03d98dfbddef2a41199e59119cb5db3d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 12 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Uncertainty
12 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Uncertainty
 Uncertainty is Pervasive u What is uncertain in economic systems? – tomorrow’s prices – future wealth – future availability of commodities – present and future actions of other people. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2
Uncertainty is Pervasive u What is uncertain in economic systems? – tomorrow’s prices – future wealth – future availability of commodities – present and future actions of other people. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2
 Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 3
Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 3
 States of Nature u Possible states of Nature: – “car accident” (a) – “no car accident” (na). u Accident occurs with probability a, does not with probability na ; a + na = 1. u Accident causes a loss of $L. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 4
States of Nature u Possible states of Nature: – “car accident” (a) – “no car accident” (na). u Accident occurs with probability a, does not with probability na ; a + na = 1. u Accident causes a loss of $L. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 4
 Contingencies u. A contract implemented only when a particular state of Nature occurs is state-contingent. u E. g. the insurer pays only if there is an accident. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 5
Contingencies u. A contract implemented only when a particular state of Nature occurs is state-contingent. u E. g. the insurer pays only if there is an accident. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 5
 Contingencies u. A state-contingent consumption plan is implemented only when a particular state of Nature occurs. u E. g. take a vacation only if there is no accident. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 6
Contingencies u. A state-contingent consumption plan is implemented only when a particular state of Nature occurs. u E. g. take a vacation only if there is no accident. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 6
 State-Contingent Budget Constraints $1 of accident insurance costs . u Consumer has $m of wealth. u Cna is consumption value in the noaccident state. u Ca is consumption value in the accident state. u Each © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 7
State-Contingent Budget Constraints $1 of accident insurance costs . u Consumer has $m of wealth. u Cna is consumption value in the noaccident state. u Ca is consumption value in the accident state. u Each © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 7
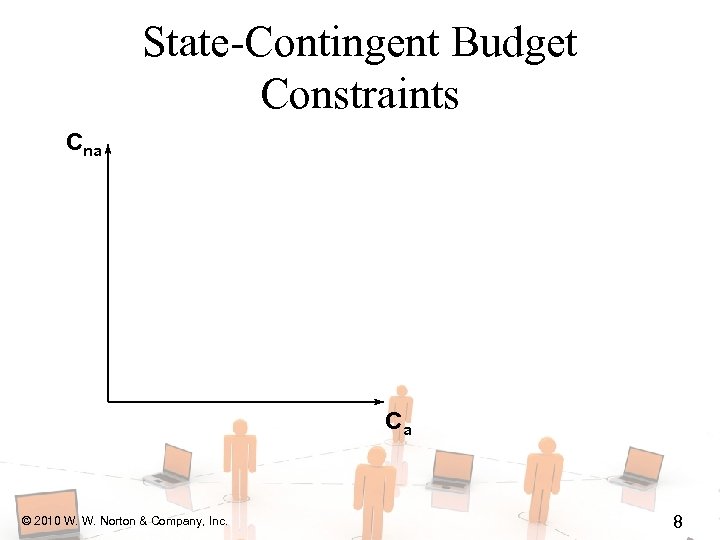 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 8
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 8
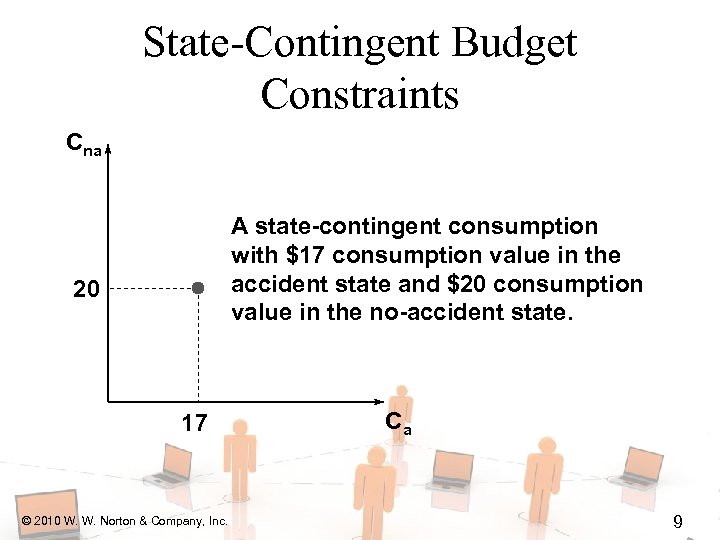 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna A state-contingent consumption with $17 consumption value in the accident state and $20 consumption value in the no-accident state. 20 17 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Ca 9
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna A state-contingent consumption with $17 consumption value in the accident state and $20 consumption value in the no-accident state. 20 17 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Ca 9
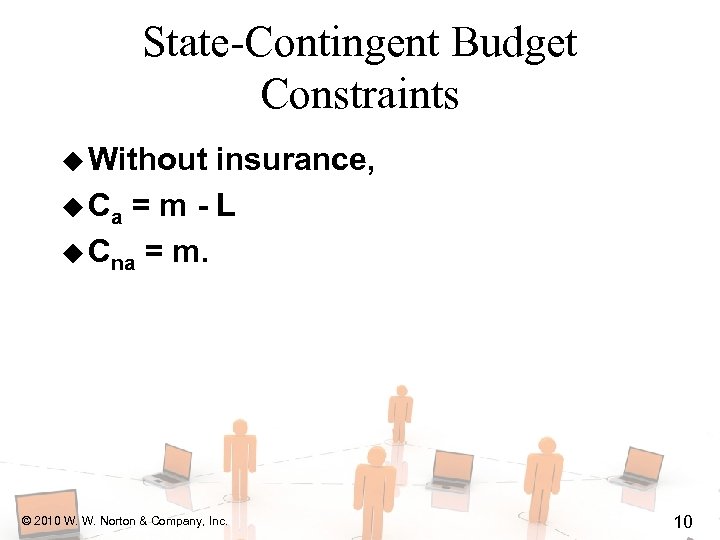 State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Without insurance, u Ca = m - L u Cna = m. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 10
State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Without insurance, u Ca = m - L u Cna = m. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 10
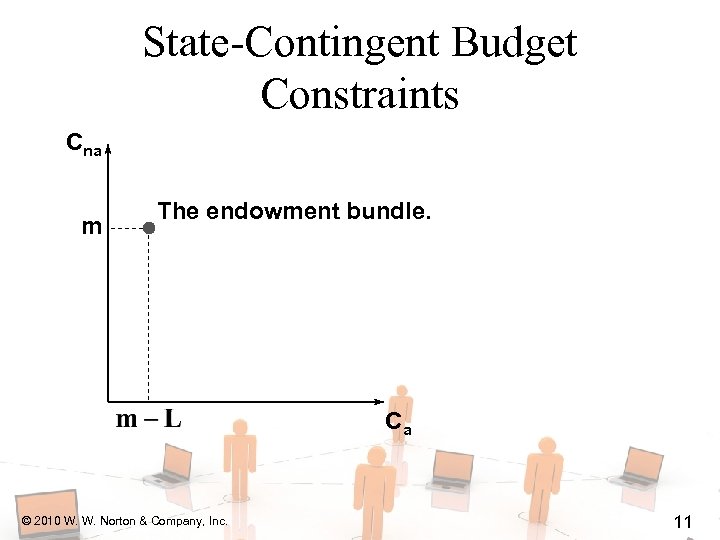 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 11
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 11
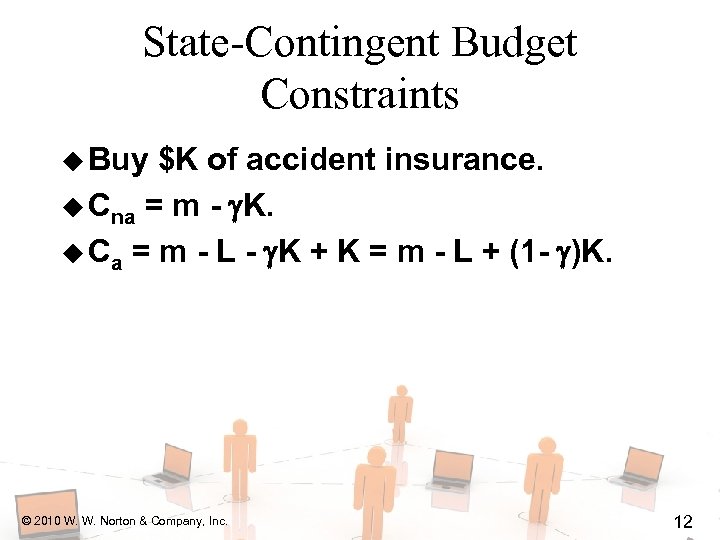 State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 12
State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 12
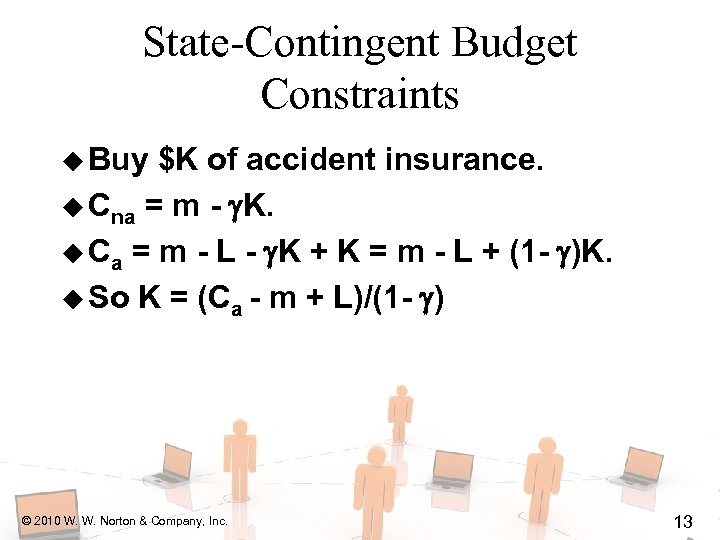 State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 13
State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 13
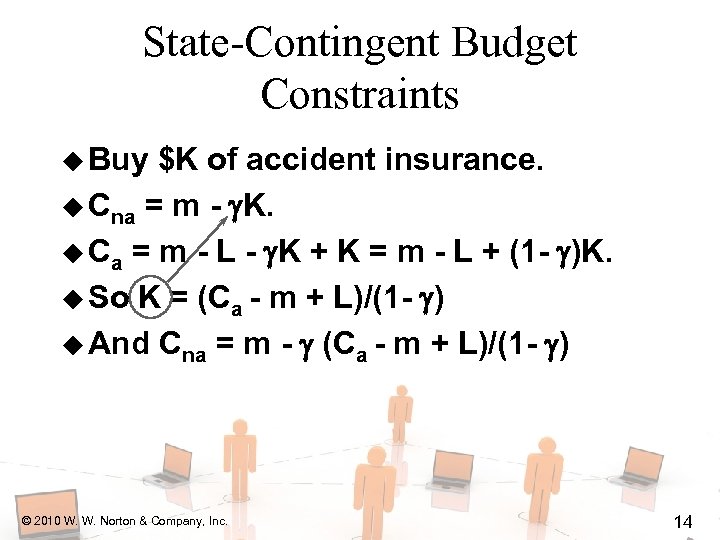 State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u And Cna = m - (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 14
State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u And Cna = m - (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 14
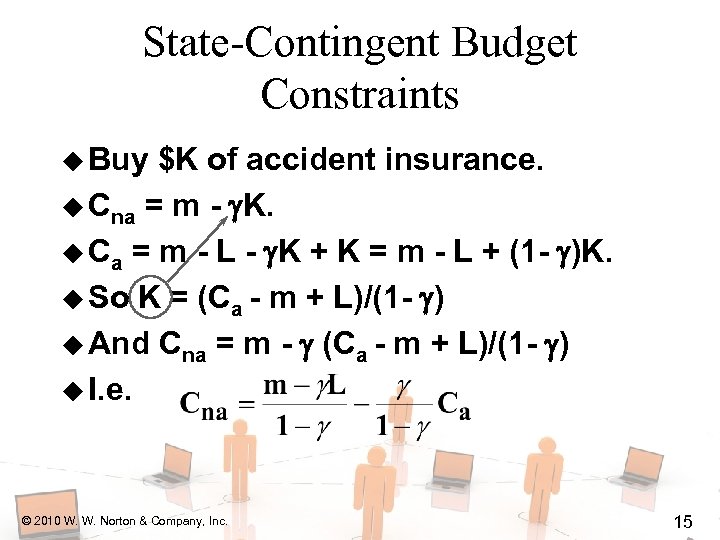 State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u And Cna = m - (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u I. e. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 15
State-Contingent Budget Constraints u Buy $K of accident insurance. u Cna = m - K. u Ca = m - L - K + K = m - L + (1 - )K. u So K = (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u And Cna = m - (Ca - m + L)/(1 - ) u I. e. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 15
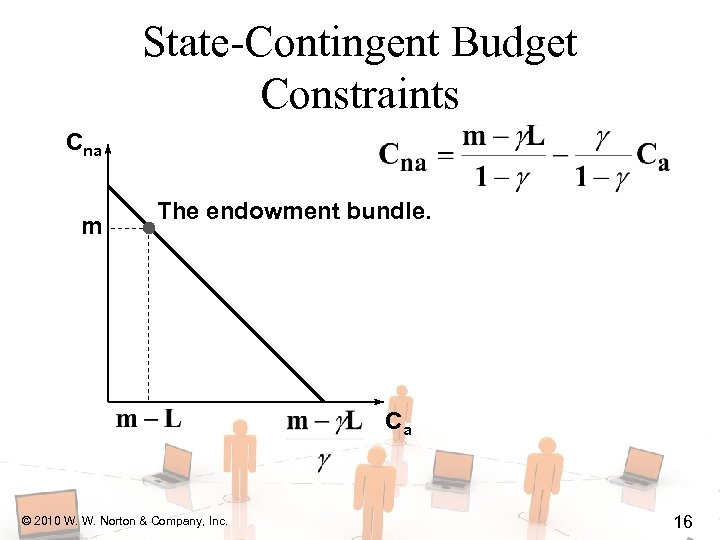 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 16
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 16
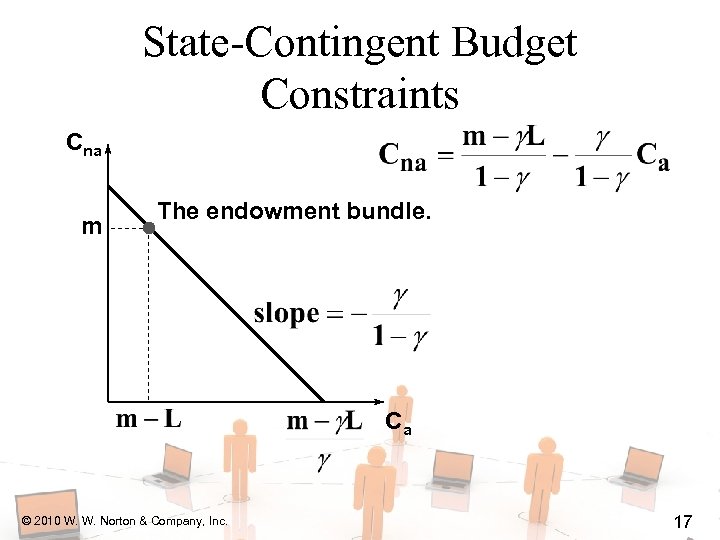 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 17
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 17
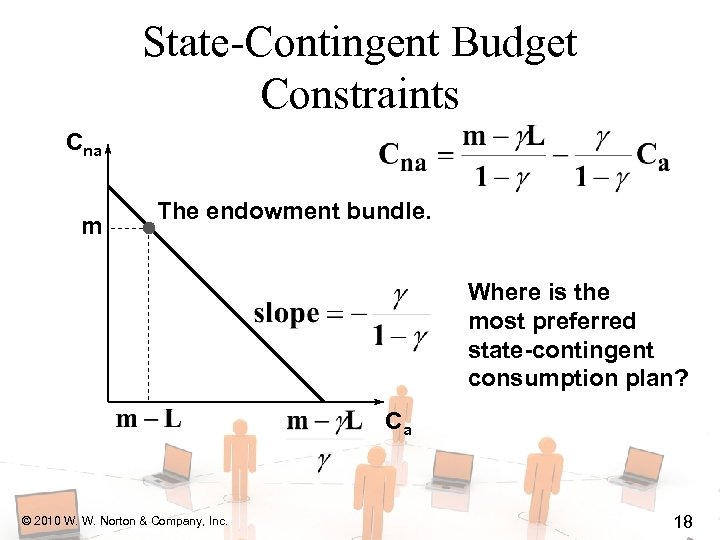 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 18
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 18
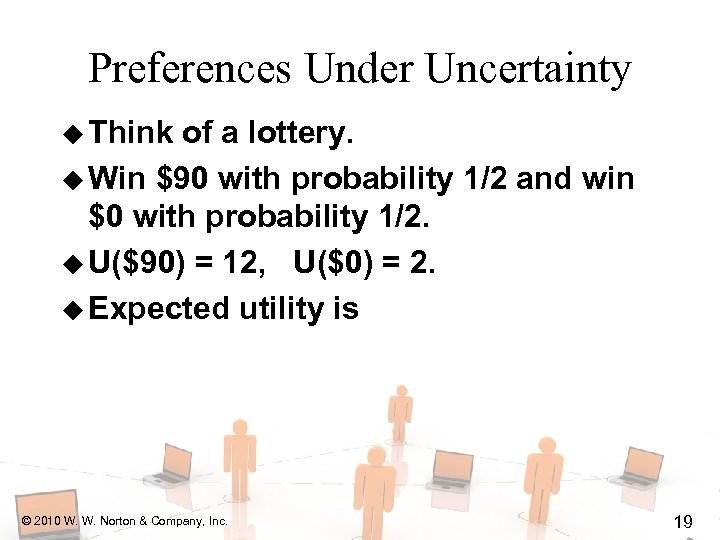 Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u U($90) = 12, U($0) = 2. u Expected utility is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 19
Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u U($90) = 12, U($0) = 2. u Expected utility is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 19
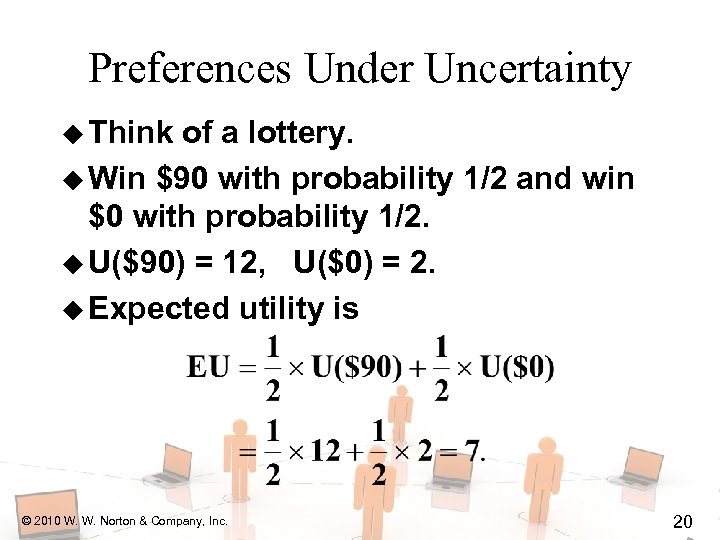 Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u U($90) = 12, U($0) = 2. u Expected utility is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 20
Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u U($90) = 12, U($0) = 2. u Expected utility is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 20
 Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u Expected money value of the lottery is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 21
Preferences Under Uncertainty u Think of a lottery. u Win $90 with probability 1/2 and win $0 with probability 1/2. u Expected money value of the lottery is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 21
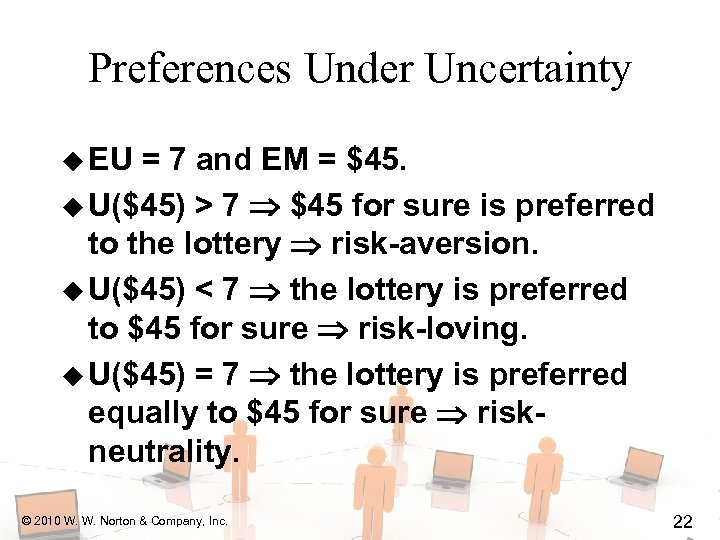 Preferences Under Uncertainty u EU = 7 and EM = $45. u U($45) > 7 $45 for sure is preferred to the lottery risk-aversion. u U($45) < 7 the lottery is preferred to $45 for sure risk-loving. u U($45) = 7 the lottery is preferred equally to $45 for sure riskneutrality. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 22
Preferences Under Uncertainty u EU = 7 and EM = $45. u U($45) > 7 $45 for sure is preferred to the lottery risk-aversion. u U($45) < 7 the lottery is preferred to $45 for sure risk-loving. u U($45) = 7 the lottery is preferred equally to $45 for sure riskneutrality. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 22
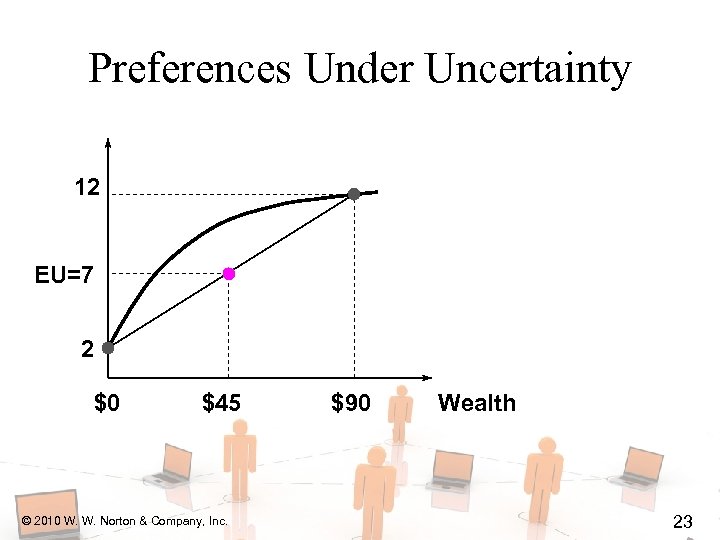 Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 23
Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 23
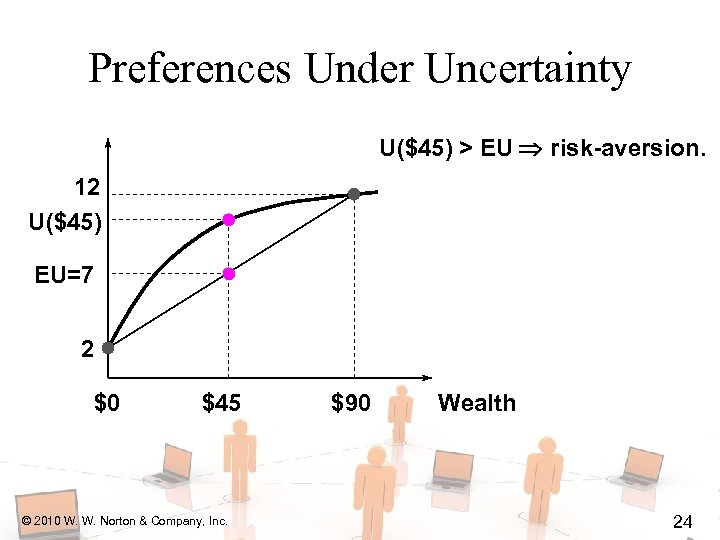 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) > EU risk-aversion. 12 U($45) EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 24
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) > EU risk-aversion. 12 U($45) EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 24
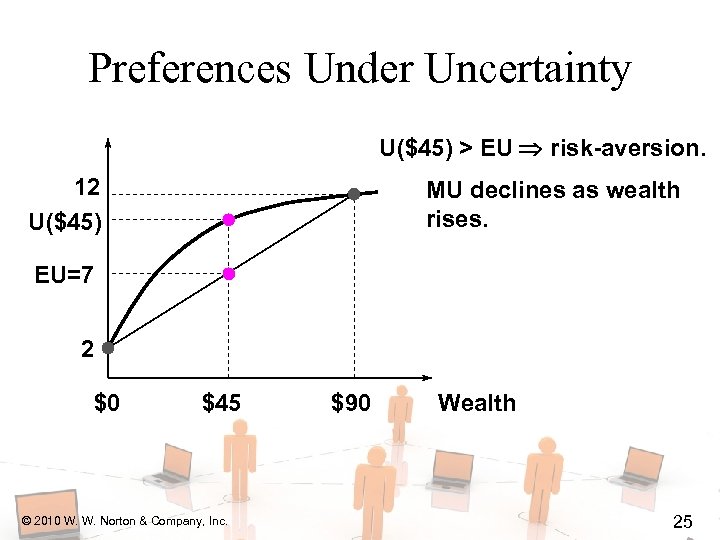 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) > EU risk-aversion. 12 U($45) MU declines as wealth rises. EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 25
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) > EU risk-aversion. 12 U($45) MU declines as wealth rises. EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 25
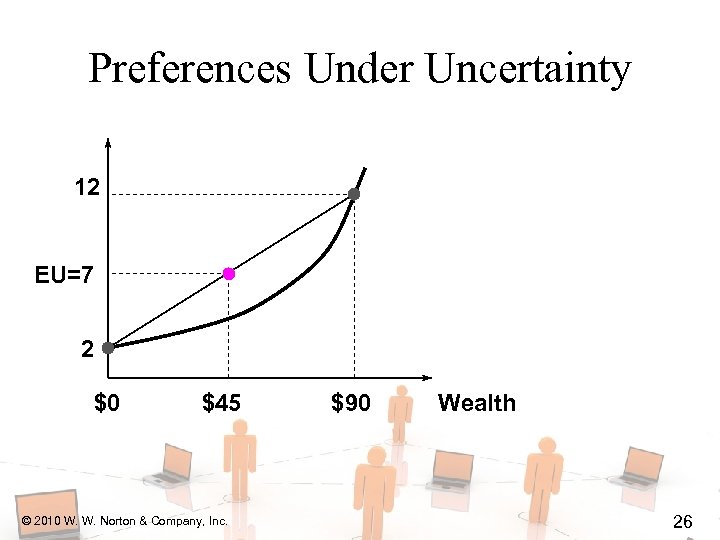 Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 26
Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 26
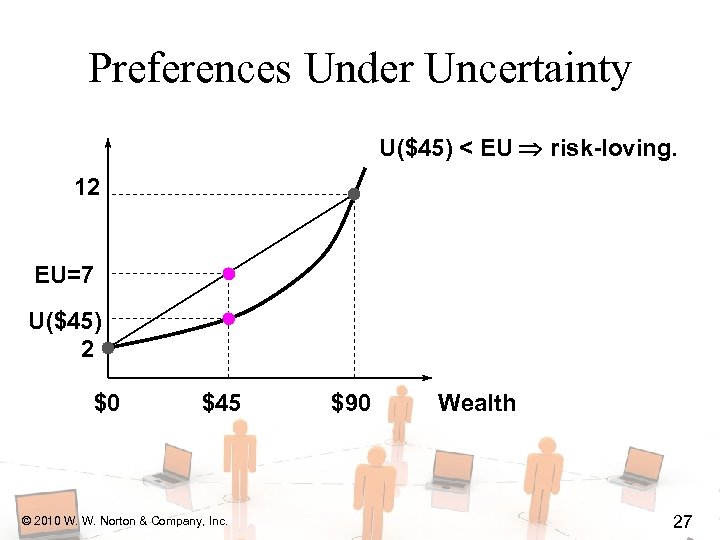 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) < EU risk-loving. 12 EU=7 U($45) 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 27
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) < EU risk-loving. 12 EU=7 U($45) 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 27
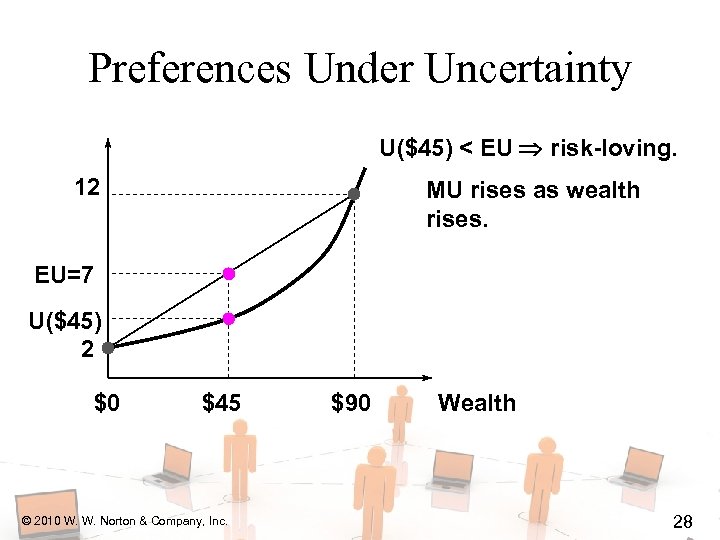 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) < EU risk-loving. 12 MU rises as wealth rises. EU=7 U($45) 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 28
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) < EU risk-loving. 12 MU rises as wealth rises. EU=7 U($45) 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 28
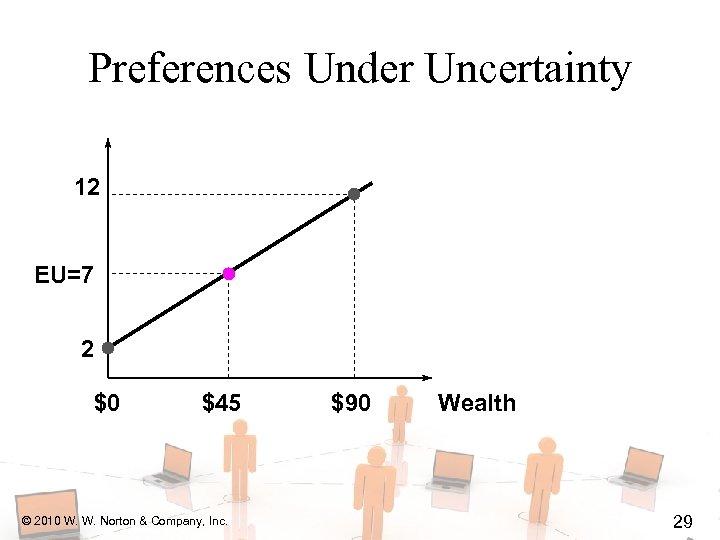 Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 29
Preferences Under Uncertainty 12 EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 29
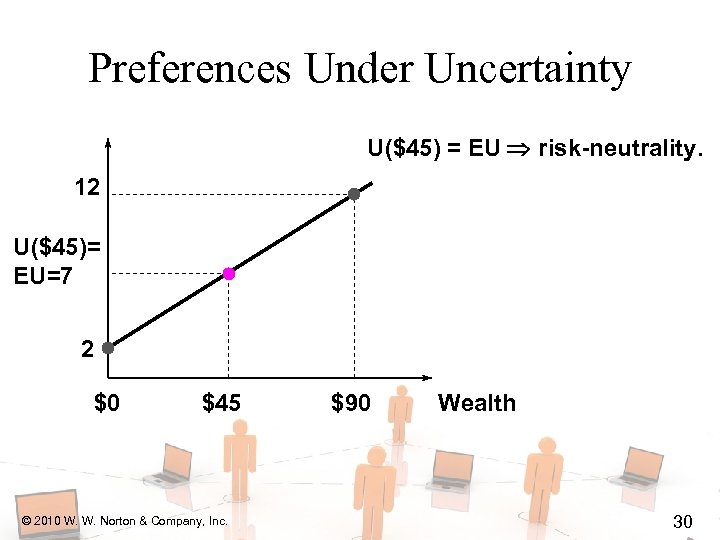 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) = EU risk-neutrality. 12 U($45)= EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 30
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) = EU risk-neutrality. 12 U($45)= EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 30
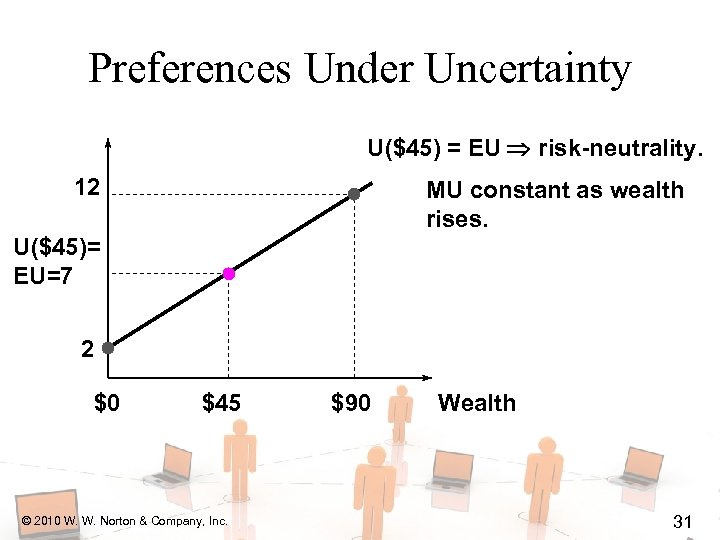 Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) = EU risk-neutrality. 12 MU constant as wealth rises. U($45)= EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 31
Preferences Under Uncertainty U($45) = EU risk-neutrality. 12 MU constant as wealth rises. U($45)= EU=7 2 $0 $45 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. $90 Wealth 31
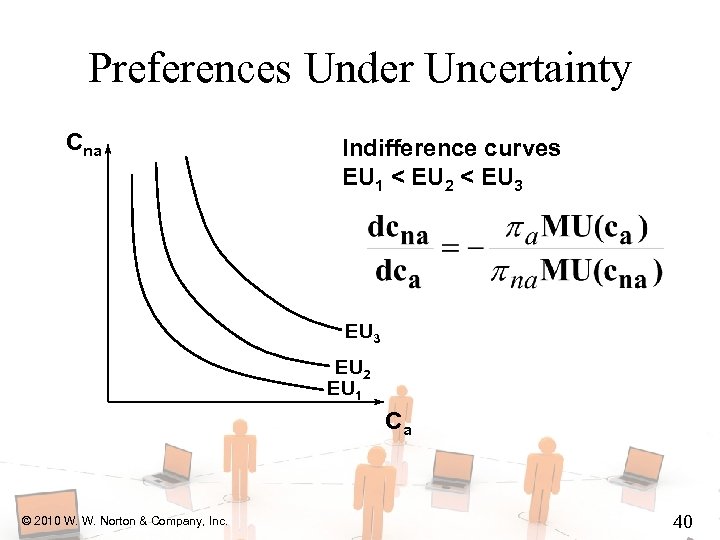
 Preferences Under Uncertainty u State-contingent consumption plans that give equal expected utility are equally preferred. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 32
Preferences Under Uncertainty u State-contingent consumption plans that give equal expected utility are equally preferred. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 32
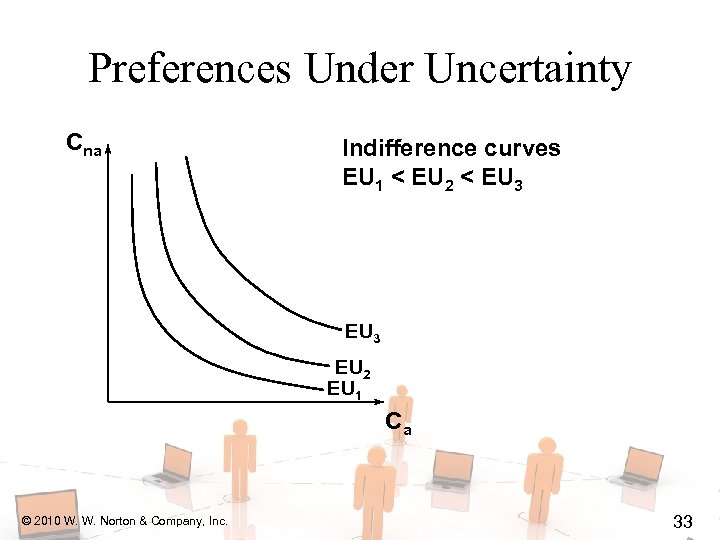 Preferences Under Uncertainty Cna Indifference curves EU 1 < EU 2 < EU 3 EU 2 EU 1 Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 33
Preferences Under Uncertainty Cna Indifference curves EU 1 < EU 2 < EU 3 EU 2 EU 1 Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 33
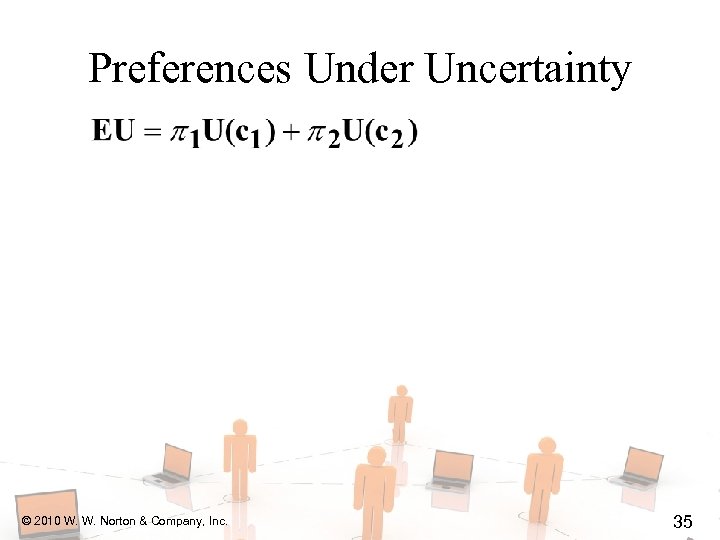
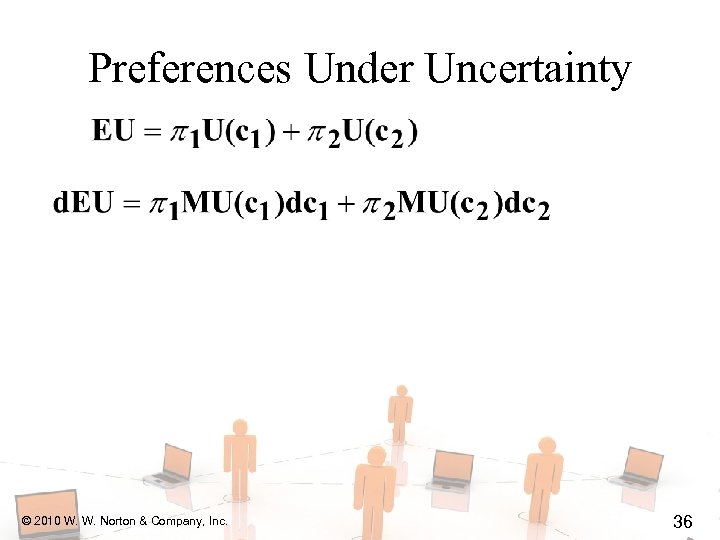
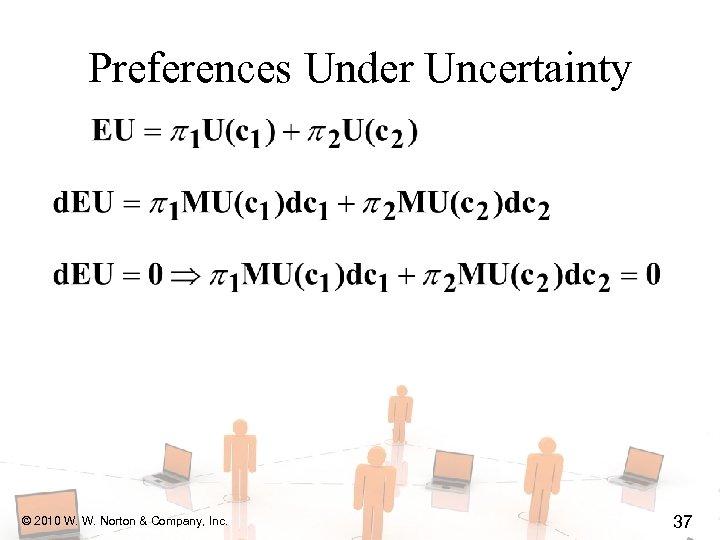
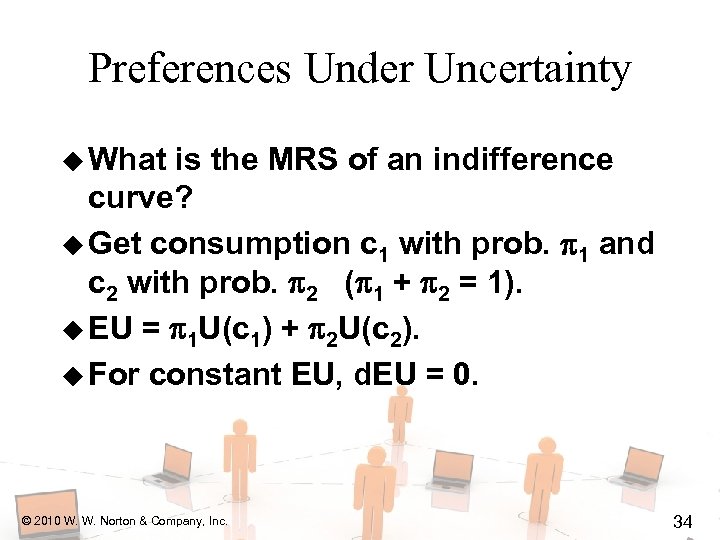 Preferences Under Uncertainty u What is the MRS of an indifference curve? u Get consumption c 1 with prob. 1 and c 2 with prob. 2 ( 1 + 2 = 1). u EU = 1 U(c 1) + 2 U(c 2). u For constant EU, d. EU = 0. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 34
Preferences Under Uncertainty u What is the MRS of an indifference curve? u Get consumption c 1 with prob. 1 and c 2 with prob. 2 ( 1 + 2 = 1). u EU = 1 U(c 1) + 2 U(c 2). u For constant EU, d. EU = 0. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 34
 Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 35
Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 35
 Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 36
Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 36
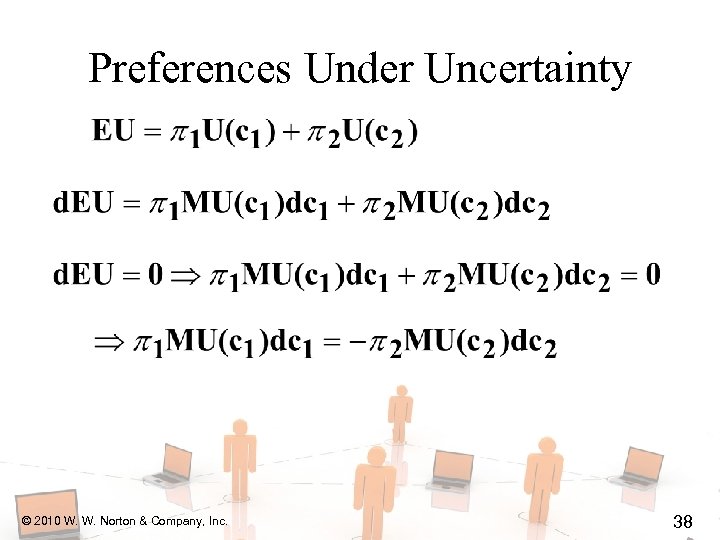
 Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 37
Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 37
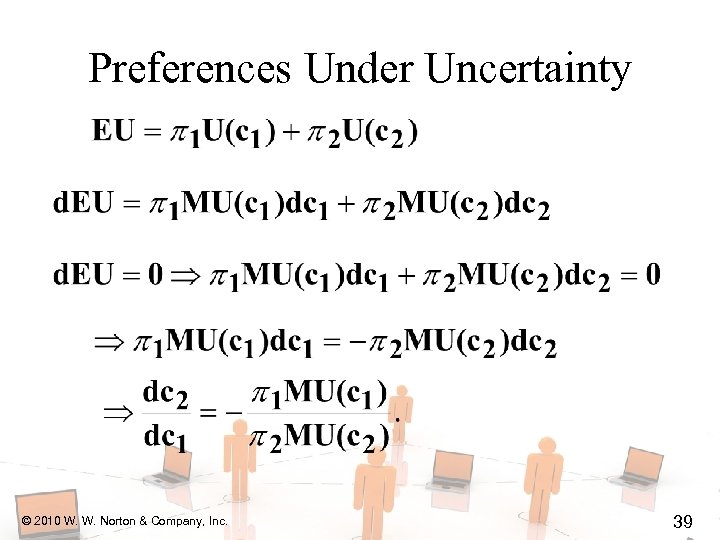
 Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 38
Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 38
 Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 39
Preferences Under Uncertainty © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 39
 Preferences Under Uncertainty Cna Indifference curves EU 1 < EU 2 < EU 3 EU 2 EU 1 Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 40
Preferences Under Uncertainty Cna Indifference curves EU 1 < EU 2 < EU 3 EU 2 EU 1 Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 40
 Choice Under Uncertainty u Q: How is a rational choice made under uncertainty? u A: Choose the most preferred affordable state-contingent consumption plan. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 41
Choice Under Uncertainty u Q: How is a rational choice made under uncertainty? u A: Choose the most preferred affordable state-contingent consumption plan. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 41
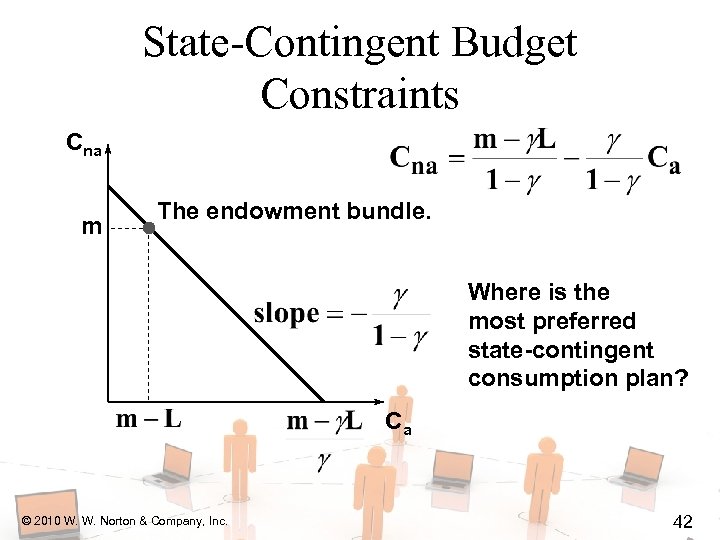 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 42
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 42
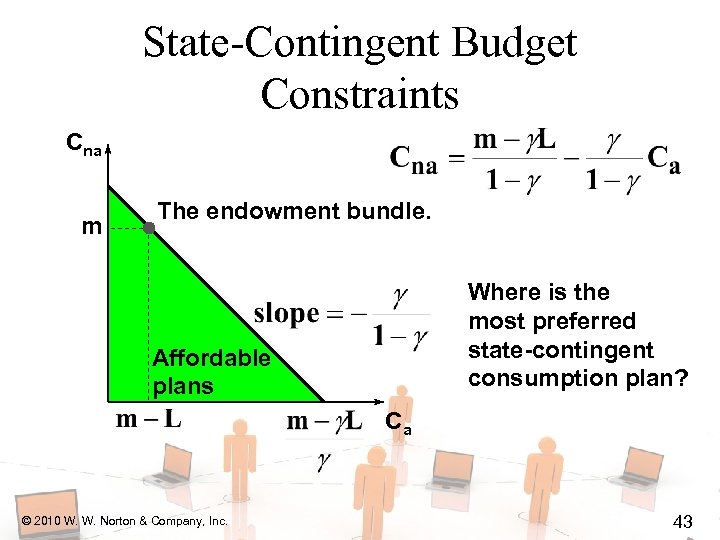 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Affordable plans Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 43
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m The endowment bundle. Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Affordable plans Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 43
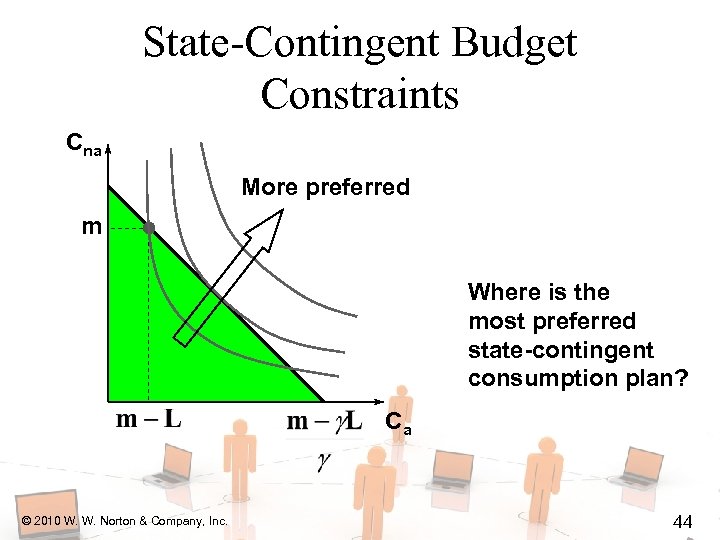 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna More preferred m Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 44
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna More preferred m Where is the most preferred state-contingent consumption plan? Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 44
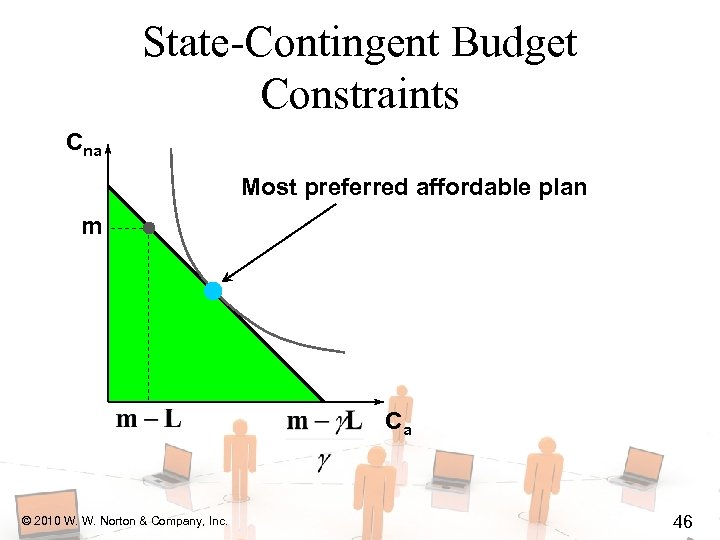
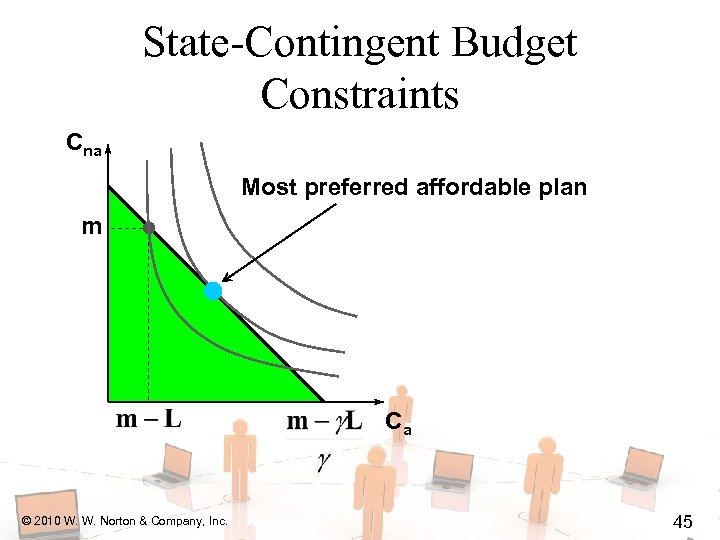 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Most preferred affordable plan m Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 45
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Most preferred affordable plan m Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 45
 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Most preferred affordable plan m Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 46
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna Most preferred affordable plan m Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 46
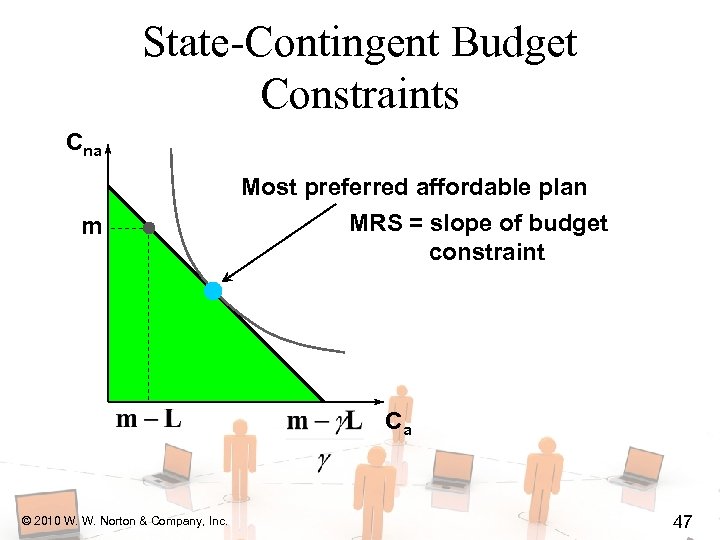 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m Most preferred affordable plan MRS = slope of budget constraint Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 47
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m Most preferred affordable plan MRS = slope of budget constraint Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 47
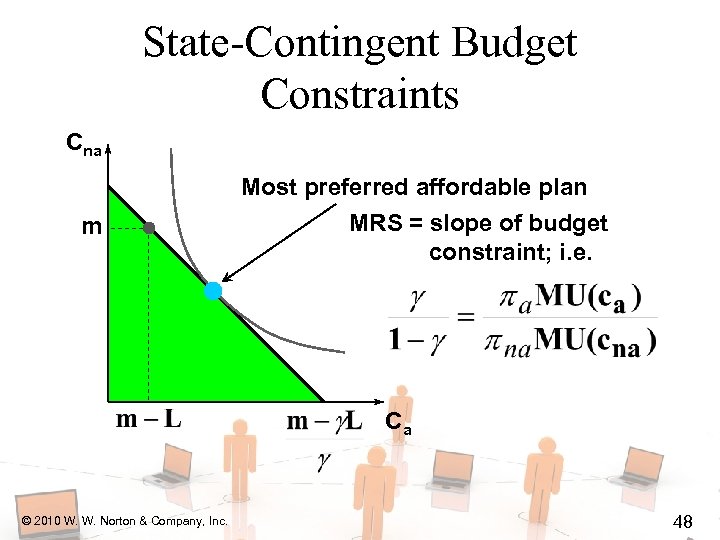 State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m Most preferred affordable plan MRS = slope of budget constraint; i. e. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 48
State-Contingent Budget Constraints Cna m Most preferred affordable plan MRS = slope of budget constraint; i. e. Ca © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 48
 Competitive Insurance u Suppose entry to the insurance industry is free. u Expected economic profit = 0. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K = 0. u I. e. free entry = a. u If price of $1 insurance = accident probability, then insurance is fair. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 49
Competitive Insurance u Suppose entry to the insurance industry is free. u Expected economic profit = 0. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K = 0. u I. e. free entry = a. u If price of $1 insurance = accident probability, then insurance is fair. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 49
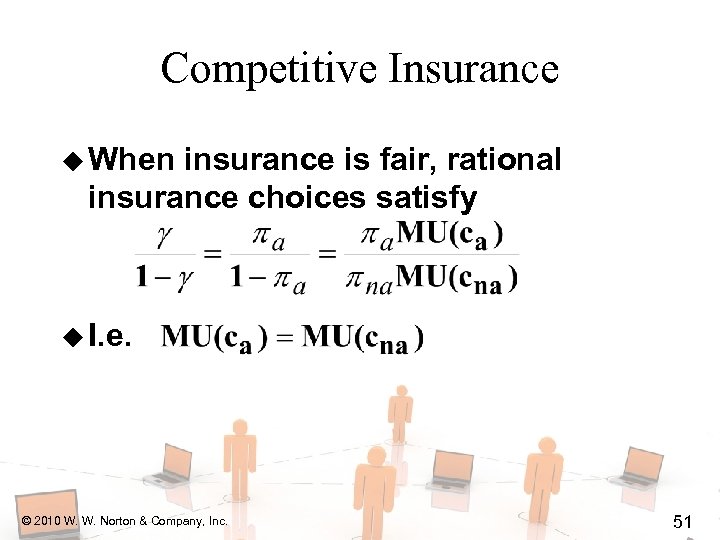
 Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 50
Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 50
 Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy u I. e. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 51
Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy u I. e. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 51
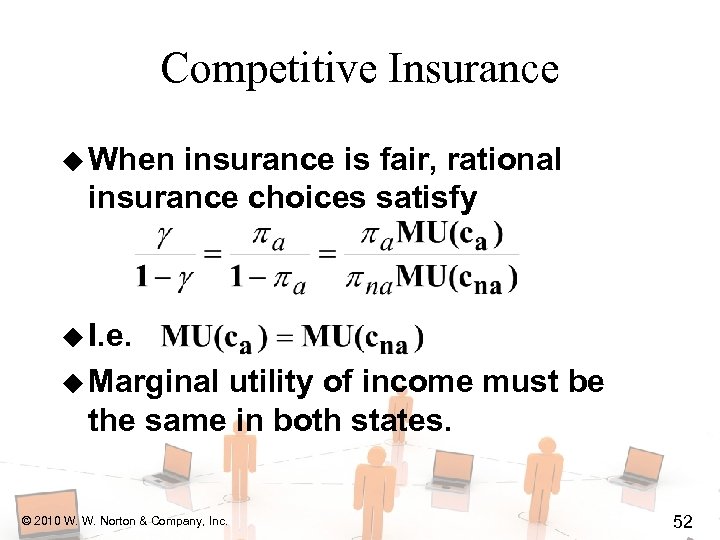 Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy u I. e. u Marginal utility of income must be the same in both states. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 52
Competitive Insurance u When insurance is fair, rational insurance choices satisfy u I. e. u Marginal utility of income must be the same in both states. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 52
 Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 53
Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 53
 Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. MU(c) as c . 54
Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. MU(c) as c . 54
 Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion MU(c) as c . u Hence © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 55
Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion MU(c) as c . u Hence © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 55
 Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion MU(c) as c . u Hence u I. e. full-insurance. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 56
Competitive Insurance u How much fair insurance does a riskaverse consumer buy? u Risk-aversion MU(c) as c . u Hence u I. e. full-insurance. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 56
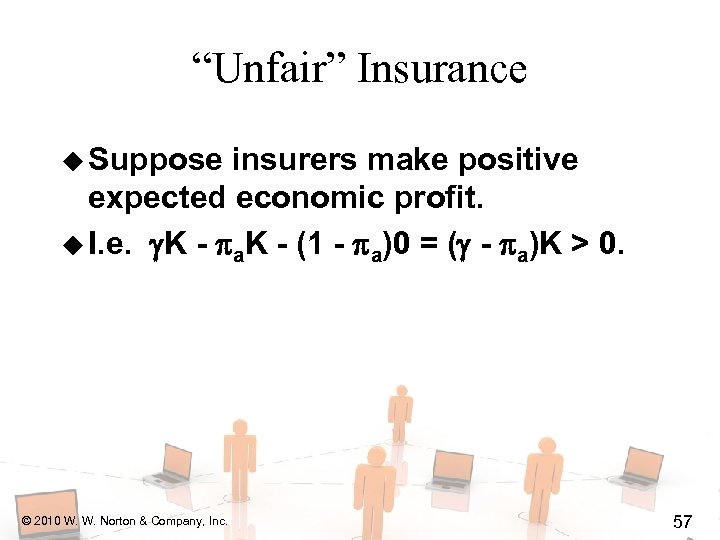 “Unfair” Insurance u Suppose insurers make positive expected economic profit. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K > 0. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 57
“Unfair” Insurance u Suppose insurers make positive expected economic profit. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K > 0. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 57
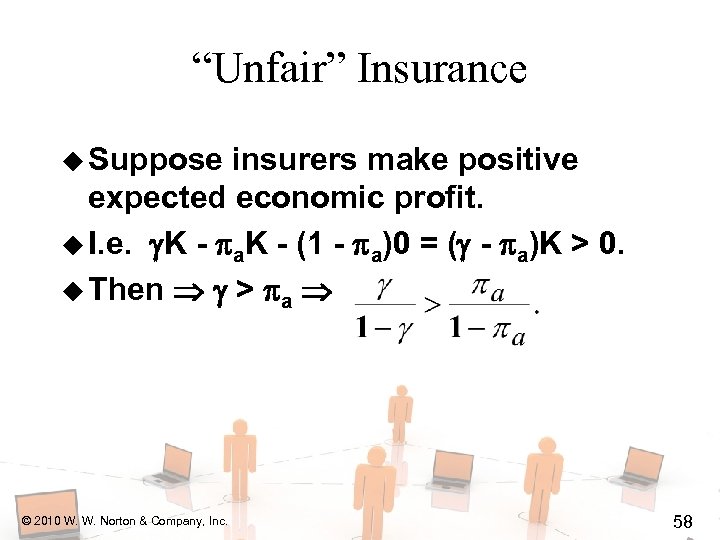 “Unfair” Insurance u Suppose insurers make positive expected economic profit. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K > 0. u Then > a © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 58
“Unfair” Insurance u Suppose insurers make positive expected economic profit. u I. e. K - a. K - (1 - a)0 = ( - a)K > 0. u Then > a © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 58
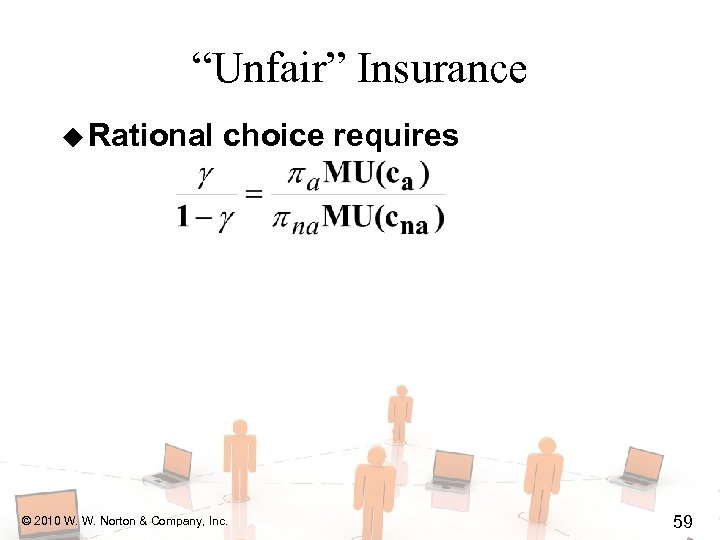 “Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 59
“Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 59
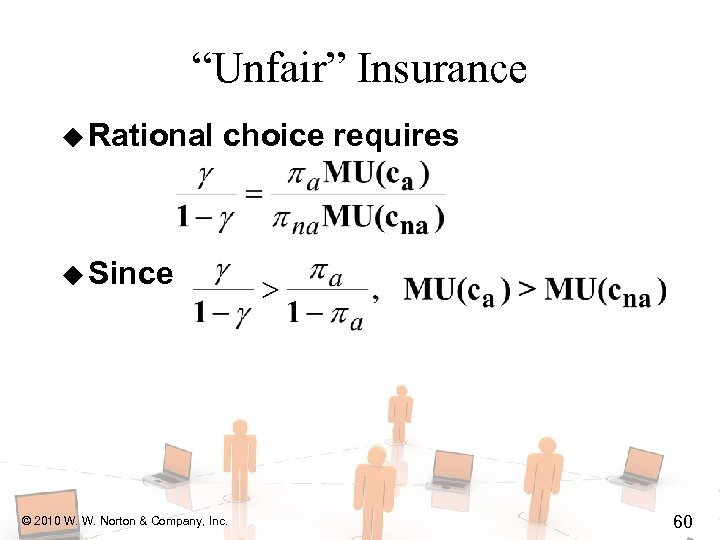 “Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 60
“Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 60
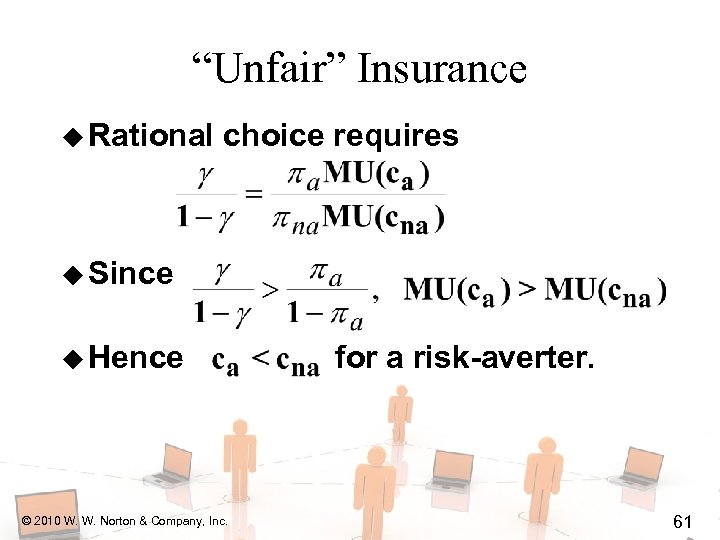 “Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since u Hence © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. for a risk-averter. 61
“Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since u Hence © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. for a risk-averter. 61
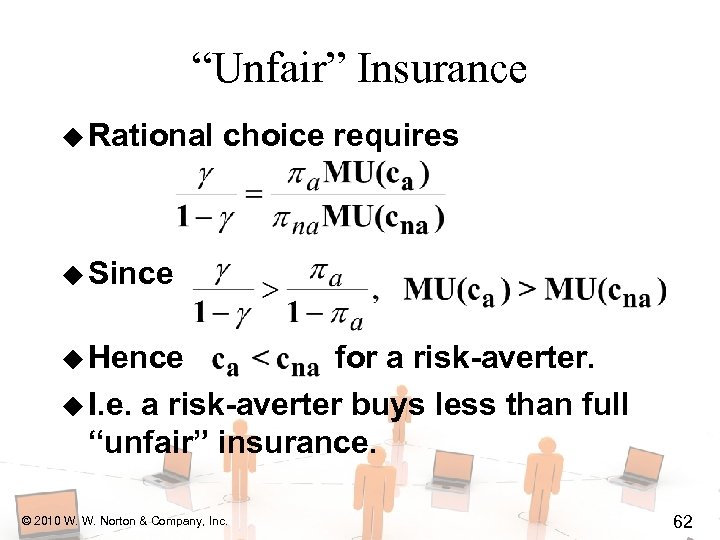 “Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since u Hence for a risk-averter. u I. e. a risk-averter buys less than full “unfair” insurance. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 62
“Unfair” Insurance u Rational choice requires u Since u Hence for a risk-averter. u I. e. a risk-averter buys less than full “unfair” insurance. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 62
 Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 63
Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 63
 Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 64
Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 64
 Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) ? – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 65
Uncertainty is Pervasive u What are rational responses to uncertainty? – buying insurance (health, life, auto) ? – a portfolio of contingent consumption goods. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 65
 Diversification u Two firms, A and B. Shares cost $10. u With prob. 1/2 A’s profit is $100 and B’s profit is $20. u With prob. 1/2 A’s profit is $20 and B’s profit is $100. u You have $100 to invest. How? © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 66
Diversification u Two firms, A and B. Shares cost $10. u With prob. 1/2 A’s profit is $100 and B’s profit is $20. u With prob. 1/2 A’s profit is $20 and B’s profit is $100. u You have $100 to invest. How? © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 66
 Diversification u Buy only firm A’s stock? u $100/10 = 10 shares. u You earn $1000 with prob. 1/2 and $200 with prob. 1/2. u Expected earning: $500 + $100 = $600 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 67
Diversification u Buy only firm A’s stock? u $100/10 = 10 shares. u You earn $1000 with prob. 1/2 and $200 with prob. 1/2. u Expected earning: $500 + $100 = $600 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 67
 Diversification u Buy only firm B’s stock? u $100/10 = 10 shares. u You earn $1000 with prob. 1/2 and $200 with prob. 1/2. u Expected earning: $500 + $100 = $600 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 68
Diversification u Buy only firm B’s stock? u $100/10 = 10 shares. u You earn $1000 with prob. 1/2 and $200 with prob. 1/2. u Expected earning: $500 + $100 = $600 © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 68
 Diversification u Buy 5 shares in each firm? u You earn $600 for sure. u Diversification has maintained expected earning and lowered risk. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 69
Diversification u Buy 5 shares in each firm? u You earn $600 for sure. u Diversification has maintained expected earning and lowered risk. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 69
 Diversification u Buy 5 shares in each firm? u You earn $600 for sure. u Diversification has maintained expected earning and lowered risk. u Typically, diversification lowers expected earnings in exchange for lowered risk. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 70
Diversification u Buy 5 shares in each firm? u You earn $600 for sure. u Diversification has maintained expected earning and lowered risk. u Typically, diversification lowers expected earnings in exchange for lowered risk. © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 70
 Risk Spreading/Mutual Insurance u 100 risk-neutral persons each independently risk a $10, 000 loss. u Loss probability = 0. 01. u Initial wealth is $40, 000. u No insurance: expected wealth is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 71
Risk Spreading/Mutual Insurance u 100 risk-neutral persons each independently risk a $10, 000 loss. u Loss probability = 0. 01. u Initial wealth is $40, 000. u No insurance: expected wealth is © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 71
 Risk Spreading/Mutual Insurance u Mutual insurance: Expected loss is u Each of the 100 persons pays $1 into a mutual insurance fund. u Mutual insurance: expected wealth is u Risk-spreading © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. benefits everyone. 72
Risk Spreading/Mutual Insurance u Mutual insurance: Expected loss is u Each of the 100 persons pays $1 into a mutual insurance fund. u Mutual insurance: expected wealth is u Risk-spreading © 2010 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. benefits everyone. 72


