62ceee11f6ea53484f52076bc0ab70b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 15. 393 -MAS 967 Technology Strategy for New Enterprises Class 2: The evolution of industries, technologies & markets Professor Fiona Murray
15. 393 -MAS 967 Technology Strategy for New Enterprises Class 2: The evolution of industries, technologies & markets Professor Fiona Murray
 Course Details u u Reading is missing from the course pack – it is now available on Sloanspace & the course website. Course website is mas 967 The updated syllabus is also available on the websites Today’s slides are also there
Course Details u u Reading is missing from the course pack – it is now available on Sloanspace & the course website. Course website is mas 967 The updated syllabus is also available on the websites Today’s slides are also there
 High failure rates…classic challenges for start-ups u Ralph Waldo Emerson’s problem. . . u Robert Kearns’ problem. . . u Xerox PARC’s problem… …Technology Strategy is about a powerful set of tools to solve these problems -- geared towards emerging technologies & technology-based start-ups
High failure rates…classic challenges for start-ups u Ralph Waldo Emerson’s problem. . . u Robert Kearns’ problem. . . u Xerox PARC’s problem… …Technology Strategy is about a powerful set of tools to solve these problems -- geared towards emerging technologies & technology-based start-ups
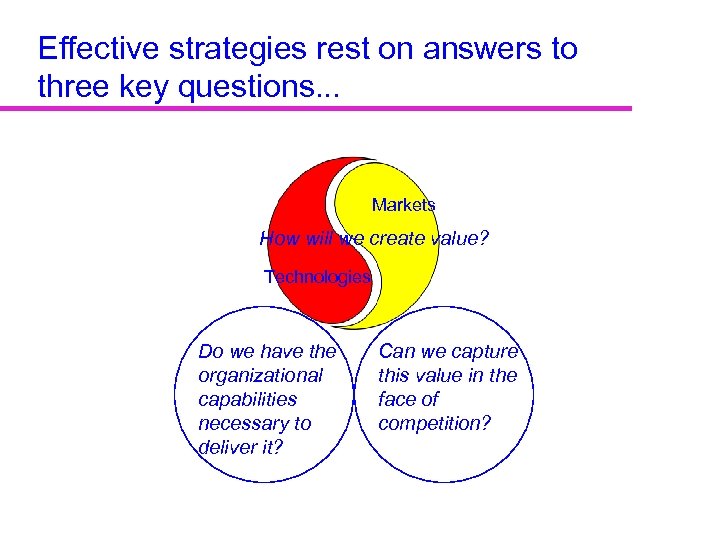 Effective strategies rest on answers to three key questions. . . Markets How will we create value? Technologies Do we have the organizational capabilities necessary to deliver it? Can we capture this value in the face of competition?
Effective strategies rest on answers to three key questions. . . Markets How will we create value? Technologies Do we have the organizational capabilities necessary to deliver it? Can we capture this value in the face of competition?
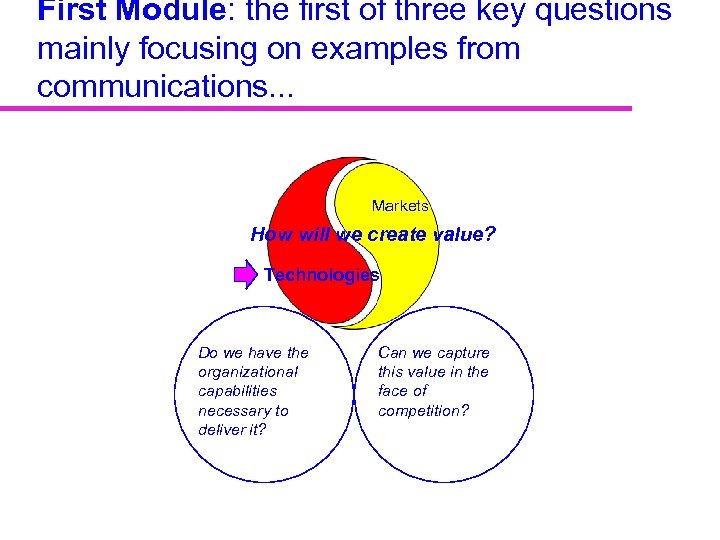 First Module: the first of three key questions mainly focusing on examples from communications. . . Markets How will we create value? Technologies Do we have the organizational capabilities necessary to deliver it? Can we capture this value in the face of competition?
First Module: the first of three key questions mainly focusing on examples from communications. . . Markets How will we create value? Technologies Do we have the organizational capabilities necessary to deliver it? Can we capture this value in the face of competition?
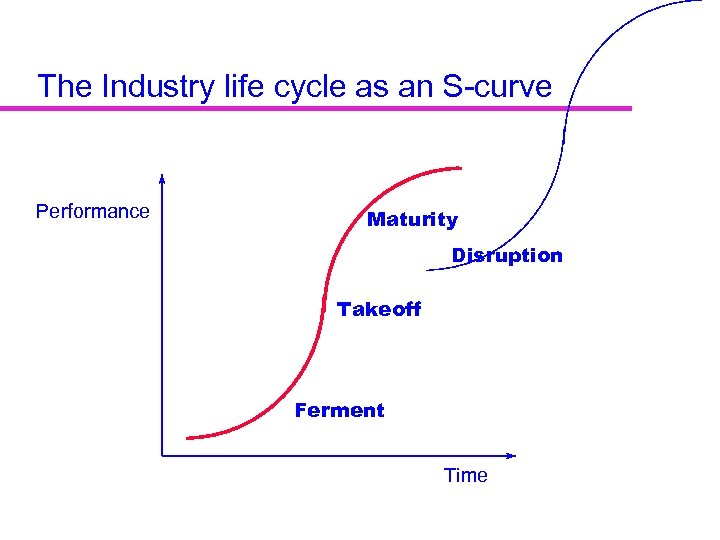 The Industry life cycle as an S-curve Performance Maturity Disruption Takeoff Ferment Time
The Industry life cycle as an S-curve Performance Maturity Disruption Takeoff Ferment Time
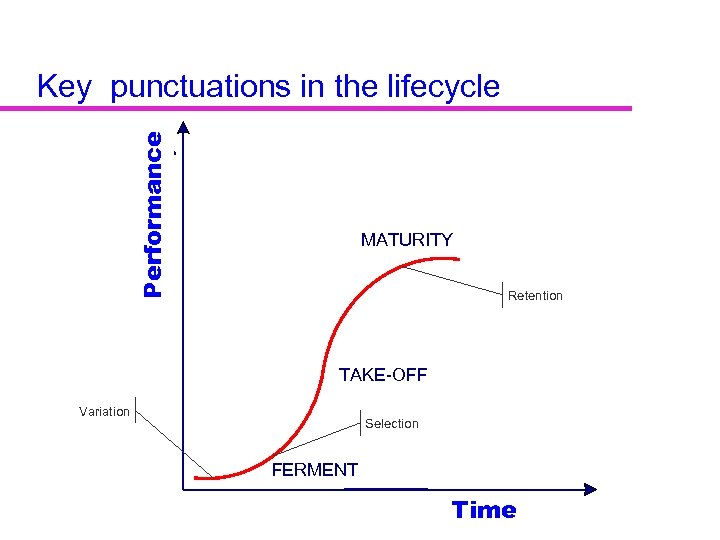 Technical Performance Efficiency Key punctuations in the lifecycle MATURITY Retention TAKE-OFF Variation Selection FERMENT Time Effort R&D
Technical Performance Efficiency Key punctuations in the lifecycle MATURITY Retention TAKE-OFF Variation Selection FERMENT Time Effort R&D
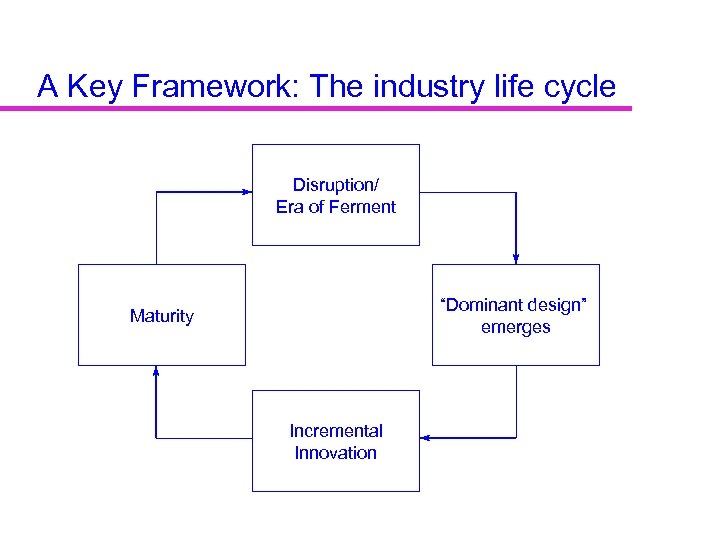 A Key Framework: The industry life cycle Disruption/ Era of Ferment “Dominant design” emerges Maturity Incremental Innovation
A Key Framework: The industry life cycle Disruption/ Era of Ferment “Dominant design” emerges Maturity Incremental Innovation
 Era of Ferment: u No one is sure how the new product » » u u u Can be packaged or sold Who will value it How it can be produced/distributed Whethere is money in supplying it Industry is up for “grabs” PDAs used to be like this e. Books are like this now There is ENORMOUS uncertainty in many dimensions !!! Its fun !!!
Era of Ferment: u No one is sure how the new product » » u u u Can be packaged or sold Who will value it How it can be produced/distributed Whethere is money in supplying it Industry is up for “grabs” PDAs used to be like this e. Books are like this now There is ENORMOUS uncertainty in many dimensions !!! Its fun !!!
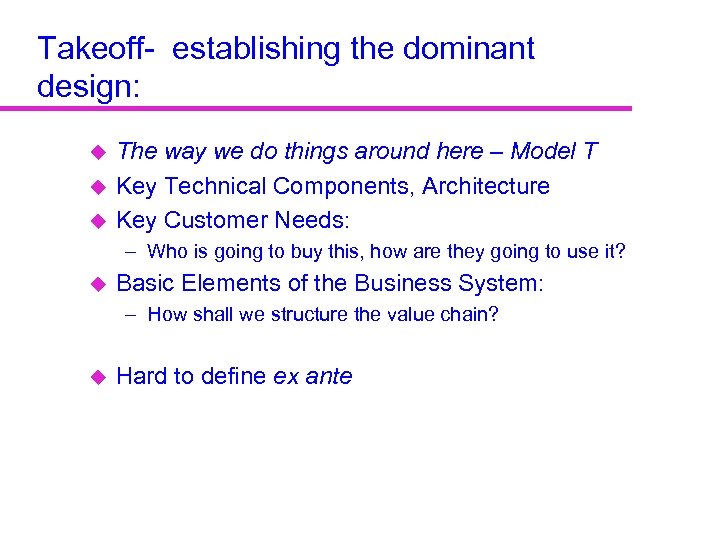 Takeoff- establishing the dominant design: u u u The way we do things around here – Model T Key Technical Components, Architecture Key Customer Needs: – Who is going to buy this, how are they going to use it? u Basic Elements of the Business System: – How shall we structure the value chain? u Hard to define ex ante
Takeoff- establishing the dominant design: u u u The way we do things around here – Model T Key Technical Components, Architecture Key Customer Needs: – Who is going to buy this, how are they going to use it? u Basic Elements of the Business System: – How shall we structure the value chain? u Hard to define ex ante
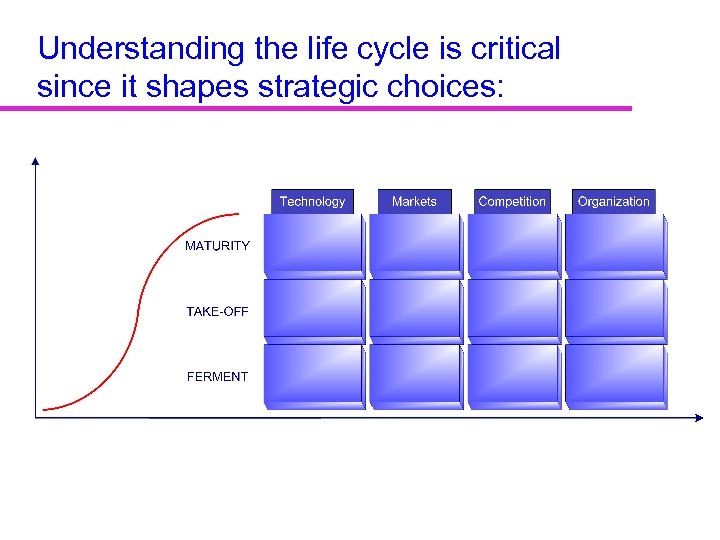 Understanding the life cycle is critical since it shapes strategic choices:
Understanding the life cycle is critical since it shapes strategic choices:
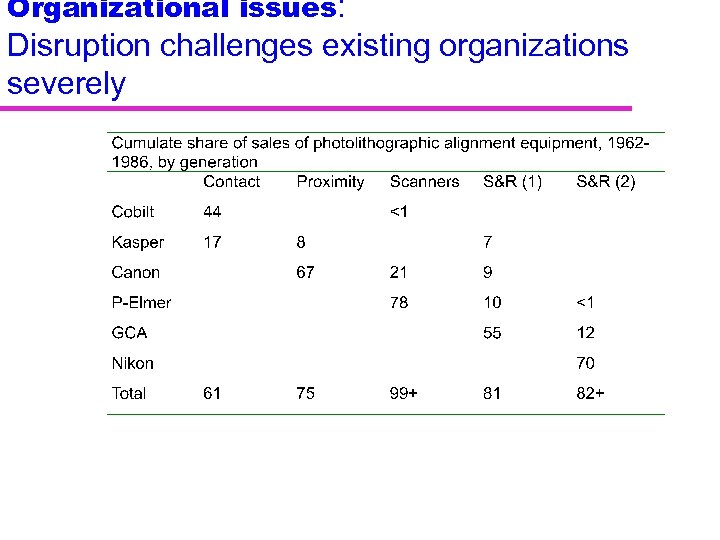 Organizational issues: Disruption challenges existing organizations severely
Organizational issues: Disruption challenges existing organizations severely
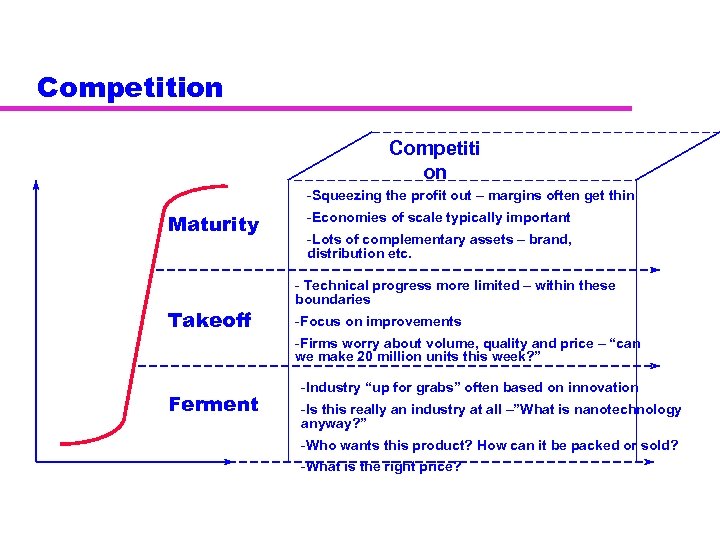 Competition Competiti on -Squeezing the profit out – margins often get thin Maturity Takeoff -Economies of scale typically important -Lots of complementary assets – brand, distribution etc. - Technical progress more limited – within these boundaries -Focus on improvements -Firms worry about volume, quality and price – “can we make 20 million units this week? ” Ferment -Industry “up for grabs” often based on innovation -Is this really an industry at all –”What is nanotechnology anyway? ” -Who wants this product? How can it be packed or sold? -What is the right price?
Competition Competiti on -Squeezing the profit out – margins often get thin Maturity Takeoff -Economies of scale typically important -Lots of complementary assets – brand, distribution etc. - Technical progress more limited – within these boundaries -Focus on improvements -Firms worry about volume, quality and price – “can we make 20 million units this week? ” Ferment -Industry “up for grabs” often based on innovation -Is this really an industry at all –”What is nanotechnology anyway? ” -Who wants this product? How can it be packed or sold? -What is the right price?
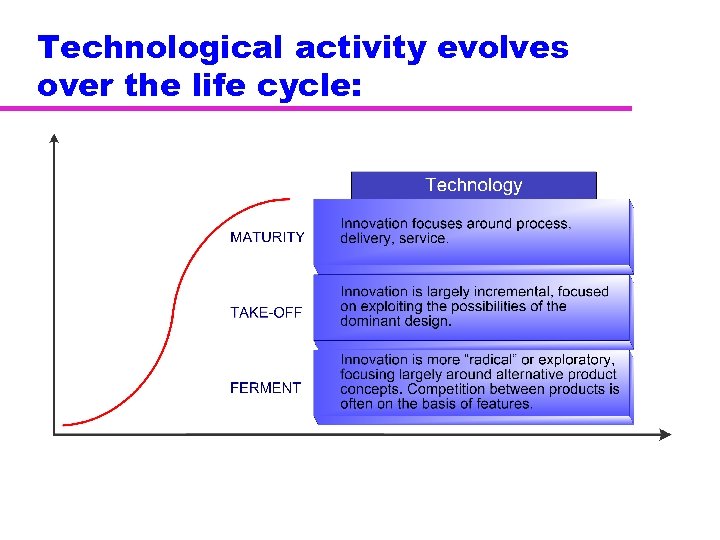 Technological activity evolves over the life cycle:
Technological activity evolves over the life cycle:
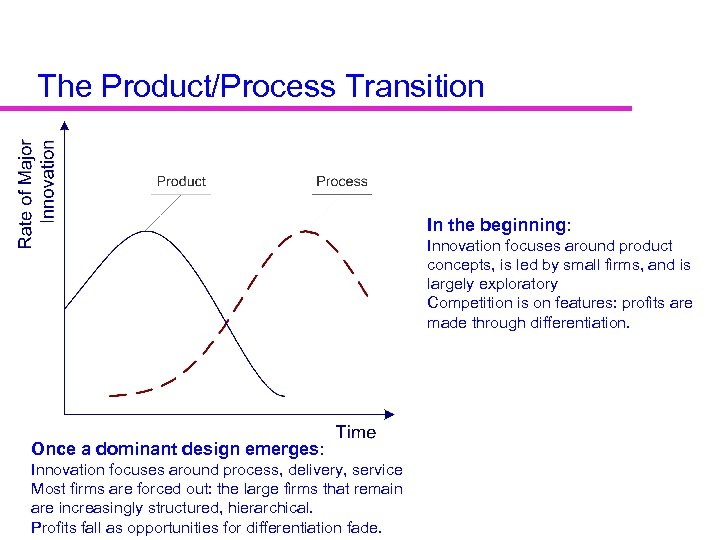 The Product/Process Transition In the beginning: Innovation focuses around product concepts, is led by small firms, and is largely exploratory Competition is on features: profits are made through differentiation. Once a dominant design emerges: Innovation focuses around process, delivery, service Most firms are forced out: the large firms that remain are increasingly structured, hierarchical. Profits fall as opportunities for differentiation fade.
The Product/Process Transition In the beginning: Innovation focuses around product concepts, is led by small firms, and is largely exploratory Competition is on features: profits are made through differentiation. Once a dominant design emerges: Innovation focuses around process, delivery, service Most firms are forced out: the large firms that remain are increasingly structured, hierarchical. Profits fall as opportunities for differentiation fade.
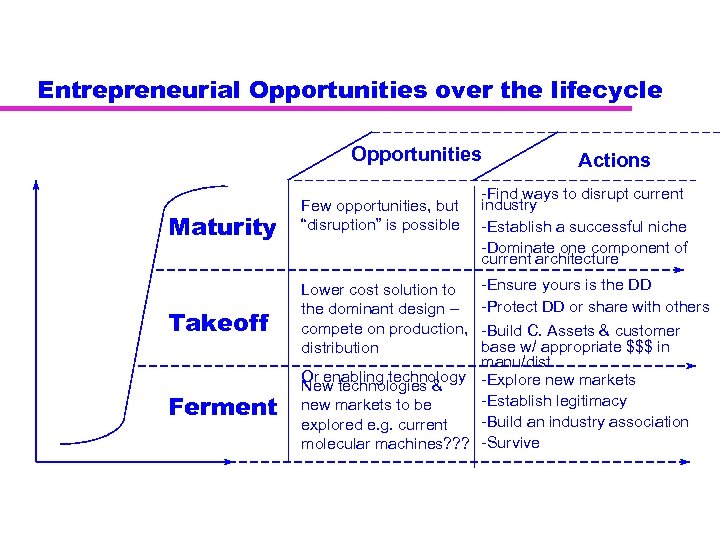 Entrepreneurial Opportunities over the lifecycle Opportunities Maturity Takeoff Ferment Few opportunities, but “disruption” is possible Actions -Find ways to disrupt current industry -Establish a successful niche -Dominate one component of current architecture -Ensure yours is the DD -Protect DD or share with others -Build C. Assets & customer base w/ appropriate $$$ in manu/dist. Or enabling technology -Explore new markets New technologies & -Establish legitimacy new markets to be -Build an industry association explored e. g. current molecular machines? ? ? -Survive Lower cost solution to the dominant design – compete on production, distribution
Entrepreneurial Opportunities over the lifecycle Opportunities Maturity Takeoff Ferment Few opportunities, but “disruption” is possible Actions -Find ways to disrupt current industry -Establish a successful niche -Dominate one component of current architecture -Ensure yours is the DD -Protect DD or share with others -Build C. Assets & customer base w/ appropriate $$$ in manu/dist. Or enabling technology -Explore new markets New technologies & -Establish legitimacy new markets to be -Build an industry association explored e. g. current molecular machines? ? ? -Survive Lower cost solution to the dominant design – compete on production, distribution
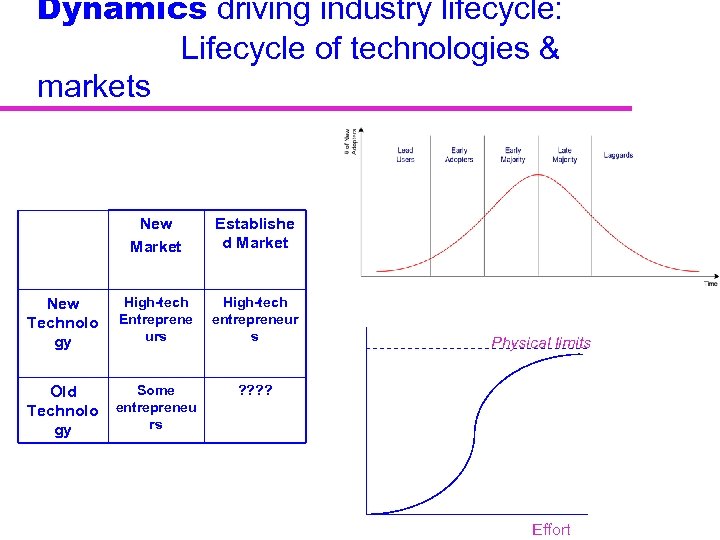 Dynamics driving industry lifecycle: Lifecycle of technologies & markets New Market Establishe d Market New Technolo gy High-tech Entreprene urs High-tech entrepreneur s Old Technolo gy Some entrepreneu rs ? ? Physical limits Effort
Dynamics driving industry lifecycle: Lifecycle of technologies & markets New Market Establishe d Market New Technolo gy High-tech Entreprene urs High-tech entrepreneur s Old Technolo gy Some entrepreneu rs ? ? Physical limits Effort
 Technology dynamics
Technology dynamics
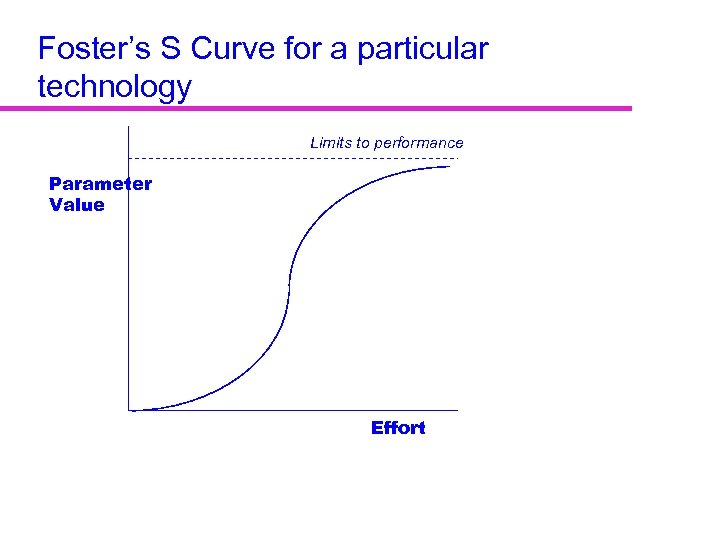 Foster’s S Curve for a particular technology Limits to performance Parameter Value Effort
Foster’s S Curve for a particular technology Limits to performance Parameter Value Effort
 S curve examples: u Artificial Hearts Sailing ships Joint replacement Protein separation Switches u …. your favorite example u u
S curve examples: u Artificial Hearts Sailing ships Joint replacement Protein separation Switches u …. your favorite example u u
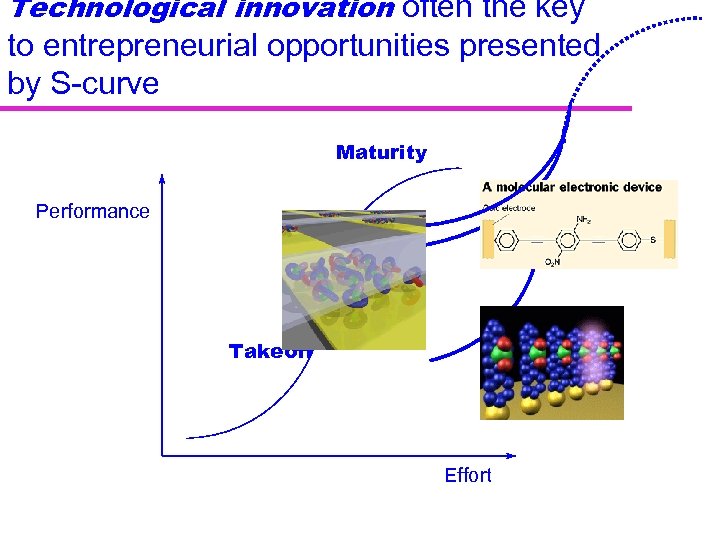 Technological innovation often the key to entrepreneurial opportunities presented by S-curve Maturity Performance Takeoff Effort
Technological innovation often the key to entrepreneurial opportunities presented by S-curve Maturity Performance Takeoff Effort
 Technology-oriented opportunities u Bring improved performance through entirely new technology – e. g. molecular switches u Bring alternative performance through new technology – e. g. nano-robotics u Reframing the problem is an alternative way of stretching existing performance for entrepreneurs – e. g. human insulin – e. g. flexible chip manufacturing u Entrepreneur’s challenge is to stay on the S-curve and ensure that “their curve” becomes the dominant design
Technology-oriented opportunities u Bring improved performance through entirely new technology – e. g. molecular switches u Bring alternative performance through new technology – e. g. nano-robotics u Reframing the problem is an alternative way of stretching existing performance for entrepreneurs – e. g. human insulin – e. g. flexible chip manufacturing u Entrepreneur’s challenge is to stay on the S-curve and ensure that “their curve” becomes the dominant design


