03b43e044782e9d0952549c84eb2c21e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 13 Power and Politics 13 -0
13 Power and Politics 13 -0
 Learning Objectives n n n n n Define power, and contrast leadership and power. Contrast the five bases of power. Identify nine power or influence tactics and their contingencies. Show the connection between sexual harassment and the abuse of power. Distinguish between legitimate and illegitimate political behavior. Identify the causes and consequences of political behavior. Apply impression management techniques. Determine whether a political action is ethical. Show the influence of culture on the uses and perceptions of politics. 13 -1
Learning Objectives n n n n n Define power, and contrast leadership and power. Contrast the five bases of power. Identify nine power or influence tactics and their contingencies. Show the connection between sexual harassment and the abuse of power. Distinguish between legitimate and illegitimate political behavior. Identify the causes and consequences of political behavior. Apply impression management techniques. Determine whether a political action is ethical. Show the influence of culture on the uses and perceptions of politics. 13 -1
 A Definition of Power n A’s capacity to influence the behavior of B so that B agrees to A’s wishes n n Exists as a potential or fully used influence over a dependent relationship Dependency n n B’s relationship to A when A possesses something that B requires The greater B's dependence, the more power A has 13 -2
A Definition of Power n A’s capacity to influence the behavior of B so that B agrees to A’s wishes n n Exists as a potential or fully used influence over a dependent relationship Dependency n n B’s relationship to A when A possesses something that B requires The greater B's dependence, the more power A has 13 -2
 Contrasting Leadership and Power n n Power Leadership Focuses on goal achievement Requires goal compatibility with followers Focuses influence downward Research Focus n Leadership styles and relationships with followers n n Used as a means for achieving goals Requires follower dependency Used to gain lateral and upward influence Research Focus n Power tactics for gaining compliance (agreement) 13 -3
Contrasting Leadership and Power n n Power Leadership Focuses on goal achievement Requires goal compatibility with followers Focuses influence downward Research Focus n Leadership styles and relationships with followers n n Used as a means for achieving goals Requires follower dependency Used to gain lateral and upward influence Research Focus n Power tactics for gaining compliance (agreement) 13 -3
 Bases of Power: Formal Power n Established by an individual’s position in an organization n Three bases: n Coercive Power n A power base dependent on fear of negative results n Reward Power n Compliance achieved based on the ability to distribute rewards that others view as valuable n Legitimate Power n The formal authority to control and use resources based on a person’s position in the formal 13 -4 hierarchy
Bases of Power: Formal Power n Established by an individual’s position in an organization n Three bases: n Coercive Power n A power base dependent on fear of negative results n Reward Power n Compliance achieved based on the ability to distribute rewards that others view as valuable n Legitimate Power n The formal authority to control and use resources based on a person’s position in the formal 13 -4 hierarchy
 Bases of Power: Personal Power n Power that comes from an individual’s unique characteristics – these are the most effective n n Expert Power n Influence based on special skills or knowledge Referent Power n Influence based on possession by an individual of desirable resources or personal traits 13 -5
Bases of Power: Personal Power n Power that comes from an individual’s unique characteristics – these are the most effective n n Expert Power n Influence based on special skills or knowledge Referent Power n Influence based on possession by an individual of desirable resources or personal traits 13 -5
 Dependency: The Key to Power n The General Dependency Assumption n n The greater B’s dependency on A, the greater the power A has over B Possession/control of scarce organizational resources that others need makes a manager powerful Access to optional resources (e. g. , multiple suppliers) reduces the resource holder’s power Dependency increases when resources are: n Important n Scarce n Non-substitutable (no alternatives) 13 -6
Dependency: The Key to Power n The General Dependency Assumption n n The greater B’s dependency on A, the greater the power A has over B Possession/control of scarce organizational resources that others need makes a manager powerful Access to optional resources (e. g. , multiple suppliers) reduces the resource holder’s power Dependency increases when resources are: n Important n Scarce n Non-substitutable (no alternatives) 13 -6
 Power Tactics n n Ways in which individuals translate power bases into specific actions Nine influence tactics: n Legitimacy n Rational persuasion* n Inspirational appeals* n Consultation* n Exchange n Personal appeals * Most effective n Ingratiation (Pressure is the least effective) n Pressure 13 -7 n Coalitions
Power Tactics n n Ways in which individuals translate power bases into specific actions Nine influence tactics: n Legitimacy n Rational persuasion* n Inspirational appeals* n Consultation* n Exchange n Personal appeals * Most effective n Ingratiation (Pressure is the least effective) n Pressure 13 -7 n Coalitions
 Factors Influencing Power Tactics n Choice and effectiveness of influence tactics are moderated by: n Sequencing of tactics n Softer to harder tactics work best n Political skill of the user n The culture of the organization n Culture affects user’s choice of tactic 13 -8
Factors Influencing Power Tactics n Choice and effectiveness of influence tactics are moderated by: n Sequencing of tactics n Softer to harder tactics work best n Political skill of the user n The culture of the organization n Culture affects user’s choice of tactic 13 -8
 Sexual Harassment: An Example of Unequal Power n n Sexual Harassment: n Any unwanted activity of a sexual nature that affects an individual’s employment and creates a hostile work environment n Direct/open actions, like unwanted touching, are relatively easy to spot n Subtle actions, like jokes or looks, can become harassment Sexual harassment is about abusing an unequal power relationship n Harassment can damage the well-being of the individual, work group, and organization 13 -9
Sexual Harassment: An Example of Unequal Power n n Sexual Harassment: n Any unwanted activity of a sexual nature that affects an individual’s employment and creates a hostile work environment n Direct/open actions, like unwanted touching, are relatively easy to spot n Subtle actions, like jokes or looks, can become harassment Sexual harassment is about abusing an unequal power relationship n Harassment can damage the well-being of the individual, work group, and organization 13 -9
 Politics: Power in Action n Political Behavior n n Activities that are not required as part of one’s formal role in the organization, but that influence, or attempt to influence, the distribution of advantages or disadvantages within the organization Legitimate Political Behavior Normal everyday politics - complaining, Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice bypassing, obstructing Hall n 13 -10
Politics: Power in Action n Political Behavior n n Activities that are not required as part of one’s formal role in the organization, but that influence, or attempt to influence, the distribution of advantages or disadvantages within the organization Legitimate Political Behavior Normal everyday politics - complaining, Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice bypassing, obstructing Hall n 13 -10
 Managerial Actions to Prevent Sexual Harassment n n n Make sure a policy against it is in place. Ensure that employees will not have any problems if they make a complaint. Investigate every complaint and include the human resource and legal departments. Make sure offenders are disciplined or terminated (fired) Set up in-house workshops and training. 13 -11
Managerial Actions to Prevent Sexual Harassment n n n Make sure a policy against it is in place. Ensure that employees will not have any problems if they make a complaint. Investigate every complaint and include the human resource and legal departments. Make sure offenders are disciplined or terminated (fired) Set up in-house workshops and training. 13 -11
 The Reality of Politics n n n Limited resources lead to competition and political behaviors Judgments on quality of resource distribution differ based on a person’s perception n “Blaming others” or “fixing responsibility” n “Documenting decisions” n “Perfectionist” or “attentive to detail” Most decisions are made under ambiguous (unclear) conditions n Lack of a clear standard encourages political behaviour 13 -12
The Reality of Politics n n n Limited resources lead to competition and political behaviors Judgments on quality of resource distribution differ based on a person’s perception n “Blaming others” or “fixing responsibility” n “Documenting decisions” n “Perfectionist” or “attentive to detail” Most decisions are made under ambiguous (unclear) conditions n Lack of a clear standard encourages political behaviour 13 -12
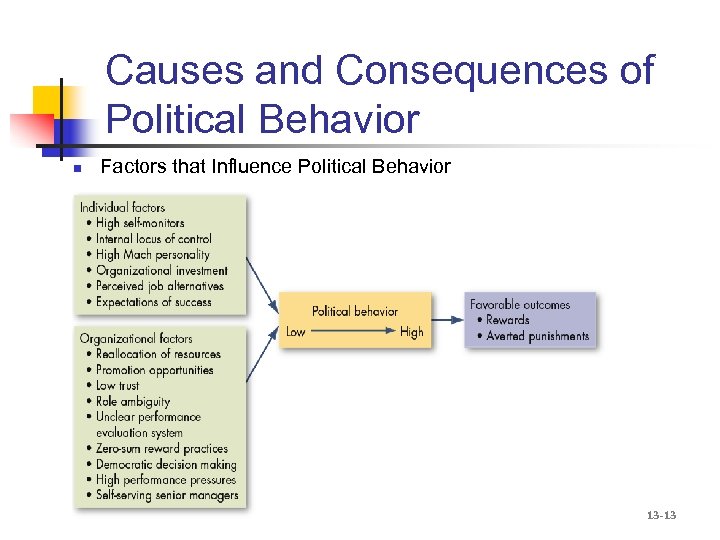 Causes and Consequences of Political Behavior n Factors that Influence Political Behavior 13 -13
Causes and Consequences of Political Behavior n Factors that Influence Political Behavior 13 -13
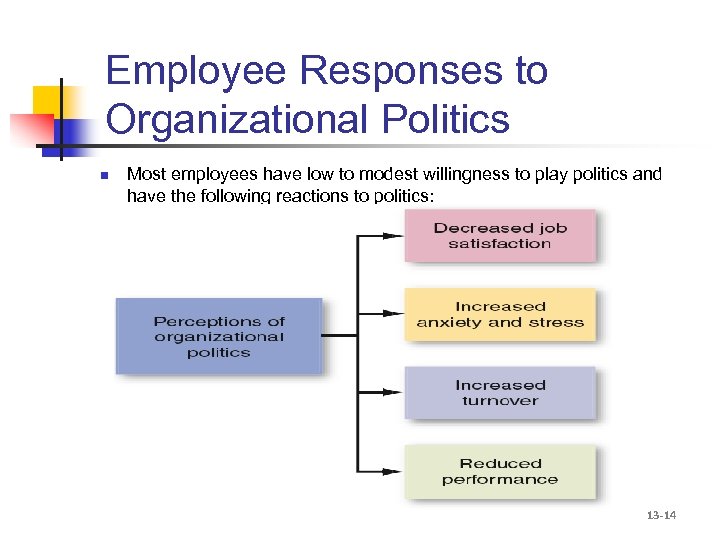 Employee Responses to Organizational Politics n Most employees have low to modest willingness to play politics and have the following reactions to politics: 13 -14
Employee Responses to Organizational Politics n Most employees have low to modest willingness to play politics and have the following reactions to politics: 13 -14
 Defensive Behaviors n n Employees who perceive politics as a threat have defensive reactions n May be helpful in the short run, dangerous in the long run Types of defensive behaviors n Avoiding Action n Over-conforming, passing the buck, playing dumb, stalling n Avoiding Blame n Bluffing, playing safe, justifying, scapegoating n Avoiding Change n Prevention, self-protection 13 -15
Defensive Behaviors n n Employees who perceive politics as a threat have defensive reactions n May be helpful in the short run, dangerous in the long run Types of defensive behaviors n Avoiding Action n Over-conforming, passing the buck, playing dumb, stalling n Avoiding Blame n Bluffing, playing safe, justifying, scapegoating n Avoiding Change n Prevention, self-protection 13 -15
 Impression Management (IM) n n The process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form of them IM Techniques n Conformity (conforming behaviour) n Excuses n Apologies n Self-Promotion n Flattery (praise) n Favors n Association Source: Based on B. R. Schlenker, Impression Management (Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1980); W. L. Gardner and M. J. Martinko, “Impression Management in Organizations, ” Journal of Management, June 1988, p. 332; and R. B. Cialdini, “Indirect Tactics of Image Management Beyond Basking, ” in R. A. Giacalone and P. Rosenfeld (eds. ), Impression Management in the Organization (Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1989), pp. 45– 71. 13 -16
Impression Management (IM) n n The process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form of them IM Techniques n Conformity (conforming behaviour) n Excuses n Apologies n Self-Promotion n Flattery (praise) n Favors n Association Source: Based on B. R. Schlenker, Impression Management (Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1980); W. L. Gardner and M. J. Martinko, “Impression Management in Organizations, ” Journal of Management, June 1988, p. 332; and R. B. Cialdini, “Indirect Tactics of Image Management Beyond Basking, ” in R. A. Giacalone and P. Rosenfeld (eds. ), Impression Management in the Organization (Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1989), pp. 45– 71. 13 -16
 IM Effectiveness n n Job Interview Success n IM does work and most people use it n Self-promotion techniques are important n Ingratiation (winning someone’s approval) is of secondary importance Performance Evaluations n Ingratiation is positively related to ratings n Self-promotion tends to backfire 13 -17
IM Effectiveness n n Job Interview Success n IM does work and most people use it n Self-promotion techniques are important n Ingratiation (winning someone’s approval) is of secondary importance Performance Evaluations n Ingratiation is positively related to ratings n Self-promotion tends to backfire 13 -17
 The Ethics of Behaving Politically n n It is difficulty to tell ethical from unethical politicking (internal politics) Three questions help: 1. What is the benefit of engaging in the behavior? 2. Does the benefit balance out any harm done by the action? 3. Does the action conform to standards of equity and justice? 13 -18
The Ethics of Behaving Politically n n It is difficulty to tell ethical from unethical politicking (internal politics) Three questions help: 1. What is the benefit of engaging in the behavior? 2. Does the benefit balance out any harm done by the action? 3. Does the action conform to standards of equity and justice? 13 -18
 Global Implications n n n Politics Perceptions n Negative consequences to the perception of politics seem to be widespread Preference for Power Tactics n The choice of effective tactics is very dependent on the culture of the country in which they are to be used Effectiveness of Power Tactics n Still open to debate; too little research has been done 13 -19
Global Implications n n n Politics Perceptions n Negative consequences to the perception of politics seem to be widespread Preference for Power Tactics n The choice of effective tactics is very dependent on the culture of the country in which they are to be used Effectiveness of Power Tactics n Still open to debate; too little research has been done 13 -19
 Summary and Managerial Implications n n Increase your power by having others depend on you more. Expert and knowledge power are far more effective than is coercion(forcing someone to do something). n Greater employee motivation, performance, commitment, and satisfaction n Personal power basis, not organizational Effective managers accept the political nature of organizations. Political astuteness (cleverness) and IM can result in higher evaluations, salary increases, and promotions. 13 -20
Summary and Managerial Implications n n Increase your power by having others depend on you more. Expert and knowledge power are far more effective than is coercion(forcing someone to do something). n Greater employee motivation, performance, commitment, and satisfaction n Personal power basis, not organizational Effective managers accept the political nature of organizations. Political astuteness (cleverness) and IM can result in higher evaluations, salary increases, and promotions. 13 -20


