12 — 1 Spinal Nerves AP 150 Chapter








- Размер: 911.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 23
Описание презентации 12 — 1 Spinal Nerves AP 150 Chapter по слайдам
 12 — 1 Spinal Nerves AP 150 Chapter
12 — 1 Spinal Nerves AP 150 Chapter
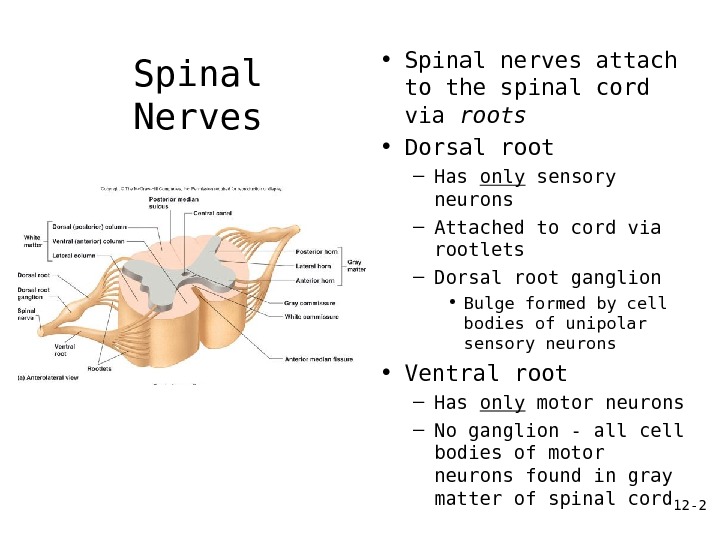
 12 — 2 Spinal Nerves • Spinal nerves attach to the spinal cord via roots • Dorsal root – Has only sensory neurons – Attached to cord via rootlets – Dorsal root ganglion • Bulge formed by cell bodies of unipolar sensory neurons • Ventral root – Has only motor neurons – No ganglion — all cell bodies of motor neurons found in gray matter of spinal cord
12 — 2 Spinal Nerves • Spinal nerves attach to the spinal cord via roots • Dorsal root – Has only sensory neurons – Attached to cord via rootlets – Dorsal root ganglion • Bulge formed by cell bodies of unipolar sensory neurons • Ventral root – Has only motor neurons – No ganglion — all cell bodies of motor neurons found in gray matter of spinal cord
 12 — 3 Spinal Nerves • 31 pair – each contains thousands of nerve fibers – All are mixed nerves have both sensory and motor neurons) • Connect to the spinal cord • Named for point of issue from the spinal cord – 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C 1 -C 8 ) – 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T 1 -T 12 ) – 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L 1 -L 5 ) – 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S 1 -S 5 ) – 1 pair of coccygeal nerves (Co 1 )
12 — 3 Spinal Nerves • 31 pair – each contains thousands of nerve fibers – All are mixed nerves have both sensory and motor neurons) • Connect to the spinal cord • Named for point of issue from the spinal cord – 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C 1 -C 8 ) – 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T 1 -T 12 ) – 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L 1 -L 5 ) – 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S 1 -S 5 ) – 1 pair of coccygeal nerves (Co 1 )
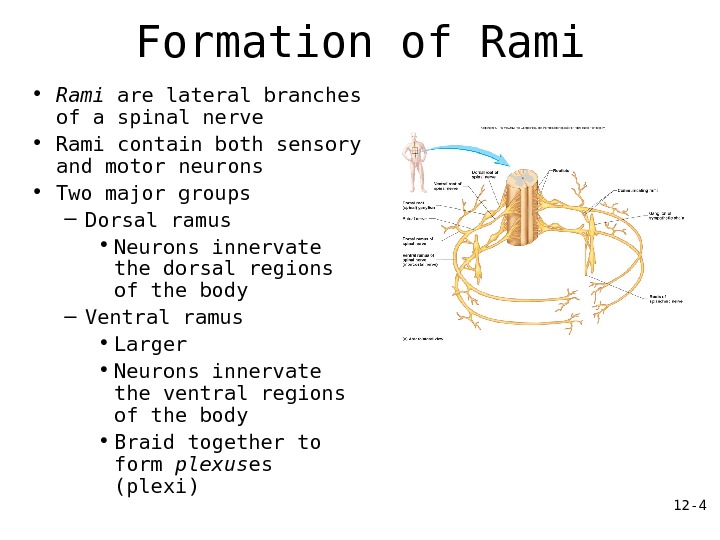
 12 — 4 Formation of Rami • Rami are lateral branches of a spinal nerve • Rami contain both sensory and motor neurons • Two major groups – Dorsal ramus • Neurons innervate the dorsal regions of the body – Ventral ramus • Larger • Neurons innervate the ventral regions of the body • Braid together to form plexus es (plexi)
12 — 4 Formation of Rami • Rami are lateral branches of a spinal nerve • Rami contain both sensory and motor neurons • Two major groups – Dorsal ramus • Neurons innervate the dorsal regions of the body – Ventral ramus • Larger • Neurons innervate the ventral regions of the body • Braid together to form plexus es (plexi)
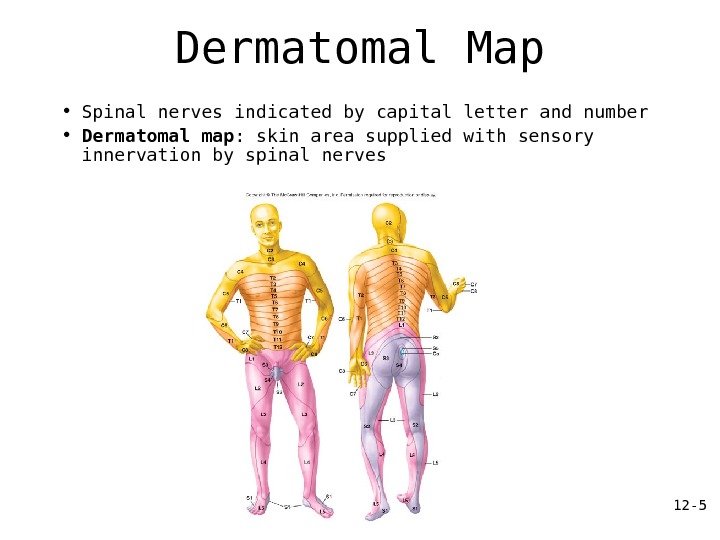
 12 — 5 Dermatomal Map • Spinal nerves indicated by capital letter and number • Dermatomal map : skin area supplied with sensory innervation by spinal nerves
12 — 5 Dermatomal Map • Spinal nerves indicated by capital letter and number • Dermatomal map : skin area supplied with sensory innervation by spinal nerves
 12 — 6 Introduction to Nerve Plexuses • Nerve plexus – A network of ventral rami • Ventral rami (except T 2 -T 12 ) – Branch and join with one another – Form nerve plexuses • In cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions • No plexus formed in thoracic region of s. c.
12 — 6 Introduction to Nerve Plexuses • Nerve plexus – A network of ventral rami • Ventral rami (except T 2 -T 12 ) – Branch and join with one another – Form nerve plexuses • In cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions • No plexus formed in thoracic region of s. c.
 12 — 7 The Cervical Plexus • Buried deep in the neck – Under the sternocleidomastoid muscle • Formed by ventral rami of first four cervical nerves • Most are cutaneous nerves • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck • Phrenic nerve – the most important nerve of the cervical plexus
12 — 7 The Cervical Plexus • Buried deep in the neck – Under the sternocleidomastoid muscle • Formed by ventral rami of first four cervical nerves • Most are cutaneous nerves • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck • Phrenic nerve – the most important nerve of the cervical plexus
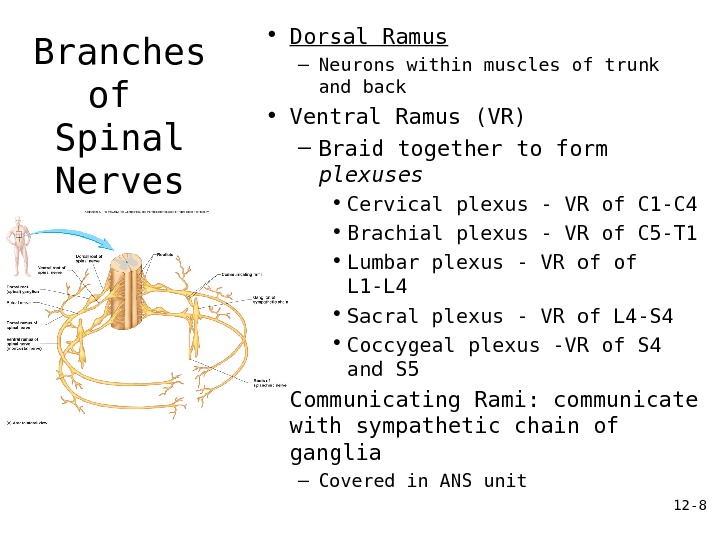
 12 — 8 Branches of Spinal Nerves • Dorsal Ramus – Neurons within muscles of trunk and back • Ventral Ramus (VR) – Braid together to form plexuses • Cervical plexus — VR of C 1 -C 4 • Brachial plexus — VR of C 5 -T 1 • Lumbar plexus — VR of of L 1 -L 4 • Sacral plexus — VR of L 4 -S 4 • Coccygeal plexus -VR of S 4 and S 5 • Communicating Rami: communicate with sympathetic chain of ganglia – Covered in ANS unit
12 — 8 Branches of Spinal Nerves • Dorsal Ramus – Neurons within muscles of trunk and back • Ventral Ramus (VR) – Braid together to form plexuses • Cervical plexus — VR of C 1 -C 4 • Brachial plexus — VR of C 5 -T 1 • Lumbar plexus — VR of of L 1 -L 4 • Sacral plexus — VR of L 4 -S 4 • Coccygeal plexus -VR of S 4 and S 5 • Communicating Rami: communicate with sympathetic chain of ganglia – Covered in ANS unit
 12 — 9 Cervical Plexus • Buried deep in the neck – Under the sternocleidomastoid muscle • Formed by ventral rami of first four cervical nerves (C 1 -C 4) • Most are cutaneous nerves • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck, posterior portion of head • Phrenic nerve – the most important nerve of the cervical plexus • Phrenic nerve – Innervate diaphragm
12 — 9 Cervical Plexus • Buried deep in the neck – Under the sternocleidomastoid muscle • Formed by ventral rami of first four cervical nerves (C 1 -C 4) • Most are cutaneous nerves • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck, posterior portion of head • Phrenic nerve – the most important nerve of the cervical plexus • Phrenic nerve – Innervate diaphragm
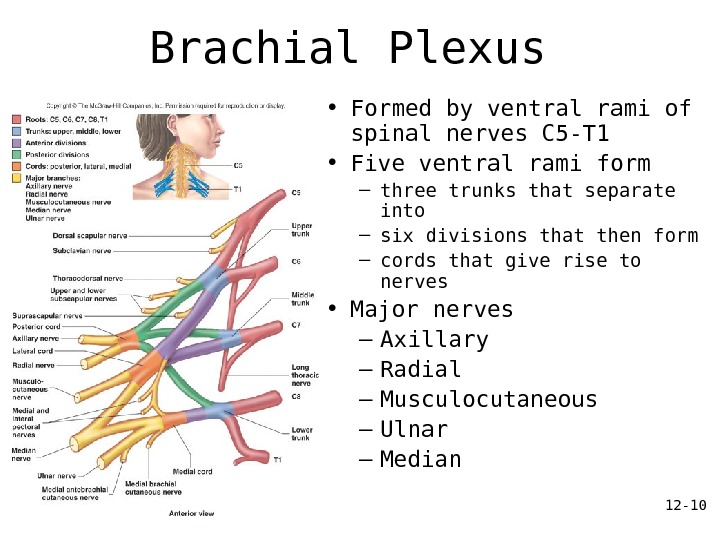
 12 — 10 Brachial Plexus • Formed by ventral rami of spinal nerves C 5 -T 1 • Five ventral rami form – three trunks that separate into – six divisions that then form – cords that give rise to nerves • Major nerves – Axillary – Radial – Musculocutaneous – Ulnar – Median
12 — 10 Brachial Plexus • Formed by ventral rami of spinal nerves C 5 -T 1 • Five ventral rami form – three trunks that separate into – six divisions that then form – cords that give rise to nerves • Major nerves – Axillary – Radial – Musculocutaneous – Ulnar – Median
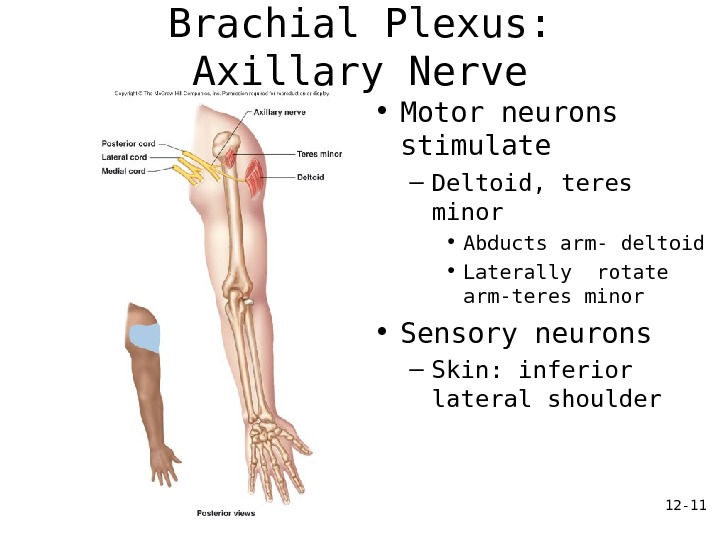
 12 — 11 Brachial Plexus: Axillary Nerve • Motor neurons stimulate – Deltoid, teres minor • Abducts arm- deltoid • Laterally rotate arm-teres minor • Sensory neurons – Skin: inferior lateral shoulder
12 — 11 Brachial Plexus: Axillary Nerve • Motor neurons stimulate – Deltoid, teres minor • Abducts arm- deltoid • Laterally rotate arm-teres minor • Sensory neurons – Skin: inferior lateral shoulder
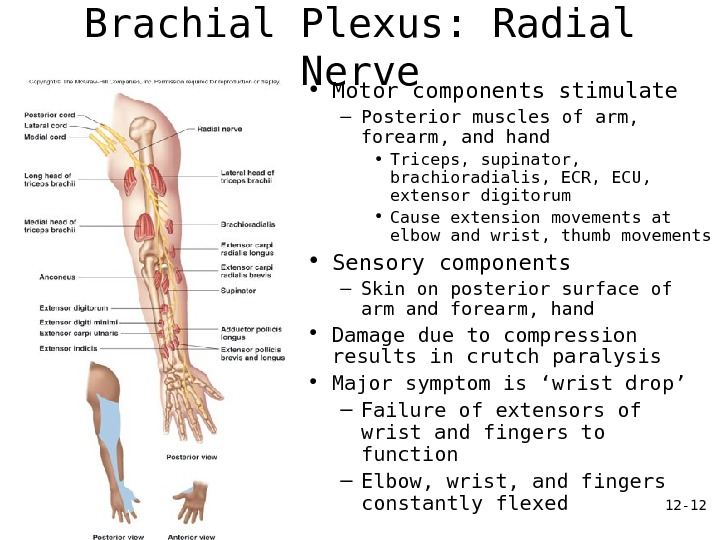
 12 — 12 Brachial Plexus: Radial Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Posterior muscles of arm, forearm, and hand • Triceps, supinator, brachioradialis, ECR, ECU, extensor digitorum • Cause extension movements at elbow and wrist, thumb movements • Sensory components – Skin on posterior surface of arm and forearm, hand • Damage due to compression results in crutch paralysis • Major symptom is ‘wrist drop’ – Failure of extensors of wrist and fingers to function – Elbow, wrist, and fingers constantly flexed
12 — 12 Brachial Plexus: Radial Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Posterior muscles of arm, forearm, and hand • Triceps, supinator, brachioradialis, ECR, ECU, extensor digitorum • Cause extension movements at elbow and wrist, thumb movements • Sensory components – Skin on posterior surface of arm and forearm, hand • Damage due to compression results in crutch paralysis • Major symptom is ‘wrist drop’ – Failure of extensors of wrist and fingers to function – Elbow, wrist, and fingers constantly flexed
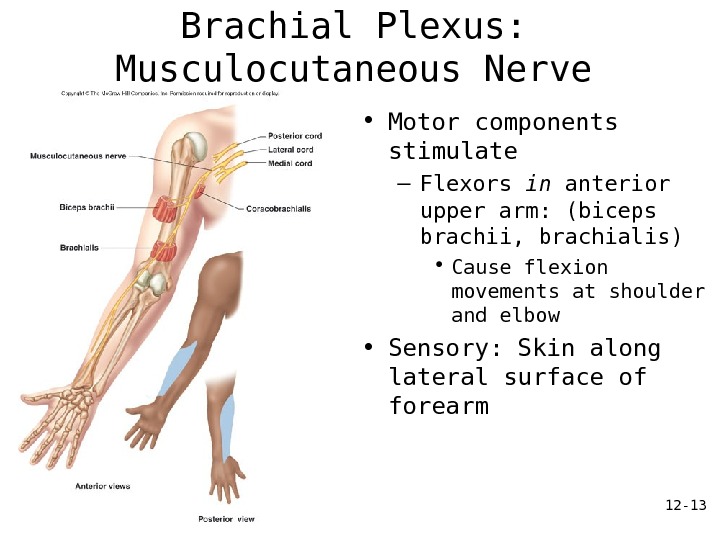
 12 — 13 Brachial Plexus: Musculocutaneous Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Flexors in anterior upper arm: (biceps brachii, brachialis) • Cause flexion movements at shoulder and elbow • Sensory: Skin along lateral surface of forearm
12 — 13 Brachial Plexus: Musculocutaneous Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Flexors in anterior upper arm: (biceps brachii, brachialis) • Cause flexion movements at shoulder and elbow • Sensory: Skin along lateral surface of forearm
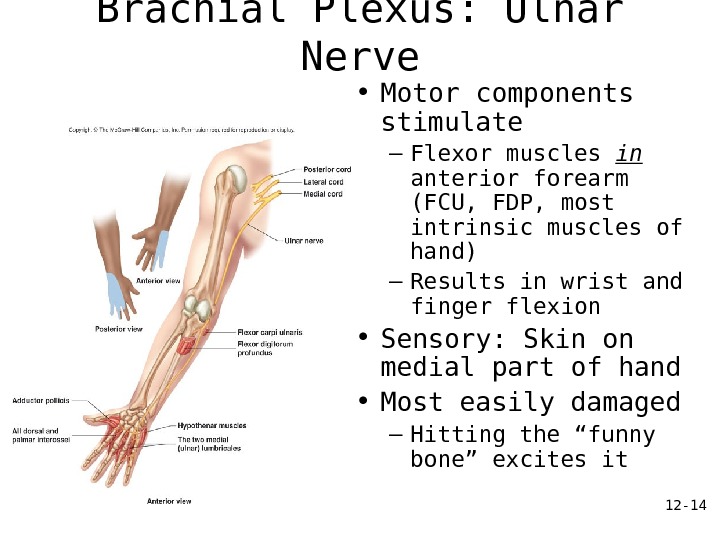
 12 — 14 Brachial Plexus: Ulnar Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Flexor muscles in anterior forearm (FCU, FDP, most intrinsic muscles of hand) – Results in wrist and finger flexion • Sensory: Skin on medial part of hand • Most easily damaged – Hitting the “funny bone” excites it
12 — 14 Brachial Plexus: Ulnar Nerve • Motor components stimulate – Flexor muscles in anterior forearm (FCU, FDP, most intrinsic muscles of hand) – Results in wrist and finger flexion • Sensory: Skin on medial part of hand • Most easily damaged – Hitting the “funny bone” excites it
 12 — 15 Brachial Plexus: Median Nerve • Motor components stimulate – All but one of the flexors of the wrist and fingers, and thenar muscles at base of thumb (Palmaris longus, FCR, FDS, FPL, pronator) – Causes flexion of the wrist and fingers and thumb • Sensory components – Stimulate skin on lateral part of hand • Damaged in carpal tunnel and suicide attempts
12 — 15 Brachial Plexus: Median Nerve • Motor components stimulate – All but one of the flexors of the wrist and fingers, and thenar muscles at base of thumb (Palmaris longus, FCR, FDS, FPL, pronator) – Causes flexion of the wrist and fingers and thumb • Sensory components – Stimulate skin on lateral part of hand • Damaged in carpal tunnel and suicide attempts
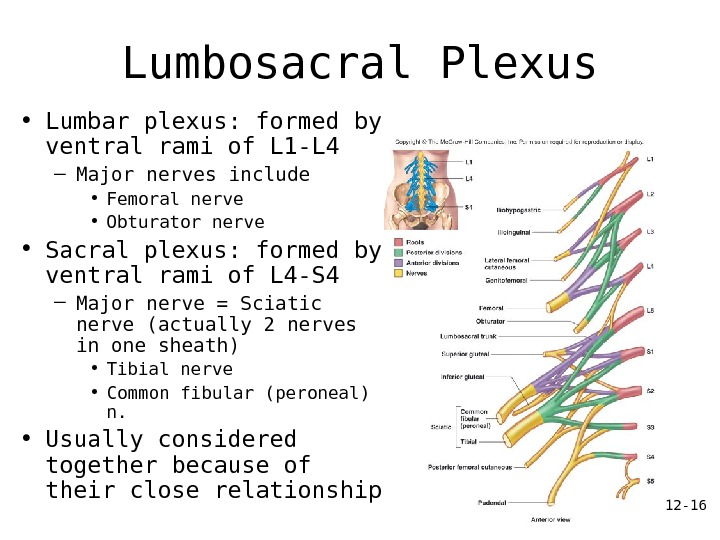
 12 — 16 Lumbosacral Plexus • Lumbar plexus: formed by ventral rami of L 1 -L 4 – Major nerves include • Femoral nerve • Obturator nerve • Sacral plexus: formed by ventral rami of L 4 -S 4 – Major nerve = Sciatic nerve (actually 2 nerves in one sheath) • Tibial nerve • Common fibular (peroneal) n. • Usually considered together because of their close relationship
12 — 16 Lumbosacral Plexus • Lumbar plexus: formed by ventral rami of L 1 -L 4 – Major nerves include • Femoral nerve • Obturator nerve • Sacral plexus: formed by ventral rami of L 4 -S 4 – Major nerve = Sciatic nerve (actually 2 nerves in one sheath) • Tibial nerve • Common fibular (peroneal) n. • Usually considered together because of their close relationship
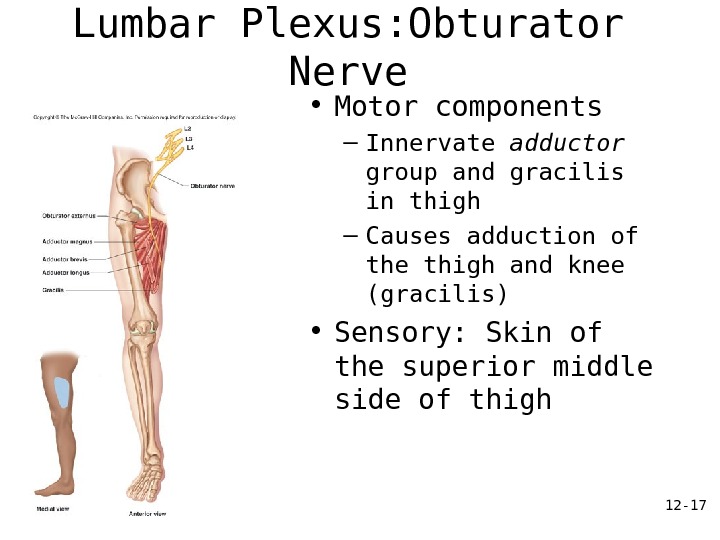
 12 — 17 Lumbar Plexus: Obturator Nerve • Motor components – Innervate adductor group and gracilis in thigh – Causes adduction of the thigh and knee (gracilis) • Sensory: Skin of the superior middle side of thigh
12 — 17 Lumbar Plexus: Obturator Nerve • Motor components – Innervate adductor group and gracilis in thigh – Causes adduction of the thigh and knee (gracilis) • Sensory: Skin of the superior middle side of thigh
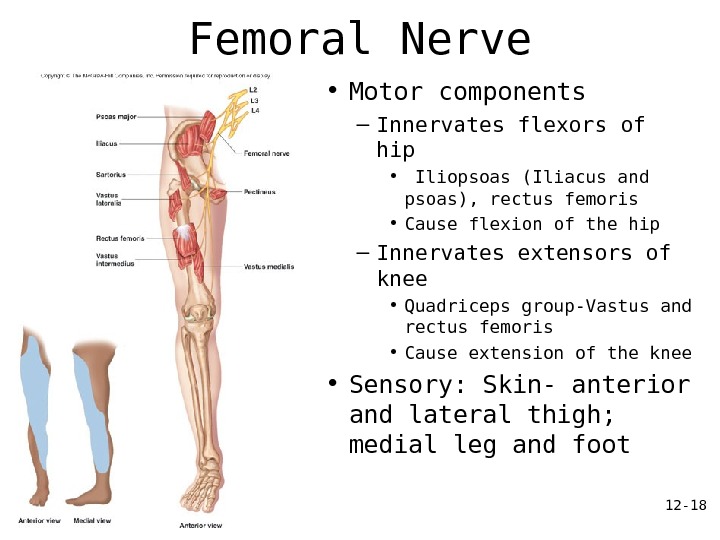
 12 — 18 Femoral Nerve • Motor components – Innervates flexors of hip • Iliopsoas (Iliacus and psoas), rectus femoris • Cause flexion of the hip – Innervates extensors of knee • Quadriceps group-Vastus and rectus femoris • Cause extension of the knee • Sensory: Skin- anterior and lateral thigh; medial leg and foot
12 — 18 Femoral Nerve • Motor components – Innervates flexors of hip • Iliopsoas (Iliacus and psoas), rectus femoris • Cause flexion of the hip – Innervates extensors of knee • Quadriceps group-Vastus and rectus femoris • Cause extension of the knee • Sensory: Skin- anterior and lateral thigh; medial leg and foot
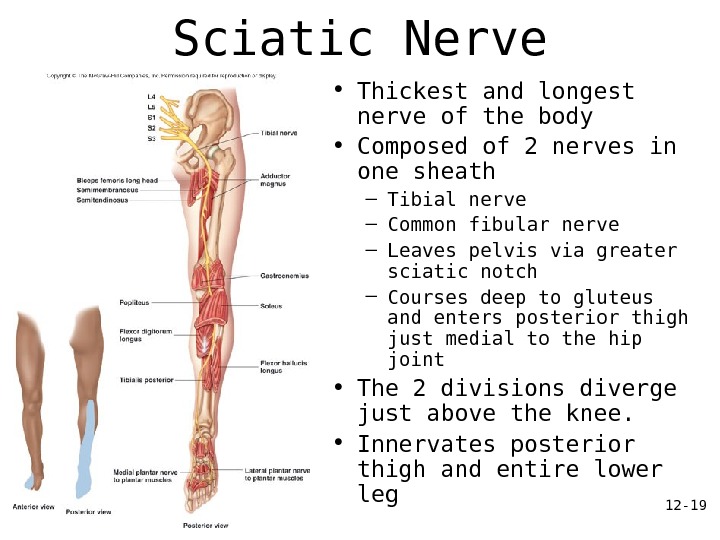
 12 — 19 Sciatic Nerve • Thickest and longest nerve of the body • Composed of 2 nerves in one sheath – Tibial nerve – Common fibular nerve – Leaves pelvis via greater sciatic notch – Courses deep to gluteus and enters posterior thigh just medial to the hip joint • The 2 divisions diverge just above the knee. • Innervates posterior thigh and entire lower leg
12 — 19 Sciatic Nerve • Thickest and longest nerve of the body • Composed of 2 nerves in one sheath – Tibial nerve – Common fibular nerve – Leaves pelvis via greater sciatic notch – Courses deep to gluteus and enters posterior thigh just medial to the hip joint • The 2 divisions diverge just above the knee. • Innervates posterior thigh and entire lower leg
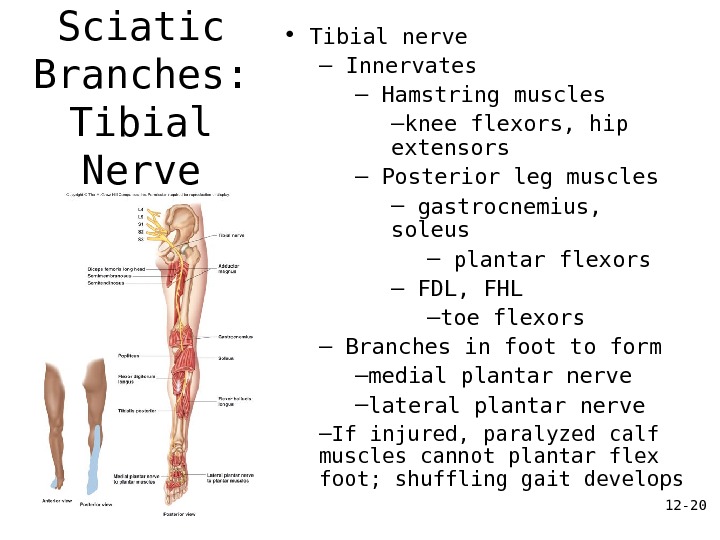
 12 — 20 Sciatic Branches: Tibial Nerve • Tibial nerve – Innervates – Hamstring muscles – knee flexors, hip extensors – Posterior leg muscles – gastrocnemius, soleus – plantar flexors – FDL, FHL – toe flexors – Branches in foot to form – medial plantar nerve – lateral plantar nerve – If injured, paralyzed calf muscles cannot plantar flex foot; shuffling gait develops
12 — 20 Sciatic Branches: Tibial Nerve • Tibial nerve – Innervates – Hamstring muscles – knee flexors, hip extensors – Posterior leg muscles – gastrocnemius, soleus – plantar flexors – FDL, FHL – toe flexors – Branches in foot to form – medial plantar nerve – lateral plantar nerve – If injured, paralyzed calf muscles cannot plantar flex foot; shuffling gait develops
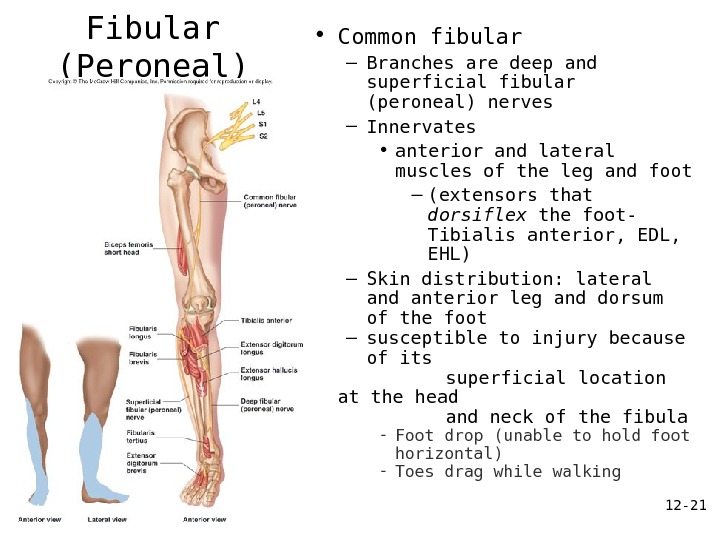
 12 — 21 Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve • Common fibular – Branches are deep and superficial fibular (peroneal) nerves – Innervates • anterior and lateral muscles of the leg and foot – (extensors that dorsiflex the foot- Tibialis anterior, EDL, EHL) – Skin distribution: lateral and anterior leg and dorsum of the foot – susceptible to injury because of its superficial location at the head and neck of the fibula — Foot drop (unable to hold foot horizontal) — Toes drag while walking
12 — 21 Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve • Common fibular – Branches are deep and superficial fibular (peroneal) nerves – Innervates • anterior and lateral muscles of the leg and foot – (extensors that dorsiflex the foot- Tibialis anterior, EDL, EHL) – Skin distribution: lateral and anterior leg and dorsum of the foot – susceptible to injury because of its superficial location at the head and neck of the fibula — Foot drop (unable to hold foot horizontal) — Toes drag while walking
 12 — 22 Other Nerves of the Lumbosacral Plexus • Nerves that innervate the skin of the suprapubic area, external genitalia, superior medial thigh, posterior thigh – Iliohypogastric nerve • Innervates muscles of abdominal wall and pubic region – Genitofemoral nerve • Skin of scrotum (males) and labia (females); inferior abdominal muscles – Pudendal nerve • Innervates muscles and skin of the perineum (see Fig 10. 21, p. 346) – region encompasssing external genitalia and anus • external anal sphincter • Stimulates muscle involved in developing an erection • Involved in voluntary control of urination • the “shameful” nerve
12 — 22 Other Nerves of the Lumbosacral Plexus • Nerves that innervate the skin of the suprapubic area, external genitalia, superior medial thigh, posterior thigh – Iliohypogastric nerve • Innervates muscles of abdominal wall and pubic region – Genitofemoral nerve • Skin of scrotum (males) and labia (females); inferior abdominal muscles – Pudendal nerve • Innervates muscles and skin of the perineum (see Fig 10. 21, p. 346) – region encompasssing external genitalia and anus • external anal sphincter • Stimulates muscle involved in developing an erection • Involved in voluntary control of urination • the “shameful” nerve
 12 — 23 Coccygeal Plexus • S 4 -S 5; coccygeal nerve • Muscles of pelvic floor • Sensory information from skin over coccyx
12 — 23 Coccygeal Plexus • S 4 -S 5; coccygeal nerve • Muscles of pelvic floor • Sensory information from skin over coccyx

