Wage Determination.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 13 Wage Determination Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
13 Wage Determination Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Labor, Wages, and Earnings • Wages • Price paid for labor • Direct pay plus fringe benefits • Wage rate • Nominal wage • Real wage • General level of wages LO 1 13 -2
Labor, Wages, and Earnings • Wages • Price paid for labor • Direct pay plus fringe benefits • Wage rate • Nominal wage • Real wage • General level of wages LO 1 13 -2
 Role of Productivity • Labor demand depends on • LO 1 productivity U. S. labor is highly productive • Plentiful capital • Access to abundant natural resources • Advanced technology • Labor quality • Other factors 13 -3
Role of Productivity • Labor demand depends on • LO 1 productivity U. S. labor is highly productive • Plentiful capital • Access to abundant natural resources • Advanced technology • Labor quality • Other factors 13 -3
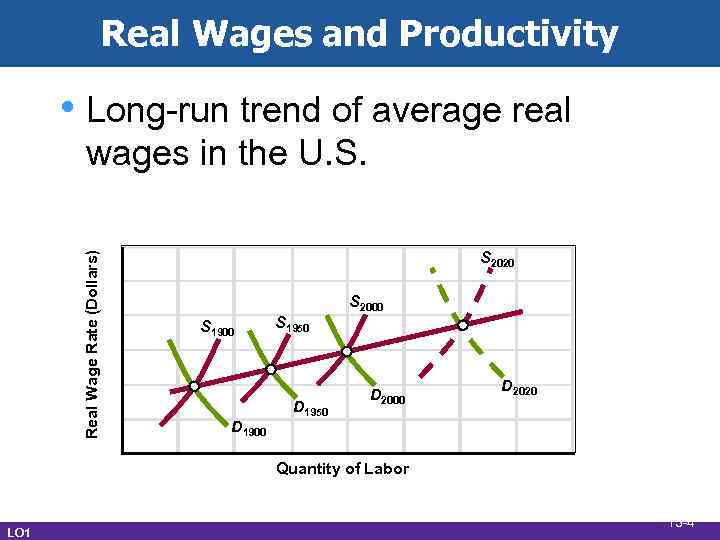 Real Wages and Productivity • Long-run trend of average real Real Wage Rate (Dollars) wages in the U. S. S 2020 S 1900 D 1900 S 1950 D 1950 S 2000 D 2020 Quantity of Labor LO 1 13 -4
Real Wages and Productivity • Long-run trend of average real Real Wage Rate (Dollars) wages in the U. S. S 2020 S 1900 D 1900 S 1950 D 1950 S 2000 D 2020 Quantity of Labor LO 1 13 -4
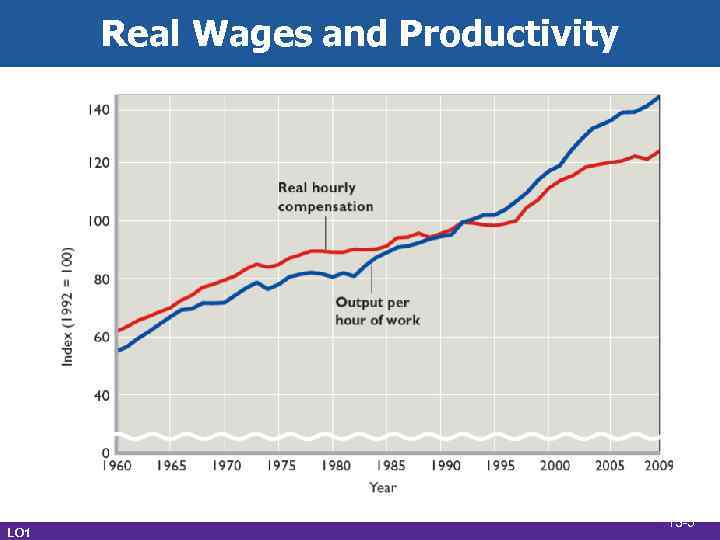 Real Wages and Productivity LO 1 13 -5
Real Wages and Productivity LO 1 13 -5
 Competitive Labor Market • Market demand for labor • Sum of firm demand • Example: carpenters • Market supply for labor • Upward sloping • Competition among industries • Labor market equilibrium • MRP = MRC rule LO 2 13 -6
Competitive Labor Market • Market demand for labor • Sum of firm demand • Example: carpenters • Market supply for labor • Upward sloping • Competition among industries • Labor market equilibrium • MRP = MRC rule LO 2 13 -6
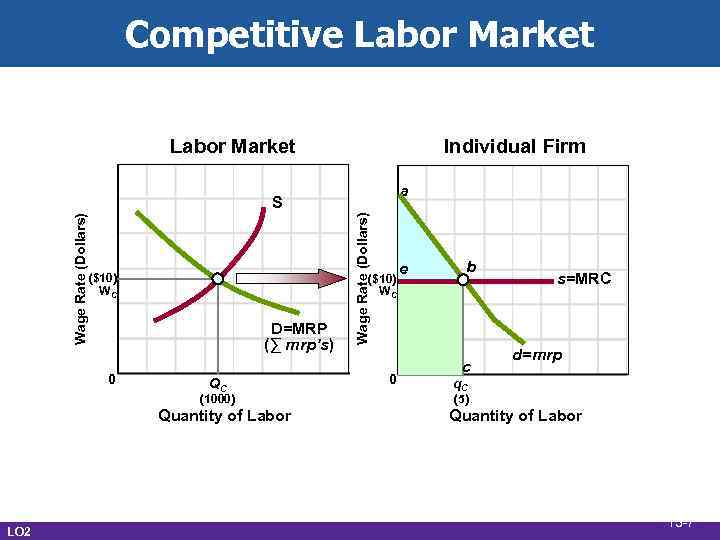 Competitive Labor Market Individual Firm a ($10) WC D=MRP (∑ mrp’s) 0 QC (1000) Quantity of Labor LO 2 Wage Rate (Dollars) S 0 e b c s=MRC d=mrp q. C (5) Quantity of Labor 13 -7
Competitive Labor Market Individual Firm a ($10) WC D=MRP (∑ mrp’s) 0 QC (1000) Quantity of Labor LO 2 Wage Rate (Dollars) S 0 e b c s=MRC d=mrp q. C (5) Quantity of Labor 13 -7
 Monopsony Model • Employer has buying power • Characteristics • Single buyer • Labor immobile • Firm “wage maker” • Firm labor supply is upward sloping • MRC higher than wage rate • Equilibrium LO 3 13 -8
Monopsony Model • Employer has buying power • Characteristics • Single buyer • Labor immobile • Firm “wage maker” • Firm labor supply is upward sloping • MRC higher than wage rate • Equilibrium LO 3 13 -8
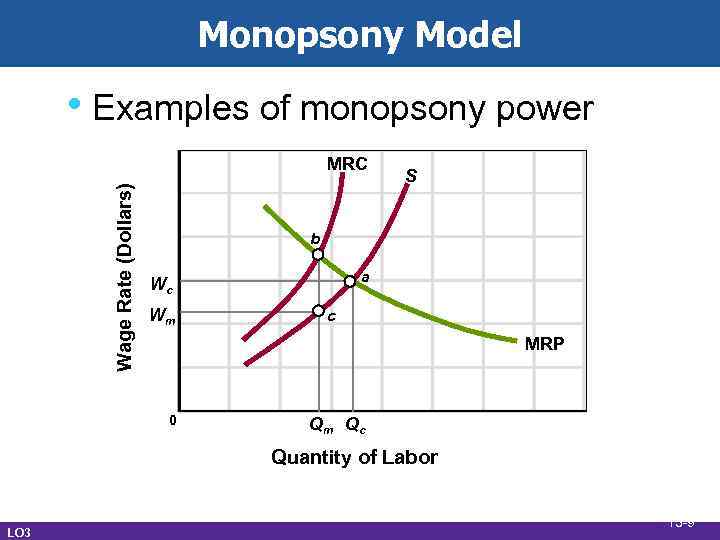 Monopsony Model • Examples of monopsony power Wage Rate (Dollars) MRC S b a Wc Wm c MRP 0 Qm Qc Quantity of Labor LO 3 13 -9
Monopsony Model • Examples of monopsony power Wage Rate (Dollars) MRC S b a Wc Wm c MRP 0 Qm Qc Quantity of Labor LO 3 13 -9
 Monopsony Power • Maximize profit by hiring smaller • • LO 3 number of workers Examples of monopsony power • Nurses • Professional Athletes • Teachers Three union models 13 -10
Monopsony Power • Maximize profit by hiring smaller • • LO 3 number of workers Examples of monopsony power • Nurses • Professional Athletes • Teachers Three union models 13 -10
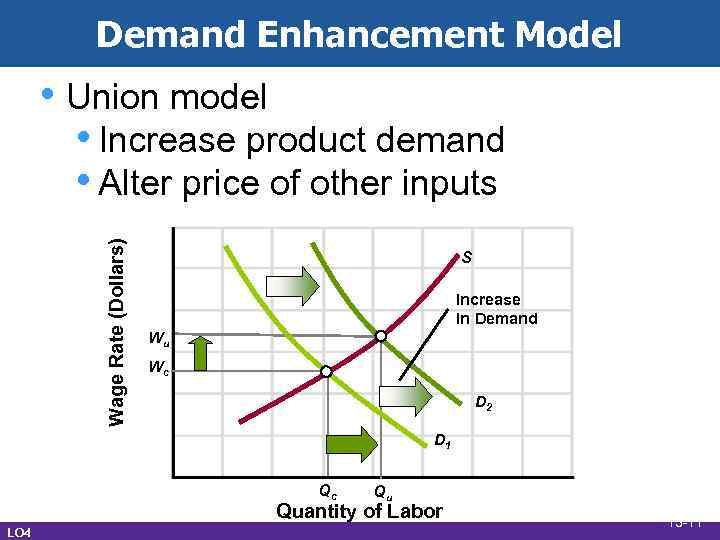 Demand Enhancement Model Wage Rate (Dollars) • Union model • Increase product demand • Alter price of other inputs S Increase In Demand Wu Wc D 2 D 1 Qc Qu Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -11
Demand Enhancement Model Wage Rate (Dollars) • Union model • Increase product demand • Alter price of other inputs S Increase In Demand Wu Wc D 2 D 1 Qc Qu Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -11
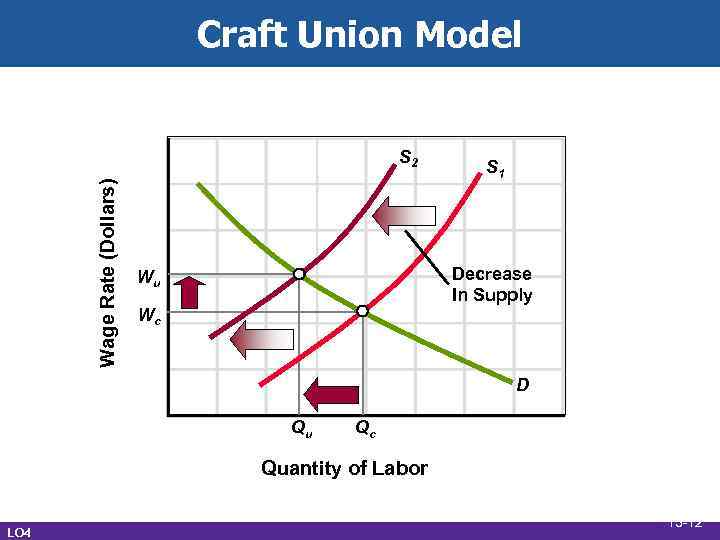 Craft Union Model Wage Rate (Dollars) S 2 S 1 Decrease In Supply Wu Wc D Qu Qc Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -12
Craft Union Model Wage Rate (Dollars) S 2 S 1 Decrease In Supply Wu Wc D Qu Qc Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -12
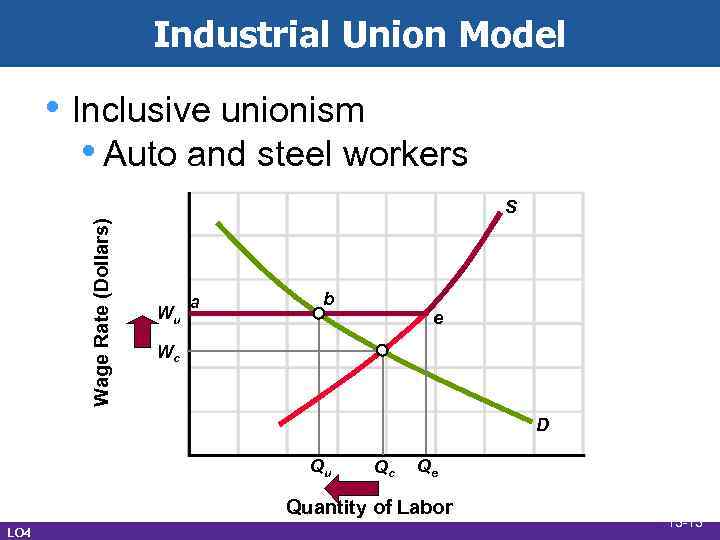 Industrial Union Model • Inclusive unionism • Auto and steel workers Wage Rate (Dollars) S Wu a b e Wc D Qu Qc Qe Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -13
Industrial Union Model • Inclusive unionism • Auto and steel workers Wage Rate (Dollars) S Wu a b e Wc D Qu Qc Qe Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -13
 Bilateral Monopoly Model • Monopsony and inclusive unionism • Single buyer and seller • Not uncommon • Indeterminate outcome • Desirability LO 4 13 -14
Bilateral Monopoly Model • Monopsony and inclusive unionism • Single buyer and seller • Not uncommon • Indeterminate outcome • Desirability LO 4 13 -14
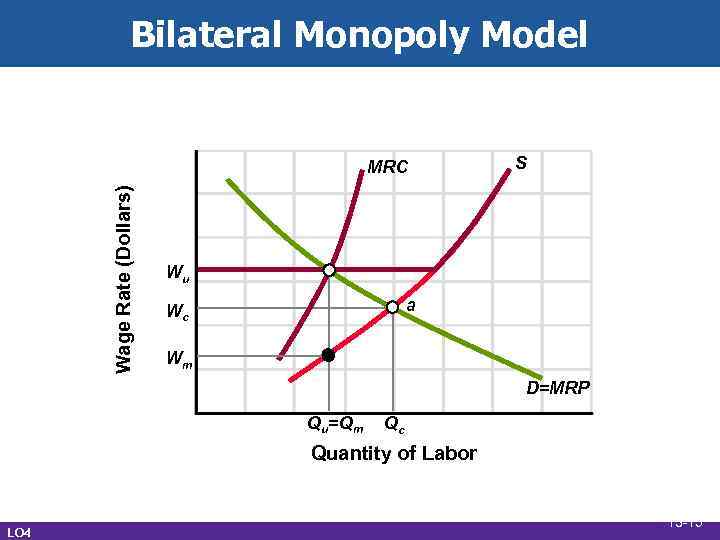 Bilateral Monopoly Model Wage Rate (Dollars) MRC S Wu a Wc Wm D=MRP Qu=Qm Qc Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -15
Bilateral Monopoly Model Wage Rate (Dollars) MRC S Wu a Wc Wm D=MRP Qu=Qm Qc Quantity of Labor LO 4 13 -15
 The Minimum Wage Controversy • Case against minimum wage • Case for minimum wage • State and locally set rates • Evidence and conclusions LO 5 13 -16
The Minimum Wage Controversy • Case against minimum wage • Case for minimum wage • State and locally set rates • Evidence and conclusions LO 5 13 -16
 Wage Differentials • Differences across occupations • What explains wage differentials? • Marginal revenue productivity • Noncompeting groups • Ability • Education and training • Compensating differences LO 5 13 -17
Wage Differentials • Differences across occupations • What explains wage differentials? • Marginal revenue productivity • Noncompeting groups • Ability • Education and training • Compensating differences LO 5 13 -17
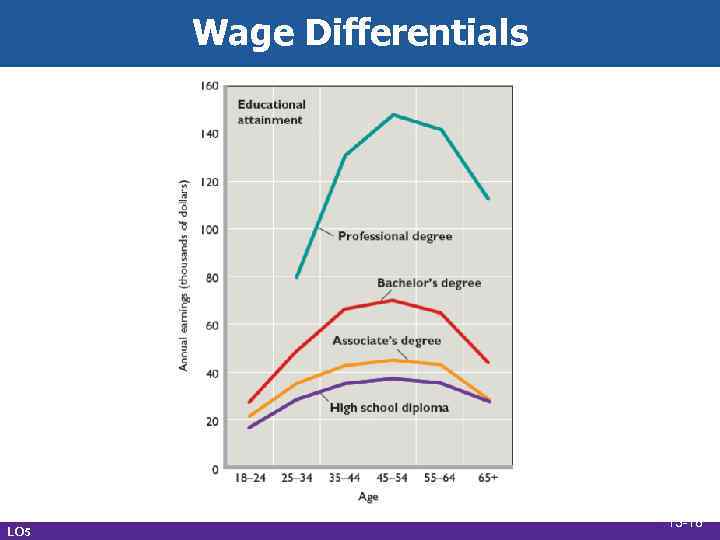 Wage Differentials LO 5 13 -18
Wage Differentials LO 5 13 -18
 Wage Differentials • Workers prevented from moving to • LO 5 higher paying jobs Market imperfections • Lack of job information • Geographic immobility • Unions and government restraints • Discrimination 13 -19
Wage Differentials • Workers prevented from moving to • LO 5 higher paying jobs Market imperfections • Lack of job information • Geographic immobility • Unions and government restraints • Discrimination 13 -19
 Pay for Performance • The principal-agent problem • Incentive pay plan • Piece rates • Commissions or royalties • Bonuses, stock options, and profit • LO 6 sharing • Efficiency wages Negative side-effects 13 -20
Pay for Performance • The principal-agent problem • Incentive pay plan • Piece rates • Commissions or royalties • Bonuses, stock options, and profit • LO 6 sharing • Efficiency wages Negative side-effects 13 -20


