3771af82daf7f9a58add7648f62e8d19.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107
 1950’s THE COLD WAR
1950’s THE COLD WAR
 • PEOPLE SCARED – RED SCARE – ROSENBERGS – USSR A-BOMB – RED CHINA
• PEOPLE SCARED – RED SCARE – ROSENBERGS – USSR A-BOMB – RED CHINA

 RDS-1, the first Soviet atomic test, code-named by the US as Joe 1
RDS-1, the first Soviet atomic test, code-named by the US as Joe 1

 Mc. Carthyism 1950
Mc. Carthyism 1950

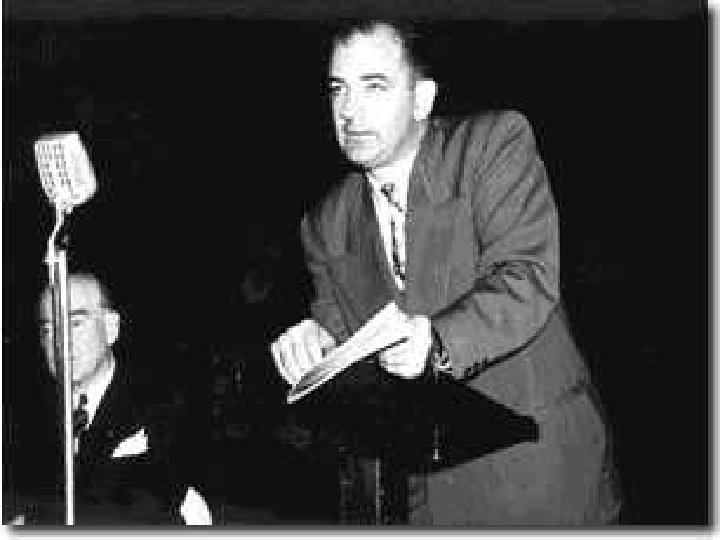
 • Joseph Mc. Carthy (1908 -1957) was a Republican Senator, on February 9 th 1950, Mc. Carthy claimed to have a list of 205 Communists in the State Department.
• Joseph Mc. Carthy (1908 -1957) was a Republican Senator, on February 9 th 1950, Mc. Carthy claimed to have a list of 205 Communists in the State Department.

 • Conformity • Mc. Carthy's attacks emerged within a climate of political and social conformity. – One state required pro wrestlers to take a loyalty oath before stepping into the ring. – In Indiana, a group of anti-communists indicted Robin Hood (and its vaguely socialistic message that the book's titular hero had a right to rob from the rich and give to the poor) forced librarians to pull the book from the shelves.
• Conformity • Mc. Carthy's attacks emerged within a climate of political and social conformity. – One state required pro wrestlers to take a loyalty oath before stepping into the ring. – In Indiana, a group of anti-communists indicted Robin Hood (and its vaguely socialistic message that the book's titular hero had a right to rob from the rich and give to the poor) forced librarians to pull the book from the shelves.
 "You read books, eh? "
"You read books, eh? "
 • Baseball's Cincinnati Reds renamed themselves the "Redlegs. " • Cosmetics companies recalled a face powder called "Russian Sable" and renamed it "Dark. " • Starting in Dearborn, Michigan, and spreading to other parts of the country, "Miss Loyalty" beauty contests became the rage.
• Baseball's Cincinnati Reds renamed themselves the "Redlegs. " • Cosmetics companies recalled a face powder called "Russian Sable" and renamed it "Dark. " • Starting in Dearborn, Michigan, and spreading to other parts of the country, "Miss Loyalty" beauty contests became the rage.
 • In the spring of 1954, however, the tables turned when Mc. Carthy charged United States Army. • The ensuing hearings proved to be Mc. Carthy's downfall.
• In the spring of 1954, however, the tables turned when Mc. Carthy charged United States Army. • The ensuing hearings proved to be Mc. Carthy's downfall.
 "I have here in my hand. . . " In the course of testimony Mc. Carthy submitted evidence that was identified as fraudulent. As both public and politicians watched the bullying antics of the Senator, they became increasingly disenchanted.
"I have here in my hand. . . " In the course of testimony Mc. Carthy submitted evidence that was identified as fraudulent. As both public and politicians watched the bullying antics of the Senator, they became increasingly disenchanted.

 • For the first time, television broadcast allowed the general public to see the Senator as a bully. • "Mc. Carthyism" lives on to describe anti-Communist fervor, reckless accusations, and guilt by association
• For the first time, television broadcast allowed the general public to see the Senator as a bully. • "Mc. Carthyism" lives on to describe anti-Communist fervor, reckless accusations, and guilt by association
 Effects of Mc. Carthyism • Many people lost their jobs and livelihoods. • Blacklists and the banning of the Communist Party in America. • Anti-democratic atmosphere.
Effects of Mc. Carthyism • Many people lost their jobs and livelihoods. • Blacklists and the banning of the Communist Party in America. • Anti-democratic atmosphere.
 Effects of Mc. Carthyism 9, 500 civil servants were dismissed and 15, 000 resigned; 600 teachers lost their jobs and many fine actors and scriptwriters were unable to work again. Charlie Chaplin, the biggest Hollywood movie star of the pre-war years (and also a Communist) left America in disgust. The 1950 Mc. Carran Internal Security Act forced organizations to give lists of members (they might be Communists) and the 1954 Communist Control Act banned the Communist Party altogether.
Effects of Mc. Carthyism 9, 500 civil servants were dismissed and 15, 000 resigned; 600 teachers lost their jobs and many fine actors and scriptwriters were unable to work again. Charlie Chaplin, the biggest Hollywood movie star of the pre-war years (and also a Communist) left America in disgust. The 1950 Mc. Carran Internal Security Act forced organizations to give lists of members (they might be Communists) and the 1954 Communist Control Act banned the Communist Party altogether.
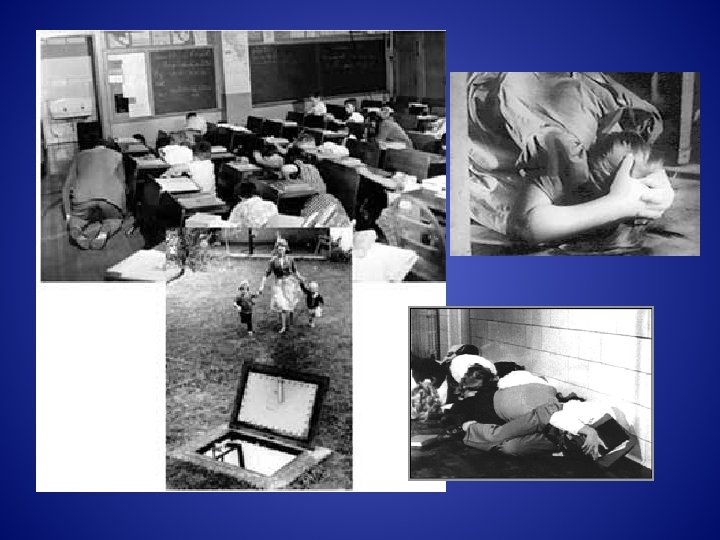
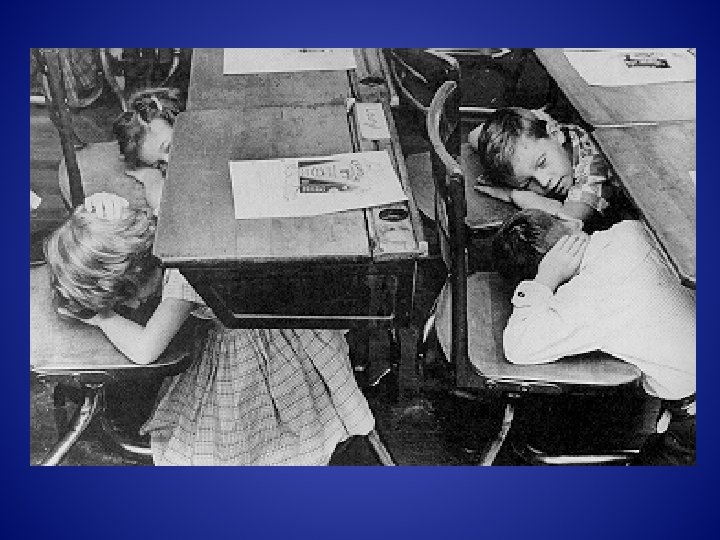
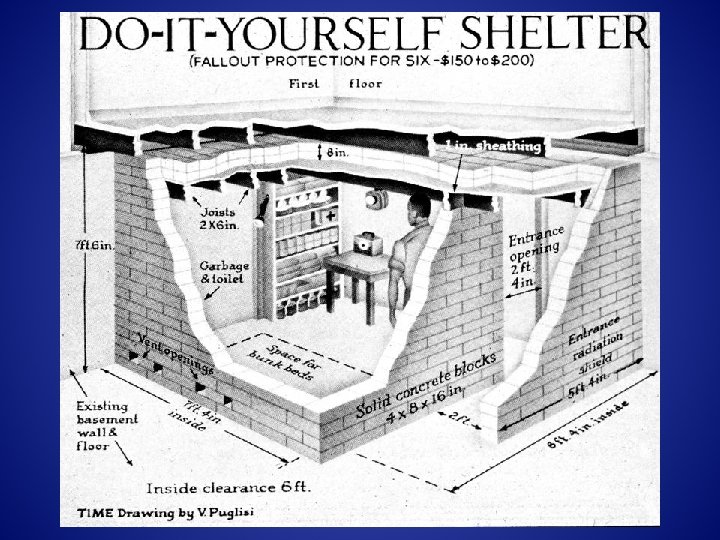
 Civil Defense! 1951 We Have To Be Prepared!
Civil Defense! 1951 We Have To Be Prepared!







 The Korean War 1950– 53
The Korean War 1950– 53
 • The Korean War was the time when the Cold War became a GLOBAL CONFLICT!
• The Korean War was the time when the Cold War became a GLOBAL CONFLICT!
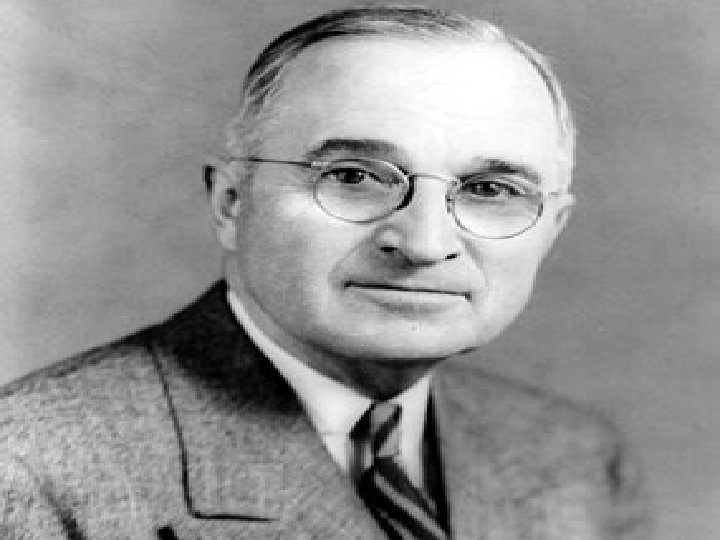
 What caused it? • President Truman was interested in the Far East • DUCKS
What caused it? • President Truman was interested in the Far East • DUCKS
 • Domino theory: Europe was not the only place where Communists were coming to power. • In the Far East, too, they were getting powerful – China turned Communist in 1949. • Truman believed that, if one country fell to Communism, then others would follow, like a line of Dominoes. • He was worried that, if Korea fell, the Communists would capture Japan.
• Domino theory: Europe was not the only place where Communists were coming to power. • In the Far East, too, they were getting powerful – China turned Communist in 1949. • Truman believed that, if one country fell to Communism, then others would follow, like a line of Dominoes. • He was worried that, if Korea fell, the Communists would capture Japan.

 • Undermine Communism: In April 1950, the American National Security Council issued a report (NSC 68) recommending that America abandon 'containment' and start 'rolling back' Communism
• Undermine Communism: In April 1950, the American National Security Council issued a report (NSC 68) recommending that America abandon 'containment' and start 'rolling back' Communism
 • Cold War: Truman realized the USA was in a competition for world domination with the USSR. • By supporting South Korea, America was able to fight Communism without directly attacking Russia.
• Cold War: Truman realized the USA was in a competition for world domination with the USSR. • By supporting South Korea, America was able to fight Communism without directly attacking Russia.
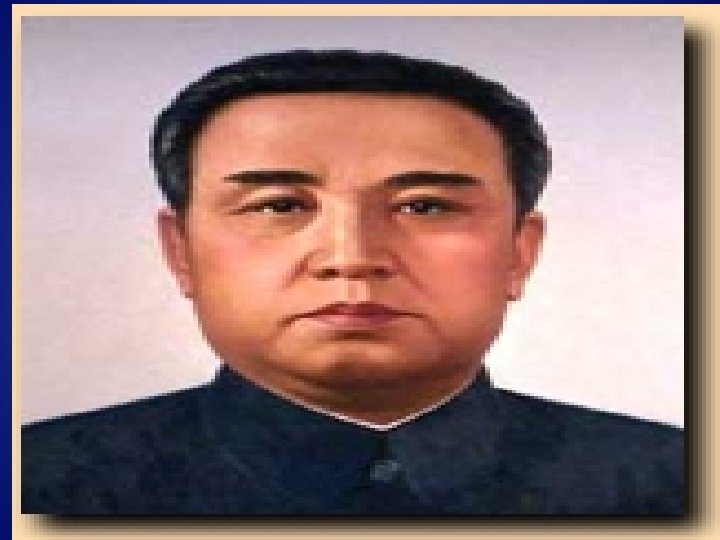
 • Stalin, also, was involved in the Far East: • Kim i. I Sung visited Stalin. In 1949, he persuaded Stalin that he could conquer South Korea. • Stalin did not think that America would dare to get involved, so he gave his agreement.
• Stalin, also, was involved in the Far East: • Kim i. I Sung visited Stalin. In 1949, he persuaded Stalin that he could conquer South Korea. • Stalin did not think that America would dare to get involved, so he gave his agreement.
 • Stalin saw a chance to continue the Cold War and discomfort America, but ‘at arm’s length’ – without directly confronting the Americans. • Kim II Sung also went to see Mao Zedong, the leader of China, to get his agreement.
• Stalin saw a chance to continue the Cold War and discomfort America, but ‘at arm’s length’ – without directly confronting the Americans. • Kim II Sung also went to see Mao Zedong, the leader of China, to get his agreement.

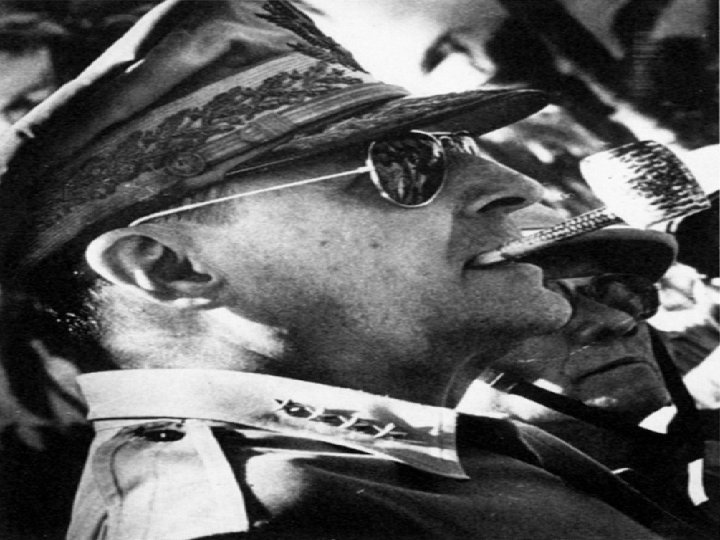
 • Syngman Rhee (leader of South Korea) In 1950 boasted that he was going to attack North Korea. It was a good enough excuse – the North Koreans invaded South Korea.
• Syngman Rhee (leader of South Korea) In 1950 boasted that he was going to attack North Korea. It was a good enough excuse – the North Koreans invaded South Korea.
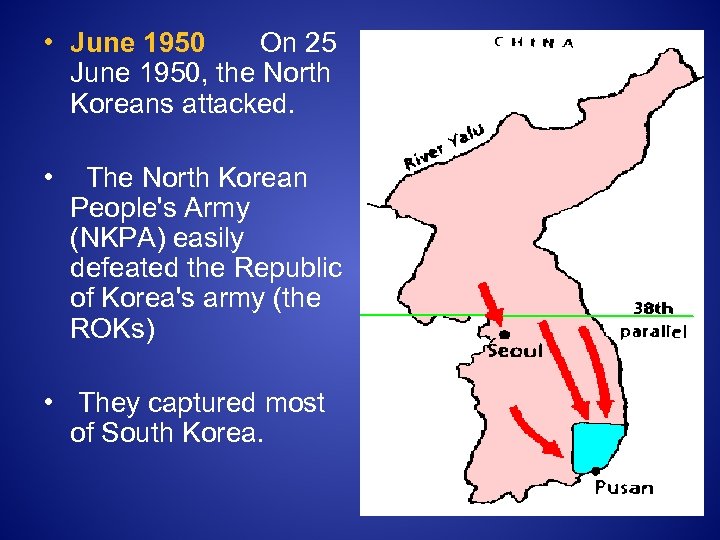 • June 1950 On 25 June 1950, the North Koreans attacked. • The North Korean People's Army (NKPA) easily defeated the Republic of Korea's army (the ROKs) • They captured most of South Korea.
• June 1950 On 25 June 1950, the North Koreans attacked. • The North Korean People's Army (NKPA) easily defeated the Republic of Korea's army (the ROKs) • They captured most of South Korea.
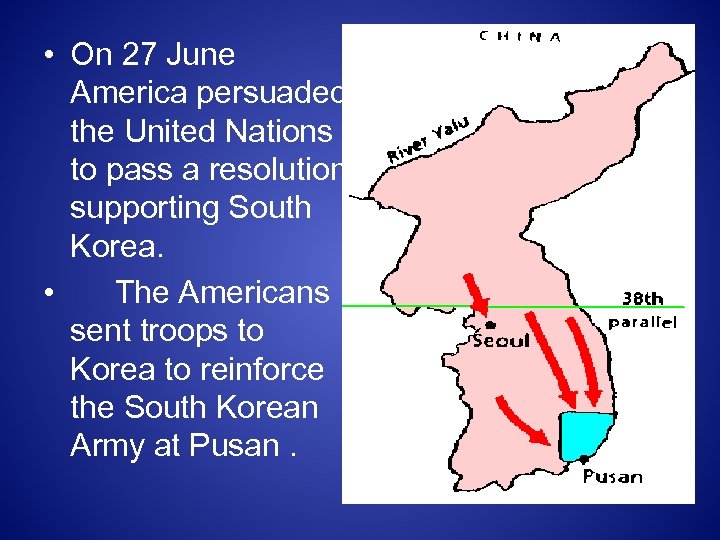 • On 27 June America persuaded the United Nations to pass a resolution supporting South Korea. • The Americans sent troops to Korea to reinforce the South Korean Army at Pusan.
• On 27 June America persuaded the United Nations to pass a resolution supporting South Korea. • The Americans sent troops to Korea to reinforce the South Korean Army at Pusan.
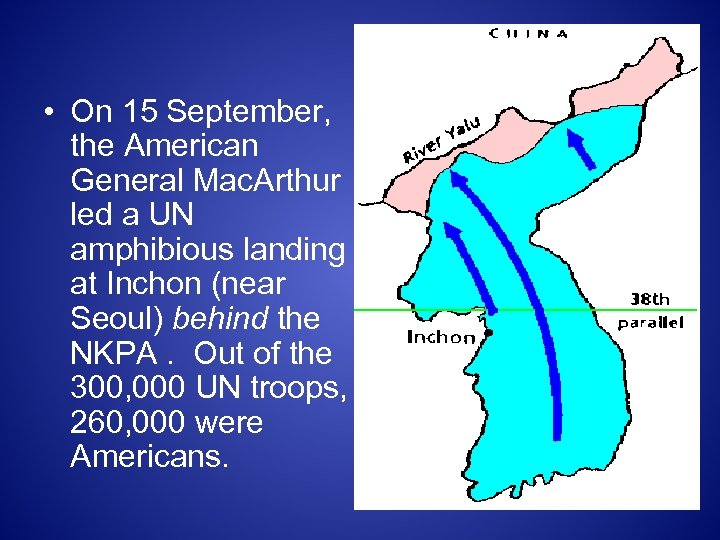 • On 15 September, the American General Mac. Arthur led a UN amphibious landing at Inchon (near Seoul) behind the NKPA. Out of the 300, 000 UN troops, 260, 000 were Americans.
• On 15 September, the American General Mac. Arthur led a UN amphibious landing at Inchon (near Seoul) behind the NKPA. Out of the 300, 000 UN troops, 260, 000 were Americans.

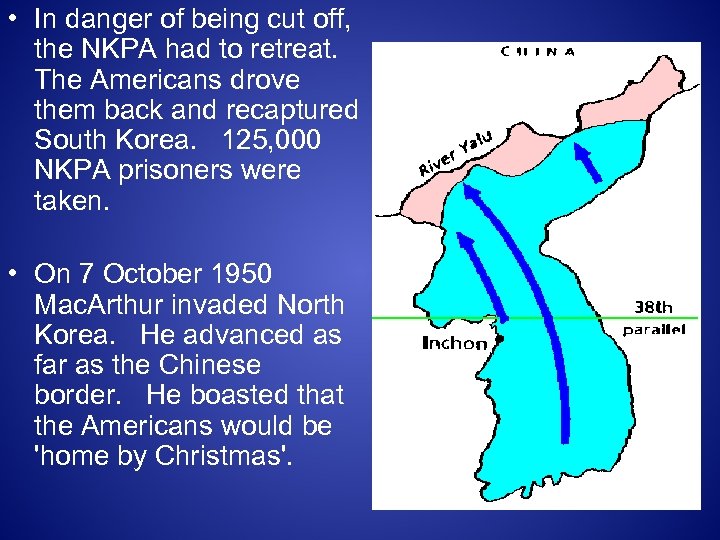 • In danger of being cut off, the NKPA had to retreat. The Americans drove them back and recaptured South Korea. 125, 000 NKPA prisoners were taken. • On 7 October 1950 Mac. Arthur invaded North Korea. He advanced as far as the Chinese border. He boasted that the Americans would be 'home by Christmas'.
• In danger of being cut off, the NKPA had to retreat. The Americans drove them back and recaptured South Korea. 125, 000 NKPA prisoners were taken. • On 7 October 1950 Mac. Arthur invaded North Korea. He advanced as far as the Chinese border. He boasted that the Americans would be 'home by Christmas'.
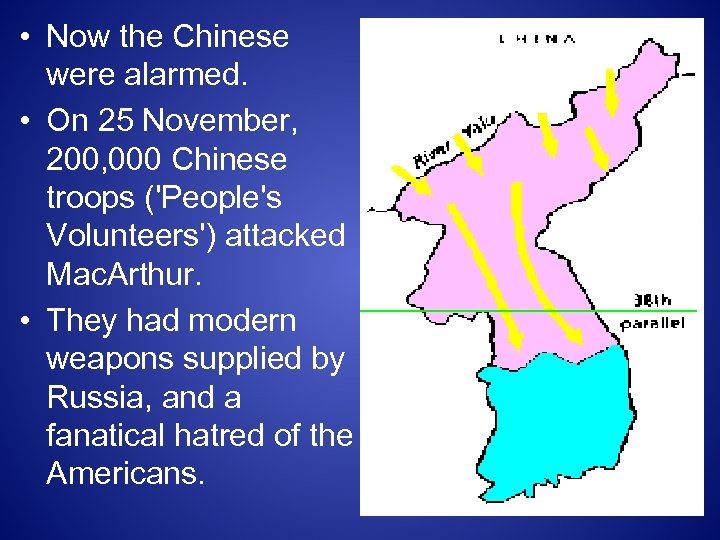 • Now the Chinese were alarmed. • On 25 November, 200, 000 Chinese troops ('People's Volunteers') attacked Mac. Arthur. • They had modern weapons supplied by Russia, and a fanatical hatred of the Americans.
• Now the Chinese were alarmed. • On 25 November, 200, 000 Chinese troops ('People's Volunteers') attacked Mac. Arthur. • They had modern weapons supplied by Russia, and a fanatical hatred of the Americans.
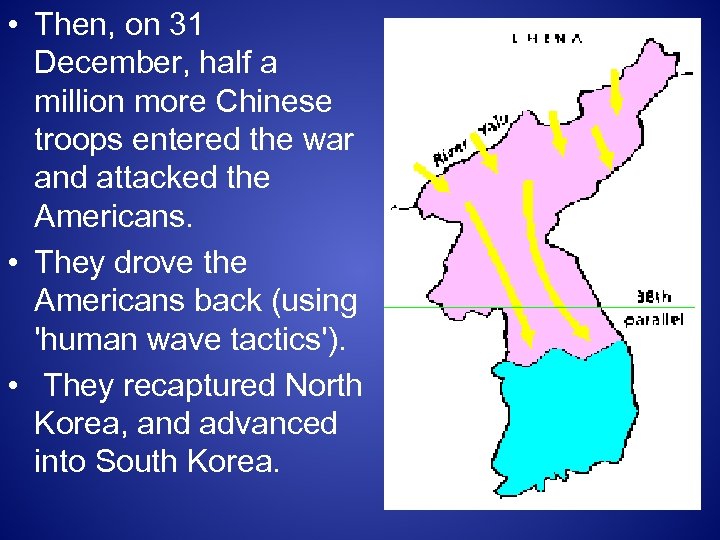 • Then, on 31 December, half a million more Chinese troops entered the war and attacked the Americans. • They drove the Americans back (using 'human wave tactics'). • They recaptured North Korea, and advanced into South Korea.
• Then, on 31 December, half a million more Chinese troops entered the war and attacked the Americans. • They drove the Americans back (using 'human wave tactics'). • They recaptured North Korea, and advanced into South Korea.
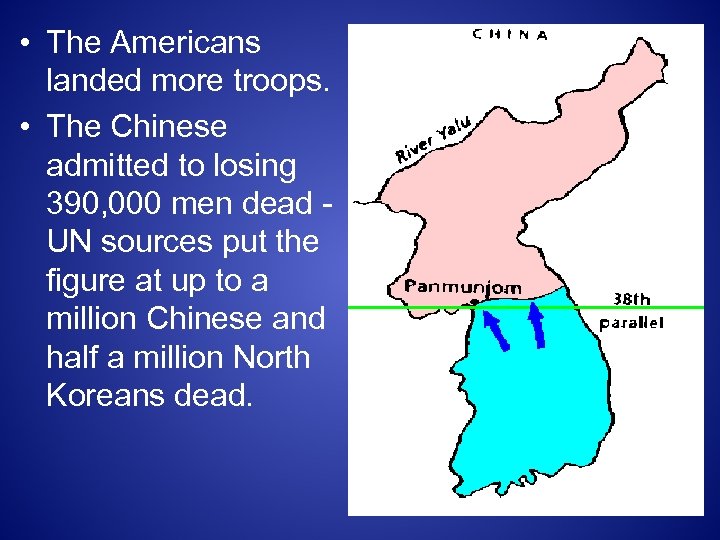 • The Americans landed more troops. • The Chinese admitted to losing 390, 000 men dead - UN sources put the figure at up to a million Chinese and half a million North Koreans dead.
• The Americans landed more troops. • The Chinese admitted to losing 390, 000 men dead - UN sources put the figure at up to a million Chinese and half a million North Koreans dead.
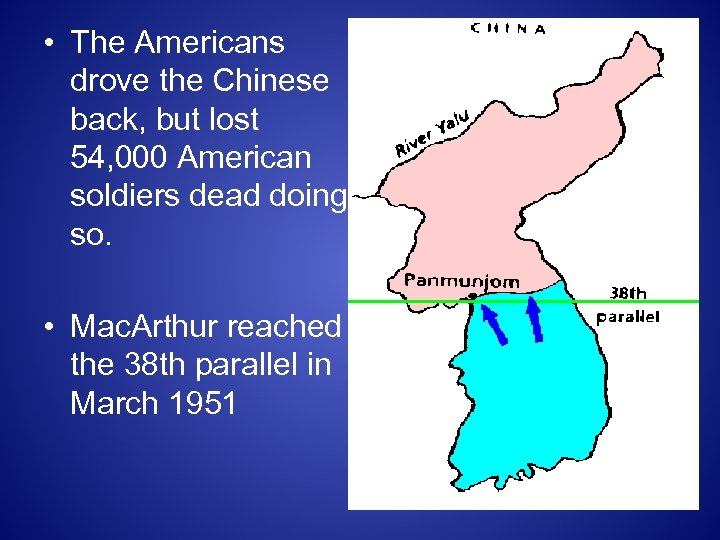 • The Americans drove the Chinese back, but lost 54, 000 American soldiers dead doing so. • Mac. Arthur reached the 38 th parallel in March 1951
• The Americans drove the Chinese back, but lost 54, 000 American soldiers dead doing so. • Mac. Arthur reached the 38 th parallel in March 1951
 March 1951 – 1953 • Truman told Mac. Arthur to stop. Mac. Arthur was fired when he publicly criticized Truman’s order. • In 1953, Eisenhower became American president. • The Americans threatened to use the atomic bomb if China did not stop fighting. The Chinese agree to a truce, which was signed on 27 July 1953. • It is estimated that 10 million people died in the war - as many as died in the First World War.
March 1951 – 1953 • Truman told Mac. Arthur to stop. Mac. Arthur was fired when he publicly criticized Truman’s order. • In 1953, Eisenhower became American president. • The Americans threatened to use the atomic bomb if China did not stop fighting. The Chinese agree to a truce, which was signed on 27 July 1953. • It is estimated that 10 million people died in the war - as many as died in the First World War.
 • Eventually a cease-fire was established on July 27 th, 1953, by which time the front line was back in the proximity of the 38 th parallel. • Demilitarized zone (DMZ) was established around it, which is still defended today by North Korean troops on one side and South Korean and American troops on the other.
• Eventually a cease-fire was established on July 27 th, 1953, by which time the front line was back in the proximity of the 38 th parallel. • Demilitarized zone (DMZ) was established around it, which is still defended today by North Korean troops on one side and South Korean and American troops on the other.
 • No peace treaty has yet been signed to date!!!!!!
• No peace treaty has yet been signed to date!!!!!!
 RESULTS • The Korean War was the first armed confrontation of the Cold War. • It created the idea of a limited war, where the two superpowers would fight without descending to an all out war that could involve nuclear weapons. • It also expanded the Cold War, which to that point had mostly been concerned with Europe
RESULTS • The Korean War was the first armed confrontation of the Cold War. • It created the idea of a limited war, where the two superpowers would fight without descending to an all out war that could involve nuclear weapons. • It also expanded the Cold War, which to that point had mostly been concerned with Europe
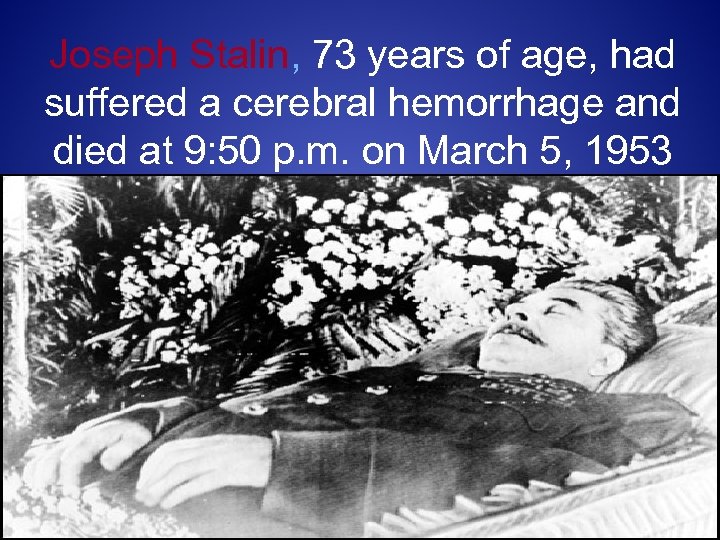 Joseph Stalin, 73 years of age, had suffered a cerebral hemorrhage and died at 9: 50 p. m. on March 5, 1953
Joseph Stalin, 73 years of age, had suffered a cerebral hemorrhage and died at 9: 50 p. m. on March 5, 1953
 The Rosenbergs 1953
The Rosenbergs 1953
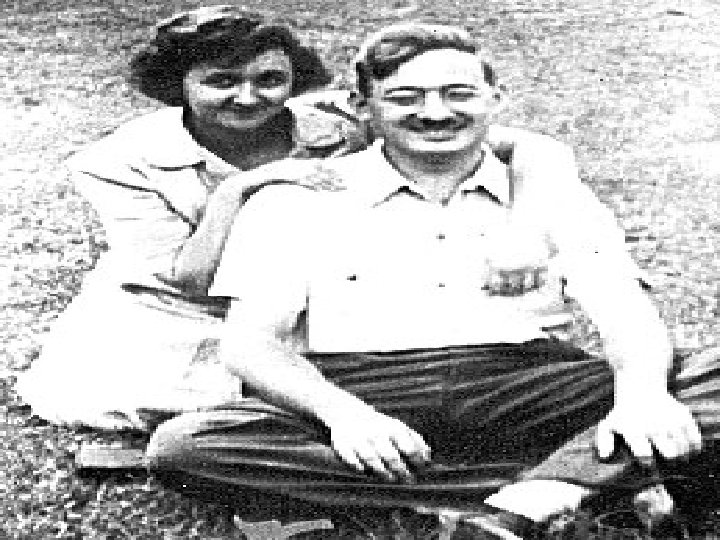
 …a lengthy and controversial espionage case. In 1950, the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Julius Rosenberg (1918– 53), an electrical engineer who had worked (1940– 45) for the U. S. army signal corps, and his wife Ethel (1916– 53); They were indicted for conspiracy to transmit classified military information to the Soviet Union. In the trial that followed (Mar. , 1951), the government charged that in 1944 and 1945 the Rosenbergs had persuaded Ethel's brother, David Greenglass—an employee at the Los Alamos atomic bomb project— to provide them and a third person, Harry Gold, with top-secret data on nuclear weapons. The chief Julius and Ethel Rosenberg evidence against the Rosenbergs came from Ethel’s brother Greenglass and his wife, Ruth.
…a lengthy and controversial espionage case. In 1950, the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Julius Rosenberg (1918– 53), an electrical engineer who had worked (1940– 45) for the U. S. army signal corps, and his wife Ethel (1916– 53); They were indicted for conspiracy to transmit classified military information to the Soviet Union. In the trial that followed (Mar. , 1951), the government charged that in 1944 and 1945 the Rosenbergs had persuaded Ethel's brother, David Greenglass—an employee at the Los Alamos atomic bomb project— to provide them and a third person, Harry Gold, with top-secret data on nuclear weapons. The chief Julius and Ethel Rosenberg evidence against the Rosenbergs came from Ethel’s brother Greenglass and his wife, Ruth.

 Both Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were found guilty (1951) and received the death sentence; Morton Sobell, a codefendant, received a 30 -year prison term, as did Harry Gold; and David Greenglass was later sentenced to 15 years imprisonment. Despite many court appeals and pleas for executive clemency, the Rosenbergs were executed on June 19, 1953. Julius was taken to the electric chair first and given one last chance to confess – if he did, he was assured that Ethel’s sentence would be commuted. He remained silent and was executed. Ethel was brought in – she was much smaller than her husband the authorities failed to adjust the chair’s connections. The first jolt of electricity failed to kill her …. They would have to shock her two more times before she would be declared dead. They became the first U. S. civilians to suffer the death penalty in an espionage trial – Ethel was the first women executed in the electric chair. It would later be revealed that the testimony against Ethel was false. She was only guilty of being Julius Rosenberg’s wife.
Both Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were found guilty (1951) and received the death sentence; Morton Sobell, a codefendant, received a 30 -year prison term, as did Harry Gold; and David Greenglass was later sentenced to 15 years imprisonment. Despite many court appeals and pleas for executive clemency, the Rosenbergs were executed on June 19, 1953. Julius was taken to the electric chair first and given one last chance to confess – if he did, he was assured that Ethel’s sentence would be commuted. He remained silent and was executed. Ethel was brought in – she was much smaller than her husband the authorities failed to adjust the chair’s connections. The first jolt of electricity failed to kill her …. They would have to shock her two more times before she would be declared dead. They became the first U. S. civilians to suffer the death penalty in an espionage trial – Ethel was the first women executed in the electric chair. It would later be revealed that the testimony against Ethel was false. She was only guilty of being Julius Rosenberg’s wife.
 1954. . . . things begin to get warm. . . .
1954. . . . things begin to get warm. . . .
 Soviet Union sets up the KGB.
Soviet Union sets up the KGB.
 • Komitet Gosudarstvennoy Bezopasnosti or Committee for State Security. • It was the Soviet Union's premier internal security, intelligence, and secret police organization.
• Komitet Gosudarstvennoy Bezopasnosti or Committee for State Security. • It was the Soviet Union's premier internal security, intelligence, and secret police organization.
 CIA Coup in Iran
CIA Coup in Iran
 The 1954 Coup in Iran was the CIA's (Central Intelligence Agency) first successful overthrow of a foreign government. Great Britain initiated the plot in 1952 to guarantee access to Iranian oil and approached the US. The Truman administration rejected it, but President Eisenhower approved it shortly after taking office in 1953, because of fears about oil and Communism. CIA agents orchestrating the Iran coup worked directly with royalist Iranian military officers, handpicked the prime minister's replacement, sent a stream of envoys to bolster the shah's courage, directed a campaign of bombings by Iranians posing as members of the Communist Party, and planted articles and editorial cartoons in newspapers. A harsh military dictatorship was setup. The coup was a turning point in modern Iranian history and remains a persistent irritant in Tehran-Washington relations. It consolidated the power of the shah, who ruled with an iron hand for 26 more years in close contact with the United States.
The 1954 Coup in Iran was the CIA's (Central Intelligence Agency) first successful overthrow of a foreign government. Great Britain initiated the plot in 1952 to guarantee access to Iranian oil and approached the US. The Truman administration rejected it, but President Eisenhower approved it shortly after taking office in 1953, because of fears about oil and Communism. CIA agents orchestrating the Iran coup worked directly with royalist Iranian military officers, handpicked the prime minister's replacement, sent a stream of envoys to bolster the shah's courage, directed a campaign of bombings by Iranians posing as members of the Communist Party, and planted articles and editorial cartoons in newspapers. A harsh military dictatorship was setup. The coup was a turning point in modern Iranian history and remains a persistent irritant in Tehran-Washington relations. It consolidated the power of the shah, who ruled with an iron hand for 26 more years in close contact with the United States.
 CIA Coup in Guatemala
CIA Coup in Guatemala
 CIA Coup in Guatemala In the 1950 s, the Guatemalans dared to challenge an American business that controlled much of its economy. In 1954, the CIA helped overthrow the democratically elected government of Guatemalan President Jacobo Arbenz. Why? Because Arbenz incurred Washington's wrath with his Agrarian Reform Plan, which, among other things, confiscated lands owned by the U. S. -based United Fruit Company and redistributed it to peasants.
CIA Coup in Guatemala In the 1950 s, the Guatemalans dared to challenge an American business that controlled much of its economy. In 1954, the CIA helped overthrow the democratically elected government of Guatemalan President Jacobo Arbenz. Why? Because Arbenz incurred Washington's wrath with his Agrarian Reform Plan, which, among other things, confiscated lands owned by the U. S. -based United Fruit Company and redistributed it to peasants.
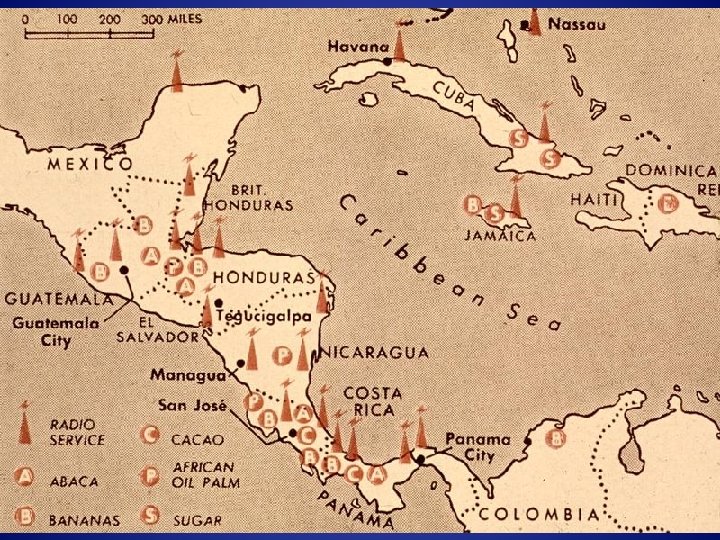
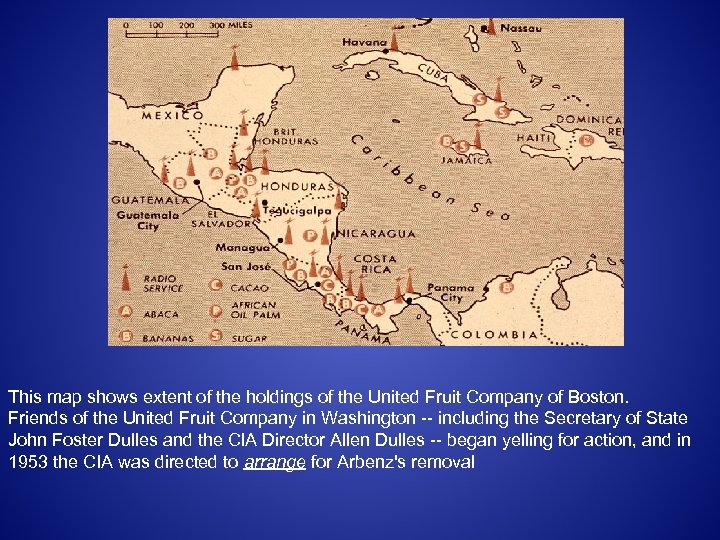 This map shows extent of the holdings of the United Fruit Company of Boston. Friends of the United Fruit Company in Washington -- including the Secretary of State John Foster Dulles and the CIA Director Allen Dulles -- began yelling for action, and in 1953 the CIA was directed to arrange for Arbenz's removal
This map shows extent of the holdings of the United Fruit Company of Boston. Friends of the United Fruit Company in Washington -- including the Secretary of State John Foster Dulles and the CIA Director Allen Dulles -- began yelling for action, and in 1953 the CIA was directed to arrange for Arbenz's removal
 Gasoline depot bombed by CIA rebel air force.
Gasoline depot bombed by CIA rebel air force.
 The agency began funding a small band of rebels based in neighboring Honduras, and on June 18, 1954, these forces attacked. At first they made little progress, but a CIA radio propaganda campaign exaggerated the size of the rebel force and contributed to the defection of Arbenz's officer corps. Arbenz fled into exile and a military junta took control of the Guatemalan government.
The agency began funding a small band of rebels based in neighboring Honduras, and on June 18, 1954, these forces attacked. At first they made little progress, but a CIA radio propaganda campaign exaggerated the size of the rebel force and contributed to the defection of Arbenz's officer corps. Arbenz fled into exile and a military junta took control of the Guatemalan government.
 Guatemala now had a government installed by the CIA – a military dictatorship. . . But it wasn’t Communist!
Guatemala now had a government installed by the CIA – a military dictatorship. . . But it wasn’t Communist!
 The Nuclear Arms Race The Soviet atomic bomb motivated the USA to The U. S. monopoly on nuclear weapons regain its nuclear advantage; when the USSR technology ended in 1949 In 1952, the U. S. successfully tested their bomb (1, 000 bomb tested the 1 st hydrogen own atomic times more powerful than the a-bomb) The Soviets responded with their own hydrogen bomb in 1953
The Nuclear Arms Race The Soviet atomic bomb motivated the USA to The U. S. monopoly on nuclear weapons regain its nuclear advantage; when the USSR technology ended in 1949 In 1952, the U. S. successfully tested their bomb (1, 000 bomb tested the 1 st hydrogen own atomic times more powerful than the a-bomb) The Soviets responded with their own hydrogen bomb in 1953
 First Indochina War 1946 -1954
First Indochina War 1946 -1954
 • Throughout the 1930 s and 40 s, rural uprisings in French Indochina organized by Ho Chi Minh and the Communist Party became common occurrences. However, the British and the Nationalist Chinese sided with the French.
• Throughout the 1930 s and 40 s, rural uprisings in French Indochina organized by Ho Chi Minh and the Communist Party became common occurrences. However, the British and the Nationalist Chinese sided with the French.
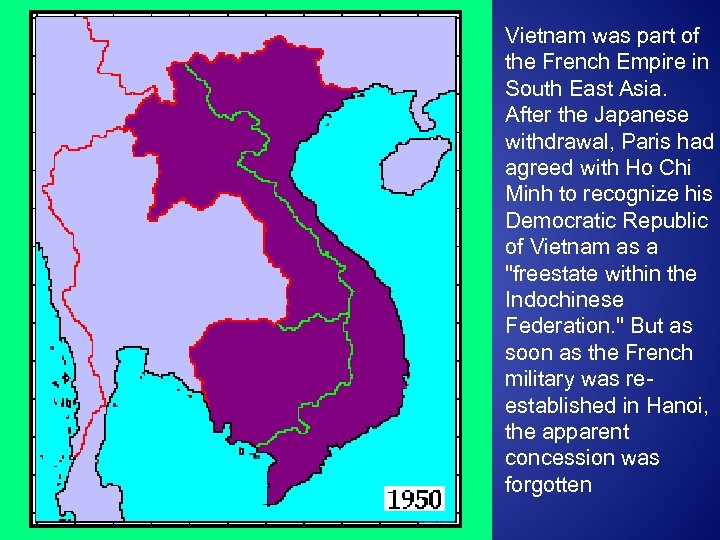 Vietnam was part of the French Empire in South East Asia. After the Japanese withdrawal, Paris had agreed with Ho Chi Minh to recognize his Democratic Republic of Vietnam as a "freestate within the Indochinese Federation. " But as soon as the French military was reestablished in Hanoi, the apparent concession was forgotten
Vietnam was part of the French Empire in South East Asia. After the Japanese withdrawal, Paris had agreed with Ho Chi Minh to recognize his Democratic Republic of Vietnam as a "freestate within the Indochinese Federation. " But as soon as the French military was reestablished in Hanoi, the apparent concession was forgotten
 • Since WWI Ho Chi Minh sought independence from France. • Ho Chi Minh turned to USSR for aid • Put US in difficult spot
• Since WWI Ho Chi Minh sought independence from France. • Ho Chi Minh turned to USSR for aid • Put US in difficult spot
 • France had agreed with Ho Chi Minh to recognize his Democratic Republic of Vietnam as a "freestate within the Indochinese Federation. " • But as soon as the French took over from the Japanese after WWII the apparent concession was forgotten
• France had agreed with Ho Chi Minh to recognize his Democratic Republic of Vietnam as a "freestate within the Indochinese Federation. " • But as soon as the French took over from the Japanese after WWII the apparent concession was forgotten
 In December 1946, negotiations with Ho Chi Minh failed, and fighting broke out again between the French and Ho's Viet Minh. The first Indochina war had begun, and it would continue for another eight years.
In December 1946, negotiations with Ho Chi Minh failed, and fighting broke out again between the French and Ho's Viet Minh. The first Indochina war had begun, and it would continue for another eight years.
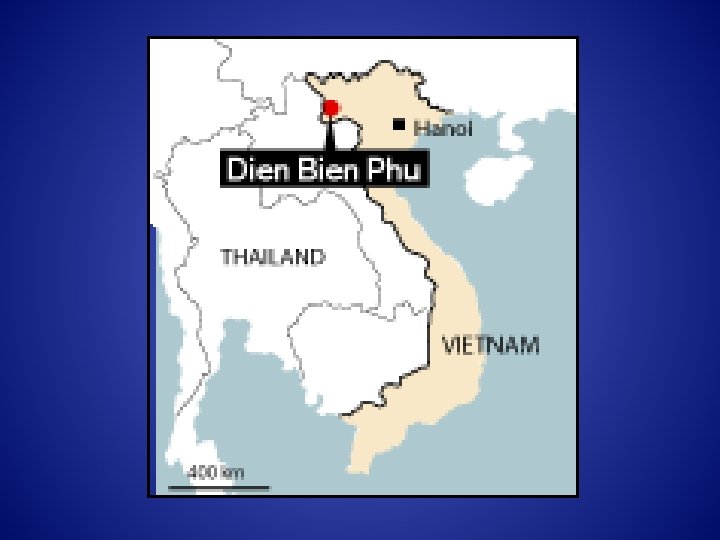
 7 May 1954 Dien Bien Phu
7 May 1954 Dien Bien Phu
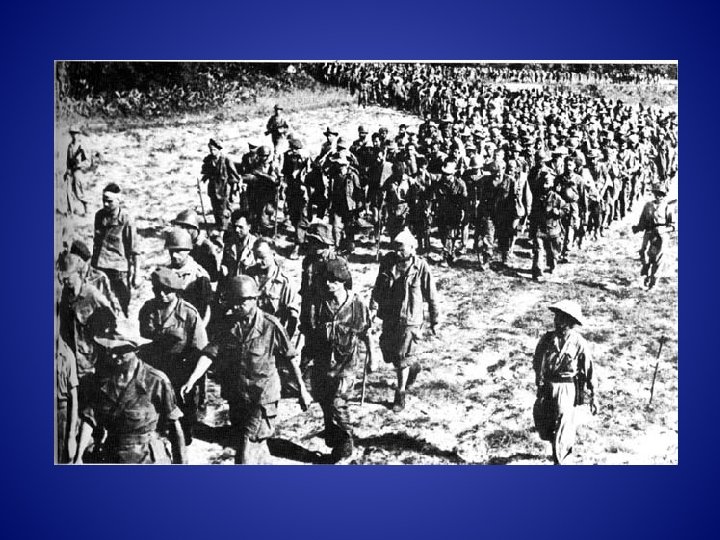

 On May, 8 1954 the Viet Minh counted 11, 721 prisoners, amongst whom were 4, 436 wounded. 858 of the most seriously wounded were evacuated under the control of the Red Cross. Of the remaining 10, 863 prisoners, including 3, 578 wounded, the Viet Minh returned only 3, 290 four months later. The number of men who died in the camps, 7, 573, represents a percentage on the order of 70%.
On May, 8 1954 the Viet Minh counted 11, 721 prisoners, amongst whom were 4, 436 wounded. 858 of the most seriously wounded were evacuated under the control of the Red Cross. Of the remaining 10, 863 prisoners, including 3, 578 wounded, the Viet Minh returned only 3, 290 four months later. The number of men who died in the camps, 7, 573, represents a percentage on the order of 70%.
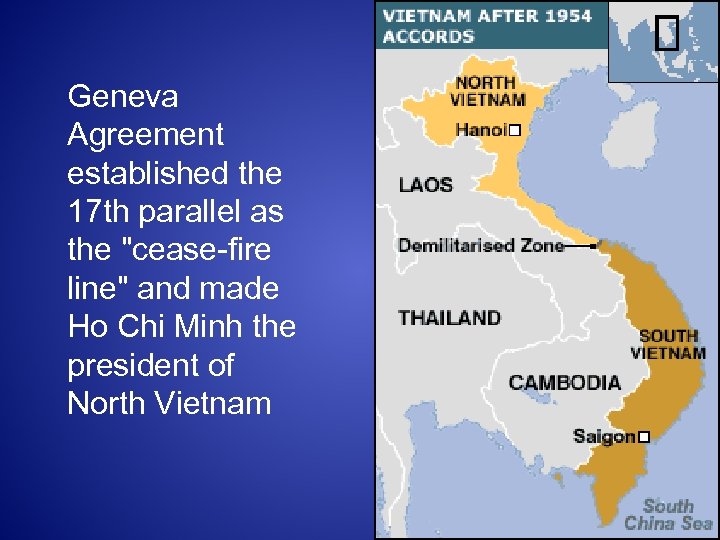 Geneva Agreement established the 17 th parallel as the "cease-fire line" and made Ho Chi Minh the president of North Vietnam
Geneva Agreement established the 17 th parallel as the "cease-fire line" and made Ho Chi Minh the president of North Vietnam
 At the same time, the first major refugee movement had began. Almost a million Catholic Vietnamese from North Vietnam, led by their priests and transported by the United States Navy moved to South Vietnam. While more than 50, 000 people from South Vietnam moved to the North.
At the same time, the first major refugee movement had began. Almost a million Catholic Vietnamese from North Vietnam, led by their priests and transported by the United States Navy moved to South Vietnam. While more than 50, 000 people from South Vietnam moved to the North.
 The United States refused to bail France out. “We shall fight no land war in Asia. ”
The United States refused to bail France out. “We shall fight no land war in Asia. ”
 Warsaw Pact • The Warsaw Pact, officially named the Treaty of Friendship, cooperation and mutual assistance was a military alliance of the Eastern European Eastern Bloc countries • Who intended to organize against the perceived threat from the NATO alliance
Warsaw Pact • The Warsaw Pact, officially named the Treaty of Friendship, cooperation and mutual assistance was a military alliance of the Eastern European Eastern Bloc countries • Who intended to organize against the perceived threat from the NATO alliance
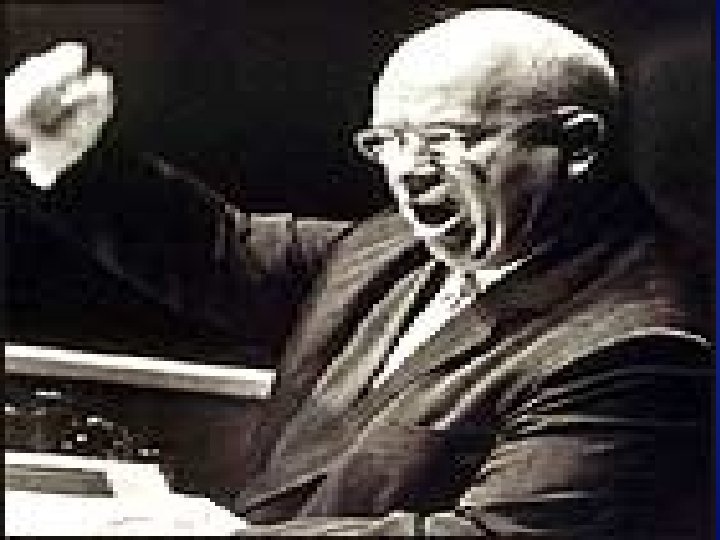

 • The Warsaw treaty was drafted by Nikita Khrushchev in 1955 and signed in Warsaw on May 14, 1955.
• The Warsaw treaty was drafted by Nikita Khrushchev in 1955 and signed in Warsaw on May 14, 1955.
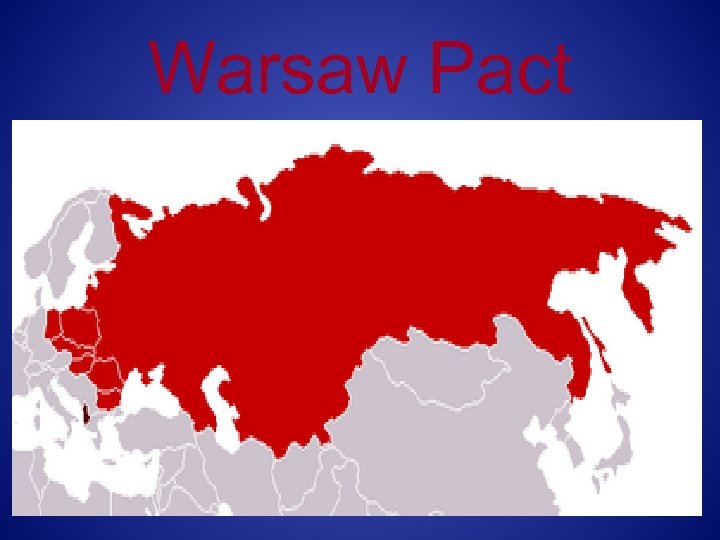 Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
 Warsaw Pact Members • • Soviet Union Albania Bulgaria Romania East Germany Hungary Poland Czechoslovakia
Warsaw Pact Members • • Soviet Union Albania Bulgaria Romania East Germany Hungary Poland Czechoslovakia
 The Hungarian Rebellion The First Domino November 14, 1956
The Hungarian Rebellion The First Domino November 14, 1956

 Causes • Poverty – Hungarians were poor, yet much of the food and industrial goods they produced was sent to Russia. • Russian Control – The Hungarians were very patriotic, and they hated Russian control – which included censorship, the vicious secret police (called the AVH after 1948) and Russian control of what the schools taught. –
Causes • Poverty – Hungarians were poor, yet much of the food and industrial goods they produced was sent to Russia. • Russian Control – The Hungarians were very patriotic, and they hated Russian control – which included censorship, the vicious secret police (called the AVH after 1948) and Russian control of what the schools taught. –
 • Catholic Church – The Hungarians were religious, but the Communist Party had banned religion, and put the leader of the Catholic Church in prison. • Help from the West – Hungarians thought that the United Nations or the new US president, Eisenhower, would help them.
• Catholic Church – The Hungarians were religious, but the Communist Party had banned religion, and put the leader of the Catholic Church in prison. • Help from the West – Hungarians thought that the United Nations or the new US president, Eisenhower, would help them.
 • Destalinisation – When the Communist Party tried to Destalinise Hungary, things got out of control. The Hungarian leader Rakosi asked for permission to arrest 400 trouble-makers, but Khrushchev would not let him.
• Destalinisation – When the Communist Party tried to Destalinise Hungary, things got out of control. The Hungarian leader Rakosi asked for permission to arrest 400 trouble-makers, but Khrushchev would not let him.
 János Kádár Communist leader 1956 -1988
János Kádár Communist leader 1956 -1988
 At 5: 20 a. m. , Hungarian Prime Minister Imre Nagy announced the invasion to the nation in a grim, 35 second broadcast, declaring: "Our troops are fighting. The Government is in its place. " However, within hours Nagy himself would seek asylum at the Yugoslav Embassy in Budapest while his former colleague and imminent replacement, János Kádár, who had been flown secretly from Moscow to the city of Szolnok, 60 miles southeast of the capital, prepared to take power with Moscow's backing.
At 5: 20 a. m. , Hungarian Prime Minister Imre Nagy announced the invasion to the nation in a grim, 35 second broadcast, declaring: "Our troops are fighting. The Government is in its place. " However, within hours Nagy himself would seek asylum at the Yugoslav Embassy in Budapest while his former colleague and imminent replacement, János Kádár, who had been flown secretly from Moscow to the city of Szolnok, 60 miles southeast of the capital, prepared to take power with Moscow's backing.
 On November 22, after receiving assurances of safe passage from Kádár and the Soviets, Nagy finally agreed to leave the Yugoslav Embassy. But he was immediately arrested by Soviet security officers and flown to a secret location in Romania.
On November 22, after receiving assurances of safe passage from Kádár and the Soviets, Nagy finally agreed to leave the Yugoslav Embassy. But he was immediately arrested by Soviet security officers and flown to a secret location in Romania.

 By then, the fighting had mostly ended, the Hungarian resistance had essentially been destroyed, and Kádár was entering the next phase of his strategy to neutralize dissent for the long term. The defeat of the Hungarian revolution was one of the darkest moments of the Cold War.
By then, the fighting had mostly ended, the Hungarian resistance had essentially been destroyed, and Kádár was entering the next phase of his strategy to neutralize dissent for the long term. The defeat of the Hungarian revolution was one of the darkest moments of the Cold War.
 TWO reasons why the West did not help Hungary: • 1. Britain and France were involved in the Suez crisis in Egypt. • 2. Eisenhower did not think Hungary worth a world war. When the UN suggested an investigation, Russia used its veto to stop
TWO reasons why the West did not help Hungary: • 1. Britain and France were involved in the Suez crisis in Egypt. • 2. Eisenhower did not think Hungary worth a world war. When the UN suggested an investigation, Russia used its veto to stop
 The Suez Crisis 1956
The Suez Crisis 1956
 Great Britain decided to join with France and Israel in a military intervention to attempt to prevent General Nasser from nationalizing the Suez Canal in the autumn of 1956. Nasser was promoting Arab nationalism throughout the Middle East and had become an increasing source of irritation to the British and the French.
Great Britain decided to join with France and Israel in a military intervention to attempt to prevent General Nasser from nationalizing the Suez Canal in the autumn of 1956. Nasser was promoting Arab nationalism throughout the Middle East and had become an increasing source of irritation to the British and the French.
 The Anglo-French assault upon Egypt, which began on 31 October 1956, provoked a furious response from the USA. President Eisenhower's condemnation of the attack triggered a sterling crisis which forced the government to withdraw from the venture.
The Anglo-French assault upon Egypt, which began on 31 October 1956, provoked a furious response from the USA. President Eisenhower's condemnation of the attack triggered a sterling crisis which forced the government to withdraw from the venture.
 Coup in Cuba Former Cuban president Fulgencio Batista y Zaldivar seized power by coup, and ruled as dictator until he fled from the forces of Fidel Castro (January 1, 1959) CIA tried to stop Fidel Castro from taking over Cuba but failed resulting in Cuba becoming a communist country.
Coup in Cuba Former Cuban president Fulgencio Batista y Zaldivar seized power by coup, and ruled as dictator until he fled from the forces of Fidel Castro (January 1, 1959) CIA tried to stop Fidel Castro from taking over Cuba but failed resulting in Cuba becoming a communist country.
 Sputnik 1957
Sputnik 1957
 History changed on October 4, 1957, when the Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik I. The world's first artificial satellite was about the size of a basketball, weighed only 183 pounds, and took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth on its elliptical path. That launch ushered in new political, military, technological, and scientific developments. While the Sputnik launch was a single event, it marked the start of the space age and the U. S. -U. S. S. R space race.
History changed on October 4, 1957, when the Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik I. The world's first artificial satellite was about the size of a basketball, weighed only 183 pounds, and took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth on its elliptical path. That launch ushered in new political, military, technological, and scientific developments. While the Sputnik launch was a single event, it marked the start of the space age and the U. S. -U. S. S. R space race.

 Tension grows between USSR and US • • • 1. Sputnik (1957) Sputnik = psychological 2. Castro in (1959) Castro = communist right next to US 3. China accused Khrushchev of being soft on America • A summit was planned for May 1960 between the two superpowers
Tension grows between USSR and US • • • 1. Sputnik (1957) Sputnik = psychological 2. Castro in (1959) Castro = communist right next to US 3. China accused Khrushchev of being soft on America • A summit was planned for May 1960 between the two superpowers
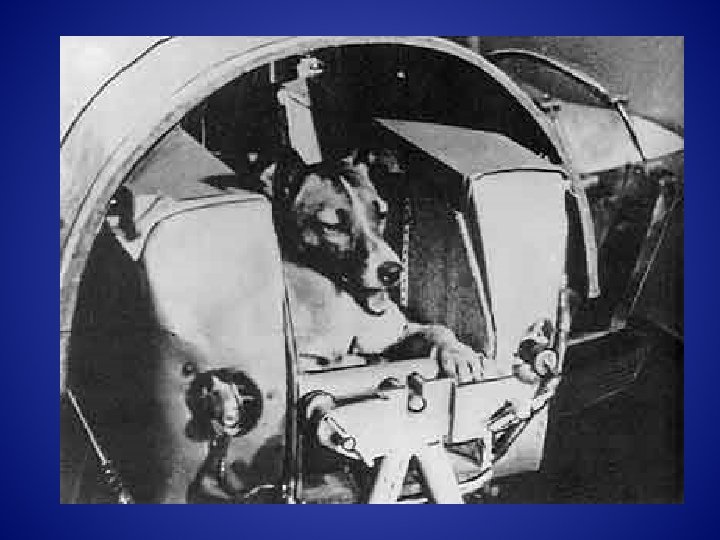
 The second Sputnik satellite was launched on Nov 3, 1957 and carried a dog, named Laika, into space. Laika died a few hours after launch from stress and overheating. Her true cause of death was not made public until decades after the flight, with officials stating that she was either euthanized by poisoned food or died when the oxygen ran out. Some former Soviet scientists have since expressed regret for allowing Laika to die. The last Sputnik installment was intended to be a space laboratory for study of Earth's magnetic field and radiation belt. After its launch on May 15, 1958, it remained in orbit for nearly two years.
The second Sputnik satellite was launched on Nov 3, 1957 and carried a dog, named Laika, into space. Laika died a few hours after launch from stress and overheating. Her true cause of death was not made public until decades after the flight, with officials stating that she was either euthanized by poisoned food or died when the oxygen ran out. Some former Soviet scientists have since expressed regret for allowing Laika to die. The last Sputnik installment was intended to be a space laboratory for study of Earth's magnetic field and radiation belt. After its launch on May 15, 1958, it remained in orbit for nearly two years.


