69dd4f3f6c21a3b11cc434c742d6a64e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 13 th Japan-Germany Forum on Information Technology Virtual Sales Agent for Personalized Internet Shopping Wolfgang Wahlster German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, DFKI Gmb. H Stuhlsatzenhausweg 3 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany phone: (+49 681) 302 -5252/4162 fax: (+49 681) 302 -5341 e-mail: wahlster@dfki. de WWW: http: //www. dfki. de/~wahlster
13 th Japan-Germany Forum on Information Technology Virtual Sales Agent for Personalized Internet Shopping Wolfgang Wahlster German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, DFKI Gmb. H Stuhlsatzenhausweg 3 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany phone: (+49 681) 302 -5252/4162 fax: (+49 681) 302 -5341 e-mail: wahlster@dfki. de WWW: http: //www. dfki. de/~wahlster
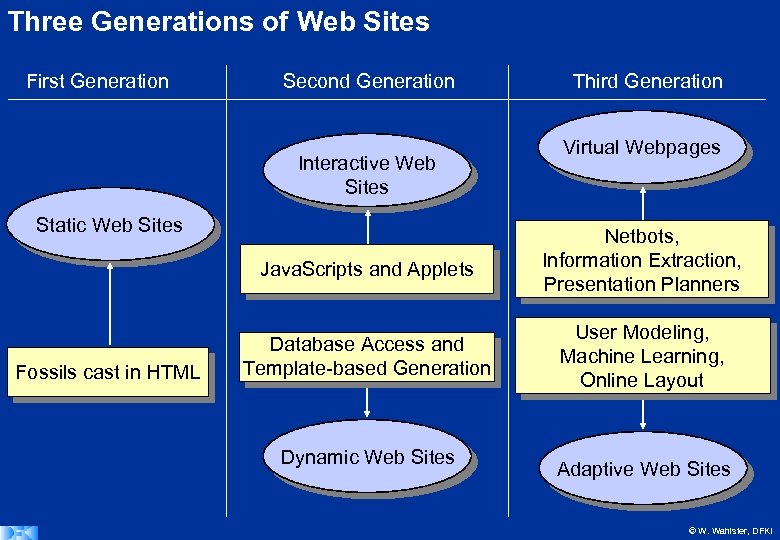 Three Generations of Web Sites First Generation Second Generation Interactive Web Sites Static Web Sites Third Generation Virtual Webpages Java. Scripts and Applets Fossils cast in HTML Netbots, Information Extraction, Presentation Planners Database Access and Template-based Generation User Modeling, Machine Learning, Online Layout Dynamic Web Sites Adaptive Web Sites © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Three Generations of Web Sites First Generation Second Generation Interactive Web Sites Static Web Sites Third Generation Virtual Webpages Java. Scripts and Applets Fossils cast in HTML Netbots, Information Extraction, Presentation Planners Database Access and Template-based Generation User Modeling, Machine Learning, Online Layout Dynamic Web Sites Adaptive Web Sites © W. Wahlster, DFKI
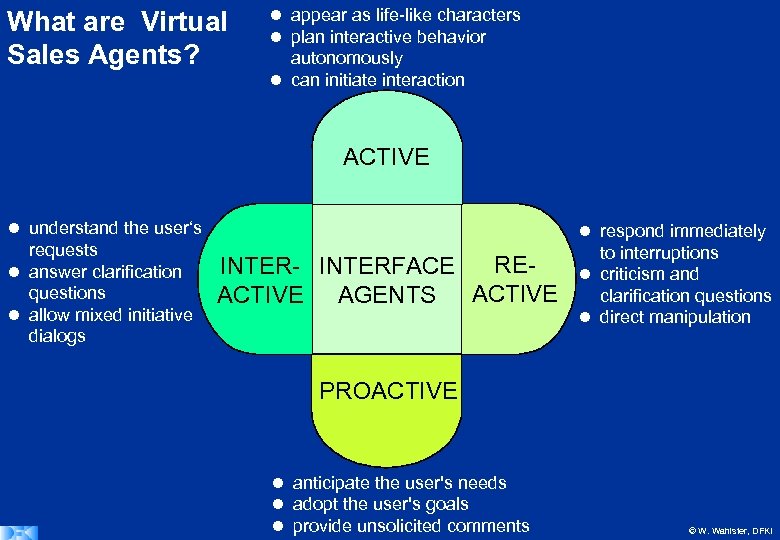 What are Virtual Sales Agents? appear as life-like characters plan interactive behavior autonomously can initiate interaction ACTIVE understand the user‘s requests answer clarification questions allow mixed initiative dialogs REINTER- INTERFACE ACTIVE AGENTS ACTIVE respond immediately to interruptions criticism and clarification questions direct manipulation PROACTIVE anticipate the user's needs adopt the user's goals provide unsolicited comments © W. Wahlster, DFKI
What are Virtual Sales Agents? appear as life-like characters plan interactive behavior autonomously can initiate interaction ACTIVE understand the user‘s requests answer clarification questions allow mixed initiative dialogs REINTER- INTERFACE ACTIVE AGENTS ACTIVE respond immediately to interruptions criticism and clarification questions direct manipulation PROACTIVE anticipate the user's needs adopt the user's goals provide unsolicited comments © W. Wahlster, DFKI
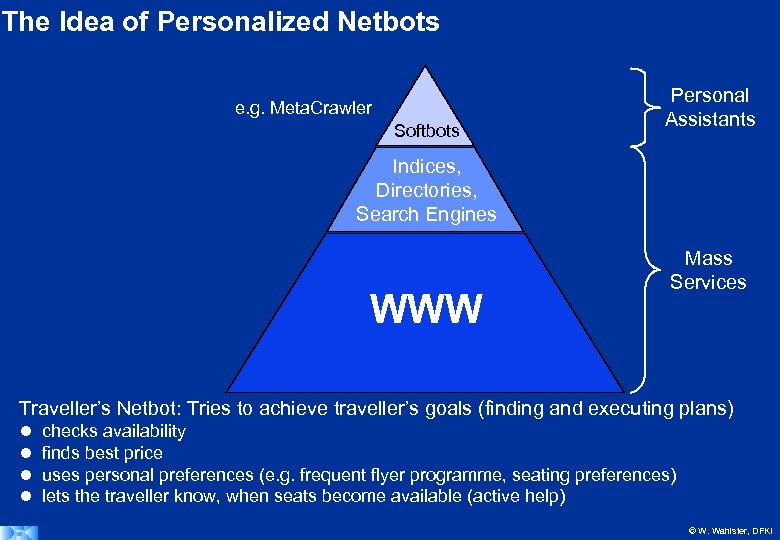 The Idea of Personalized Netbots e. g. Meta. Crawler Softbots Personal Assistants Indices, Directories, Search Engines WWW Mass Services Traveller’s Netbot: Tries to achieve traveller’s goals (finding and executing plans) checks availability finds best price uses personal preferences (e. g. frequent flyer programme, seating preferences) lets the traveller know, when seats become available (active help) © W. Wahlster, DFKI
The Idea of Personalized Netbots e. g. Meta. Crawler Softbots Personal Assistants Indices, Directories, Search Engines WWW Mass Services Traveller’s Netbot: Tries to achieve traveller’s goals (finding and executing plans) checks availability finds best price uses personal preferences (e. g. frequent flyer programme, seating preferences) lets the traveller know, when seats become available (active help) © W. Wahlster, DFKI
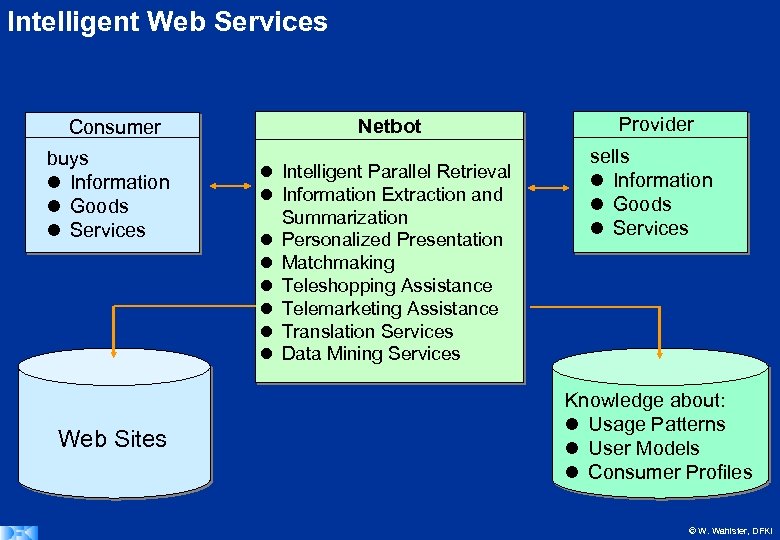 Intelligent Web Services Consumer buys Information Goods Services Web Sites Netbot Intelligent Parallel Retrieval Information Extraction and Summarization Personalized Presentation Matchmaking Teleshopping Assistance Telemarketing Assistance Translation Services Data Mining Services Provider sells Information Goods Services Knowledge about: Usage Patterns User Models Consumer Profiles © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Intelligent Web Services Consumer buys Information Goods Services Web Sites Netbot Intelligent Parallel Retrieval Information Extraction and Summarization Personalized Presentation Matchmaking Teleshopping Assistance Telemarketing Assistance Translation Services Data Mining Services Provider sells Information Goods Services Knowledge about: Usage Patterns User Models Consumer Profiles © W. Wahlster, DFKI
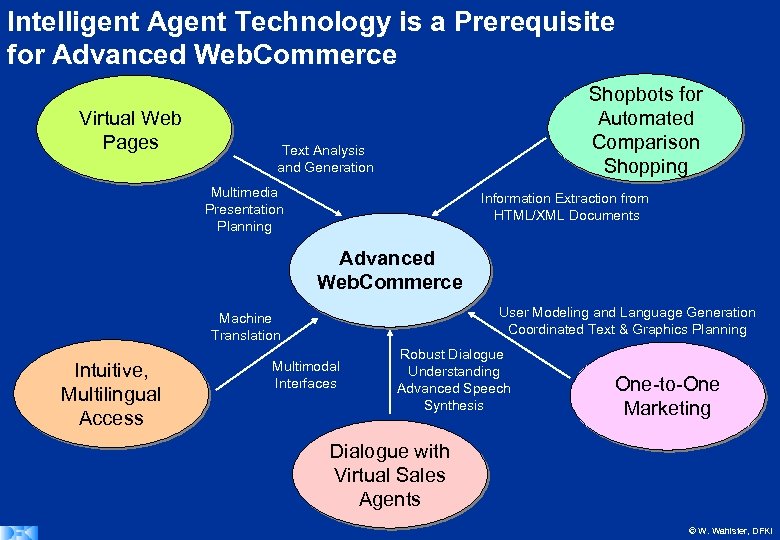 Intelligent Agent Technology is a Prerequisite for Advanced Web. Commerce Virtual Web Pages Shopbots for Automated Comparison Shopping Text Analysis and Generation Multimedia Presentation Planning Information Extraction from HTML/XML Documents Advanced Web. Commerce User Modeling and Language Generation Coordinated Text & Graphics Planning Machine Translation Intuitive, Multilingual Access Multimodal Interfaces Robust Dialogue Understanding Advanced Speech Synthesis One-to-One Marketing Dialogue with Virtual Sales Agents © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Intelligent Agent Technology is a Prerequisite for Advanced Web. Commerce Virtual Web Pages Shopbots for Automated Comparison Shopping Text Analysis and Generation Multimedia Presentation Planning Information Extraction from HTML/XML Documents Advanced Web. Commerce User Modeling and Language Generation Coordinated Text & Graphics Planning Machine Translation Intuitive, Multilingual Access Multimodal Interfaces Robust Dialogue Understanding Advanced Speech Synthesis One-to-One Marketing Dialogue with Virtual Sales Agents © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Virtual Market Places with Human and Machine Agents © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Virtual Market Places with Human and Machine Agents © W. Wahlster, DFKI
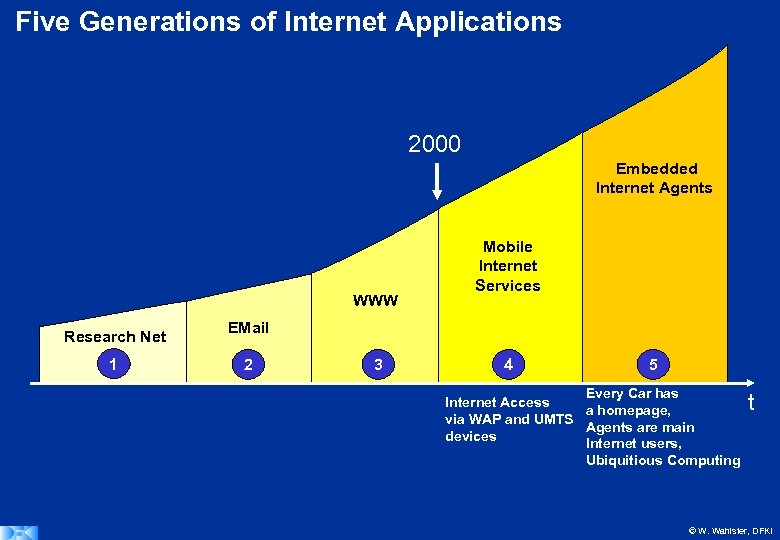 Five Generations of Internet Applications 2000 Embedded Internet Agents WWW Research Net 1 Mobile Internet Services EMail 2 3 4 5 Every Car has Internet Access a homepage, via WAP and UMTS Agents are main devices Internet users, Ubiquitious Computing t © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Five Generations of Internet Applications 2000 Embedded Internet Agents WWW Research Net 1 Mobile Internet Services EMail 2 3 4 5 Every Car has Internet Access a homepage, via WAP and UMTS Agents are main devices Internet users, Ubiquitious Computing t © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Towards Mobile and Speech-based E-Commerce Using WAP Phones WAP phones (Wireless Application Protocol for Cellular Phones) WML as a markup language for interactive content Mobile access to virtual shops allows price comparisons during real shopping Multimodal dialog: Voice In (Speech) - Web Out (Graphics, Hypertext) Voice input using advanced speech understanding technology Easy to use: customers simply say what they want © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Towards Mobile and Speech-based E-Commerce Using WAP Phones WAP phones (Wireless Application Protocol for Cellular Phones) WML as a markup language for interactive content Mobile access to virtual shops allows price comparisons during real shopping Multimodal dialog: Voice In (Speech) - Web Out (Graphics, Hypertext) Voice input using advanced speech understanding technology Easy to use: customers simply say what they want © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 What is a Virtual Web Page? Virtual Memory, Virtual Relation, Virtual Reality. . . A Virtual Web Page l is generated on the fly as a combination of various media objects from multiple web sites or as a transformation of a real web page. l looks like a real web page, but is not persistently stored. l integrates generated and retrieved material in a coordinated way. l can be tailored to a particular user profile and adapted to a particular interaction context. l has an underlying representation of the presentation context so that an Interface Agent can comment, point to and explain its components. © W. Wahlster, DFKI
What is a Virtual Web Page? Virtual Memory, Virtual Relation, Virtual Reality. . . A Virtual Web Page l is generated on the fly as a combination of various media objects from multiple web sites or as a transformation of a real web page. l looks like a real web page, but is not persistently stored. l integrates generated and retrieved material in a coordinated way. l can be tailored to a particular user profile and adapted to a particular interaction context. l has an underlying representation of the presentation context so that an Interface Agent can comment, point to and explain its components. © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Virtual Webpage Retrieved from 5 Different Servers © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Virtual Webpage Retrieved from 5 Different Servers © W. Wahlster, DFKI
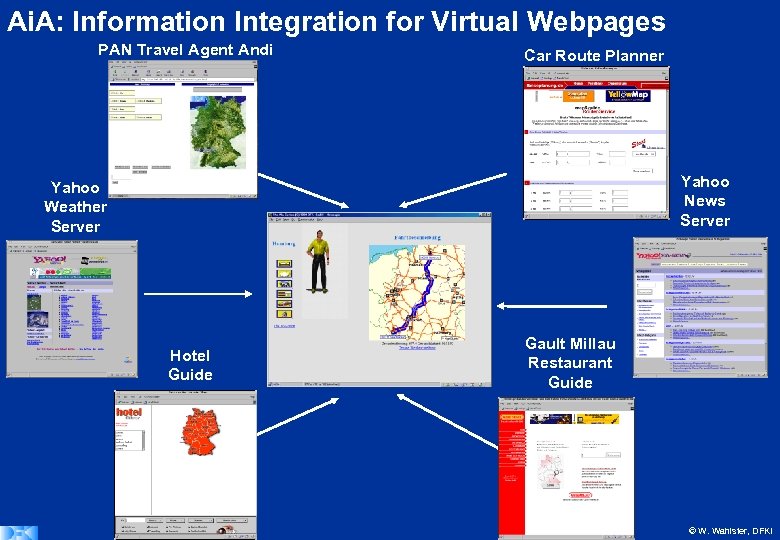 Ai. A: Information Integration for Virtual Webpages PAN Travel Agent Andi Car Route Planner Yahoo News Server Yahoo Weather Server Hotel Guide Gault Millau Restaurant Guide © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Ai. A: Information Integration for Virtual Webpages PAN Travel Agent Andi Car Route Planner Yahoo News Server Yahoo Weather Server Hotel Guide Gault Millau Restaurant Guide © W. Wahlster, DFKI
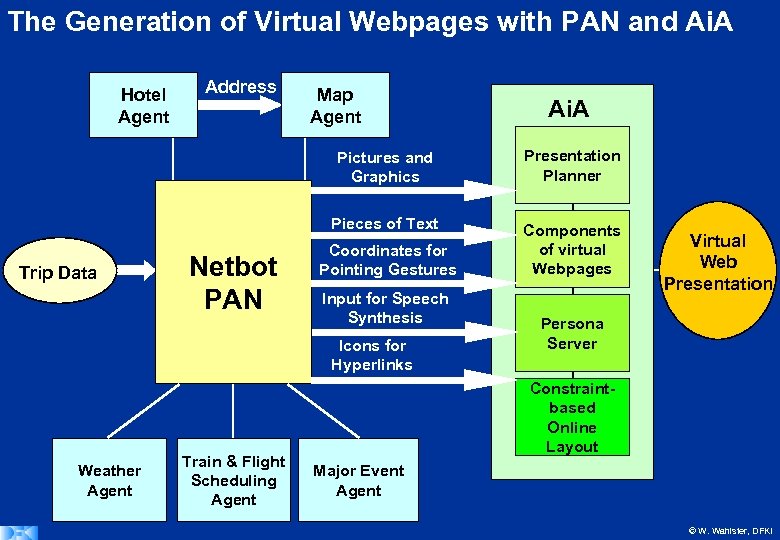 The Generation of Virtual Webpages with PAN and Ai. A Hotel Agent Address Map Agent Ai. A Pictures and Graphics Pieces of Text Trip Data Netbot PAN Presentation Planner Components of virtual Webpages Coordinates for Pointing Gestures Input for Speech Synthesis Icons for Hyperlinks Weather Agent Train & Flight Scheduling Agent Virtual Web Presentation Persona Server Constraintbased Online Layout Major Event Agent © W. Wahlster, DFKI
The Generation of Virtual Webpages with PAN and Ai. A Hotel Agent Address Map Agent Ai. A Pictures and Graphics Pieces of Text Trip Data Netbot PAN Presentation Planner Components of virtual Webpages Coordinates for Pointing Gestures Input for Speech Synthesis Icons for Hyperlinks Weather Agent Train & Flight Scheduling Agent Virtual Web Presentation Persona Server Constraintbased Online Layout Major Event Agent © W. Wahlster, DFKI
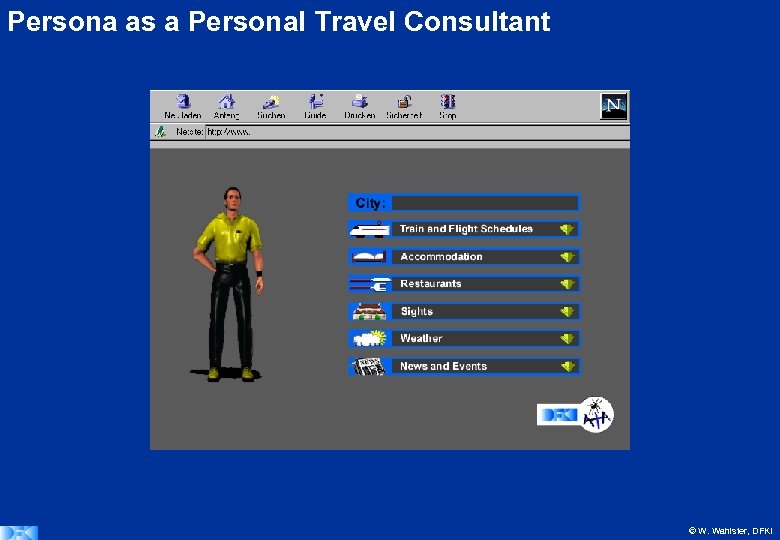 Persona as a Personal Travel Consultant © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Persona as a Personal Travel Consultant © W. Wahlster, DFKI
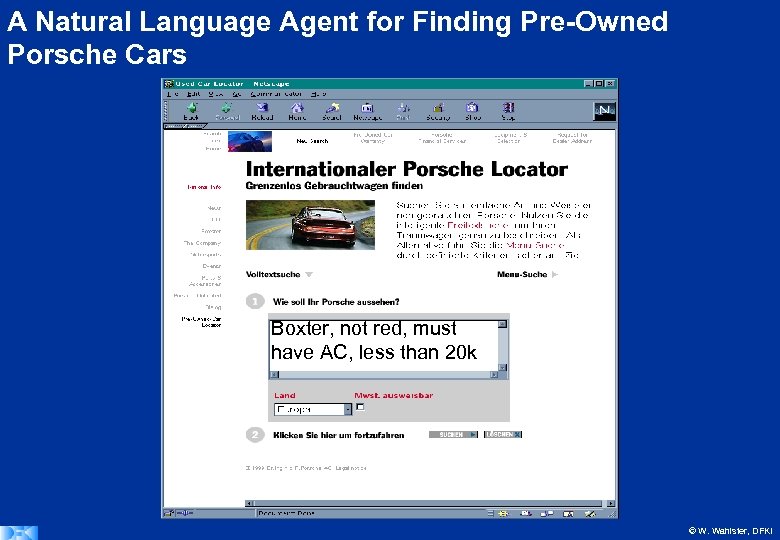 A Natural Language Agent for Finding Pre-Owned Porsche Cars Boxter, not red, must have AC, less than 20 k © W. Wahlster, DFKI
A Natural Language Agent for Finding Pre-Owned Porsche Cars Boxter, not red, must have AC, less than 20 k © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Enhanced ECommerce through Personalization System is able to flexibly tailor product presentations to the individual user and the current situation. An animated character serves as “Alter Ego” of the presentation system. Personalized Presenters at DFKI © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Enhanced ECommerce through Personalization System is able to flexibly tailor product presentations to the individual user and the current situation. An animated character serves as “Alter Ego” of the presentation system. Personalized Presenters at DFKI © W. Wahlster, DFKI
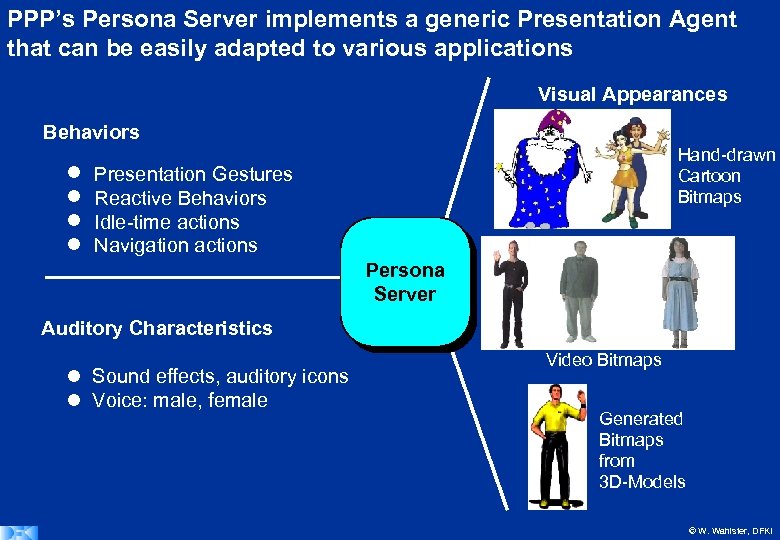 PPP’s Persona Server implements a generic Presentation Agent that can be easily adapted to various applications Visual Appearances Behaviors Hand-drawn Cartoon Bitmaps Presentation Gestures Reactive Behaviors Idle-time actions Navigation actions Persona Server Auditory Characteristics Sound effects, auditory icons Voice: male, female Video Bitmaps Generated Bitmaps from 3 D-Models © W. Wahlster, DFKI
PPP’s Persona Server implements a generic Presentation Agent that can be easily adapted to various applications Visual Appearances Behaviors Hand-drawn Cartoon Bitmaps Presentation Gestures Reactive Behaviors Idle-time actions Navigation actions Persona Server Auditory Characteristics Sound effects, auditory icons Voice: male, female Video Bitmaps Generated Bitmaps from 3 D-Models © W. Wahlster, DFKI
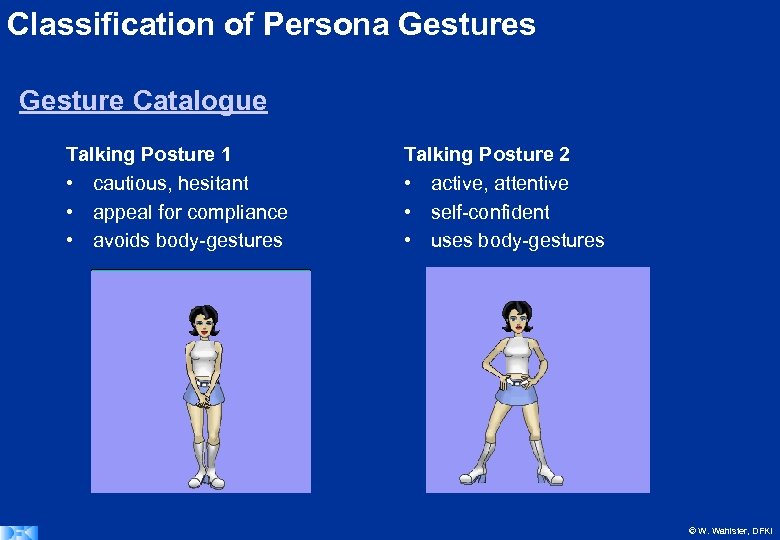 Classification of Persona Gestures Gesture Catalogue Talking Posture 1 • cautious, hesitant • appeal for compliance • avoids body-gestures Talking Posture 2 • active, attentive • self-confident • uses body-gestures © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Classification of Persona Gestures Gesture Catalogue Talking Posture 1 • cautious, hesitant • appeal for compliance • avoids body-gestures Talking Posture 2 • active, attentive • self-confident • uses body-gestures © W. Wahlster, DFKI
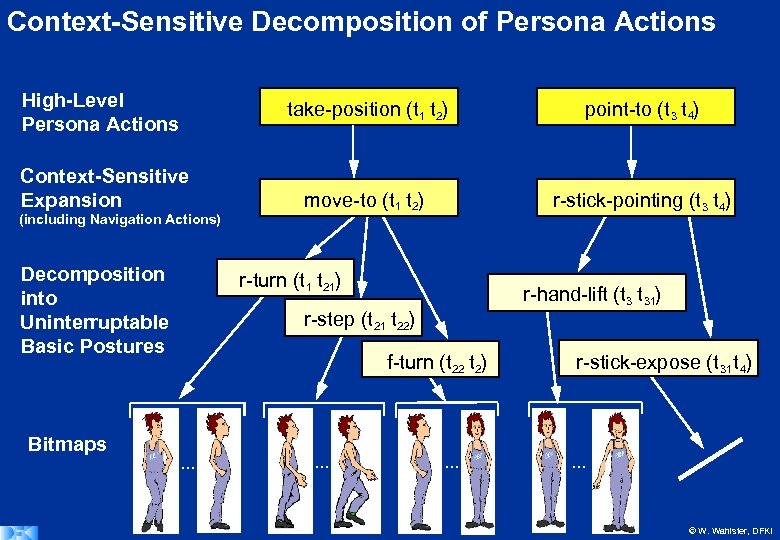 Context-Sensitive Decomposition of Persona Actions High-Level Persona Actions take-position (t 1 t 2) Context-Sensitive Expansion (including Navigation Actions) Decomposition into Uninterruptable Basic Postures Bitmaps point-to (t 3 t 4) move-to (t 1 t 2) r-stick-pointing (t 3 t 4) r-turn (t 1 t 21) r-hand-lift (t 3 t 31) r-step (t 21 t 22) f-turn (t 22 t 2) . . r-stick-expose (t 31 t 4) . . . © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Context-Sensitive Decomposition of Persona Actions High-Level Persona Actions take-position (t 1 t 2) Context-Sensitive Expansion (including Navigation Actions) Decomposition into Uninterruptable Basic Postures Bitmaps point-to (t 3 t 4) move-to (t 1 t 2) r-stick-pointing (t 3 t 4) r-turn (t 1 t 21) r-hand-lift (t 3 t 31) r-step (t 21 t 22) f-turn (t 22 t 2) . . r-stick-expose (t 31 t 4) . . . © W. Wahlster, DFKI
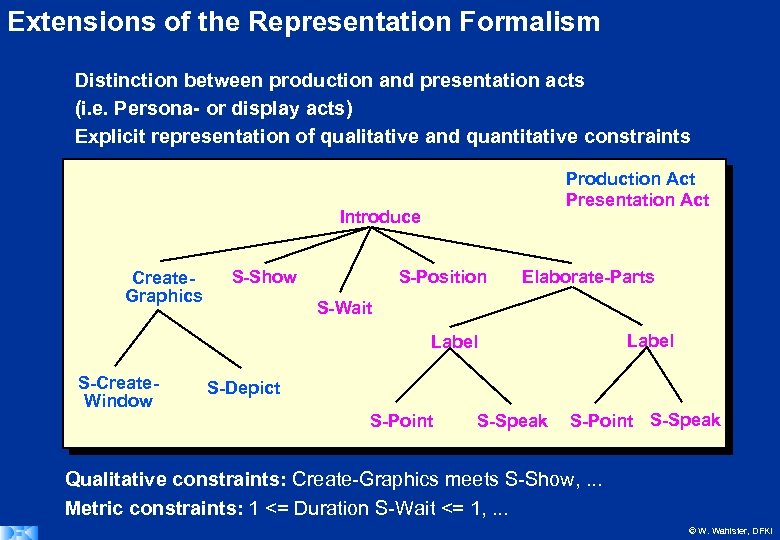 Extensions of the Representation Formalism Distinction between production and presentation acts (i. e. Persona- or display acts) Explicit representation of qualitative and quantitative constraints Production Act Presentation Act Introduce Create. Graphics S-Show S-Position Elaborate-Parts S-Wait Label S-Create. Window S-Depict S-Point S-Speak Qualitative constraints: Create-Graphics meets S-Show, . . . Metric constraints: 1 <= Duration S-Wait <= 1, . . . © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Extensions of the Representation Formalism Distinction between production and presentation acts (i. e. Persona- or display acts) Explicit representation of qualitative and quantitative constraints Production Act Presentation Act Introduce Create. Graphics S-Show S-Position Elaborate-Parts S-Wait Label S-Create. Window S-Depict S-Point S-Speak Qualitative constraints: Create-Graphics meets S-Show, . . . Metric constraints: 1 <= Duration S-Wait <= 1, . . . © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 PET: Persona-Enabling Toolkit Objective: Enable non-professional computer users to populate their web pages with lifelike characters PET comes with: a set of characters and basic gestures an easy-to-learn Persona markup language Developer’s PET will include: a character design tool which enables users to build their own characters Technical Realization: Based on XML and Java © W. Wahlster, DFKI
PET: Persona-Enabling Toolkit Objective: Enable non-professional computer users to populate their web pages with lifelike characters PET comes with: a set of characters and basic gestures an easy-to-learn Persona markup language Developer’s PET will include: a character design tool which enables users to build their own characters Technical Realization: Based on XML and Java © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 The Persona Markup Language Specification of Persona actions
The Persona Markup Language Specification of Persona actions
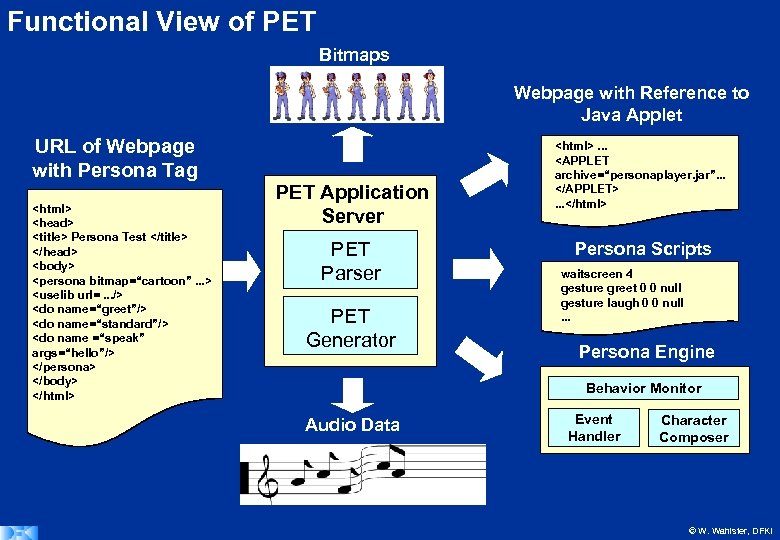 Functional View of PET Bitmaps Webpage with Reference to Java Applet URL of Webpage with Persona Tag
Functional View of PET Bitmaps Webpage with Reference to Java Applet URL of Webpage with Persona Tag
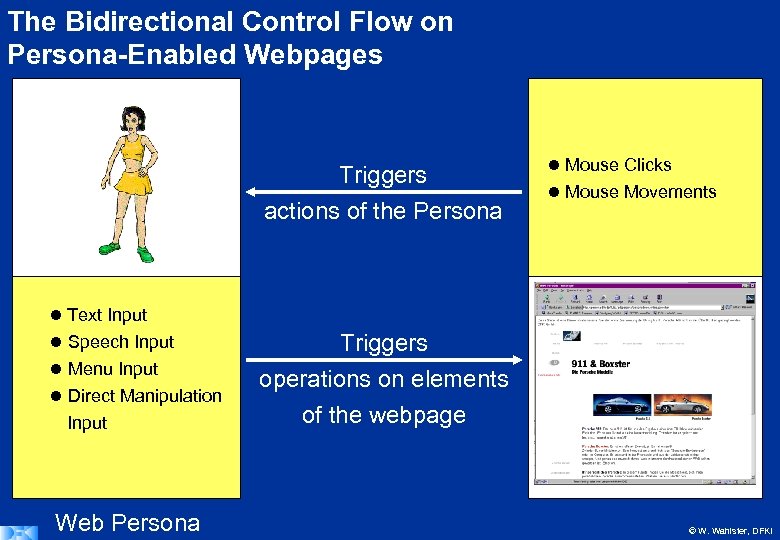 The Bidirectional Control Flow on Persona-Enabled Webpages Triggers actions of the Persona Mouse Clicks Mouse Movements Text Input Speech Input Menu Input Direct Manipulation Input Web Persona Triggers operations on elements of the webpage © W. Wahlster, DFKI
The Bidirectional Control Flow on Persona-Enabled Webpages Triggers actions of the Persona Mouse Clicks Mouse Movements Text Input Speech Input Menu Input Direct Manipulation Input Web Persona Triggers operations on elements of the webpage © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Porsche 9 11 & Boxter © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Porsche 9 11 & Boxter © W. Wahlster, DFKI
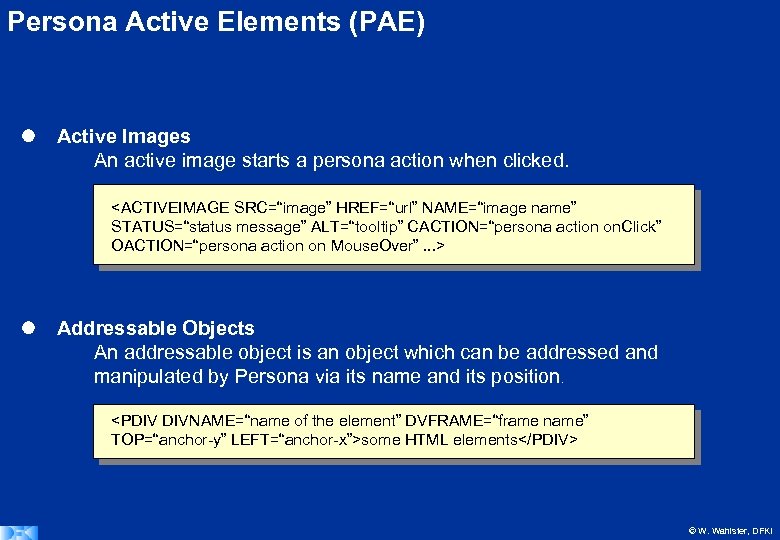 Persona Active Elements (PAE) l Active Images An active image starts a persona action when clicked.
Persona Active Elements (PAE) l Active Images An active image starts a persona action when clicked.
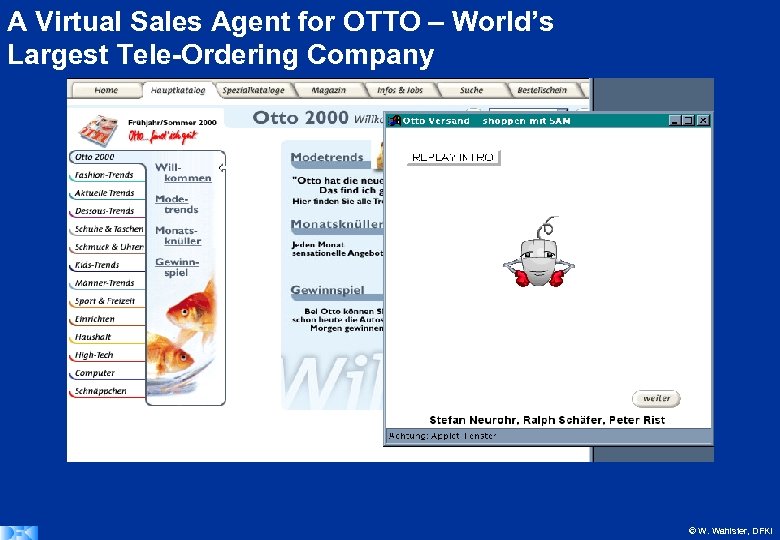 A Virtual Sales Agent for OTTO – World’s Largest Tele-Ordering Company © W. Wahlster, DFKI
A Virtual Sales Agent for OTTO – World’s Largest Tele-Ordering Company © W. Wahlster, DFKI
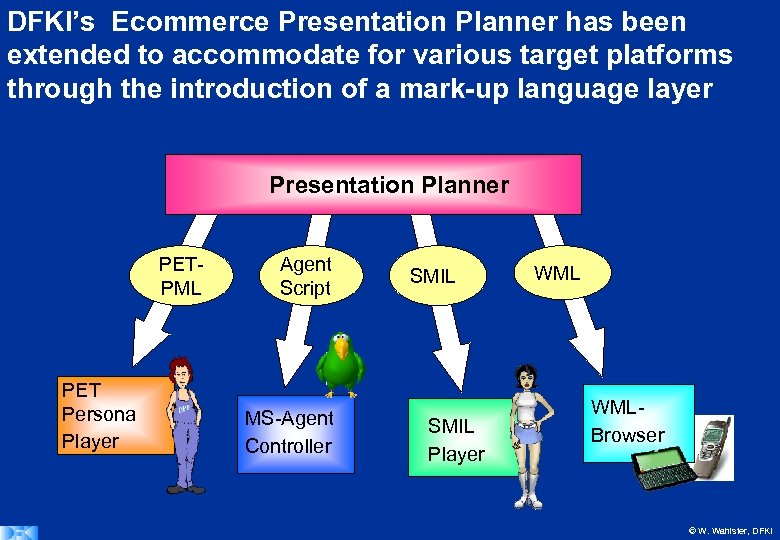 DFKI’s Ecommerce Presentation Planner has been extended to accommodate for various target platforms through the introduction of a mark-up language layer Presentation Planner PETPML PET Persona Player Agent Script MS-Agent Controller SMIL Player WMLBrowser © W. Wahlster, DFKI
DFKI’s Ecommerce Presentation Planner has been extended to accommodate for various target platforms through the introduction of a mark-up language layer Presentation Planner PETPML PET Persona Player Agent Script MS-Agent Controller SMIL Player WMLBrowser © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Information Extraction Agents • Information Filtering • Information Retrieval • Information Integration identify relevant documents –. . . – identify and extract relevant pieces of information – transform them into canonical form wrappers • operational descriptions of a target concept • abstract from concrete occurrence within document • robust against modifications © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Information Extraction Agents • Information Filtering • Information Retrieval • Information Integration identify relevant documents –. . . – identify and extract relevant pieces of information – transform them into canonical form wrappers • operational descriptions of a target concept • abstract from concrete occurrence within document • robust against modifications © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Use of a Life-like Character for Electronic Commerce Digital Assistant Selector © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Use of a Life-like Character for Electronic Commerce Digital Assistant Selector © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Simulated Dialogues as a Novel Presentation Technique • Presentation teams convey certain rhetorical relationships in a more canonical way – Provide pros and cons • The single presenters can serve as indices which help the user to classify information. – Provide information from different points of view, e. g. businessman versus tourist • Presentation teams can serve as rhetorical devices that allow for a continuous reinforcement of beliefs – involve pseudo-experts to increase evidence © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Simulated Dialogues as a Novel Presentation Technique • Presentation teams convey certain rhetorical relationships in a more canonical way – Provide pros and cons • The single presenters can serve as indices which help the user to classify information. – Provide information from different points of view, e. g. businessman versus tourist • Presentation teams can serve as rhetorical devices that allow for a continuous reinforcement of beliefs – involve pseudo-experts to increase evidence © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Presentation Teams for Advanced ECommerce I recommend you this SLX limousine. © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Presentation Teams for Advanced ECommerce I recommend you this SLX limousine. © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Underlying Knowledge Base • Representation of domain – FACT attribute car_1 consumption_car_1 • Value dimensions for cars adopted from a study of the German car market – safety, economy, comfort, sportiness, prestige, family and environmental friendliness – FACT polarity consumption_car_1 economy negative • Difficulty to infer implication of dimension on attribute – FACT difficulty consumption_car_1 economy low © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Underlying Knowledge Base • Representation of domain – FACT attribute car_1 consumption_car_1 • Value dimensions for cars adopted from a study of the German car market – safety, economy, comfort, sportiness, prestige, family and environmental friendliness – FACT polarity consumption_car_1 economy negative • Difficulty to infer implication of dimension on attribute – FACT difficulty consumption_car_1 economy low © W. Wahlster, DFKI
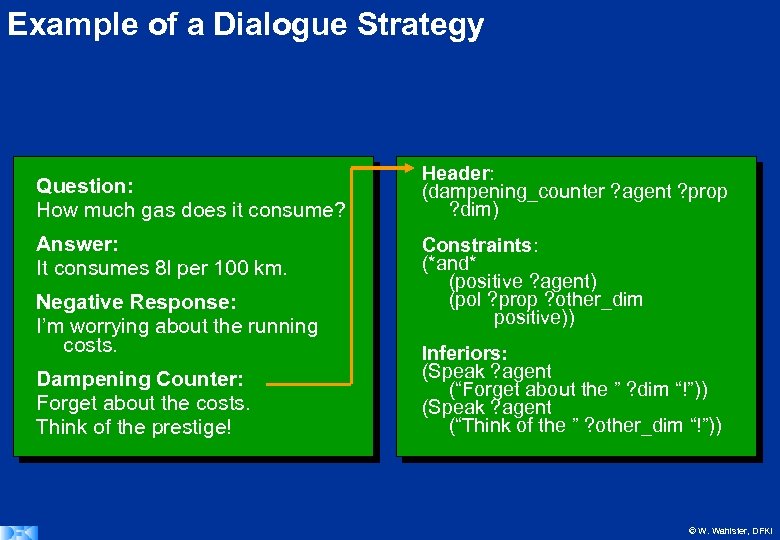 Example of a Dialogue Strategy Question: How much gas does it consume? Answer: It consumes 8 l per 100 km. Negative Response: I’m worrying about the running costs. Dampening Counter: Forget about the costs. Think of the prestige! Header: (dampening_counter ? agent ? prop ? dim) Constraints: (*and* (positive ? agent) (pol ? prop ? other_dim positive)) Inferiors: (Speak ? agent (“Forget about the ” ? dim “!”)) (Speak ? agent (“Think of the ” ? other_dim “!”)) © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Example of a Dialogue Strategy Question: How much gas does it consume? Answer: It consumes 8 l per 100 km. Negative Response: I’m worrying about the running costs. Dampening Counter: Forget about the costs. Think of the prestige! Header: (dampening_counter ? agent ? prop ? dim) Constraints: (*and* (positive ? agent) (pol ? prop ? other_dim positive)) Inferiors: (Speak ? agent (“Forget about the ” ? dim “!”)) (Speak ? agent (“Think of the ” ? other_dim “!”)) © W. Wahlster, DFKI
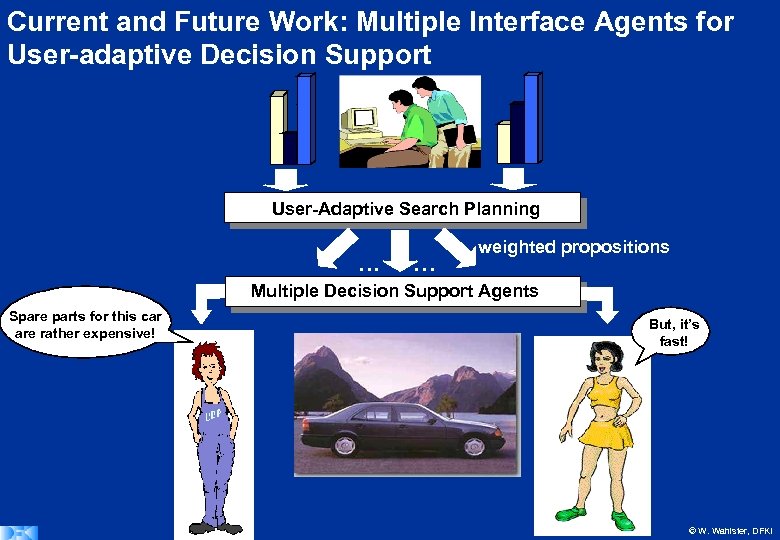 Current and Future Work: Multiple Interface Agents for User-adaptive Decision Support User-Adaptive Search Planning . . . weighted propositions Multiple Decision Support Agents Spare parts for this car are rather expensive! But, it’s fast! © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Current and Future Work: Multiple Interface Agents for User-adaptive Decision Support User-Adaptive Search Planning . . . weighted propositions Multiple Decision Support Agents Spare parts for this car are rather expensive! But, it’s fast! © W. Wahlster, DFKI
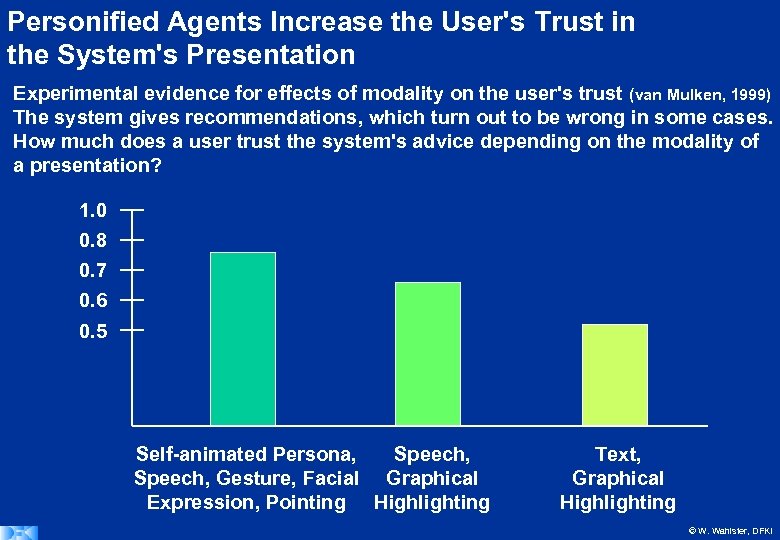 Personified Agents Increase the User's Trust in the System's Presentation Experimental evidence for effects of modality on the user's trust (van Mulken, 1999) The system gives recommendations, which turn out to be wrong in some cases. How much does a user trust the system's advice depending on the modality of a presentation? 1. 0 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 Self-animated Persona, Speech, Gesture, Facial Graphical Expression, Pointing Highlighting Text, Graphical Highlighting © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Personified Agents Increase the User's Trust in the System's Presentation Experimental evidence for effects of modality on the user's trust (van Mulken, 1999) The system gives recommendations, which turn out to be wrong in some cases. How much does a user trust the system's advice depending on the modality of a presentation? 1. 0 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 Self-animated Persona, Speech, Gesture, Facial Graphical Expression, Pointing Highlighting Text, Graphical Highlighting © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Impact of the modality of a Presentation on the User's Trustfulness Result: Conclusion: Persona > Speech > Text If the presentation is more human-like, recommendations are more readily followed For decision support systems tutoring systems recommendation systems virtual sales agents personified interface agents have a clear advantage: They increase the user's trust in the information presented by the system © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Impact of the modality of a Presentation on the User's Trustfulness Result: Conclusion: Persona > Speech > Text If the presentation is more human-like, recommendations are more readily followed For decision support systems tutoring systems recommendation systems virtual sales agents personified interface agents have a clear advantage: They increase the user's trust in the information presented by the system © W. Wahlster, DFKI
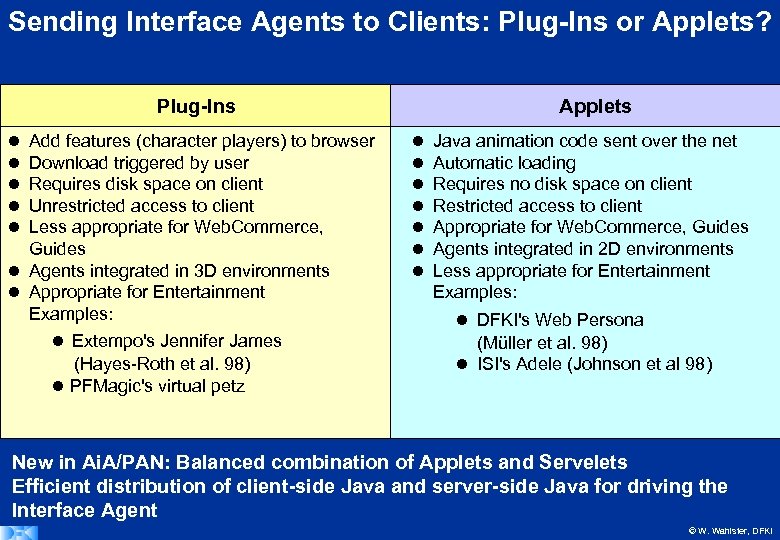 Sending Interface Agents to Clients: Plug-Ins or Applets? Plug-Ins Add features (character players) to browser Download triggered by user Requires disk space on client Unrestricted access to client Less appropriate for Web. Commerce, Guides Agents integrated in 3 D environments Appropriate for Entertainment Examples: Extempo's Jennifer James (Hayes-Roth et al. 98) PFMagic's virtual petz Applets Java animation code sent over the net Automatic loading Requires no disk space on client Restricted access to client Appropriate for Web. Commerce, Guides Agents integrated in 2 D environments Less appropriate for Entertainment Examples: DFKI's Web Persona (Müller et al. 98) ISI's Adele (Johnson et al 98) New in Ai. A/PAN: Balanced combination of Applets and Servelets Efficient distribution of client-side Java and server-side Java for driving the Interface Agent © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Sending Interface Agents to Clients: Plug-Ins or Applets? Plug-Ins Add features (character players) to browser Download triggered by user Requires disk space on client Unrestricted access to client Less appropriate for Web. Commerce, Guides Agents integrated in 3 D environments Appropriate for Entertainment Examples: Extempo's Jennifer James (Hayes-Roth et al. 98) PFMagic's virtual petz Applets Java animation code sent over the net Automatic loading Requires no disk space on client Restricted access to client Appropriate for Web. Commerce, Guides Agents integrated in 2 D environments Less appropriate for Entertainment Examples: DFKI's Web Persona (Müller et al. 98) ISI's Adele (Johnson et al 98) New in Ai. A/PAN: Balanced combination of Applets and Servelets Efficient distribution of client-side Java and server-side Java for driving the Interface Agent © W. Wahlster, DFKI
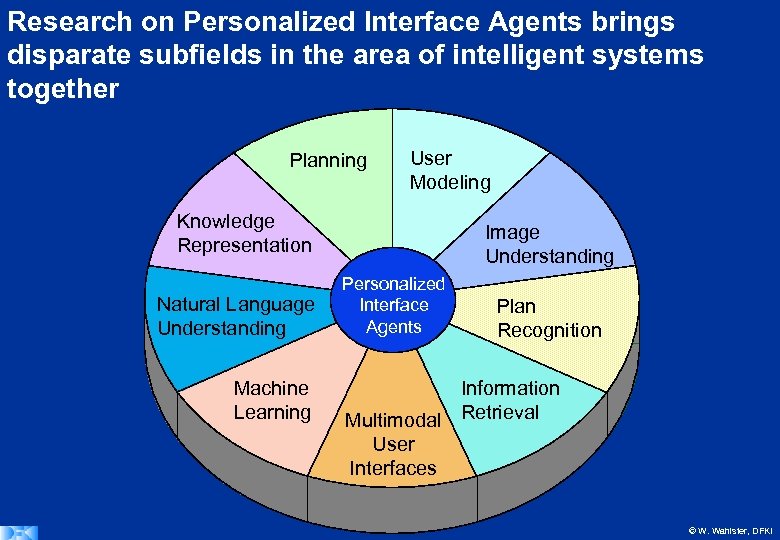 Research on Personalized Interface Agents brings disparate subfields in the area of intelligent systems together Planning User Modeling Knowledge Representation Image Understanding Personalized Intelligent Natural Language Interface Web Agents Understanding Services Machine Learning Plan Recognition Information Multimodal Retrieval User Interfaces © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Research on Personalized Interface Agents brings disparate subfields in the area of intelligent systems together Planning User Modeling Knowledge Representation Image Understanding Personalized Intelligent Natural Language Interface Web Agents Understanding Services Machine Learning Plan Recognition Information Multimodal Retrieval User Interfaces © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Conclusion ECommerce projects of DFKI have shown that research on personalized interface agents can be transferred to real world applications: Dekra (largest European organization of used car dealers): Fair. Car as an ECommerce platform with NL access and a comparison shopping agent for used cars Daimler. Chrysler: online user modelling in a one-to-one marketing system for Mercedes cars Otto/Shopping 24/Eddie Bauer (largest European tele-order company): virtual sales agents for one-to-one marketing of fashion and computer hardware Porsche: Virtual Market for Pre-owned Porsche Cars © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Conclusion ECommerce projects of DFKI have shown that research on personalized interface agents can be transferred to real world applications: Dekra (largest European organization of used car dealers): Fair. Car as an ECommerce platform with NL access and a comparison shopping agent for used cars Daimler. Chrysler: online user modelling in a one-to-one marketing system for Mercedes cars Otto/Shopping 24/Eddie Bauer (largest European tele-order company): virtual sales agents for one-to-one marketing of fashion and computer hardware Porsche: Virtual Market for Pre-owned Porsche Cars © W. Wahlster, DFKI
 Conclusion The generation of virtual webpages with personalized interface agents leads to innovative applications in: Electronic Commerce, Electronic TV Guides (EPG) Telelearning environments, Call Centers and Help Desks Two Research Challenges: Making the Interface agents sensitive to temporary limitations of the user‘s time and working memory capacity (cf. our READY project, Jameson et al. , p. 79 -85 in IUI 99 Proceedings) Making the agents instructible, so that they can learn from the user in a dialog, how to extract information in a new domain (cf. Mathias Bauer, Dietmar Dengler Tr. IAs: Trainable Information Assistants for Cooperative Problem Solving in Agents'99, on Tuesday) © W. Wahlster, DFKI
Conclusion The generation of virtual webpages with personalized interface agents leads to innovative applications in: Electronic Commerce, Electronic TV Guides (EPG) Telelearning environments, Call Centers and Help Desks Two Research Challenges: Making the Interface agents sensitive to temporary limitations of the user‘s time and working memory capacity (cf. our READY project, Jameson et al. , p. 79 -85 in IUI 99 Proceedings) Making the agents instructible, so that they can learn from the user in a dialog, how to extract information in a new domain (cf. Mathias Bauer, Dietmar Dengler Tr. IAs: Trainable Information Assistants for Cooperative Problem Solving in Agents'99, on Tuesday) © W. Wahlster, DFKI


