credibility 3 - 37 Communication
 Conclusion © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Defined quality n Stated why quality is important n Explained total quality management n Explained tools for total quality management (TQM) n Described inspection 3 - 38
Conclusion © 1997 Prentice-Hall, Inc. n Defined quality n Stated why quality is important n Explained total quality management n Explained tools for total quality management (TQM) n Described inspection 3 - 38


