b15c477b07405aedbae2a94b949a5ef7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

 • 1974 -1977 • Only President never elected • Washington Insider • Likeable • Unpretentious
• 1974 -1977 • Only President never elected • Washington Insider • Likeable • Unpretentious
 • Administration was plagued by questions about Nixon • Ford grants Nixon a full and unconditional pardon • Accused of a “corrupt bargain” • Nixon never serves time or faces a trial • Some former aides were convicted and served jail time
• Administration was plagued by questions about Nixon • Ford grants Nixon a full and unconditional pardon • Accused of a “corrupt bargain” • Nixon never serves time or faces a trial • Some former aides were convicted and served jail time
 • Democratic Party continues to search CIA for abuses • CIA accused of engineering the assassination of the Marxist president of Chile, Allende • Ford makes Bush 41 new head of CIA
• Democratic Party continues to search CIA for abuses • CIA accused of engineering the assassination of the Marxist president of Chile, Allende • Ford makes Bush 41 new head of CIA
 • Ford unable to get additional funds from Congress for the South Vietnamese, who were facing strong communist attacks in 1974 • Fall of Saigon in 1975 • Genocide in Cambodia − US supported government falls to Khmer Rouge − US merchant ship Mayaguez captured by Cambodia − US attacks Cambodia naval base and rescue the Mayaguez, but 38 Marines die
• Ford unable to get additional funds from Congress for the South Vietnamese, who were facing strong communist attacks in 1974 • Fall of Saigon in 1975 • Genocide in Cambodia − US supported government falls to Khmer Rouge − US merchant ship Mayaguez captured by Cambodia − US attacks Cambodia naval base and rescue the Mayaguez, but 38 Marines die
 • Inflation continues • Asks businesses and consumers to use voluntary measures like wearing WIN buttons • Inflation continues • Economy sunk into deeper recession • Unemployment rose for over 9 percent • Ford gives into Democratic economic package
• Inflation continues • Asks businesses and consumers to use voluntary measures like wearing WIN buttons • Inflation continues • Economy sunk into deeper recession • Unemployment rose for over 9 percent • Ford gives into Democratic economic package
 • International agreement signed in 1975, designed to reduce tension between the Soviet and Western blocs. • It was an attempt to secure common acceptance of the post-World War II status quo in Europe, including the division of Germany. • They were sought by the Soviet Union to gain implicit recognition of its postwar hegemony in eastern Europe. • In return, the U. S. and its western European allies pressed for respect for human rights and cooperation in economic, scientific, and other humanitarian areas.
• International agreement signed in 1975, designed to reduce tension between the Soviet and Western blocs. • It was an attempt to secure common acceptance of the post-World War II status quo in Europe, including the division of Germany. • They were sought by the Soviet Union to gain implicit recognition of its postwar hegemony in eastern Europe. • In return, the U. S. and its western European allies pressed for respect for human rights and cooperation in economic, scientific, and other humanitarian areas.
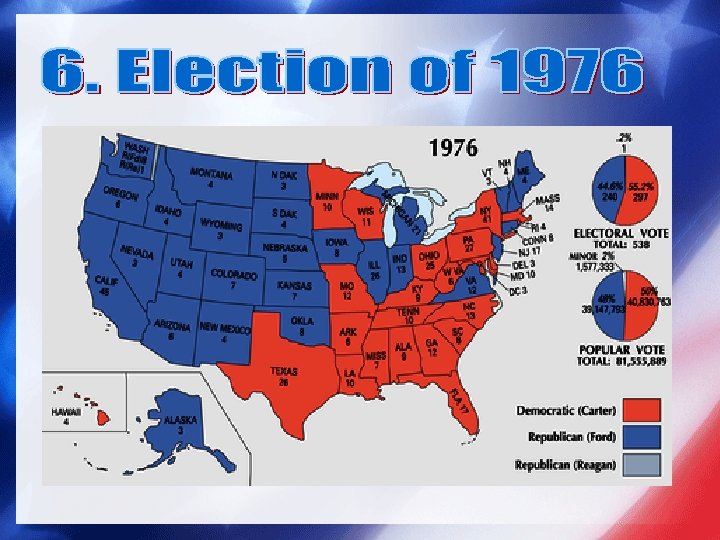
 • Presidential election of 1976 followed the resignation of President Richard M. Nixon in the wake of the Watergate scandal. • It pitted incumbent President Gerald Ford against the relatively unknown former governor of Georgia, Jimmy Carter. • Ford was saddled with a slow economy and paid a political price for his pardon of Nixon. • Carter ran as an outsider and a reformer and won.
• Presidential election of 1976 followed the resignation of President Richard M. Nixon in the wake of the Watergate scandal. • It pitted incumbent President Gerald Ford against the relatively unknown former governor of Georgia, Jimmy Carter. • Ford was saddled with a slow economy and paid a political price for his pardon of Nixon. • Carter ran as an outsider and a reformer and won.
 • Carter’s Foreign Policy is based on HUMAN RIGHTS!!!!! • Human Rights Diplomacy − Denounces oppression in South Africa − Cuts off aid to human rights violating governments in Argentina and Chile
• Carter’s Foreign Policy is based on HUMAN RIGHTS!!!!! • Human Rights Diplomacy − Denounces oppression in South Africa − Cuts off aid to human rights violating governments in Argentina and Chile
 • Carter attempted to correct inequities of the Panama Canal Treaty in 1903 • After debate, Senate ratifies a new treaty with Panama • Panamanians gradually gain control of the Canal • 100% in Panamanian control by 2000 • Seen as a “give away”
• Carter attempted to correct inequities of the Panama Canal Treaty in 1903 • After debate, Senate ratifies a new treaty with Panama • Panamanians gradually gain control of the Canal • 100% in Panamanian control by 2000 • Seen as a “give away”
 • Agreements reached between Menachem Begin of Israel and Anwar el-Sadat of Egypt with the help of U. S. President Jimmy Carter. • Created a framework for negotiations to arrive at a peace treaty between Egypt and Israel, formally ending some 30 years of being in a state of war. • Created a framework for a broader peace in the region that included a plan for Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The latter provisions were not implemented.
• Agreements reached between Menachem Begin of Israel and Anwar el-Sadat of Egypt with the help of U. S. President Jimmy Carter. • Created a framework for negotiations to arrive at a peace treaty between Egypt and Israel, formally ending some 30 years of being in a state of war. • Created a framework for a broader peace in the region that included a plan for Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The latter provisions were not implemented.
 • Anti-American sentiment in Iran — fueled in part by close ties between the U. S. and the Shah of Iran. • Shah is overthrown by the Ayatollah Khomeini in 1979. • Oil production ground to a halt, causing oil prices to skyrocket • Shah comes to the US for medical treatment which further angers the Ayatollah • Iranian militants seize the US embassy in Teheran and hold 50 American citizens hostage • Carter tries use diplomacy to free hostages • In 1980 he approves a rescue mission- helicopters break down on the way • Hostages are released on the day of Reagan’s inauguration
• Anti-American sentiment in Iran — fueled in part by close ties between the U. S. and the Shah of Iran. • Shah is overthrown by the Ayatollah Khomeini in 1979. • Oil production ground to a halt, causing oil prices to skyrocket • Shah comes to the US for medical treatment which further angers the Ayatollah • Iranian militants seize the US embassy in Teheran and hold 50 American citizens hostage • Carter tries use diplomacy to free hostages • In 1980 he approves a rescue mission- helicopters break down on the way • Hostages are released on the day of Reagan’s inauguration
 • Attempts to continue the Nixon-Ford policy of détente • Signs SALT II in 1979 (never ratified by the Senate) • Soviet Union invades Afghanistan in 1979 − Carter places embargo on grain export and sale of technology to the USSR − Boycotts the 1980 Olympics in Moscow − Forced to move to an arms buildup
• Attempts to continue the Nixon-Ford policy of détente • Signs SALT II in 1979 (never ratified by the Senate) • Soviet Union invades Afghanistan in 1979 − Carter places embargo on grain export and sale of technology to the USSR − Boycotts the 1980 Olympics in Moscow − Forced to move to an arms buildup
 • Tries to curb inflation, but unsuccessful (inflation rises to 13%) • Raises interest rates to counteract inflation (to 20%) − Backfires − Buying slows − Deficit increases to pay for Social programs − 10, 000 s workers laid off in automobile and building industries
• Tries to curb inflation, but unsuccessful (inflation rises to 13%) • Raises interest rates to counteract inflation (to 20%) − Backfires − Buying slows − Deficit increases to pay for Social programs − 10, 000 s workers laid off in automobile and building industries
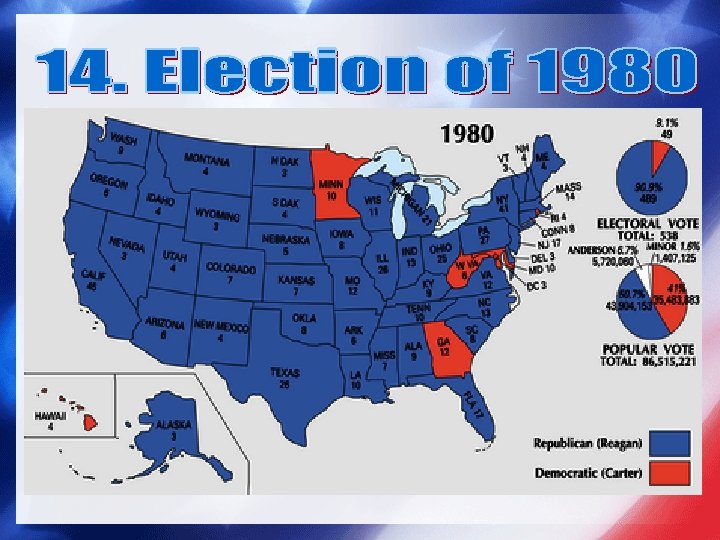
 • Candidates − Carter (Democrat) − Reagan (Republican) • Issues − Taxpayer’s Revolt − Moral Rival − “Reserve discrimination” • Regents of the University of California v. Bakke (1978)
• Candidates − Carter (Democrat) − Reagan (Republican) • Issues − Taxpayer’s Revolt − Moral Rival − “Reserve discrimination” • Regents of the University of California v. Bakke (1978)
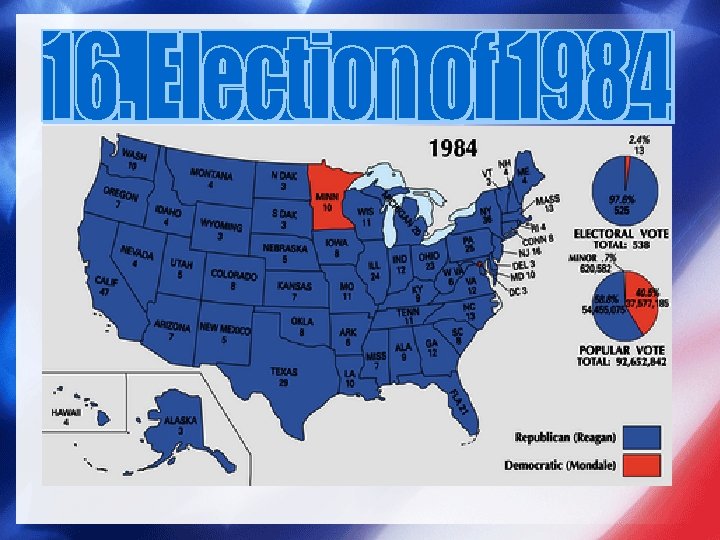
 • Reaganomics − Tax cuts (25% in 3 yrs) − decreased social spending − Increased military spending − Deregulation of domestic markets − Antiunion policies − Recession and Recovery − Social Issues
• Reaganomics − Tax cuts (25% in 3 yrs) − decreased social spending − Increased military spending − Deregulation of domestic markets − Antiunion policies − Recession and Recovery − Social Issues
 • Federal deficits reached over $200 million − Tax cuts − Military spending − led to a trade deficit Congress passes the Gramm-Rudman-Hollings Balanced Budget Act of 1985 to balance the budget.
• Federal deficits reached over $200 million − Tax cuts − Military spending − led to a trade deficit Congress passes the Gramm-Rudman-Hollings Balanced Budget Act of 1985 to balance the budget.
 • Military Buildup − USSR was the EVIL EMPIRE − Billions spent to build new weapons − Strategic Defense initiative (SDI or Star Wars) • Plan to build high tech lasers and particle beams to destroy enemy missiles in the air
• Military Buildup − USSR was the EVIL EMPIRE − Billions spent to build new weapons − Strategic Defense initiative (SDI or Star Wars) • Plan to build high tech lasers and particle beams to destroy enemy missiles in the air
 • Under the Reagan Doctrine, the U. S. provided overt and covert aid to anti-communist resistance movements in an effort to "rollback" Soviet-backed communist governments in Africa, Asia and Latin America. • The doctrine was designed to serve the dual purposes of diminishing Soviet influence in these regions of the world, while also potentially opening the door for democracy in nations that were largely being governed by Soviet-supported autocrats.
• Under the Reagan Doctrine, the U. S. provided overt and covert aid to anti-communist resistance movements in an effort to "rollback" Soviet-backed communist governments in Africa, Asia and Latin America. • The doctrine was designed to serve the dual purposes of diminishing Soviet influence in these regions of the world, while also potentially opening the door for democracy in nations that were largely being governed by Soviet-supported autocrats.
 • Reagan supported “friendly” right wing dictators to keep out communists • Worked to overthrow Marxist regimes such as the Sandinistas who had take over Nicaragua in 1979 • US funded “contra” rebels in a attempt to seize power • Democrats passed the Boland Amendment to prohibit this in 1985
• Reagan supported “friendly” right wing dictators to keep out communists • Worked to overthrow Marxist regimes such as the Sandinistas who had take over Nicaragua in 1979 • US funded “contra” rebels in a attempt to seize power • Democrats passed the Boland Amendment to prohibit this in 1985
 • Grenada − Reagan orders the Marines to invade Grenada to prevent the establishment of a Communist military bases − US is successful
• Grenada − Reagan orders the Marines to invade Grenada to prevent the establishment of a Communist military bases − US is successful
 • In 1985 the US authorized sales of weapons to Iran in an attempt to secure the release of U. S. hostages held in Lebanon by pro-Iranian terrorist groups. • The deal contravened stated policy regarding both dealings with terrorists and military aid to Iran. • At the instigation of Oliver North, a NSC staff member, part of the $48 million paid by Iran for the arms was diverted to the Nicaraguan contras, in direct violation of a 1984 law banning such assistance. • A Senate investigation resulted in the conviction of North and Poindexter on charges of obstructing justice and related offenses, though their convictions were later overturned. • Pres. Ronald Reagan accepted responsibility for the arms-forhostages deal but denied any knowledge of the diversion.
• In 1985 the US authorized sales of weapons to Iran in an attempt to secure the release of U. S. hostages held in Lebanon by pro-Iranian terrorist groups. • The deal contravened stated policy regarding both dealings with terrorists and military aid to Iran. • At the instigation of Oliver North, a NSC staff member, part of the $48 million paid by Iran for the arms was diverted to the Nicaraguan contras, in direct violation of a 1984 law banning such assistance. • A Senate investigation resulted in the conviction of North and Poindexter on charges of obstructing justice and related offenses, though their convictions were later overturned. • Pres. Ronald Reagan accepted responsibility for the arms-forhostages deal but denied any knowledge of the diversion.
 • Reagan initially rejected détente and confronted the Soviet Union through a policy of "peace through strength, " including increased military spending, firm foreign policies against the USSR and support for anti-communist groups around the world. • Glasnost • Perestroika • Removal of troops from Afghanistan 1988 • End to Iraq-Iran War
• Reagan initially rejected détente and confronted the Soviet Union through a policy of "peace through strength, " including increased military spending, firm foreign policies against the USSR and support for anti-communist groups around the world. • Glasnost • Perestroika • Removal of troops from Afghanistan 1988 • End to Iraq-Iran War


