c77de595e2ffacac302587154caa2907.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 17 Chapter 16: Trends in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World
17 Chapter 16: Trends in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World
 Reasons for Slow Development u Rework l Using the wrong software l Not meeting minimum quality standards u Shifting l requirements and project changes Changes to design and construction u Improper l tools and techniques for project Reduces quality, increases development time u Poor Project Management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
Reasons for Slow Development u Rework l Using the wrong software l Not meeting minimum quality standards u Shifting l requirements and project changes Changes to design and construction u Improper l tools and techniques for project Reduces quality, increases development time u Poor Project Management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
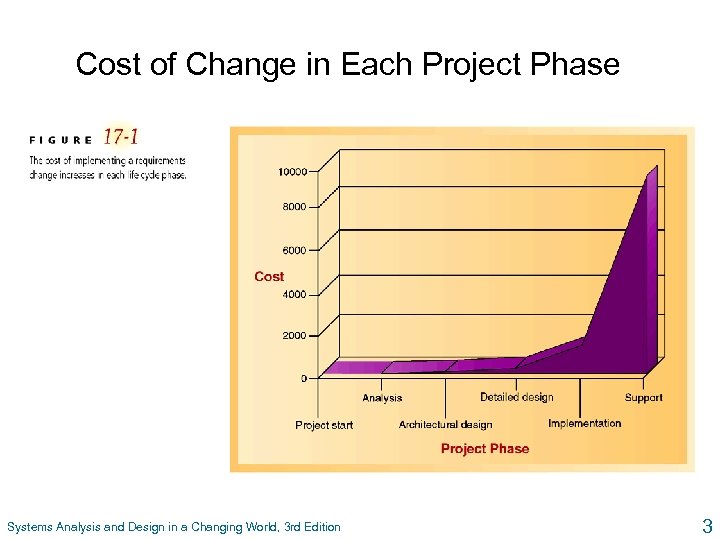 Cost of Change in Each Project Phase Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
Cost of Change in Each Project Phase Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
 What is RAD? u Collection of development approaches, techniques, tools, and technologies u RAD proven to shorten development schedules u No universal RAD approach shortens every project schedule u No technique, tools or technology fits perfectly u Key is identifying overall development approach and matching set of techniques, tools, techniques most suitable to approach and specific project Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
What is RAD? u Collection of development approaches, techniques, tools, and technologies u RAD proven to shorten development schedules u No universal RAD approach shortens every project schedule u No technique, tools or technology fits perfectly u Key is identifying overall development approach and matching set of techniques, tools, techniques most suitable to approach and specific project Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
 Rapid Application Development u RAD is overused and poorly understood u Software developers claim they do, but cannot precisely define u Equated with tools and techniques l Prototyping, fourth-generation programming languages, CASE tools l Object-oriented analysis, design, and development u Tool vendors and methodologies claim RAD u Competing and confusing claims Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
Rapid Application Development u RAD is overused and poorly understood u Software developers claim they do, but cannot precisely define u Equated with tools and techniques l Prototyping, fourth-generation programming languages, CASE tools l Object-oriented analysis, design, and development u Tool vendors and methodologies claim RAD u Competing and confusing claims Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
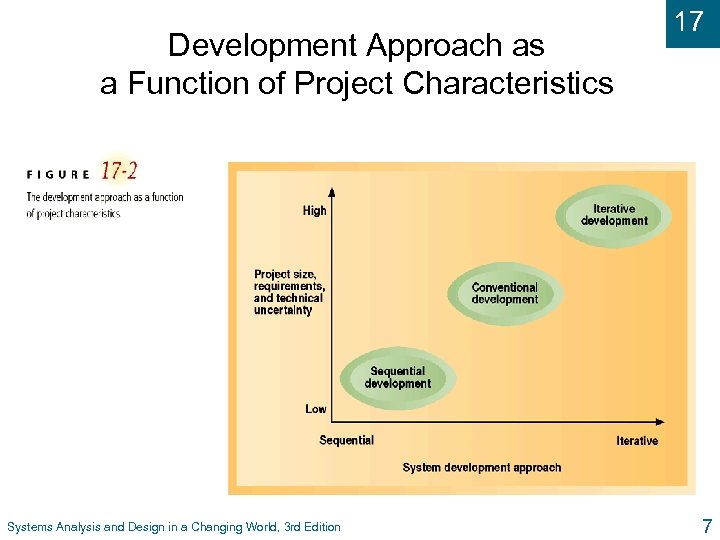 Development Approach as a Function of Project Characteristics Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17 7
Development Approach as a Function of Project Characteristics Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17 7
 Prototyping Approach to Development u Discovery prototype l Used in analysis or early design l Uncover or refine system requirements l Can be thrown away u Developmental prototype l Not thrown away l Part of iterative development until final system complete Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
Prototyping Approach to Development u Discovery prototype l Used in analysis or early design l Uncover or refine system requirements l Can be thrown away u Developmental prototype l Not thrown away l Part of iterative development until final system complete Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
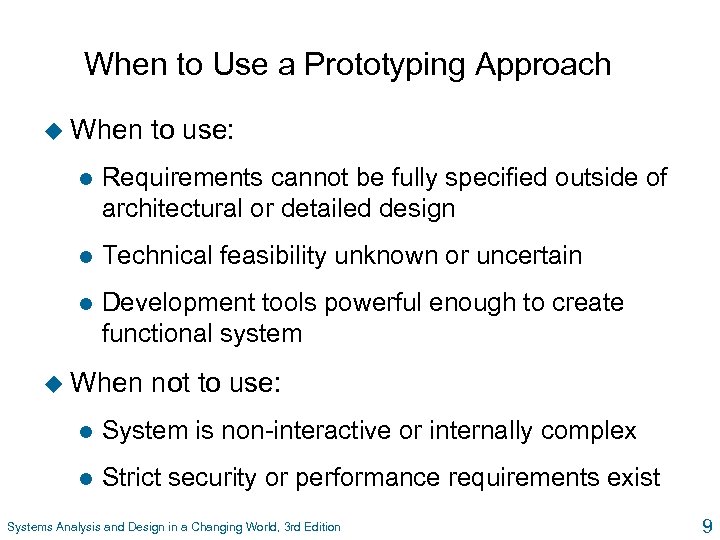 When to Use a Prototyping Approach u When to use: l Requirements cannot be fully specified outside of architectural or detailed design l Technical feasibility unknown or uncertain l Development tools powerful enough to create functional system u When not to use: l System is non-interactive or internally complex l Strict security or performance requirements exist Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
When to Use a Prototyping Approach u When to use: l Requirements cannot be fully specified outside of architectural or detailed design l Technical feasibility unknown or uncertain l Development tools powerful enough to create functional system u When not to use: l System is non-interactive or internally complex l Strict security or performance requirements exist Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
 Prototyping Tool Requirements u Development u Flexibility speed and power u Techniques and capabilities l WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) l Generation of complete programs, program skeletons, or database schemas from diagrams l Rapid customization of software libraries or components l Error-checking and debugging capabilities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10
Prototyping Tool Requirements u Development u Flexibility speed and power u Techniques and capabilities l WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) l Generation of complete programs, program skeletons, or database schemas from diagrams l Rapid customization of software libraries or components l Error-checking and debugging capabilities Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10
 Prototyping Tools u Simple l Access l Excel l Graphical u Visual Studio. NET u Power. Builder u Oracle Forms Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
Prototyping Tools u Simple l Access l Excel l Graphical u Visual Studio. NET u Power. Builder u Oracle Forms Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
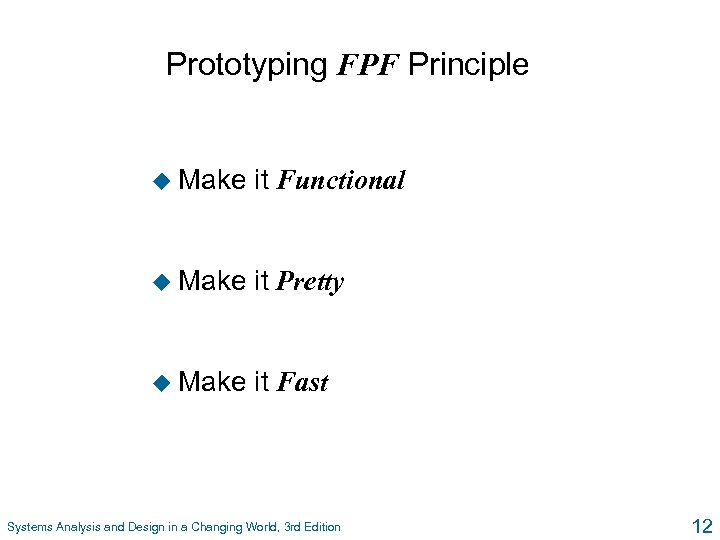 Prototyping FPF Principle u Make it Functional u Make it Pretty u Make it Fast Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
Prototyping FPF Principle u Make it Functional u Make it Pretty u Make it Fast Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
 Spiral Approach to Development u Iterative l development approach Each iteration may include combination of planning, analysis, design, or development steps u More radical departure from traditional development than prototyping development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 13
Spiral Approach to Development u Iterative l development approach Each iteration may include combination of planning, analysis, design, or development steps u More radical departure from traditional development than prototyping development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 13
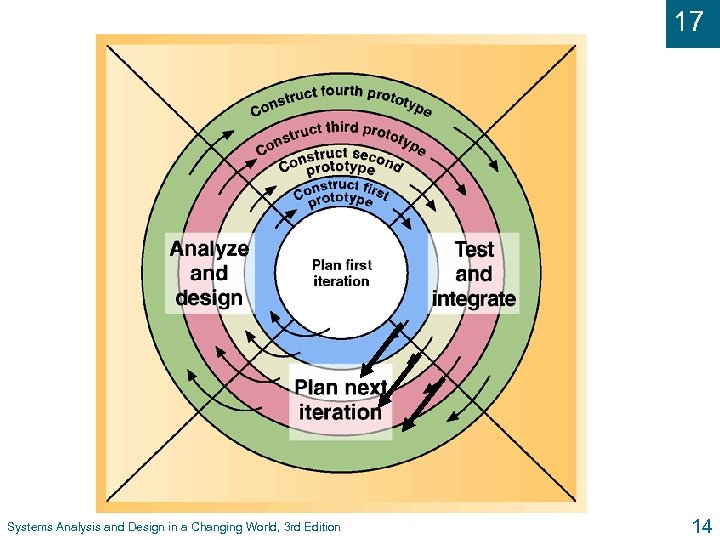 17 The Spiral Life Cycle Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
17 The Spiral Life Cycle Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
 Steps in the Spiral Development Approach u Criteria for feature selection for each prototype l User priorities l Uncertain requirements l Function reuse l Implementation risk u Break into categories l “Must have”, “Should have”, “Nice to have” l Complete high priorities earlier to reduce risk Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
Steps in the Spiral Development Approach u Criteria for feature selection for each prototype l User priorities l Uncertain requirements l Function reuse l Implementation risk u Break into categories l “Must have”, “Should have”, “Nice to have” l Complete high priorities earlier to reduce risk Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
 Benefits and Risks of Spiral Development u Benefits l High parallelism l High user involvement l Gradual resource commitment l Frequent product delivery u Risks l Management difficulties and design complexity l More potential for rework Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
Benefits and Risks of Spiral Development u Benefits l High parallelism l High user involvement l Gradual resource commitment l Frequent product delivery u Risks l Management difficulties and design complexity l More potential for rework Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
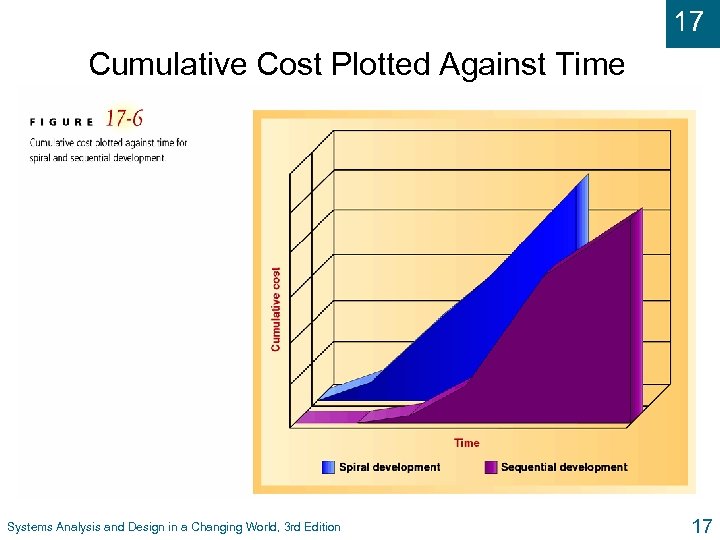 17 Cumulative Cost Plotted Against Time Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17
17 Cumulative Cost Plotted Against Time Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 17
 The Unified Process u Comprehensive development approach l Originally developed by Jacobsen, Booch, and Rumbaugh in late 1990 s l Dominant approach for developing software with OO models and tools l Adopts iteration from prototyping and spiral development approaches l Exclusive reliance on OO models, tools, and techniques Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 23
The Unified Process u Comprehensive development approach l Originally developed by Jacobsen, Booch, and Rumbaugh in late 1990 s l Dominant approach for developing software with OO models and tools l Adopts iteration from prototyping and spiral development approaches l Exclusive reliance on OO models, tools, and techniques Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 23
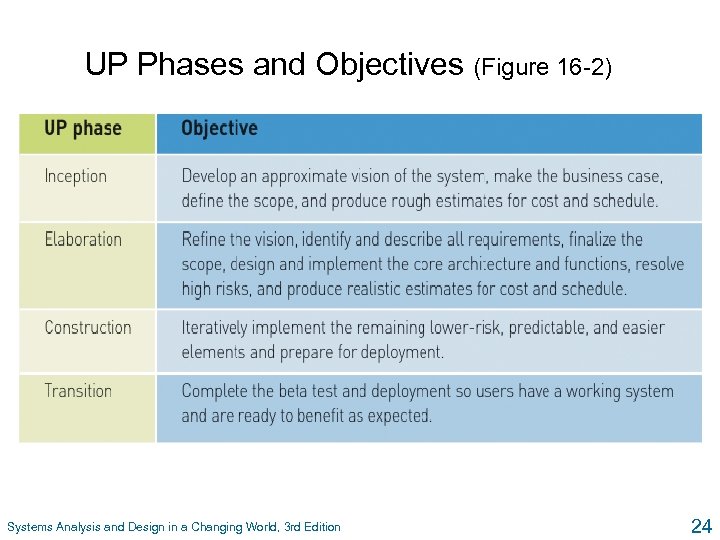 UP Phases and Objectives (Figure 16 -2) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 24
UP Phases and Objectives (Figure 16 -2) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 24
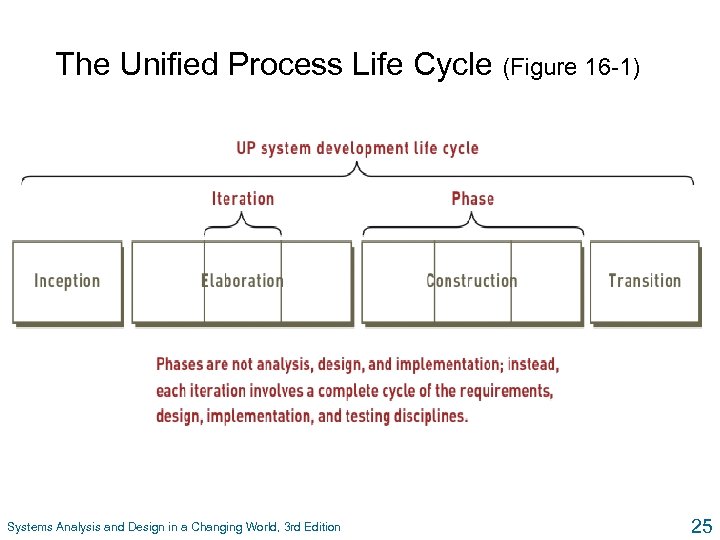 The Unified Process Life Cycle (Figure 16 -1) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 25
The Unified Process Life Cycle (Figure 16 -1) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 25
 When to Use the Unified Process u Benefits u Major and risks mirror spiral development obstacles to adopt UP include: l Complex project management (compared to sequential development) required l Need to adopt OO models, tools, techniques throughout project u UP’s formal steps, well-defined roles, attention to model building and validation makes UP preferred approach for large-scale development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
When to Use the Unified Process u Benefits u Major and risks mirror spiral development obstacles to adopt UP include: l Complex project management (compared to sequential development) required l Need to adopt OO models, tools, techniques throughout project u UP’s formal steps, well-defined roles, attention to model building and validation makes UP preferred approach for large-scale development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
 Rapid Development Techniques u Collection of guidelines used to help an analyst complete system development activities or tasks l Risk management l Joint application design (JAD) l Tool-based development l Software reuse l Object frameworks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 30
Rapid Development Techniques u Collection of guidelines used to help an analyst complete system development activities or tasks l Risk management l Joint application design (JAD) l Tool-based development l Software reuse l Object frameworks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 30
 Components and the Development Life Cycle u Purchased system components can form part or all of u Components provide one model for designing and deploying systems u Component issues l Internally developed components l Object-oriented techniques l Designing components for reuse Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 43
Components and the Development Life Cycle u Purchased system components can form part or all of u Components provide one model for designing and deploying systems u Component issues l Internally developed components l Object-oriented techniques l Designing components for reuse Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 43
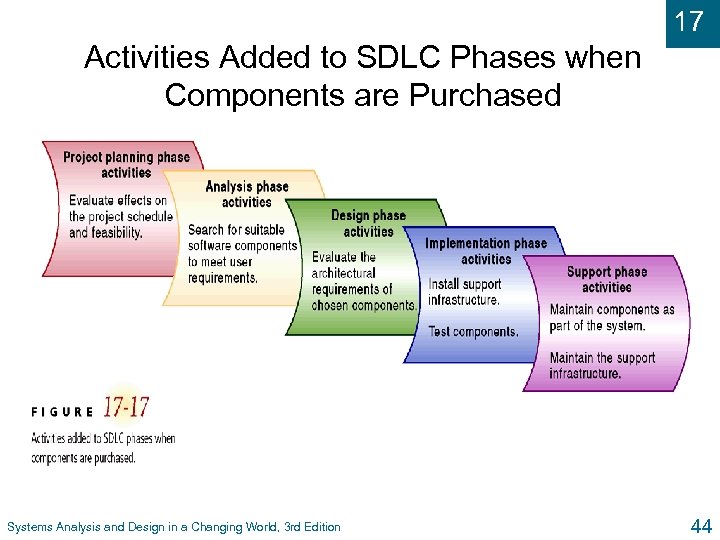 17 Activities Added to SDLC Phases when Components are Purchased Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 44
17 Activities Added to SDLC Phases when Components are Purchased Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 44


