081119170c234951fcc98fe4886eb409.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

13 - 15 November 2012 SARS Customs Modernisation WTO – Trade Facilitation Symposium For African Countries Michael Velile Lekala Customs Modernisation Strategy & Design 1

2 From SARS Vision to Customs Delivery The Customs Mandate SARS Vision To be an innovative Revenue and Customs agency that enhances economic growth and social development, and that supports the country’s integration into the global economy in a way that benefits all South Africans. Collect all revenues due Ensure efficient & effective revenue collection Advise the Ministers of Finance and Trade Ensure efficient & effective control over the movement and manufacturing of goods First line of defence at borders to secure the supply chain and Customs to protect the economy and society by controlling movement Mandate of goods into, from, through and between SA ports of entry 2
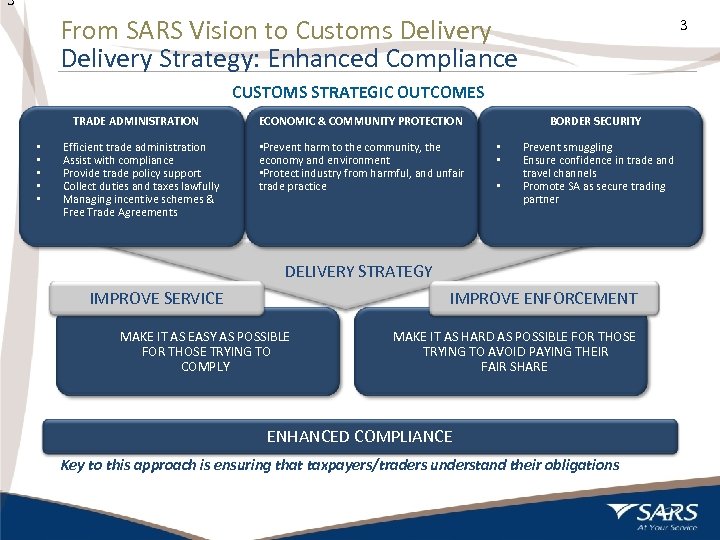
3 From SARS Vision to Customs Delivery Strategy: Enhanced Compliance 3 CUSTOMS STRATEGIC OUTCOMES TRADE ADMINISTRATION • • • Efficient trade administration Assist with compliance Provide trade policy support Collect duties and taxes lawfully Managing incentive schemes & Free Trade Agreements BORDER SECURITY ECONOMIC & COMMUNITY PROTECTION • Prevent harm to the community, the economy and environment • Protect industry from harmful, and unfair trade practice • • • Prevent smuggling Ensure confidence in trade and travel channels Promote SA as secure trading partner DELIVERY STRATEGY IMPROVE SERVICE IMPROVE ENFORCEMENT MAKE IT AS EASY AS POSSIBLE FOR THOSE TRYING TO COMPLY MAKE IT AS HARD AS POSSIBLE FOR THOSE TRYING TO AVOID PAYING THEIR FAIR SHARE ENHANCED COMPLIANCE Key to this approach is ensuring that taxpayers/traders understand their obligations 3
The Need to Change The SARS Reality - Our Vision! SARS vision is to transform the administration system to: • Make it simpler, quicker and hassle free for Tax Payers and Traders • Make the process labour intensive and less cumbersome. • Improve the service offered to clients, BUT………………. . . • Ensure maximum compliance. This vision implied a clear path for Customs Modernisation… 4 4

Customs Tomorrow Strategic Reality 5 Trade Facilitation • High levels of transparency and predictability of policy, legislation and supply chain impact; • Preferential treatment of compliant and trusted traders; • Development of a mature organisation with high skill levels and efficient, effective systems and processes; and • Facilitate Regional Economic Integration. Economic Security • Protect domestic industry through application of trade tariffs; • Collect all trade taxes due to the fiscus; and • Apply trade policy and all international Safety and Security • Creation of a data rich environment with mandatory advanced information to facilitate effective targeting; • Implement an approach dependent on high levels of trust and compliance and self-regulation; and • Assure consumer and trade protection from illicit and dangerous goods. 5 trade and customs commitments.
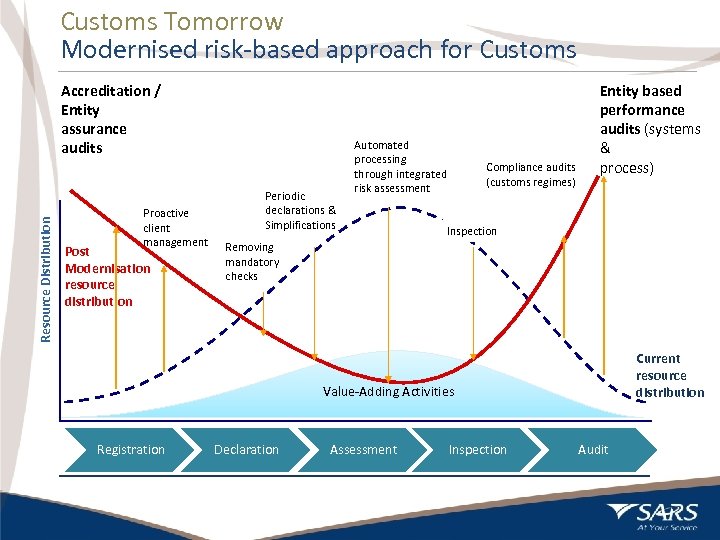
Customs Tomorrow Modernised risk-based approach for Customs Resource Distribution Accreditation / Entity assurance audits Proactive client management Post Modernisation resource distribution Periodic declarations & Simplifications Automated processing through integrated risk assessment Compliance audits (customs regimes) Entity based performance audits (systems & process) Inspection Removing mandatory checks Current resource distribution Value-Adding Activities Registration 6 Declaration Assessment Inspection Audit
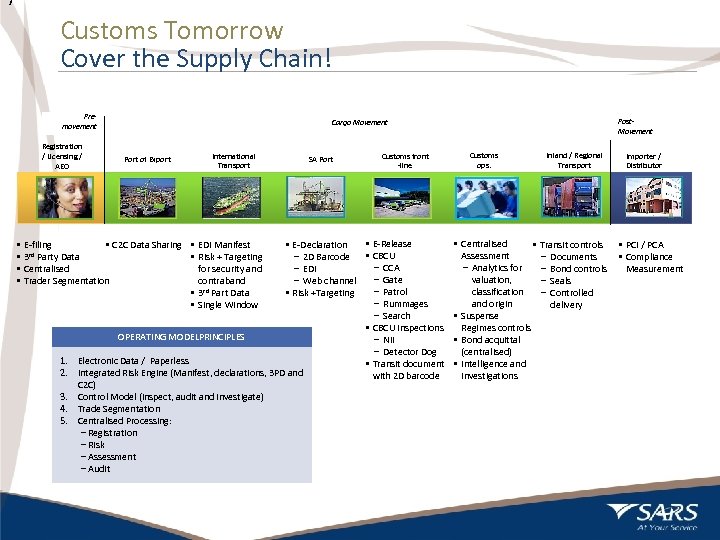
7 Customs Tomorrow Cover the Supply Chain! Premovement Registration / Licensing / AEO Port of Export International Transport 3. 4. 5. 7 SA Port Customs front -line • E-Release • E-Declaration • CBCU – 2 D Barcode – CCA – EDI – Gate – Web channel – Patrol • Risk +Targeting – Rummages – Search • CBCU Inspections OPERATING MODELPRINCIPLES – NII – Detector Dog Electronic Data / Paperless • Transit document Integrated Risk Engine (Manifest, declarations, 3 PD and with 2 D barcode C 2 C) Control Model (inspect, audit and investigate) Trade Segmentation Centralised Processing: – Registration – Risk – Assessment – Audit • E-filing • C 2 C Data Sharing • EDI Manifest • 3 rd Party Data • Risk + Targeting • Centralised for security and • Trader Segmentation contraband • 3 rd Part Data • Single Window 1. 2. Post. Movement Cargo Movement Customs ops. Inland / Regional Transport • Centralised • Transit controls Assessment – Documents – Analytics for – Bond controls valuation, – Seals classification – Controlled and origin delivery • Suspense Regimes controls • Bond acquittal (centralised) • Intelligence and Investigations Importer / Distributor • PCI / PCA • Compliance Measurement
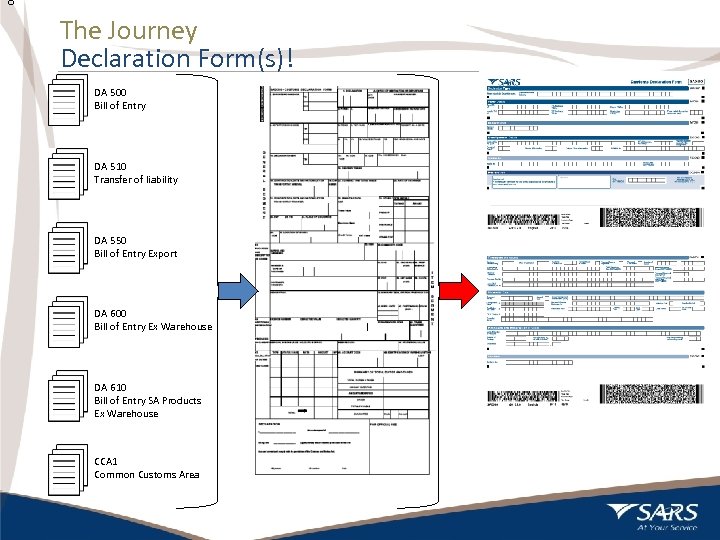
8 The Journey Declaration Form(s)! DA 500 Bill of Entry DA 510 Transfer of liability DA 550 Bill of Entry Export DA 600 Bill of Entry Ex Warehouse DA 610 Bill of Entry SA Products Ex Warehouse CCA 1 Common Customs Area 8
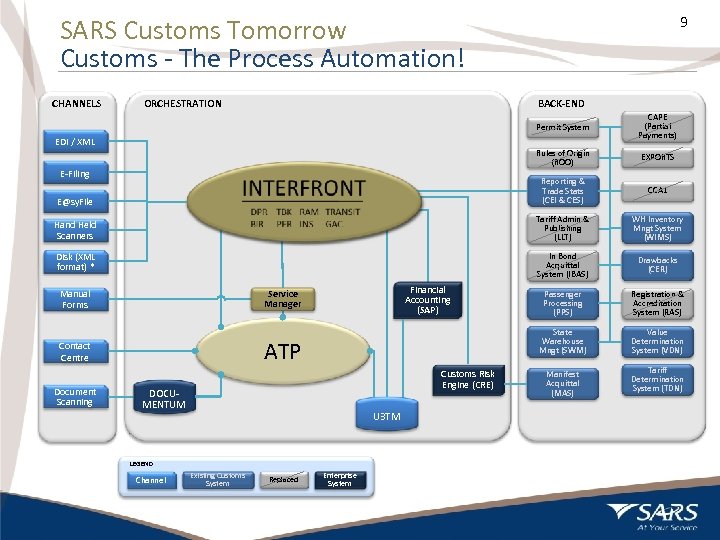
9 SARS Customs Tomorrow Customs - The Process Automation! CHANNELS ORCHESTRATION BACK-END Permit System CAPE (Partial Payments) Rules of Origin (ROO) EXPORTS E@sy. File Reporting & Trade Stats (CEI & CES) CCA 1 Hand Held Scanners Tariff Admin & Publishing (LLT) WH Inventory Mngt System (WIMS) Disk (XML format) * In Bond Acquittal System (IBAS) Drawbacks (CER) Passenger Processing (PPS) Registration & Accreditation System (RAS) State Warehouse Mngt (SWM) Value Determination System (VDN) Manifest Acquittal (MAS) Tariff Determination System (TDN) EDI / XML E-Filing ATP Contact Centre Document Scanning Financial Accounting (SAP) Service Manager Manual Forms Customs Risk Engine (CRE) DOCUMENTUM U 3 TM LEGEND Channel 9 Existing Customs System Replaced Enterprise System
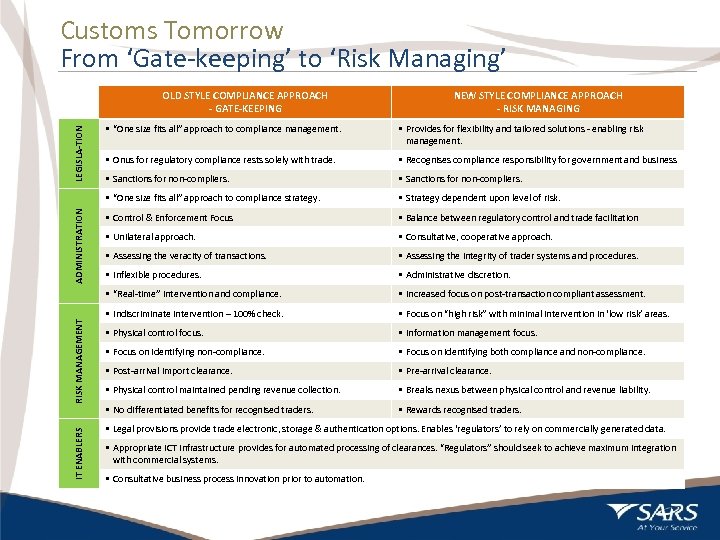
Customs Tomorrow From ‘Gate-keeping’ to ‘Risk Managing’ OLD STYLE COMPLIANCE APPROACH - GATE-KEEPING NEW STYLE COMPLIANCE APPROACH - RISK MANAGING LEGISLA-TION ADMINISTRATION RISK MANAGEMENT • Onus for regulatory compliance rests solely with trade. • Recognises compliance responsibility for government and business • Sanctions for non-compliers. • Strategy dependent upon level of risk. • Control & Enforcement Focus • Balance between regulatory control and trade facilitation • Unilateral approach. • Consultative, cooperative approach. • Assessing the veracity of transactions. • Assessing the integrity of trader systems and procedures. • Inflexible procedures. • Administrative discretion. • “Real-time” intervention and compliance. IT ENABLERS • Provides for flexibility and tailored solutions - enabling risk management. • “One size fits all” approach to compliance strategy. 10 • “One size fits all” approach to compliance management. • Increased focus on post-transaction compliant assessment. • Indiscriminate intervention – 100% check. • Focus on “high risk” with minimal intervention in ‘low risk’ areas. • Physical control focus. • Information management focus. • Focus on identifying non-compliance. • Focus on identifying both compliance and non-compliance. • Post-arrival import clearance. • Pre-arrival clearance. • Physical control maintained pending revenue collection. • Breaks nexus between physical control and revenue liability. • No differentiated benefits for recognised traders. • Rewards recognised traders. • Legal provisions provide trade electronic, storage & authentication options. Enables ‘regulators’ to rely on commercially generated data. • Appropriate ICT infrastructure provides for automated processing of clearances. “Regulators” should seek to achieve maximum integration with commercial systems. • Consultative business process innovation prior to automation.
11
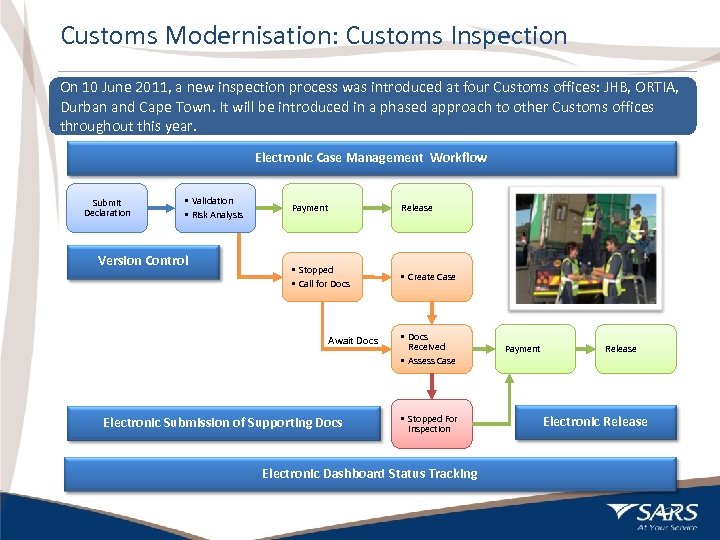
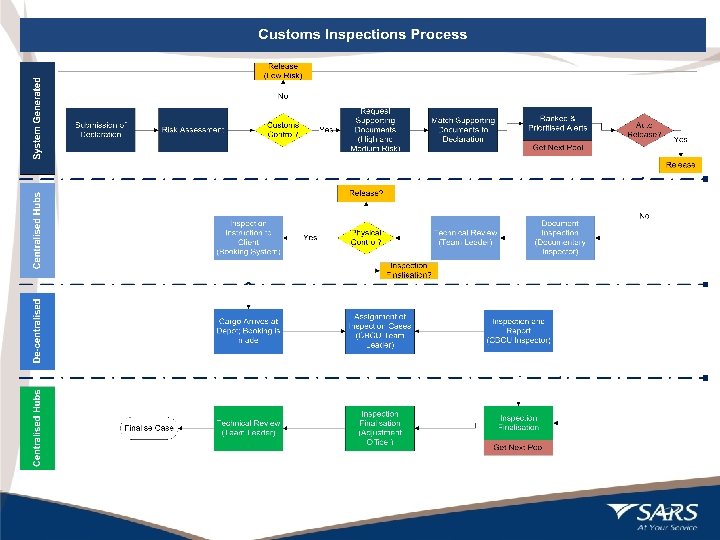
Customs Modernisation: Customs Inspection On 10 June 2011, a new inspection process was introduced at four Customs offices: JHB, ORTIA, Durban and Cape Town. It will be introduced in a phased approach to other Customs offices throughout this year. Electronic Case Management Workflow Submit Declaration • Validation • Risk Analysis Version Control Payment Release • Stopped • Call for Docs • Create Case Await Docs Electronic Submission of Supporting Docs • Docs Received • Assess Case • Stopped For Inspection Electronic Dashboard Status Tracking 12 Payment Release Electronic Release
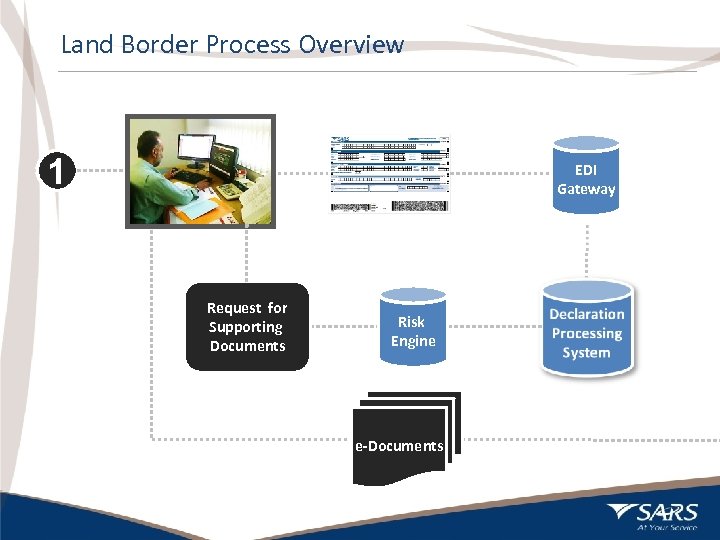
Land Border Process Overview Customs Declaration 1 EDI Gateway Request for Supporting Documents Risk Engine e-Documents 13

2 Review of Electronic Supporting Documents at Centralised Processing Centre 14
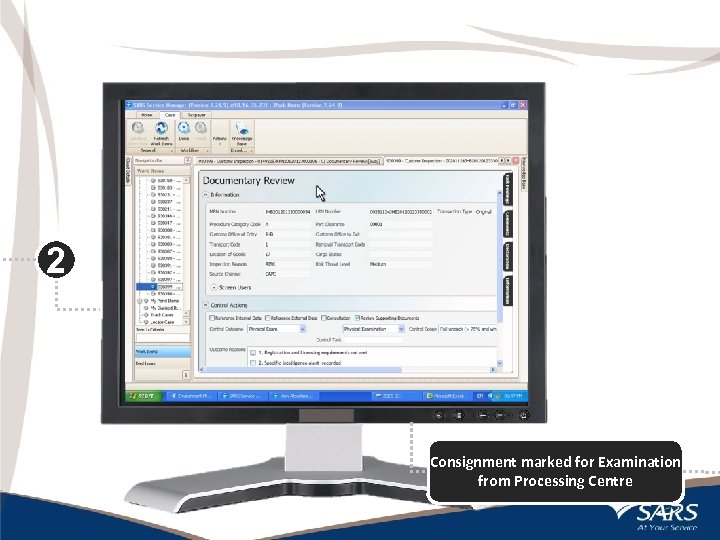
2 Consignment marked for Examination from Processing Centre 15

Clearance received and Carrier proceeds to Border 3 4 16 Manifest number presented on arrival
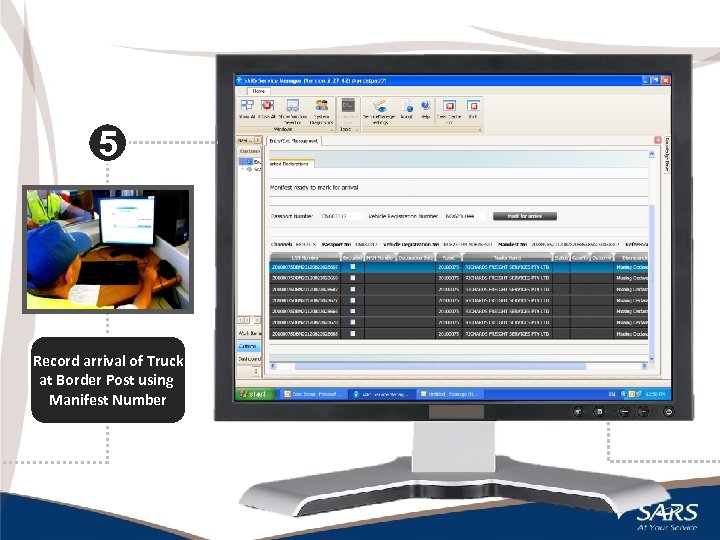
5 Record arrival of Truck at Border Post using Manifest Number 17
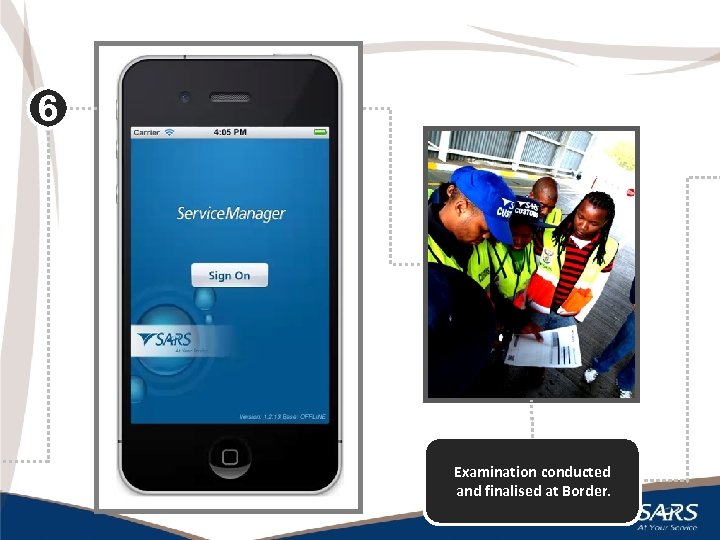
6 Examination conducted and finalised at Border. 18

7 Record exit of Truck at Border Post 19 END
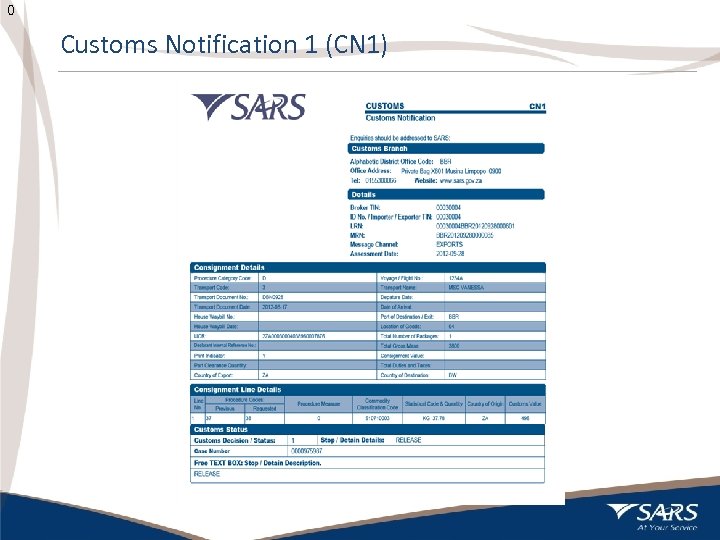
0 Customs Notification 1 (CN 1) 20

1 Customs Notification 2 (CN 2) 21

Overview Accreditation & Preferred Trader • Little partnership culture, or understanding of the client’s own controls and compliance • No formal framework to give real benefits to reward level of good standing. • Segment clients based on their demonstrated competency to perform Customs procedures • SARS validate via Assurance Audit • Client compliance rated Tomorrow • Transactional data used to inform risk, triggering documentary & physical controls Today Yesterday SARS aims to assist key strategic industries and traders to become complaint, and subsequently, improve service and reduce cost of doing business. By working with compliant clients, SARS can refocus resources on high risk • SARS manages >50% of volumes and value within PT Account & service model • A specific program will be offered to each client type, as per needs of SARS and the clients • Further benefits e. g. periodic declaration, Simplifications when Act & systems enable • Manage client relationship & service 22 • Accreditation status and relevant Benefits will awarded befit their compliance standing • SARS-wide client model

Release 2 & 3 Modernisation Journey Release Two of Customs modernisation mainly introduced the Service Manager front-end for officers and the electronic supporting documents process for traders, high speed bulk scanning to free up branch operations from processing bulk documents. Delivery Challenges‘ from Traders 1. 2. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Service Manager Front-End for Inspection Case Management Get next inspection workflow Electronic Supporting Document- e@sy. Scan Removal of the 7070 code Centralisation of all back-end processing Enhanced vehicle movement control at the border post (CN 2) Export and VOC Risk Engine TBK testing has started Highlights 1. 2. 3. 23 An electronic release system, reducing the need for paper and authorising stamps at branches. Enhanced traffic flow of trucks through the control area, . Move L&R to Alberton 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ensuring that all pages are A 4 size Ensuring that all pages are clearly printed not faded Ensure that the case number is clearly indicated on the first page Inclusion of SAD 500 as a supporting doc , when supporting docs are requested Paperclips, staples or any other binding material from the pages Torn, folded, crumpled or smeared with any liquid or dirt pages Bulk pages more than 10 pages Training on the use of SARS e@ scan …and the modernisation journey continues…
Passenger Processing System (PPS) Modernisation Journey The purpose of this project is to enhance the traveller experience when entering or leaving the country as well as ensuring enhanced security and data exchange between the different border agencies. Delivery Highlights 1. 2. 3. 4. Passenger Processing System (PPS) deployed on top of the existing Movement Control System (MCS) platform The Traveller Card which will be completed by all passengers entering South Africa and it will be scanned at the Ports of Entry. The Risk Engine will determine if a passenger needs to be directed through the Green or Red channel and processing a customs declaration, automatically compute duties payable. The Assessment (Invoice) to be handed to travellers, are also being redesigned to make it more user friendly. . 2. 3. 4. Discontinuation of the printing of form (DA 331) – automated process Signature pads for digital signature. Passport scanner. Development of a Informal Trader portfolio (7070) Challenges' 1. The bandwidth at remote land borders …and the modernisation journey continues… 24
Automated Cargo Management(ACM) Modernisation Journey ACM is SARS’s automated solution for the receipt and processing of prescribed reports in respect of imported cargo and the means of transport with which those goods are imported from abroad. It is necessary because ; in line with international practices, that cargo be reported to it prior to arrival for the purposes of screening and risk assessment. Delivery Highlights 1. Replacing MAS with ACM 2. 3. 4. New system will ensure the receipt of “clean” data that meets appropriate standards Process and validate cargo reports at a much faster rate than what was possible before Allow the holistic and automated risk profiling of goods by subjecting both the goods declaration and the cargo declaration to the SARS Customs Risk Engine (CRE) Allow for the resolution of mismatches (entry to manifest and outturn) on a formal case management basis. Challenges‘ From Trade 1. Registration of shipping lines, airlines, freight forwarders, groupage operators, consolidators and other parties that transport goods on behalf of foreign shippers on bills of lading and air waybills to South Africa (by sea and air), or their local agents, to register as soon as possible. …and the modernisation journey continues… 25

Preferred Trader Modernisation Journey SARS Preferred Trader project aims to assist key strategic industries and traders to become complaint, and subsequently, improve service and reduce cost of doing business. By working with compliant clients, SARS can refocus resources on high risk. Delivery Highlights 1. 2. 1. 3. 4. 5. Engage top 200+ by invitation / application List of Top 300 traders created to enable next set of clients Ongoing work on Audit / Accounts – (push to complete top 100 clients) Review Board Ongoing Client communication on PT process Next generation Audit Training plans underway with Academy 2. 3. 4. 5. Segment clients based on their demonstrated competency to perform Customs procedures SARS validate via Assurance Audit Client compliance rated Accreditation status and relevant Benefits will awarded befit their compliance standing Manage client compliance, relationship & service Benefits 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 26 Appointment of a Customs Relationship Manager tasked with facilitating the relationship between the client and customs; Reduction of the amount of any security required for compliance with a customs procedure; Fewer routine documentary and physical inspections; Prioritising a request for tariff and valuation determinations; Prioritising access to non-intrusive inspection techniques when goods are stopped or detained for inspection. …and the modernisation journey continues…

The End For Now! 27 Thank You ! 27
081119170c234951fcc98fe4886eb409.ppt