4e292e85dc4526c81db7941eebaa733d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 12 Lead-ACS Fleming College Paramedic Program
12 Lead-ACS Fleming College Paramedic Program
 Focus of ACS Common reason for transport ¡ Much can be done during transfer ¡ Reduce risk of morbidity and mortality ¡ The first step = recognizing the ACS ¡ Signs and symptoms ¡ ECG changes ¡ Biochemical changes
Focus of ACS Common reason for transport ¡ Much can be done during transfer ¡ Reduce risk of morbidity and mortality ¡ The first step = recognizing the ACS ¡ Signs and symptoms ¡ ECG changes ¡ Biochemical changes
 Summary Strategies for reducing morbidity and mortality l l l Reduce cardiac workload Improve perfusion to cardiac tissue Reduce risk of fatal arrhythmias Reduce extension of clot formation Reperfuse the ischemic myocardium
Summary Strategies for reducing morbidity and mortality l l l Reduce cardiac workload Improve perfusion to cardiac tissue Reduce risk of fatal arrhythmias Reduce extension of clot formation Reperfuse the ischemic myocardium
 Myocardial Infarction ASA (2 x 80 mg) P. O. ¡ O 2 therapy ¡ IV access ¡ NTG via SL, transdermal, and/or IV ¡ Morphine ¡ Heparin and/or Beta blockers ¡ 12 Lead ECG as soon as possible ¡
Myocardial Infarction ASA (2 x 80 mg) P. O. ¡ O 2 therapy ¡ IV access ¡ NTG via SL, transdermal, and/or IV ¡ Morphine ¡ Heparin and/or Beta blockers ¡ 12 Lead ECG as soon as possible ¡
 Pre-hospital Thrombolysis Air Ambulance-Ornge ¡ Oshawa Land ALS ¡ Positive empirical trends ¡
Pre-hospital Thrombolysis Air Ambulance-Ornge ¡ Oshawa Land ALS ¡ Positive empirical trends ¡
 Pre-hospital Thrombolysis ¡ prolonged transport time ¡ no thrombolysis at the sending facility ¡ Long delays
Pre-hospital Thrombolysis ¡ prolonged transport time ¡ no thrombolysis at the sending facility ¡ Long delays
 Indications - Thrombolysis ¡ Ischemic ¡ Less C. P. than 12 hours duration
Indications - Thrombolysis ¡ Ischemic ¡ Less C. P. than 12 hours duration
 Ischemic Chest Pain? O - at rest or with exertion P – better or worse Q - heaviness, tightening, sharp, weakness etc R - neck, jaw and/or left arm S - varies T - consistent, does NOT come & go
Ischemic Chest Pain? O - at rest or with exertion P – better or worse Q - heaviness, tightening, sharp, weakness etc R - neck, jaw and/or left arm S - varies T - consistent, does NOT come & go
 12 Lead ECG Criteria ¡ ¡ ¡ ST segment elevation New onset Left Bundle Branch Block with S&S? Some acute coronary syndromes (A. C. S. ) do not benefit from thrombolysis
12 Lead ECG Criteria ¡ ¡ ¡ ST segment elevation New onset Left Bundle Branch Block with S&S? Some acute coronary syndromes (A. C. S. ) do not benefit from thrombolysis
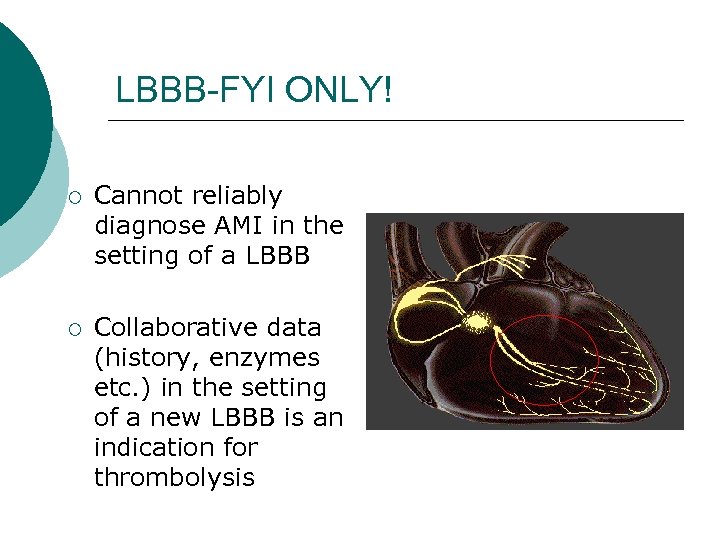 LBBB-FYI ONLY! ¡ Cannot reliably diagnose AMI in the setting of a LBBB ¡ Collaborative data (history, enzymes etc. ) in the setting of a new LBBB is an indication for thrombolysis
LBBB-FYI ONLY! ¡ Cannot reliably diagnose AMI in the setting of a LBBB ¡ Collaborative data (history, enzymes etc. ) in the setting of a new LBBB is an indication for thrombolysis
 What are the Benefits? ¡ ¡ Varies between subgroups of patients Time to thrombolysis l l “Infarct to Drug Time” shorter the better the outcome
What are the Benefits? ¡ ¡ Varies between subgroups of patients Time to thrombolysis l l “Infarct to Drug Time” shorter the better the outcome
 Its all about Timing ¡ ¡ ¡ Thrombolytics within one hour of onset of CP - 50% reduction in infarct size Thrombolytics within two hour of onset of CP - 30% reduction in infarct size Thrombolytics within 3 -4 hour of onset of CP - 13% reduction in infarct size TIME IS MUSCLE - after 6 -12 hours less helpful
Its all about Timing ¡ ¡ ¡ Thrombolytics within one hour of onset of CP - 50% reduction in infarct size Thrombolytics within two hour of onset of CP - 30% reduction in infarct size Thrombolytics within 3 -4 hour of onset of CP - 13% reduction in infarct size TIME IS MUSCLE - after 6 -12 hours less helpful
 Examples of Thrombolytics Retaplase ¡ Tenectoplase (TNK) ¡ Streptokinase ¡ Tissue plasmingen activator (TPA) ¡
Examples of Thrombolytics Retaplase ¡ Tenectoplase (TNK) ¡ Streptokinase ¡ Tissue plasmingen activator (TPA) ¡
 Absolute Contraindications for Thrombolytics ¡ Aortic dissection ¡ Active (significant) bleeding ¡ Pericarditis
Absolute Contraindications for Thrombolytics ¡ Aortic dissection ¡ Active (significant) bleeding ¡ Pericarditis
 Relative Contraindications CPR >10 minutes ¡ Pregnancy ¡ Uncompressible puncture site (from IV etc) ¡ Age (>75) ¡ Recent surgery or trauma or stroke (>2 wks) ¡ Current use of warfarin or other anticoagulant ¡
Relative Contraindications CPR >10 minutes ¡ Pregnancy ¡ Uncompressible puncture site (from IV etc) ¡ Age (>75) ¡ Recent surgery or trauma or stroke (>2 wks) ¡ Current use of warfarin or other anticoagulant ¡
 Aortic Dissection ¡ How to not get fooled l l l CP radiating into back Tearing vs pressure Unequal pulses or blood pressures in limbs Neurological symptoms Hypertension ++ (or low if they are leaking) CXR
Aortic Dissection ¡ How to not get fooled l l l CP radiating into back Tearing vs pressure Unequal pulses or blood pressures in limbs Neurological symptoms Hypertension ++ (or low if they are leaking) CXR
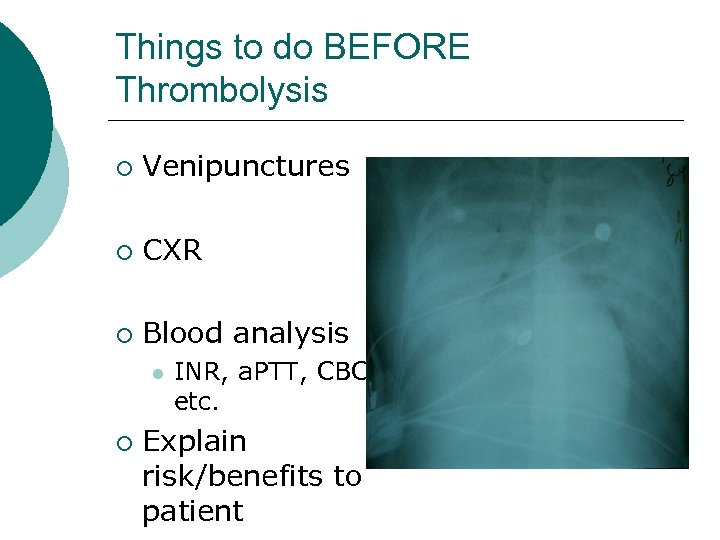 Things to do BEFORE Thrombolysis ¡ Venipunctures ¡ CXR ¡ Blood analysis l ¡ INR, a. PTT, CBC etc. Explain risk/benefits to patient
Things to do BEFORE Thrombolysis ¡ Venipunctures ¡ CXR ¡ Blood analysis l ¡ INR, a. PTT, CBC etc. Explain risk/benefits to patient
 Pericarditis ¡ How not to get fooled? ¡ Non-specific CP - sometimes severe ¡ ST segment elevation (ah. . ha! But where? )
Pericarditis ¡ How not to get fooled? ¡ Non-specific CP - sometimes severe ¡ ST segment elevation (ah. . ha! But where? )
 Pericarditis ¡ How to not get fooled l l l Atypical ischemic CP Sitting forward can decrease discomfort Fever or systemic illness Younger without cardiac risk factors ST elevation is diffuse, no anatomical pattern Serial ECG’s
Pericarditis ¡ How to not get fooled l l l Atypical ischemic CP Sitting forward can decrease discomfort Fever or systemic illness Younger without cardiac risk factors ST elevation is diffuse, no anatomical pattern Serial ECG’s
 Active Bleeding ¡ Non-compressible site(s) ¡ most common are GI and GU
Active Bleeding ¡ Non-compressible site(s) ¡ most common are GI and GU
 More Relative Contraindications The grey area l intracranial/intraspinal surgery l intracranial neoplasm, A-V malformation, aneurysm l bleeding diathesis l severe hypertension
More Relative Contraindications The grey area l intracranial/intraspinal surgery l intracranial neoplasm, A-V malformation, aneurysm l bleeding diathesis l severe hypertension
 What is the Risk? ¡ Intracranial hemorrhage ¡ Overall rate - 0. 9% ¡ Varies considerably between patients
What is the Risk? ¡ Intracranial hemorrhage ¡ Overall rate - 0. 9% ¡ Varies considerably between patients
 What is the Risk? ¡ Baseline risk w/o RF - 0. 75% ¡ 2 -3% up to 5% in anterior ¡ As low as 1% in inferior
What is the Risk? ¡ Baseline risk w/o RF - 0. 75% ¡ 2 -3% up to 5% in anterior ¡ As low as 1% in inferior
 What is the Risk? ¡ Age > 65 add 0. 5% ¡ Add another 0. 5% > 75 y. o. ¡ >80 y. o. ¡ >85 y. o. ¡
What is the Risk? ¡ Age > 65 add 0. 5% ¡ Add another 0. 5% > 75 y. o. ¡ >80 y. o. ¡ >85 y. o. ¡
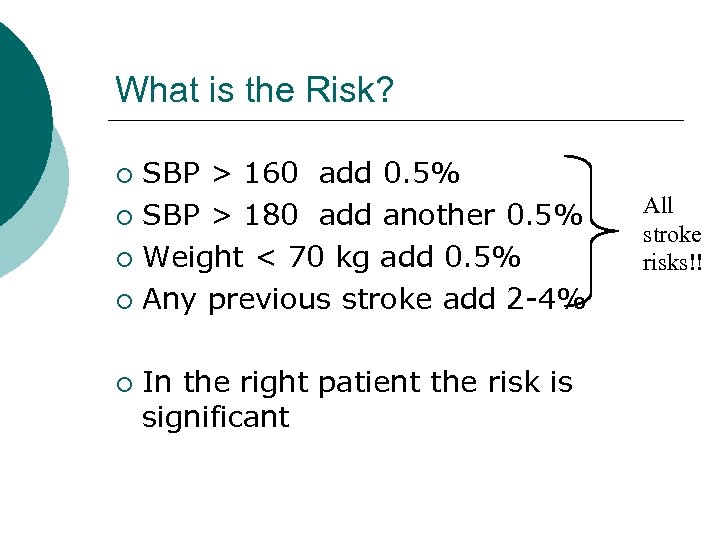 What is the Risk? SBP > 160 add 0. 5% ¡ SBP > 180 add another 0. 5% ¡ Weight < 70 kg add 0. 5% ¡ Any previous stroke add 2 -4% ¡ ¡ In the right patient the risk is significant All stroke risks!!
What is the Risk? SBP > 160 add 0. 5% ¡ SBP > 180 add another 0. 5% ¡ Weight < 70 kg add 0. 5% ¡ Any previous stroke add 2 -4% ¡ ¡ In the right patient the risk is significant All stroke risks!!
 Other Treatment Options ASA ¡ Heparin ¡ Beta Blockers ¡ IIB/IIIA inhibitors ¡
Other Treatment Options ASA ¡ Heparin ¡ Beta Blockers ¡ IIB/IIIA inhibitors ¡
 Primary PTCA ¡ ¡ Best option in patients with increased risk or in patients with limited benefit Potential for ambulances close to these centers (tertiary care centres) e. g Peterborough, Kingston, toronto, Ottawa
Primary PTCA ¡ ¡ Best option in patients with increased risk or in patients with limited benefit Potential for ambulances close to these centers (tertiary care centres) e. g Peterborough, Kingston, toronto, Ottawa
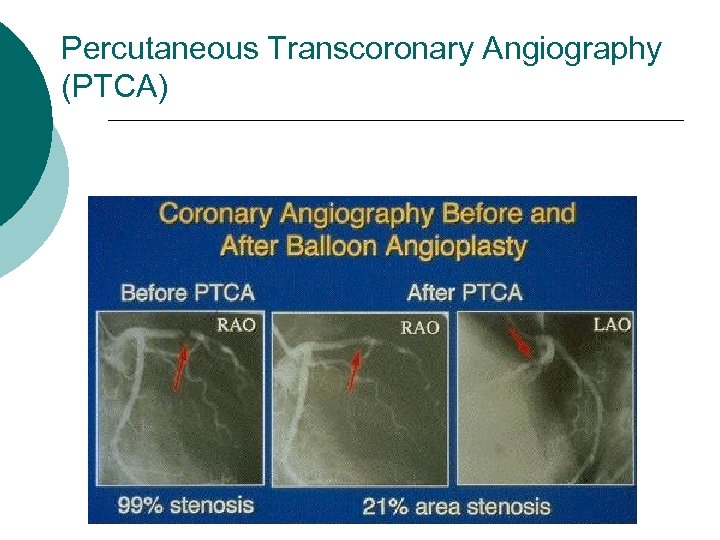 Percutaneous Transcoronary Angiography (PTCA)
Percutaneous Transcoronary Angiography (PTCA)
 Success Approx. 70% of patients regain patency of the vessel ¡ Pain relief ¡ Reduction in ST segment deviation ¡ Arrhythmia's ¡
Success Approx. 70% of patients regain patency of the vessel ¡ Pain relief ¡ Reduction in ST segment deviation ¡ Arrhythmia's ¡
 Access ¡ Specialty procedure ¡ Rescue angioplasty (fast transfers!!) l l high risk for thrombolytics Rx thrombolytics failed to correct the problem
Access ¡ Specialty procedure ¡ Rescue angioplasty (fast transfers!!) l l high risk for thrombolytics Rx thrombolytics failed to correct the problem
 Post Thrombolytic Care ¡ Watch for reperfusion arrhythmias l l l ¡ Usually benign Usually transient Watch for signs of bleeding!
Post Thrombolytic Care ¡ Watch for reperfusion arrhythmias l l l ¡ Usually benign Usually transient Watch for signs of bleeding!
 Now to the 12 lead bit….
Now to the 12 lead bit….
 Introduction to 12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ Diagnostic 12 lead is performed to rule in/out various pathologies Standard limb leads (I, III) Augmented vector leads (a. VL, a. VR, a. VF) Precordial or chest leads
Introduction to 12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ Diagnostic 12 lead is performed to rule in/out various pathologies Standard limb leads (I, III) Augmented vector leads (a. VL, a. VR, a. VF) Precordial or chest leads
 The Importance of a 12 lead EKG ¡ ¡ Many calls involve the CVS 12 lead ECG is a useful tool in the cardiac assessment.
The Importance of a 12 lead EKG ¡ ¡ Many calls involve the CVS 12 lead ECG is a useful tool in the cardiac assessment.
 What Can be Assessed on the 12 lead EKG? Axis ¡ Bundle branch conduction ¡ Hypertrophy ¡ Fascicular conduction ¡ Ischemia/Injury/Infarction patterns ¡ Pericarditis ¡ Electrolyte disturbances ¡ Drug intoxication ¡ AND MUCH MORE!!!!! ¡
What Can be Assessed on the 12 lead EKG? Axis ¡ Bundle branch conduction ¡ Hypertrophy ¡ Fascicular conduction ¡ Ischemia/Injury/Infarction patterns ¡ Pericarditis ¡ Electrolyte disturbances ¡ Drug intoxication ¡ AND MUCH MORE!!!!! ¡
 Required Skills to Interpret the 12 lead EKG ¡ Comprehension of electrophysiology l electrolyte and cellular functions during normal and abnormal de/repolarization ¡ Advanced knowledge of cardiac pathophysiology ¡ Recognizing normal versus abnormal ¡ Ability to follow an organized and sequential approach ¡ LOTS AND LOTS OF PRACTICE!!!!!
Required Skills to Interpret the 12 lead EKG ¡ Comprehension of electrophysiology l electrolyte and cellular functions during normal and abnormal de/repolarization ¡ Advanced knowledge of cardiac pathophysiology ¡ Recognizing normal versus abnormal ¡ Ability to follow an organized and sequential approach ¡ LOTS AND LOTS OF PRACTICE!!!!!
 Fundamentals of 12 Lead Interpretation ¡Review of cardiac conduction ¡Refresh the understanding of the anatomy and physiology applicable to EKG interpretation
Fundamentals of 12 Lead Interpretation ¡Review of cardiac conduction ¡Refresh the understanding of the anatomy and physiology applicable to EKG interpretation
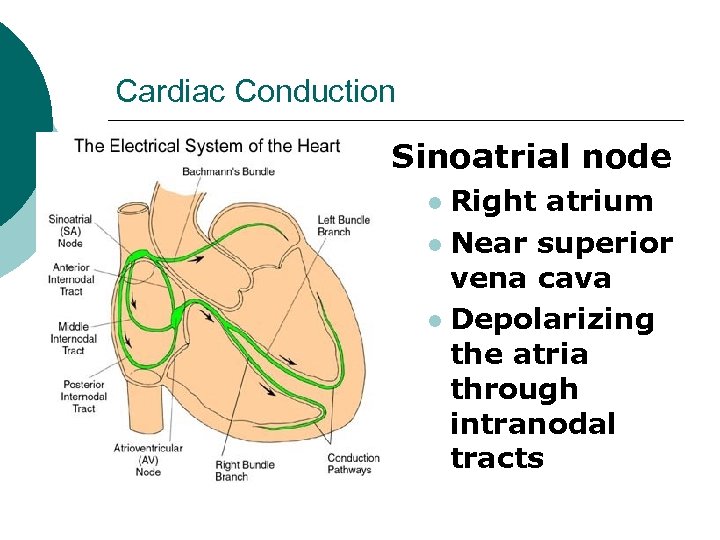 Cardiac Conduction Sinoatrial node Right atrium l Near superior vena cava l Depolarizing the atria through intranodal tracts l
Cardiac Conduction Sinoatrial node Right atrium l Near superior vena cava l Depolarizing the atria through intranodal tracts l
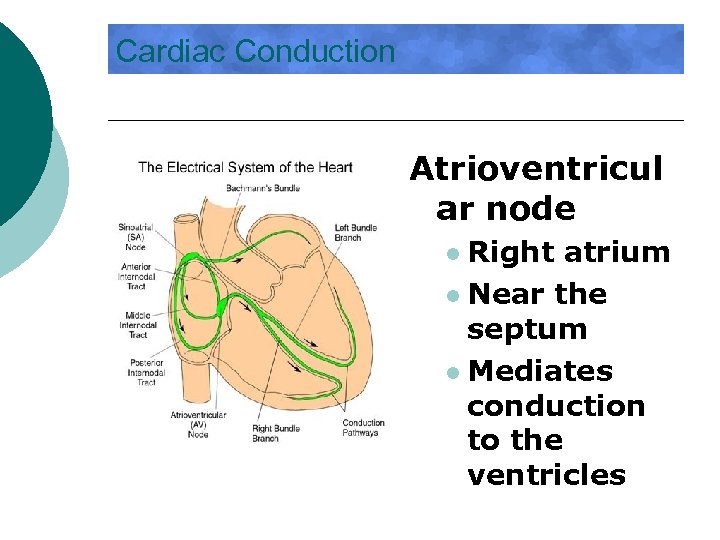 Cardiac Conduction Atrioventricul ar node Right atrium l Near the septum l Mediates conduction to the ventricles l
Cardiac Conduction Atrioventricul ar node Right atrium l Near the septum l Mediates conduction to the ventricles l
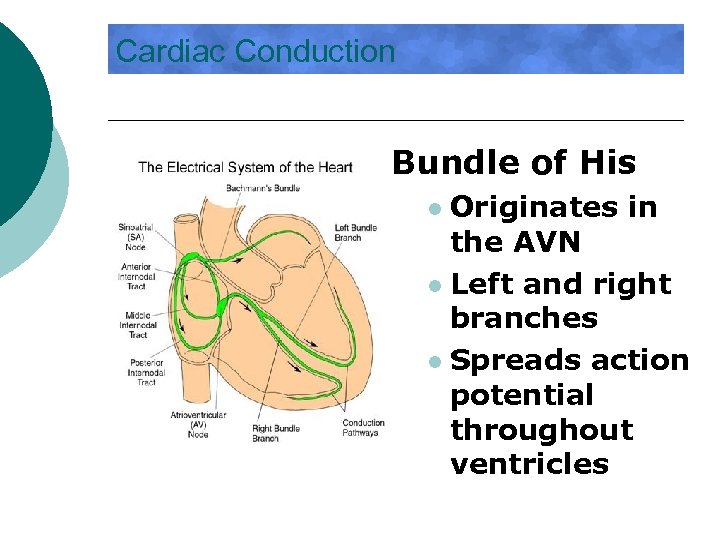 Cardiac Conduction Bundle of His Originates in the AVN l Left and right branches l Spreads action potential throughout ventricles l
Cardiac Conduction Bundle of His Originates in the AVN l Left and right branches l Spreads action potential throughout ventricles l
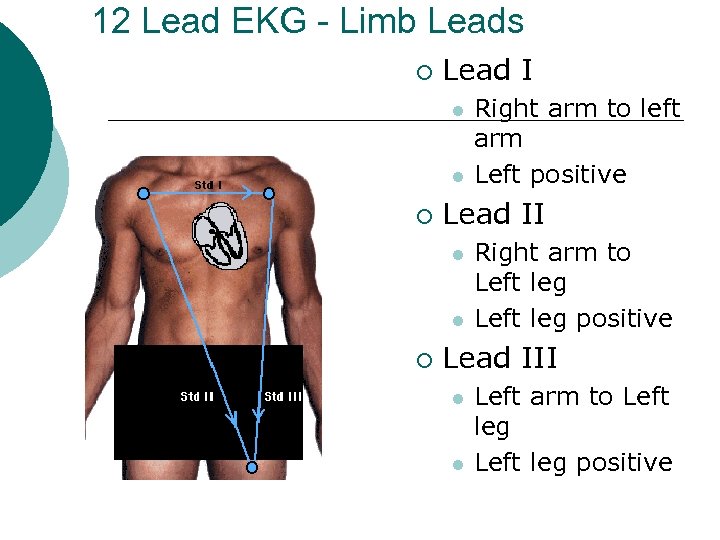 12 Lead EKG - Limb Leads ¡ Lead I l l ¡ Lead II l l ¡ Right arm to left arm Left positive Right arm to Left leg positive Lead III l l Left arm to Left leg positive
12 Lead EKG - Limb Leads ¡ Lead I l l ¡ Lead II l l ¡ Right arm to left arm Left positive Right arm to Left leg positive Lead III l l Left arm to Left leg positive
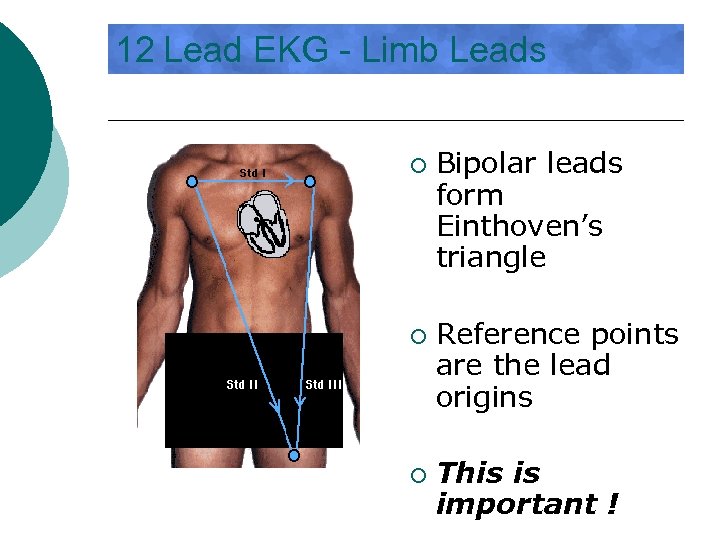 12 Lead EKG - Limb Leads ¡ ¡ ¡ Bipolar leads form Einthoven’s triangle Reference points are the lead origins This is important !
12 Lead EKG - Limb Leads ¡ ¡ ¡ Bipolar leads form Einthoven’s triangle Reference points are the lead origins This is important !
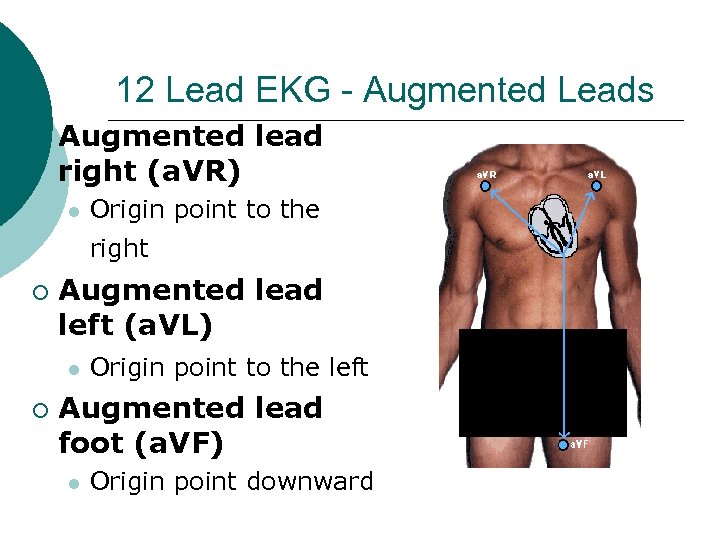 12 Lead EKG - Augmented Leads ¡ Augmented lead right (a. VR) l Origin point to the right ¡ Augmented lead left (a. VL) l ¡ Origin point to the left Augmented lead foot (a. VF) l Origin point downward
12 Lead EKG - Augmented Leads ¡ Augmented lead right (a. VR) l Origin point to the right ¡ Augmented lead left (a. VL) l ¡ Origin point to the left Augmented lead foot (a. VF) l Origin point downward
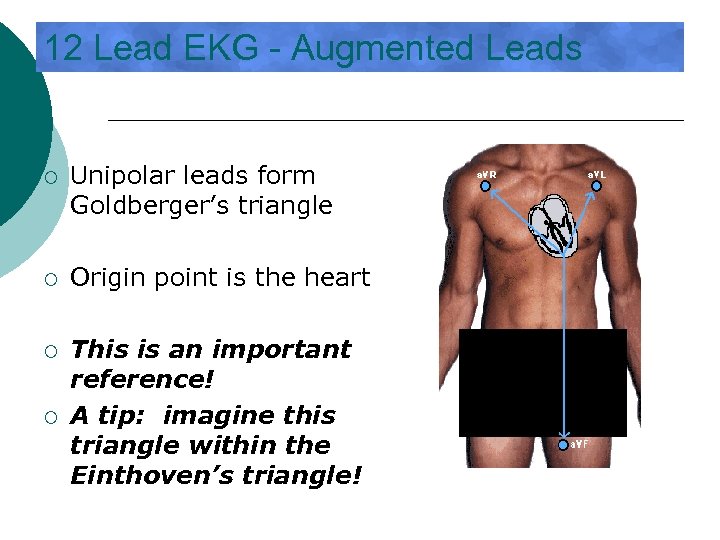 12 Lead EKG - Augmented Leads ¡ Unipolar leads form Goldberger’s triangle ¡ Origin point is the heart ¡ This is an important reference! A tip: imagine this triangle within the Einthoven’s triangle! ¡
12 Lead EKG - Augmented Leads ¡ Unipolar leads form Goldberger’s triangle ¡ Origin point is the heart ¡ This is an important reference! A tip: imagine this triangle within the Einthoven’s triangle! ¡
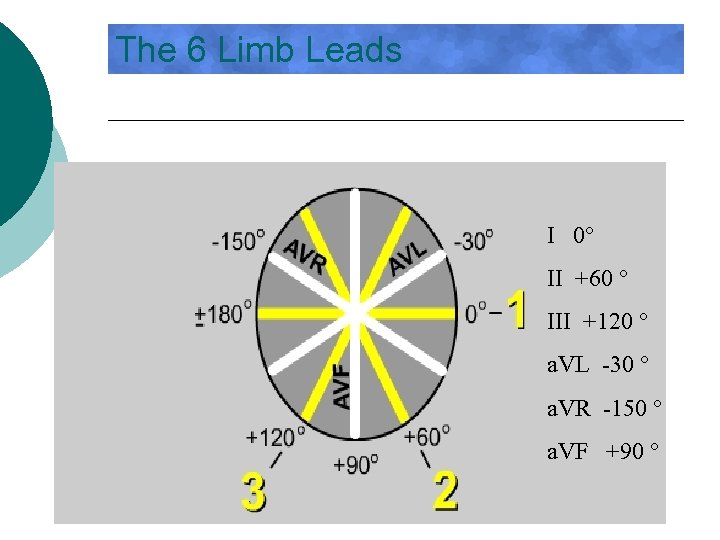 The 6 Limb Leads I 0° II +60 ° III +120 ° a. VL -30 ° a. VR -150 ° a. VF +90 °
The 6 Limb Leads I 0° II +60 ° III +120 ° a. VL -30 ° a. VR -150 ° a. VF +90 °
 What Part of the Heart? ¡ Frontal plane leads look at different segments of the heart ¡ Know what area the leads focus on ¡ Relationship l l l Leads II, III and a. VF view the inferior wall Leads I and a. VL view the lateral wall Lead a. VR is not helpful here
What Part of the Heart? ¡ Frontal plane leads look at different segments of the heart ¡ Know what area the leads focus on ¡ Relationship l l l Leads II, III and a. VF view the inferior wall Leads I and a. VL view the lateral wall Lead a. VR is not helpful here
 Purpose of the 12 Lead ¡ Identify ST elevation/depression ¡ T wave inversion ¡ Identify VT in wide complex rhythms ¡ Electrical axis and hypertrophy ¡ Bundle branch blocks
Purpose of the 12 Lead ¡ Identify ST elevation/depression ¡ T wave inversion ¡ Identify VT in wide complex rhythms ¡ Electrical axis and hypertrophy ¡ Bundle branch blocks
 Indications? ¡ Ischemic chest pain (unstable angina) ¡ Chest pain – NYD ¡ Change in chest pain presentation ¡ To rule out cardiac involvement
Indications? ¡ Ischemic chest pain (unstable angina) ¡ Chest pain – NYD ¡ Change in chest pain presentation ¡ To rule out cardiac involvement
 Rule of Thumb ¡ Perform a 12 -lead when considering differential diagnoses l l ¡ It It could be be angina an MI an aneurysm pericarditis Don’t do it unless you are prepared (or someone else is) to act on the result!
Rule of Thumb ¡ Perform a 12 -lead when considering differential diagnoses l l ¡ It It could be be angina an MI an aneurysm pericarditis Don’t do it unless you are prepared (or someone else is) to act on the result!
 Precordial Leads - 12 Lead
Precordial Leads - 12 Lead
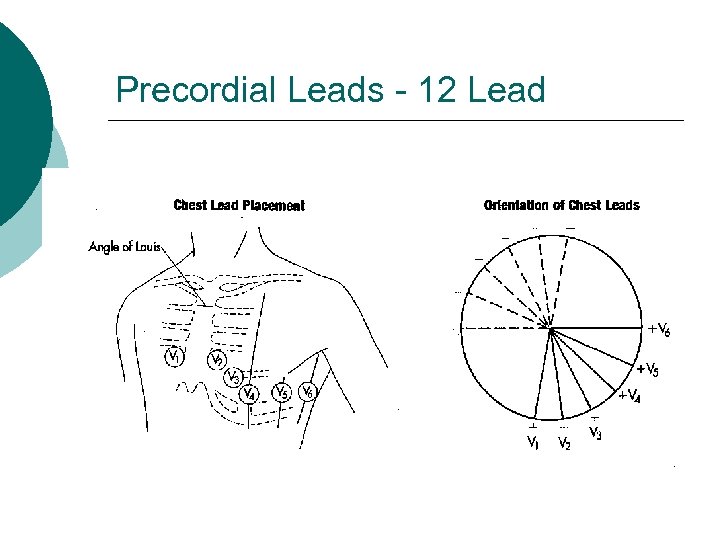
 Precordial Leads - How are they placed? V 1 - 4 th intercostal space, R sternal border ¡ V 2 - 4 th intercostal space, L sternal border ¡ V 4 - 5 th intercostal space, midclavicular line ¡ V 3 - between V 2 and V 4 ¡ V 6 - 5 th intercostal space, midaxillary line ¡ V 5 – anterior axillary line between V 4 and V 6 ¡
Precordial Leads - How are they placed? V 1 - 4 th intercostal space, R sternal border ¡ V 2 - 4 th intercostal space, L sternal border ¡ V 4 - 5 th intercostal space, midclavicular line ¡ V 3 - between V 2 and V 4 ¡ V 6 - 5 th intercostal space, midaxillary line ¡ V 5 – anterior axillary line between V 4 and V 6 ¡
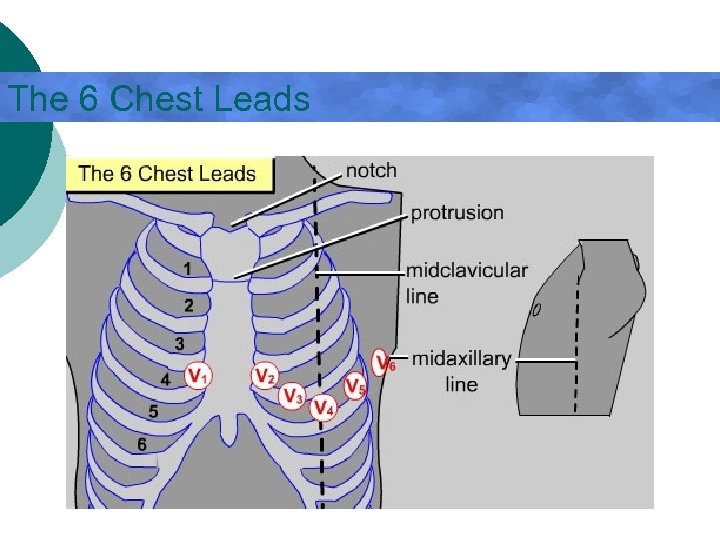 The 6 Chest Leads
The 6 Chest Leads
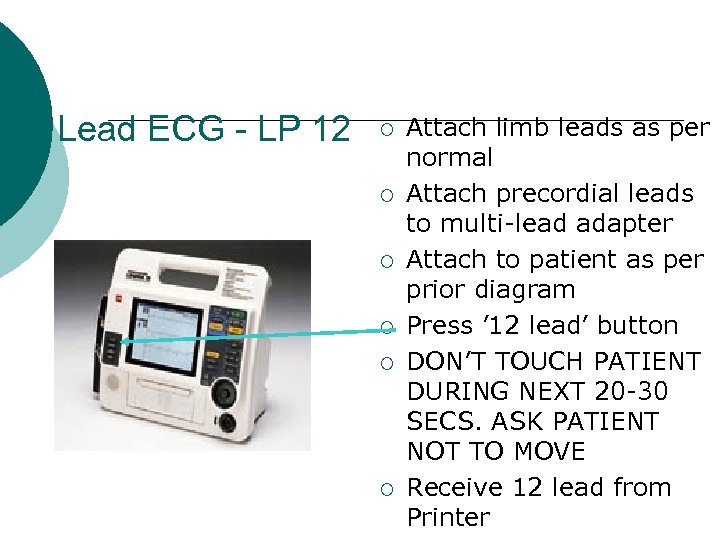 12 Lead ECG - LP 12 ¡ ¡ ¡ Attach limb leads as per normal Attach precordial leads to multi-lead adapter Attach to patient as per prior diagram Press ’ 12 lead’ button DON’T TOUCH PATIENT DURING NEXT 20 -30 SECS. ASK PATIENT NOT TO MOVE Receive 12 lead from Printer
12 Lead ECG - LP 12 ¡ ¡ ¡ Attach limb leads as per normal Attach precordial leads to multi-lead adapter Attach to patient as per prior diagram Press ’ 12 lead’ button DON’T TOUCH PATIENT DURING NEXT 20 -30 SECS. ASK PATIENT NOT TO MOVE Receive 12 lead from Printer
 12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ Each of the 12 leads views the left ventricle from the positive electrode In the precordial leads, it is assumed this is in the center of the heart Review 12 lead information in Bledsoe
12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ Each of the 12 leads views the left ventricle from the positive electrode In the precordial leads, it is assumed this is in the center of the heart Review 12 lead information in Bledsoe
 Myocardial Infarction The BIG ONE!
Myocardial Infarction The BIG ONE!
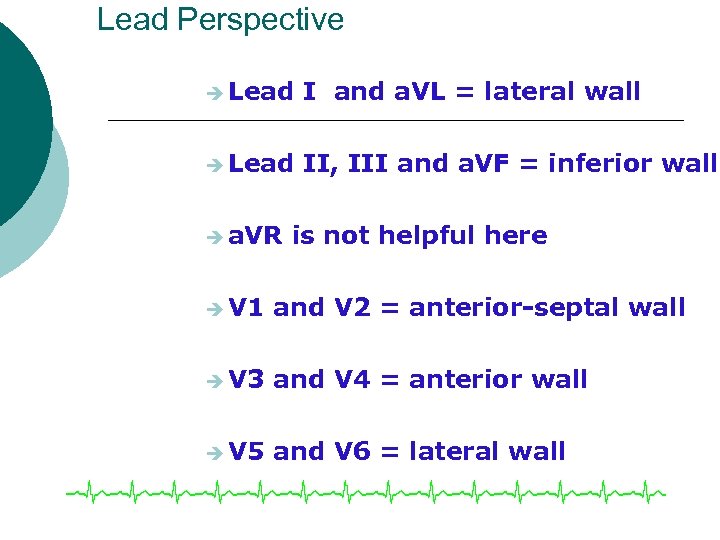 Lead Perspective è Lead I and a. VL = lateral wall è Lead II, III and a. VF = inferior wall è a. VR is not helpful here è V 1 and V 2 = anterior-septal wall è V 3 and V 4 = anterior wall è V 5 and V 6 = lateral wall
Lead Perspective è Lead I and a. VL = lateral wall è Lead II, III and a. VF = inferior wall è a. VR is not helpful here è V 1 and V 2 = anterior-septal wall è V 3 and V 4 = anterior wall è V 5 and V 6 = lateral wall
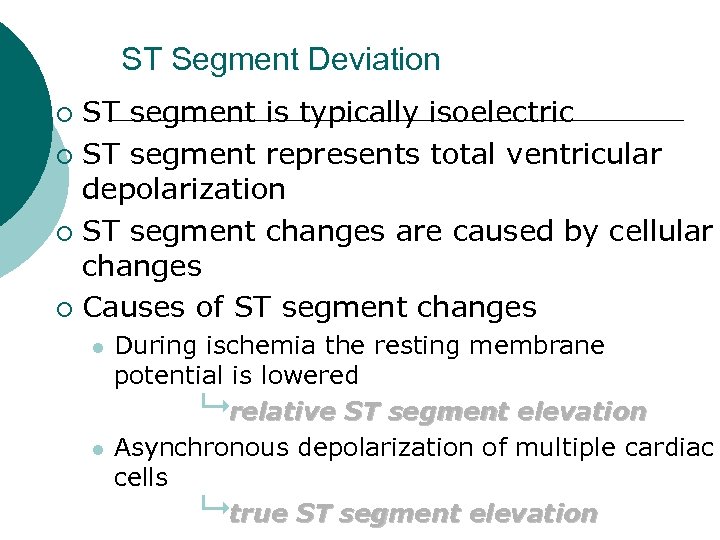 ST Segment Deviation ST segment is typically isoelectric ¡ ST segment represents total ventricular depolarization ¡ ST segment changes are caused by cellular changes ¡ Causes of ST segment changes ¡ l l During ischemia the resting membrane potential is lowered 9 relative ST segment elevation Asynchronous depolarization of multiple cardiac cells 9 true ST segment elevation
ST Segment Deviation ST segment is typically isoelectric ¡ ST segment represents total ventricular depolarization ¡ ST segment changes are caused by cellular changes ¡ Causes of ST segment changes ¡ l l During ischemia the resting membrane potential is lowered 9 relative ST segment elevation Asynchronous depolarization of multiple cardiac cells 9 true ST segment elevation
 Criteria for Cardiac Injury on the EKG ¡ Transmural cardiac injury l l ¡ Limb ST segment elevation of 1 mm and extending at least 2 mm out from the J point Precordial ST segment elevation of 2 mm Other findings may include l Inverted or flipped T waves l Pathological Q waves
Criteria for Cardiac Injury on the EKG ¡ Transmural cardiac injury l l ¡ Limb ST segment elevation of 1 mm and extending at least 2 mm out from the J point Precordial ST segment elevation of 2 mm Other findings may include l Inverted or flipped T waves l Pathological Q waves
 Phases of an Acute MI Hyper acute phase - ST segment elevation begins in the first hours and may last 1 -6 weeks Evolved phase - deep T waves and onset of pathological Q waves Resolution phase - T waves return to normal morphology and position Chronic phase - pathological Q waves
Phases of an Acute MI Hyper acute phase - ST segment elevation begins in the first hours and may last 1 -6 weeks Evolved phase - deep T waves and onset of pathological Q waves Resolution phase - T waves return to normal morphology and position Chronic phase - pathological Q waves
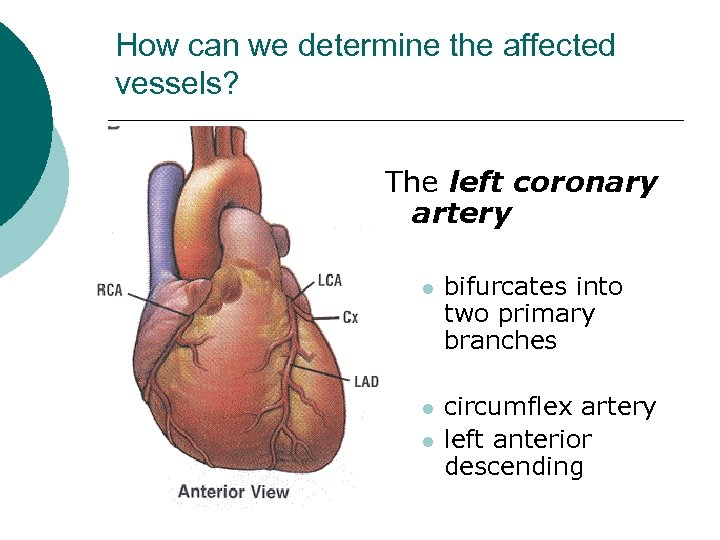 How can we determine the affected vessels? The left coronary artery l bifurcates into two primary branches l circumflex artery left anterior descending l
How can we determine the affected vessels? The left coronary artery l bifurcates into two primary branches l circumflex artery left anterior descending l
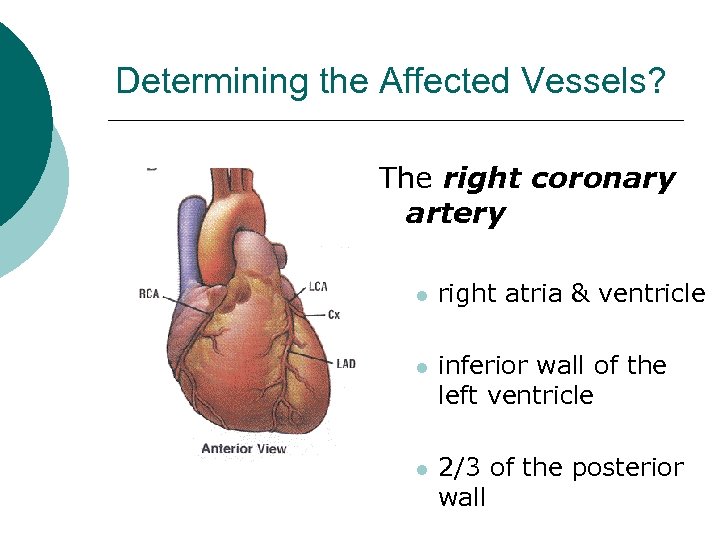 Determining the Affected Vessels? The right coronary artery l right atria & ventricle l inferior wall of the left ventricle l 2/3 of the posterior wall
Determining the Affected Vessels? The right coronary artery l right atria & ventricle l inferior wall of the left ventricle l 2/3 of the posterior wall
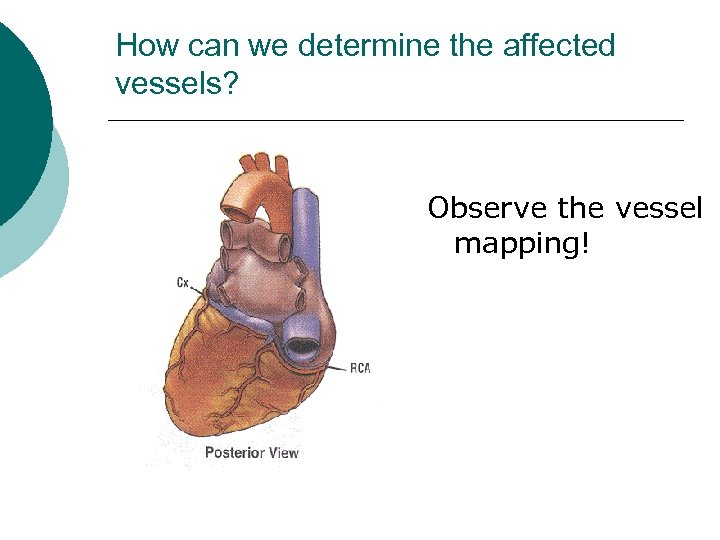 How can we determine the affected vessels? Observe the vessel mapping!
How can we determine the affected vessels? Observe the vessel mapping!
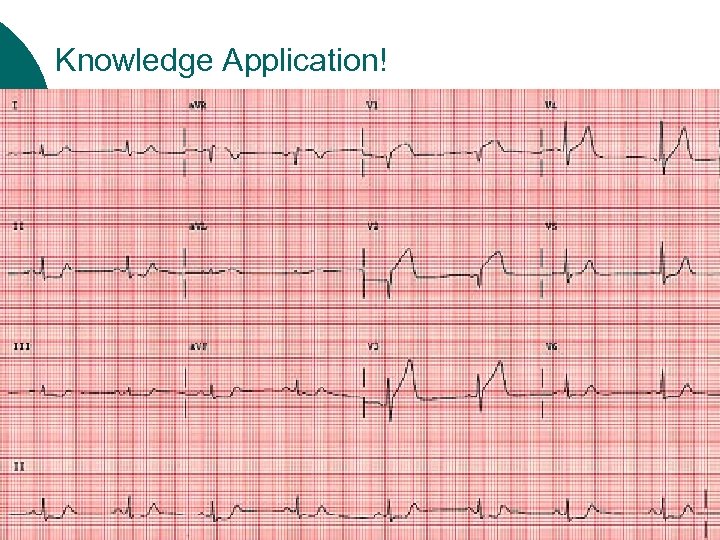 Knowledge Application! ¡ ¡ ¡ Is there any ST segment deviation? What leads are affected? What area do these leads look at?
Knowledge Application! ¡ ¡ ¡ Is there any ST segment deviation? What leads are affected? What area do these leads look at?
 Reciprocal Changes ST changes opposite from the anatomical location of the injured region ¡ ‘mirror-like’ image ¡ ST segment depression is reciprocal to ST elevation ¡ Investigate further to rule out/in injury pattern ¡
Reciprocal Changes ST changes opposite from the anatomical location of the injured region ¡ ‘mirror-like’ image ¡ ST segment depression is reciprocal to ST elevation ¡ Investigate further to rule out/in injury pattern ¡
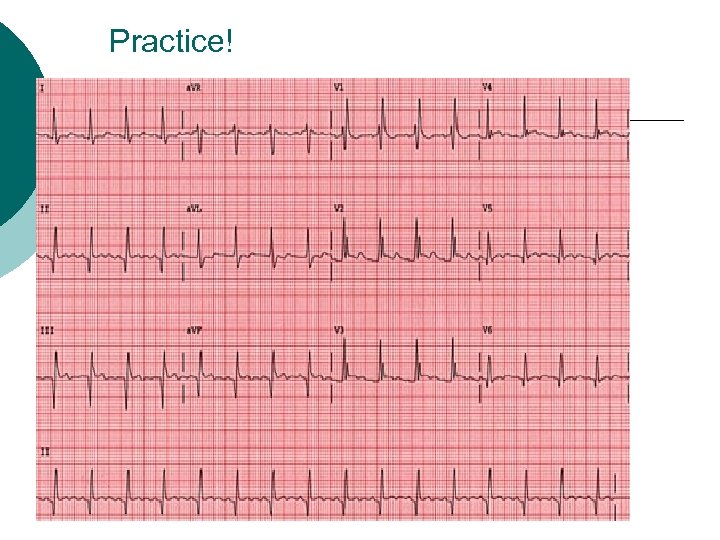 Practice!
Practice!
 Differential Diagnosis - ST Segment Elevation Acute myocarditis ¡ Hyperkalemia ¡ Hypothermia ¡ Acute cor pulmonale ¡ Cerebrovascular hemorrhage ¡ Cardiac tumor ¡ Even occasionally in healthy individuals!!! ¡
Differential Diagnosis - ST Segment Elevation Acute myocarditis ¡ Hyperkalemia ¡ Hypothermia ¡ Acute cor pulmonale ¡ Cerebrovascular hemorrhage ¡ Cardiac tumor ¡ Even occasionally in healthy individuals!!! ¡
 Ischemia
Ischemia
 Electrophysiology - Ischemia Cells quickly lose O 2 and nutrient supply ¡ CO 2 removal is impeded ¡ Unable to completely repolarize ¡ ECG ¡ l l ¡ depressed ST segment and/or inverted T waves = ventricular repolarization ST depression of 2 mm or greater = pathology
Electrophysiology - Ischemia Cells quickly lose O 2 and nutrient supply ¡ CO 2 removal is impeded ¡ Unable to completely repolarize ¡ ECG ¡ l l ¡ depressed ST segment and/or inverted T waves = ventricular repolarization ST depression of 2 mm or greater = pathology
 Other Multi-lead ECG Configurations 15 lead ECG and 18 lead ECG
Other Multi-lead ECG Configurations 15 lead ECG and 18 lead ECG
 Right Side EKG ä To provide a more specific look at the right ventricle Leave V 1 in place - this becomes V 2 R Leave V 2 in place - this becomes V 1 R Move V 4 to the 5 th ICS on the right midclavicular line = V 4 R Move V 3 halfway between V 2 R and V 4 R = V 3 R Move V 5 to the right anterior axillary line in the 5 th ICS = V 5 R Move V 6 to the right midaxillary line = V 6 R
Right Side EKG ä To provide a more specific look at the right ventricle Leave V 1 in place - this becomes V 2 R Leave V 2 in place - this becomes V 1 R Move V 4 to the 5 th ICS on the right midclavicular line = V 4 R Move V 3 halfway between V 2 R and V 4 R = V 3 R Move V 5 to the right anterior axillary line in the 5 th ICS = V 5 R Move V 6 to the right midaxillary line = V 6 R
 Posterior EKG ä To provide a closer look at the posterior wall of the heart Move 3 precordial leads to the same horizontal plane as V 5 & V 6 Be sure to note which leads you have repositioned Position them at the bottom of the left shoulder blade left of the vertebral column
Posterior EKG ä To provide a closer look at the posterior wall of the heart Move 3 precordial leads to the same horizontal plane as V 5 & V 6 Be sure to note which leads you have repositioned Position them at the bottom of the left shoulder blade left of the vertebral column
 Utility of a 12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ It is only as good as the interpretation Treat the patient first! Start with the basics - O 2, NTG, MS, IV etc. Closely monitoring patients with suspected ACS
Utility of a 12 Lead ECG ¡ ¡ It is only as good as the interpretation Treat the patient first! Start with the basics - O 2, NTG, MS, IV etc. Closely monitoring patients with suspected ACS
 Practice ¡ Google it! ¡ Buy a book ¡ ¡ Try it on everyone in EMERG with chest pain! Volunteer
Practice ¡ Google it! ¡ Buy a book ¡ ¡ Try it on everyone in EMERG with chest pain! Volunteer


