4c53454ae645dc610712ea8f2a1446f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

12 chapter Marketing and Consumer Behavior Better Business 2 nd Edition Solomon (Contributing Editor) · Poatsy · Martin © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -1

Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. How has marketing evolved over the production concept era, the sales concept era, the marketing concept era, and the customer relationship era? What are the benefits of marketing to customers, sellers, investors, employees, and society at large, and what are the criticisms of marketing? What are the two basic elements of a marketing strategy and the 4 Ps of the marketing mix? How do firms implement a marketing strategy by applying the marketing process? How do the various factors in the marketing environment influence a firm’s ability to manipulate its marketing mix? What is the marketing research process and what are the elements of a good marketing plan? How do the buying decisions and marketing processes in B 2 B markets compare to those in the consumer market? © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -2

Marketing Fundamentals • Marketing o An organizational function o A set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers o Management of customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders • Product o Any tangible good, service, or idea available for purchase in a market o Plus any intangible benefits derived from its consumption © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -3
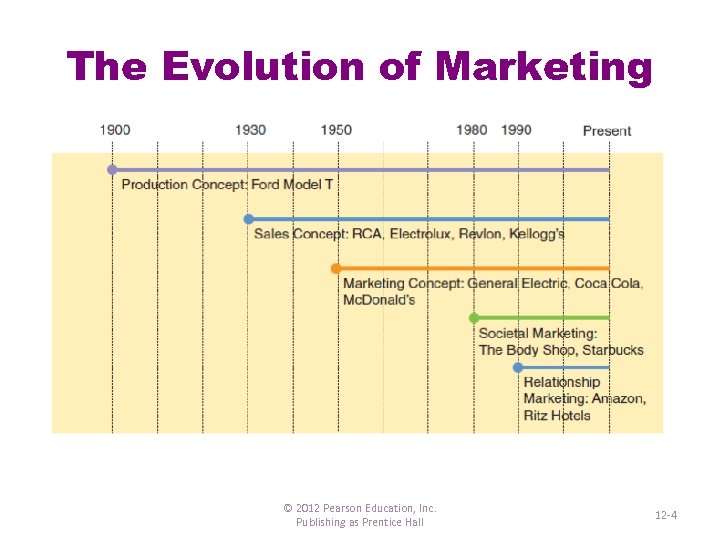
The Evolution of Marketing © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -4
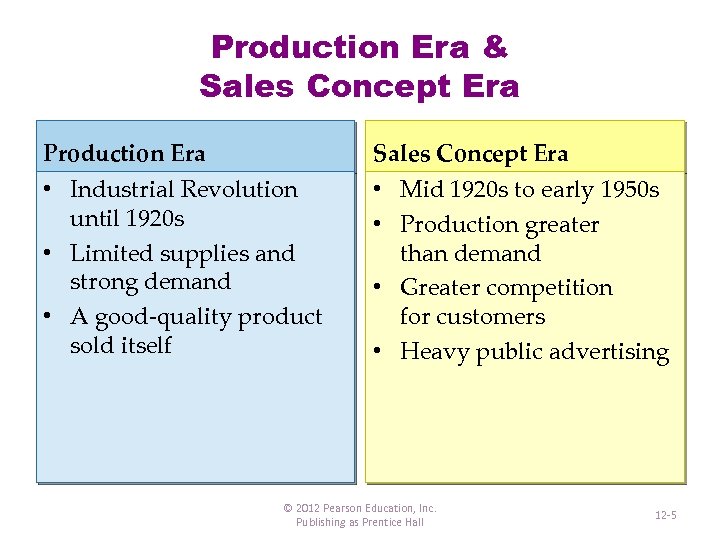
Production Era & Sales Concept Era Production Era Sales Concept Era • Industrial Revolution until 1920 s • Limited supplies and strong demand • A good-quality product sold itself • Mid 1920 s to early 1950 s • Production greater than demand • Greater competition for customers • Heavy public advertising © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -5
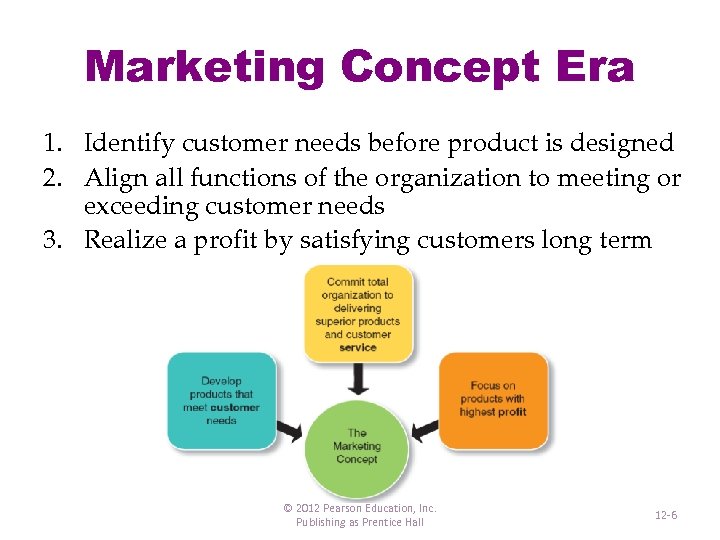
Marketing Concept Era 1. Identify customer needs before product is designed 2. Align all functions of the organization to meeting or exceeding customer needs 3. Realize a profit by satisfying customers long term © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -6

Customer Relationship Era • Customer relationship management (CRM) • Since the late 1990 s • Focuses a company’s efforts on long-term customer satisfaction • Combines computer information technology with customer service and marketing communications • Encourages customers to buy similar or supplementary products © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -7

Nontraditional Marketing • Not-for-profit organizations must market their events, causes, locations, or individuals o Charitable organizations o Countries, states, and cities o Churches o Museums o People © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -8
Benefits of Marketing • Customers • • o Utility • Form • Ownership • Time • Place Investors Employees Society Sellers o Value = benefits/costs © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -9

Criticisms of Marketing • Misuse of personal information • Hidden Fees • Consequences of purchase © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -10

Marketing Strategy © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -11
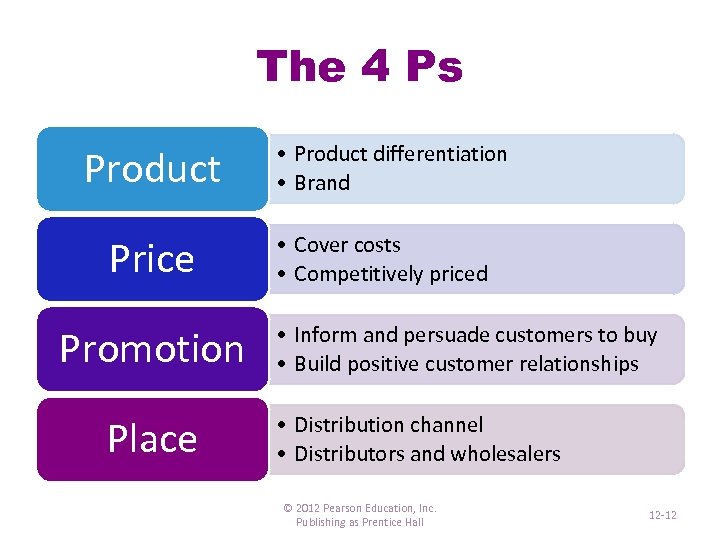
The 4 Ps Product Price Promotion Place • Product differentiation • Brand • Cover costs • Competitively priced • Inform and persuade customers to buy • Build positive customer relationships • Distribution channel • Distributors and wholesalers © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -12
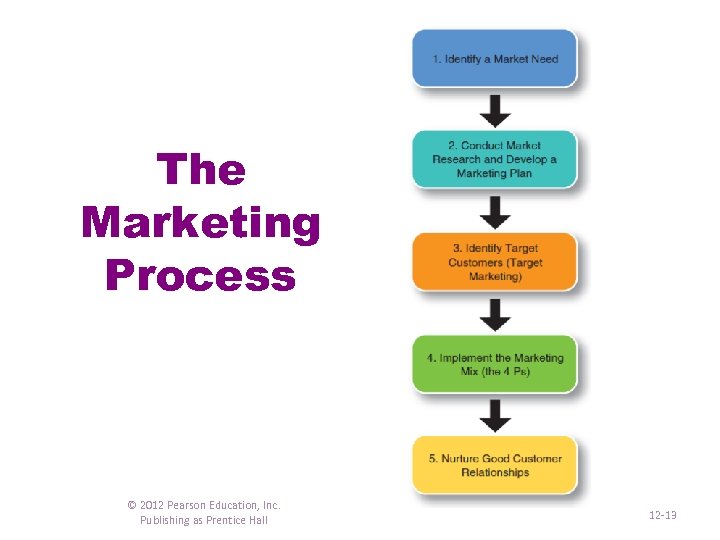
The Marketing Process © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -13
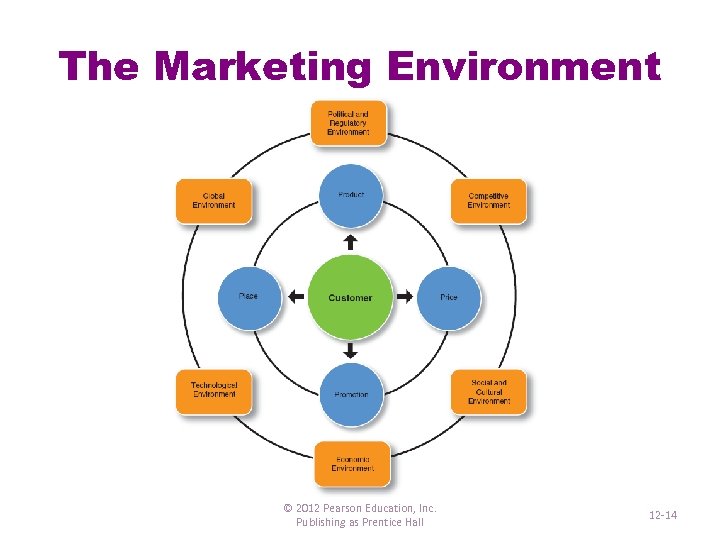
The Marketing Environment © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -14
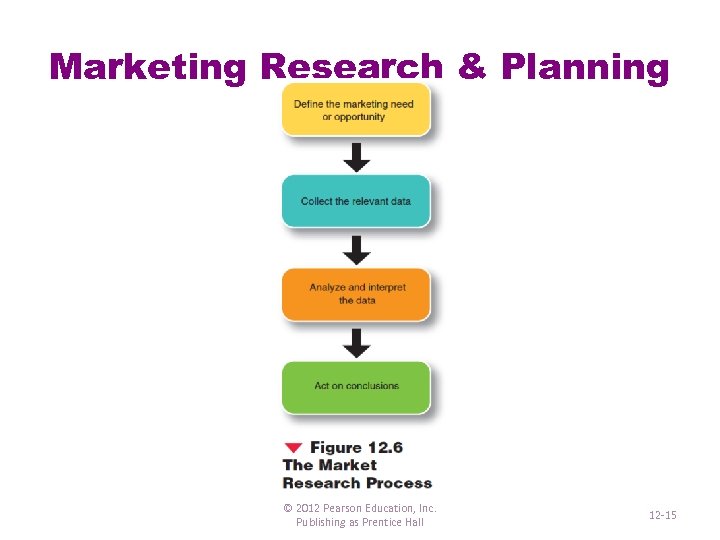
Marketing Research & Planning © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -15
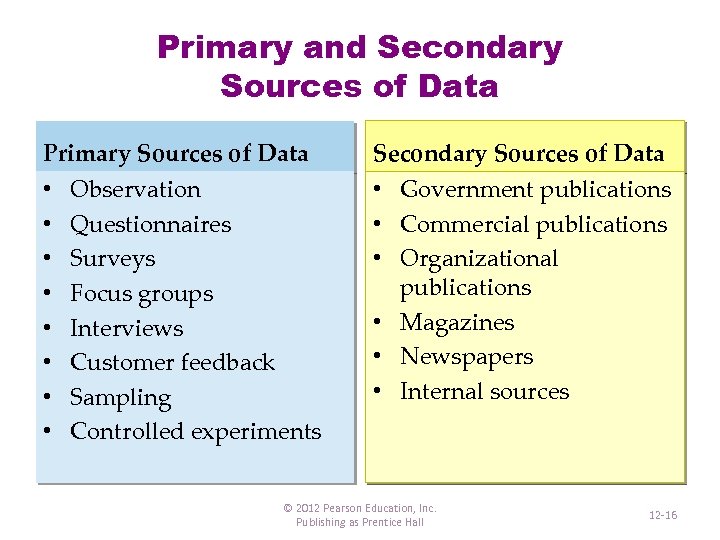
Primary and Secondary Sources of Data Primary Sources of Data • • Observation Questionnaires Surveys Focus groups Interviews Customer feedback Sampling Controlled experiments Secondary Sources of Data • Government publications • Commercial publications • Organizational publications • Magazines • Newspapers • Internal sources © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -16

The Marketing Plan A written document with: • A clearly written marketing objective • Performance of situational SWOT analysis • Selection of a target market • Implementation, evaluation, and control of the marketing mix (the 4 Ps) © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -17

The 5 Cs of Marketing © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -18

Target Markets © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -19

Consumer Behavior • The ways individuals or organizations search for, evaluate, purchase, use, and dispose of goods and services • Consumer behavior is different in the consumer market vs. the B 2 B market • Knowledge of consumer behavior helps marketers: o Select the most profitable target markets o Implement the marketing mix (4 Ps) © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -20

Consumer Markets 1. Need recognition 2. Information search 3. Evaluation of alternatives 4. Purchase or no purchase decision 5. Post-purchase evaluation © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -21

What Influences Consumer Decision Making? © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -22

Differences Between B 2 B and Consumer Markets © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -23

Business Buying Decisions • Steps are similar to the five steps in the consumer decision-making process • 4 Ps of the marketing mix remain relevant for a business purchase • Business purchases are generally more rational, reasoned, and objective, based on influences such as: o The state of the economy o Technological factors o The degree of competition facing the company o Political and regulatory concerns o Organizational objectives, policies, and procedures © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -24

Chapter Summary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. How has marketing evolved over the production concept era, the sales concept era, the marketing concept era, and the customer relationship era? What are the benefits of marketing to customers, sellers, investors, employees, and society at large, and what are the criticisms of marketing? What are the two basic elements of a marketing strategy and the 4 Ps of the marketing mix? How do firms implement a marketing strategy by applying the five steps of the marketing process? How do the various factors in the marketing environment influence a firm’s ability to manipulate its marketing mix? What are the five steps of the marketing research process and the four elements of a good marketing plan? How do the buying decisions and marketing processes in business-tobusiness markets compare to those in the consumer market? © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -25

© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12 -26
4c53454ae645dc610712ea8f2a1446f9.ppt